Failure Analysis of Biological Treatment Units Under Shock Loads of Rubber Industry Wastewater Containing Emerging Pollutants: Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Characteristics of the Research Object
2.2. Wastewater Analysis Methods
2.3. Methods of Sewage Sludge Analysis
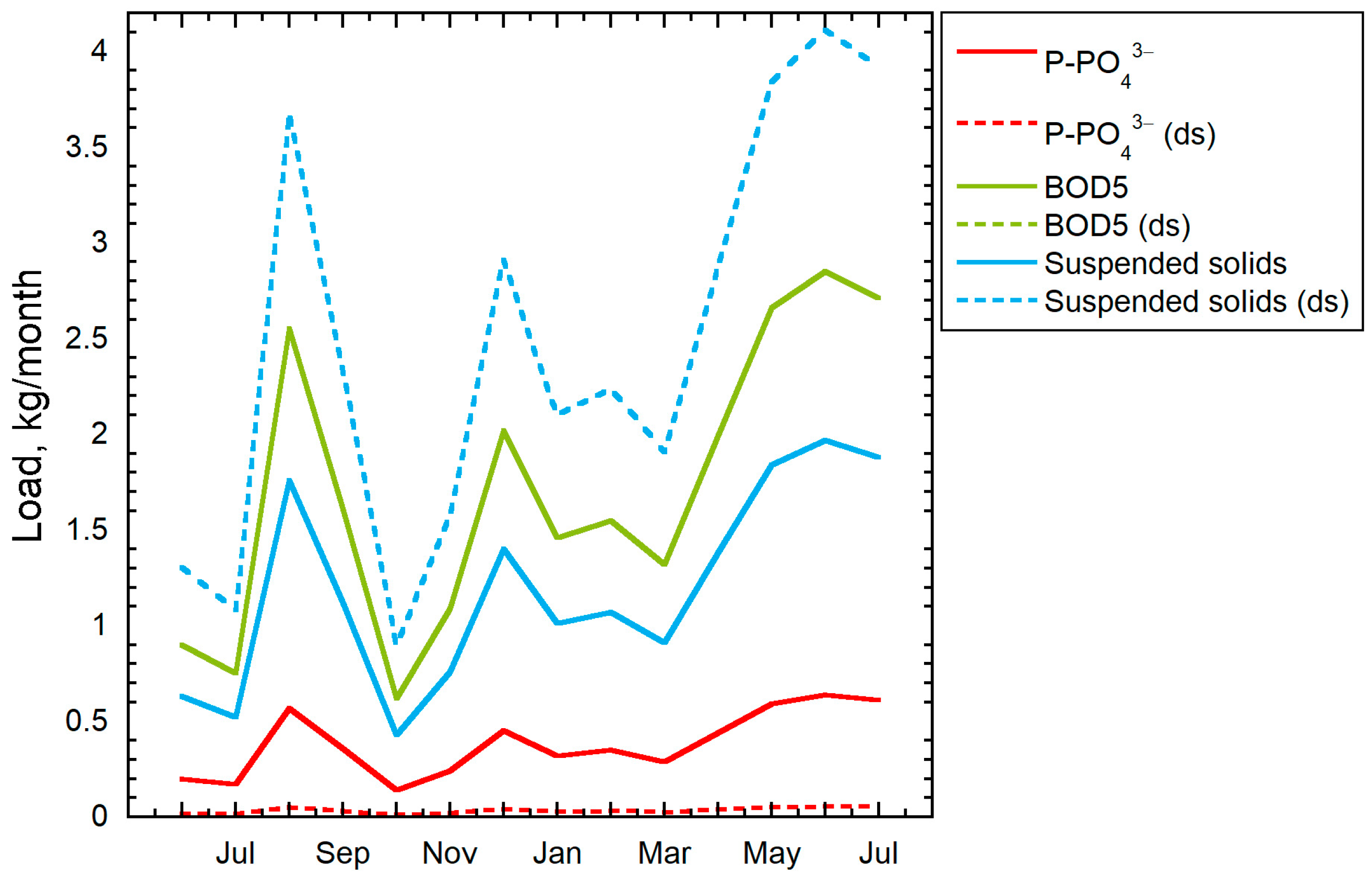
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Water Supply and Sanitation Systems
3.2. Characteristics of Wastewater and Treatment Facilities of the Facility
- −
- At least by 80% for BOD5, or ensure that the BOD5 concentration at the outlet of the treatment facilities does not exceed 15 mg/L (corresponds);
- −
- At least by 90% for total phosphorus, or ensure that the total phosphorus concentration at the outlet of the treatment facilities does not exceed 0.5 mg/L (does not correspond to the HELCOM recommendation in the existing treatment technology);
- −
- At least by 70% for total nitrogen, or ensure that the total nitrogen concentration at the outlet of the treatment facilities does not exceed 10 mg/L (does not correspond to the HELCOM recommendation in the existing treatment technology).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, E.R.; Bierkens, M.F.; Wanders, N.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; van Beek, L.P.; van Vliet, M.T. Current wastewater treatment targets are insufficient to protect surface water quality. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Mushtaq, A. Untreated wastewater reasons and causes: A review of most affected areas and cities. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 121–143. [Google Scholar]
- Anikin, Y.V.; Shilkov, V.I. Modern materials and technologies of industrial wastewater treatment. Russ. J. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazieva, I.I.; Biysultanova, M.A.; Vizirova, H.R.; Daudov, I.M. The economy of a small innovative enterprise in the implementation of oil and wastewater treatment technologies. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1399, 055084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Ravindran, V.; Gopinath, A.; Kumar, M.S. Emerging technologies for mixed industrial wastewater treatment in developing countries: An overview. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2022, 31, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speece, R.E. Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1983, 17, 416A–427A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, R.C.; Van Haandel, A.C.; Zeeman, G.; Lettinga, G. The effects of operational and environmental variations on anaerobic wastewater treatment systems: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantskevich, V.; Kuis, D.; Borovskiy, D.; Kazlouski, V.; Rakovets, A.; Romanovski, V. Cracking failure analysis of potash fertilizer drying drums: Calculations, modeling, experiment. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 165, 108739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanovski, V.; Hedberg, Y.S.; Paspelau, A.; Frantskevich, V.; Noël, J.J.; Romanovskaia, E. Corrosion failure of titanium tubes of a heat exchanger for the heating of dissolving lye. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 129, 105722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanovski, V.; Frantskevich, V.; Kazlouski, V.; Kasach, A.; Paspelau, A.; Hedberg, Y.; Romanovskaia, E. Inappropriate cleaning treatments of stainless steel AISI 316L caused a corrosion failure of a liquid transporter truck. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 117, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaeva, K.M.; Vatin, N.I.; Karpov, D.F.; Romanovski, V. Monitoring Hybrid Glass-Basalt Plastic Pipes: A Fractal Approach to Failure Analysis. Mater. Res. Express 2025, 12, 075307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, M.; Singh, D.; Wani, A.B. Treatment strategies for wastewater from rubber and polymer industries: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106360. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. Challenges and perspectives in the application of biological treatment to industrial rubber wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100608. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, L.; Yadav, A.K.; Suthar, S. Fate of rubber-processing effluents in biological treatment systems: Case studies and technological implications. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J. Performance of enhanced coagulation and sedimentation in rubber wastewater treatment. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 157, 308–316. [Google Scholar]
- Maheswari, P.; Ramesh, K. Characterization and treatment of rubber industry effluents: A case study from Tamil Nadu. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, N.; Cui, Y.; Saif Ur Rehman, M. Application of chemical coagulation for treatment of synthetic and real rubber wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126739. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, C.F.; de Souza, J.; Borges, A.C. Use of ozone and activated carbon for polishing treatment of synthetic rubber wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114585. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://tvprus.ru/products/biologicheskaya-zagruzka/ershovaya-zagruzka/ (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://meganorm.ru/Data2/1/4293739/4293739334.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/31090.html (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://nd.gostinfo.ru/document/6110083.aspx (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://meganorm.ru/Data2/1/4293739/4293739330.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://meganorm.ru/Data2/1/4293770/4293770987.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Romanovski, V.; Gruzinova, V. Aggregate from Spent Ion-Exchange Resins for Petroleum Products Removal from Wastewater. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzinova, V.; Romanovski, V. Optimizing Oil-Contaminated wastewater purification with aluminum coagulants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzinova, V.; Romanovski, V. Optimizing Oil-Contaminated wastewater purification with polypropylene thread waste. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 16, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.lumexinstruments.com/files/21LEN01.20.01-1_Fluorat.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://informproekt.ru/docs/436728043/ (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://www.oei.by/pagevalues/view?model_id=551&node_id=53 (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/36917.html (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://meganorm.ru/Data2/1/4293753/4293753703.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://www.ccenter.msk.ru/upload/File/ПНД%20Ф/ПНД%20Ф%2014.1%202%204.183-02.PDF (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://normacs.net/Doclist/doc/1V4G5.html (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://www.oei.by/pagevalues/view?model_id=572&node_id=53 (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/11961.html (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Miao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liao, R.; Shi, P.; Li, A. Assessment of phenol effect on microbial community structure and function in an anaerobic denitrifying process treating high concentration nitrate wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Mehrdadi, N.; Parvizian, F. Combined physico-chemical and biological treatment of rubber industry wastewater: Pilot-scale study. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 334–344. [Google Scholar]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Bernat, K.; Rusanowska, P.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Inhibition of Nitrification in Wastewater from the Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Industry: A Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3014. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Isa, M.H.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Lawal, I.M.; Usman, A.K.; Birniwa, A.H.; Noor, A.; Abubakar, S.; Umaru, I.; et al. Toxic Effects of Xenobiotic Compounds on the Microbial Community in Wastewater Treatment Systems. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 100492. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, R. Long-term effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater and bacterial community shift in activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7284–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Avilés, P.; Vargas, J.B.D.; Akizuki, S.; Kodera, T.; Ida, J.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, G. Cumulative effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in UASB process during wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalf & Eddy. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Georgantzopoulou, A.; Almeida Carvalho, P.; Vogelsang, C.; Tilahun, M.; Ndungu, K.; Booth, A.M.; Macken, A. Ecotoxicological effects of transformed silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the effluent from a lab-scale wastewater treatment system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9431–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qian, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Fan, X.; Lu, B.; Guo, W. Toxicity of three crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles in activated sludge: Bacterial cell death modes differentially weaken sludge dewaterability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4542–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, T.; Thanh, N.T.; Tsuruoka, N.; Tanikawa, D.; Kuroda, K.; Huong, N.L.; Yamaguchi, T. Development of a BR–UASB–DHS system for natural rubber processing wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, D.; Kataoka, T.; Ueno, T.; Minami, T.; Motokawa, D.; Itoiri, Y.; Kimura, Z.I. Seeding the drainage canal of a wastewater treatment system for the natural rubber industry with rubber for the enhanced removal of organic matter and nitrogen. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.dricfume.com/innovative-rubber-wastewater-treatment-solution.html (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Agustina, T.E.; Sirait, E.J.; Silalahi, H. Treatment of rubber industry wastewater by using Fenton reagent and activated carbon. J. Teknol. Sci. Eng. 2017, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



| System | Water Consumption | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| m3/Day | m3/h | L/s | |
| B1 (general) | 20.98 | 10.39 | 3.51 |
| including T3, T4 | 8.27 | 4.69 | 2.10 |
| System Name | Water Consumption | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| m3/Day | m3/h | L/s | |
| Domestic sewerage | 20.82 | 10.27 | 5.11 |
| Industrial sewerage | 0.16 | 0.12 | – |
| Total | 20.98 | 10.39 | 5.11 |
| Indicators | WW1 | WW2 | WW3 | Discharge Standard *,**, mg/L | Cleaning Efficiency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 9.8 | 8.3 | 7.8 | n.e. | – |
| Ammonium nitrogen | 6.37 | 68.6 | 26.1 | n.e. | 62.0 |
| Nitrate nitrogen | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | 3 | – |
| Surfactants | 5.25 | 0.502 | 0.044 | n.e. | 91.2 |
| BOD5 | 238 | 16.2 | 10.4 | 15 | 35.8 |
| COD | 1254 | 82 | 30 | n.e. | 63.4 |
| Suspended solids | 45.6 | 12.4 | 7.2 | 15 | 41.9 |
| Oil products | 6.76 | 0.796 | 0.124 | n.e. | 84.4 |
| Dry residue | 1253 | 573 | 459 | n.e. | 19.9 |
| Phenols | 0.081 | 0.023 | 0.008 | n.e. | 65.2 |
| Phosphate phosphorus | 0.593 | 2.39 | 2.32 | 0.2 | 2.9 |
| Total phosphorus | 1.08 | 4.06 | 3.71 | n.e. | 8.6 |
| Zinc | 0.016 | 0.009 | <0.005 | n.e. | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romanovski, V. Failure Analysis of Biological Treatment Units Under Shock Loads of Rubber Industry Wastewater Containing Emerging Pollutants: Case Study. Water 2025, 17, 2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162419
Romanovski V. Failure Analysis of Biological Treatment Units Under Shock Loads of Rubber Industry Wastewater Containing Emerging Pollutants: Case Study. Water. 2025; 17(16):2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162419
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomanovski, Valentin. 2025. "Failure Analysis of Biological Treatment Units Under Shock Loads of Rubber Industry Wastewater Containing Emerging Pollutants: Case Study" Water 17, no. 16: 2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162419
APA StyleRomanovski, V. (2025). Failure Analysis of Biological Treatment Units Under Shock Loads of Rubber Industry Wastewater Containing Emerging Pollutants: Case Study. Water, 17(16), 2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162419






