Abstract
Accelerated urbanization and intensified urban development globally lead to increased sewage discharge, challenging environmental protection. Therefore, exploring the correlation mechanism between the economic development level (EDL) and sewage discharge intensity (SDI) is crucial for sustainable development. This study uses panel data from 288 Chinese cities between 2003 and 2021, employs spatial analysis techniques to uncover the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of SDI, and investigates the influence of economic development on this intensity using spatial panel models. The results reveal that (1) while the spatial distribution of SDI in China generally exhibits a downward trend, changes in the Northeast region are relatively modest, with SDI remaining higher than in other regions. Global autocorrelation analysis further indicates significant spatial agglomeration and positive correlation effects in urban SDI. (2) Economic development exerts a notable inhibitory effect on SDI, with a 0.570% decrease for every 1% rise in GDP per capita, thus demonstrating a significant spatial spillover effect. (3) For megacities, large cities, and small and medium-sized cities, EDLs have significant negative spatial spillover effects on SDI, with a more pronounced impact on large cities. This study provides a theoretical foundation for sewage management and empirical support for environmental policies, crucial for sustainable urban development.
1. Introduction
In the 21st century, water issues have risen to the forefront of global concerns. With the continuous growth of the global population, accelerating urbanization, intensifying climate change, and increasing overexploitation activities, the total volume of sewage discharge worldwide is rapidly escalating, posing an increasingly severe threat to the ecological environment and human health. In light of this dire situation, the United Nations outlined 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015, which explicitly include ensuring sustainable water resource management and sanitation facilities, as well as promoting access to clean water and sanitation services [1,2,3]. However, the rapid advancement of urbanization and industrialization, while driving continuous economic growth, has also entailed enormous environmental and resource costs [4,5]. In particular, the issue of sewage discharge has emerged as a major bottleneck hindering sustainable development. At present, there is no consensus among academics and industry professionals regarding the relationship between economic development and sewage discharge intensity (SDI).
Foreign studies have shown that there is a significant correlation between urban economic development and wastewater discharge intensity. By the 1990s, wastewater treatment rates in the cities of developed industrialized countries had reached over 80%, with some approaching 100%. However, economic growth remains the core driver of resource consumption and environmental degradation. As population growth, urbanization, and improvements in living standards continue, the volume of wastewater generated by household, industrial, and commercial activities continues to increase [6]. The Croatian case demonstrates that its industrial production density is higher than that of comparable countries, resulting in greater wastewater discharge per unit of industrial value added. Additionally, productivity indicators struggle to fully reflect sectoral differences, highlighting the significant impact of the industrial sector on wastewater discharge [7]. In Manado City, Indonesia, wastewater discharge issues have worsened due to economic growth, high population pressure, and inadequate government governance [8]. Research in Dhaka, Bangladesh, also confirms that economic expansion directly drives increases in wastewater discharge [9]. These studies collectively indicate that urban economic development must balance growth and environmental protection through technological innovation and policy optimization.
Several studies have highlighted the close link between economic development and SDI. For instance, Zhuo et al. found that wastewater discharge increases by 1,746,000 tons for every additional CNY 100 million in GDP, illustrating a direct numerical relationship between sewage discharge and economic growth [3]. Further analysis shows that urban sewage discharge efficiency is correlated with labor force disposable income and GDP. When discharge efficiency reaches a high level, growth in these economic indicators further enhances efficiency [10]. At a macro level, economic development significantly impacts industrial wastewater discharge within a province while restraining discharge in neighboring provinces. As a province’s economic development level (EDL) rises, economic agglomeration attracts more people, increasing pollutant discharge and potentially altering pollution levels in adjacent regions [11]. In 2020, Ma et al. analyzed the spatiotemporal dynamics of industrial wastewater discharge across China from 2004 to 2015, concluding that economic factors are pivotal in driving industrial sewage output [12]. Coastal regions, particularly the Yangtze River’s upper reaches, have seen intensified convergence of high-polluting industries due to rapid economic growth and regional planning, leading to persistently high industrial sewage discharge [13]. At the regional level, cities like Fuzhou, Xiamen, and Quanzhou in Fujian Province have experienced rapid economic growth and urbanization, resulting in increased sewage discharge and pollutants such as chemical oxygen demand (COD) and ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), posing significant ecological challenges [14].
However, some studies suggest that economic development can inhibit sewage discharge. For example, Shen et al. found that increased GDP per capita significantly reduces industrial sewage discharge [15], reflecting a shift toward sustainable practices as economic growth slows or reverses discharge increases [16]. Technological advancements driven by economic development also play a crucial role, significantly curbing energy consumption and environmental pollution, particularly in sewage discharge and electricity consumption. Wang and Wang highlighted that such advancements improve resource efficiency and reduce overall sewage discharge levels [17]. Additionally, the expansion of international trade, especially in services, helps lower pollution emission intensity, offering new pathways for environmental protection [18]. Tang simulated that increased environmental investments from economic growth reduce discharge ratios, supporting sustainable development [19]. Regionally, the Yangtze River Economic Belt shows declining sewage discharge growth rates alongside economic growth [20], and the Beiyun River Basin has improved wastewater treatment capabilities due to rising GDP and environmental investments [21]. Similarly, Shaanxi and Xinjiang have achieved strong decoupling between sewage discharge and economic growth, offering insights for balancing economic and environmental goals [22].
Furthermore, some studies reveal an uncorrelated or curvilinear relationship between economic development and SDI. For instance, Chen and Chen found that despite China’s rapid industrial growth, industrial wastewater discharge remained stable, indicating that economic expansion did not significantly increase pollution burdens on aquatic ecosystems [13]. Other research suggests an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic development and industrial sewage discharge, where discharge initially rises with economic growth but later declines [23]. For instance, Leng and Yuan observed this trend in the Nansi Lake area, where industrial wastewater discharge increased during early economic growth but decreased as growth accelerated [24]. Similarly, Bu et al. confirmed this inverted U-shaped pattern across 30 Chinese provinces, aligning with the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) [11], with Heilongjiang and Guangdong showing the most pronounced effects [13].
However, not all regions follow this pattern. Liang found no evidence of an EKC in Sichuan Province from 2007 to 2017, indicating that economic development did not lead to reduced sewage discharge [25]. At the city level, Shanghai’s industrial wastewater index and Shenzhen’s industrial sewage discharge, electricity consumption, and SO2 emissions align with the inverted U-shaped EKC trend [26]. In rural areas, the relationship between rural sewage pollutant discharge intensity and rural residents’ disposable income shows an inverted U-shaped trend, while total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) discharge intensities follow an N-shaped pattern, reflecting fluctuating increases. These findings provide a nuanced perspective on the complex relationship between economic development and environmental pollution [27].
Investigating the relationship between EDLs and urban SDI is a crucial topic in environmental economics and sustainable development research. However, the impact of economic development on urban SDI is intricate; current research on the interplay between urban economic development and SDI remains limited. To enrich the relevant research, we focus on 288 cities in China, using spatial panel data from 2003 to 2021 and spatial regression models to explore the relationship between urban economic development and SDI. Additionally, this study constructs a dynamic spatial regression model to provide a new perspective for quantifying and analyzing the spatiotemporal characteristics of the direct, indirect, and total effects of economic development on sewage discharge intensity. Through this study, we aim to clarify the interactive relationship between economic development and urban SDI and provide scientific evidence for future environmental policy formulation and urban planning.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Variable Selection
2.1.1. Dependent Variable: Sewage Discharge Intensity (SDI)
SDI, which refers to the amount of sewage generated per unit of GDP, is a crucial indicator reflecting the relationship between urban economic development and environmental pollution. A high SDI suggests that the city’s economic growth may come at a high environmental cost, thus posing challenges to both sustainable urban development and the maintenance of environmental quality. Consequently, by taking SDI as the explanatory variable, we can gain a deeper insight into the relationship between EDL and sewage discharge.
2.1.2. Independent Variables: Explanatory and Control Variables
Economic development level: Economic development accelerates industrialization and urbanization, significantly increasing wastewater from industrial and urban sources, which influences both the volume and quality of wastewater released into the environment [16]. GDP per capita (PGDP) reflects a city’s economic strength and living standards. Thus, it is selected as the key metric to measure the extent of a city’s economic development.
Population agglomeration degree: Population agglomeration impacts urban sewage discharge in complex ways. While it can enhance scale and technological efficiencies in sewage treatment, potentially reducing discharge through better management, it also increases water consumption and strains resources, leading to higher sewage output [28]. Population density, as a measure of individuals per unit area, serves as a key indicator to capture the intensity of population concentration.
Urban development intensity: Urban development intensity is a key indicator of urbanization progress and spatial expansion. As urbanization accelerates, built-up areas expand, attracting more people and increasing economic activities and living demands. This growth intensifies water consumption and sewage discharge, highlighting the importance of the built-up-to-urban-area ratio as a measure of urban development intensity. This ratio reflects both urban sprawl and the environmental pressures it generates.
Urbanization rate: The urbanization rate, defined as the ratio of the urban population to the total population, is a key indicator of urbanization development. As urbanization increases, the urban population grows and cities expand, leading to higher water consumption for daily life, industrial production, and commercial activities. This results in increased wastewater generation and sewage discharge. Studies have shown that urbanization significantly impacts sewage discharge [29].
Industrial structure: Secondary industries are major sources of municipal wastewater due to their high water consumption and discharge levels. The level of industrialization is closely correlated with sewage discharge, as cities with a higher proportion of industrial activities tend to produce more wastewater [30,31]. Therefore, the value added of the secondary industry as a percentage of GDP is selected to characterize the industrial structure. Table 1 provides the complete variable information.

Table 1.
Definitions for the variables.
2.2. Data Sources and Statistical Analysis of Indicators
Given the availability and completeness of data, 288 cities in China (including municipalities and prefecture-level cities) were selected as research units, excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan. Using the “urban district population” from the Seventh National Population Census, cities were categorized as follows: megacities (>10,000,000), megalopolises (5,000,000–10,000,000), large cities (1,000,000–5,000,000), medium-sized cities (500,000–1,000,000), and small cities (<500,000). The 288 cities were grouped into three categories: 21 megacities (>5,000,000), 80 large cities (1,000,000–5,000,000), and 187 small and medium-sized cities (<1,000,000), as illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Classification of Chinese cities and their city size classes covered in this study.
The data required for this study, including urban sewage discharge, urban area, urban population, urban district population, and urban built-up area, were sourced from the “China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook”. Data regarding the PGDP, regional GDP, and secondary industry value added were procured from the “China City Statistical Yearbook” covering the period of 2003–2021. Some data were supplemented and revised through linear interpolation methods, the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model, and provincial and municipal statistical yearbooks. Notably, “sewage discharge” refers to the total discharge of domestic sewage and industrial wastewater. We conducted descriptive statistical analyses on all variables to reveal the distribution characteristics of the data (Table 2 and Figure 2).

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of variables (2003–2021).

Figure 2.
Box plot of urban SDI data for China from 2003 to 2021.
To reveal the spatiotemporal evolution of urban SDI in China from 2003 to 2021, we select urban SDI data from six sections (2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2017, and 2021, respectively) and use ArcGIS 10.7 for visualization. We classify the data into five classes using the Manual method, with thresholds set at 10, 20, 30, and 40 m3/million yuan, after which we sequentially define them as low, medium–low, medium, medium–high, and high-discharge classes. These are further plotted as the spatiotemporal pattern map of urban SDI.
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. OLS Model
Ordinary least squares (OLS) constitutes a fundamental and conceptually straightforward approach for estimating the parametric relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables in a regression model. Its calculation formula is given by
where t represents the year, i represents the city (i = 1, 2, …, 288), j represents the five influencing factors, and is the SDI for city i in year t. In addition, is the parameter to be estimated for j influences; represents the explanatory variable, which is the value of the influencing factor; denotes the spatial individual fixed effect; and represents the time-fixed effect. We applied logarithmic normalization to dependent and independent variables. However, given that the UR, UDI, and the InStr were all presented as proportions, they are not standardized.
2.3.2. Spatial Regression Model
To address OLS limitations, we use spatial panel data models (spatial lag model (SLM), spatial error model (SEM), spatial Durbin model (SDM)) that incorporate spatial and temporal dimensions, reducing bias from unobserved heterogeneity.
The SLM not only reflects the relationship between changes in SDI in a particular city and the factors that influence it but also shows the impact of a city’s SDI on changes in the SDI in other neighboring cities. The SLM is expressed as [32]
where represents the spatial lag coefficient, and Wij denotes the spatial weight matrix. Considering the spatial dependence that arises from the geographical adjacency of the research objects, we choose a spatial weight matrix based on geographical proximity.
The SEM accounts for the potential spatial autocorrelation among the independent error terms within the spatial data model, thus ensuring a more accurate and nuanced portrayal of spatial relationships [33] by including a spatial lag term for the dependent variable. The SEM is expressed as [34]
where represents the spatial error coefficient, and denotes the spatial autocorrelation error term.
The SDM combines the characteristics of SLM and SEM, considering both the spatial lag terms of explanatory variables and the spatial dependence of error terms. It can more comprehensively capture the complex spatial relationships between economic development and wastewater discharge in this study, which are influenced by local and surrounding economic activities as well as unobserved spatial factors. The SDM can be formulated as follows:
Panel data models encompass fixed-effect (FE) and random-effect (RE) models. The Hausman test serves as a valuable tool in deciding between these two models for a given study. When the H statistic of the Hausman test rejects the null hypothesis at a 1% significance level, it provides compelling evidence for the existence of fixed effects. Consequently, it is more appropriate and reasonable to opt for an FE model over an RE model in such circumstances. Conversely, if the null hypothesis is not rejected, an RE model would be the more suitable choice.
Before examining the effect of EDL on urban SDI, we conducted a model fitness test to ensure the accuracy of the analytical results. First, the Lagrange multiplier (LM) test and the LM test for robustness were conducted, and the resulting LM-lag, LM-error, Robust LM-lag, and Robust LM-error values all rejected the original hypothesis at the 1% level, thus confirming that the SDM should be considered. Further, we used the likelihood ratio (LR) test and Wald test for further fitness tests, and the results showed that the Wald_spatial_lag, LR_spatial_lag, Wald_spatial_error, and LR_spatial_error values significantly rejected the original hypothesis at the 0.01 level, indicating that the SDM could not be simplified to the SLM or SEM. Therefore, the SDM was determined to be the optimal model.
The SDM includes three main effects: direct, indirect, and total effects. “Direct effects” measure the impact of changes in independent variables within a region on its dependent variable. “Indirect effects” or “spillover effects” capture the influence of independent variables in neighboring regions on the dependent variable, reflecting spatial dependence. “Total effects” combine direct and indirect effects, representing the overall impact of independent variables on the dependent variable across all regions. Moreover, our rigorous analysis encompassed both FE and RE tests for the SPDM. Notably, the Hausman test emphatically rejected the RE hypothesis at a significance level of 0.01, thereby emphasizing the importance of utilizing fixed effects in our subsequent investigations. Given the dynamic nature of urban SDI over time, we deemed it essential to account for the temporal effect. Therefore, we opted for the individual–time double-fixed-effect SDM to conduct parameter estimation.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution and Agglomeration Characteristics of Urban SDI
From 2003 to 2021, China’s urban SDI witnessed significant changes, with the overall spatial distribution gradually showing a weakening trend (Figure 3). However, the change in SDI in Northeast China during this period is relatively small, and its intensity remains relatively high compared with other regions. In 2003, the urban SDI ranged from 0.1251 to 452.4525 m3/10,000 yuan, with significant differences among cities. There are 151 high-discharge cities, accounting for 52.43% of the total, while only 10 low-discharge cities exist, indicating a high level of urban SDI in China. By 2007, the SDI in various Chinese cities had slightly decreased, with the number of high-discharge cities reduced to 34 and mainly concentrated in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, Northeast China, as well as Guangxi, Fujian, Tibet, and Ningxia, which are predominantly industrial cities. In 2010, there was a significant decrease in urban SDI compared to previous years. Some cities with higher SDIs were distributed irregularly, with only five high-discharge cities remaining.
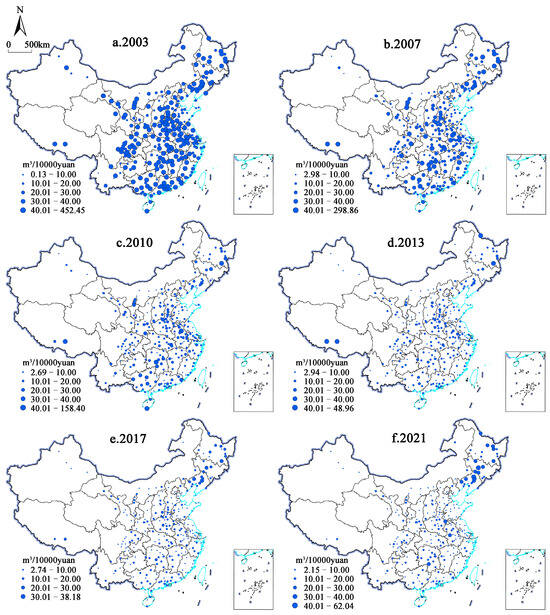
Figure 3.
Spatiotemporal pattern of urban SDI in China from 2003 to 2021.
By 2013, China’s urban SDI ranged from 2.9354 to 48.9647 m3/10,000 yuan, with a clear trend of weakening. Four high-discharge cities were in Heilongjiang and Tibet, specifically Mudanjiang, Heihe, Lhasa, and Xigaze, reflecting the impact of energy conservation and discharge reduction policies. In 2017, low-discharge cities increased to 162 (55.25% of the total), with Northeast China exhibiting significantly higher SDI and spatial agglomeration. In 2021, the SDI range widened to 2.1542 to 62.0399 m3/10,000 yuan, with 182 low-discharge cities and only 2 high-discharge cities, both in Northeast China. This spatiotemporal evolution indicates a gradual weakening of urban SDI, demonstrating the effectiveness of energy conservation and discharge reduction measures. However, Northeast China, dominated by heavy industries, continues to exhibit high wastewater consumption and discharge.
On this basis, we used global spatial autocorrelation analysis to measure the spatial clustering characteristics of urban SDI in China from 2003 to 2021 (Table 3). The results reveal that, except for 2010, the Moran’s I values for SDI in 288 cities in China in 2003, 2007, 2013, 2017, and 2021 were all significant at the 0.01 level, and the Moran’s I indices were all positive. These results indicate that the SDI in Chinese cities exhibits significant spatial agglomeration and positive spatial correlation in terms of spatial distribution. After 2010, Moran’s I value gradually increased, indicating that the spatial agglomeration of urban SDI has gradually strengthened.

Table 3.
Spatial correlation index of SDI in 288 cities of China in 2003–2021.
In addition, we examined the longitudinal changes in SDI for megacities, large cities, and small and medium-sized cities (Figure 4). From 2003 to 2021, the average SDI of all three sizes of cities shows a decreasing trend, with larger fluctuations in the decreasing trend from 2003 to 2007, and a relatively stable decreasing trend after 2010. When comparing the average SDI of the three sizes of cities, it is found that the average SDI of small and medium-sized cities is consistently higher than that of megacities and large cities, and the gap is gradually narrowing over time. This trend also reflects the effectiveness of the government’s environmental protection policies and the construction and management of sewage treatment facilities.

Figure 4.
Longitudinal variation in SDI in different-sized cities.
3.2. Spatial Regression Analysis of Urban SDI
Model (4), which shows the estimation results of this double fixed-effect SDM, stands out in comparison to Models (1), (2), and (3). Specifically, Model (4) boasts a significantly higher R2 value of 0.814, indicating a substantially superior fit. Consequently, our subsequent analysis and interpretations will be grounded in the findings of this double fixed-effect model (Table 4).

Table 4.
Benchmark regression results (OLS).
Relying solely on regression coefficients to assess the impact of explanatory variables on explained variables is insufficient due to factors like spatial lag feedback effects [35]. Thus, initial estimates were treated as preliminary judgments. For a more accurate analysis, partial differential decomposition was used to examine direct (LR_Direct), indirect (LR_Indirect), and total (LR_Total) effects.
The spatial effect decomposition of the SDM in Table 5 reveals interesting insights. First, considering the direct effect, a 1% rise in PGDP within a city will reduce SDI by 0.248%, highlighting the link between economic growth and environmental sustainability. Moving to the indirect effects, economic development negatively impacts neighboring cities’ SDI, with a 1% PGDP increase reducing surrounding regions’ SDI by 0.322%, emphasizing regional interconnectedness in pollution control. In terms of the total effect, a 1% rise in PGDP decreases SDI across the entire study area by 0.570%, underscoring the role of economic growth in fostering regional environmental improvement.

Table 5.
Decomposition of the spatial effect of EDL on the SDI.
Furthermore, within a city, PopDen positively impacts the SDI, but interestingly, it exhibits a negative spatial spillover effect on the SDI of neighboring cities. To elaborate, a 1% increase in PopDen enhances the SDI locally, but this upward trend mitigates the SDI in surrounding cities by 0.163% due to spatial spillover. This seemingly paradoxical phenomenon underscores the intricate interplay between population dynamics and their environmental repercussions at both local and regional levels.
The ratio of the built-up area to the overall urban landscape serves as a mirror of a city’s development intensity and construction efforts. As urbanization progresses, urban construction activities not only consume vast amounts of water resources but also spawn significant quantities of sewage. Notably, in terms of indirect impact, a 1% surge in UDI within a region prompts a corresponding 1.7% rise in SDI in neighboring cities. This result underscores the positive spatial spillover effect of UDI, exhibiting distinct regional characteristics.
The UR, a pivotal metric in gauging the level of urbanization, profoundly captures the advancements in urban economic and social development. Within the city limits, there exists a positive correlation between the UR and SDI. In other words, an increase in the urban population’s share directly correlates to an escalation in SDI. Specifically, at a 0.01 significance level, for every 1% increment in the urbanization rate, urban SDI increases by 0.3%. However, from an indirect effect perspective, the urbanization level of neighboring cities does not exert a significant influence on the SDI of a given city, indicating the independence of SDI among cities.
The InStr, a cornerstone of a city’s economy, offers profound insights into its level of industrialization and the developmental phase. Analyzing its direct effects, we find that a 1% increase in the secondary industry’s added value to PGDP reduces SDI by 0.4%, likely due to technological and managerial advancements that enhance resource efficiency and pollution control. When considering the indirect effects, industrial structure optimization not only lowers SDI within a city but also reduces it in neighboring cities by 1.9%. In terms of the overall impact, every 1% improvement in InStr decreases SDI across the entire study area by 2.3%, highlighting its critical role in protecting regional water environments. This optimization not only reduces local pollution but also promotes sustainable development through spatial spillover effects.
3.3. Impact of EDL of Different-Sized Cities on SDI
To explore, in more detail, the influence mechanism of EDL on SDI across cities of different scales, we used the partial differential decomposition method of SDM to analyze the spatial effects between PGDP and SDI. This approach provides a clearer understanding of the relationship between economic development and environmental protection in cities of varying sizes.
For megacities, EDL has a significant spatial effect on SDI (Table 6 and Figure 5). Specifically, the direct effect shows that a 1% increase in PGDP reduces SDI by 0.222%, highlighting the positive role of economic development in improving sewage discharge management. From the perspective of indirect effect analysis, EDL growth not only has a positive impact on the region but also leads to the reduced SDI of neighboring cities through the spatial spillover effect. In other words, for every 1% increase in PGDP, the SDI of the neighboring cities will also be reduced by 0.066%. At the level of the total effect, EDL has a significant negative spatial spillover effect on all study units; that is, for every 1% increase in PGDP, the SDI of megacities will be reduced by 0.287%. In summary, EDL has a significant spatial spillover effect on the SDI of megacities in terms of direct, indirect, and total effects.

Table 6.
Spatial effect decomposition of EDL on SDI in different-sized cities.
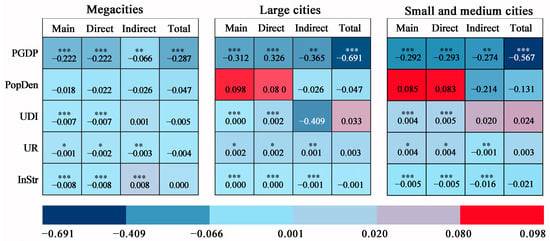
Figure 5.
Heat map of spatial effect decomposition of EDL on SDI. t-statistics in parentheses, ***, **, and * represent the 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 significant levels, respectively.
For large cities, a significant correlation exists between SDI and EDL growth. In terms of the direct effect, a 1% increase in PGDP reduces SDI by 0.326%. From the perspective of the indirect effect, every 1% growth in PGDP has a positive impact on the city and, in turn, prompts the neighboring big cities to reduce the SDI by 0.365% through the spatial spillover effect. From the perspective of the total effect, a 1% rise in PGDP decreases SDI by 0.691%, demonstrating a significant negative spatial spillover effect. In summary, the EDL exerts a significant spatial spillover influence on the SDI of large cities, whether from direct, indirect, or total effects.
For small and medium-sized cities, the relationship between EDL and SDI is equally significant. From the point of view of the direct effect, every 1% increase in PGDP will trigger a corresponding decrease of 0.292% in SDI. Shifting to indirect effects, a 1% increase in GDP per capita elicits a reduction of 0.274% in the SDI of neighboring small and medium-sized cities, thereby demonstrating a spatial spillover phenomenon. At the level of the total effect, the EDL exerts a negative spatial spillover effect across all study units, with each 1% rise in PGDP contributing to an aggregate decrease of 0.567% in the SDI of small and medium-sized cities. Consequently, it is evident that the EDL possesses a significant spatial spillover impact on the SDIs of these cities, regardless of whether this is analyzed through direct, indirect, or total effects.
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Urban SDI
From 2003 to 2021, China’s urban SDI exhibited a consistent downward trend, indicating an overall improvement in sustainability. In 2003, significant disparities in SDI among cities existed but gradually narrowed over time. High-discharge cities declined markedly, while low-discharge cities increased. This trend aligns with Shen et al.’s findings on industrial wastewater discharge in North China from 2003 to 2019 [15] and highlights the uneven effectiveness of environmental protection measures [36]. The decline in SDI since 2013 is closely tied to national energy-saving and discharge-reduction policies, advancements in environmental technologies, and increased public awareness. For example, the National Water Ecological Civilization City Construction Pilot (WECCP) policy, implemented in 278 cities since 2013, significantly reduced industrial sewage discharges in pilot cities, with peak effectiveness between 2014 and 2018 [37].
Despite the overall decline, Northeast China maintains a high SDI with minor fluctuations, largely due to its heavy industrial base, which involves significant water consumption and pollutant discharge. Yao et al. have identified industrial expansion and resource exploitation as primary drivers of high effluent discharge in the region [38]. Additionally, lagging environmental infrastructure and wastewater treatment technologies exacerbate the issue. For instance, in the Liaohe River Basin, economic growth has increased domestic and industrial wastewater discharge, straining the environment due to insufficient sewage treatment facilities [39]. Urgent measures, such as industrial restructuring, infrastructure enhancement, and technological upgrades, are needed to reduce SDI and improve environmental quality in Northeast China.
Based on global spatial autocorrelation analysis, the results are positive, indicating that from 2003 to 2021, the spatial distribution of urban SDI in China exhibited pronounced spatial clustering, which implies that cities with high or low discharge intensities tend to cluster together. This discovery aligns with previous research, such as the [13] study on industrial wastewater discharges, which highlighted the significant spatial autocorrelation between local provinces and their neighboring regions, further indicating that this correlation has been gradually intensifying over time. Disparities in economic progress, resource allocation, and environmental policies among cities lead to inconsistent sewage treatment and discharge standards, contributing to the geographical concentration of SDI. For instance, in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, sewage treatment plants are concentrated in the Central and Western regions, while the Northwestern and Southwestern regions show high per capita sewage output, reflecting uneven distribution and functionality of wastewater treatment facilities [40].
4.2. Relationship Between EDL and SDI
First, the present study found that every 1% increase in per capita GDP led to a 0.570% decrease in SDI, which means that a negative correlation exists between EDL and urban SDI, similar to the results of some previous studies [10,17]. Previous studies have argued that urban economic development promotes sewage discharge [3] or identified nonlinear relationships [13,24], such as the inverted U-shaped environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) observed in China’s megacities [16]. This study clarifies that EDL and environmental protection are not mutually exclusive. As economies expand and living standards rise, the demand for cleaner environments drives investments in green technologies and environmental protection. In China, technological innovation has been central to reducing pollutants [41], with advanced technologies and improved financial efficiency effectively lowering SDI [3].
Second, EDL exhibits a notable spatial spillover effect on SDI, implying that a region’s economic development not only impacts its environmental protection but also positively influences neighboring regions. This is supported by findings that provincial GDP growth, technological innovation, and increased environmental governance investments reduce industrial sewage discharges in adjacent provinces [11]. Accelerated economic development also enhances water pollution control capacity, further reinforcing this spillover effect [42]. Market integration among neighboring regions also helps curb local pollution discharges [43], while higher centralized wastewater treatment rates positively impact adjacent areas [44]. In regions like the Pearl River–West River Economic Belt, pollution in one county exacerbates neighboring counties’ pollution levels due to similar industrial structures and industrial transfers [45,46]. These findings highlight the importance of strengthening inter-regional cooperation to promote green development and improve overall environmental protection.
At the same time, the EDL of megacities, large cities, and small and medium-sized cities adversely affects the SDI, which does not simply follow the traditional theory of the EKC. This phenomenon stems from factors such as industrial structure optimization, environmental policies, technological advancements, and increased public environmental awareness. Economic growth prompts cities to shift to less polluting industries, supported by stricter regulations and better sewage treatment, while rising living standards boost public demand for environmental protection and water conservation. This synergy between economic growth and environmental protection challenges the EKC theory, demonstrating their coexistence under effective policies and technological support. Large cities better inhibit SDI due to superior infrastructure, stricter regulations, and higher awareness, whereas megacities face greater discharge pressures; small and medium-sized cities need targeted support for balanced environmental and economic development.
In addition, increases in PopDen, UDI, and UR elevate urban SDI, as concentrated residential and commercial activities escalate water consumption and discharge. This aligns with [47] findings that urbanization significantly drives water pollutant discharges. However, the increase in InStr reduces urban SDI, reflecting the dual impact of industrialization and technological advancements, such as efficient water use and advanced pollution control technologies [48]. Furthermore, industrial structure optimization not only benefits local areas but also positively influences neighboring cities through regional industrial upgrading and the diffusion of environmental initiatives. In China’s Eastern, Central, and Western regions, industrial structure upgrades have significantly mitigated environmental pollution, highlighting its transformative role in fostering sustainable regional development [49]. This effect extends beyond individual cities, radiating positive impacts through interregional industrial linkages and the spread of environmental technologies.
4.3. Limitations
However, this study is not devoid of limitations. First, in terms of variable selection, only five independent variables were chosen in this study. Thus, the data may not fully cover all relevant variables, such as the technological advancement level, foreign investment intensity, government investment strength, and the enforcement of urban environmental protection policies. These variables, which potentially have a profound influence on sewage discharges, have not been thoroughly investigated in this study. Second, from a methodological perspective, the spatial panel model employed might not adequately capture the intricacies of all the factors influencing sewage discharge, especially those that are difficult to quantify, such as public awareness of environmental protection and the level of corporate management, which are not adequately captured in the model. Additionally, the proposed model may have neglected the dynamic interaction effects among cities, such as technology diffusion and policy imitation, which interact with each other among cities and jointly affect SDI. Furthermore, this study did not consider the possible nonlinear relationship between economic development and sewage discharge. In addition, China’s large regional differences may cause the relationship between urban sewage discharge and economic development to have unique spatial characteristics, but current research has not sufficiently explored the spatial distribution patterns and heterogeneity of this relationship in different regions. In future studies, we will consider using methods, such as nonlinear modeling or adding quadratic terms, to further explore this issue in depth.
5. Conclusions
Urban sewage discharge is an important topic in the field of research of environmental economics and sustainable development. In this study, we took the SDIs of 288 cities in China from 2003 to 2021 as examples and used spatial panel modeling to explore in depth the impact of the level of urban economic development on sewage discharge. The conclusions of the study are as follows:
First, economic development has an inhibitory effect on SDI; that is, for every 1% increase in PGDP, the SDI of the whole study area will be reduced by 0.570%, and there will be a significant spatial spillover effect. However, the EDL and SDI of different-scale cities have varying degrees of influence, and the effect on large cities is more significant.
Second, from the spatiotemporal evolution of urban SDI from 2003 to 2021, China’s urban SDI changed significantly, and the overall spatial distribution shows a trend of gradual weakening. In comparison, the change in SDI in the Northeast region during this period is relatively small, and its intensity is still higher compared with other regions. Related to this, the global autocorrelation results reveal that China’s urban SDI shows significant spatial clustering and a positive correlation phenomenon.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y. and Y.W. (Yang Wang); methodology, X.Y., Y.W. (Yang Wang), and G.S.; software, X.Y.; validation, X.Y. and Y.W. (Yang Wang); formal analysis, X.Y. and Y.W. (Yang Wang); investigation, X.Y.; resources, Y.W. (Yang Wang); data curation, X.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Y., W.L., and Y.W. (Yufei Wang); writing—review and editing, Y.W. (Yingmei Wu) and Y.W. (Yang Wang); visualization, X.Y.; supervision, Y.W. (Yingmei Wu), Y.W. (Yang Wang), and H.Z.; project administration, Y.W. (Yingmei Wu) and Y.W. (Yang Wang); funding acquisition, Y.W. (Yingmei Wu), Y.W. (Yang Wang), and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42130712); the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (Grant No. 202401AS070037; No. 202301AT070062); Yunnan Province Philosophy and Social Science Innovation Team Project (grant No. 2014CXP02); Yunnan Province Innovation Team Project (202305AS350003); “Yunnan Revitalization Talent Support Program” in Yunnan Province (Grant No. XDYC-WHMJ-2022-0016; Grant No. XDYC-QNRC-2022-0740).
Data Availability Statement
The data will be provided if requested.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China; the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects; Yunnan Province Philosophy and Social Science Innovation Team Project; Yunnan Province Innovation Team Project; “Yunnan Revitalization Talent Support Program” in Yunnan Province.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bleischwitz, R.; Spataru, C.; VanDeveer, S.D.; Obersteiner, M.; Van Der Voet, E.; Johnson, C.; Andrews-Speed, P.; Boersma, T.; Hoff, H.; Van Vuuren, D.P. Resource nexus perspectives towards the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Giupponi, C.; Wada, Y. Measuring global water security towards sustainable development goals. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.F.; Mao, Y.H.; Rong, J.X. Policy dividend or “policy trap”? Environmental welfare of establishing free trade zone in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.; Zhao, L.; Shi, T.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Mao, G.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, Y. Pollution control and cost analysis of wastewater treatment at industrial parks in Taihu and Haihe water basins, China. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 172, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Ding, C.; Zhou, G.X.; Han, L. How magnitude of PM2.5 exposure disparities have evolved across Chinese urban-rural population during 2010–2019. J. Clean Prod. 2023, 382, 135333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; McCornick, P.G.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P.S. The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agr. Water Manage. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegar, S.; Bogovic, N.D.; Jugovic, A. Impact of intersectoral dependencies in national production on wastewater discharges: An extended input-output study of the Croatian economy. Water 2022, 14, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasut, M.T.; Jensen, K.R.; Shivakoti, G. Analysis of constraints and potentials for wastewater management in the coastal city of Manado, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.L.; Islam, M.S.; Ju, M.D. Urban river pollution in the densely populated city of Dhaka, Bangladesh: Big picture and rehabilitation experience from other developing countries. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 321, 129040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.R.; Zhang, Y.; Xiu, P.S.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhu, S.K. Index-based analysis of industrial structure and environmental efficiency based on sewage discharge assessment in China. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Wang, E.D.; Jiang, Z.Y. Evaluating spatial characteristics and influential factors of industrial wastewater discharge in China: A spatial econometric approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Tian, G.; Kong, L. Spatial-temporal characteristics of China’s industrial wastewater discharge at different scales. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8103–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, H.Q. Spatiotemporal coupling measurement of industrial wastewater discharge and industrial economy in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46319–46333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.D. Driving forces and spatio-temporal differentiation of pollutants discharge from industrial wastewater and domestic sewage in Fujian Province. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2022, 42, 485–494. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.Y.; Yang, Z.J.; Li, L. The spatial and temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of industrial pollution in North China. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, F.L.; Yan, L. Interactions among electricity consumption, disposable income, wastewater discharge, and economic growth: Evidence from megacities in China from 1995 to 2018. Energy 2022, 260, 124910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.F. A simulation study of an innovation-driven sustainable development model and its impacts and applications: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2021, 42, e13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, W.Z. Determining whether trade can affect regional environmental sustainability from the perspective of environmental pollution. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.P.; Mei, Z.A.; Song, T.; Yang, C.X. Gearing urban metabolism toward the carbon neutrality target: A case study of Hebei province, China. Energies 2022, 15, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, M.Y.; Yang, R.J.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.Y. Decoupling water environment pressures from economic growth in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Wei, Y.S.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.X. A comprehensive analysis of impacts of socio-economic development and land use on river water quality in a megacity-region: A case study. Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.X.; Cai, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Zhao, M.J. Decoupling analysis of water use and economic development in arid region of China-Based on quantity and quality of water use. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Li, Z.B.; Wang, Z.J. Whether openness and inclusiveness exacerbates urban pollution: Evidence from China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2022, 148, 05022018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.F.; Yuan, L.D. An empirical of the environmental Kuznets curve in the Huaihe River basin. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 8740–8748. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.D.; Gong, Q.X.; Zheng, H.T.; Xu, J. Examining the impact factors of the water environment using the extended STIRPAT model: A case study in Sichuan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12942–12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.H. Coordinated environment and economy in coastal development based on industrial wastewater and SO2 emissions. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 109, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Zhao, X.T.; Cai, N.; Chen, M.M.; Wang, H. Pollution discharge and environmental treatment efficiency of rural domestic sewage in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, M.; Sarkis, J.; Xue, B.; Zhang, L.; Fujita, T.; Yu, X.; Ren, W.; Zhang, L.; Dong, H. Spatial-temporal patterns and driving factors for industrial wastewater emission in China. J. Clean Prod. 2014, 76, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zheng, S.Q.; Zhao, M.Y.; Wu, H.T.; Guo, Y.X.; Li, Y.W. Reexamining the relationships among urbanization, industrial structure, and environmental pollution in China—New evidence using the dynamic threshold panel model. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.Y.; Huang, G.H.; Liu, L.R.; Guan, Y.R.; Zhai, M.Y. Dynamic wastewater-induced research based on input-output analysis for Guangdong Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Xia, R.; Ma, S.; Jia, R.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Bin, L. Understanding China’s industrialization driven water pollution stress in 2002–2015—A multi-pollutant based net gray water footprint analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Kho, Y. GeoDa: An introduction to spatial data analysis. Geogr. Anal. 2006, 38, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, K.M.; Zhao, Y.B.; Wang, C.J.; Zhang, H.O. Examining the effects of the built environment on housing rents in the Pearl River Delta of China. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2022, 15, 289–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbia, G. Spatial Econometrics: Statistical Foundations and Applications to Regional Economic Growth; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lesage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Z.X. China sewage treatment engineering issues assessment. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 377, 134391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.R.; Liu, X.Y.; Ji, L.L.; Lou, Z.X.; Yuan, X.M. The emission reduction effect of industrial wastewater in the pilot city policy of water ecological civilization. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wei, Y.G.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Yu, Y.J.; Huang, W.Y. What influences the urban sewage discharge in China? The effect of diversified factors on the urban sewage discharge in different regions of China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 6099–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tang, J.; Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lyu, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, Z. A GIS-based method for identification of blindness in former site selection of sewage treatment plants and exploration of optimal siting areas: A case study in Liao River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.H.; Tang, C.C.; Wang, Z.R. Spatial patterns and influencing factors of sewage treatment plants in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.M.; Wen, L.; Sheng, M.S.; Poletti, S. Appraising the role of energy conservation and emission reduction policy for eco-friendly productivity improvements: An entropy-balancing DID approach. Energy Econ. 2024, 132, 107422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z. Spatiotemporal differentiation and the obstacle factors influencing the coupling coordination between economic development and water pollution control capability in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75681–75698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Shao, S.; Fan, S. Market integration and environmental quality: Evidence from the Yangtze River delta region of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Qi, L. Assessing the impact of green transformation on ecological well-being performance: A case study of 78 cities in western China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 9, 11200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Q. Impact mechanism of new urbanization on environmental pollution: Empirical analysis based on spatial panel model. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 928100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, K. Study on driving factors and spatial effects of environmental pollution in the Pearl River-Xijiang River Economic Belt, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Wu, J.X.; Qian, Z.D.; Fan, J.; Wang, Q. Spatial effects on emission reduction of water pollutants and its driving forces in Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 885–895. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, L.; Tan, Z.; Luo, C.X.; Qiao, N. Exploring the contribution of the river chief system on controlling industrial water pollution under quasi-natural experimental conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 89415–89429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Zhai, P. Economic growth, industrial structure upgrading and environmental pollution: Evidence from China. Kybernetes 2023, 52, 518–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).