A New Depth-Averaged Eulerian SPH Model for Passive Pollutant Transport in Open Channel Flows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. 2D SPH-Based Discretized System of Governing Equations
2.3. The Hydrostatic Reconstruction Method
2.4. HLLC (Harten–Lax–Van Leer Contact) Approximate Riemann Solver
2.5. Implicit Treatment of Bed Friction
2.6. Viscous Term Treatment in SPH
2.7. Anisotropic Diffusion Formulation in SPH
3. Results and Discussion
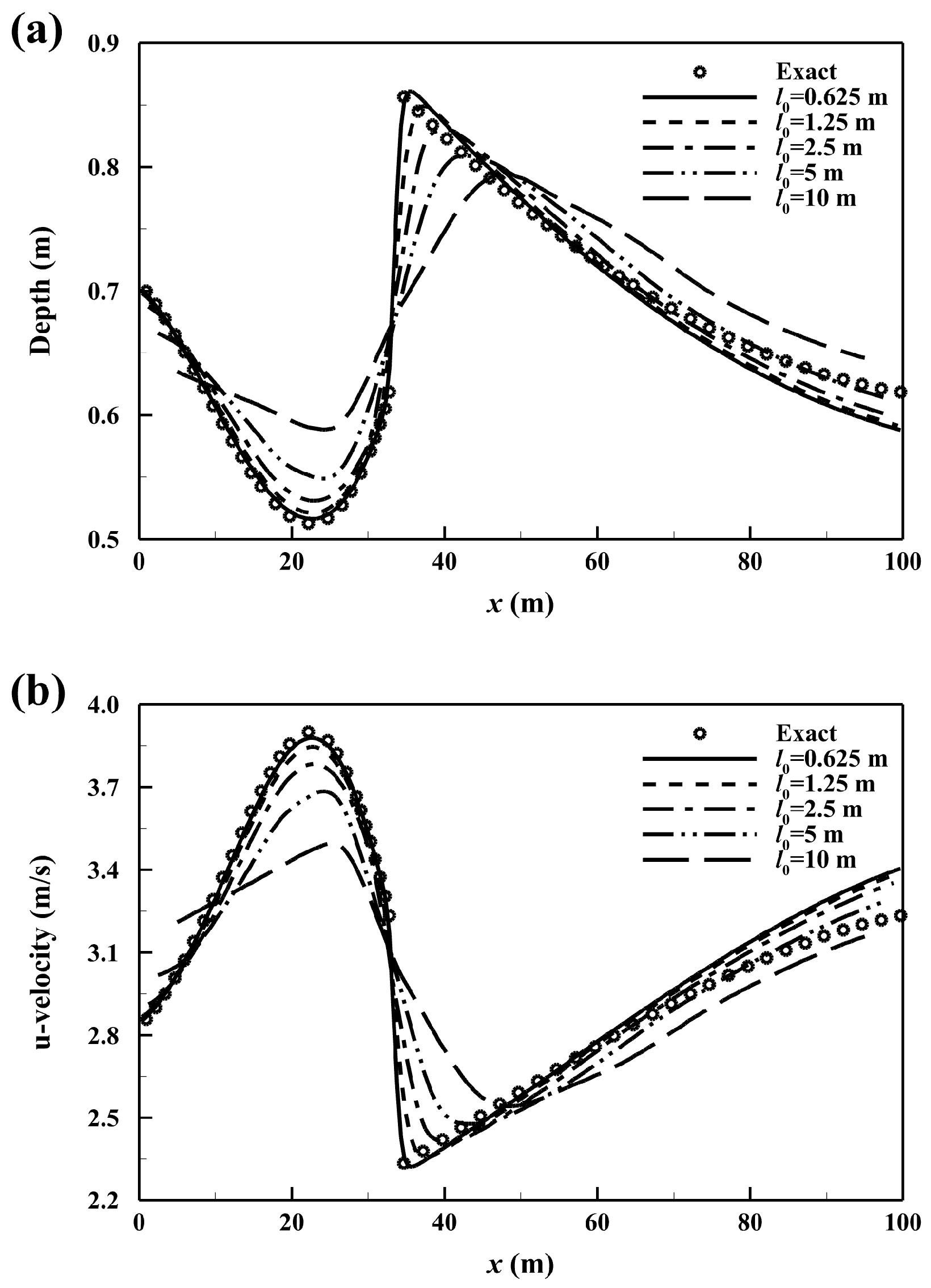
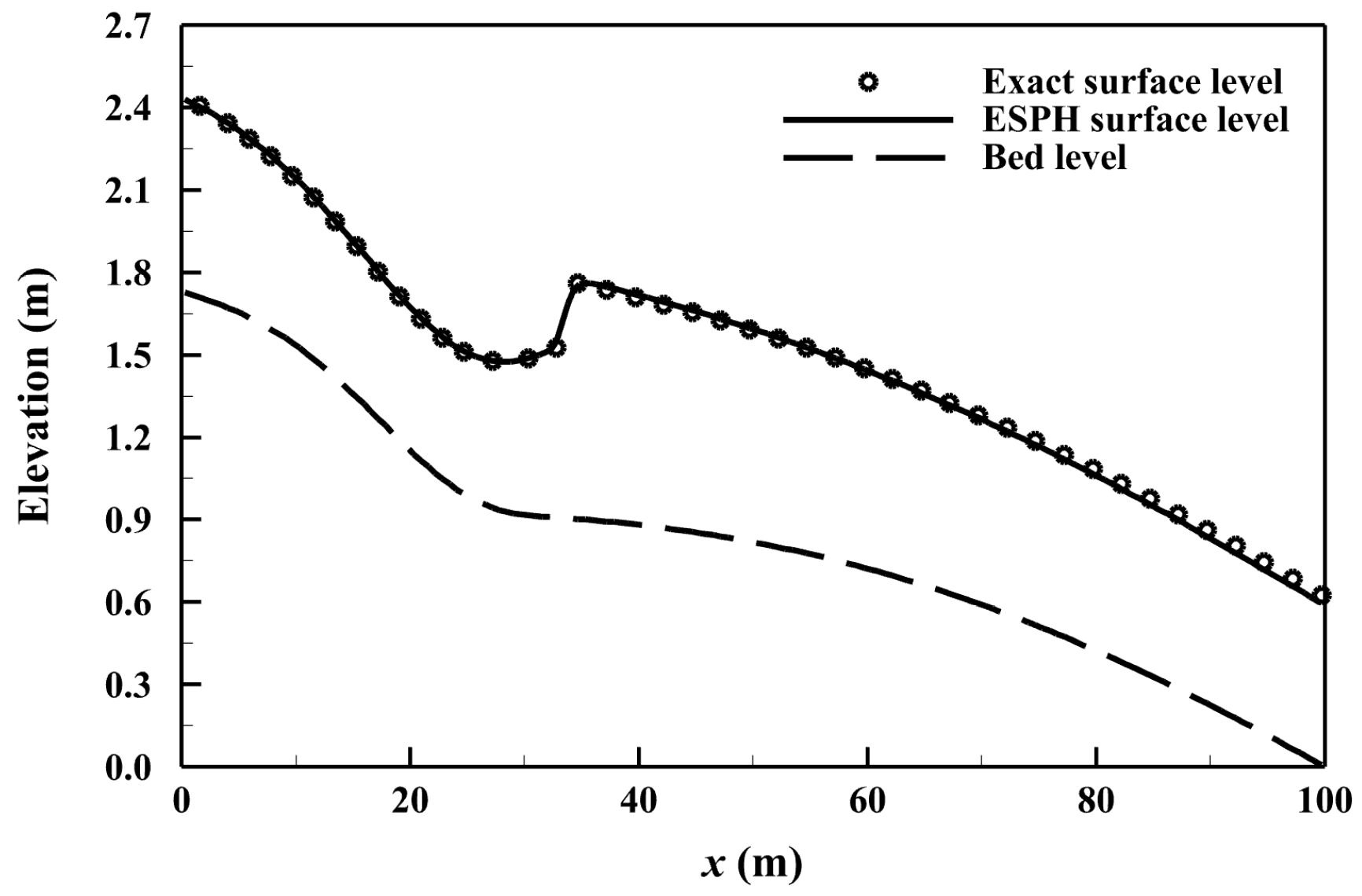
3.1. Analytical Super-Subcritical Flow in a Rectangular Channel
3.2. Two-Dimensional Isotropic and Anisotropic Diffusion in Still Water
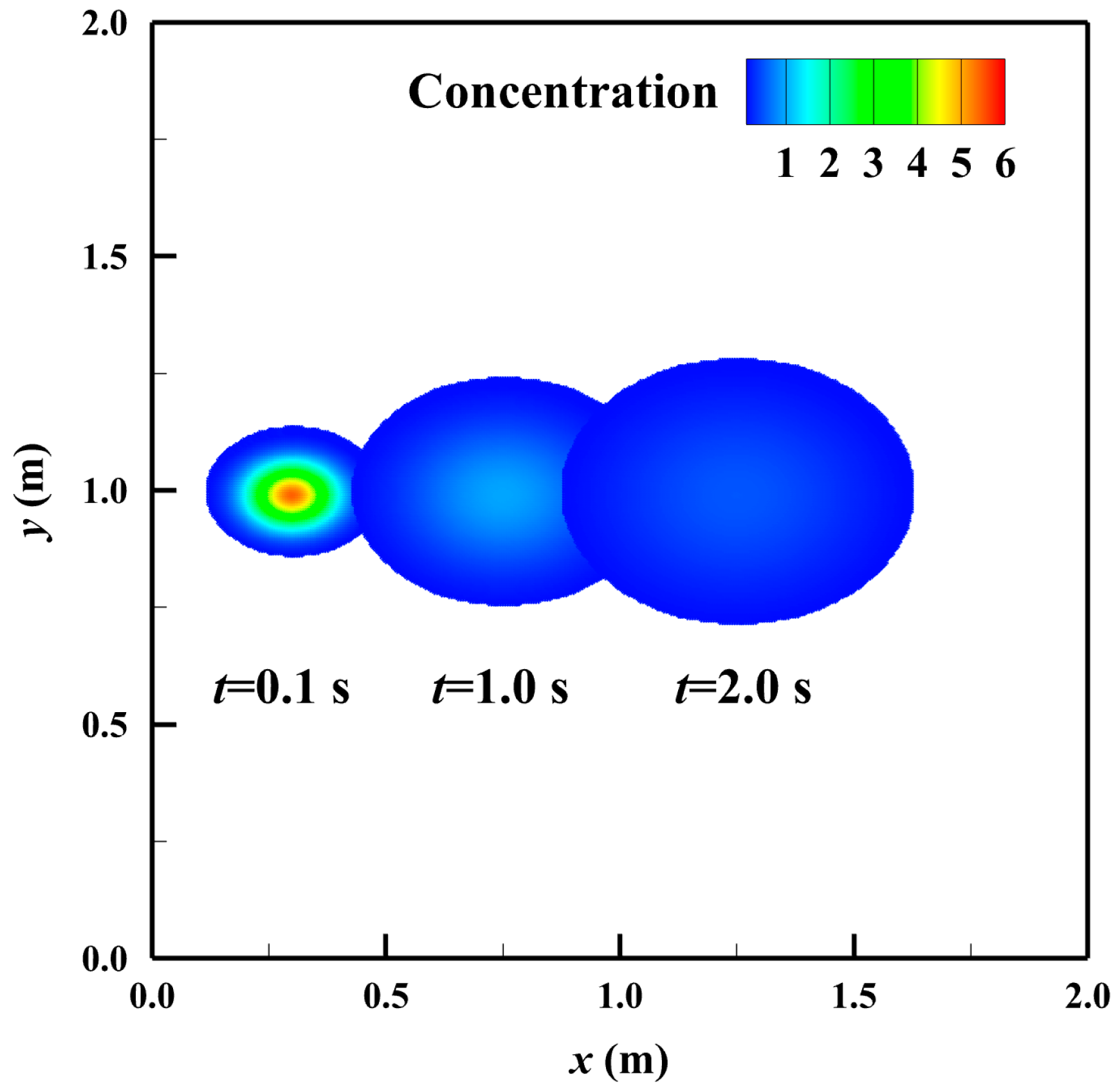
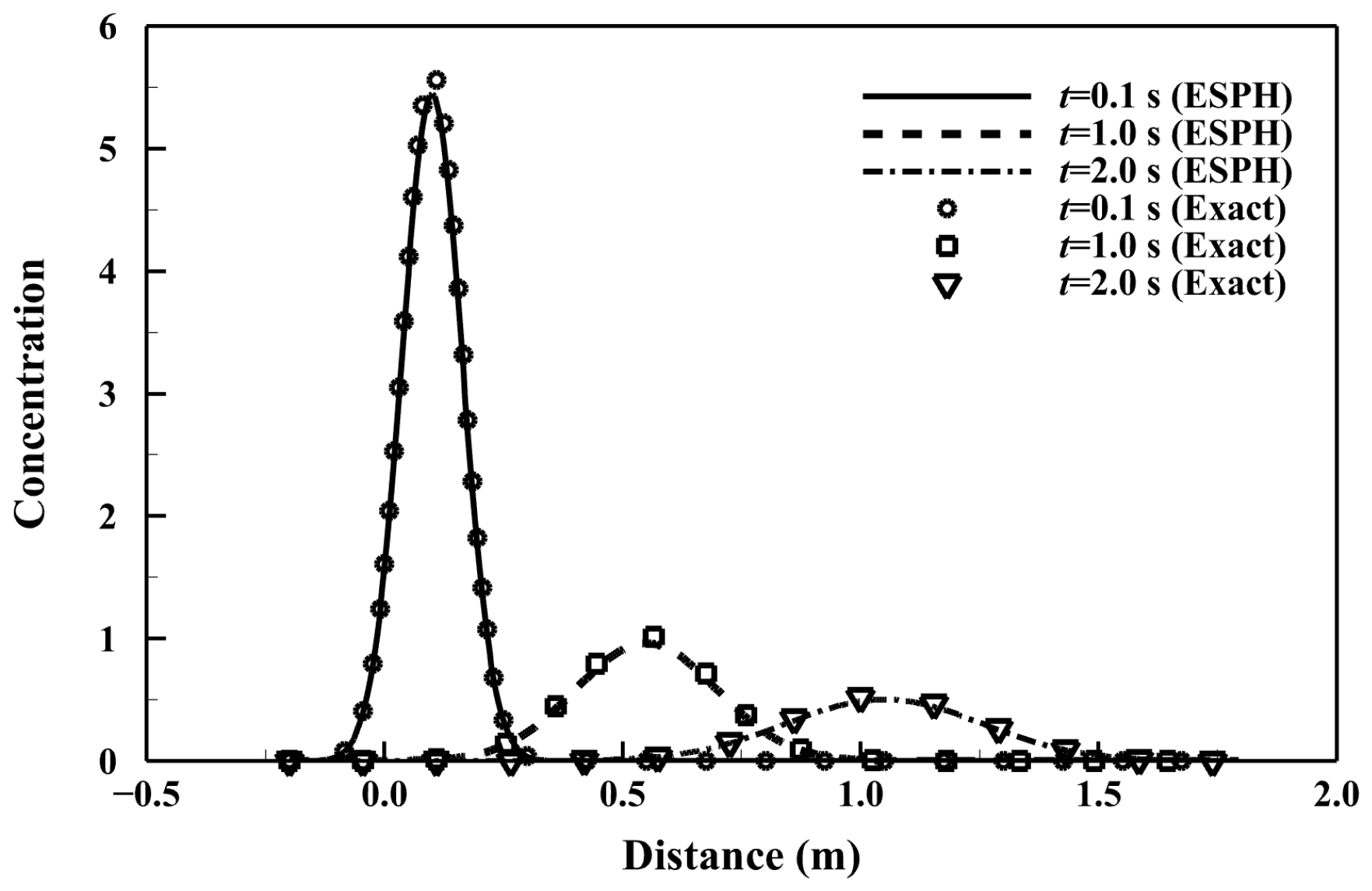
3.3. Advection and Diffusion in a Two-Dimensional Uniform Flow
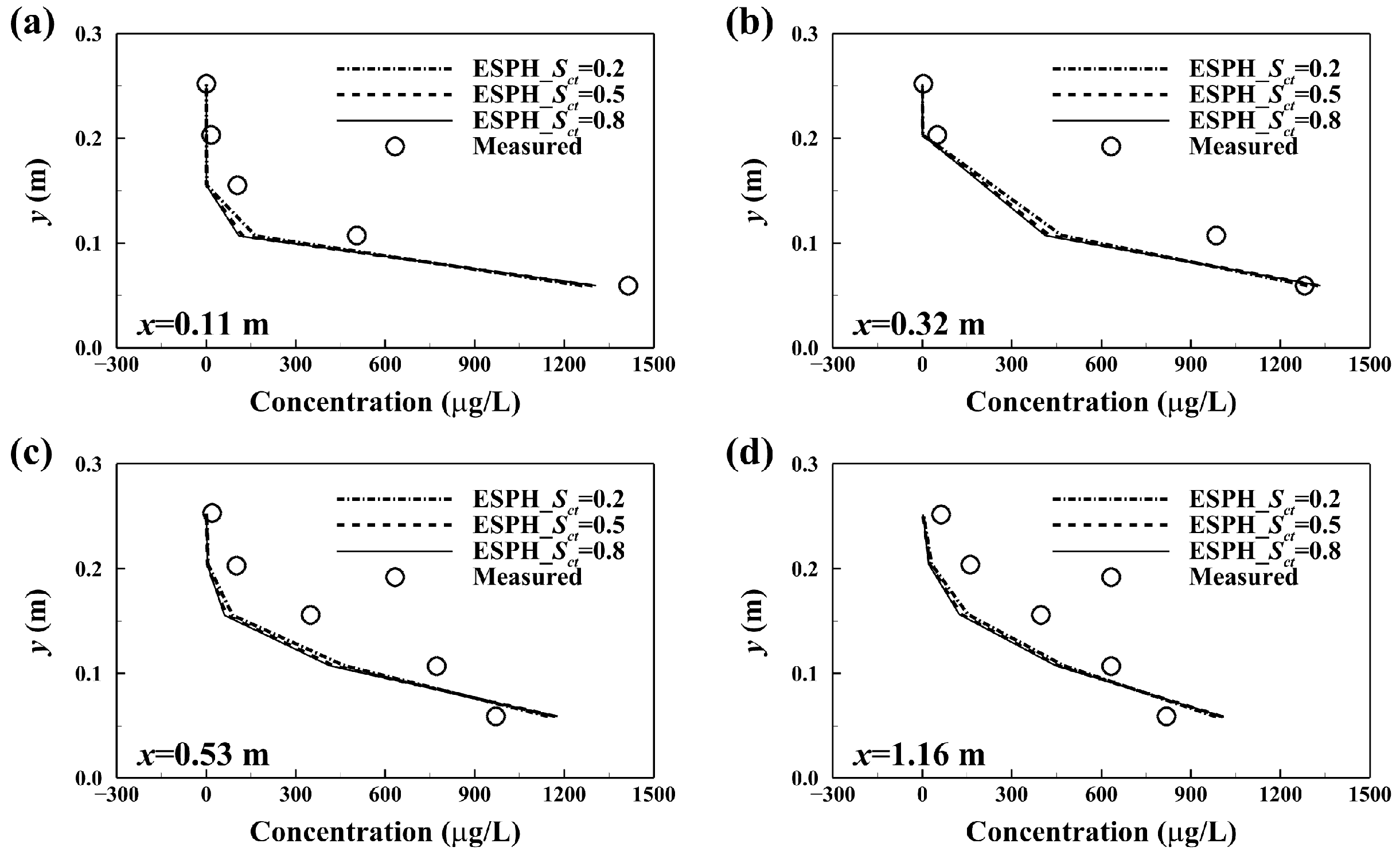
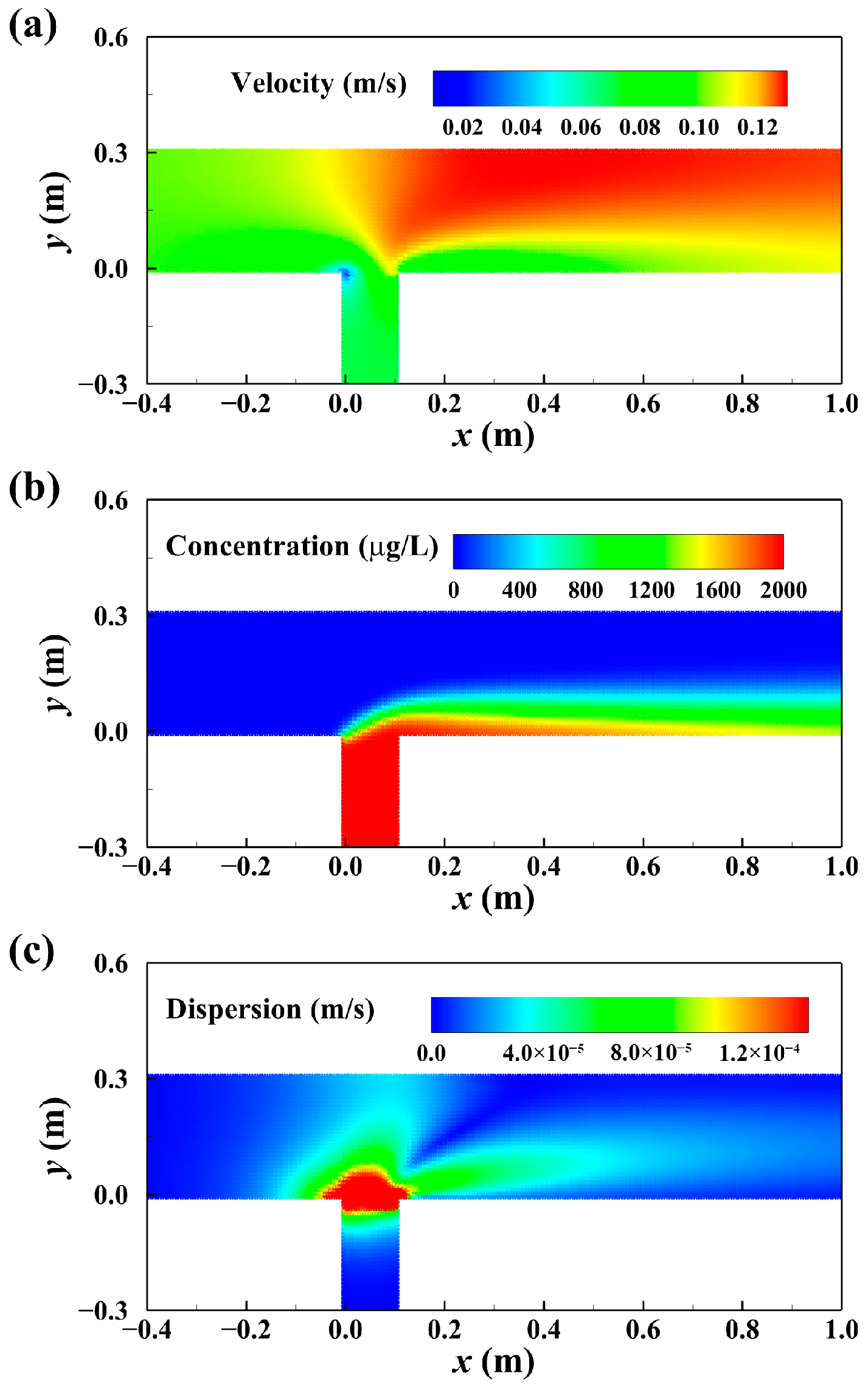
3.4. Two-Dimensional Pollutant Dispersion in a 90° Junction Channel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Locke, M.A.; Weaver, M.A.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Steinriede, R.W.; Bryson, C.T.; Cullum, R.F. Constructed Wetlands as a Component of the Agricultural Landscape: Mitigation of Herbicides in Simulated Runoff from Upland Drainage Areas. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, R.J.; Hunt, W.F.; Kennedy, S.G.; Merriman, L.S.; Chandler, J.; Brown, D. Evaluation of Floating Treatment Wetlands as Retrofits to Existing Stormwater Retention Ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournebize, J.; Chaumont, C.; Mander, Ü. Implications for Constructed Wetlands to Mitigate Nitrate and Pesticide Pollution in Agricultural Drained Watersheds. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Yan, P.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Guo, Z.; et al. Constructed Wetlands for Pollution Control. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, C.; Kröger, R. Use of Vegetated Drainage Ditches and Low-Grade Weirs for Aquaculture Effluent Mitigation: II. Suspended Sediment. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 60, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsenga kumwimba, M.; Zhu, B.; Wang, T.; Dzakpasu, M.; Li, X. Nutrient Dynamics and Retention in a Vegetated Drainage Ditch Receiving Nutrient-Rich Sewage at Low Temperatures. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsenga kumwimba, M.; Zhu, B.; Moore, M.T.; Wang, T.; Li, X. Can Vegetated Drainage Ditches Be Effective in a Similar Way as Constructed Wetlands? Heavy Metal and Nutrient Standing Stock by Ditch Plant Species. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 166, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Chardon, W.J.; Kronvang, B. Riparian Buffer Strips as a Multifunctional Management Tool in Agricultural Landscapes: Introduction. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, F.A.; Roebeling, P. Modelling Impacts of Nature-Based Solutions on Surface Water Quality: A Rapid Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q. A Well-Balanced and Non-Negative Numerical Scheme for Solving the Integrated Shallow Water and Solute Transport Equations. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2010, 7, 1049–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, J.; García-Navarro, P. Improved Riemann Solvers for Complex Transport in Two-Dimensional Unsteady Shallow Flow. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 7202–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Son, S. An Efficient HLL-Based Scheme for Capturing Contact-Discontinuity in Scalar Transport by Shallow Water Flow. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 127, 107531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yin, J. A Robust Coupled Model for Solute Transport Driven by Severe Flow Conditions. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Riviere, N.; Dewals, B. Formulations and Diffusivity Coefficients of the 2D Depth-Averaged Advection-Diffusion Models: A Literature Review. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2023WR035053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Pan, D.; Huang, C.; Liu, M. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) for Complex Fluid Flows: Recent Developments in Methodology and Applications. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Touzé, D.; Colagrossi, A. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics for Free-Surface and Multiphase Flows: A Review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2025, 88, 037001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.-H.; Sheu, T.W.-H.; Chang, T.-J. A 1D–2D Coupled SPH-SWE Model Applied to Open Channel Flow Simulations in Complicated Geometries. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 115, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; Chang, T.-J.; Garcia, M.H. A Well-Balanced and Positivity-Preserving SPH Method for Shallow Water Flows in Open Channels. J. Hydraul. Res. 2021, 59, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacondio, R.; Rogers, B.D.; Stansby, P.K.; Mignosa, P. SPH Modeling of Shallow Flow with Open Boundaries for Practical Flood Simulation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Shao, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X. Applications of Shallow Water SPH Model in Mountainous Rivers. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2015, 8, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liang, Q. A GPU-Accelerated Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Model for the Shallow Water Equations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 75, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Gu, S.; Shao, S.; Wu, Y. Turbulent Models of Shallow-Water Equations-Based Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 107164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-S.; Chang, T.-J. SPH Simulations of Solute Transport in Flows with Steep Velocity and Concentration Gradients. Water 2017, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, Q.; Lian, J.; Zhang, A.; Dang, J. Coastal Pollutant Transport Modeling Using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics with Diffusive Flux. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 146, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, Q.; Lei, X.; Lian, J.; Dang, J. SPH Modeling of Substance Transport in Flows with Large Deformation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 991969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Gu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C. Numerical Investigation of Pollutant Transport in a Realistic Terrain with the SPH-SWE Method. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 889526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H. A Novel Eulerian SPH Shallow Water Model for 2D Overland Flow Simulations. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; Wu, Y.-T.; Wang, C.-H.; Chang, T.-J. A New 2D ESPH Bedload Sediment Transport Model for Rapidly Varied Flows over Mobile Beds. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Español, P.; Revenga, M. Smoothed Dissipative Particle Dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 026705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran-Duc, T.; Bertevas, E.; Phan-Thien, N.; Khoo, B.C. Simulation of Anisotropic Diffusion Processes in Fluids with Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2016, 82, 730–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biriukov, S.; Price, D.J. Stable Anisotropic Heat Conduction in Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 4901–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Z.; Liu, H.; Xing, L.; Ding, Y. A Well-Balanced Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Depth-Averaged Advection–Diffusion Equation with Variable Water Depth. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 379, 113745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.H. Open-Channel Flow; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-96446-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Noelle, S. A New Hydrostatic Reconstruction Scheme Based on Subcell Reconstructions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2017, 55, 758–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, E.F. Computational Algorithms for Shallow Water Equations; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-3-031-61394-4. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Liang, Q. A New Efficient Implicit Scheme for Discretising the Stiff Friction Terms in the Shallow Water Equations. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 117, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molls, T.; Zhao, G.; Molls, F. Friction Slope in Depth-Averaged Flow. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.P.; Fox, P.J.; Zhu, Y. Modeling Low Reynolds Number Incompressible Flows Using SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 1997, 136, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagorinsky, J. General Circulation Experiments with the Primitive Equations: I. The Basic Experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pham, C.; Deleersnijder, E.; Bousmar, D.; Soares-Frazão, S. Simulation of Flow in Compound Open-Channel Using a Discontinuous Galerkin Finite-Element Method with Smagorinsky Turbulence Closure. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, C.; Angeloudis, A.; Bombardelli, F.; Jha, S.; Stoesser, T. On the Values for the Turbulent Schmidt Number in Environmental Flows. Fluids 2017, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I. Test Problems with Analytic Solutions for Steady Open Channel Flow; Numerical Analysis Reports; University of Reading, Department of Mathematics: Berkshire, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Vanzo, D.; Siviglia, A.; Toro, E.F. Pollutant Transport by Shallow Water Equations on Unstructured Meshes: Hyperbolization of the Model and Numerical Solution via a Novel Flux Splitting Scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 2016, 321, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Feng, M.; Zhang, T.; Teng, S. Study on distribution of pollutant concentrations in intersection of open channel. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2019, 38, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Particle Number | Time Step Size (s) | Total Simulation Time (s) | CPU Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 25,600 | 0.08 | 900 | 664 |
| Case 2 | 160,000 | 0.05 | 1800 | 4890 |
| Case 3 | 160,000 | 0.0001 | 2 | 3211 |
| Case 4 | 19,800 | 0.001 | 180 | 3199 |
| Isotropic | Weakly Anisotropic | Strongly Anisotropic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| t = 10 s | 0.41% | 0.26% | 0.09% |
| t = 30 s | 0.47% | 0.29% | 0.10% |
| Velocity | Concentration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cs | Sct | |||||
| 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | ||
| y = 0.05 m | 9.22% | 9.14% | x = 0.11 m | 11.51% | 12.33% | 12.58% |
| y = 0.15 m | 1.72% | 1.17% | x = 0.32 m | 16.04% | 17.38% | 17.87% |
| y = 0.25 m | 1.58% | 1.54% | x = 0.53 m | 15.60% | 17.23% | 17.75% |
| x = 1.16 m | 14.56% | 16.00% | 16.40% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, K.-H.; Shih, K.-H.; Wang, Y.-C. A New Depth-Averaged Eulerian SPH Model for Passive Pollutant Transport in Open Channel Flows. Water 2025, 17, 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152205
Chang K-H, Shih K-H, Wang Y-C. A New Depth-Averaged Eulerian SPH Model for Passive Pollutant Transport in Open Channel Flows. Water. 2025; 17(15):2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152205
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Kao-Hua, Kai-Hsin Shih, and Yung-Chieh Wang. 2025. "A New Depth-Averaged Eulerian SPH Model for Passive Pollutant Transport in Open Channel Flows" Water 17, no. 15: 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152205
APA StyleChang, K.-H., Shih, K.-H., & Wang, Y.-C. (2025). A New Depth-Averaged Eulerian SPH Model for Passive Pollutant Transport in Open Channel Flows. Water, 17(15), 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152205






