Abstract
Rapid socio-economic development and the impact of human activities have exerted tremendous pressure on the groundwater system of the Dawen River Basin (DRB), the largest tributary in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Hydrochemical studies on the DRB have largely centered on the upstream Muwen River catchment and downstream Dongping Lake, with some focusing solely on karst groundwater. Basin-wide evaluations suggest good overall groundwater quality, but moderate to severe contamination is confined to the lower Dongping Lake area. The hydrogeologically complex mid-reach, where the Muwen and Chaiwen rivers merge, warrants specific focus. This region, adjacent to populous areas and industrial/agricultural zones, features diverse aquifer systems, necessitating a thorough analysis of its hydrochemistry and origins. This study presents an integrated hydrochemical, isotopic investigation and EWQI evaluation of groundwater quality and formation mechanisms within the multiple groundwater types of the central DRB. Central DRB groundwater has a pH of 7.5–8.2 (avg. 7.8) and TDSs at 450–2420 mg/L (avg. 1075.4 mg/L) and is mainly brackish, with Ca2+ as the primary cation (68.3% of total cations) and SO42− (33.6%) and NO3− (28.4%) as key anions. The Piper diagram reveals complex hydrochemical types, primarily HCO3·SO4-Ca and SO4·Cl-Ca. Isotopic analysis (δ2H, δ18O) confirms atmospheric precipitation as the principal recharge source, with pore water showing evaporative enrichment due to shallow depths. The Gibbs diagram and ion ratios demonstrate that hydrochemistry is primarily controlled by silicate and carbonate weathering (especially calcite dissolution), active cation exchange, and anthropogenic influences. EWQI assessment (avg. 156.2) indicates generally “good” overall quality but significant spatial variability. Pore water exhibits the highest exceedance rates (50% > Class III), driven by nitrate pollution from intensive vegetable cultivation in eastern areas (Xiyangzhuang–Liangzhuang) and sulfate contamination from gypsum mining (Guojialou–Nanxiyao). Karst water (26.7% > Class III) shows localized pollution belts (Huafeng–Dongzhuang) linked to coal mining and industrial discharges. Compared to basin-wide studies suggesting good quality in mid-upper reaches, this intensive mid-reach sampling identifies critical localized pollution zones within an overall low-EWQI background. The findings highlight the necessity for aquifer-specific and land-use-targeted groundwater protection strategies in this hydrogeologically complex region.
1. Introduction
Groundwater, an indispensable cornerstone of human existence and societal progress, critically influences ecosystem health and regional sustainability [1,2,3]. Its superior stability, reliability, and resilience to contamination compared to surface water make it indispensable, especially in arid/semi-arid regions [4,5,6]. However, intensifying climate change and human activities are exacerbating global water scarcity and pollution, posing a dual threat of constrained development and compromised ecological/soil security in groundwater-dependent areas [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. The chemical makeup of groundwater is shaped over time by a complex interplay of physical processes, chemical reactions, and biological activity as water moves through aquifers. These ongoing interactions with surrounding rock formations, rainfall infiltration, and microbial processes gradually determine the water’s final ion composition [14,15,16], serving as a fundamental indicator for deciphering flow paths, recharge sources, and evolutionary mechanisms, intrinsically linked to climate. As a primary drinking source, its quality directly impacts public health [7,17], shaped by natural hydrological exchange and anthropogenic inputs [18,19]. Consequently, scientifically assessing groundwater quality and understanding its hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms are paramount for sustainable resource management [20,21,22,23]. Economic activities are significantly altering groundwater chemistry, while over-exploitation-induced water table decline further disrupts hydrochemical equilibria, heightening risks. Health hazards from contamination, such as links between nitrate-enriched groundwater and intestinal cancers or methemoglobinemia [18,24,25], underscore the urgent need for health risk assessments based on precise hydrochemical understanding. Groundwater quality evaluation bridges pollution and health, providing essential scientific support for safeguarding water security [26,27]. Therefore, in-depth investigation into local groundwater chemistry and its changes is essential for system comprehension and supporting sustainable water management.
Multivariate statistical analysis and hydrogeochemical interpretation represent two predominant methodological approaches in the groundwater hydrochemistry domain, integrating diverse analytical methods like Piper diagrams (for hydrochemical facies classification), Gibbs diagrams (elucidating controlling factors of natural evolution), rock weathering end-member diagrams, chloro-alkaline indices (assessing ion exchange), geostatistical analysis (characterizing spatial variability), and ion ratio analyses (exploring ion associations) [28,29]. Piper diagrams facilitate the visualization of hydrochemical types to decipher evolutionary characteristics and solute origins [30], while Gibbs diagrams dissect natural evolutionary drivers and dominant controlling factors [31,32,33]. Pearson correlation analysis reveals statistical relationships between variables. Boudibi et al. applied ordinary kriging method to assess and predict groundwater chemical parameter concentrations in southeastern Algeria [34]; Zhan et al. combined multivariate statistics and hydrogeochemical techniques to investigate evolutionary mechanisms under the influence of chemical plant wastewater in rural northern China [35]; Ha et al. utilized the WQI and multivariate analysis to demonstrate significant anthropogenic impacts on groundwater in southern Vietnam [36]. Globally, research consistently focuses on two core influencing factors: natural geological settings and anthropogenic activities. Prior research has utilized diverse methodologies for groundwater quality assessment, such as fuzzy mathematical models, analytic hierarchy processing, and artificial neural network implementations [37,38,39]. Within this methodological spectrum, the EWQI emerges as a key methodology for characterizing the combined impacts of natural and human factors on integrated water quality metrics [40]. Its methodological robustness and unbiased quantification are driving its extensive adoption in contemporary hydrogeological research [41,42].
The Dawen River Basin (DRB) sits in the heart of Shandong. The Dawen River significantly contributes to Shandong Province’s economic growth and water resources. In recent years, accelerated socioeconomic progress has coincided with intensifying anthropogenic pressures on groundwater systems. Consequently, environmental hydrogeological challenges including aquifer over-exploitation, groundwater contamination, land subsidence, and ground fissures have been progressively aggravated. Prior research has examined hydrochemistry, forming processes, and quality evaluation in the DRB. Feng et al. (2019) characterized principal ionic constituents and controlling mechanisms in porous aquifer systems of DRB [43]; Zhao et al. (2020) documented progressive downstream contamination intensification in the DRB and wet-season quality deterioration [44]. Pollution source apportionment by Liu et al. (2021a) identified industrial effluents and agricultural spready sources as primary contributors [17]. Through comprehensive sampling of porous, fractured, and karst groundwater, Liu et al. (2023) established rock weathering dominance in hydrochemical evolution [45]. Most recently, Wei et al. (2025) applied an index combining the EWQI and NPI to assess groundwater contamination in the DRB [46]. However, hydrochemical investigations within the DRB have predominantly focused on specific sub-regions, notably the middle-upper Muwen River catchment [47,48] and lower reaches of Dongping Lake [49]. Furthermore, certain studies have concentrated exclusively on singular aquifer types, particularly karst groundwater systems [50]. Recent basin-wide assessments indicate generally favorable groundwater quality overall, with moderate to severe contamination primarily localized in the Dongping Lake zone of the lower basin [46]. The mid-reach section—characterized by the confluence of the Muwen and Chaiwen Rivers—demands particular attention due to its hydrogeologically complex setting. This zone interfaces with densely populated areas (e.g., Dawenkou, Ciyao, and Huafeng Towns), industrial parks, and agricultural irrigation districts that constitute potential contamination sources. Crucially, it exhibits the coexistence of multi-aquifer systems including unconsolidated, fractured, and karst groundwater. Consequently, comprehensive analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and genetic mechanisms within the mid-reach Dawenkou catchment is imperative.
Therefore, this study focuses on conducting an integrated analysis of hydrochemical characteristics, genetic mechanisms, and evolutionary processes across multi-aquifer systems (unconsolidated, fractured, and karst groundwater) in the mid-reach Dawen River Basin. The investigation aims to delineate dominant controlling factors governing groundwater contamination in distinct aquifer types. Furthermore, the EWQI technique is utilized for classifying water quality evaluations in the central basin segment, with comparative analysis against prior evaluation outcomes. This research provides actionable insights for hydrogeochemical interpretation and aquifer conservation methods for the study area.
2. Study Area
The DRB lies in Tai’an, the heart of Shandong Province [45,46]. The Dawen River flows from the northern slopes of Xuangu Mountain in Yiyuan County, Shandong Province. Its main stem stretches some 208 km, encompassing a vast basin area of 9069 square kilometers. In the DRB, the groundwater resources in 2023 were approximately 778 million m3, accounting for 85% of the total groundwater resources in Tai’an city [51]. The total groundwater exploitation in Tai’an City for 2023 reached about 516 million m3, with agricultural use constituting 67.5% of the exploitation, domestic use 26.4%, and industrial use 6.1% [51].
The study region is located in the central DRB, extending from 117°00′ E to 117°15′ E and 35°50′ N to 36°00′ N, encompassing 416 km2. Within the central portion of the Dawen River, the area has an extensive river system. The Muwen River from northeast section and Chaiwen River from southeast part converge in the research zone and form Dawen River (Figure 1). The research region has a total resident population of approximately 0.4 million. Within this region, the groundwater resources in 2023 amounted to roughly 206 million m3, representing approximately 26.5% of the total groundwater resources in the DRB [51]. Hydrological analysis of 62-year records (1956–2017) indicates a mean annual precipitation of 889 mm, of which 60–80% occurs during June–September [51]. The mean annual evaporation reaches 865 mm.
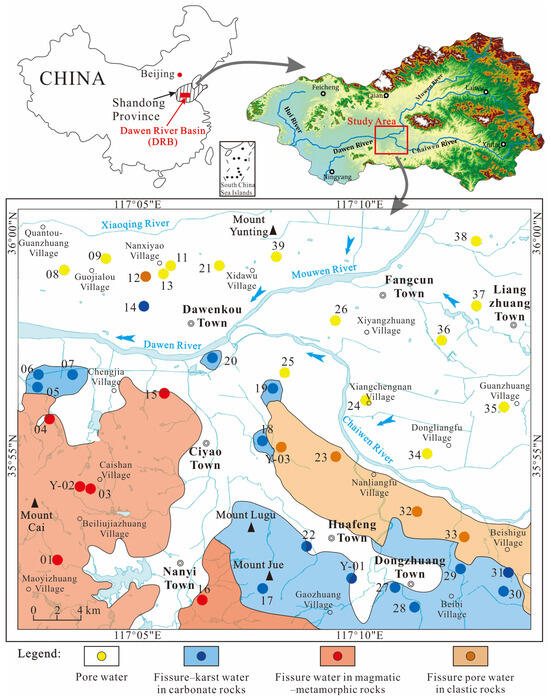
Figure 1.
Study area map with sampling point locations.
Topographic analysis in the study region reveals a south-to-north elevation gradient, with terrain sloping southeast to northwest. The highest elevation point is located at Mount Cai in the western sector, contrasting with the lowest elevation near Quantou-Guanzhuang village in the northwest. Geomorphological units are distinctly divided by the Dawen–Chaiwen river system: (1) the northern alluvial–fluvial plain (80–140 m); (2) southern low-mountain and hilly terrain (100–350 m).
The study area comprises four principal types of groundwater systems: pore water in loose sediments, fissure–karst water in carbonate rock formation, porous fracture water present in clastic rocks, and fracture-based water contained within igneous and metamorphic rock layers [45,46] (Figure 1). Porous water in unconsolidated deposits are distributed along the Dawen River, the Muwen River, the Chaiwen River, and their tributaries. These aquifers primarily occur within the modern channel deposits, characterized by alluvial and fluvial sediments mainly consisting of fine, medium, and coarse sands, along with gravel. The aquifer system is typically overlain by silt or silty clay, with direct exposures observed in riverbeds and floodplains. Fissure–karst water in carbonate rocks is predominantly found in the southeastern sector of the study region, near Beibi Village–Gaozhuang Village. The aquifer consists of Ordovician limestone, exhibiting well-developed fracture networks and karst features. Drilling cores reveal extensive fissures and honeycomb-shaped dissolution pores, indicative of significant secondary permeability. Porous fracture water in clastic rocks is predominantly located in the eastern area, near Nanliangfu–Beishigu Village. The aquifer is composed of Paleogene calcareous conglomerates. Fissure water in magmatic–metamorphic rocks is primarily distributed in the southwestern area, near Caishan, Beiliujiazhuang, and Maoyizhuang Village. Multiphase intrusive rock contact zones exhibit enhanced fracture development, providing favorable storage spaces and hydraulic conduits for groundwater.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Distribution
To assess hydrochemistry and groundwater quality in the central DRB, 40 samples were collected from July to August 2024 (dry season). Handheld GPS units were employed to log the precise geographical coordinates of every sampling point (Figure 1). The sampling strategy was designed to comprehensively represent the regional groundwater system, accounting for hydrogeological conditions and topographic features. The samples included 14 from porous unconsolidated deposits, 15 from fractured–karst carbonate samples, 5 from fracture–pore clastic rock samples, and 6 from fissured magmatic–metamorphic rock samples.
3.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
3.2.1. Sample Collection and Preservation
The sample collection and preservation procedures were implemented in compliance with “Methods for analysis of groundwater quality” [52]. Water samples were gathered in sterilized 500 mL plastic bottles. And duplicate specimens were obtained per sampling location. Prior to collection, each bottle underwent initial cleaning with 500 mL of distilled water and then three source water washes from the sampling site. To prevent the inclusion of pipeline-retained water and entrapped gases, a 5–10 min well purging procedure preceded actual sampling at every monitoring well. Immediately after collection, bottles were completely filled (eliminating headspace), securely sealed, and maintained under 4 °C refrigeration. All specimens were conveyed to the Water Quality Laboratory of Shandong Provincial Bureau of Geo-mineral Exploration within 3 days of collection for analysis, while isotope studies were performed at the Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, CNNC.
3.2.2. Analytical Methods
Analyses were conducted for the following parameters: K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42−, HCO3−, NO3−, TDS, TH, and pH [52]. HCO3− determinations employed 50 mL acidimetric titration. pH quantification utilized a PHS-3C digital pH meter (INESA Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Anions, including Cl−, SO42−, and NO3−, were identified using an ICS-1100 ion chromatography system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Cationic ions (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+) were measured using ICP-OES on an Avio™ 200 instrument (PerkinElmer Instruments Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA). The Picarro L2120 liquid water isotope analyzer (Picarro Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) measured the δ2H and δ18O stable isotopes, with results reported relative to the VSMOW standard (in ‰). Analytical accuracy was ±0.5‰ for δ2H and ±0.2‰ for δ18O, respectively.
The percentage of Ionic Balance Error (IBE%) was employed for analytical quality control, calculated as
(c) represents the total cationic charge (K++ Na++ Ca2++ Mg2+), while (a) denotes the total anionic charge (HCO3-+ SO42−+ Cl−+ NO3−). Cation and anion levels were measured in milliequivalents per liter (meq/L). The IBE of the samples varied between −1.5% and 2.75%, averaging at 0.84%. Significantly, the IBE results for the vast majority of samples fell within the acceptable ±5% error margin. This high proportion indicates strong analytical accuracy in determining the groundwater’s ionic composition.
3.3. Geostatistical Methods
To delineate hydrochemical properties, ascertain forming processes, and evaluate groundwater quality within the central part of DRB, an integrated geostatistical method was employed. The initial phase involved statistical analysis to define the fundamental chemical characteristics of the groundwater. Subsequently, hydrochemical facies was classified using the Piper diagram. To identify the dominant influences governing groundwater chemistry, Pearson correlation analysis, the Gibbs diagram, ionic ratios, and isotopic analysis were applied. In isotopic studies, the Global and Local Meteoric Water Line (GMWL and LMWL) for Tai’an were introduced. We used these two references to ascertain the source and primary determinants in research region groundwater.
3.4. EWQI Method
The EWQI determines the weights of evaluation indicators by calculating their information entropy. The entropy weight method exhibits strong objectivity, and the water quality evaluation results are more accurate and reliable. Consequently, an increasing number of scholars are adopting the entropy weight method for water quality evaluation [53,54,55]. The calculation process of the EWQI has been illustrated in previous studies [53,54,55].
The groundwater quality was classified into 5 categories based on the calculation results (Table 1).

Table 1.
EWQI level categorization.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemical Composition Characteristics
Forty groundwater samples were gathered for this investigation, with statistical analysis conducted on various ion types. Major ion levels in the central DRB groundwater were characterized as follows (Table 2). The notably high NO3− concentrations suggest considerable anthropogenic impacts on the aquifer system.

Table 2.
Mass concentration statistics of major ions/mg·L−1.
In terms of hydrochemical composition, groundwater samples from the central DRB displayed a clear anion sequence of SO42− > NO3− > HCO3− and cation hierarchy of Ca2+ > Na+ > Mg2+ based on mean concentrations (Table 1). Geochemical facies analysis revealed dominant ion pairs with Ca2+ contributing 68.3% of total cationic mass on average and SO42− accounting for 33.6% of total anionic mass (Figure 2), indicating pronounced Ca2+-SO42− geochemical characteristics in the study area.
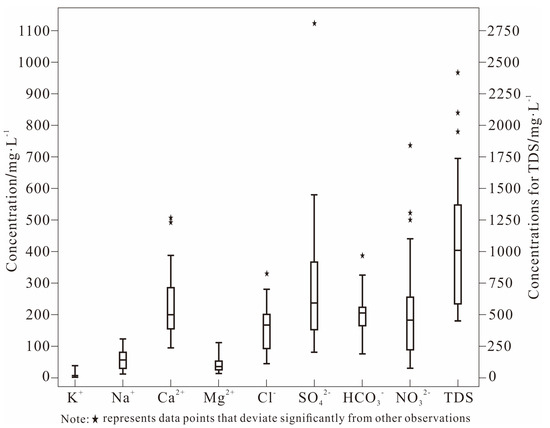
Figure 2.
Box plot of hydrochemical properties in groundwater samples from the study region.
Sampling points 34, 36, 24, 08, 13, and 11 are distributed from upstream to downstream in the porous unconsolidated aquifer zone, while sampling points 31, 27, 22, 20, 06, and 07 correspondingly span upstream to downstream in the carbonate karst aquifer zone (Figure 3). Analysis reveals distinct evolutionary patterns of hydrochemical parameters along the flow path between these two groundwater systems.
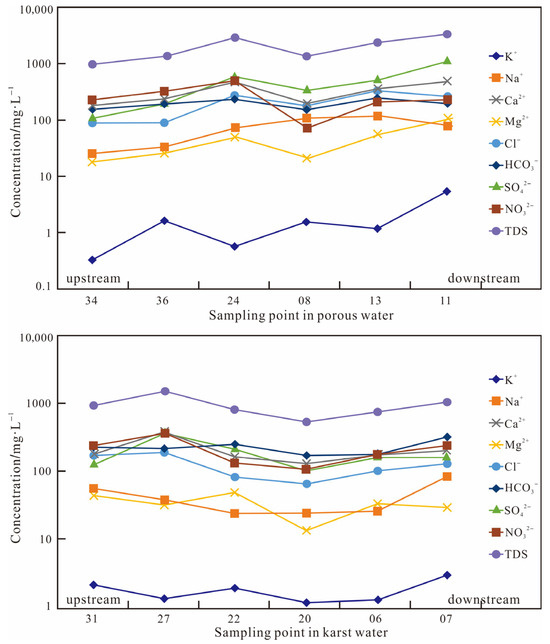
Figure 3.
Variations in the hydrochemical properties of groundwater along the direction of flow within the investigated region.
In the porous unconsolidated aquifer system, K+, Na+, Mg2+, SO42−, and TDS cations/anions exhibit slightly increasing trends downstream, with stable concentrations of Ca2+, Cl−, HCO3−, and NO3− (Figure 3 and Figure 4). For the carbonate karst aquifer system, all major ions demonstrate relatively stable concentrations along the flow direction without significant spatial variation.
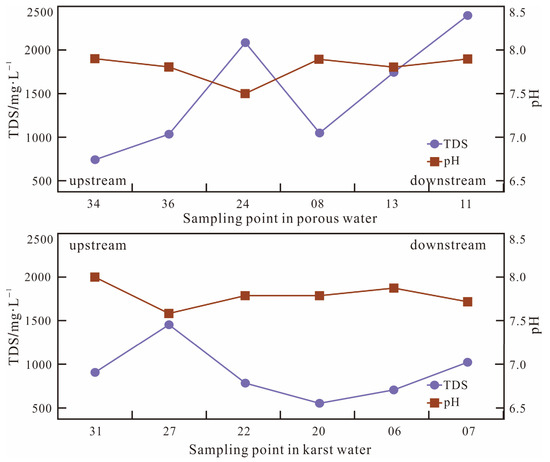
Figure 4.
Changes in pH and TDSs from upstream to downstream.
Groundwater samples across the investigated region display pH levels varying between 7.5 and 8.2, with over 80% of samples maintaining pH >7.7 and an average value of 7.9, indicating consistent weakly alkaline conditions. Both aquifer types show minimal longitudinal variation in pH values along their flow gradients. Total dissolved solid (TDS) measurements revealed that basin-wide TDS levels vary between 450 and 2420 mg/L (mean = 1056.1 mg/L), slightly exceeding the brackish water threshold (1000 mg/L). In the porous unconsolidated aquifer system, progressive TDSs increase downstream, attributed to enhanced water–rock interactions during groundwater migration, facilitating continuous mineral dissolution. In the karst system, relatively stable TDS values reflect mature hydrogeochemical evolution processes characteristic of established carbonate systems.
4.2. Groundwater Hydrochemical Types
The Piper trilinear diagram facilitates the analysis of groundwater chemical composition changes. The relative concentrations of various ions can be visually identified through this method [56,57]. In the investigated region, groundwater samples are predominantly clustered in the lower-left section of the Piper diagram, while displaying dispersed patterns in both the diamond-shaped field and right lower triangle (Figure 5). This indicates relatively stable major cations dominated by Ca2+ followed by Na+, whereas significant variations exist among anions. Most groundwater samples are characterized by predominant Cl− and SO42− anions, with certain samples showing markedly elevated SO42− concentrations. Pollution source investigations within the study area reveal potential contributions from chemical plants, domestic waste, and livestock farms, which likely account for these observed anion discrepancies. Combined analysis of sampling locations and the diamond-shaped field demonstrates a distinct evolution pattern in groundwater hydrochemical types along the groundwater flow direction: transitioning progressively from the HCO3·SO4-Ca type towards the SO4·Cl-Ca type, preliminarily indicating water quality deterioration downstream. Specifically, fissure water in magmatic/metamorphic rocks predominantly exhibits HCO3·SO4-Ca-type characteristics, fissure–karst water in carbonate rocks primarily manifests as the HCO3·SO4-Ca type, while pore water in unconsolidated sediments mainly displays SO4·Cl-Ca- and HCO3·Cl·SO4-Ca-type characteristics.
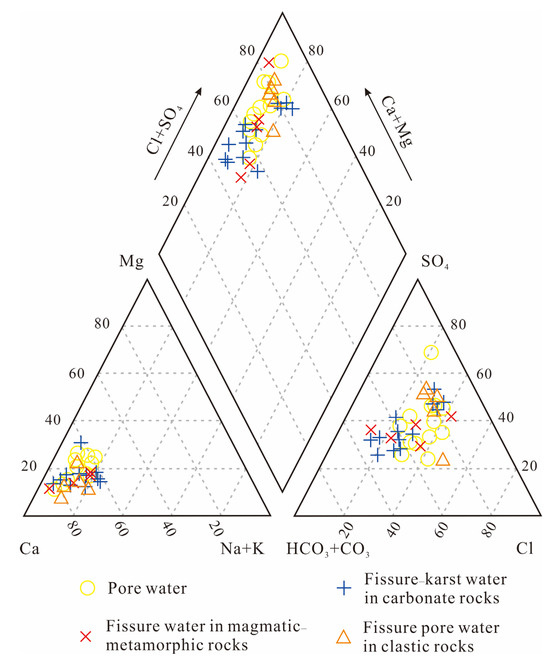
Figure 5.
Piper trilinear plot of hydrochemical properties in groundwater across the study region.
4.3. Interrelationships Among Chemical Indicators
The associations among various groundwater chemical components are significantly tied to their origins, and Pearson correlation analysis among chemical components is commonly employed to investigate ion origins [58,59]. As depicted in the groundwater chemical correlation matrix for the study region (Table 3), TDSs are positively associated with concentrations of Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42−, and NO3− (p < 0.01), indicating these ions make substantial contributions to TDSs. Notably, TDSs demonstrate the strongest correlations with Ca2+ (r = 0.969) and SO42− (r = 0.854), suggesting that these two ions serve as primary contributors to TDS concentrations. Significant correlations are observed between SO42− and Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ (p < 0.01), implying common genetic sources likely associated with sulfate mineral dissolution from surrounding magmatic and metamorphic rocks. Similarly, Cl− shows strong correlations with Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+, further supporting shared origin mechanisms potentially linked to water–rock interactions or anthropogenic influences requiring further investigation.

Table 3.
Correlations between conventional indicators.
4.4. Groundwater Recharge Sources
δ2H and δ18O isotopes are frequently used for identifying groundwater recharge origins, with different aquifers exhibiting distinct stable isotopic compositions indicative of varying recharge origins [59]. Consequently, groundwater flow pathways can be inferred by identifying specific δ2H and δ18O value ranges in groundwater systems. The analysis detects notable variations in isotopic profiles across diverse groundwater categories within the study region (Table 4). Notably, pore water in loose sediments demonstrates higher δ2H and δ18O values compared to other groundwater types, with mean values of −50.7‰ and −6.8‰, respectively. This phenomenon primarily results from relatively shallow groundwater burial depths in these formations, rendering them more susceptible to evaporation effects.

Table 4.
Statistics of δ2H and δ18O values in investigated region’s groundwater samples.
Surface water samples collected from the Dawen River exhibit pronounced enrichment of heavy isotopes, suggesting significant influence from evaporative concentration processes.
Based on δ2H and δ18O data from various water sampling points, a relationship diagram between δ2H and δ18O values of various water sources in the research region was constructed (Figure 6). The solid line and dashed line represent the GMWL: δ2H = 8δ18O + 10 [60] and LMWL: δ2H = 8.02δ18O + 7.66 [61], respectively. The blue circular dots represent the collected values [62,63] of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in fissure–karst water from the mid-upper region of the DRB.
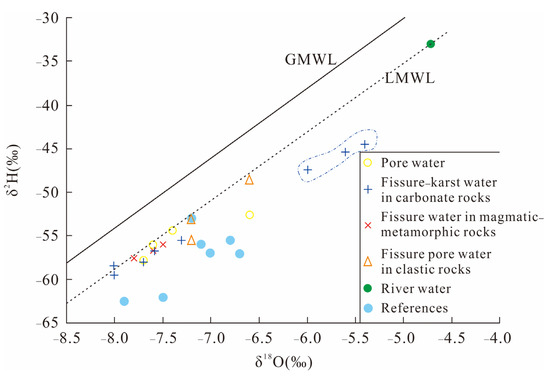
Figure 6.
Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic ratios in groundwater samples from the study region. The blue points were cited from references [62,63].
As shown, most samples are plotted beneath the GMWL, clustering around the LMWL, with a few below it. This distribution suggests that atmospheric precipitation is the primary source of groundwater recharge, while also exhibiting a certain degree of evaporative enrichment [64]. Further analysis reveals that the karst water samples are clustered within two distinct regions. The samples within the blue dashed region (points 05, 19, 20) exhibit isotopic values closer to those of surface river water. Geographically, these points are situated in close proximity to the Dawen River, suggesting significant influence from seepage recharge of surface water, coupled with strong evaporative enrichment leading to higher concentrations of heavier isotopes. The remaining karst water samples exhibit similar isotopic signatures as other groundwater types and previously reported karst water values cited from the literature [62,63]. This cluster is notably distant from the isotopic range of river water, indicating minimal impact from recent surface water infiltration.
4.5. Assessment of Key Chemical Influences on Groundwater
4.5.1. Water–Rock Interaction
Groundwater’s chemical makeup is heavily shaped by its interactions with aquifer materials. Gibbs diagrams are commonly employed to investigate water–rock interactions, categorizing ion sources into three processes based on major ion relationships from global rivers and oceans: evaporative crystallization dominance, atmospheric precipitation influence, and rock weathering control [65,66].
Figure 7 shows the preponderance of groundwater samples from the study region that lie within the rock weathering category. This suggests that rock weathering is the primary contributor to the significant ions found in the shallow aquifer, exerting a controlling influence on the groundwater’s chemical signature. The sample locations are significantly removed from the atmospheric precipitation endpoint, suggesting the minimal contribution of rainfall to the major ion composition. Regarding groundwater types, porous water samples exhibit a closer proximity to the evaporation–concentration dominance zone compared to other groundwater types. This suggests that evaporation-induced enrichment contributes to the formation of the hydrochemical properties in porous water. Within the study area, porous water is primarily found in basin plains and river valleys, characterized by relatively shallow water tables and lithology dominated by sandy clay, silt, and gravel. These conditions render it more susceptible to evaporation-concentration processes. Furthermore, a subset of karst water samples shows a tendency towards the evaporation–concentration zone, consistent with findings from the hydrogen and oxygen isotope analysis. Cross-referencing with sampling locations confirms that these specific karst water points (e.g., those plotted near the evaporation zone) are located in the DRB valley regions and also feature relatively shallow depths. Additionally, several sample points fall outside the delineated confidence region. This deviation may potentially be attributed to anthropogenic influences or ion exchange processes [67].
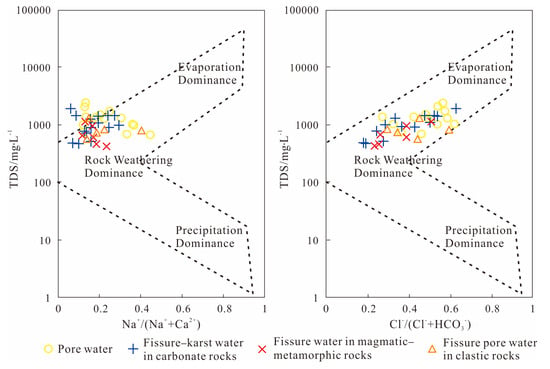
Figure 7.
Groundwater Gibbs diagram for the investigation zone.
The end-member diagram can be applied to identify the types of rock weathering influencing hydrochemical composition [68,69]. Gaillardet et al. [68] established characteristic molar ratios for key end-members. Figure 8 shows most groundwater samples from the study area fall between the silicate and carbonate compositional extremes, while residing considerably distant from the evaporite end-member. The geographic spread of these findings strongly supports the idea that the chemical makeup of shallow groundwater in the region is largely shaped by the natural breakdown and dissolving of silicate and carbonate rock formations. Karst water samples notably approach carbonate weathering end-members more closely than other water types, confirming stronger carbonate dissolution influences in these systems.
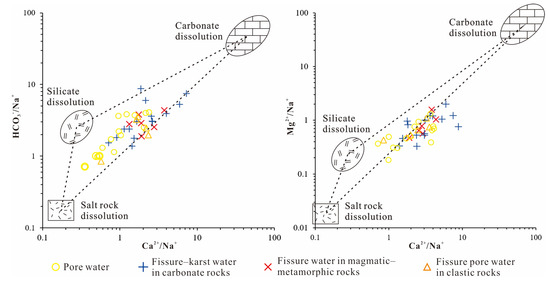
Figure 8.
Ca2+/Na+, HCO3−/Na+, and Mg2+/Na+ ratios in central DRB waters.
4.5.2. Ion Exchange and Sources of Major Components in Groundwater
The Na++K+-to-Cl− milliequivalent ratio in groundwater reveals the principal origins of Na+ and K+ ions. When halite dissolution is the main cation source, the milliequivalent ratio nears 1 [70]. Figure 9a illustrates that the majority of groundwater samples from the investigated region cluster above the 1:1 line. This pattern strongly implies that the water chemistry is influenced by the dissolution of aluminosilicate minerals rich in sodium and potassium, such as feldspar, or by cation exchange reactions.
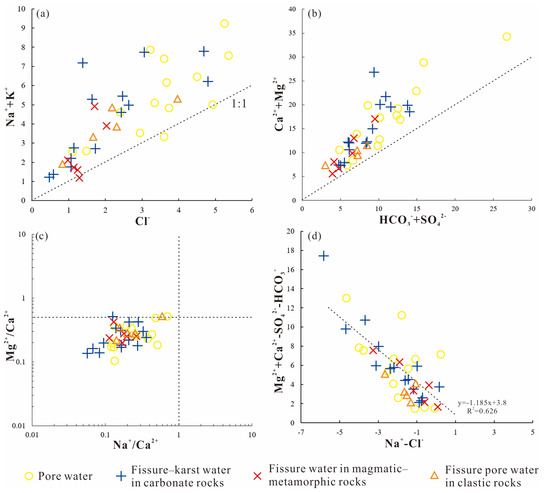
Figure 9.
Scatter plot of groundwater ions in the Dawenkou Basin.
The Ca2++Mg2+-to-HCO3−+SO42− milliequivalent ratio helps identify groundwater Ca2+ and Mg2+ ion origins. A ratio above 1 implies that carbonate rock dissolution dominates, whereas a value below 1 points to silicate rocks and evaporites as sources [71]. Figure 9b reveals that most groundwater samples from the research site are plotted above the [Ca2++Mg2+]/[HCO3−+SO42−] = 1 threshold, showing a clear dominance of calcium and magnesium ions. This pattern strongly suggests that the dissolution of carbonate rocks serves as the main contributor to these dissolved minerals in the local aquifer system.
The Mg2+/Ca2+ and Na+/Ca2+ milliequivalent ratios indicate the influence of calcite versus dolomite dissolution on groundwater ion chemistry in carbonate systems. Groundwater dominated by calcite dissolution typically exhibits lower Mg2+/Ca2+ and Na+/Ca2+ values, whereas dolomite-dominated dissolution results in lower Na+/Ca2+ but higher Mg2+/Ca2+ values [72,73]. Figure 9c shows that the majority of groundwater samples from the research region are under the Mg2+/Ca2+ ratio of 0.5 with Na+/Ca2+ values < 0.8, indicating that water–rock interactions are predominantly controlled by the dissolution of low-magnesium minerals such as calcite.
As stated earlier, the groundwater in the study region shows distinct Na+ and K+ reduction alongside Ca2+ and Mg2+ accumulation, which may result from cation exchange reactions in groundwater systems. A scatter diagram was used to assess cation exchange by comparing (Ca2++Mg2+-HCO3–-SO42−) with (Na+-Cl−) in the study region [74,75]. If cation exchange significantly controls groundwater ionic composition, a linear relationship with a slope ≈−1.0 should exist between these parameters. Figure 9d reveals that increases in K+ and Na+ concentrations correlate with decreases in (Mg2++Ca2+) or increases in (HCO3−+SO42−), with most samples distributed around a linear trend (slope = −1.18). The significant negative correlation (R2 = 0.626) between (Ca2+ + Mg2+ − HCO3− − SO42−) and (Na+-Cl−) confirms the active participation of Na+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ in cation exchange processes.
4.5.3. Industrial and Agricultural Activity Impacts
The ratios of SO42−/Ca2+ and NO3−/Ca2+ are employed to analyze human activity influences on groundwater ion composition. When SO42−/Ca2+ > NO3−/Ca2+, it shows major effects from industrial and mining operations, while the opposite points to substantial contributions from farming and household wastewater [76].
As shown in Figure 10, pore water in loose sediments within the study area demonstrates notable susceptibility to industrial/mining impacts. Field investigations reveal that the Guojialou–Nanxiyiao–Xidawu Village zone (Figure 10) serves as a concentrated gypsum mining zone in the northern study region, identified as the primary contributor to shallow pore water pollution and sulfate enrichment in local groundwater. Conversely, elevated nitrate pollution in shallow pore waters of the eastern Xiyangzhuang–Chengnan–Liangzhuang vegetable cultivation belt correlates strongly with extensive pesticide and fertilizer applications.
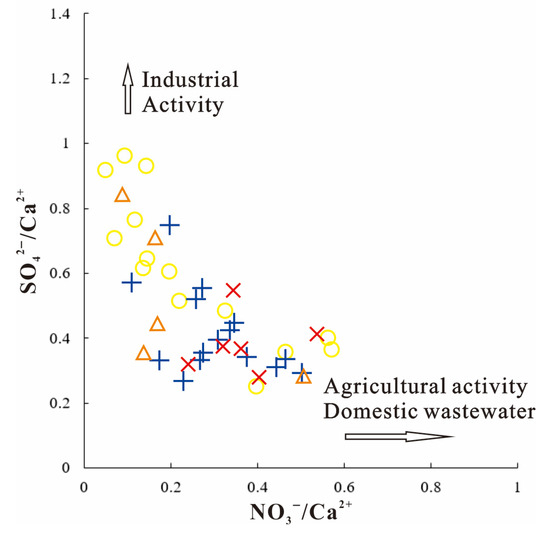
Figure 10.
Relationship between SO42−/Ca2+ and NO3−/Ca2+ in groundwater.
In the clastic rock pore–fracture water systems, localized sulfate enrichment occurs primarily along the northeastern Huafeng Town-to-Chaiwen River west bank region (Figure 10). This zone hosts the Huafeng Coal Mine and Chemical Industry Park, where mine drainage and leaching from industrial waste residues constitute major pollution sources. Within karst aquifer systems, sporadic sulfate anomalies appear south of the Dawenkou Township shoreline, coinciding spatially with the Ningyang County High-Tech Industrial Park. Effluent discharges from manufacturing enterprises within this industrial complex are postulated as primary contamination contributors to karst groundwater degradation.
4.6. EWQI Assessment
Based on water quality analysis of 40 sample groups, this study selected parameters with notably elevated exceedance rates for EWQI evaluation. The results were compared with previous assessments of the entire Dawen River Basin. Ten parameters were selected: K+, Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42−, HCO3−, NO3−, TDS, and TH. Evaluation thresholds primarily followed Class III limits from the Groundwater Quality Standards [77], with WHO-recommended values [78] applied for K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− (lacking standards in GB/T). Table 5 displays EWQI values for the study region, fluctuating between 67.3 and 352.4. The mean EWQI of 156.2 signifies predominantly favorable water quality throughout the region. Groundwater quality classification is primarily controlled by burial conditions and hydrodynamic settings. Porous water exhibited significant exceedance rates (50% exceeding Class III). Karst water demonstrated better quality than porous water (26.7% exceeding Class III). Fractured water and fractured–porous water showed comparatively better quality with lower contamination levels.

Table 5.
Groundwater quality classification of study area based on EWQI.
Based on the EWQI’s planar contour map of the investigated region (Figure 11), high-pollution zones in porous water are primarily distributed in the eastern region (Xiyangzhuang Village–Liangzhuang Town), followed by the Guojialou–Nanxiyao Village area. High-pollution zones in karst water are mainly concentrated in the Huafeng–Dongzhuang Town belt. These findings align with the conclusions drawn from the aforementioned ion analysis.
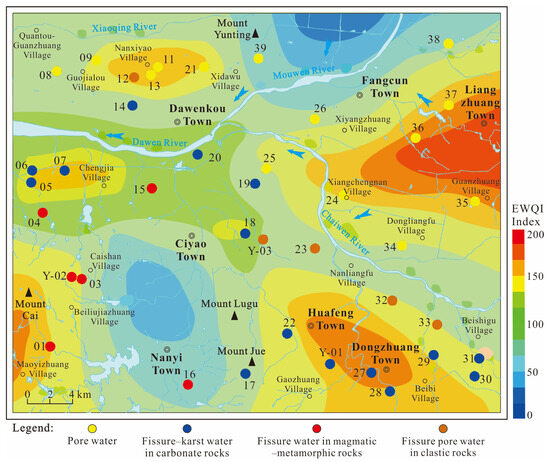
Figure 11.
Spatial patterns of computed EWQI measurements for groundwater within the study region.
Furthermore, compared with previous EWQI assessments of the entire Dawen River Basin (which indicated generally good water quality in the middle–upper reaches), this study—through intensive sampling in the midstream section—reveals localized high-pollution zones within the overall low-EWQI background. These zones are concentrated in the study area’s eastern and southern regions. The contamination is attributed to porous water pollution from excessive nitrogenous agrochemicals in eastern vegetable cultivation areas and karst water pollution from pollutant discharges in southern coal mining and industrial zones.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we meticulously collected diverse groundwater samples from the central area of the DRB. Using traditional hydrochemical analysis methods combined with hydrogen and oxygen isotopic characteristics, a thorough examination of the groundwater’s hydrochemical properties and genesis was performed. Groundwater quality was appraised via the EWQI methodology, and the outcomes were contrasted with past EWQI assessments for DRB groundwater. Listed below are the main conclusions:
- (1)
- Groundwater in the central part of the DRB exhibits pH levels between 7.5 and 8.2 (mean 7.8), signifying mild alkalinity. Concentrations of TDSs range from 450 to 2420 mg/L, with an average of 1075.4 mg/L, and the DRB is predominantly characterized by brackish water. Ca2+ is the most major cation (68.3% of total cations), with SO42− (33.6%) and NO3− (28.4%) as the dominant anions.
- (2)
- The groundwater chemical types in this region are complex and diverse, predominantly classified as HCO3·SO4-Ca and HCO3·Cl·SO4-Ca, followed by SO4·HCO3-Ca, HCO3·SO4·Cl-Ca, and Cl·SO4-Ca types.
- (3)
- Stable isotope analyses (δ2H and δδ18O) show concentrated clustering of groundwater samples near the local meteoric water line with slight downward deviation, forming linear distributions. This pattern confirms atmospheric precipitation as the primary recharge source. Notably, pore water in loose sediments exhibits higher δ2H and δ18O values compared to other groundwater types, attributed to shallow burial depths and enhanced evaporation effects during runoff processes.
- (4)
- The hydrochemical composition of groundwater in the central DRB stems from a combination of natural processes and human impact, as revealed by Gibbs plot assessments and ionic correlation studies. Rock weathering, ion exchange dynamics, and anthropogenic inputs all play a role in shaping the region’s water chemistry. Water chemistry is mainly influenced by silicate and carbonate mineral weathering and dissolution, with evolutionary trends strongly affected by calcite-dominated low-magnesium mineral dissolution. Systematic Na++K+ depletion and Ca2++Mg2+ enrichment were observed, alongside pronounced cation exchange phenomena.
- (5)
- EWQI evaluation reveals that groundwater quality in the central DRB, while generally good overall (average EWQI = 156.2), exhibits significant spatial variability controlled by hydrogeological setting. Localized high-pollution zones were identified within the basin’s midstream region, contrasting with previous basin-wide assessments. Porous water in eastern agricultural areas suffers from nitrogenous agrochemical pollution, while karst water in southern mining/industrial zones is impacted by pollutant discharges. This research underscores the urgency for customized correction measures aimed at particular aquifer categories and land-use practices within the designated areas of high risk.
Author Contributions
Methodology, C.H.; Validation, P.Q.; Writing—original draft, K.P.; Writing—review & editing, H.Z., S.L. and N.W.; Supervision, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Open Fund Project of the Shandong Provincial Engineering Research Center for Environmental Protection and Remediation on Groundwater. Grant number: 2019KF801-6.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Varol, S.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (Water Quality Index) and multivariate analysis: A case study of the Tefenni plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1725–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei Aminiyan, M.; Mirzaei Aminiyan, F.; Heydariyan, A. Study on hydrochemical characterization and annual changes of surface water quality for agricultural and drinking purposes in semi-arid area. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everest, T.; Özcan, H. Applying multivariate statistics for identification of groundwater resources and qualities in NW Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alfy, M.; Lashin, A.; Abdalla, F.; Al-Bassam, A. Assessing the hydrogeochemical processes affecting groundwater pollution in arid areas using an integration of geochemical equilibrium and multivariate statistical techniques. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Teng, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, C. Hydrochemical analysis and quality assessment of groundwater in southeast North China Plain using hydrochemical, entropy-weight water quality index, and GIS techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Chen, J.; Howard, K.W.F. Assessing groundwater pollution and potential remediation processes in a multi-layer aquifer system. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qian, H.; Ren, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, F. Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Han, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Z.; Liu, J. Assessment of the water quality of groundwater in Bohai Rim and the controlling factors—A case study of northern Shandong Peninsula, north China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arto, I.; Andreoni, V.; Rueda-Cantuche, J.M. Global use of water resources: A multiregional analysis of water use, water footprint and water trade balance. Water Resour. Econ. 2016, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N. Controlling factors and mechanism of groundwater quality variation in semiarid region of South India: An approach of water quality index (WQI) and health risk assessment (HRA). Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1725–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Xiao, J.; Li, S.; Li, Z. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and their controlling factors in the Fen River of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Sun, S.; Fu, G.; Hall, J.W.; Ni, Y.; He, L.; Yi, J.; Zhao, N.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; et al. Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yang, L.; Hu, D. Groundwater ecological sensitivity assessment in the lower Liaohe River Plain based on GIS technique. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 7428–7440. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water management: Current and future challenges and research directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, C.; Tao, H.; Jia, R.; Ji, Y.; Yang, G. Variation of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics in the plain area of the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang Region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4249–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. An investigation into the hydrochemistry, quality and risk to human health of groundwater in the central region of Shandong Province, North China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 125416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.; Hou, K.; Yang, F. Groundwater quality assessment using a new integrated-weight water quality index (IWQI) and driver analysis in the Jiaokou Irrigation District, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 111992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Chai, N.; Liu, T.; Jin, Z.; Rinklebe, J. Groundwater hydrochemistry, source identification and pollution assessment in intensive industrial areas, eastern Chinese loess plateau. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omonona, O.V.; Okogbue, C.O. Hydrochemical evolution, geospatial groundwater quality and potential health risks associated with intake of nitrate via drinking water: Case of Gboko agricultural district, central Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, V.; Aydın, S.; Sönmez, O. Production, Cost Analysis, and Marketing of Bioorganic Liquid Fertilizers and Plant Nutrition Enhancers. In Industrial Microbiology Based Entrepreneurship. Microorganisms for Sustainability; Amaresan, N., Dharumadurai, D., Cundell, D.R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 42. [Google Scholar]
- Singaraja, C. Relevance of water quality index for groundwater quality evaluation: Thoothukudi District, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2157–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, south India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Han, C.; Yuan, S.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C. Assessment of the hydrochemistry, water quality, and human health risk of groundwater in the northwest of Nansi Lake Catchment, north China. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2022, 44, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, P.; Qian, H. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Improved Water Quality Index (WQI) and Human Health Risk (HHR) evaluation in a semi-arid region of Northwest China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, V.; Neelakantan, M.A. Evaluation of groundwater quality with health risk assessment of fluoride and nitrate in Virudhunagar district, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Yuan, Q.W.; Chen, Q.Z.; Mei, S.L.; Wu, Z.H. Analysis of hydrogeochemical characteristics of tunnel groundwater based on multivariate statistical technology. Geofluids 2021, 1, 4867942. [Google Scholar]
- Loaiza, J.G.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.; Bustos-Terrones, V.; Monjardín-Armenta, S.A.; Quevedo-Castro, A.; Estrada-Vazquez, R.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G. Evaluation of the Hydrochemical and Water Quality Characteristics of an Aquifer Located in an Urbanized Area. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-Analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar]
- Marandi, A.; Shand, P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, I.; Singh, U.K. Fluoride abundance and their release mechanisms in groundwater along with associated human health risks in a geologically heterogeneous semi-arid region of east India. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; Snousy, M.G.; Alexakis, D.E.; Abdelhalim, A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Elsayed, E. Diagnosis of groundwater quality in North Assiut Province, Egypt, for drinking and irrigation uses by applying multivariate statistics and hydrochemical methods. Water 2023, 15, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudibi, S.; Sakaa, B.; Benguega, Z. Spatial variability and risk assessment of groundwater pollution in El-Outaya region, Algeria. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 176, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhou, G. Exploration of hydrogeochemical characterization and assessment of organic pollution characteristics of shallow groundwater near a chemical plant that discharged sewage illegally. Sustainability 2022, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Q.K.; Ngoc, T.D.T.; Le Vo, P.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Dang, D.H. Groundwater in Southern Vietnam: Understanding geochemical processes to better preserve the critical water resource. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.; Boving, T.; Brauns, B.; Dottridge, J.; Hynds, P.; Kebede, S.; Kreamer, D.; Misstear, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Re, V.; et al. Groundwater quality: Global challenges, emerging threats and novel approaches. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omo-Irabor, O.O.; Olobaniyi, S.B.; Oduyemi, K.; Akunna, J. Surface and groundwater water quality assessment using multivariate analytical methods: A case study of the Western Niger Delta, Nigeria. Phys. Chem. Ear. Parts A/B/C 2008, 33, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.N.; Chotpantarat, S.; Ngu, N.H.; Thunyawatcharakul, P.; Kaewdum, N. Integrating machine learning models with cross-validation and bootstrapping for evaluating groundwater quality in Kanchanaburi province, Thailand. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Pal, S.C.; Saha, A.; Ruidas, D. Arsenic and fluoride exposure in drinking water caused human health risk in coastal groundwater aquifers. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, B.; Subba Rao, N.; Dhanamjaya Rao, E. N Groundwater quality monitoring for assessment of pollution levels and potability using WPI and WQI methods from a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 25, 14785–14815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.R.; Meng, X.H.; Wen, X.H.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.J.; Wu, M.; Zhou, T. Hydrochemical characteristics, quality and health risk assessment of nitrate enriched coastal groundwater in northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 403, 136872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; He, M.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Gao, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of porewater in the Dawen Basin. Environ. Chem. 2019, 38, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.M.; Wang, S.M.; Chen, Y.P.; Wu, J.H.; Xue, L.G.; Fan, T.T. Pollution status of the Yellow River tributaries in middle and lower reaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Feng, J.; Wang, M. Identification of the hydrochemical features, genesis, water quality and potential health hazards of groundwater in Dawen River Basin, North China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Bi, D.; Wei, H.; Zheng, X.; Man, X. Evaluation of groundwater quality and health risk assessment in Dawen River Basin, North China. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, Y.X.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, J.X.; Gao, H.; Liu, C.W.; Li, B. Characterisation of groundwater chemistry in the upper reaches of the Chaiwen River, Shandong Province. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, C.C.; Liu, C.W.; Guan, Q.; Luo, F. Hydrogeological characteristics and groundwater enrichment pattern of water-bearing rock groups of the Paleocene Zhujiagou Formation in the lower reaches of the Chaiwen River, Shandong. Mod. Geol. 2021, 35, 675–681. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, Z.; Yu, S.Y.; Chen, S.; Song, Y. Clay minerals and provenancial implications of surface sediments in the Dongping Lake, North China. Quat. Int. 2023, 673, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.J.; Wan, Z.P.; He, K.Q.; Victor, K.; Liu, J.T. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of karst groundwater in middle and upper reaches of Dawen River basin. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.B.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Ma, X.Q.; Sun, D.W.; Meng, Q.L.; Ma, C.M. Study on sulfate traceability of karst groundwater system in Tai’an city, Shandong Province. Min. Anal. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DZ/T 0064.2-2021; Methods for analysis of groundwater quality—Part 2: Collection and preservation of water samples. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Goodarzi, M.R.; Abedi, M.J.; Niknam, A.R.R.; Heydaripour, M. Groundwater quality status based on a modification of water quality index in an arid area, Iran. Water Supply 2022, 22, 6245–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, N.; Mohd Razali, S.F.; Hamzah, F.B. Enhancement of water quality index prediction using support vector machine with sensitivity analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1061835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Loganathan, V.A.; Bhatt, V.K. Development of entropy and deviation- based water quality index: Case of river Ganga, India. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Ding, Y.J.; Zeng, G.X.; Wu, J.K.; Qin, J. Major ion chemistry of surface water in the upper reach of Shule River basin and the possible controls. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.Y. Hydrochemical characteristic and reasoning analysis in Siyi Town Langzhong City. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 3230–3237. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, P.; Tian, L.; Zhu, G.; Edmunds, W.M.; Zhang, Q. Groundwater recharge environments and hydrogeo-chemical evolution in the Jiuquan Basin, Northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.N. Groundwater Hydrochemical Characteristics and Hydrogeochemical Processes Approximately Along Flow Paths in the North China Plain. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.B. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope geochemistry of karst groundwater in Chongiqng. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 713–722. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Zhu, Q.J.; Xu, M.; Lv, L.; Deng, Q.J.; He, J.; Wang, X.F. The characteristics and genetic analysis of the paleogene semi-consolidated water-bearing formation on the northwestern margin of Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2018, 39, 737–748. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.Q.; Gao, Z.J.; He, J.; Li, W.; Deng, Q.J. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in typical sections of the upper reaches of dawen river basin and analysis of its influencing factors. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 7558–7566. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Li, W.; Zhu, Q.J.; Li, F.Z.; Lv, L.; Deng, Q.J.; Ma, X.M.; He, J. Characteristics of the Paleogene waterbearing Formation in the middle and upper reaches of the Dawenhe River basin, Shandong Province. Geol. China 2019, 46, 316–327. [Google Scholar]
- Dotsika, E.; Lykoudis, S.; Poutoukis, D. Spatial distribution of the isotopic composition of precipitation and spring water in Greece. Glob. Planet. Change 2010, 71, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetelat, B.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.L. Geochmistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin Rivers: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4254–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, J.L.; Nai, W.H.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Fan, W.; Li, B. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Kashgar Delta area in Xinjiang. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Louvat, P.; Allègre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, G.; Li, F. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of groundwater in the Yishu River basin. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.L.; Peng, W.H.; Gui, H.R. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of deep groundwater from the coal-bearing aquifer of the Linhuan coal-mining district, Northern Anhui Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.G.; Ji, D.S.; Gao, Z.J.; Yang, L.Z.; Zhu, H.H.; Liu, Z.Z. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evalution of groundwater in Zibo Dawu water source, Shandong Province. J. Chang. River Sci. Res. Inst. 2020, 37, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Su, C.L.; Zeng, H.B.; Li, Z.M.; Liu, W.B.; Kang, W. Evolutional processes of groundwater in Xinglong County based on hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2020, 47, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, C.L.; Ma, Y.H.; Liu, W.J. Indicators of groundwater evolution processes based on hydrochemistry and envi-ronmental isotopes: A case study of the Dongyuan drinking water source area in Ji’nan City. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Yang, X.; Rioual, P.; Qin, X.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, H.; Yu, J. Hydrogeochemistry of three watersheds (the Erlqis, Zhungarer and Yili) in northern Xinjiang, NW China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfi, S.; Zouari, K.; Feki, S.; Mami, E. Study of variation in groundwater quality in a coastal aquifer in north-eastern Tunisia using multivariate factor analysis. Quat. Int. 2013, 302, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.Z.; An, Y.L.; Wu, Q.X.; Qu, K.J.; Fan, G.H.; Ye, Z.X.; Qin, L.; Qian, J.T.; Tu, C.L. Study on the hydrochemical characteris-tics of Duliu River basin in Guizhou Province. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 2684–2690. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for groundwater quality. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Zhang, J. Study on the evolution of groundwater quality and its formation mechanism in the plain area of Yarkant River Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).