Research Progress on Emerging Pollutants in Watershed Water Bodies: A Bibliometric Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results
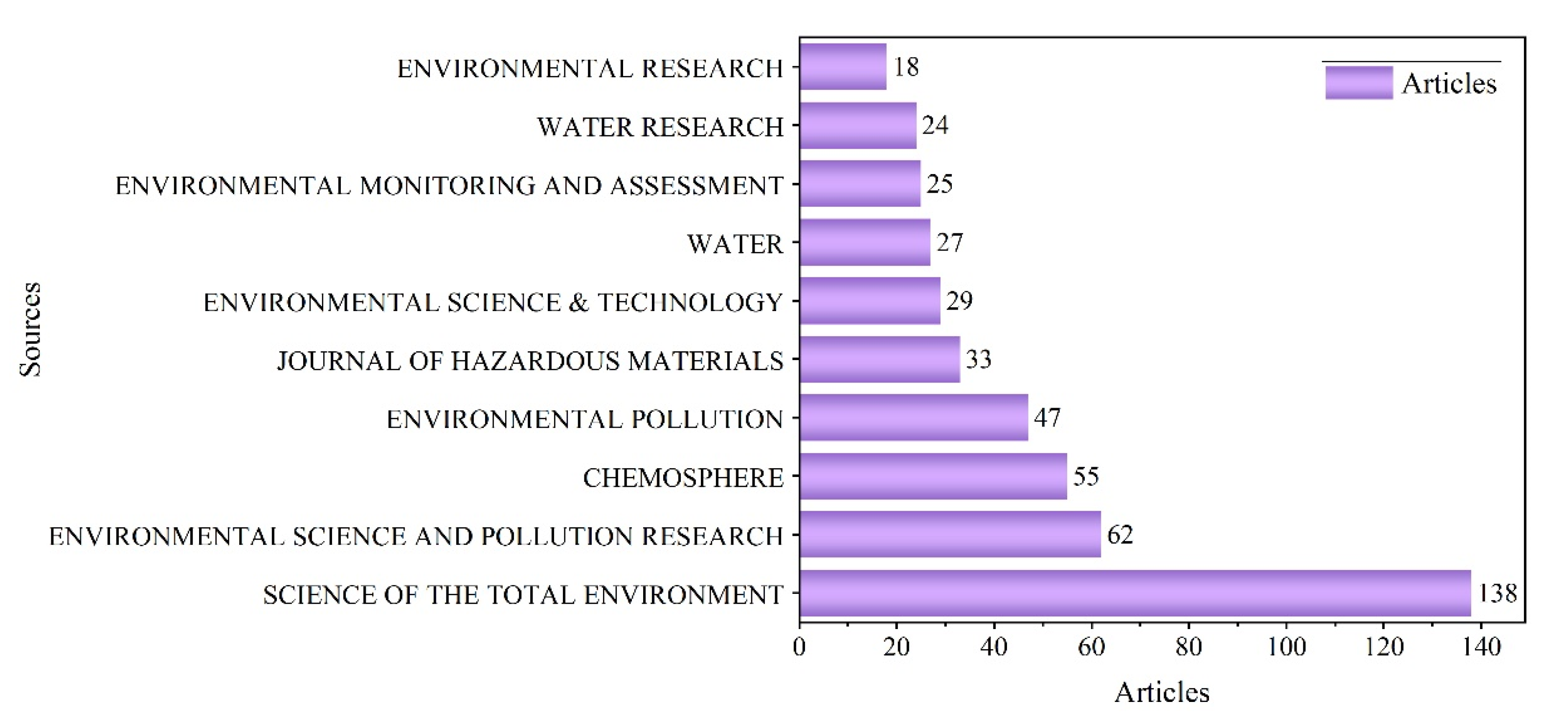
3.1. Basic Characteristics of Publications
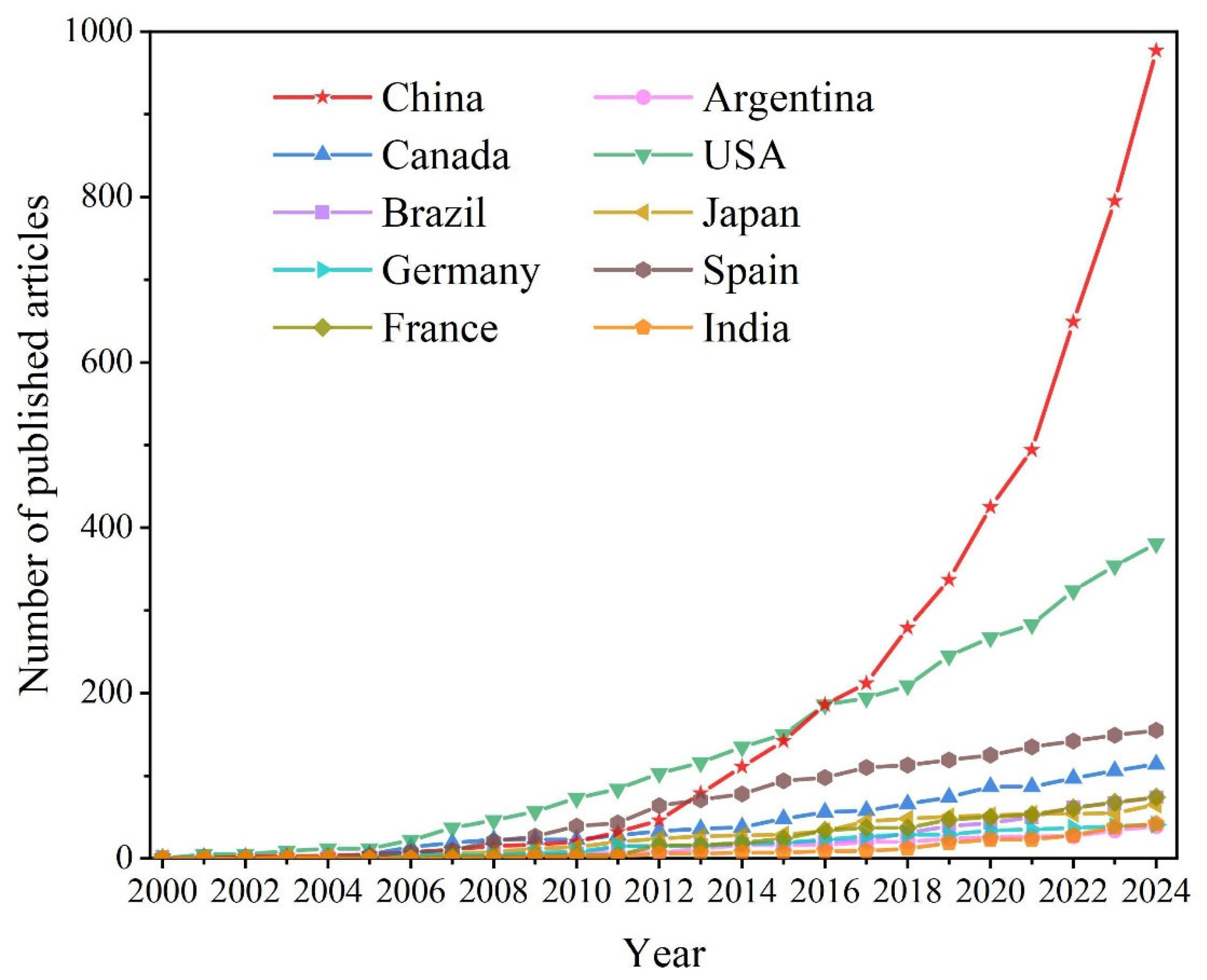
3.1.1. Annual Publication Trends
3.1.2. Types of Publications
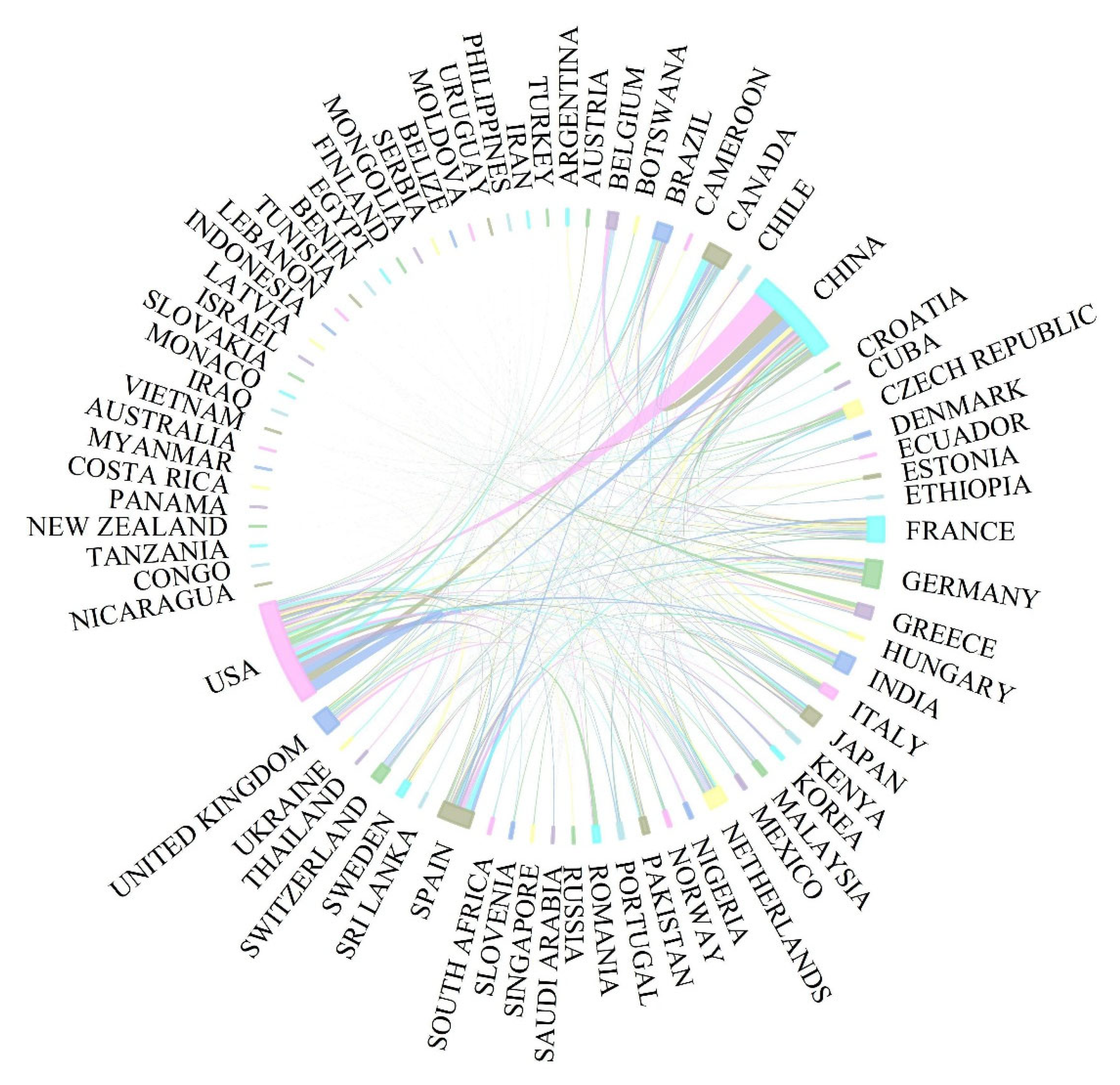
3.2. Producing Countries and Cooperation
3.3. Influential Institutions
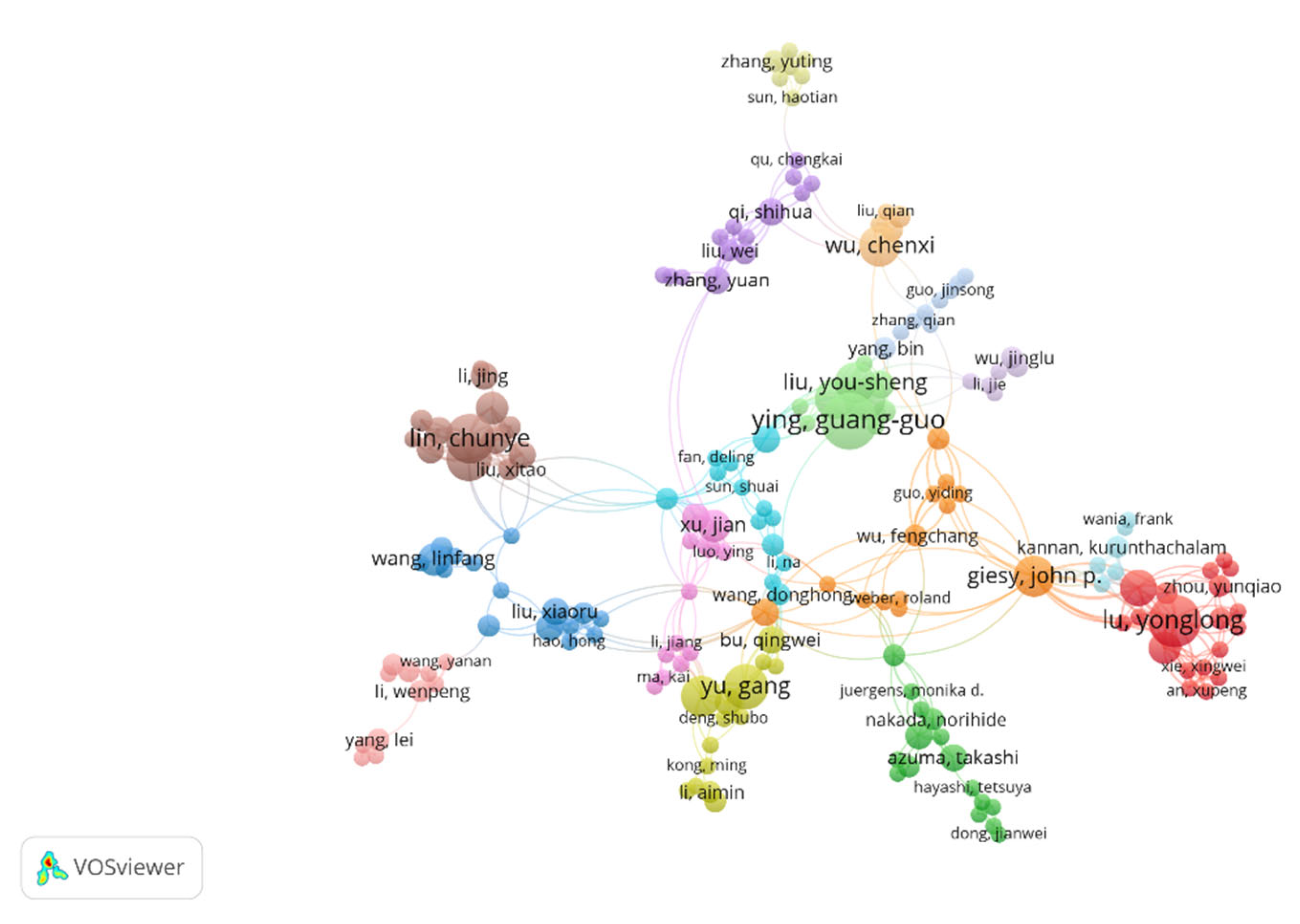
3.4. Influential Authors
3.5. Highly Cited Publications
| Rank | Title | Authors | Source | Type | Year | Total Citations | TC Per Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water [35] | Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. | Science of the Total Environment | Article | 2009 | 931 | 54.76 |
| 2 | Occurrence and Transport of Tetracycline, Sulfonamide, Quinolone, and Macrolide Antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China [43] | Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J.J. | Environmental Science & Technology | Article | 2011 | 813 | 54.2 |
| 3 | Sources and sinks of microplastics in Canadian Lake Ontario nearshore, tributary and beach sediments [44] | Ballent, A.; Corcoran, P.L.; Madden, O.; Helm, P.A.; Longstaffe, F.J. | Marine Pollution Bulletin | Article | 2016 | 475 | 47.5 |
| 4 | Plastic Debris in 29 Great Lakes Tributaries: Relations to Watershed Attributes and Hydrology [45] | Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. | Environmental Science & Technology | Article | 2016 | 474 | 47.4 |
| 5 | Legacy and Emerging Perfluoroalkyl Substances Are Important Drinking Water Contaminants in the Cape Fear River Watershed of North Carolina [46] | Sun, M.; Arevalo, E.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.; Richardson, M.; Kearns, B.; Pickett, A.; Knappe, D.R.U. | Environmental Science & Technology Letters | Article | 2016 | 468 | 46.8 |
| 6 | Occurrence of acidic pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Tuna River Basin: From waste to drinking water [39] | Carmona, E.; Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. | Science of the Total Environment | Article | 2014 | 401 | 33.42 |
| 7 | Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Wei River, in the northwest of China [41] | Ding, L.; Mao, R.F.; Guo, X.T.; Yang, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C. | Science of the Total Environment | Article | 2019 | 392 | 56 |
| 8 | Persistence of Extracellular DNA in River Sediment Facilitates Antibiotic Resistance Gene Propagation [40] | Mao, D.Q.; Luo, Y.; Mathieu, J.; Wang, Q.; Feng, L.; Mu, Q.H.; Feng, C.Y.; Alvarez, P.J.J. | Environmental Science & Technology | Article | 2014 | 358 | 29.83 |
| 9 | Assessment of the sources and inflow processes of microplastics in the river environments of Japan [47] | Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y.; Kudou, K.; Hinata, H. | Environmental Pollution | Article | 2019 | 337 | 48.14 |
| 10 | Health and ecological risk assessment of emerging contaminants (pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and artificial sweeteners) in surface and groundwater (drinking water) in the Ganges River Basin, India [42] | Sharma, B.M.; Becanová, J.; Scheringer, M.; Sharma, A.; Bharat, G.K.; Whitehead, P.G.; Klánová, J.; Nizzetto, L. | Science of the Total Environment | Article | 2019 | 324 | 46.29 |
3.6. Keywords
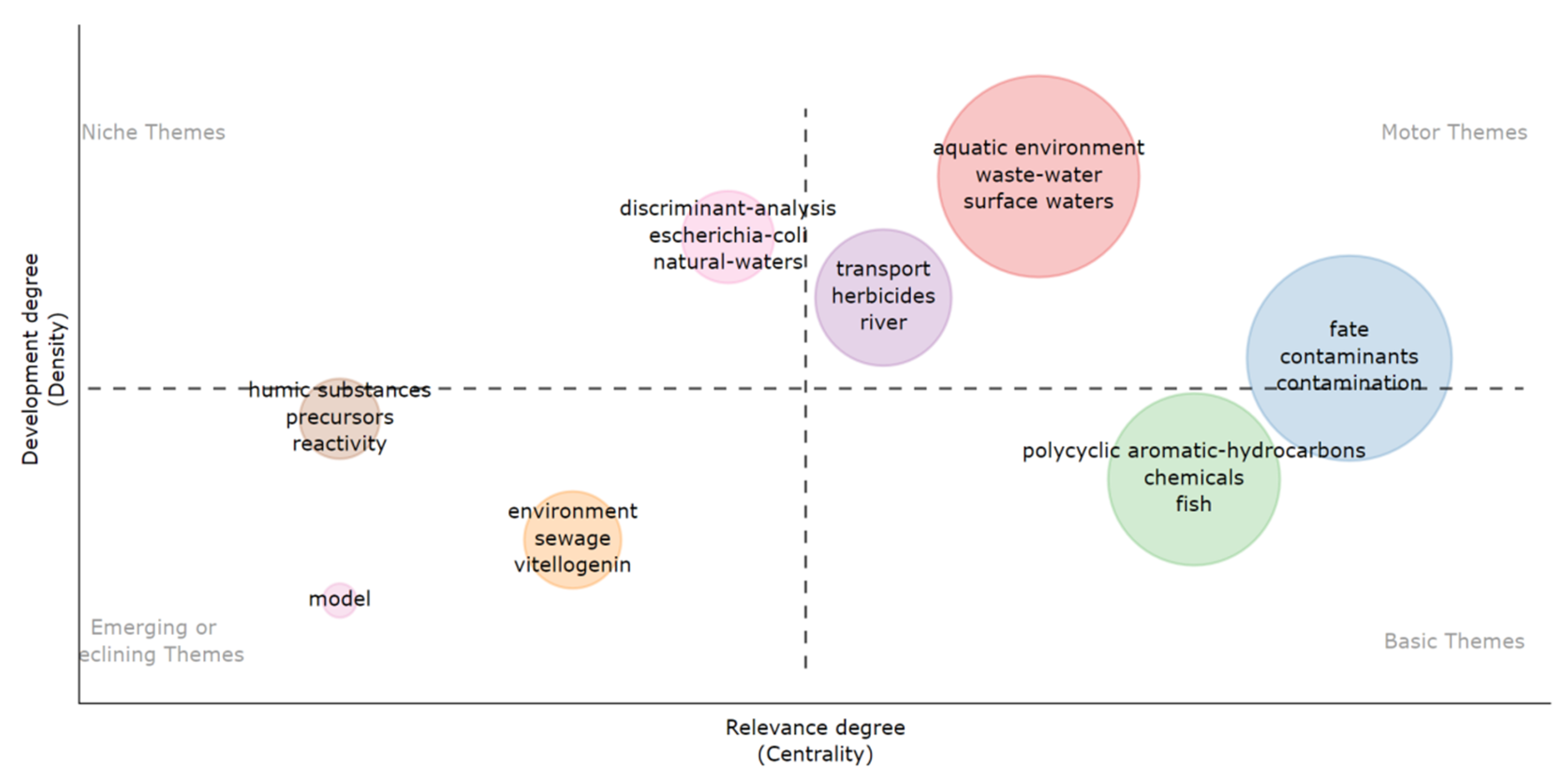
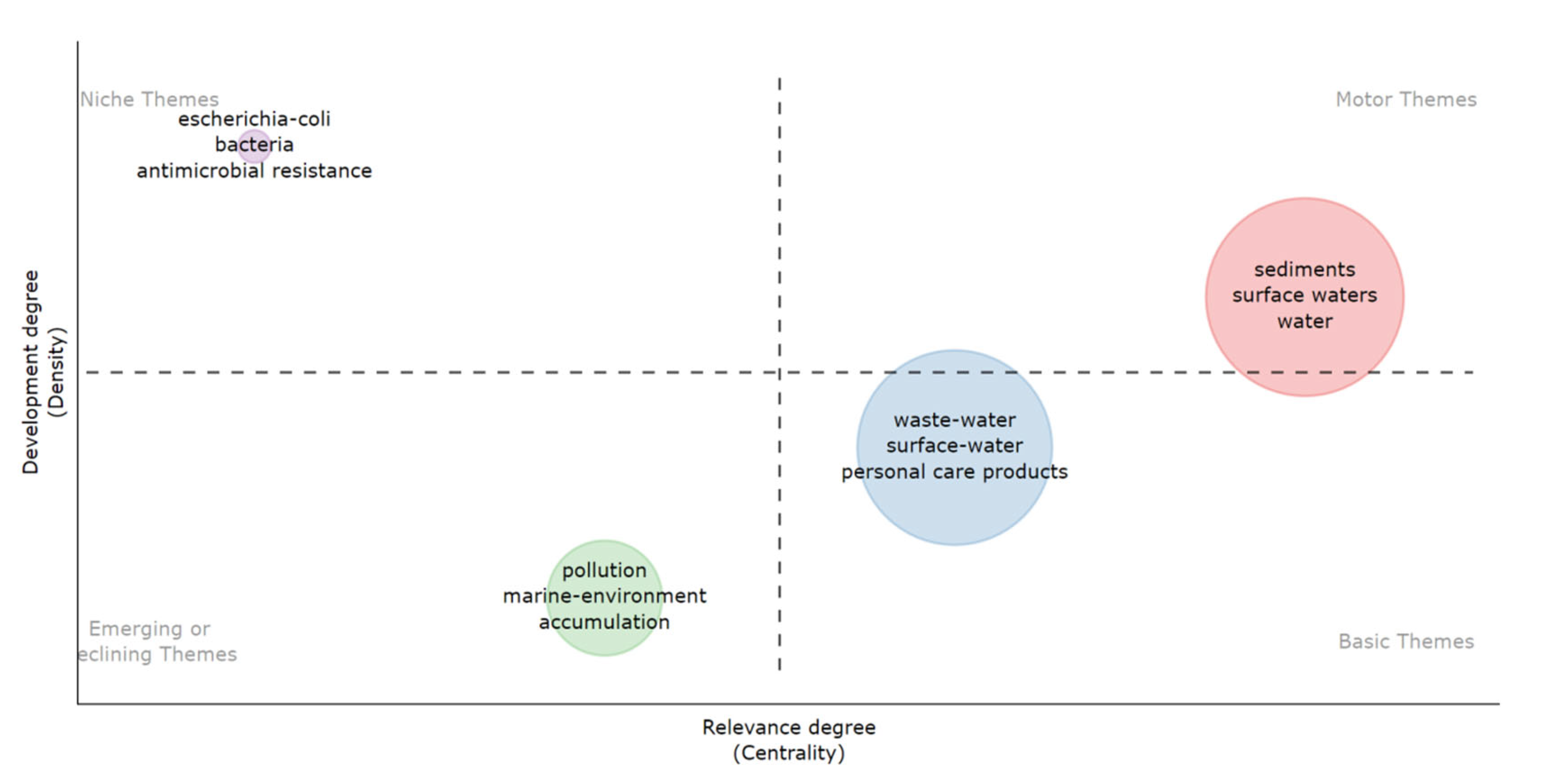
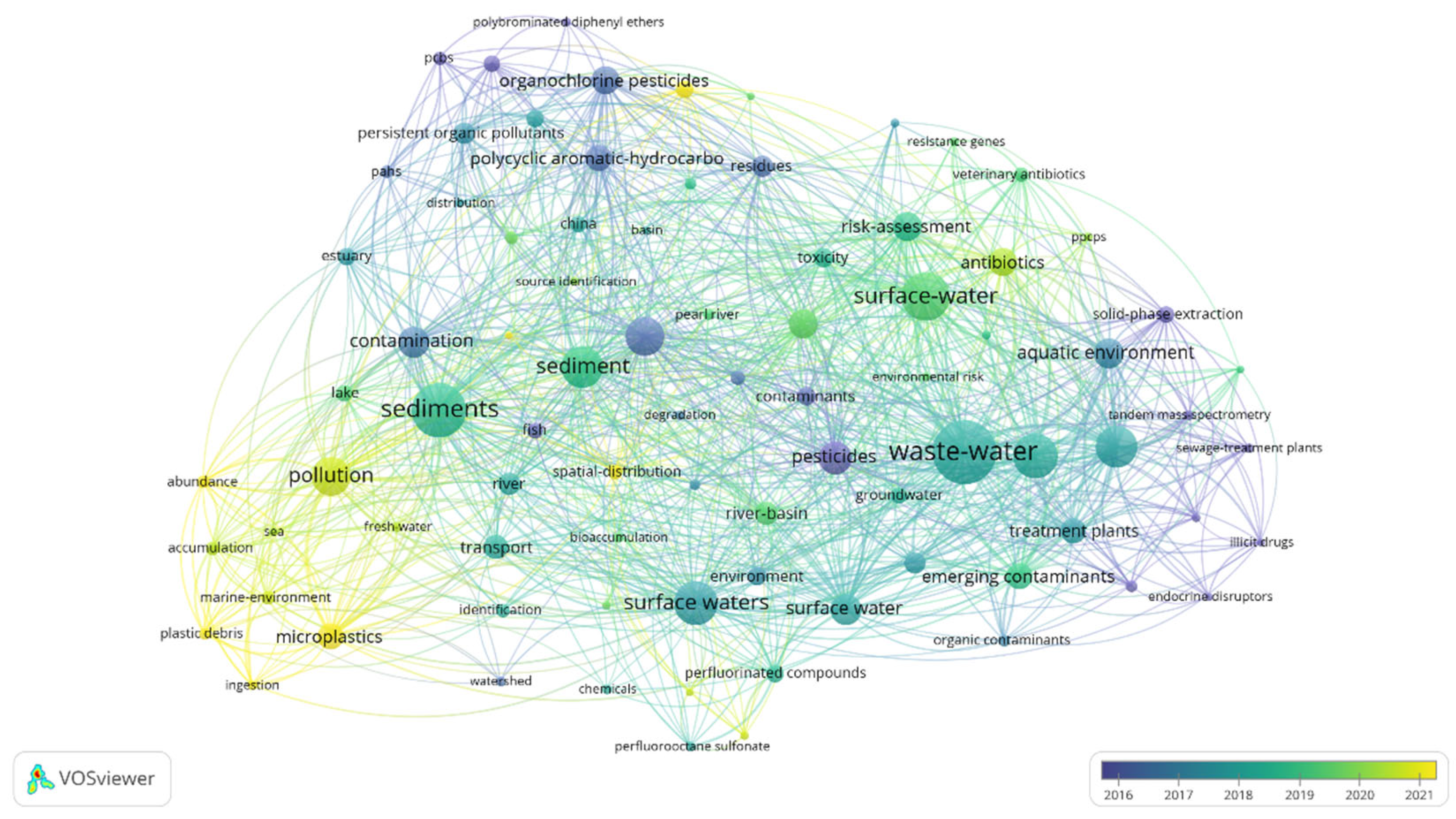
3.6.1. Topic Evolution Analysis
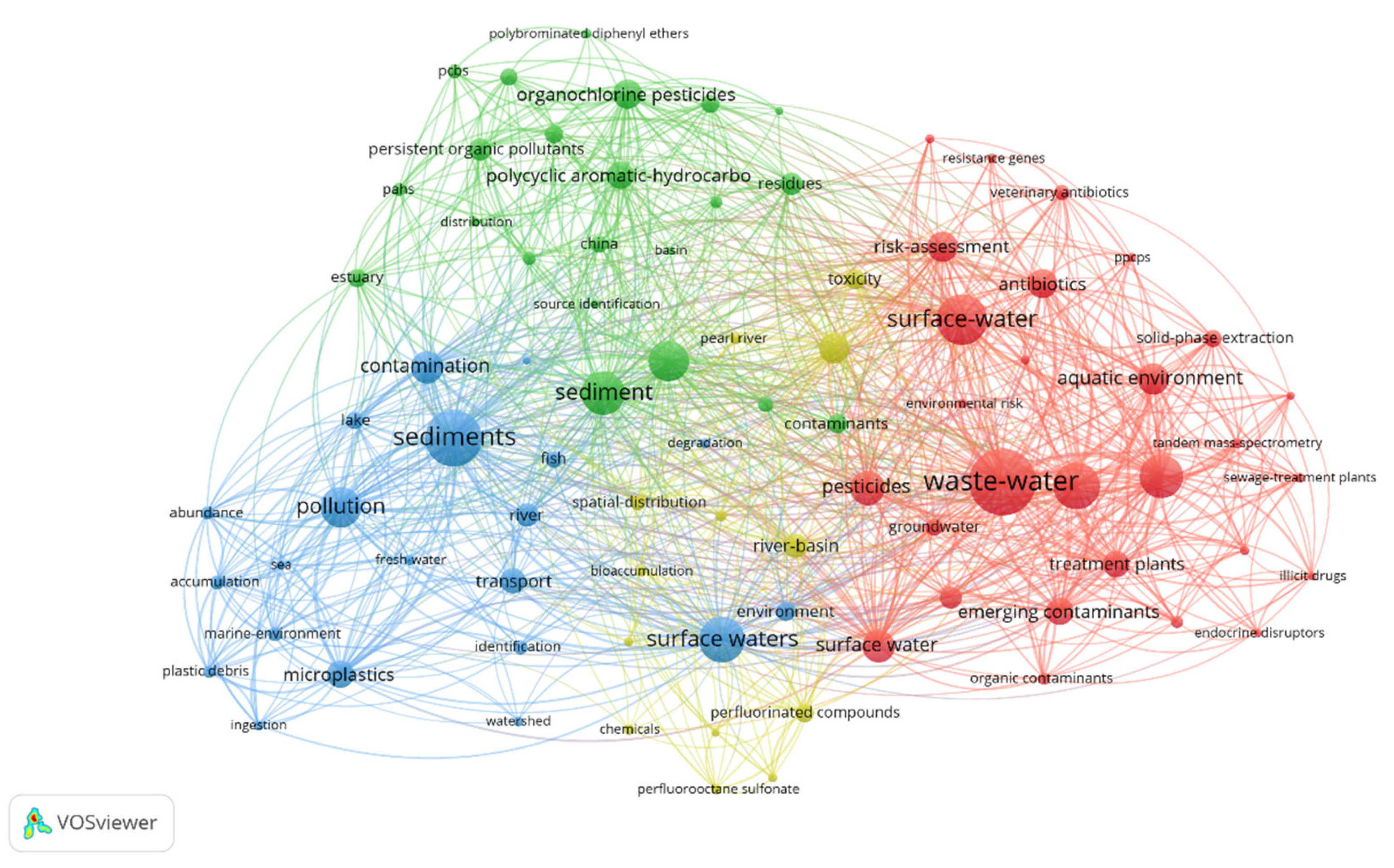
3.6.2. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
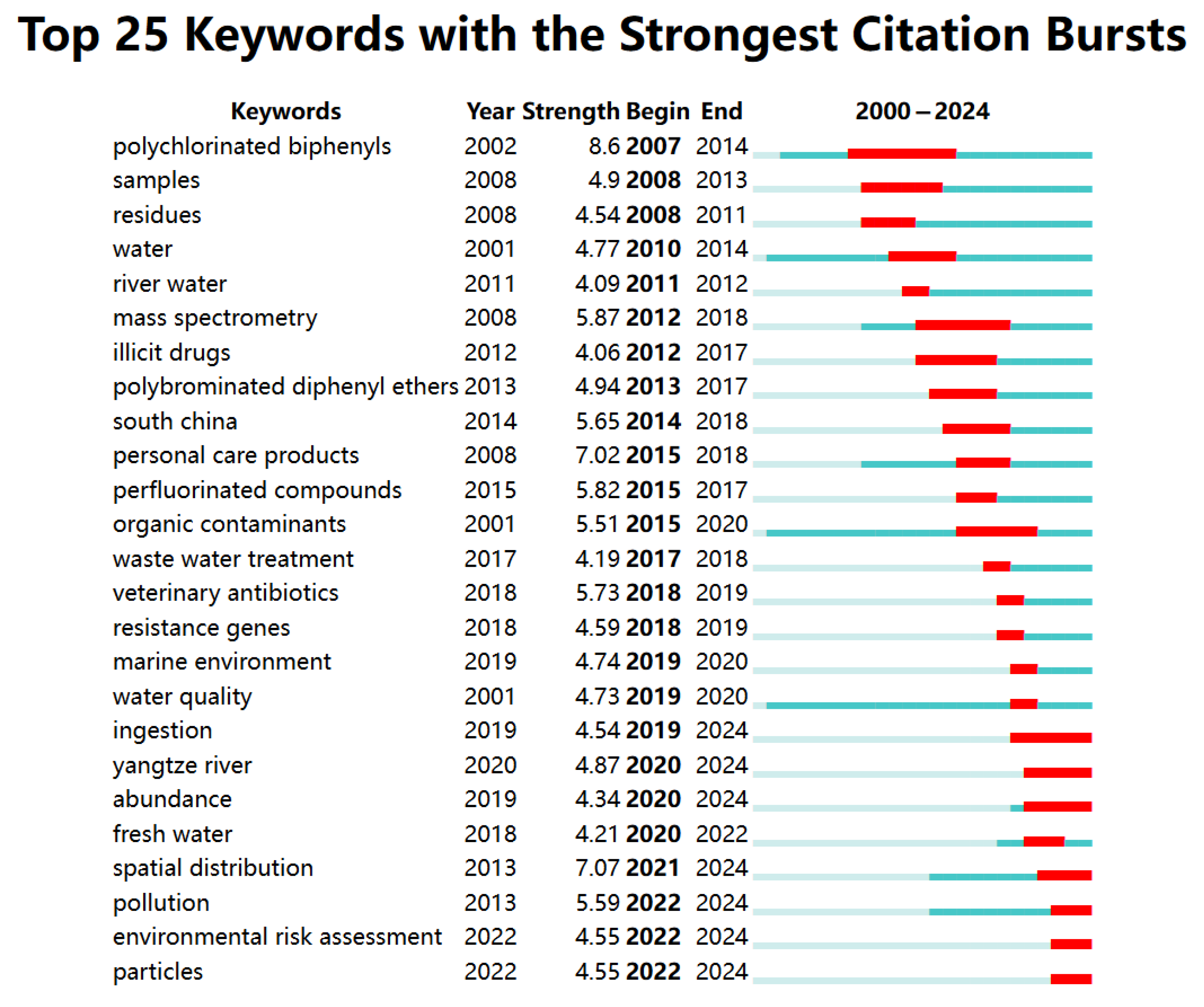
3.6.3. Keyword Burst Analysis
3.6.4. Keyword Timeline Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Policy Landscape
4.2. Current Research Status and Major Challenges
- (1)
- Most studies still focused on single environmental media, such as surface water, sediments, or wastewater discharge points, and lacked integrated modeling of cross-media and multi-pathway migration and fate processes at the watershed scale. This limitation hindered the comprehensive understanding and predictive capability regarding pollutant behavior.
- (2)
- Although advanced technologies such as mass spectrometry and non-target screening had matured, technical bottlenecks remained in identifying unknown compounds, degradation products, and mixture effects. Additionally, inconsistencies in sampling, treatment, and analytical protocols among studies weakened the comparability of data.
- (3)
- The impacts of public health emergencies, such as pandemics, on emerging pollutants in watershed water bodies have not been adequately addressed. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to increased inputs of antiviral drugs, antibiotics, and personal protective equipment (e.g., masks and gloves) into aquatic environments, elevating both pharmaceutical and microplastic pollution levels. According to Liu et al. [56], among 23 major watersheds in China, 77.27% exhibited increased microplastic abundance during the pandemic, particularly in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze and Pearl Rivers. Despite this significant impact, related research remained scarce, and systematic investigations into the resulting changes in pollutant spectra and ecological health risks were still lacking. Future studies should prioritize this area.
4.3. Future Perspectives
- (1)
- Development of Integrated Watershed Simulation Models: Multi-media coupled models should be established to simulate the migration, transformation, and accumulation of contaminants across surface water, groundwater, sediments, and biota. These models should incorporate land use, hydrodynamic processes, and socioeconomic drivers to enable holistic risk assessments and policy scenario analyses.
- (2)
- Advancement of Interdisciplinary Monitoring Technologies: Portable biosensors, Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices for real-time detection, and AI-assisted analytics should be integrated to achieve high-frequency, low-cost, and spatially distributed monitoring of multiple contaminants, thus supporting regulatory enforcement and public health interventions.
- (3)
- Innovation in Green and Efficient Removal Technologies: Priority should be given to developing high-efficiency, low-energy, and byproduct-free removal techniques such as advanced oxidation processes, membrane filtration, and biologically integrated treatment systems. Emerging green technologies should also be explored to enhance the scalability and cost-effectiveness of contaminant removal in real-world water management contexts.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, Y.F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, J.B.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Z.M. Emission of PAHs, PCBs, PBDEs and heavy metals in air, water and soil around a waste plastic recycling factory in an industrial park, Eastern China. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorsen, H.L.; Bohlin-Nizzetto, P.; Eckhardt, S.; Gusev, A.; Moeckel, C.; Shatalov, V.; Skogeng, L.P.; Breivik, K. Spatial variability and temporal changes of POPs in European background air. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 299, 119658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Labadie, P.; Botta, F.; Lestremau, F.; Lopez, B.; Geneste, E.; Pardon, P.; Dévier, M.H.; Budzinski, H. Occurrence survey and spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl surfactants in groundwater, surface water, and sediments from tropical environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.Y.; Lu, G.H.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, P.W.; Cai, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.R.; Zhu, X.H.; Yang, Y.L. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Water from the Yangtze River and Its Tributaries at the Dividing Point Between the Middle and Lower Reaches. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Fang, W.D.; Krauss, M.; Brack, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, F.L.; Zhang, X.W. Screening hundreds of emerging organic pollutants (EOPs) in surface water from the Yangtze River Delta (YRD): Occurrence, distribution, ecological risk. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørmo, E.; Lade, C.B.M.; Zhang, J.J.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Åsli, G.W.; Hubert, M.; Goranov, A.I.; Arp, H.P.H.; Cornelissen, G. Stabilization of PFAS-contaminated soil with sewage sludge- and wood-based biochar sorbents. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 170971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Pan, Y.T.; Cui, Q.Q.; Yao, B.; Wang, J.S.; Dai, J.Y. Penetration of PFASs across the blood cerebrospinal fluid barrier and its determinants in humans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13553–13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.P.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Gao, J.; Liao, C.Y.; Jiang, G.B. Co-exposure and health risks of several typical endocrine disrupting chemicals in general population in Eastern China. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Notarstefano, V.; Svelato, A.; Belloni, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Blondeel, C.; Zucchelli, E.; De Luca, C.; D’Avino, S.; Gulotta, A.; et al. Raman microspectroscopy detection and characterisation of microplastics in human breastmilk. Polymers 2022, 14, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, S.; Nolan, M.; Tyler, C.R.; Brighty, G.; Sumpter, J.P. Widespread sexual disruption in wild fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Zhang, T.C.; Bhunia, P.; Surampalli, R.Y. Treatment technologies for emerging contaminants in wastewater treatment plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.L.; Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.X.; Feng, X.; Chen, N.; Shen, F.; Zhang, H.C.; Wang, S.; Sheng, Z.Y.; Li, J. Occurrence and risk assessment of typical PPCPs and biodegradation pathway of ribavirin in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2022, 11, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.G.; Zhang, H.Z.; Yang, Y.J.; Cui, K.P.; Ao, J.J.; Tong, X.E.; Shi, M.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; et al. Comprehensive insight into the occurrence characteristics, influencing factors and risk assessments of antibiotics in the Chaohu Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.T.; Nie, H.Y.; Xu, K.H.; He, Y.H.; Hu, Y.T.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, J. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in the Pearl River along Guangzhou city and Pearl River estuary, China. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.Q.; Zhu, T.T.; Sun, J.Q.; Pan, X.L.; Li, J.; Luo, H.W. Emerging organic contaminants in sewage sludge: Current status, technological challenges and regulatory perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tan, Y.; Feng, Y.Y.; Dong, T.; Jiang, C.X.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.L. Selected legacy and emerging organic contaminants in sediments of China’s Yangtze—The world’s third longest river: Response to anthropogenic activities. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.H.; Yang, H.H.; Dong, H.K.; Ma, B.N.; Sun, H.W.; Pan, T.; Jiang, R.R.; Zhou, R.R.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.C.; et al. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of organic micropollutants in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China: A case study of water diversion. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Lin, M.W.; Zhuang, D. Wastewater treatment and emerging contaminants: Bibliometric analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 133932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.R.; Zhou, B.H.; Huang, Y.Y.; Lu, X.H.; Li, S.; Li, N. Bibliometric overview of research trends on heavy metal health risks and impacts in 1989–2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, A.T.T.; Heryanto, H.; Armynah, B.; Tahir, D. Bibliometric analysis of chitosan research for wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Han, R.R.; Lu, X.H. Bibliometric analysis of research trends on solid waste reuse and recycling during 1992–2016. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2018, 130, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Yuan, D.H. Global performance and trends of research on emerging contaminants in sewage sludge: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1990 to 2023. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2024, 281, 116597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseghian, Y.; Alimohamadi, M.; Dragoi, E.N.; Sonne, C. A global meta-analysis of phthalate esters in drinking water sources and associated health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.J.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, W.R. Bibliometric analysis of fuzzy theory research in China: A 30-year perspective. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 141, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.K.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, W.; Cheng, J.Z.; Lee, X.Q. A bibliometric review of biochar for soil carbon sequestration and mitigation from 2001 to 2020. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Shi, S.Q.; Shi, S.; Jia, Q.L.; Yuan, G.Z.; Chu, Y.G.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.H.; Cui, H.M. Bibliometric analysis of potassium channel research. Channels 2020, 14, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pu, S.Y.; Lv, X.; Gao, Y.; Ge, L. Global trends and prospects in microplastics research: A bibliometric analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasavan, S.; Yusoff, S.; Guan, N.C.; Zaman, N.S.K.; Fakri, M.F.R. Global trends of textile waste research from 2005 to 2020 using bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44780–44794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Bai, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.L. Advances in studies on the plant rhizosphere microorganisms in wetlands: A visualization analysis based on CiteSpace. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornmann, L. How are excellent (highly cited) papers defined in bibliometrics? A quantitative analysis of the literature. Res. Eval. 2014, 23, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.J.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, Z.J.; Dong, D.S.; Fang, H.; Wang, C.J.; Dong, Y.C.; Wu, J.Z.; Tan, X.Z.; Zhu, P.Y.; et al. Antibiotic resistant bacteria: A bibliometric review of literature. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1002015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, C.; Silva, V.; Gai, L.; Osman, R.; Mol, H.; Alaoui, A.; Christ, F.; Schlünssen, V.; Vested, A.; Abrantes, N.; et al. Pesticide residues in European sediments: A significant concern for the aquatic systems? Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, J.; Yin, W.; Zhang, D.; Tan, J.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, X. Research on the removal efficiency and membrane fouling analysis of nanofiltration membranes under the combined pollution of emerging contaminants. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sresung, M.; Srathongneam, T.; Paisantham, P.; Sukchawalit, R.; Whangsuk, W.; Honda, R.; Satayavivad, J.; Mongkolsuk, S.; Sirikanchana, K. Quantitative distribution of antibiotic resistance genes and crAssphage in a tropical urbanized watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, E.; Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Occurrence of acidic pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Tuna River Basin: From waste to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.Q.; Luo, Y.; Mathieu, J.; Wang, Q.; Feng, L.; Mu, Q.; Feng, C.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Persistence of Extracellular DNA in River Sediment Facilitates Antibiotic Resistance Gene Propagation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Mao, R.F.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Wei River, in the northwest of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bečanová, J.; Scheringer, M.; Sharma, A.; Bharat, G.K.; Whitehead, P.G.; Klánová, J.; Nizzetto, L. Health and ecological risk assessment of emerging contaminants (pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and artificial sweeteners) in surface and groundwater (drinking water) in the Ganges River Basin, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Occurrence and Transport of Tetracycline, Sulfonamide, Quinolone, and Macrolide Antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballent, A.; Cor-coran, P.L.; Madden, O.; Helm, P.A.; Longstaffe, F.J. Sources and sinks of microplastics in Canadian Lake Ontario nearshore, tributary and beach sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. Plastic Debris in 29 Great Lakes Tributaries: Relations to Watershed Attributes and Hydrology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Arevalo, E.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.; Richardson, M.; Kearns, B.; Pickett, A.; Knappe, D.R.U. Legacy and Emerging Perfluoroalkyl Substances Are Important Drinking Water Contaminants in the Cape Fear River Watershed of North Carolina. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y.; Kudou, K.; Hinata, H. Assessment of the sources and inflow processes of microplastics in the river environments of Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. An approach for detecting, quantifying, and visualizing the evolution of a research field: A practical application to the Fuzzy Sets Theory field. J. Informetr. 2011, 5, 146–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.J.; Xu, Z.S.; Pedrycz, W. Bibliometric analysis of rough sets research. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 94, 106467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, F.M.; Gallardo, M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Global trends in nitrate leaching research in the 1960–2017 period. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ge, L.; Shi, S.Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Shang, Y.; Wu, J.R.; Tian, J.H. Global trends and future prospects of e-waste research: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17809–17820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, T.; Liu, H.W.; Long, R.Y.; Chen, H.; Gan, X.; Liu, J.L. Research trends and hotspots related to global carbon footprint based on bibliometric analysis: 2007–2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 17671–17691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qiu, Z.W. A systematic review of transportation carbon emissions based on CiteSpace. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 54362–54384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Q.; Huang, Y.L.; Li, J.M.; Asad, M.W.A.; Chang, P. A visual knowledge map analysis of coal mine intensity based on CiteSpace software and web of science core database. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2025, 39, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerhacker, M. EU Water Framework Directive and Stockholm Convention Can we reach the targets for priority substances and persistent organic pollutants? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.Q.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Jia, B. Spatiotemporal variations and the ecological risks of microplastics in the watersheds of China: Implying the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Rank | Institution | Country | Total Publications | Total Citations | Average Citation Per Paper | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | |||||
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | China | 131 | 15.92 | 4494 | 34.31 |
| 2 | University of Chinese Academy of Sciences | China | 120 | 14.58 | 4172 | 34.77 |
| 3 | Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences | China | 53 | 6.44 | 1958 | 36.94 |
| 4 | Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas (CSIC) | Spain | 37 | 5 | 4193 | 113.32 |
| 5 | Beijing Normal University | China | 29 | 3.52 | 1196 | 41.24 |
| 6 | Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences (RCEES) | China | 28 | 3.4 | 1189 | 42.46 |
| 7 | CSIC-Centro de Investigacion y Desarrollo Pascual Vila (CID-CSIC) | Spain | 26 | 3.16 | 2962 | 113.92 |
| 8 | CSIC-Instituto de Diagnostico Ambiental y Estudios del Agua (IDAEA) | Spain | 26 | 3.16 | 2962 | 113.92 |
| 9 | Institut Catala de Recerca de l’Aigua (ICRA) | Spain | 23 | 2.79 | 2968 | 129.04 |
| 10 | Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) | France | 22 | 2.67 | 585 | 26.59 |
| Rank | Authors | Total Publications | Institutions and Countries | Total Citations | Average Citation Per Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Barcelo, Damia | 27 | Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas (CSIC), Spain | 3298 | 122.15 |
| 2 | Ying, Guang-Guo | 11 | South China Normal University, China | 567 | 51.55 |
| 3 | Lin, Chunye | 9 | Beijing Normal University, China | 445 | 49.44 |
| 4 | He, Mengchang | 8 | Beijing Normal University, China | 404 | 50.5 |
| 5 | Yu, Gang | 8 | Tsinghua University, China | 325 | 40.63 |
| 6 | Lacorte, Silvia | 7 | Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas (CSIC), Spain | 511 | 73 |
| 7 | Li, Sijia | 5 | Northeast Normal University, China | 91 | 18.2 |
| 8 | Ju, Hanyu | 4 | Chinese Academy of Sciences, China | 64 | 16 |
| 9 | Wang, Haozheng | 4 | Beijing Normal University, China | 369 | 92.25 |
| 10 | Liu, Sheng | 3 | Hohai University, China | 125 | 41.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Y. Research Progress on Emerging Pollutants in Watershed Water Bodies: A Bibliometric Approach. Water 2025, 17, 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142076
Chen L, Liu Y, Wei C, Jiang Y, Zeng S, Zhang C, Zhang W, Jin Y. Research Progress on Emerging Pollutants in Watershed Water Bodies: A Bibliometric Approach. Water. 2025; 17(14):2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142076
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lei, Yuhan Liu, Chunzhong Wei, Yanbo Jiang, Si Zeng, Chunfang Zhang, Wenjie Zhang, and Yue Jin. 2025. "Research Progress on Emerging Pollutants in Watershed Water Bodies: A Bibliometric Approach" Water 17, no. 14: 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142076
APA StyleChen, L., Liu, Y., Wei, C., Jiang, Y., Zeng, S., Zhang, C., Zhang, W., & Jin, Y. (2025). Research Progress on Emerging Pollutants in Watershed Water Bodies: A Bibliometric Approach. Water, 17(14), 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142076








