Unraveling Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Response of Integrated Sulfur-Driven Partial Denitrification and Anammox Process in Saline Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Operating Phases
2.2. Sludge and Wastewater Composition
2.3. Sampling and Analytical Methods
2.4. DNA Extraction and Microbial Community Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistical Processing
3. Results and Discussion
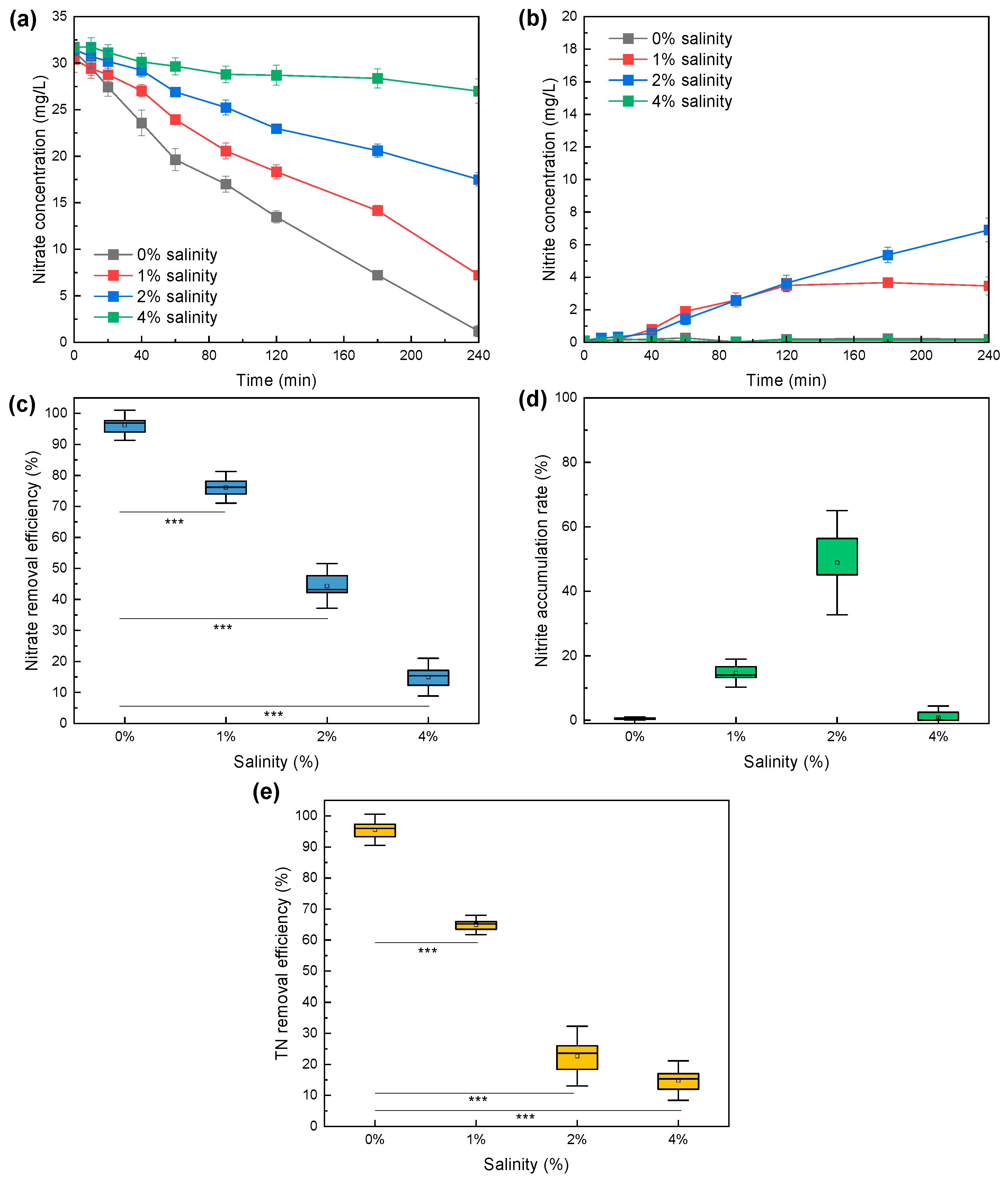
3.1. Performance of Nitrogen Conversions Under Different Salinities in Batch Tests
3.1.1. Saline Stress on Sulfur-Driven Denitrification
3.1.2. Saline Stress on Anammox
3.2. Long-Term Operational Performance of SPDA System
3.3. Changes in EPS Characteristics During Long-Term Operation
3.4. Evolution of Microbial Community
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Batch tests suggested that nitrate reduction in sulfur-driven denitrification could be suppressed under 1–4% salinity to different levels, with nitrite accumulation occurring under 1–2% salinity.
- (2)
- Batch tests suggested that TN removal efficiency of Anammox decreased from 97.6% to 17.3% with salinity increasing from 0% to 4%.
- (3)
- Long-term tests revealed that the SPDA system could be rapidly established under low-salinity conditions. With the appropriate strategy of gradual salinity elevation, SPDA could adapt to a high-salinity environment and achieve comparable performance to that in a low-salinity environment.
- (4)
- Adapted secretion of proteins in EPS, responsive enrichment of genus Sulfurimonas, and unaffected genus Brocadia retention enhanced the robustness of the SPDA system under a high-salinity environment.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Du, R.; Zhang, J.; Chai, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Qiao, J.; Peng, Y. Verifying the applicability of PD/A unit for ultimate sidestream and mainstream polishing: Operating performance, granular characteristics and active microbes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, Q.; Han, I.; Jaffé, P.R. Performance of sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification and denitrifiers for wastewater treatment under acidic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Cao, S.; Li, B.; Niu, M.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Performance and microbial community analysis of a novel DEAMOX based on partial-denitrification and anammox treating ammonia and nitrate wastewaters. Water Res. 2017, 108, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Nie, J.; You, Z.; Xiang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, X. The strategy of crushing and re-granulation promoted anammox granular sludge (AnGS) formation and performance improvement. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 510, 161572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenen, J.G. Anammox bacteria: From discovery to application. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiki, M.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Ecology and physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2784–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vandeGraaf, A.A.; deBruijn, P.; Robertson, L.A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Kuenen, J.G. Metabolic pathway of anaerobic ammonium oxidation on the basis of N-15 studies in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology 1997, 143, 2415–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, B.; Kuenen, J.G.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Sewage treatment with anammox. Science 2010, 328, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Peng, Y.; Ji, J.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Li, X. Partial denitrification providing nitrite: Opportunities of extending application for anammox. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lu, H.; Khanal, S.K.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, L.; Chen, G.-H. Granulation of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria for autotrophic denitrification. Water Res. 2016, 104, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadekar, S.; Nemati, M.; Hill, G. Batch and continuous biooxidation of sulphide by Thiomicrospira sp. CVO: Reaction kinetics and stoichiometry. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, M.; Heijnen, J.J.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Narita, Y.; Gao, L.; Ali, M.; Oshiki, M.; Okabe, S. Maximum specific growth rate of anammox bacteria revisited. Water Res. 2017, 116, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Jia, J. Long-term impact of sulfate on an autotrophic nitrogen removal system integrated partial nitrification, anammox and endogenous denitrification (PAED). Chemosphere 2019, 235, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Pratt, S.; Li, Z.; Ye, L. Adaptation and evolution of freshwater Anammox communities treating saline/brackish wastewater. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Talebi, S.; Gras, S.; Weeks, M.; Kentish, S. A review of salty waste stream management in the Australian dairy industry. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, P. Review on physicochemical, chemical, and biological processes for pharmaceutical wastewater. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Harbin, China, 8–10 December 2017; p. 012185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Sung, S.; Ni, S.-Q. Biotreatment of high-salinity wastewater: Current methods and future directions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook on Environment 2023; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera, P.; Strubbe, L.; del Río, A.V.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Volcke, E. Modelling salinity effects on aerobic granular sludge treating fish-canning wastewater. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; Capodici, M.; Di Pippo, F.; Tandoi, V.; Torregrossa, M. Comparison between kinetics of autochthonous marine bacteria in activated sludge and granular sludge systems at different salinity and SRTs. Water Res. 2019, 148, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Ran, X.; Wang, Y. Salt stimulates sulfide−driven autotrophic denitrification: Microbial network and metagenomics analyses. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Jin, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, L. Salinity effect on simultaneous nitrification and denitrification, microbial characteristics in a hybrid sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-R.; Zhang, X.-N.; Wang, H.-C.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Wang, A.-J.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Cui, C.-W.; Sun, Y.-L. Effects of salinity on sulfur-dominated autotrophic denitrification microorganisms: Microbial community succession, key microorganisms and response mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zheng, P.; Ding, A.q.; Zhang, M.; Ghulam, A.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.-P. Effects of inorganic salts on denitrifying granular sludge: The acute toxicity and working mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 204, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Pratt, S.; Crick, O.; Xia, J.; Duan, H.; Ye, L. Salinity effect on freshwater Anammox bacteria: Ionic stress and ion composition. Water Res. 2020, 188, 116432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Park, H.-D.; Park, J.-H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, F. Effect of different salinity adaptation on the performance and microbial community in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bi, Z. Simultaneous removal of ammonia and nitrate by coupled S0-driven autotrophic denitrification and Anammox process in fluorine-containing semiconductor wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Du, R.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Characteristics of sludge granulation and EPS production in development of stable partial nitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, P.; Yu, D.; Yu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, J. Inadvertently enriched cyanobacteria prompted bacterial phosphorus uptake without aeration in a conventional anaerobic/oxic reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, R.; Lu, H. Synergistic biological removal of nitrogen and sulfide from saline mariculture wastewater by halophilic consortia. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Shaw, D.R.; Saikaly, P.E. Application of an enrichment culture of the marine anammox bacterium “Ca. Scalindua sp. AMX11” for nitrogen removal under moderate salinity and in the presence of organic carbon. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Kawagoshi, Y.; Huang, X.; Hong, N.; Van Duc, L.; Yamashita, Y.; Hama, T. Nitrogen removal properties in a continuous marine anammox bacteria reactor under rapid and extensive salinity changes. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windey, K.; De Bo, I.; Verstraete, W. Oxygen-limited autotrophic nitrification–denitrification (OLAND) in a rotating biological contactor treating high-salinity wastewater. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4512–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, D.; Hou, C.; Mu, Y.; Shen, J. Enhanced anaerobic reduction of nitrobenzene at high salinity by betaine acting as osmoprotectant and regulator of metabolism. Water Res. 2022, 223, 118982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Role of extracellular polymeric substance in determining the high aggregation ability of anammox sludge. Water Res. 2015, 75, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Allen, D.G.; Droppo, I.G.; Leppard, G.G.; Liss, S.N. Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability. Water Res. 2001, 35, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Ma, T.; Shen, Y. The branched chains and branching degree of exopolysaccharides affecting the stability of anammox granular sludge. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.X.; Biswal, B.K.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Chen, G.H.; Wu, D. Long term performance and dynamics of microbial biofilm communities performing sulfur-oxidizing autotrophic denitrification in a moving-bed biofilm reactor. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.F.; Wu, D.; Huang, H.; Cui, Y.X.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Chen, G.H. Exploration and verification of the feasibility of sulfide-driven partial denitrification coupled with anammox for wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2021, 193, 116905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrotaite, Z.; Valk, L.C.; Petriglieri, F.; Singleton, C.; Nierychlo, M.; Dueholm, M.K.; Nielsen, P.H. Diversity and ecophysiology of the genus OLB8 and other abundant uncultured Saprospiraceae genera in global wastewater treatment systems. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 917553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, Y.-Y.; Liu, J. Low-carbon nitrogen removal from power plants circulating cooling water and municipal wastewater by partial denitrification-anammox. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 380, 129071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z. Optimizing carbon sources regulation in the biochemical treatment systems for coal chemical wastewater: Aromatic compounds biodegradation and microbial response strategies. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

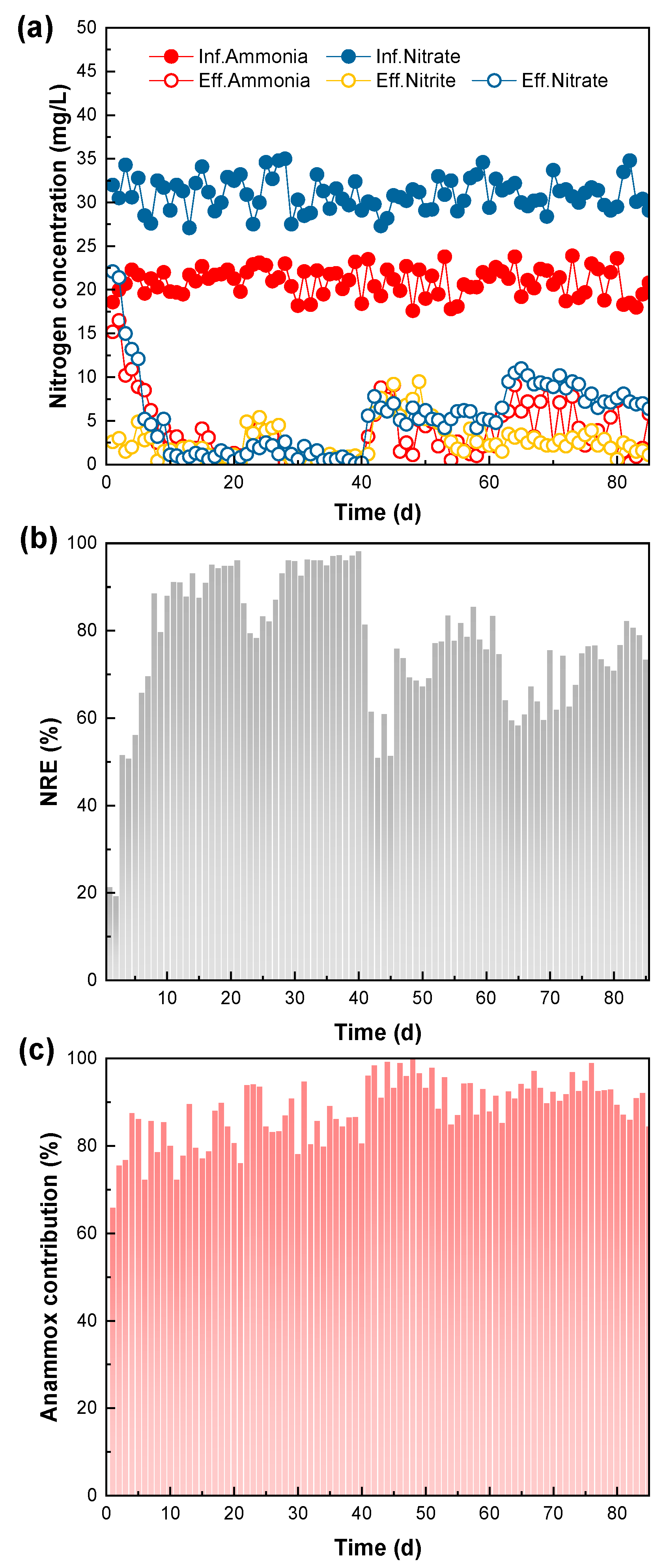




| Phases | Days | Salinity |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | 1–21 | 0% (<0.2 g/L) |
| Phase 2 | 22–40 | 1% (10 g/L) |
| Phase 3 | 41–61 | 2% (20 g/L) |
| Phase 4 | 62–85 | 4% (40 g/L) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Sun, J.; Cao, Z.; Lai, J.; Feng, H.; Guo, M. Unraveling Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Response of Integrated Sulfur-Driven Partial Denitrification and Anammox Process in Saline Wastewater Treatment. Water 2025, 17, 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152284
Li X, Sun J, Cao Z, Lai J, Feng H, Guo M. Unraveling Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Response of Integrated Sulfur-Driven Partial Denitrification and Anammox Process in Saline Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2025; 17(15):2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiangchen, Jie Sun, Zonglun Cao, Junxi Lai, Haodi Feng, and Minwen Guo. 2025. "Unraveling Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Response of Integrated Sulfur-Driven Partial Denitrification and Anammox Process in Saline Wastewater Treatment" Water 17, no. 15: 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152284
APA StyleLi, X., Sun, J., Cao, Z., Lai, J., Feng, H., & Guo, M. (2025). Unraveling Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Response of Integrated Sulfur-Driven Partial Denitrification and Anammox Process in Saline Wastewater Treatment. Water, 17(15), 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152284





