Macrozoobenthos Response to Sediment Contamination near the S/s Stuttgart Wreck: A Biological and Chemical Assessment in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
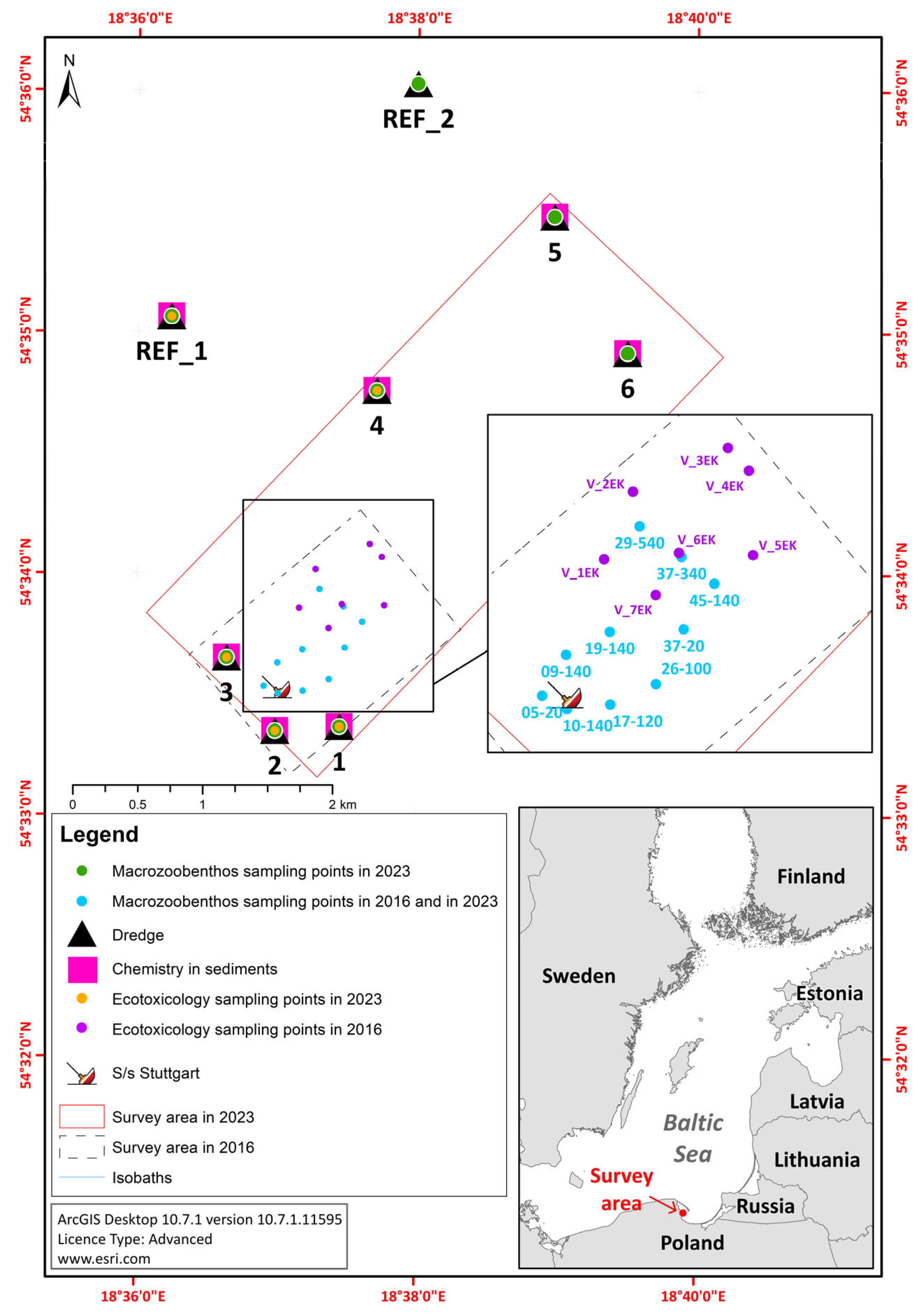
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.3. Macrozoobenthos
2.4. Condition Indices
2.5. Ecological Status Assessment
2.6. Ecotoxicological Analysis
2.7. Chemical Analysis of Sediments and Mussels
2.7.1. Organic Contaminants (PAHs, PCBs, TPH, BTs, TOC)
2.7.2. Metals and Metalloids
2.8. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Macrozoobentos
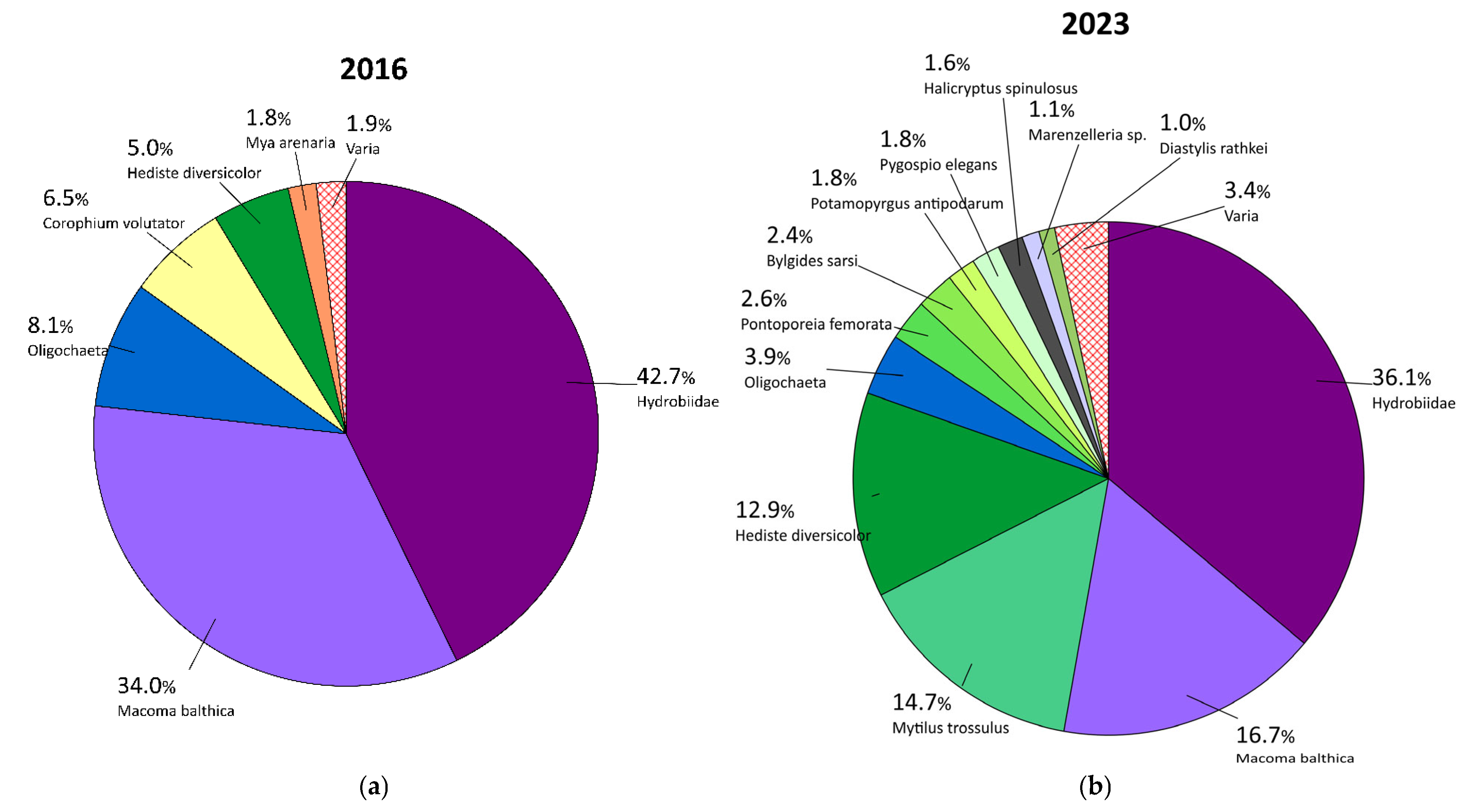
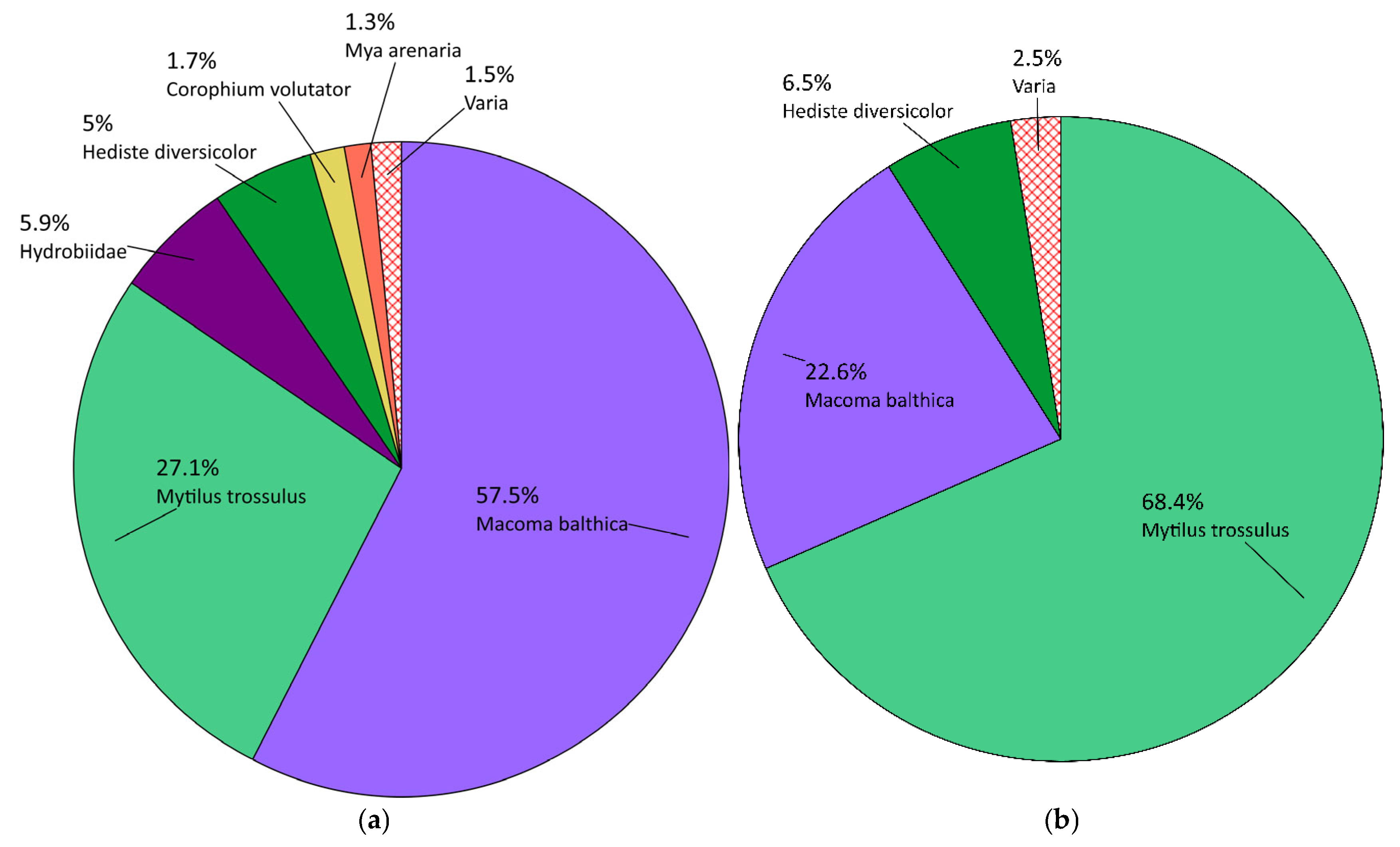
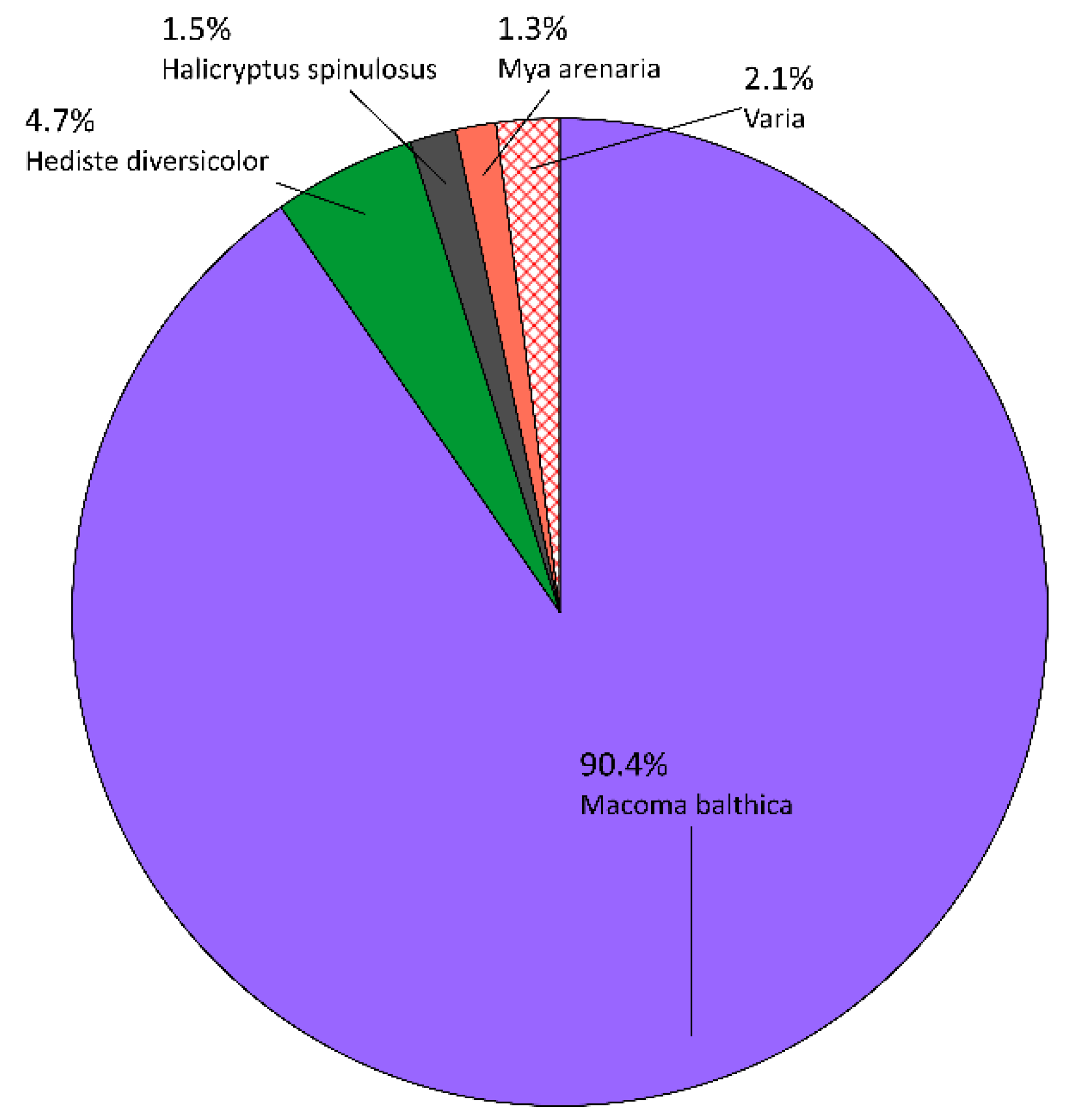
3.1.1. Qualitative Composition
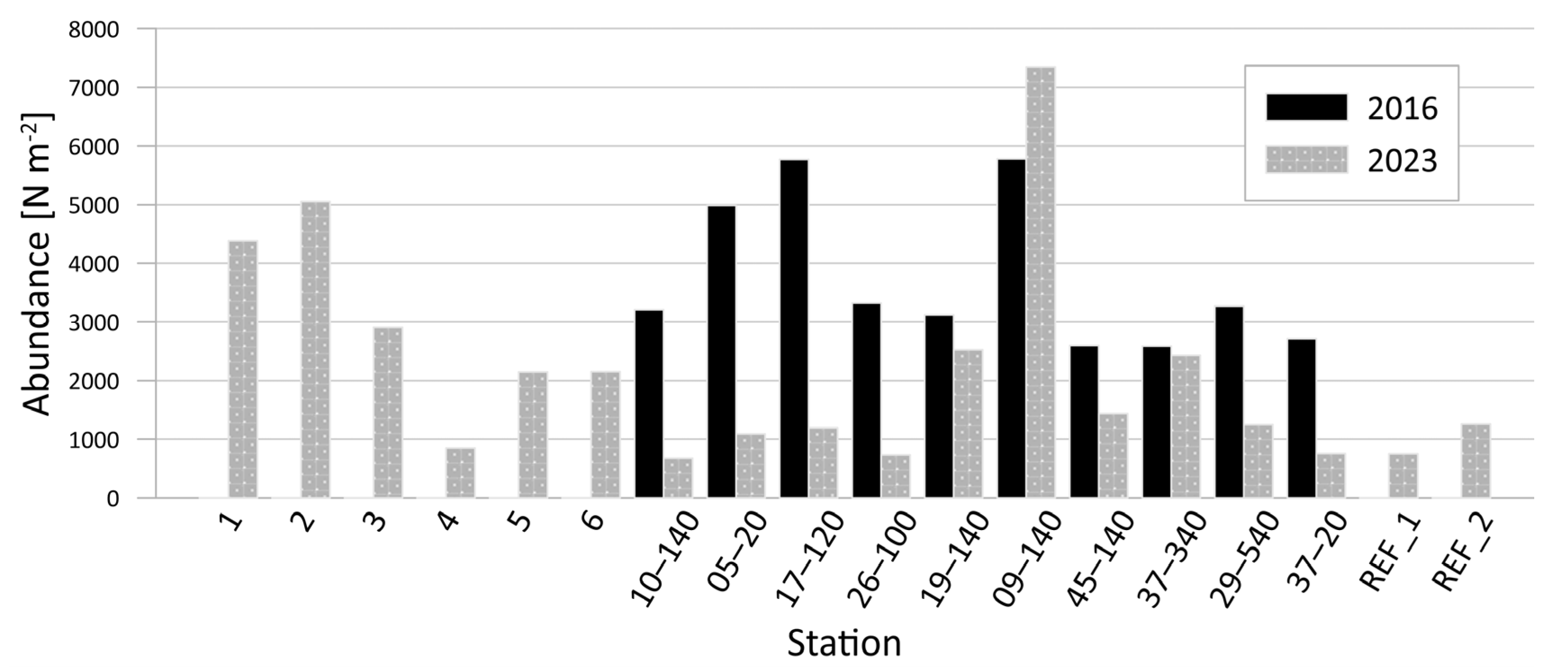
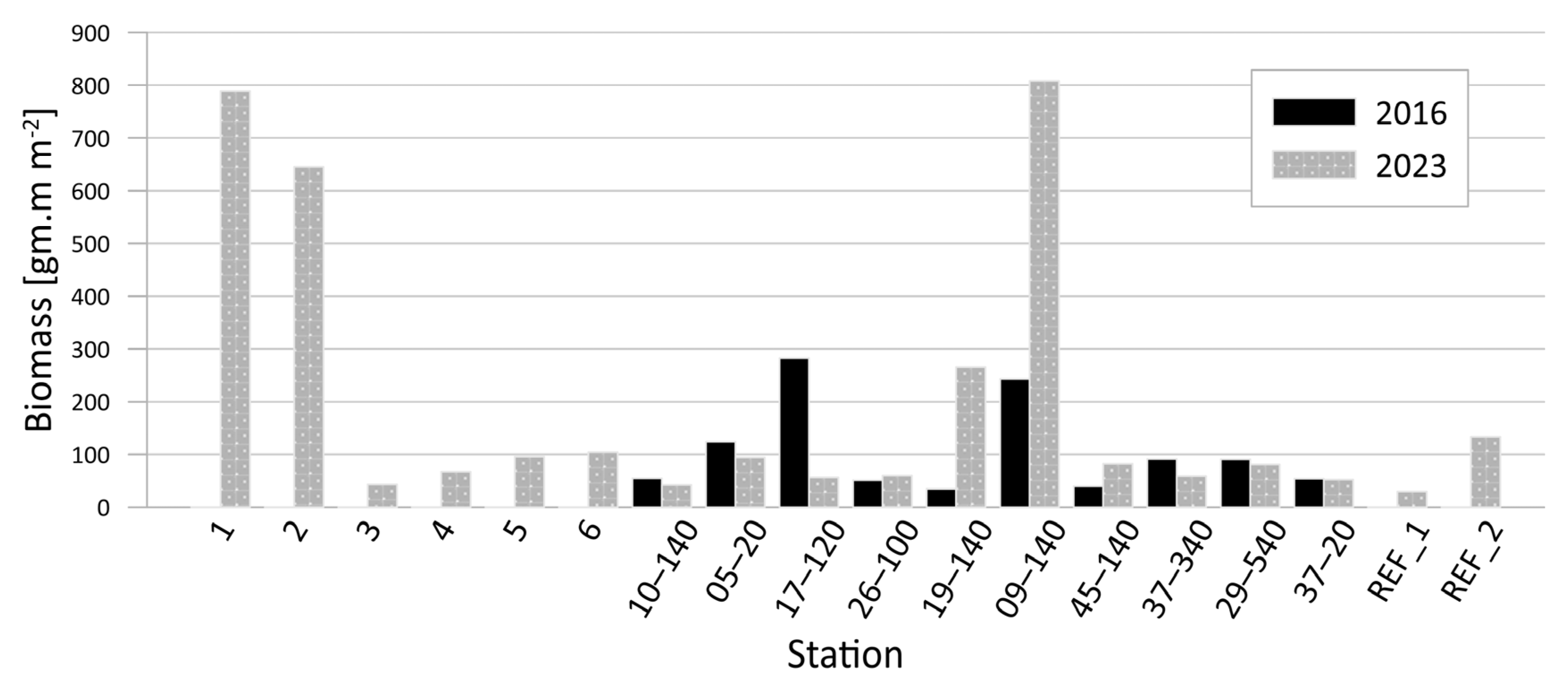
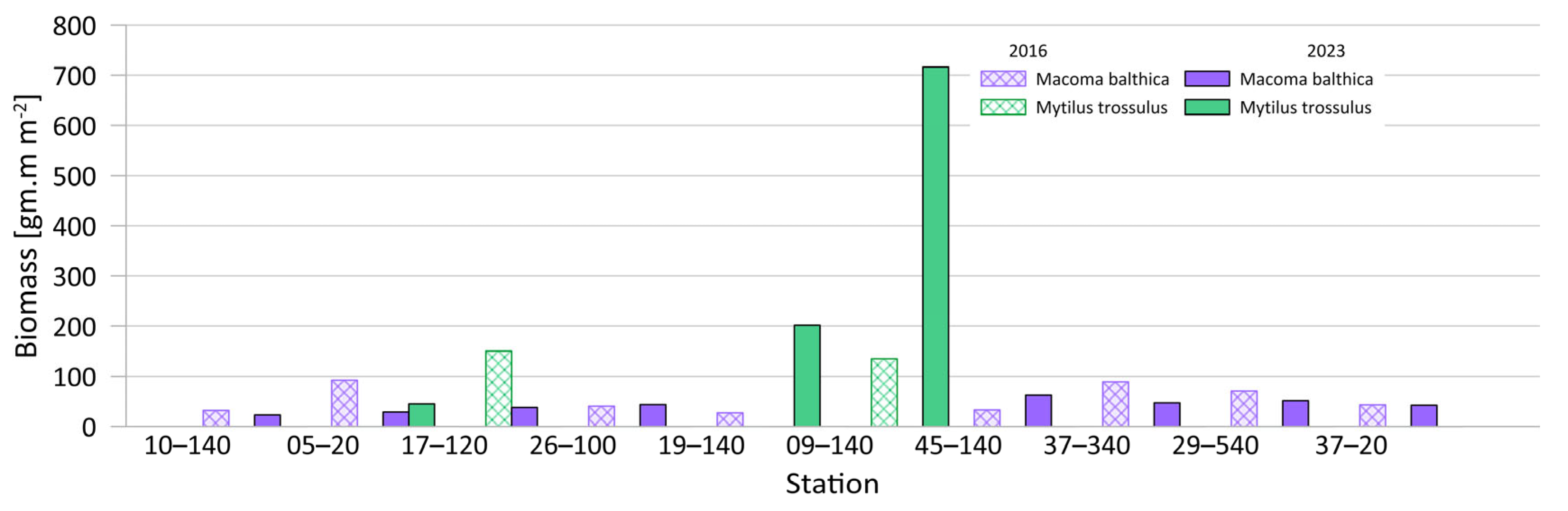
3.1.2. Quantitative Composition
3.1.3. Ecological Quality Assessment Based on B Index
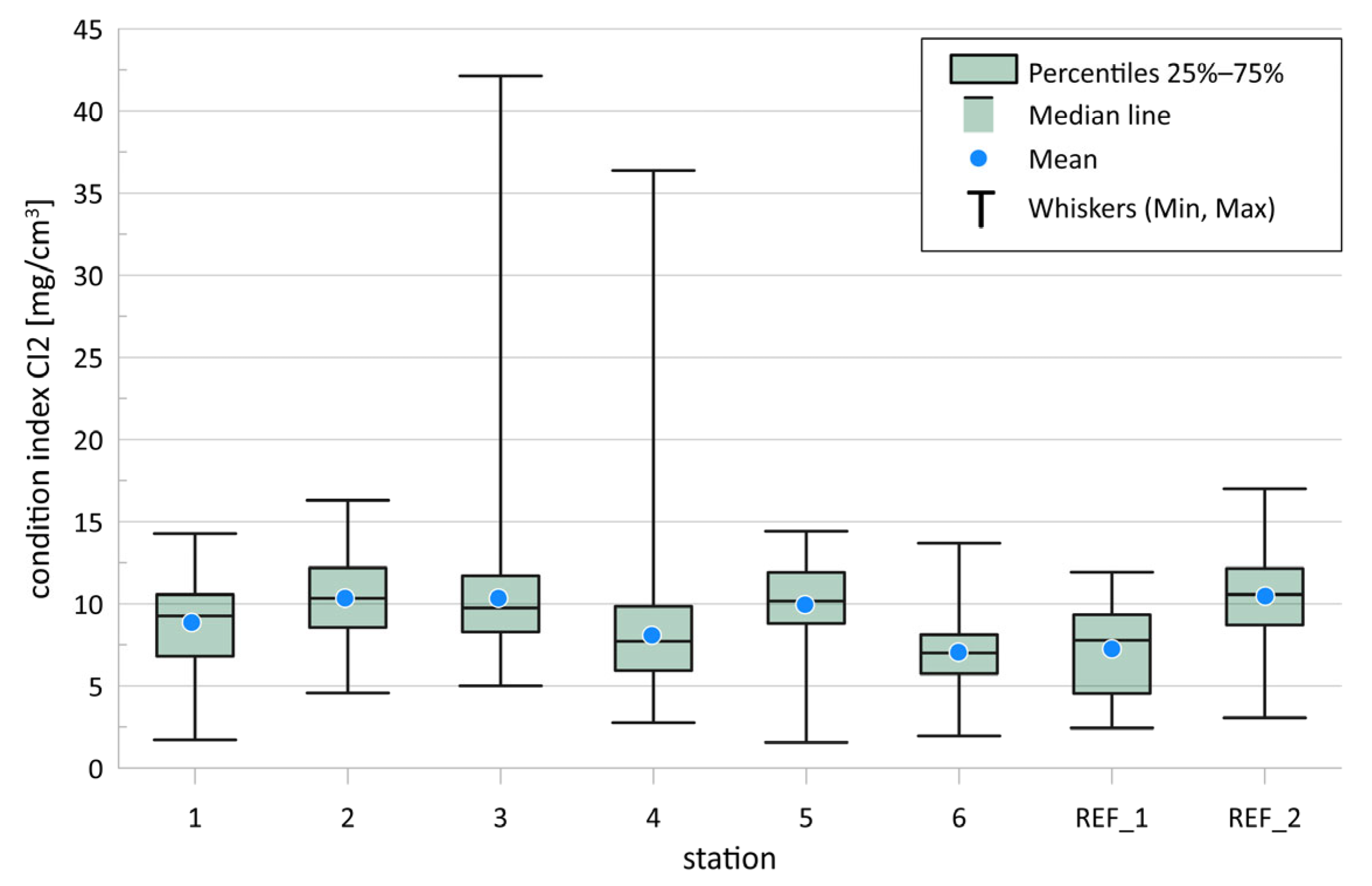
3.1.4. Macoma balthica Condition Index
3.2. Chemical Contaminants in Sediments and Mytilus trossulus Tissues: Insights into Marine Pollution
3.2.1. PAHs
3.2.2. PCBs
3.2.3. TPH
3.2.4. Butyltins (BTs)
3.2.5. Metals, Metalloids, and Labile Forms of Metals
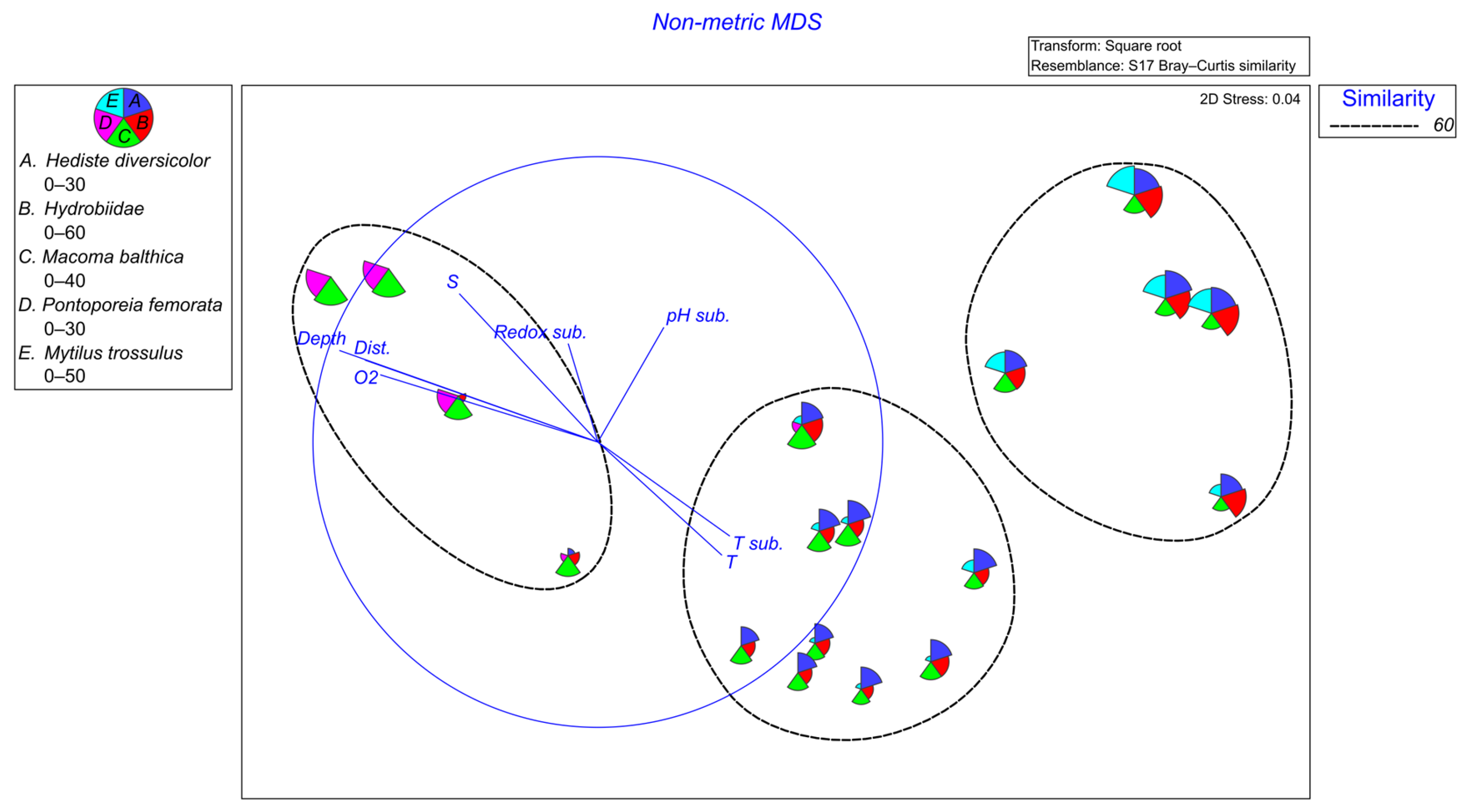
3.3. Correlations and Redundancy Analysis
3.4. Assessment and Criteria of Contamination in Sediments and Mytilus Trossulus Soft Tissues
3.5. Ecotoxicological Assessment of Sediments
3.6. Limitations and Future Directions of the Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Świeżak, J.; Smolarz, K.; Mirny, Z.; Altin, D.; Sokołowski, A. Physiological and behavioral responses of the Baltic clam Macoma balthica to a laboratory simulated CO2-leakage from a subseabed carbon storage site. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 210, 117276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiurska-Kluczek, E.; Malcharek, R.; Tomczak, W. Materiały niebezpieczne na dnie Bałtyku—Zagrożenie katastrofą ekologiczną. Kontrola Państwowa 2020, 5, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, M.L. (Ed.) Threats to Our Ocean Heritage: Potentially Polluting Wrecks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baszanowska, E.; Otremba, Z.; Kubacka, M. Fluorescent analyses of sediments and near-seabed water in the area of the WW2 shipwreck ‘Stuttgart’. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szafranska, M.; Gil, M.; Nowak, J. Toward monitoring and estimating the size of the HFO-contaminated seabed around a shipwreck using MBES backscatter data. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpiech, A.; Bojke, A.; Littwin, M.; Dzendrowska, A.; Duljas, E.; Flasińska, A.; Szczepańska, K.; Dziarkowski, T.; Dembska, G.; Pazikowska-Sapota, G.; et al. Baltic Sea shipwrecks as a source of hazardous pollution. PeerJ Anal. Chem. 2024, 6, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowska, J.; Wolska, L.; Namieśnik, J. Impacts of pollution derived from ship wrecks on the marine environment on the basis of s/s “Stuttgart” (Polish coast, Europe). Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5775–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewska, M.; Burska, D.; Sapota, G.; Bogdaniuk, M.; Borowiec, K.; Nosarzewska, I.; Bolałek, J. The relationship between the concentrations and distribution of organic pollutants and black carbon content in benthic sediments in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A.; Landrum, P.F. Toxicity of sediments. In Encyclopedia of Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks; Middleton, G.V., Church, M.J., Corigilo, M., Hardie, L.A., Longstaffe, F.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Kumari, R. Bioremediation: A sustainable tool for environmental management—A review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2013, 3, 974–993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Matchinski, E.J.; Chen, B.; Ye, X.; Jing, L.; Lee, K. Marine Oil Spills—Oil Pollution, Sources and Effects. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Sheppard, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, L.; Kohl, S.C.; Rice, J.A.; Gagne, J.P. Effects of temperature, salinity and dissolved humic substances on the sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to estuarine particles. Mar. Chem. 2005, 96, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mirnaghi, F.; Shah, K.; Lambert, P.; Hollebone, B.; Yang, C.; Brown, C.E.; Thomas, G.; Grant, R. Source identification and evolution of oils recovered from the MV Manolis L shipwreck. Fuel 2020, 271, 117684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdaniuk, M.; Sapota, G.; Dembska, G.; Aftanas, B. Determination of PAHs and PCBs in the Polish area of shipwrecks. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Osowiecki, A.; Błeńska, M. Makrobezkręgowce bentosowe. In Przewodniki Metodyczne Do Badań Terenowych i Analiz Laboratoryjnych Fitoplanktonu, Innej Flory Wodnej i Makrobezkręgowców Bentosowych w Wodach Przejściowych i Przybrzeżnych; Biblioteka Monitoringu Środowiska: Warszawa, Poland, 2010; pp. 65–84. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowski, A.; Jankowska, E.; Balazy, P.; Jędruch, A. Distribution and extent of benthic habitats in Puck Bay (Gulf of Gdańsk, southern Baltic Sea). Oceanologia 2021, 63, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Porcino, C.; Briglia, M.; Fiorino, E.; Vazzana, M.; Silvestro, S.; Faggio, C. The influence of exposure of cadmium chloride and zinc chloride on haemolymph and digestive gland cells from Mytilus galloprovincialis. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Stara, A.; Aliko, V.; Faggio, C. Impact of Neonicotinoids to Aquatic Invertebrates—In Vitro Studies on Mytilus galloprovincialis: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świacka, K.; Maculewicz, J.; Świeżak, J.; Caban, M.; Smolarz, K. A multi-biomarker approach to assess toxicity of diclofenac and 4-OH diclofenac in Mytilus trossulus mussels—First evidence of diclofenac metabolite impact on molluscs. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, H.; Bogaards, R.; Bek, T.; Polishchuk, L.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Bachelet, G.; Desperz, M.; Strelkov, P.; Sukhotin, A.; Naumov, A.; et al. Sensitivity to stress in the bivalve Macoma balthica from the most northern (Arctic) to the most southern (French) populations: Low sensitivity in Arctic populations because of genetic adaptations? Hydrobiologia 1997, 355, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, A. Wpływ metali śladowych na zmiany fizjologiczne u Macoma balthica (L.) w estuarium Wisły. Ph.D. Thesis, Uniwersytet Gdański, Wydział Oceanografii i Geografii (WOiG), Gdynia, Poland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Villnäs, A.; Norkko, A.; Lehtonen, K. Multi-level responses of Macoma balthica to recurring hypoxic disturbance. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 510, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, J. Wpływ zanieczyszczeń na zoobentos Zatoki Gdańskiej ze szczególnym uwzględnieniem określenia gatunków wskaźnikowych. Stud. i Mat. MIR Seria A 1985, 26, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament, Council of the European Union. Directive 2008/56/EC, 2008. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 164, 19. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament, Council of the European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy (Water Framework Directive). Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM. HELCOM Activities Report for the Year 2021. 2021. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/HELCOM-Activities-report-2021-BSEP186.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- World Register of Marine Species. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Odum, E. Podstawy Ekologii. Wydanie III; Państwowe Wydawnictwo Rolnicze i Leśne: Warszawa, Poland, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Trojan, P. Ekologia Ogólna, 4th ed.; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1980. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Wenne, R. Zróżnicowanie Przestrzenne i Ewolucja Wybranych Gatunków Małży Morskich. Praca Habilitacyjna; Wydawnictwo UG: Gdańsk, Poland, 1993. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Styczyńska-Jurewicz, E.; Wenne, R. Grazing condition for zooplankton and condition of the bivalve Macoma balthica L. in Pilayella Dominated Shallow-Water Ecosystem of the Puck Lagoon (Gulf of Gdańsk, Baltic Sea). In Proceedings of the 2nd International Estuary Symposium, Gdańsk, Poland, 18–22 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Honkoop, P.J.C.; van der Meer, J.; Beukema, J.J.; Kwast, D. Reproductive investment in the intertidal bivalve Macoma Balthica. J. Sea Res. 1999, 41, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation of the Minister of Infrastructure of 25 June 2021 on the Classification of Ecological Status, Ecological Potential, and Chemical Status, as well as the Method of Classification of the Status of Surface Water Bodies and Environmental Quality Standards for Priority Substances (Journal of Laws 2021, Item 1475). Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20210001475/O/D20211475.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- ISO 11348-3:2007; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio fischeri (Luminescent Bacteria Test) Part 3: Method Using Freeze-Dried Bacteria. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- ISO 6341:2012; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibition of the Mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea)—Acute Toxicity Test. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 8692:2012; Water Quality—Fresh Water Algal Growth Inhibition Test with Unicellular Green Algae. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 7346-2:1996; Water Quality—Determination of the Acute Lethal Toxicity of Substances to a Freshwater Fish [Brachydanio rerio Hamilton-Buchanan (Teleostei, Cyprinidae)]. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Janas, U.; Szaniawska, A. The influence of hydrogen sulphide on macrofaunal biodiversity in the Gulf of Gdańsk. Oceanologia 1996, 38, 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Janas, U.; Szaniawska, A. Hydrogen sulphide and other factors influencing the macrobenthic community structure in the Gulf of Gdańsk. Oceanologia 1996, 38, 379–394. [Google Scholar]
- Janas, U.; Wocial, J.; Szaniawska, A. Seasonal and annual changes in macrozoobenthic populations of the Gulf of Gdańsk with respect to hypoxia and H2S. Oceanologia 2004, 46, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Warzocha, J.; Grelowski, A.; Bolałek, J.; Białkowska, I. The response of soft bottom benthic macrofauna to environmental changes in the Gulf of Gdańsk in 2000–2001. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Memory Devices for Abundant Data Computing “Functioning of Coastal Ecosystems in Various Geographical Regions”, Gdynia, Poland, 19–22 June 2001; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Warzocha, J.; Gromisz, S.; Wodzinowski, T.; Szymanek, L. The structure of macrozoobenthic communities as an environmental status indicator in the Gulf of Gdańsk (the Outer Puck Bay). Oceanologia 2018, 60, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmudziński, L. Świat zwierzęcy Bałtyku; Wydawnictwa Szkolne i Pedagogiczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Warzocha, J. Classification and structure of macrofaunal communities in the southern Baltic. Arch. Fish. Mar. Res. 1995, 42, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Hac, B. Monitoring of the wreck m/s SLEIPNER—Possible sources of contamination of the seabed in Polish marine areas. Bull. Marit. Inst. Gdańsk 2016, 31, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, V.; Hughes, R.G. Feeding behaviour and diet of Corophium volutator in an estuary in southeastern England. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 114, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.M.; Costa, J.L.; Neves, M.; Azevedo e Silva, F.; Mota, A.; Pombo, A. Sea urchin waste as a promising nutritional source for the polychaete Hediste diversicolor (OF Müller, 1776). Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B. Tolerance of the deposit-feeding Baltic amphipods Monoporeia affinis and Pontoporeia fermorata to oxygen deficiency. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 151, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnio, M.; Mustonen, H.; Mecklin, J.P.; Järvinen, H.J. Prognosis of colorectal cancer varies in different high-risk conditions. Ann. Med. 1998, 30, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsdorff, E.; Wenne, R. A comparison of conditio indices of Macoma balthica (L.) from the Northern and Southern Baltica sea. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1989, 23, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkoop, P.J.C.; van der Meer, J. Reproductive output of Macoma balthica populations in relations to winter-temperature and intertidal-height mediate changes of body mass. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 149, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, M.; Gale, L. A review and evaluation of bivalve condition index methodologies with a suggested standard method. J. Shellfish Res. 1990, 91, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, H.; Vural, P.; Acarli, S. Condtion Index, Meat Yield and Biochemical Composition of Mediterranean Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarc, 1819) from Canakkale Strait, Turkey. Alinteri J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 36, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touahri, H.G.; Boutiba, Z.; Benguedda, W.; Shaposhnikov, S. Active biomonitoring of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis with integrated use of micronucleus assay and physiological indices to assess harbour pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, A.; Wolowicz, M.; Hummel, H.; Bogaards, R. Physiological responses of Macoma balthica to copper pollution in the Baltic. Oceanol. Acta 1999, 22, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Han, E.; Choi, K.-S.; Kwak, J.H.; Choy, E.J.; Kang, C.-K. Effect of the Hebei Spirit oil spill on the condition, reproduction, and energy storage cycle of the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum on the West Coast of Korea. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. TBT and Imposex. HELCOM Core Indicator Report. 2023. Available online: https://indicators.helcom.fi/indicator/tbt-and-imposex/ (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Lucas, A.; Beninger, P. The use of physiological condition indices in marine bivalve aquaculture. Aquaculture 1985, 44, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziaduch, D. Gametogenesis and Condition Indices in Comparative Study of the Bivalve Macoma balthica (L.) and Mytilus trossulus. Master’s Thesis, Uniwersytet Gdański, Gdańsk, Poland, 2004; pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Waszak, I.; Dąbrowska, H.; Warzocha, J. Assessment of native and alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments and mussels (Mytilus spp.) in the southern Baltic Sea. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation of the Minister of the Environment of 11 May 2015 on the recovery of waste outside installations and equipment. J. Laws 2015, item 796.
- Kowalewska, G.; Konat, J. Distribution of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments of the southern Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 1997, 39, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Pazdro, K. Persistant Organic Pollutants in sediments from the Gulf of Gdansk. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2004, 6, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Uścinowicz, S. (Ed.) Geochemia osadów powierzchniowych Morza Bałtyckiego. In Ministerstwo Środowiska; Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny: Warszawa, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ruczyńska, W.M.; Szlinder-Richert, J.; Malesa-Ciećwierz, M.; Warzocha, J. Assessment of PAH pollution in the southern Baltic Sea through the analysis of sediment, mussels and fish bile. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2011, 13, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, R.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Sharifinia, M.; Zakaria, M.P.; Rastegari Mehr, M.; Abbasi, S.; Yap, C.K.; Yousefi, M.R.; Masood, N.; Magam, S.M.; et al. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the coastal ecosystem of the Brunei Bay, Brunei. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaezzadeh, V.; Zakaria, M.P.; Bong, C.W.; Masood, N.; Magam, S.M.; Alkhadher, S.A.A. Mangrove Oyster (Crassostrea belcheri) as a Biomonitor Species for Bioavailability of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) from Sediment of the West Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2019, 39, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Kadir, A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Asghar, B.H.M. Determination of linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) in mangrove ecosystems using the oyster Crassostrea belcheri as a biosensor. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumard, P.; Budzinski, H.; Garrigues, P.; Narbonne, J.F.; Burgeot, T.; Michel, X.; Bellocq, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) burden of mussels (Mytilus sp.) in different marine environments in relation with sediment PAH contamination, and bioavailability. Mar. Environ. Res. 1999, 47, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, A.M.L.; Faxneld, S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen in Baltic Sea blue mussels: Time series data 1981–2016. Data Brief 2021, 35, 106777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapota, G. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in bottom sediments from the Baltic Sea. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2006, 35, 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Konat, J.; Kowalewska, G. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments of the southern Baltic Sea—Trends and fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 280, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenycz, M.; Sokotowski, A.; Niewińska, A.; Wołowicz, M.; Namieśnik, J.; Hummel, H.; Jansen, J. Comparison of PCBs and PAHs levels in European coastal waters using mussels from the Mytilus edulis complex as biomonitors. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrykus, J.; Albalat, A.; Pempkowiak, J.; Porte, C. Content and pattern of organic pollutants (PAHs, PCBs and DDT) in blue mussels (Mytilus trossulus) from the southern Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 2003, 45, 337–355. [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska, H.; Kopko, O.; Turja, R.; Lehtonen, K.K.; Góra, A.; Polak-Juszczak, L.; Warzocha, J.; Kholodkevich, S. Sediment contaminants and contaminant levels and biomarkers in caged mussels (Mytilus trossulus) in the southern Baltic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 84, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation of the Minister of Infrastructure of 25 February 2021 on the Adoption of the Updated Set of Characteristics for Good Environmental Status of Marine Waters. Journal of Laws 2021, Item 568. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20210000568 (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Dembska, G.; Bogdaniuk, M.; Sapota, G.; Michałek, M.; Osowiecki, A.; Hac, B.; Rudowski, S.; Kałas, M.; Zegarowski, Ł.; Littwin, M.; et al. Badanie Walorów Przyrodniczych Siedliska Dennego w Rejonie Klapowiska, Wyznaczonego Dla Portu Gdynia Oraz Wpływu Zrealizowanych Projektów Na Obszarze Natura 2000; Instytut Morski: Gdańsk, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sapota, G.; Dembska, G.; Bogdaniuk, M.; Blažauskas, K. Contamination in Sedimentsfrom the Baltic Sea Region Situation and Methods—Raport SMOCS. Baltic Sea Region Programme Project. 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301481508_Contamination_in_sediments_from_the_Baltic_Sea_region_Situation_and_Methods_wwwsmocseu?channel=doi&linkId=57162b7a08aebf0697f183d9&showFulltext=true (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Head, I.M.; Jones, D.M.; Röling, W.F. Marine microorganisms make a meal of oil. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röling, W.F.M.; Milner, M.G.; Jones, D.M.; Lee, K.; Daniel, F.; Swannell, R.J.P.; Head, I.M. Robust hydrocarbon degradation and dynamics of bacterial communities during nutrient-enhanced oil spill bioremediation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5537–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antizar-Ladislao, B. Environmental levels, toxicity and human exposure to tributyltin (TBT)-contaminated marine environment. A review. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.R.; dos Santos, D.M.; dos Santos Madureira, L.A.; de Marchi, M.R.R. Speciation of butyltin derivatives in surface sediments of three southern Brazilian harbors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipkowska, A.; Kowalewska, G.; Pavoni, B. Organotin compounds in surface sediments of the Southern Baltic coastal zone: A study on the main factors for their accumulation and degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.; Westphal, L.; Hand, I.; Lerz, A.; Jeschek, J.; Bunke, D.; Leipe, T.; Schulz-Bull, D. TBT and its metabolites in sediments: Survey at a German coastal site and the central Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.; Petersen, K.; Lehoux, A.P.; Leppänen, M.; Schaanning, M.; Snowball, I.; Øxnevad, S.; Lund, E. Contaminated Sediments: Review of Solutions for Protecting Aquatic Environment; Issue December 2020; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Background Document on Tributlytin (TBT) in Sediment, Swedish Quality Standard; Publication Number: 762/2020; OSPAR Commission: London, UK, 2020.
- Tipping, E. Humic ion-binding model VI: An improved description of the interactions of protons and metal ions with humic substances. Aquat. Geochem. 1998, 4, 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembska, G.; Bolałek, J.; Aftanas, B.; Guz, W.; Wiśniewski, S. Udział formy labilnej i całkowitej metali ciężkich w osadach z Portu Gdańskiego. In Problemy Analityczne Badań Osadów Dennych; Sympozjum Naukowe Komitetu Chemii Analitycznej PAN Komisja Analizy Wody: Poznań, Poland, 2001; pp. 83–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hendożko, E.; Szefer, P.; Warzocha, J. Heavy metals in Macoma balthica and extrable metals in sediments from southern Baltic Sea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwizdała, M.; Jeleńska, M.; Łęczyński, L. Surface sediments pollution around small shipwrecks (Munin and Abille) in the Gulf of Gdańsk: Magnetic and heavy metals study. In Magnetometry In Environmental Sciences. Studying Environmental Structure Changes and Environmental Pollution; Jeleńska, M., Łęczyński, L., Ossowski, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędruch, A.; Falkowska, L.; Saniewska, D.; Grajewska, A.; Bełdowska, M.; Meissner, W.; Kalisińska, E.; Duzinkiewicz, K.; Pacyna, J.M. Mercury in the Polish part of the Baltic Sea: A response to decreased atmospheric deposition and changing environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur-Chrzanowska, B.; Kopiec, J.; Wojtaszek, A.; Danowska, B.; Drgas, N.; Koszuta, V.; Kaśniewski, W.; Krzymiński, W.; Łysiak-Pastuszak, M.; das Neves, S.; et al. Ocena Stanu środowiska Polskich Obszarów Morskich Bałtyku Na Podstawie Danych Monitoringowych z Roku 2015 Na Tle Dziesięciolecia 2005–2014; Biblioteka Monitoringu Środowiska: Warszawa, Poland, 2016; pp. 118–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zalewska, T.; Woron, J.; Danowska, B.; Suplińska, M. Temporal changes in Hg, Pb, Cd and Zn environmental concentrations in the Southern Baltic Sea sediments dated with 210Pb method. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefer, P.; Szefer, K. Metals in molluscs and associated bottom sediments of the southern Baltic. Helgolan. Meeresunters 1990, 44, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefer, P.; Frelek, K.; Szefer, K.; Lee, C.-B.; Kim, B.S.; Warzocha, J.; Zdrojewska, I.; Ciesielski, T. Distribution and relationships of trace metals in soft tissue, byssus and shells of Mytilus edulis trossulus from the southern. Baltic. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boszke, L.; Siepak, J.; Falandysz, J. Total mercury contamination of selected organisms in Puck Bay, Baltic Sea, Poland. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, R.P.; Laporte, J.M.; Andres, S. Factors controlling the bioaccumulation of mercury, methylmercury, arsenic, selenium, and cadmium by freshwater invertebrates and fish. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Sohn, M. Aquatic arsenic: Toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuer-Lauridsen, F. Review of passive accumulation devices for monitoring organic micropollutants in the aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 136, 503–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




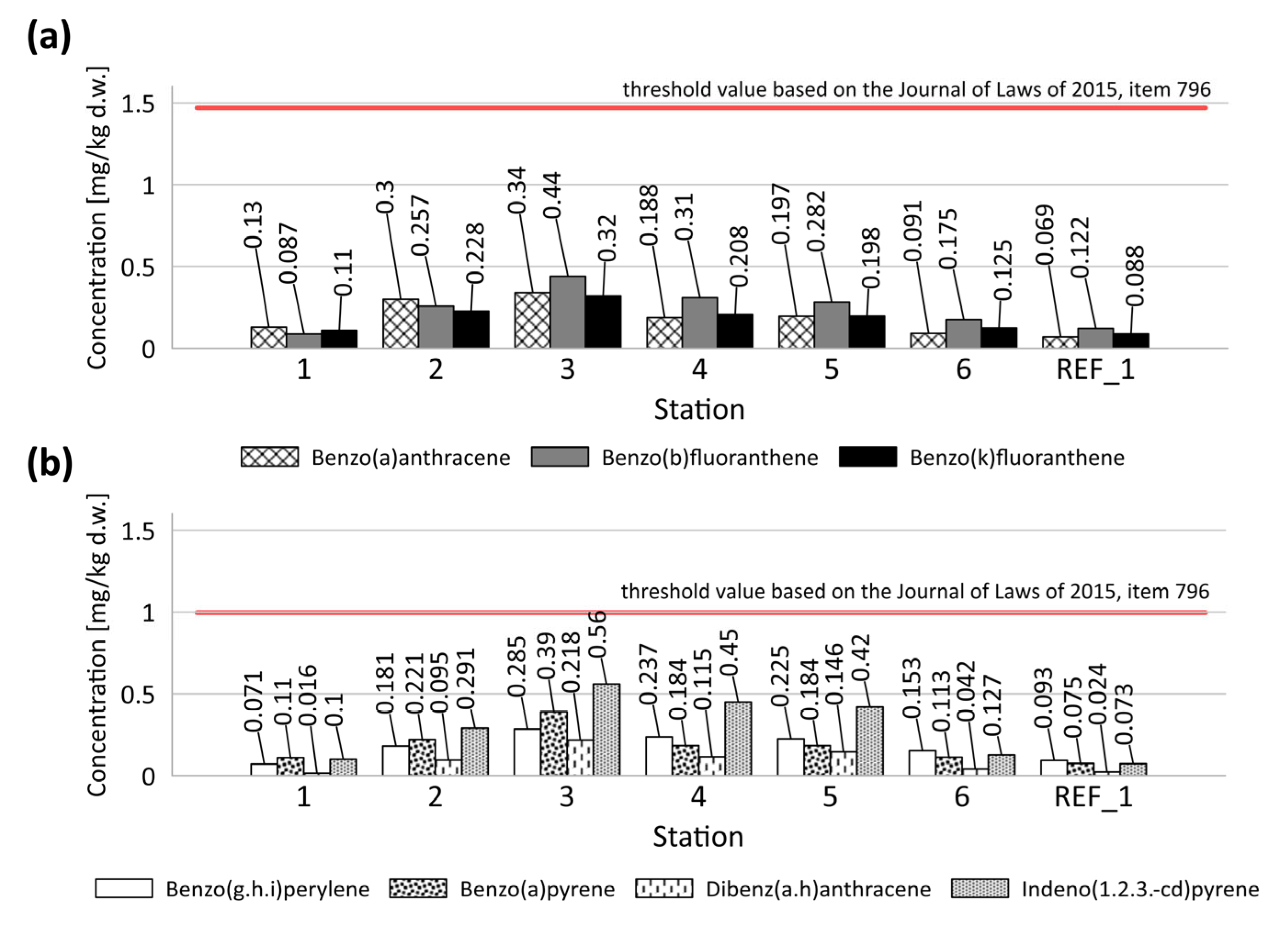
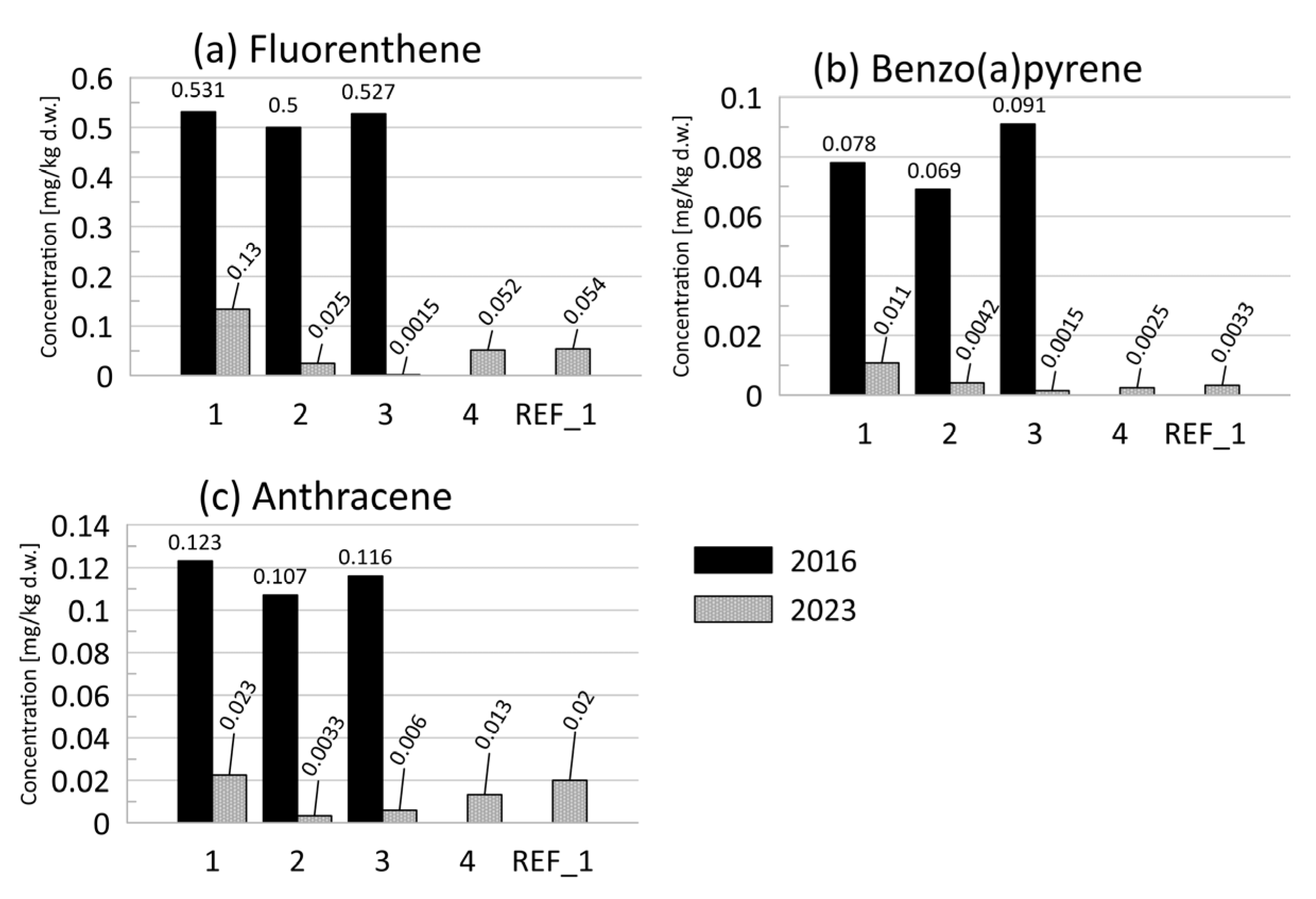

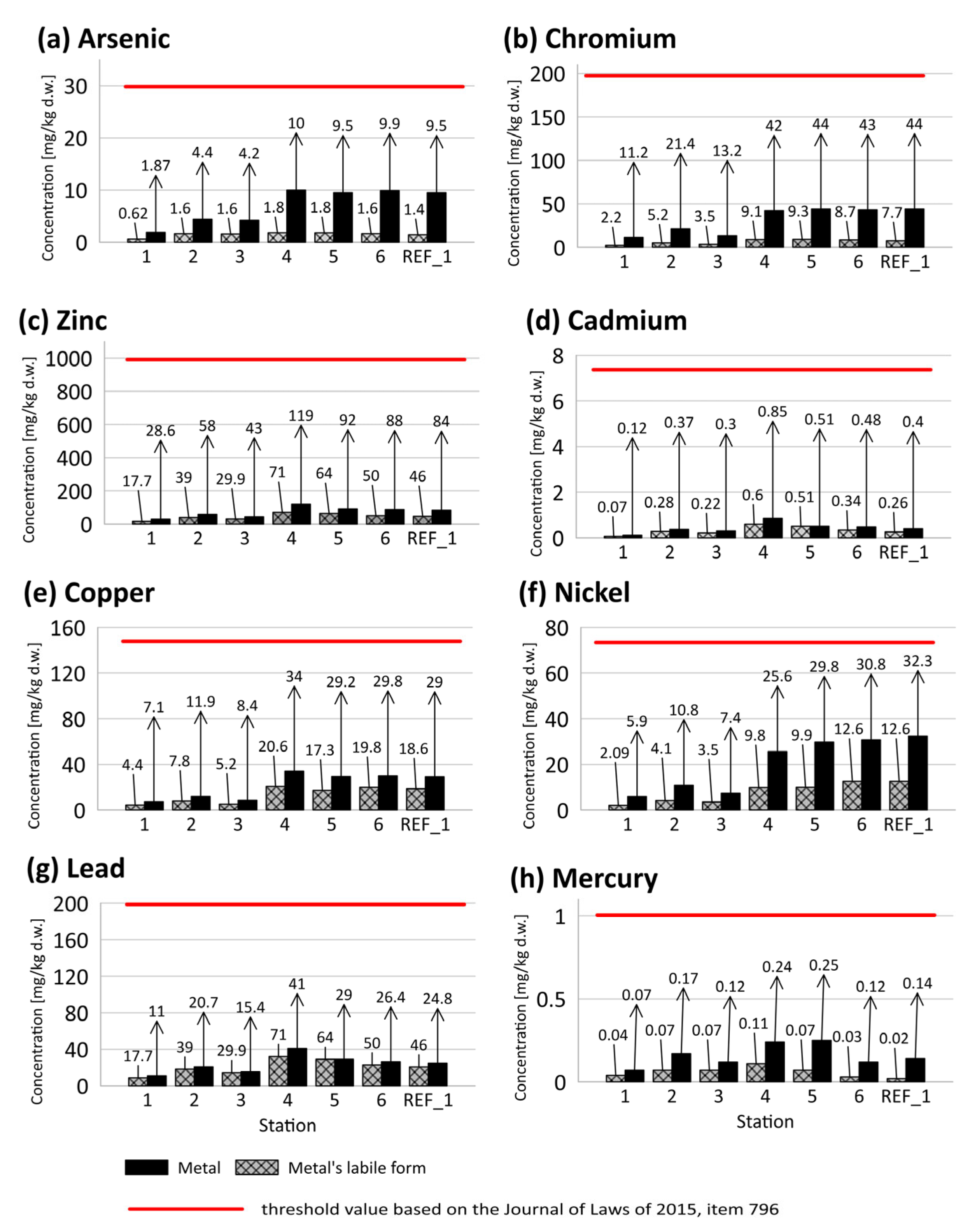

| Compound | Concentration Range (Station 1–6) | REF_1 Station |
|---|---|---|
| Naphthalene | 0.007–0.038 | 0.014 |
| Acenaphthene | 0.008–0.022 | 0.016 |
| Acenaphthylene | 0.004–0.012 | 0.002 |
| Fluorene | 0.010–0.042 | 0.009 |
| Phenanthrene | 0.068–0.200 | 0.050 |
| Anthracene | 0.016–0.221 | 0.012 |
| Fluoranthene | 0.152–0.660 | 0.117 |
| Pyrene | 0.105–0.440 | 0.076 |
| Benzo(a)anthracene | 0.091–0.340 | 0.069 |
| Chrysene | 0.074–0.320 | 0.053 |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 0.007–0.038 | 0.122 |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | 0.087–0.440 | 0.088 |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.110–0.390 | 0.075 |
| Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 0.100–0.560 | 0.073 |
| Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | 0.016–0.218 | 0.024 |
| Benzo(g,h,i)perylene | 0.071–0.285 | 0.093 |
| Groups | R | p |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 A, 2016 B | 0.829 | 0.0080 |
| 2016 A, 2023 D | 1 | 0.0010 |
| 2016 A, 2023 E | 1 | 0.0030 |
| 2016 A, 2023 C | 1 | 0.0002 |
| 2016 B, 2023 D | 1 | 0.0180 |
| 2016 B, 2023 E | 1 | 0.0290 |
| 2016 B, 2023 C | 1 | 0.0050 |
| 2023 D, 2023 E | 1 | 0.0080 |
| 2023 D, 2023 C | 0.956 | 0.0005 |
| 2023 E, 2023 C | 0.958 | 0.0010 |
| Global | 0.972 | 0.0010 |
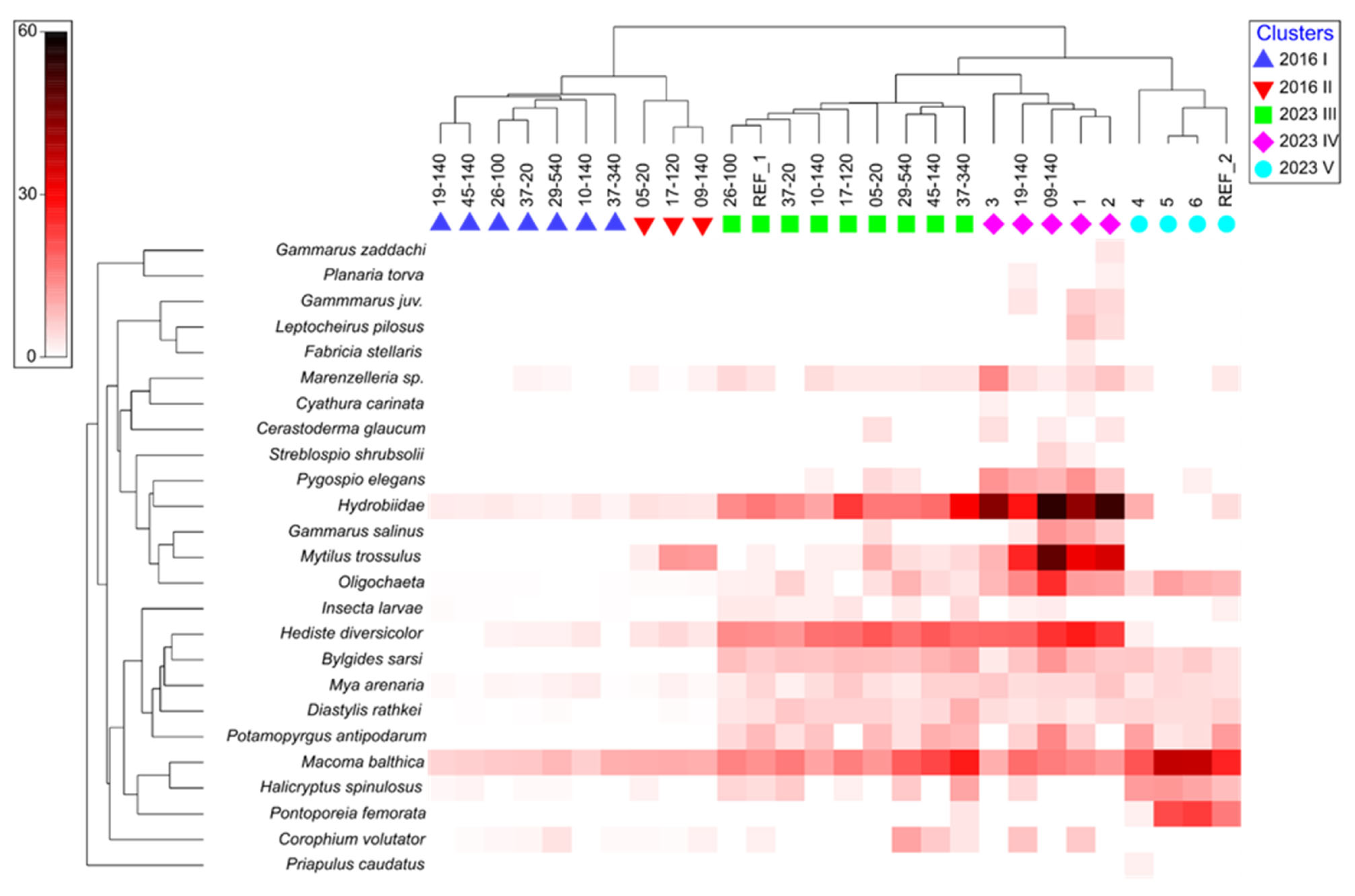
| Group | 2016 I | 2016 II | 2023 III | 2023 IV | 2023 V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. Simil. | 71.29 | 77.60 | 75.68 | 72.83 | 73.79 |
| Taxa | % | % | % | % | % |
| Macoma balthica | 62.42 | 41.73 | 19.51 | 8.75 | 36.08 |
| Mytilus trossulus | - | 21.84 | - | 15.24 | - |
| Hydrobiidae | 18.99 | - | 20.24 | 28.65 | - |
| Hediste diversicolor | - | - | 21.09 | 14.72 | - |
| Bylgides sarsi | - | - | 10.03 | - | - |
| Oligochaeta | - | - | - | 7.77 | 9.77 |
| Halicryptus spinulosus | - | - | - | - | 13.88 |
| Pontoporeia temorata | - | - | - | - | 13.60 |
| Marginal Test | Sequential Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Pseudo-F | p | Prop. var. | Pseudo-F | p | Prop. var. | Prop. Cum. var. |
| Depth | 14.2 | 0.0001 | 0.47 | 14.2 | 0.0001 | 0.47 | 0.47 |
| Dist. | 10.6 | 0.0001 | 0.40 | 0.9 | 0.4083 | 0.03 | 0.50 |
| T | 3.5 | 0.0239 | 0.18 | 3.5 | 0.0295 | 0.10 | 0.60 |
| S | 4.9 | 0.0068 | 0.23 | 2.6 | 0.0584 | 0.07 | 0.67 |
| O2 | 8.2 | 0.0005 | 0.34 | 2.7 | 0.0526 | 0.06 | 0.73 |
| T sed. | 3.4 | 0.0244 | 0.18 | 0.3 | 0.9256 | 0.01 | 0.73 |
| pH sed. | 1.3 | 0.2672 | 0.07 | 1.4 | 0.2341 | 0.03 | 0.77 |
| Redox sed. | 1.4 | 0.2482 | 0.08 | 0.4 | 0.7591 | 0.01 | 0.78 |
| No. Vars | Corr. Selections |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.605 Cu |
| 2 | 0.629 Cu, Zn |
| 3 | 0.630 Cu, Ni, Hg |
| 4 | 0.634 Cu, Zn, Ni, Cd |
| 5 | 0.634 Cu, Zn, Ni, Cd, TBT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarała, A.; Dziaduch, D.; Galer-Tatarowicz, K.; Bojke, A.; Kubacka, M.; Kalarus, M. Macrozoobenthos Response to Sediment Contamination near the S/s Stuttgart Wreck: A Biological and Chemical Assessment in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic Sea. Water 2025, 17, 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152199
Tarała A, Dziaduch D, Galer-Tatarowicz K, Bojke A, Kubacka M, Kalarus M. Macrozoobenthos Response to Sediment Contamination near the S/s Stuttgart Wreck: A Biological and Chemical Assessment in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic Sea. Water. 2025; 17(15):2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152199
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarała, Anna, Diana Dziaduch, Katarzyna Galer-Tatarowicz, Aleksandra Bojke, Maria Kubacka, and Marcin Kalarus. 2025. "Macrozoobenthos Response to Sediment Contamination near the S/s Stuttgart Wreck: A Biological and Chemical Assessment in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic Sea" Water 17, no. 15: 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152199
APA StyleTarała, A., Dziaduch, D., Galer-Tatarowicz, K., Bojke, A., Kubacka, M., & Kalarus, M. (2025). Macrozoobenthos Response to Sediment Contamination near the S/s Stuttgart Wreck: A Biological and Chemical Assessment in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic Sea. Water, 17(15), 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152199









