Seasonal Variation in Energy Balance, Evapotranspiration and Net Ecosystem Production in a Desert Ecosystem of Dengkou, Inner Mongolia, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
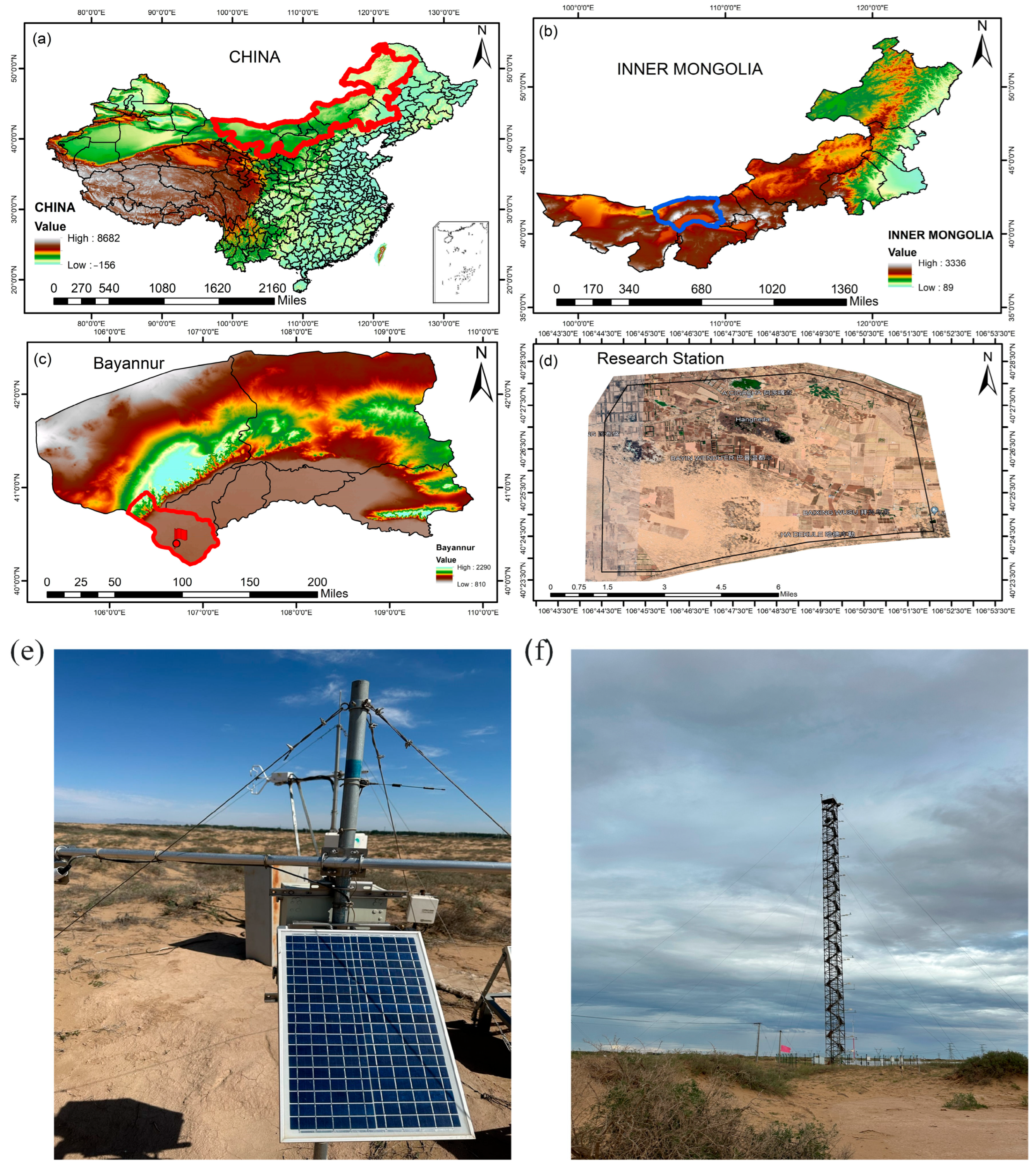
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Measurements of Meteorology and Energy Flux
2.3. Analyzing Data and Calculating Parameters
2.3.1. Data Processing
2.3.2. Closure Problem of Energy Balance
2.3.3. Estimation of Evapotranspiration and Net Ecosystem Production
2.3.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
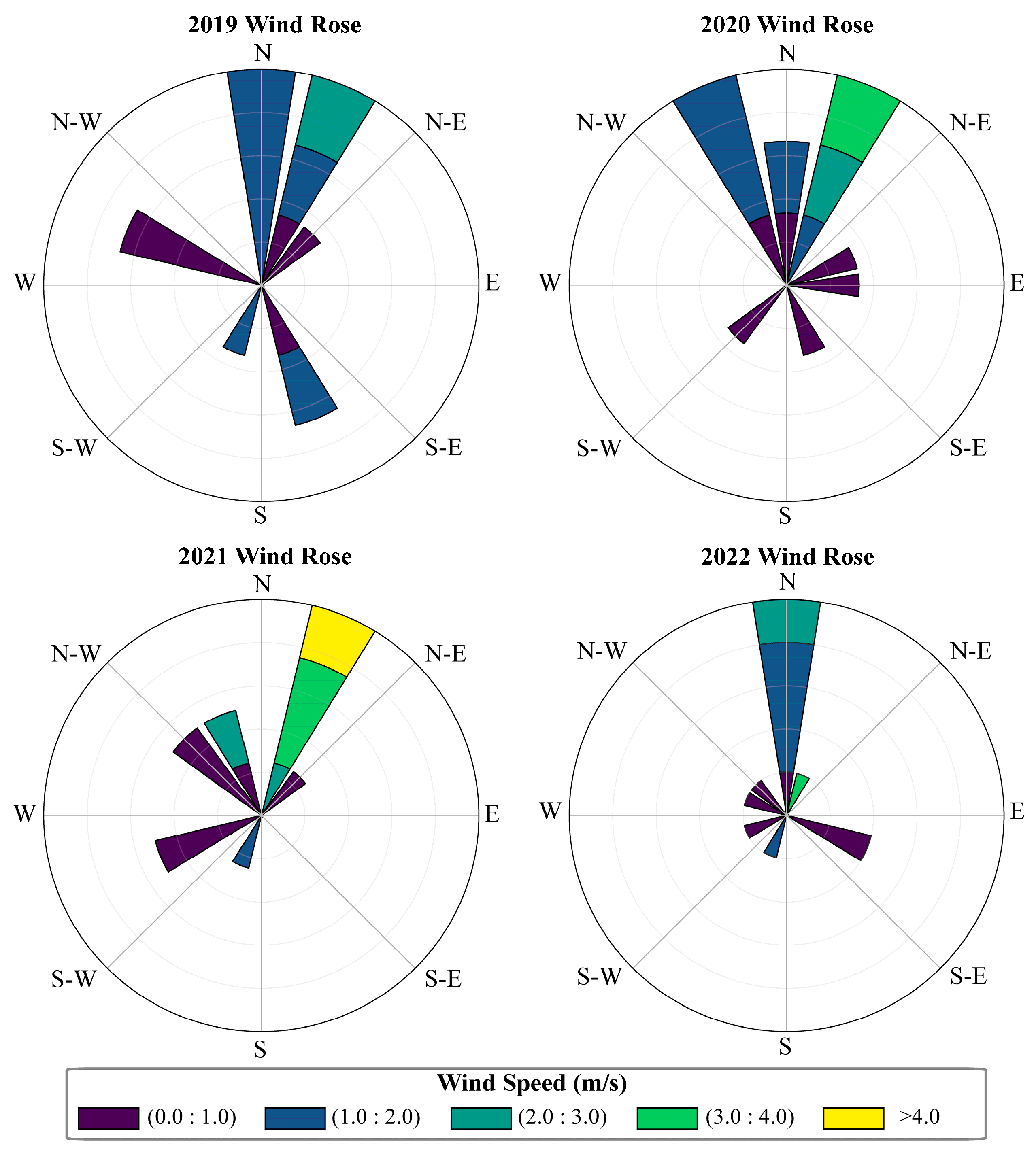
3.1. Temperature, Precipitation, Relative Humidity and Wind Speed Variation in Dengkou
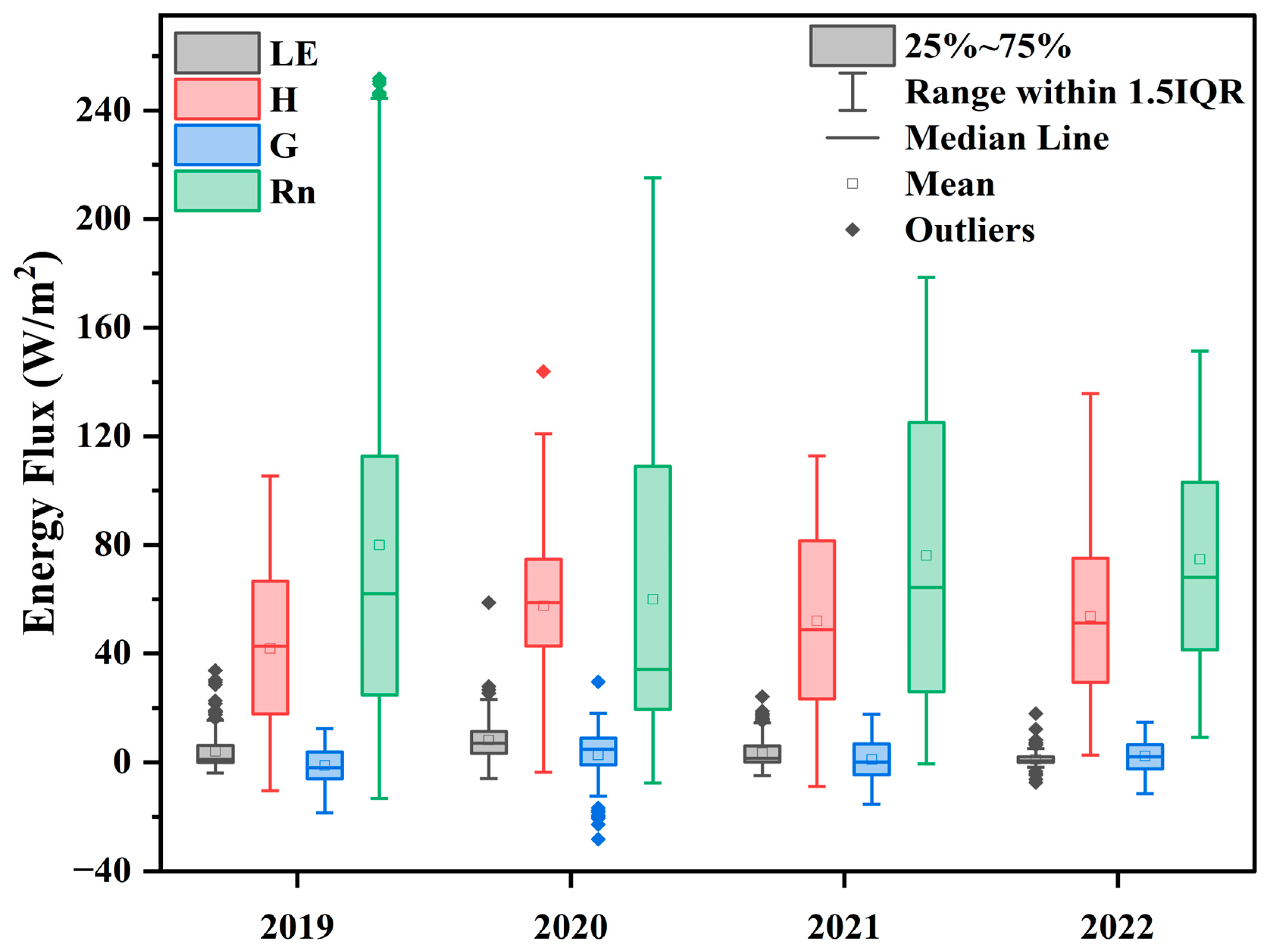
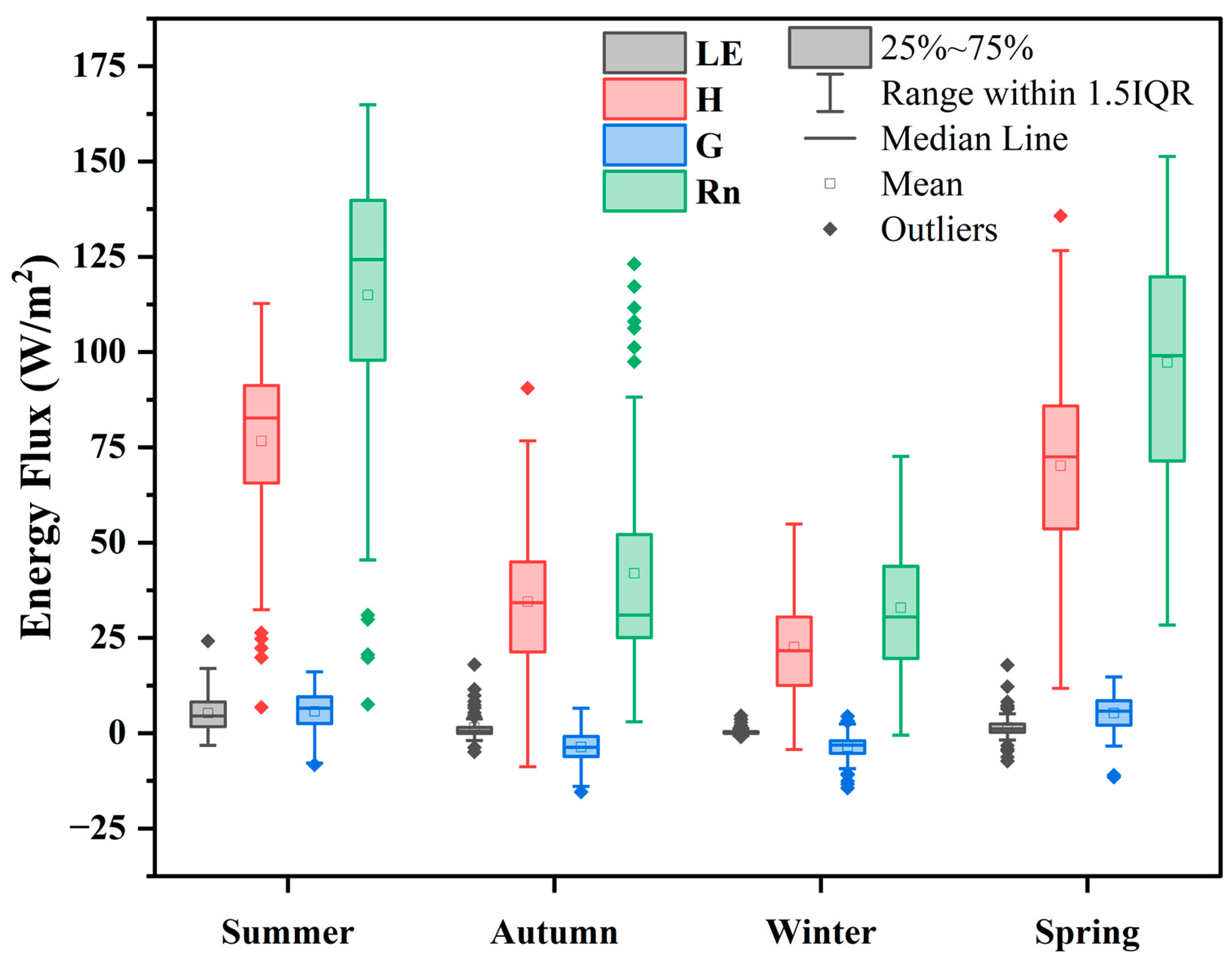
3.2. Seasonal Dynamic of Ground Heat, Sensible Heat, Latent Heat, and Net Radiation
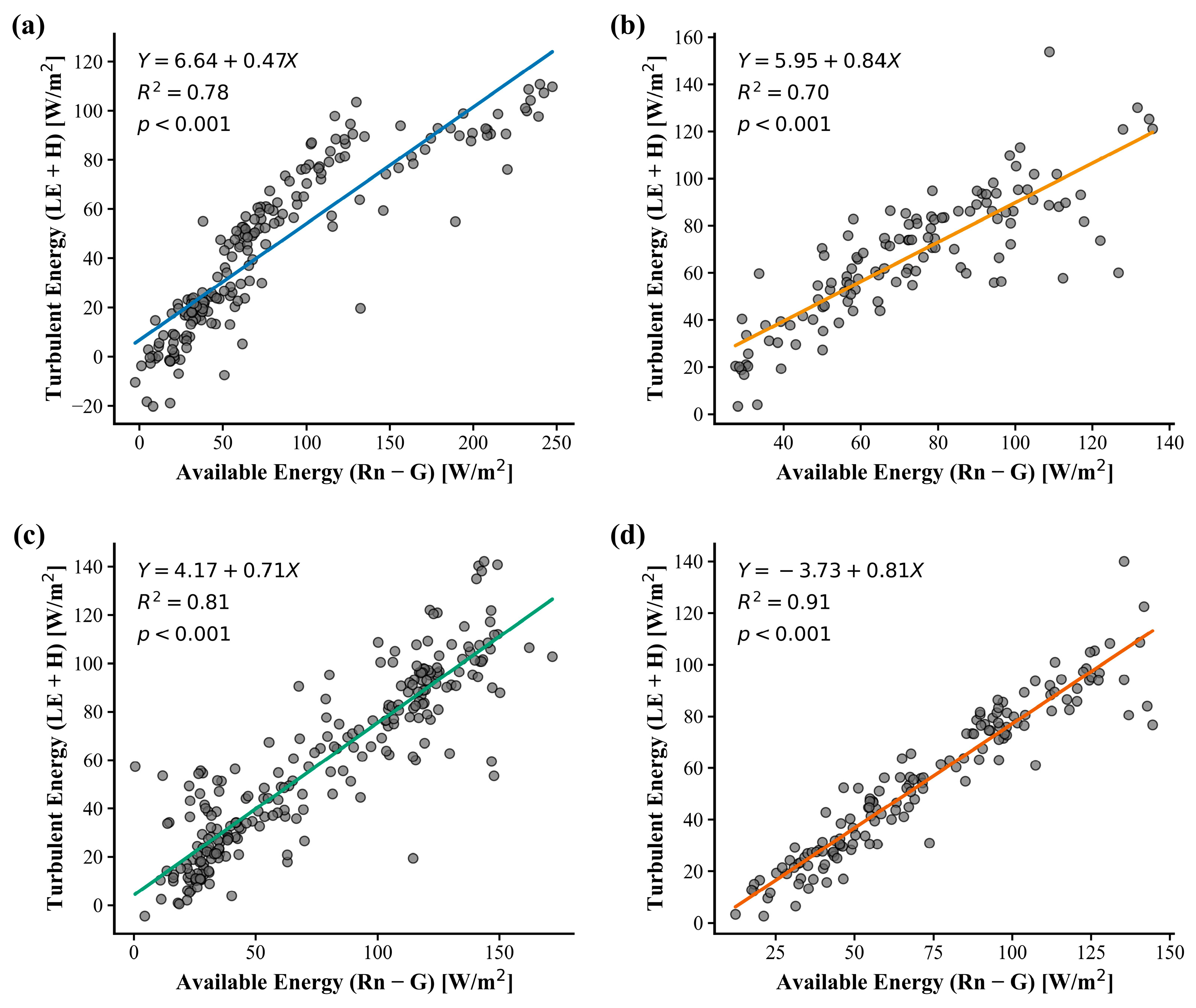
3.3. Energy Closure: Evaluation, Variability, and Influencing Factors
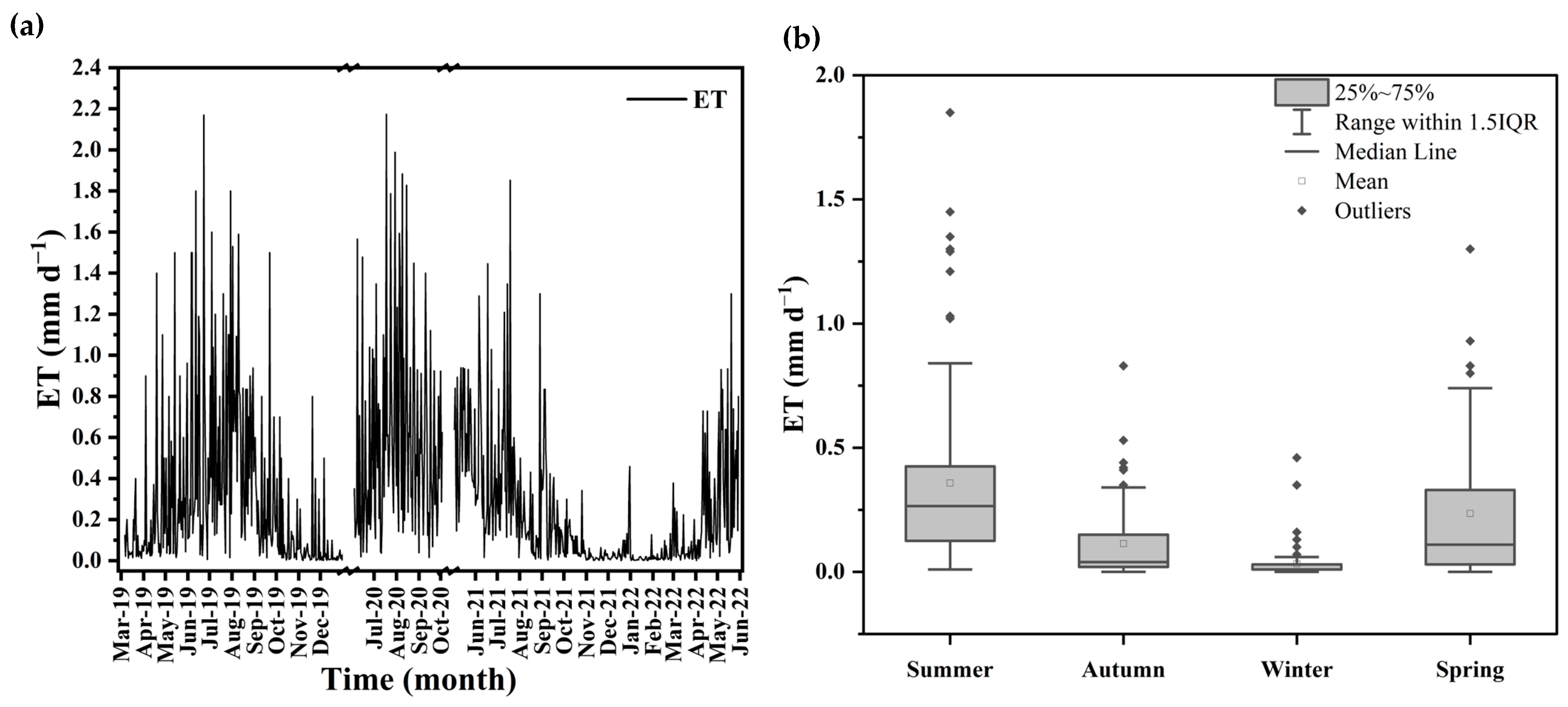
3.4. Seasonal Variation in Evapotranspiration
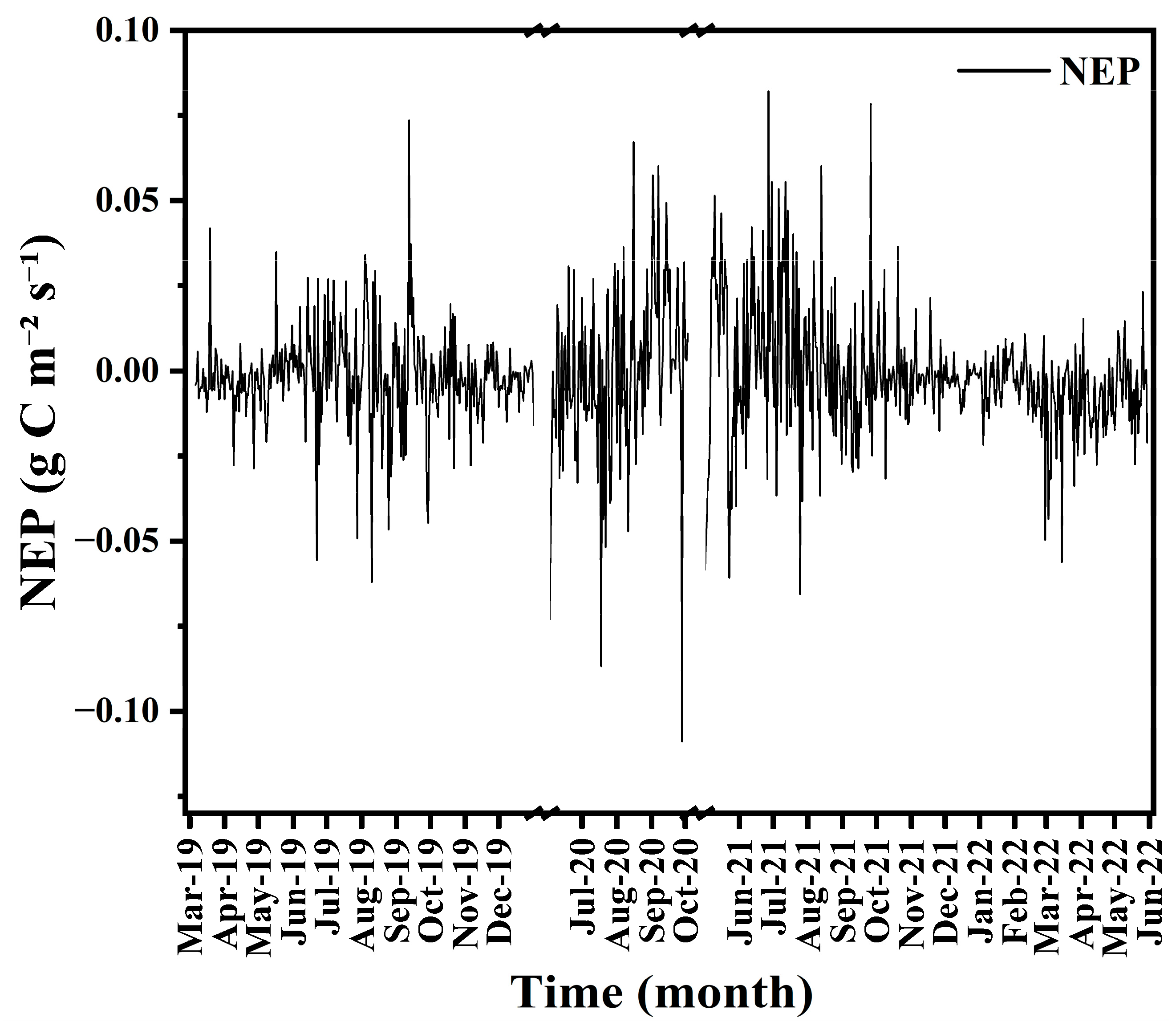
3.5. Variation in Net Ecosystem Production
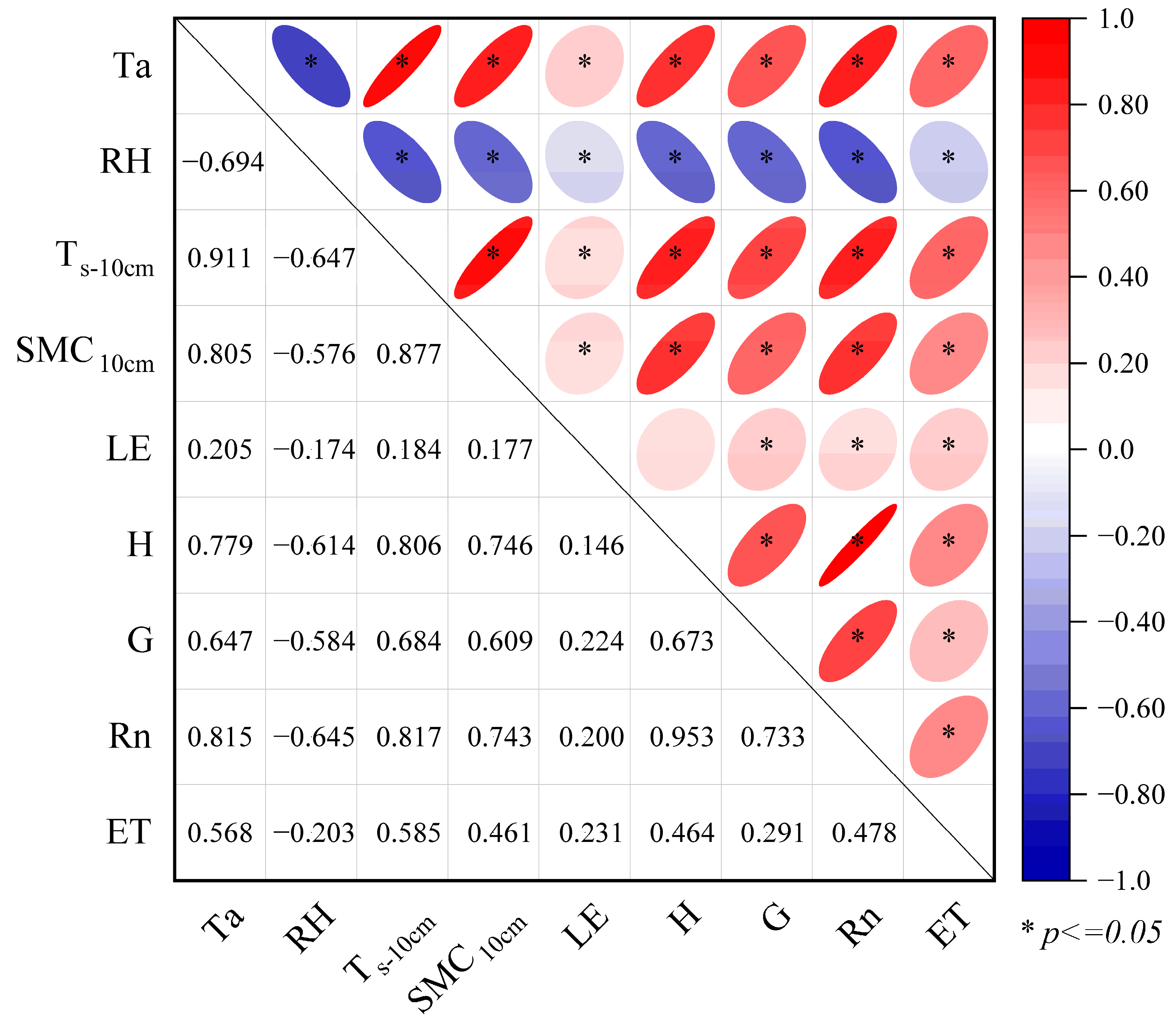
3.6. Influencing Factors of Energy Fluxes and ET
4. Discussion
4.1. Energy Closure
4.2. Evapotranspiration and Net Ecosystem Production
4.3. Influence of Environmental Factors on Energy Flux
4.4. Influence of Environmental Factors on ET and NEP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Observation System | Instrument Name | Model | Manufacturer and Origin | Observation Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vorticity Observation | Closed-Path H2O/CO2 analyzer | EC155 | Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, UT, USA | Carbon dioxide and water vapor concentration |
| 3D sonic anemometer | CSAT-3 | Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, UT, USA | Three-dimensional wind speed and sonic virtual temperature | |
| Soil heat-flux plate | 4xHFP01 | Hukseflux, Delft, The Netherlands | Soil heat flux | |
| Soil moisture and conductivity sensor | EC5 | Decagon, San Francisco, CA, USA | Soil moisture content, conductivity | |
| Averaging soil thermocouple Probe | TCAV | AVALON, USA | Soil temperature | |
| Gradient Meteorological | Four-component radiometer | CNR4 NR-LITE | Kipp & Zonen, Delft, The Netherlands | Radiation flux |
| Temperature sensor | HMP45C | Vaisala Inc., Vantaa, Finland | Air temperature and relative humidity | |
| Wind speed sensor | W10 | Banner, USA | Wind speed and direction | |
| Conventional Meteorological | Soil temperature sensor | CS616 | Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, UT, USA | Soil temperature |
| Rain gauge | JD-05 | |||
| Infrared temperature sensor | SI-111-SS | Apogee, Logan, UT, USA | Surface temperature |
References
- Brown, K.; Rosenberg, N.J. A resistance model to predict evapotranspiration and its application to a sugar beet field 1. Agron. J. 1973, 65, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.-S.; Wang, R.-Y.; Yao, Y.-B.; Wang, S.; Hao, X.-C.; Yang, F.-L.; Wang, R.-A. Effects of clouds and precipitation disturbance on the surface radiation budget and energy balance over loess plateau semi-arid grassland in China. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 62, 209201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuning, R.; van Gorsel, E.; Massman, W.J.; Isaac, P.R. Reflections on the surface energy imbalance problem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 156, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, T.P.; Hollinger, S.E. An assessment of storage terms in the surface energy balance of maize and soybean. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 125, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.G.; Wang, D. Energy budget closure observed in paired Eddy Covariance towers with increased and continuous daily turbulence. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 184, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Energy balance closure problem over a tropical seasonal rainforest in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China: Role of latent heat flux. Water 2022, 14, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ohta, T.; Nakai, T.; Kuwada, T.; Daikoku, K.i.; Iida, S.i.; Yabuki, H.; Kononov, A.V.; van der Molen, M.K.; Kodama, Y. Energy consumption and evapotranspiration at several boreal and temperate forests in the Far East. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1978–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganlin, Z.; Yaohui, L.; Xuying, S.; Tiejun, Z.; Cailing, Z. Characteristics of Surface Energy Fluxes over Different Types of Underlying Surfaces in North China. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2019, 37, 577. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Tong, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, P.; Li, J.; Zheng, N. Characteristics of energy balance of a mixed plantation in the Xiaolangdi area in the growing season. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 4492–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, C.; Wang, B.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, G. Characteristics of energy balance in a mixed forest in Jiuzhaigou Valley. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8098–8106. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Shao, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, W. Changes of climate extremes in a typical arid zone: Observations and multimodel ensemble projections. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yu, H.; Guan, X.; Wang, G.; Guo, R. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudukade, S.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Mamtimin, A.; Gao, J.; Ma, M.; Wang, W.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K. Effects of Artificial Green Land on Land–Atmosphere Interactions in the Taklamakan Desert. Land 2023, 12, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Shankman, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions: Lessons in ecological restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Yin, Y. Eco-reconstruction in Northwest China. In Water and Sustainability in Arid Regions: Bridging the Gap Between Physical and Social Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, M.F.; Wood, E.F. Scale influences on the remote estimation of evapotranspiration using multiple satellite sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyker, A.E.; Verma, S.B. Interannual water vapor and energy exchange in an irrigated maize-based agroecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rind, D.; Rosenzweig, C.; Goldberg, R. Modelling the hydrological cycle in assessments of climate change. Nature 1992, 358, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Han, X.; Baoyin, T.; Yu, G. Land-use impact on soil carbon and nitrogen sequestration in typical steppe ecosystems, Inner Mongolia. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. The change in net ecosystem productivity and its driving mechanism in a mountain ecosystem of arid regions, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-R.; Buchmann, N.; Hessen, D.O.; Stordal, F.; Erisman, J.W.; Vollsnes, A.V.; Andersen, T.; Dolman, H. Disentangling effects of natural and anthropogenic drivers on forest net ecosystem production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majozi, N.P.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Ramoelo, A.; Mathieu, R.; Nickless, A.; Verhoef, W. Analysing surface energy balance closure and partitioning over a semi-arid savanna FLUXNET site in Skukuza, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3401–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; Cox, P.; Betts, R.; Bopp, L.; von Bloh, W.; Brovkin, V.; Cadule, P.; Doney, S.; Eby, M.; Fung, I. Climate–carbon cycle feedback analysis: Results from the C4MIP model intercomparison. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3337–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ji, X.; Liu, H. Progresses in evapotranspiration research and prospect in desert oasis evapotranspiration research. Arid. Zone Res. 2011, 28, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Göckede, M.; Rebmann, C.; Foken, T. A combination of quality assessment tools for eddy covariance measurements with footprint modelling for the characterisation of complex sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 127, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-R.; Wen, X.-F.; Sun, X.-M.; Tanner, B.D.; Lee, X.; Chen, J.-Y. Overview of ChinaFLUX and evaluation of its eddy covariance measurement. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 137, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzhi, Z.; Guodong, C. A review of some problems in the study of eco-hydrological processes in arid areas. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, Y.; Qiang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Hao, X.; Sun, X. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of the Bowen smith ratio over a semi-arid grassland in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 252, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Liu, T.; Wang, G.; Duan, L.; Chen, X. Dynamic changes of water and heat fluxes and responses to environmental factors in cascade ecological zone. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 26, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Beyrich, F.; De Bruin, H.; Meijninger, W.; Schipper, J.; Lohse, H. Results from one-year continuous operation of a large aperture scintillometer over a heterogeneous land surface. Bound.-Lay. Meteorol. 2002, 105, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, S.; Mendes, K.R.; da Silva, L.L.; Mutti, P.R.; Medeiros, S.S.; Amorim, L.B.; dos Santos, C.A.; Perez-Marin, A.M.; Ramos, T.M.; Marques, T.V. Closure and partitioning of the energy balance in a preserved area of a Brazilian seasonally dry tropical forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinbank, W. The measurement of vertical transfer of heat and water vapor by eddies in the lower atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1951, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Olson, R.; Anthoni, P.; Aubinet, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Burba, G.; Ceulemans, R.; Clement, R.; Dolman, H. Gap filling strategies for defensible annual sums of net ecosystem exchange. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaughey, J. Energy balance storage terms in a mature mixed forest at Petawawa, Ontario—A case study. Bound.-Lay. Meteorol. 1985, 31, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Goldstein, A.; Falge, E.; Aubinet, M.; Baldocchi, D.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Ceulemans, R.; Dolman, H.; Field, C. Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L. Flux sampling errors for aircraft and towers. J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 1998, 15, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, S. Long-term variations in energy partitioning and evapotranspiration in a semiarid grassland in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 278, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, K.; Leinonen, I.; Bartelink, H.; Berbigier, P.; Borghetti, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Cienciala, E.; Dolman, A.; Froer, O.; Gracia, C. Evaluation of six process-based forest growth models using eddy-covariance measurements of CO2 and H2O fluxes at six forest sites in Europe. Glob. Change Biol. 2002, 8, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhatia, A.; Sehgal, V.K.; Tomer, R.; Jain, N.; Pathak, H. Net ecosystem exchange of carbon dioxide in rice-spring wheat system of northwestern Indo-Gangetic plains. Land 2021, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, C.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, Q.; Xiong, Z. Two approaches for net ecosystem carbon budgets and soil carbon sequestration in a rice–wheat rotation system in China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 100, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhao, W.; Jin, B.; Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Zhou, H. Seasonal variations in energy exchange and evapotranspiration of an oasis-desert ecotone in an arid region. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, T.; Hao, L.; Duan, L.; Tong, X.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, W. Seasonal variation and environmental regulation mechanisms of energy fluxes and energy allocation in dune and meadow ecosystems. CATENA 2025, 254, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuling, F. Energy balance closure at ChinaFLUX sites. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zeydalinejad, N.; Javadi, A.A.; Webber, J.L. Global perspectives on groundwater infiltration to sewer networks: A threat to urban sustainability. Water Res. 2024, 262, 122098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- III, J.W.C.; Krausman, P.R.; Rosenstock, S.S.; Turner, J.C. Mechanisms of thermoregulation and water balance in desert ungulates. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2006, 34, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazar, A.; Putnam, D. Evapotranspiration and Yield Impact Tools for More Water-Use Efficient Alfalfa Production in Desert Environments. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Carbon flux in deserts depends on soil cover type: A case study in the Gurbantunggute desert, North China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Graciano, C.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, F.; Hughes, A.C.; Ahmed, Z.; Ullah, A.; Ali, S.; Gao, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Plant root mechanisms and their effects on carbon and nutrient accumulation in desert ecosystems under changes in land use and climate. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 916–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yuan, W. Exploring the Influencing Factors of Net Ecosystem Productivity (NEP) Based on Random Forest and SHAP. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Hu, S.-J. Estimation of Evapotranspiration in the Desert–Oasis Transition Zone Using the Water Balance Method and Groundwater Level Fluctuation Method—Taking the Haloxylon ammodendron Forest at the Edge of the Gurbantunggut Desert as an Example. Water 2023, 15, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Chen, S.; Wilske, B.; Sun, G.; Chen, J. Evapotranspiration and soil water relationships in a range of disturbed and undisturbed ecosystems in the semi-arid Inner Mongolia, China. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 4, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launiainen, S.; Katul, G.G.; Kolari, P.; Lindroth, A.; Lohila, A.; Aurela, M.; Varlagin, A.; Grelle, A.; Vesala, T. Do the energy fluxes and surface conductance of boreal coniferous forests in Europe scale with leaf area? Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 4096–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zha, T.; Gong, J.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, S.; Chen, G.; Feng, W.; Kellomäki, S.; Peltola, H. Energy partitioning over a semi-arid shrubland in northern China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launiainen, S. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of energy exchange above a boreal Scots pine forest. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 3921–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Guluzade, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. A two-source non-parametric method for estimating terrestrial evapotranspiration: Validation at eddy covariance sites. J. Hydrol. 2024, 645, 132278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fa, K.; Qin, S.; She, W. Rainfall pulses modify soil carbon emission in a semiarid desert. CATENA 2017, 155, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Environmental Variables | Indicators | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | ANOVA (F-Statistic, p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Minimum | −17.50 | −20.20 | −20.60 | −20.20 | F(3, N) = 0.32, p = 0.81 No significant differences |
| Maximum | 28.60 | 28.90 | 29.60 | 28.90 | ||
| Mean | 8.73 | 8.31 | 9.58 | 8.32 | ||
| CV % | 152.51 | 159.00 | 142.74 | 159.01 | ||
| Precipitation (mm) | Minimum | 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.50 | F(3, N) = 2.15, p = 0.09 Marginal trend (not significant) |
| Maximum | 8.20 | 24.40 | 42.40 | 24.40 | ||
| Mean | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.21 | 0.37 | ||
| CV % | 391.12 | 602.86 | 1089.08 | 601.72 | ||
| Relative humidity (%) | Minimum | 10.00 | 7.30 | 8.00 | 7.30 | F(3, N) = 3.02, p = 0.03 Significant differences |
| Maximum | 88.00 | 94.50 | 87.00 | 94.50 | ||
| Mean | 43.71 | 44.89 | 40.29 | 44.94 | ||
| CV % | 38.18 | 45.87 | 38.31 | 45.86 | ||
| Wind Speed (m/s) | Minimum | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.12 | F(3, N) = 2.51, p = 0.06 Marginal trend (not significant) |
| Maximum | 7.90 | 8.30 | 8.40 | 8.01 | ||
| Mean | 3.12 | 3.0 | 3.48 | 3.05 | ||
| CV % | 49.4 | 50.7 | 47.1 | 51.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zain Ul Abidin, M.; Xiao, H.; Magsi, S.; Hongxin, F.; Muskan, K.; Hoang, P.; Hassan, M.A. Seasonal Variation in Energy Balance, Evapotranspiration and Net Ecosystem Production in a Desert Ecosystem of Dengkou, Inner Mongolia, China. Water 2025, 17, 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152307
Zain Ul Abidin M, Xiao H, Magsi S, Hongxin F, Muskan K, Hoang P, Hassan MA. Seasonal Variation in Energy Balance, Evapotranspiration and Net Ecosystem Production in a Desert Ecosystem of Dengkou, Inner Mongolia, China. Water. 2025; 17(15):2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152307
Chicago/Turabian StyleZain Ul Abidin, Muhammad, Huijie Xiao, Sanaullah Magsi, Fang Hongxin, Komal Muskan, Phuocthoi Hoang, and Muhammad Azher Hassan. 2025. "Seasonal Variation in Energy Balance, Evapotranspiration and Net Ecosystem Production in a Desert Ecosystem of Dengkou, Inner Mongolia, China" Water 17, no. 15: 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152307
APA StyleZain Ul Abidin, M., Xiao, H., Magsi, S., Hongxin, F., Muskan, K., Hoang, P., & Hassan, M. A. (2025). Seasonal Variation in Energy Balance, Evapotranspiration and Net Ecosystem Production in a Desert Ecosystem of Dengkou, Inner Mongolia, China. Water, 17(15), 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152307







