Groundwater Management Modeling in the Güzelyurt Region (Northern Cyprus): A Group Model Building Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Systems Thinking
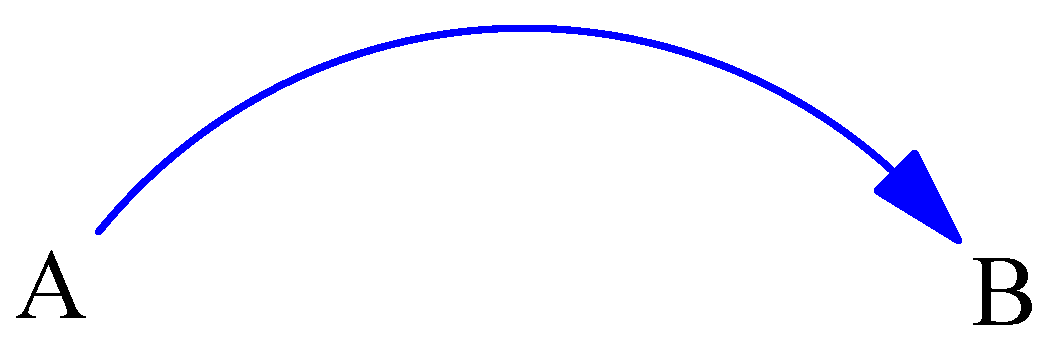
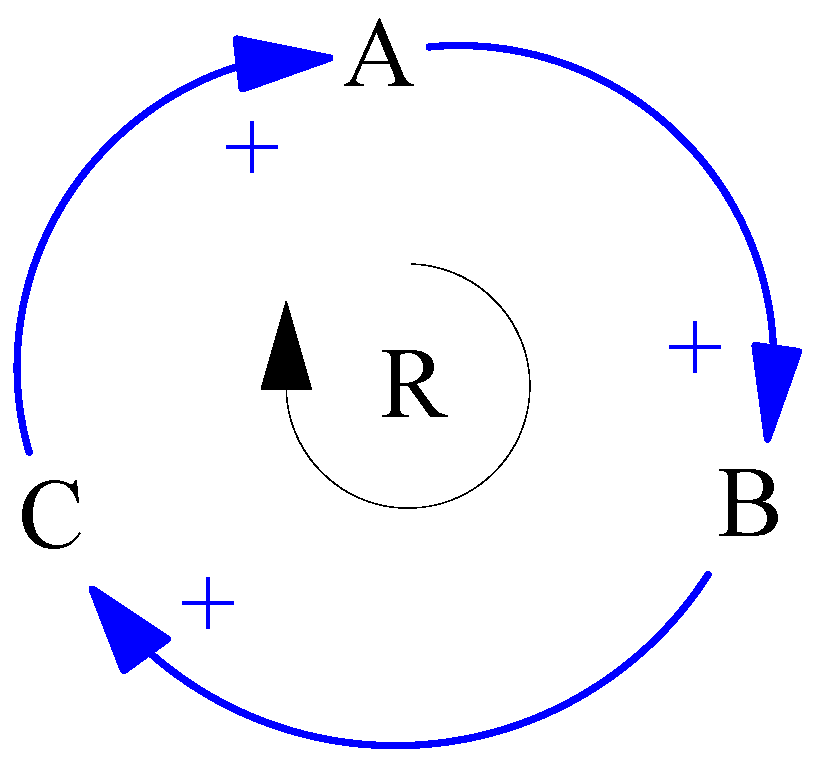
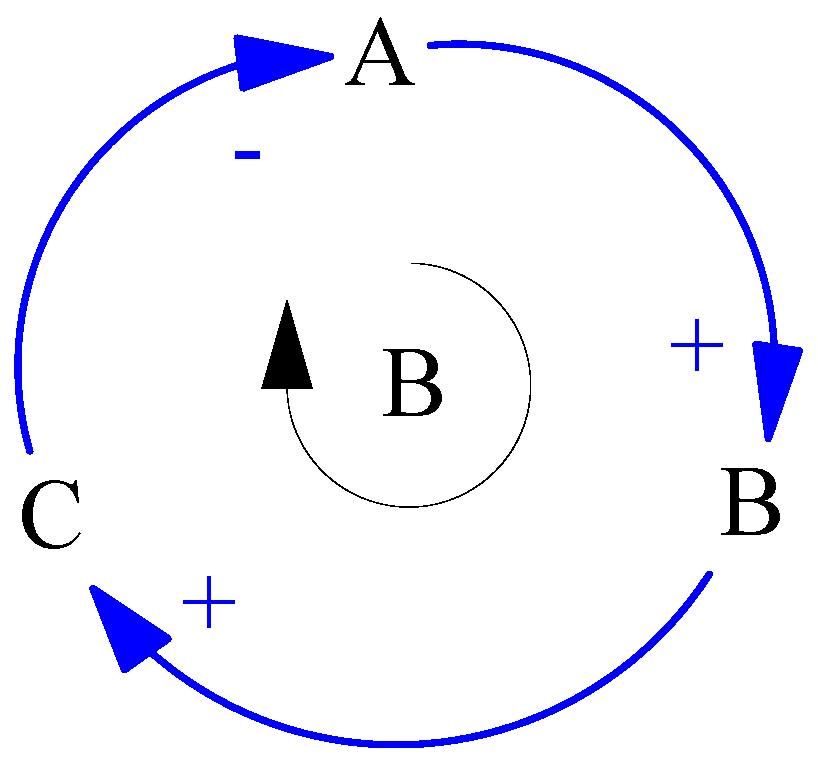
2.2. Feedback Loops
2.3. System Dynamics
2.4. Qualitative System Dynamics Approach
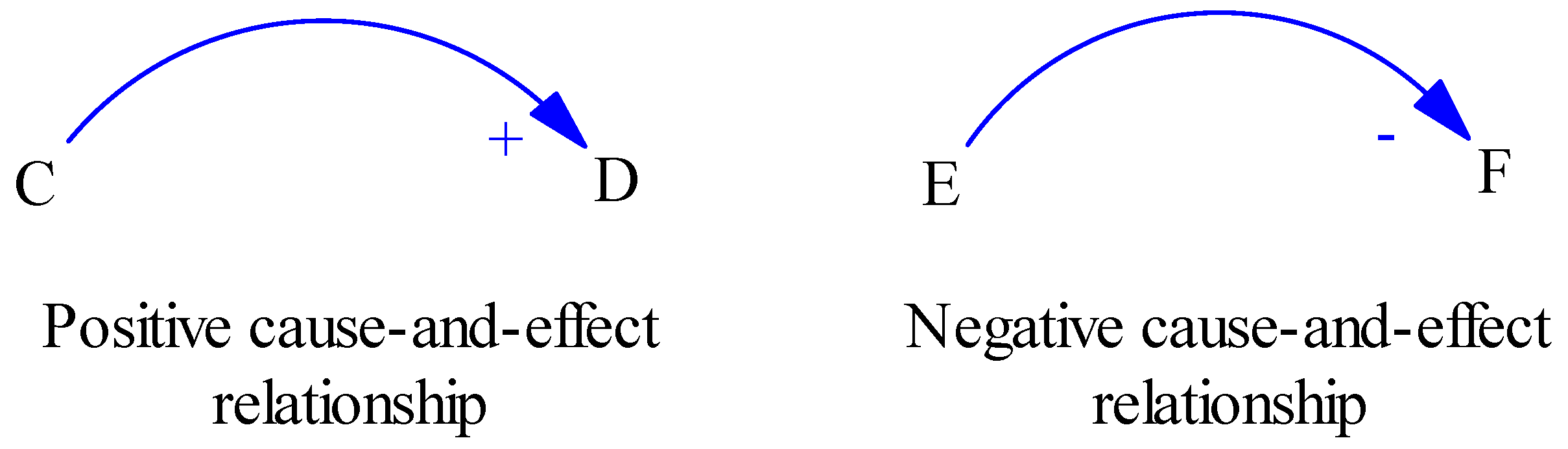
2.5. Causal Loop Diagrams
2.6. System Archetypes
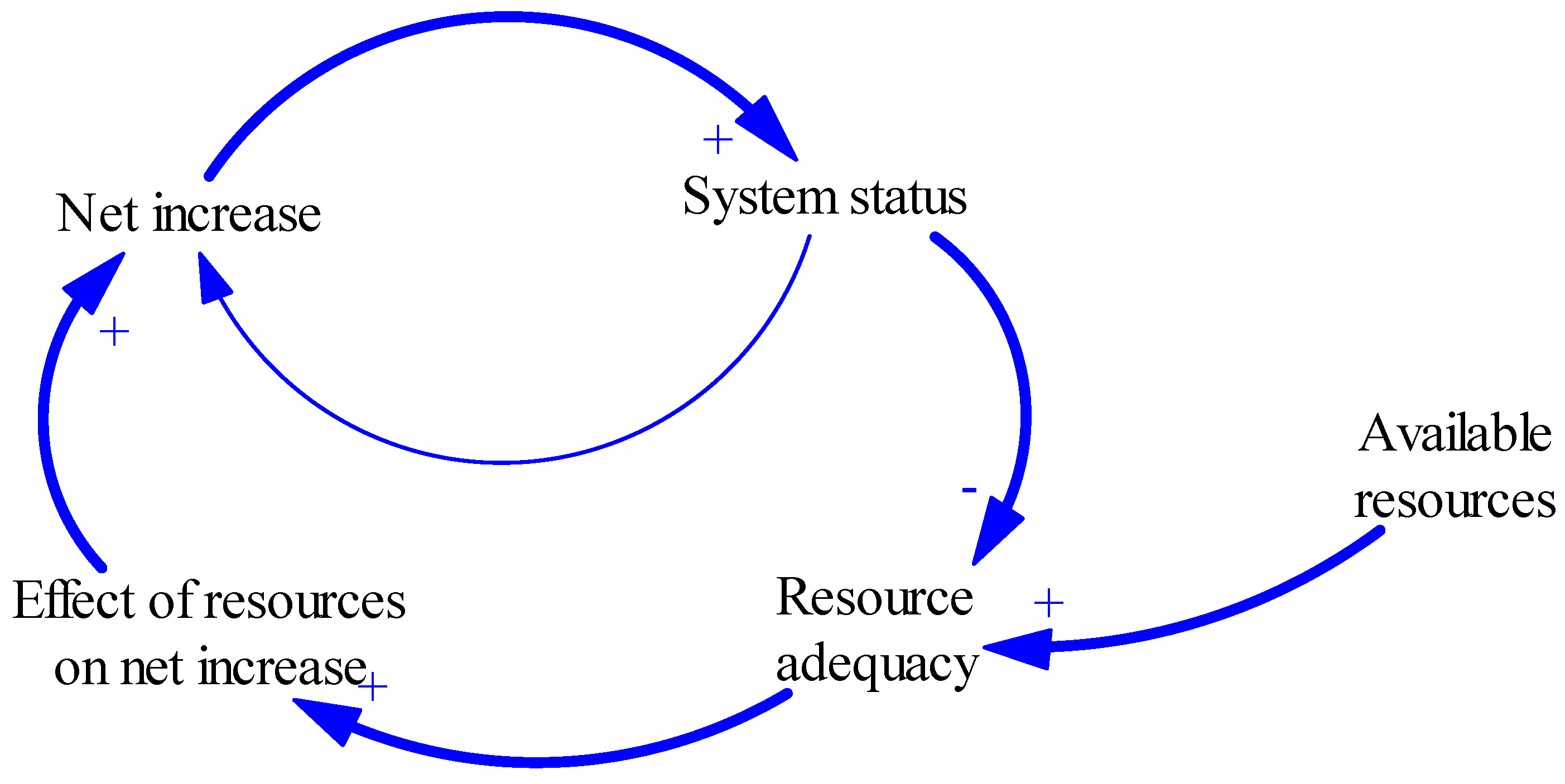
2.6.1. Limits to Growth
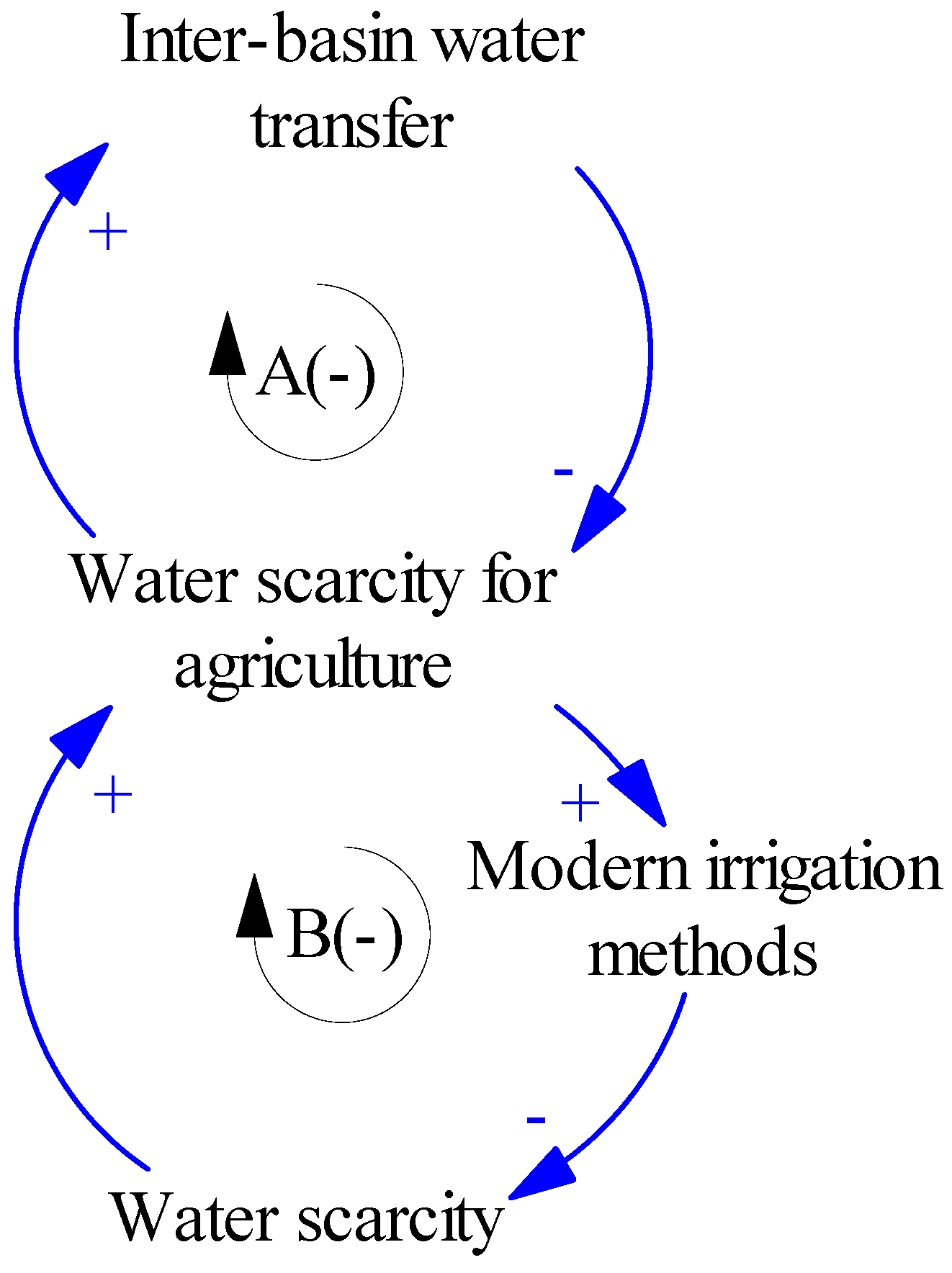
2.6.2. Fixes That Backfire
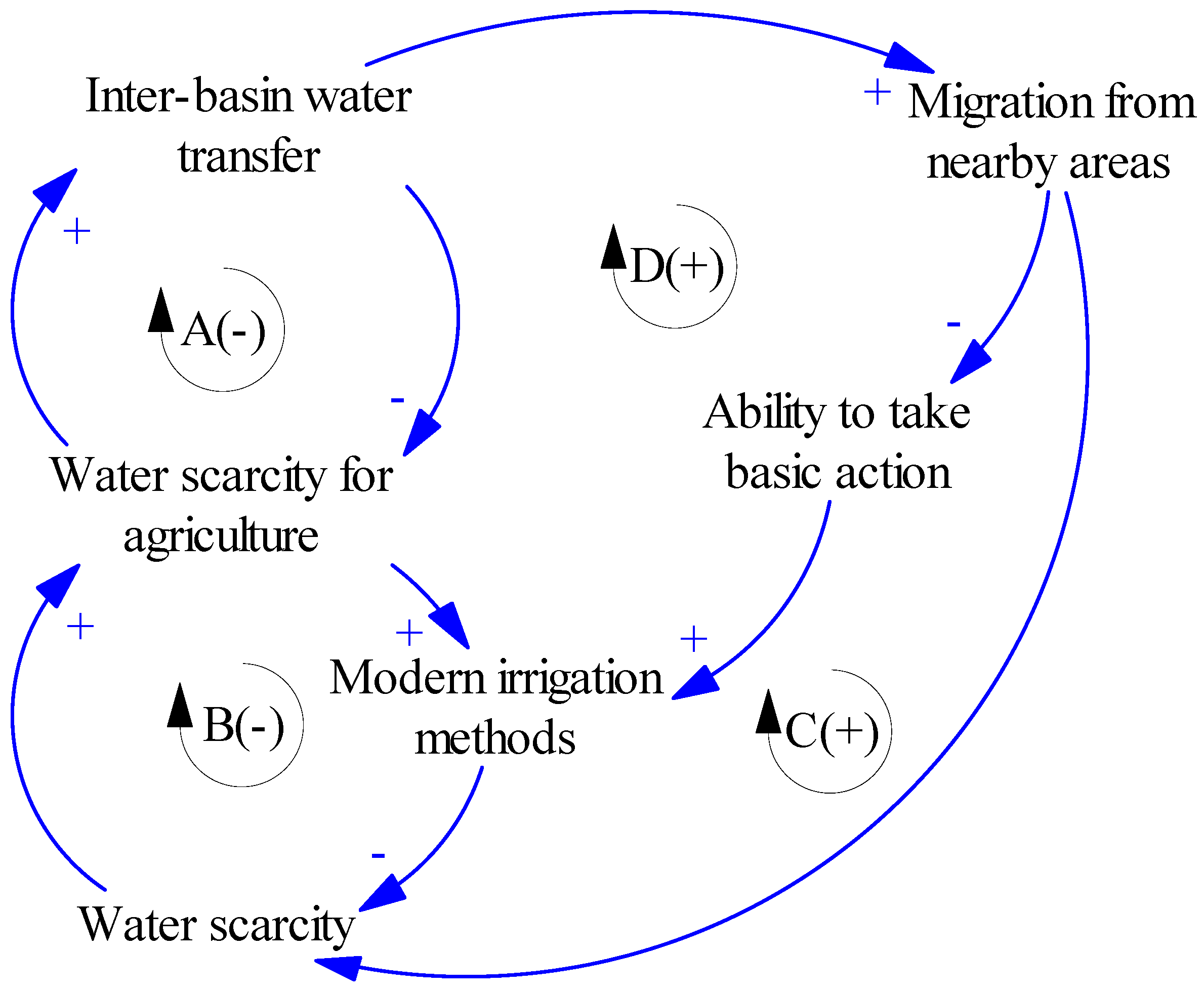
2.6.3. Side Effects of Temporary Solutions
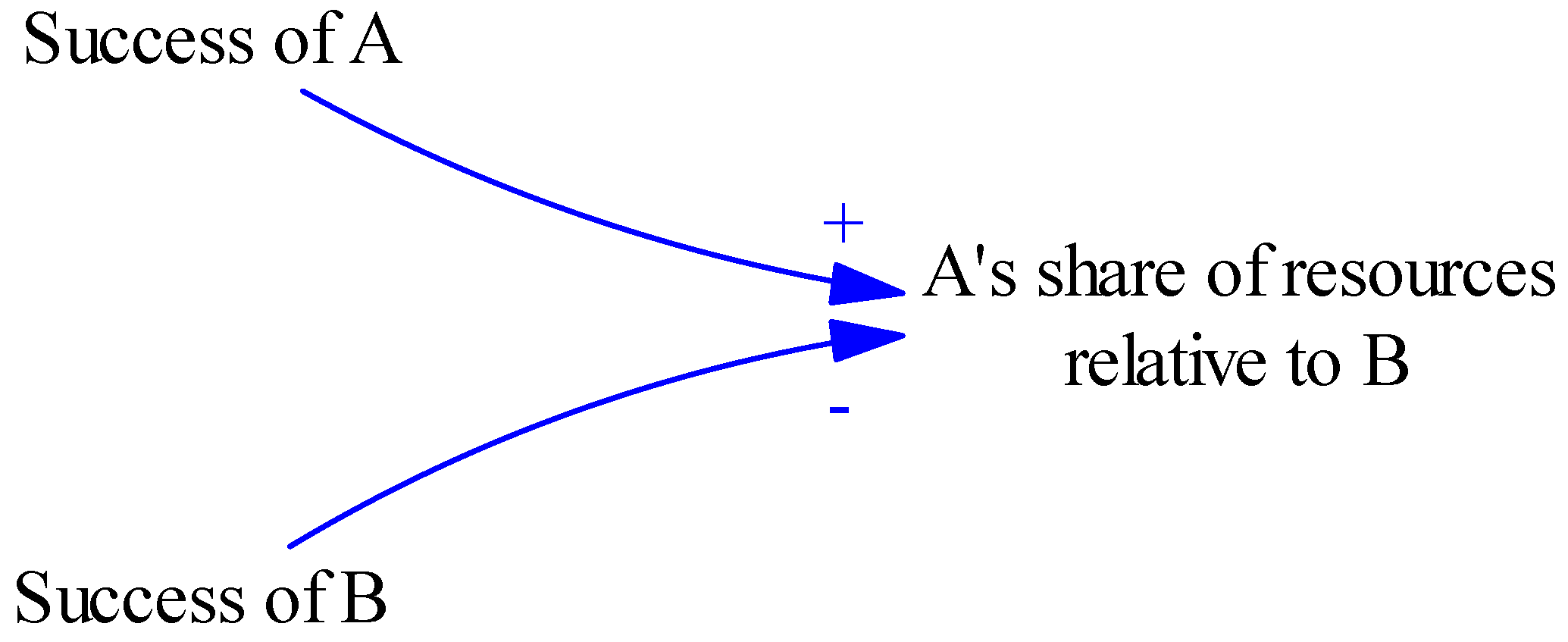
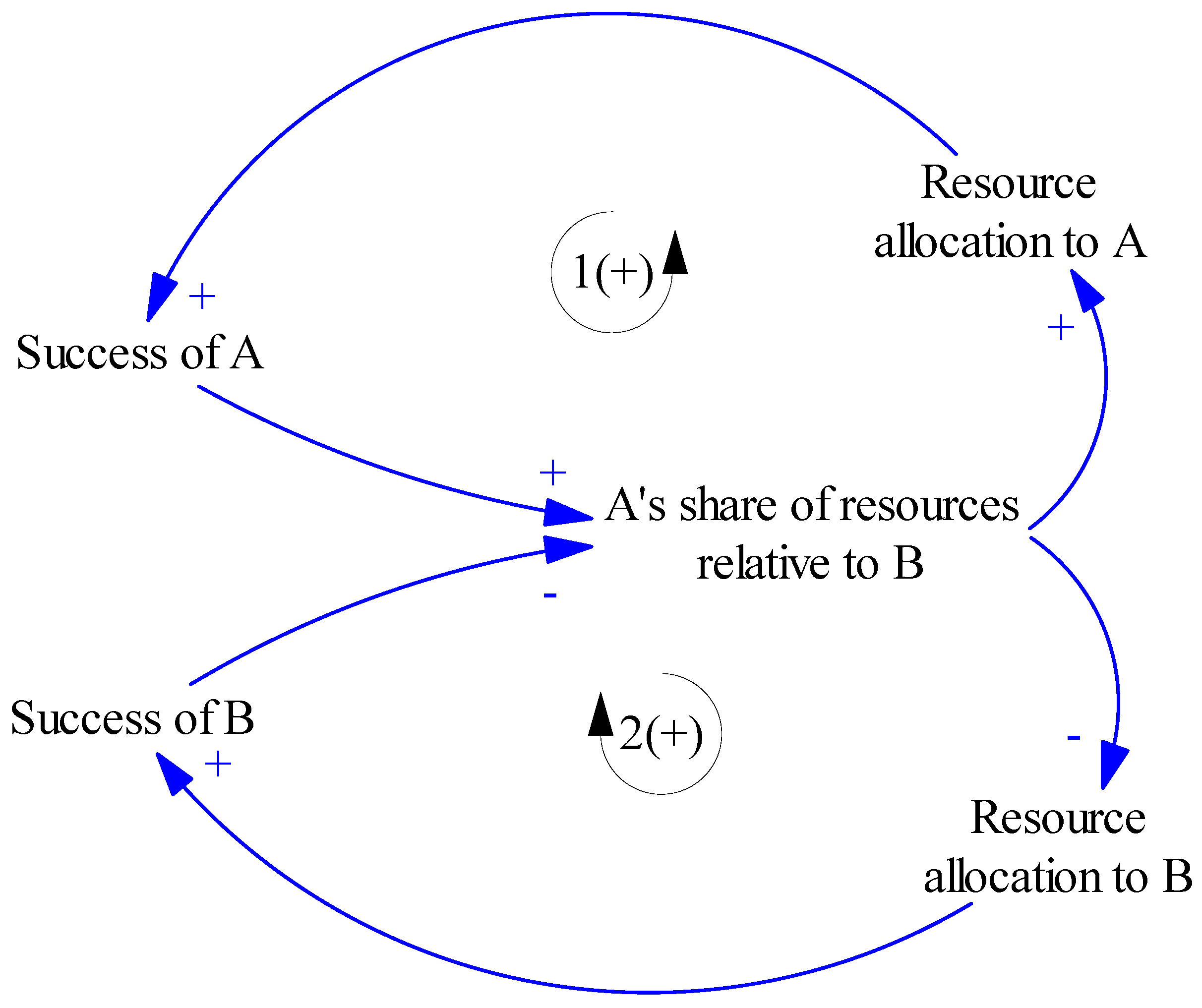
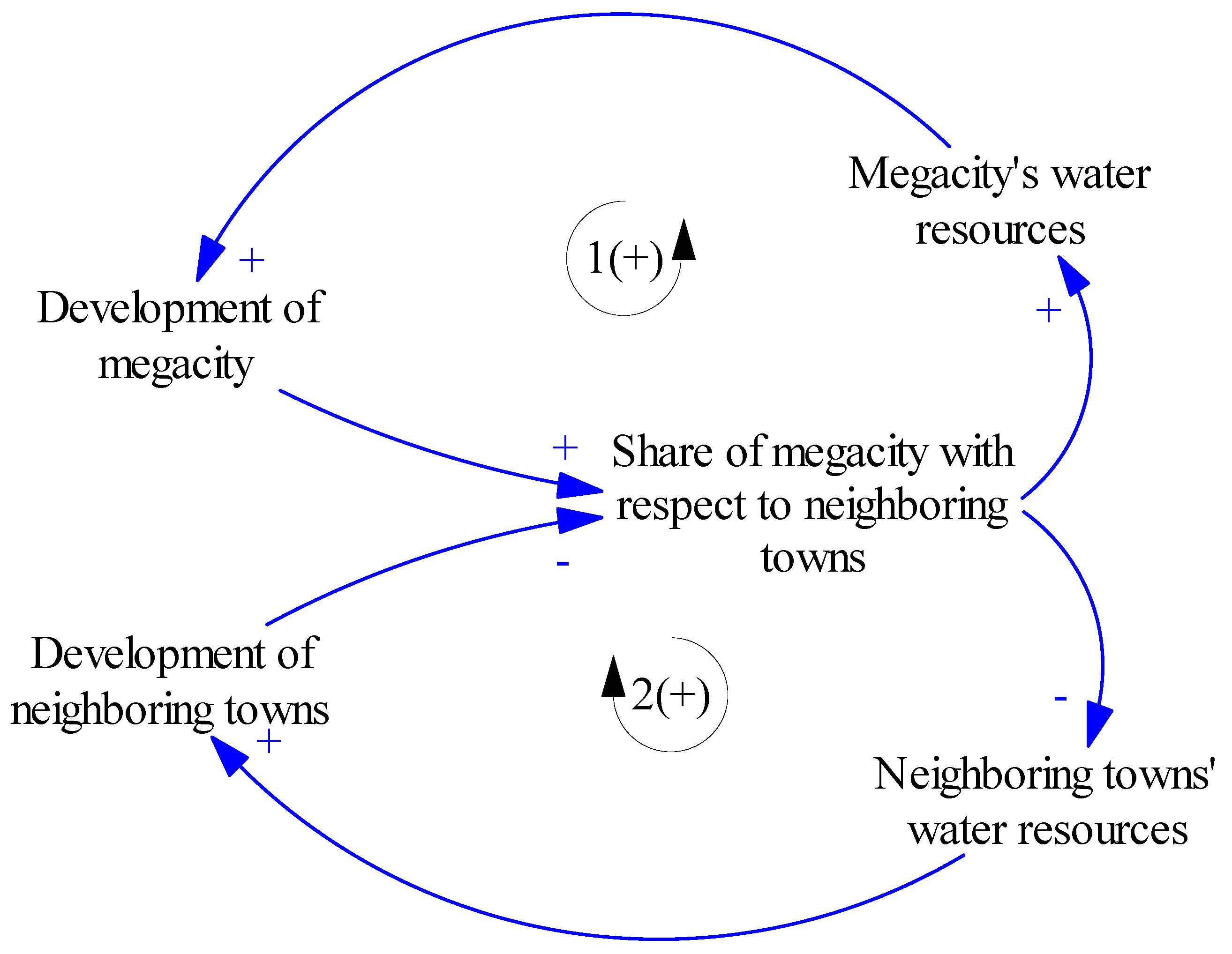
2.6.4. Success for the Successful
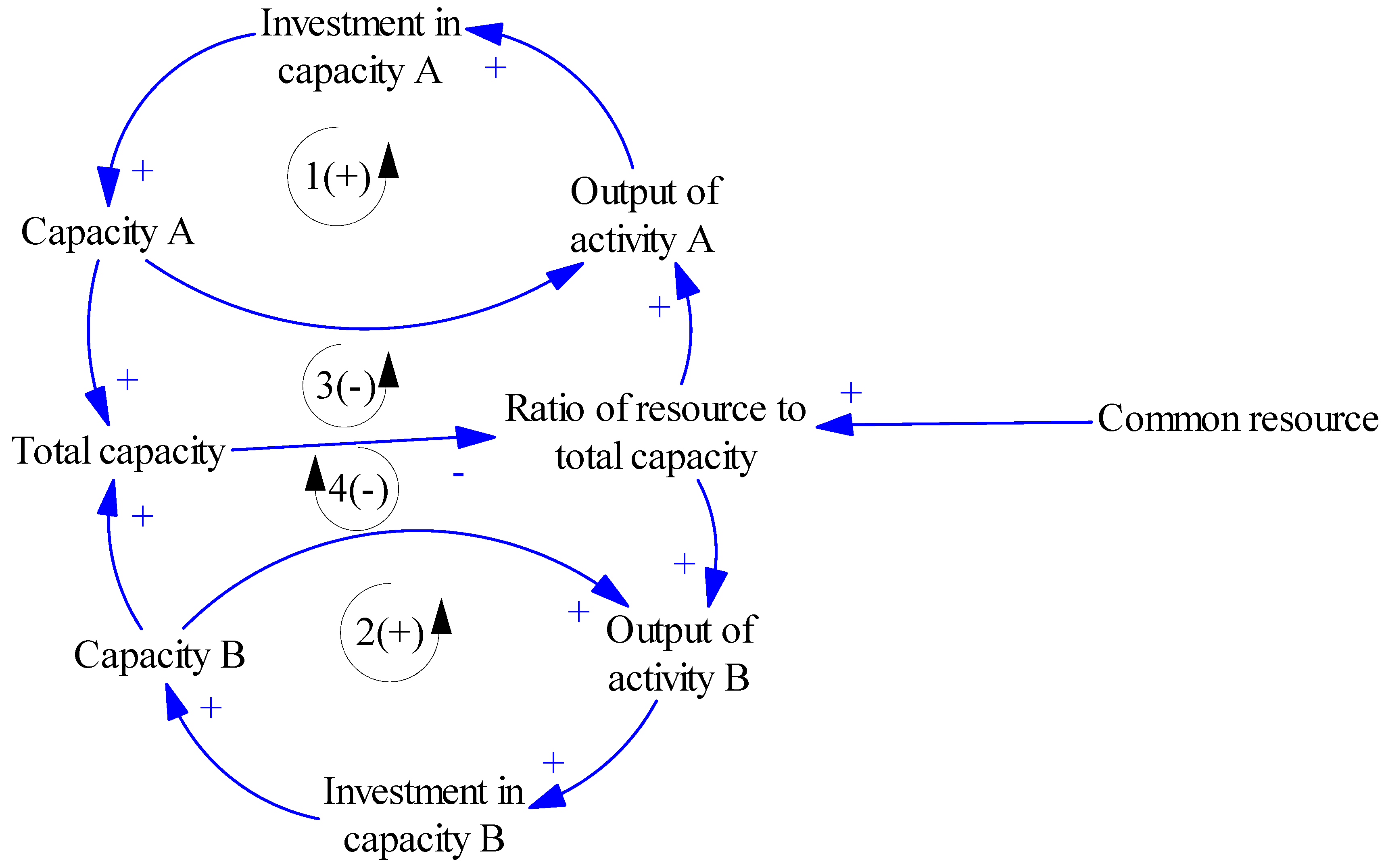
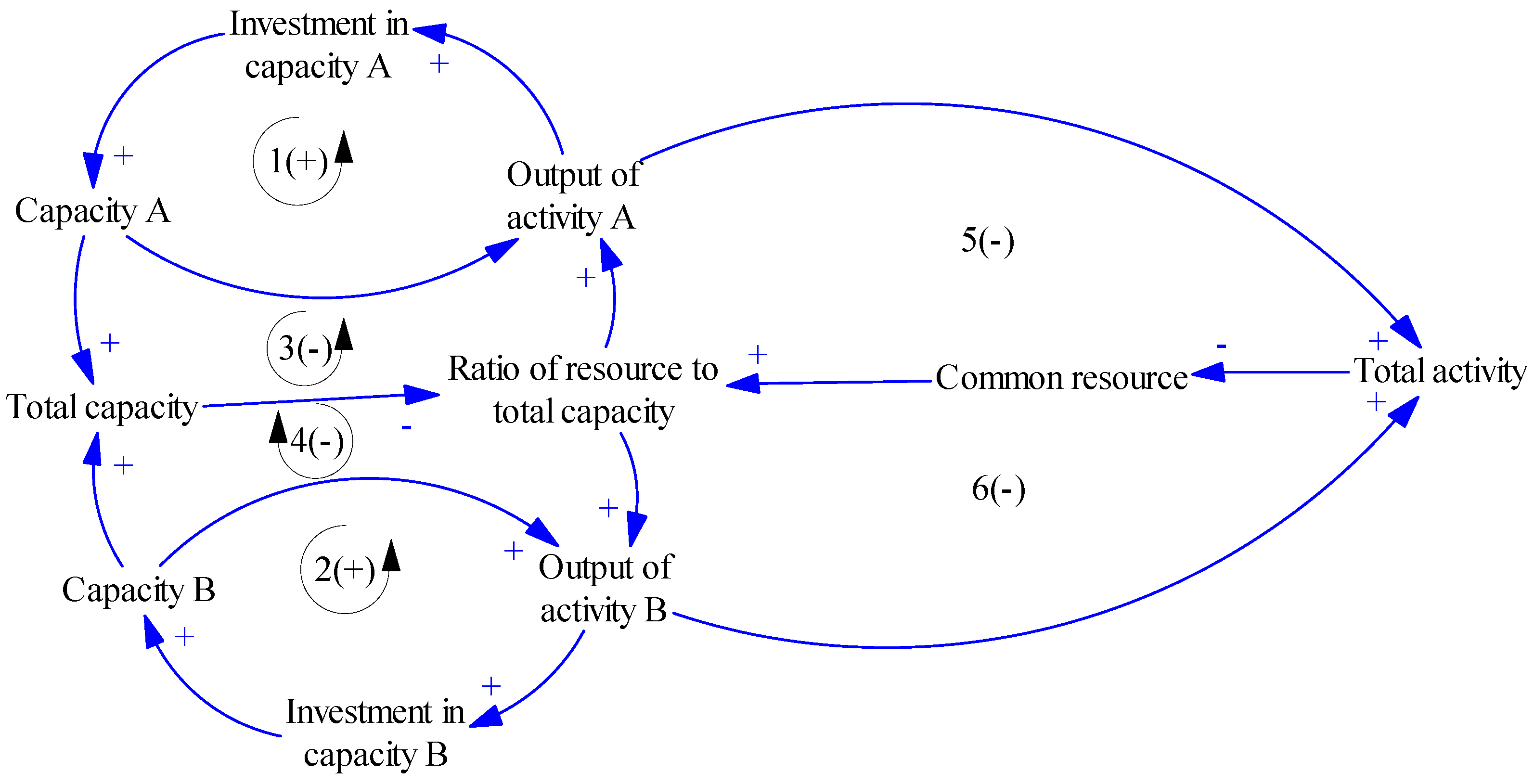
2.6.5. Tragedy of the Commons
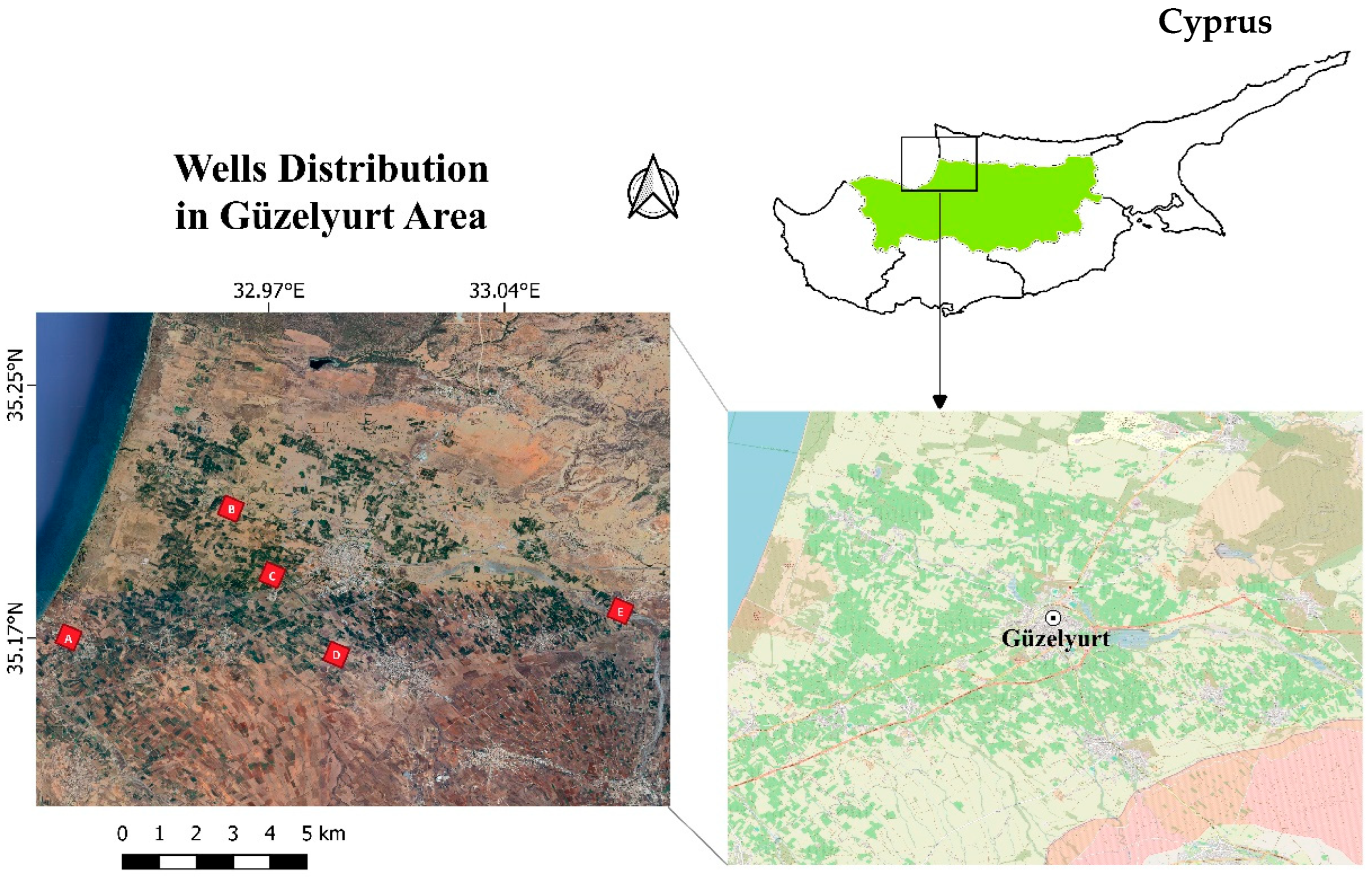
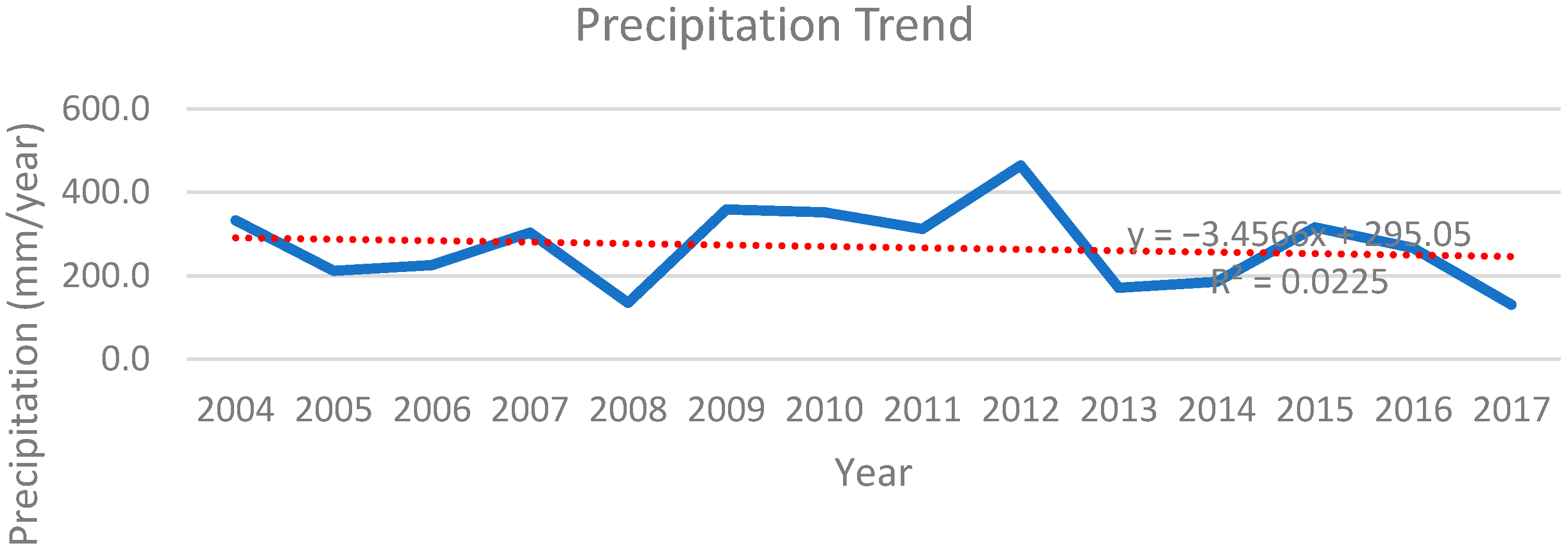
3. Case Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Group Model Building
- Divergent activities to generate a range of ideas and interpretations;
- Convergent activities to cluster and organize these ideas;
- Evaluation activities to select or rank options;
- Presentation activities to educate participants or refresh their knowledge.
4.2. Group Model Building in This Research
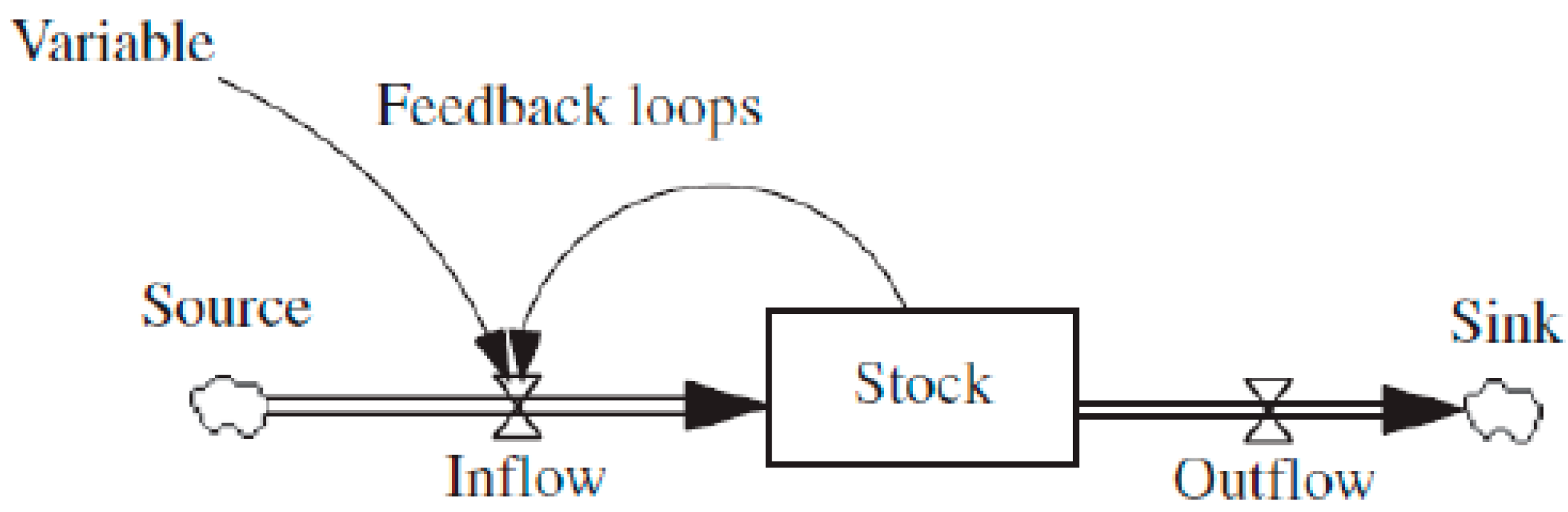
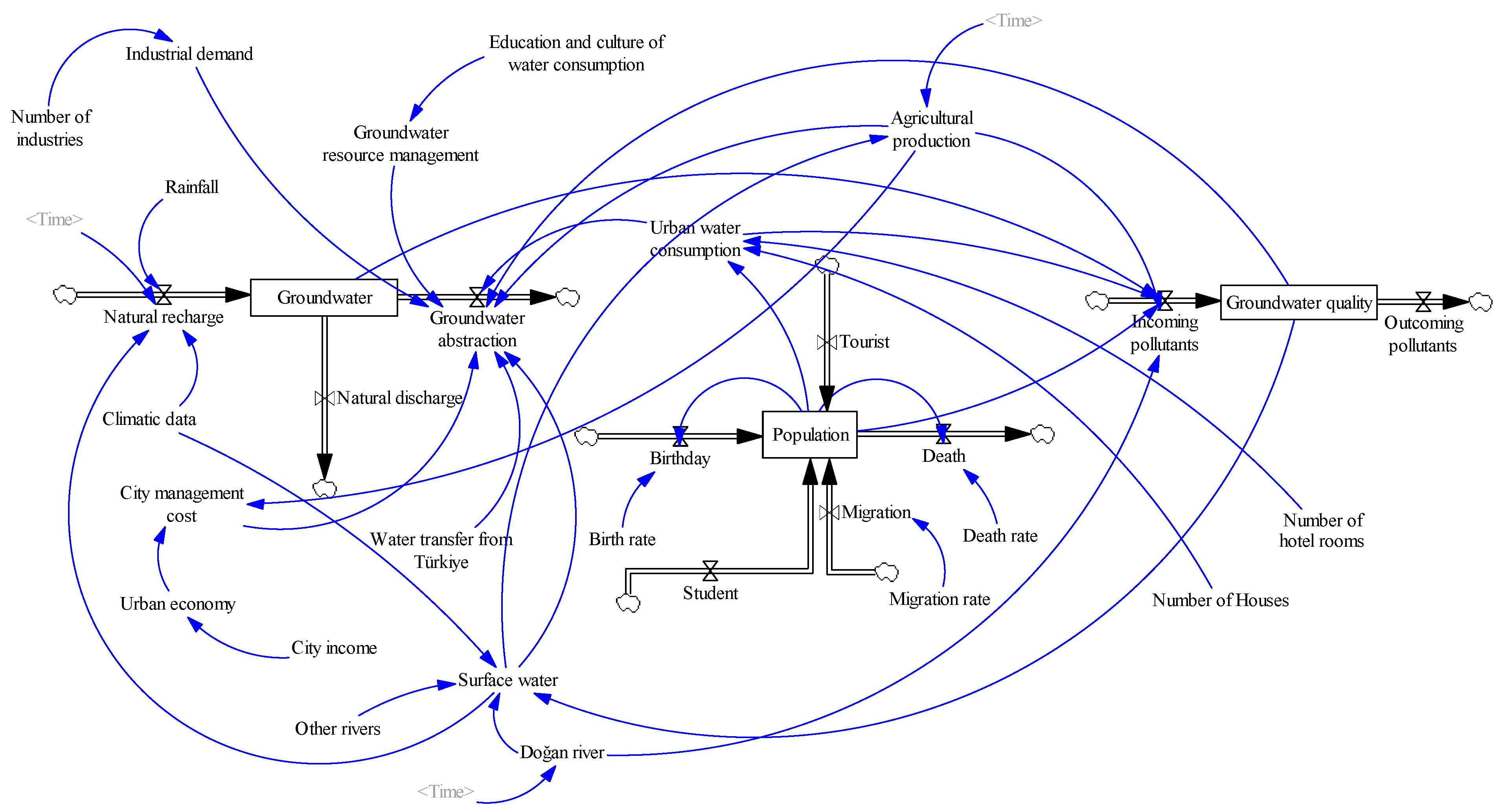
4.3. Stock–Flow Diagram and System Dynamics Modeling
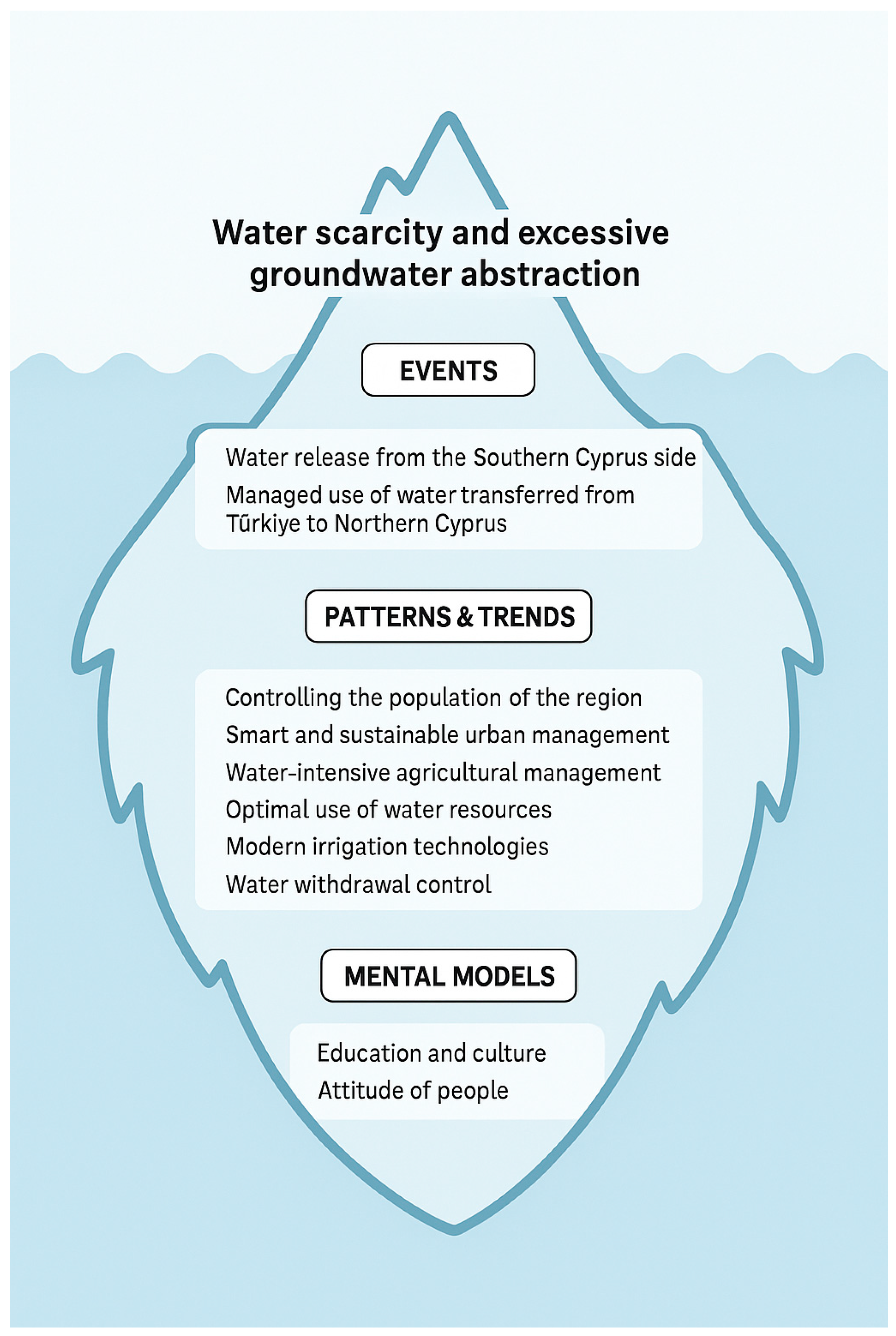
4.4. Iceberg Model
- Patterns and Trends: Through behavior over time graphs (BOTG), we can analyze data and examine gradual changes. This tool helps us to better understand existing realities and trends and provides a framework within which to discuss how and why changes occur.
- Structure: Tools such as feedback loops, causal loops, and flow asset maps help us to explore the connections within the system and identify leverage points for effective change. Thinking at this level means examining the cause-and-effect relationships between system components.
- Mental Models: The ladder of inference clarifies individuals’ deeply held beliefs about the system. These models influence their perceptions of the current and future states. Since changing mental models is challenging, the ladder of inference tool helps to make these beliefs visible and analyzable.
4.5. Iceberg Model in This Research
5. Results and Discussion
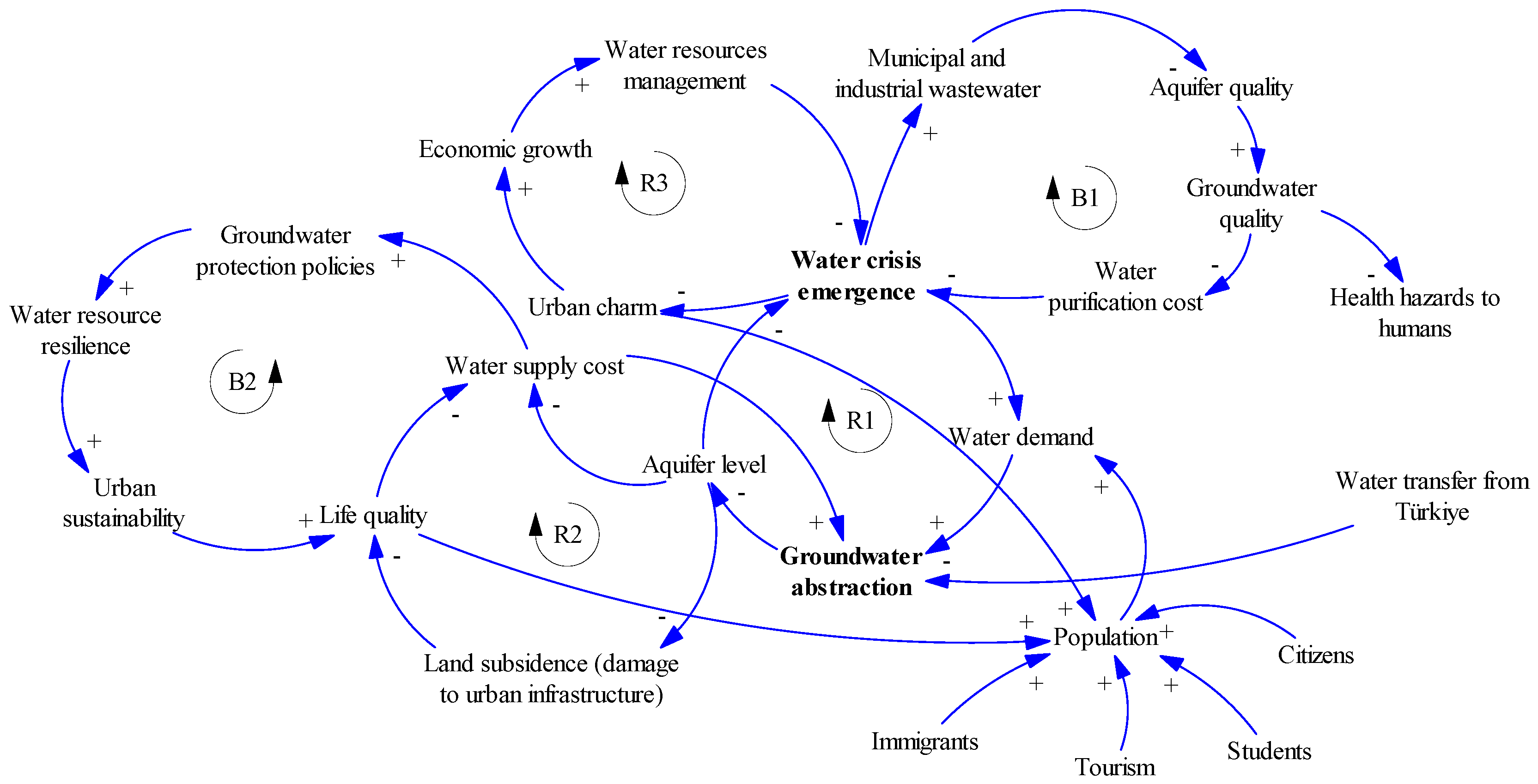
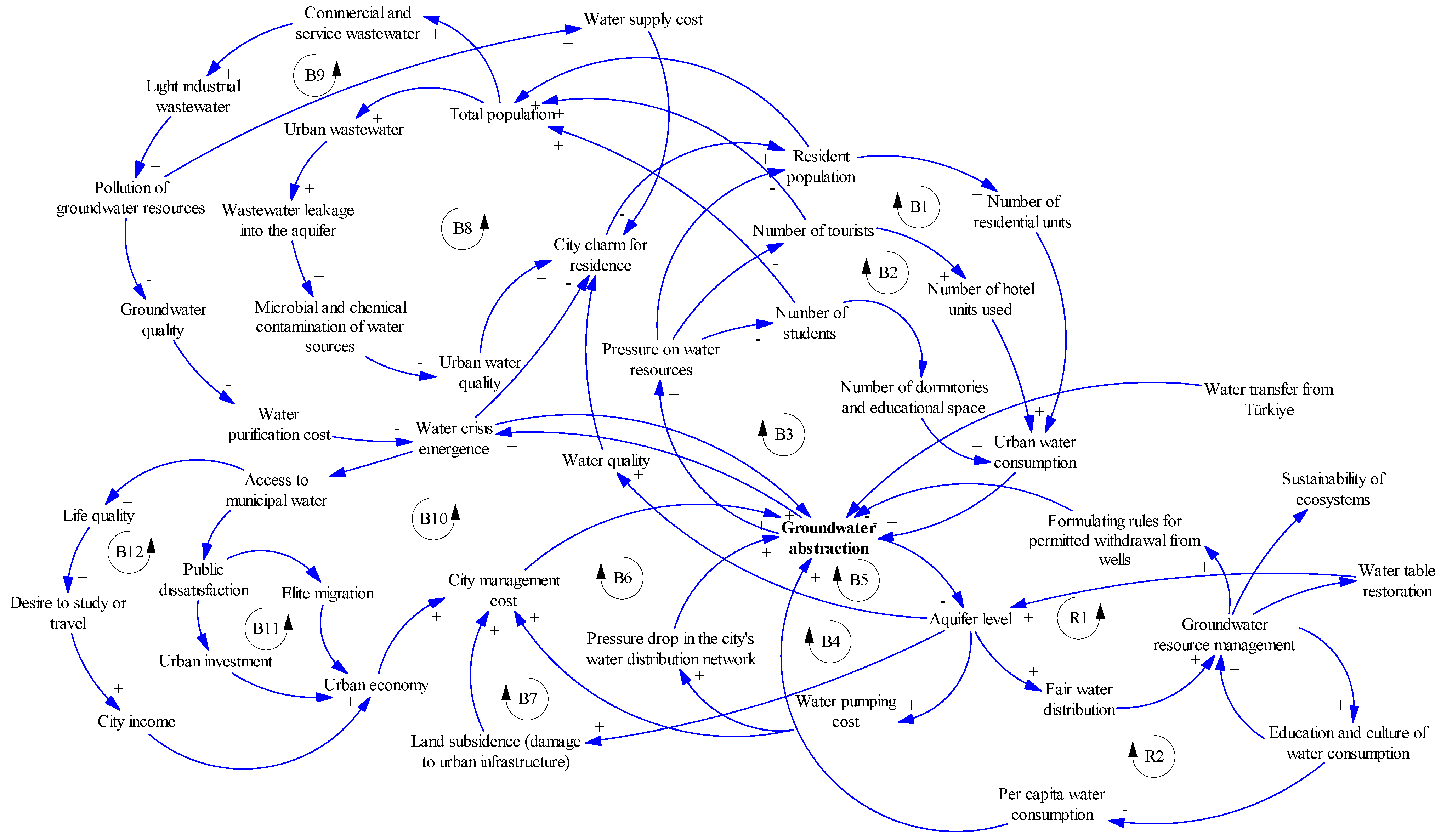
5.1. Urban Sector
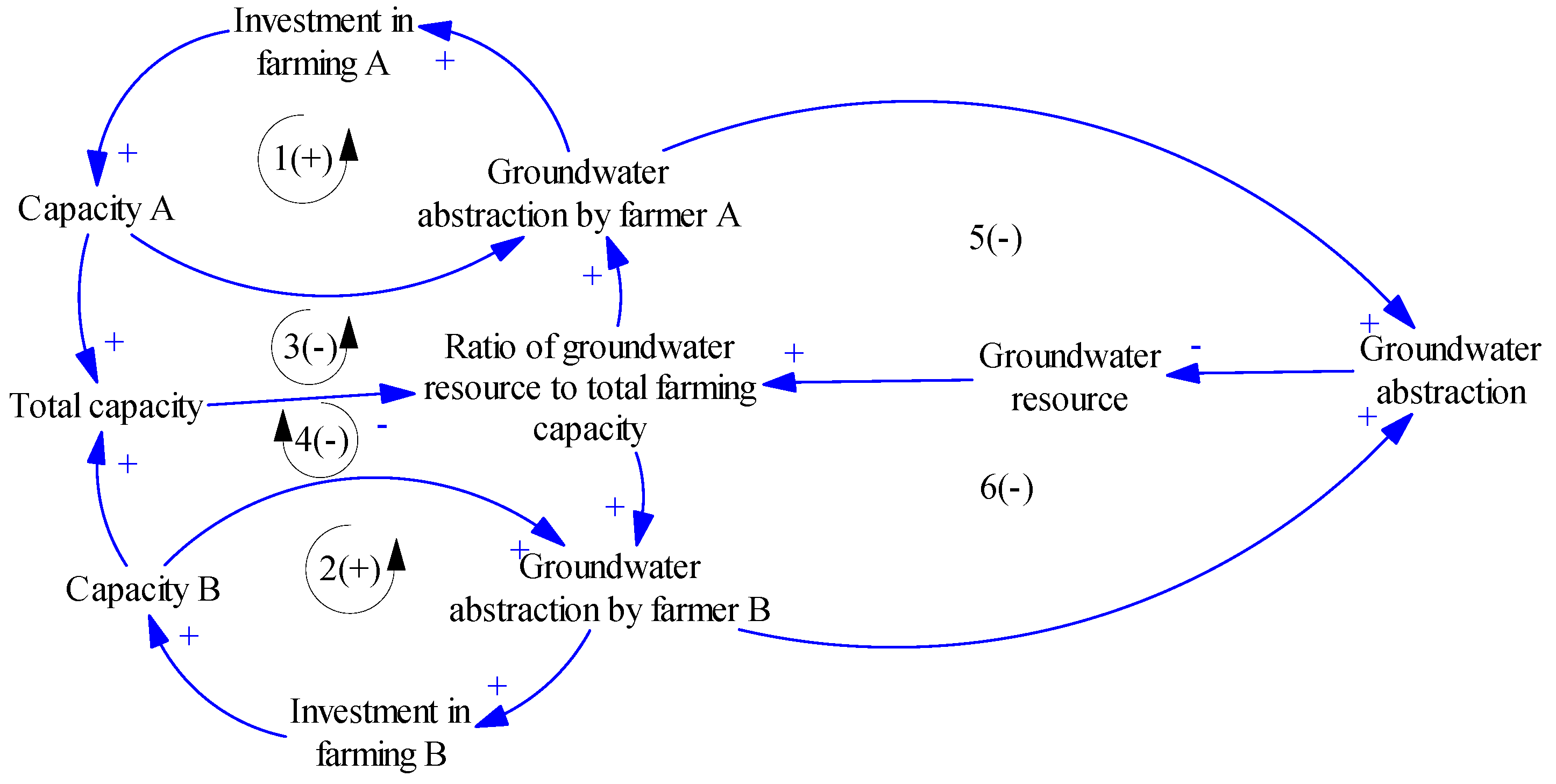
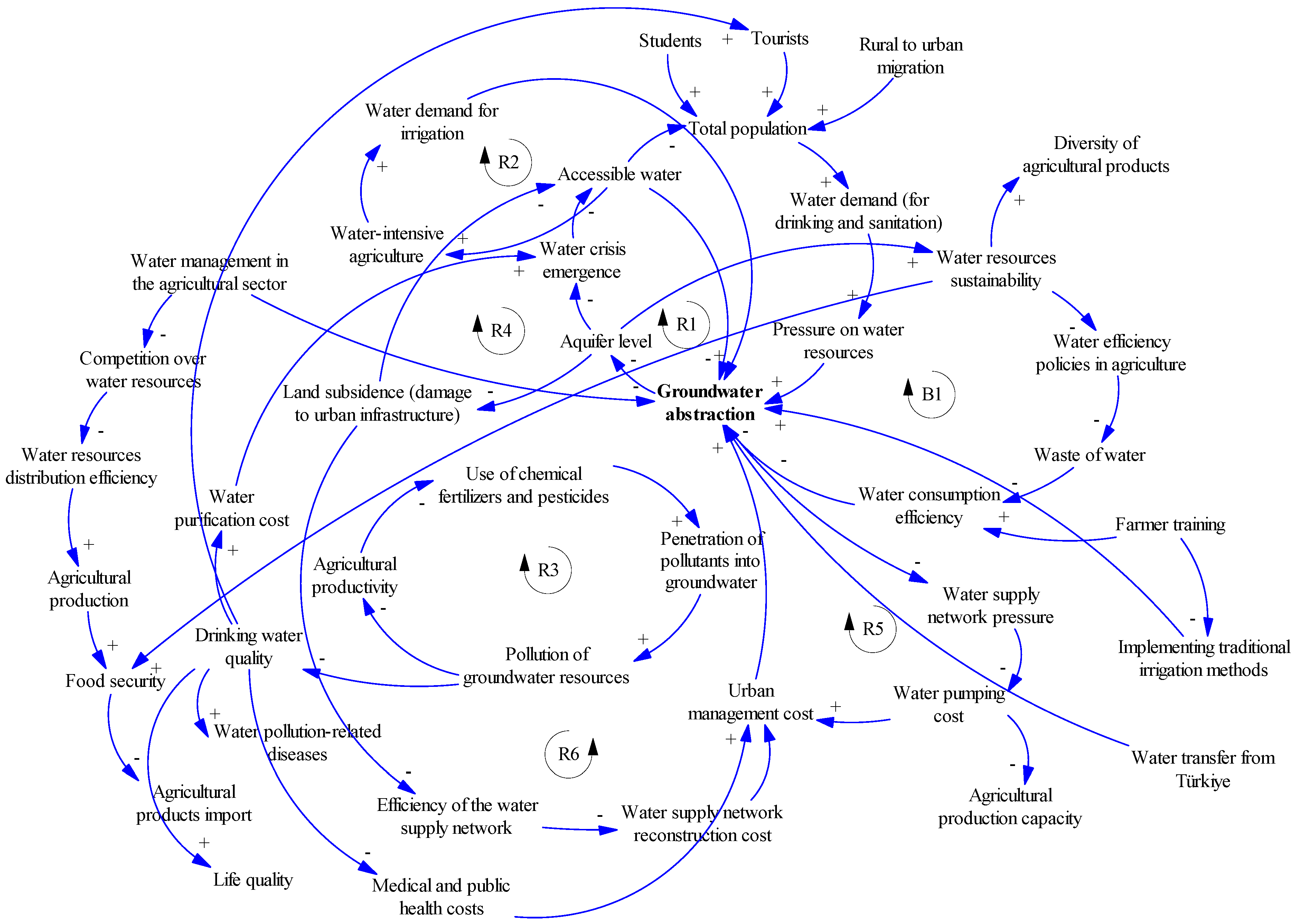
5.2. Agricultural Sector
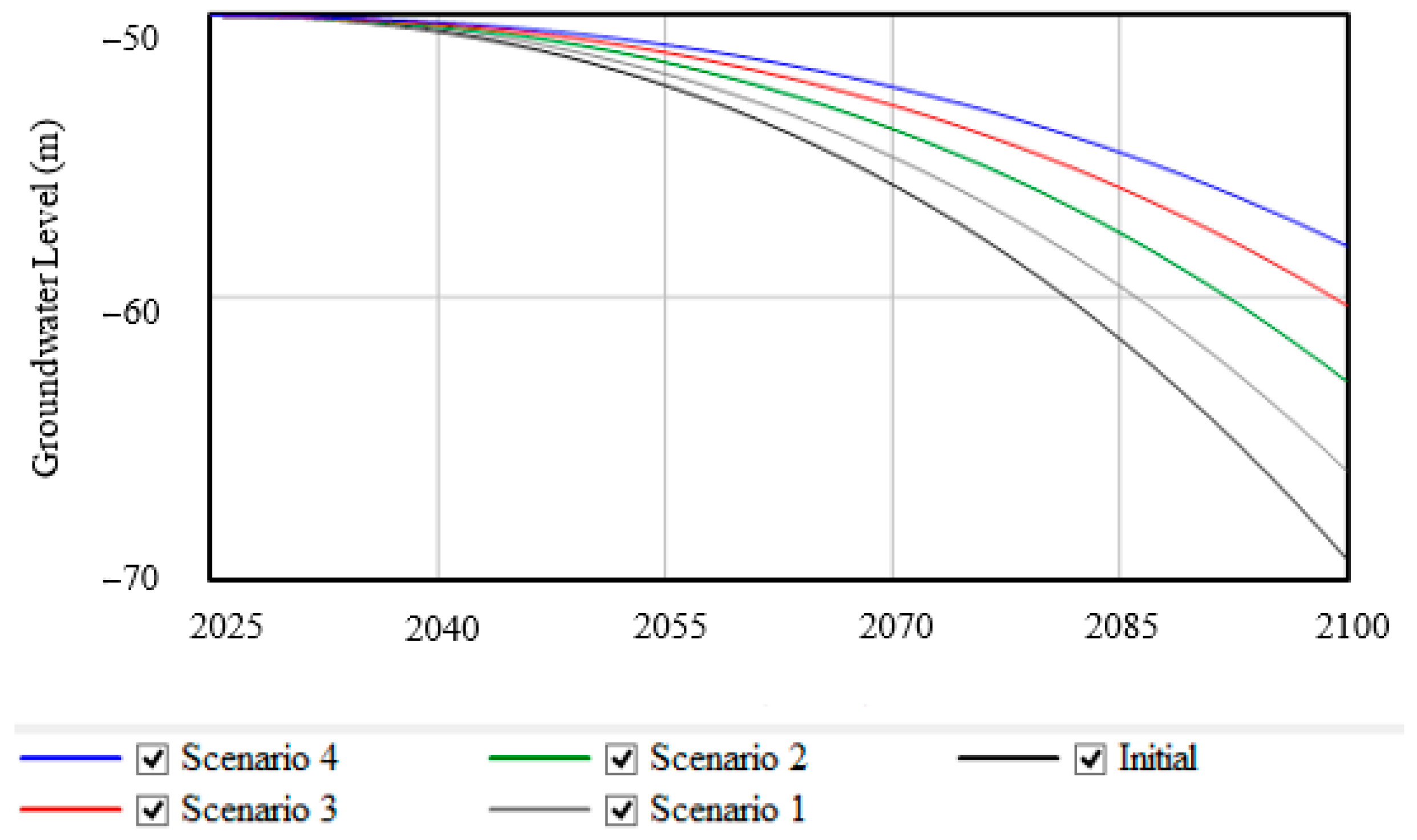
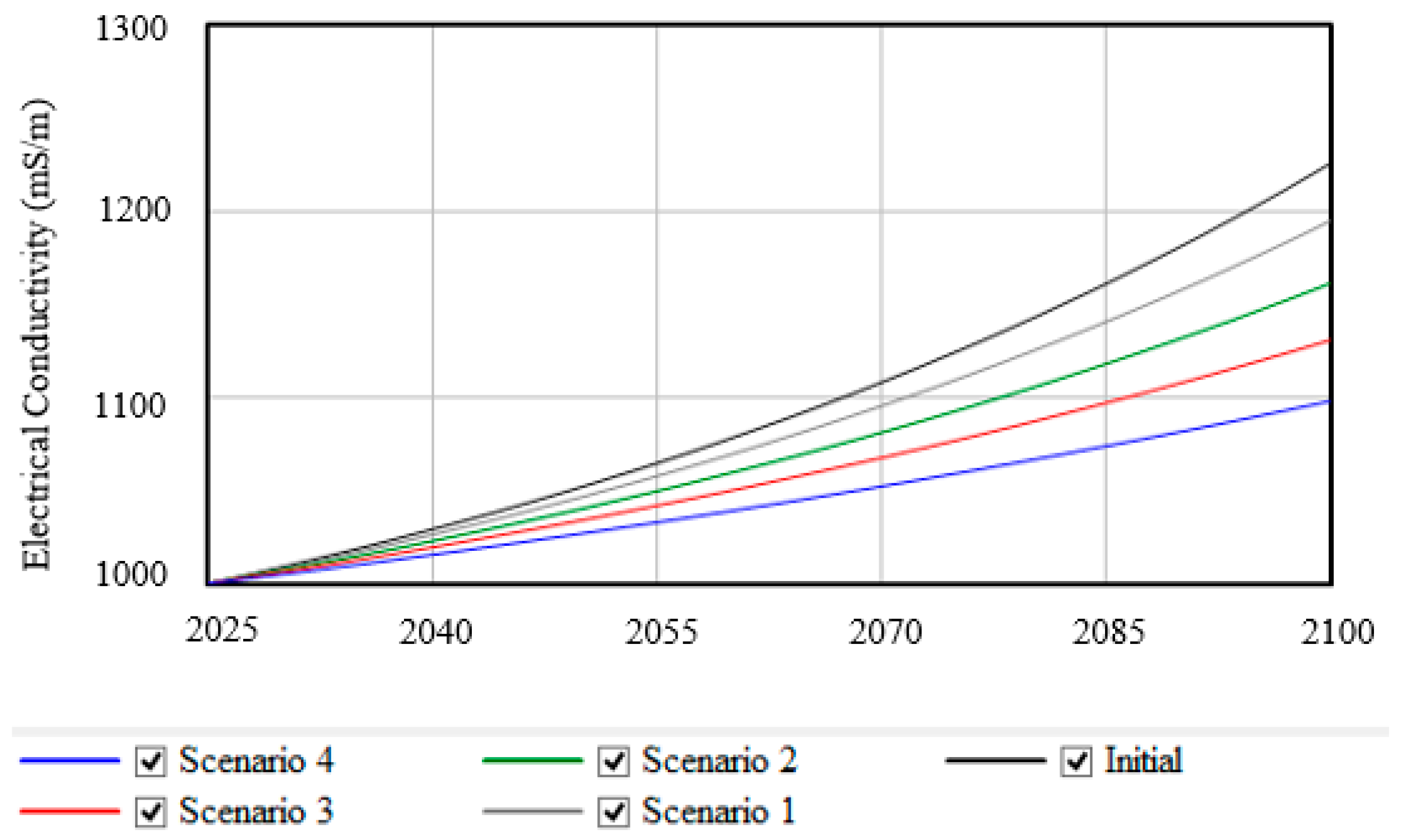
5.3. Model Validation Through Stock–Flow Diagram Model
5.4. Strategies and Iceberg Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SD | System dynamics |
| QSDA | Qualitative system dynamics approach |
| GMB | Group model building |
| CLD | Causal loop diagram |
References
- Van Vliet, M.T.; Jones, E.R.; Flörke, M.; Franssen, W.H.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Yearsley, J.R. Global water scarcity including surface water quality and expansions of clean water technologies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, Y.; Gökçekuş, H.; Mosbah, A.A.S. Prediction of monthly precipitation using various artificial models and comparison with mathematical models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 41209–41235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçekuş, H.; Bolouri, F. Transboundary Waters and Their Status in Today’s Water-Scarce World. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasik, M.; Dąbrowska, D. Groundwater quality testing in the area of municipal waste landfill sites in Dąbrowa Górnicza (southern Poland). Environ. Socio-Econ. Stud. 2022, 10, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, D.; Sołtysiak, M.; Biniecka, P.; Michalska, J.; Wasilkowski, D.; Nowak, A.; Nourani, V. Application of hydrogeological and biological research for the lysimeter experiment performance under simulated municipal landfill condition. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghanam, A.H.; Vakili, A.T.; Nourani, V.; Dąbrowska, D.; Soltysiak, M. AI-based ensemble modeling of landfill leakage employing a lysimeter, climatic data and transfer learning. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouri, F.; Gökçekuş, H.; Nourani, V. Management of Emerging Pollutants with a Circular Economy Approach: Lessons from Developed Countries and a Case Study in Northern Cyprus. In Emerging Pollutants. Advances in Water Security; Zandaryaa, S., Fares, A., Eckstein, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 317–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ohenhen, L.O.; Zhai, G.; Lucy, J.; Werth, S.; Carlson, G.; Khorrami, M.; Onyike, F.; Sadhasivam, N.; Tiwari, A.; Ghobadi-Far, K.; et al. Land subsidence risk to infrastructure in US metropolises. Nat. Cities 2025, 2, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Saghafian, B.; Golian, S. System dynamics approach for simulating water resources of an urban water system with emphasis on sustainability of groundwater. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Cai, J. Research on the urban water resources carrying capacity by using system dynamics simulation. Hydrol. Res. 2023, 54, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghami, M.; Akbariyeh, S. System dynamics modeling for complex urban water systems: Application to the city of Tabriz, IranResour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 60, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Lou, I.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y. A system dynamics urban water management model for Macau, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 50, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovmand, P.S. Group Model Building and Community-Based System Dynamics Process; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Vennix, J.A.; Akkermans, H.A.; Rouwette, E.A. Group model-building to facilitate organizational change: An exploratory study. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1996, 12, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, B. Systems thinking: Critical thinking skills for the 1990s and beyond. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1993, 9, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.W. Industrial dynamics. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1997, 48, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J. System Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Engineering Systems Division, UAS: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, G.P. Problems in causal loop diagrams revisited. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1997, 13, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, E. Using generic system archetypes to support thinking and modelling. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2004, 20, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirchi, A.; Madani, K.; Watkins, D.; Ahmad, S. Synthesis of system dynamics tools for holistic conceptualization of water resources problems. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 2421–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, K.; Mariño, M.A. System dynamics analysis for managing Iran’s Zayandeh-Rud river basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 2163–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Hjorth, P. A framework for process indicators to monitor for sustainable development: Practice to an urban water system. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2007, 9, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, G. The tragedy of the commons: The population problem has no technical solution; it requires a fundamental extension in morality. Science 1968, 162, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loáiciga, H.A. Analytic game—Theoretic approach to ground-water extraction. J. Hydrol. 2004, 297, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, K. Game theory and water resources. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergil, M.E. The salination problem of the Guzelyurt aquifer, Cyprus. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, B.; Akün, E. Management, contamination and quality evaluation of groundwater in North Cyprus. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, U.; Hansen, B.R. River Basin Management and Characterization of Water Bodies in North Cyprus. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress on Advances in Civil Engineering, Ankara, Turkey, 17–19 October 2012; pp. 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gökcekuş, H.; Iravanian, A.; Türker, U.; Oğuz, G.; Sözen, S.; Orhon, D. Massive freshwater transport: A new dimension for integrated water-wastewater management in North Cyprus. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 132, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, Y.; Gökçekuş, H.; Rizza, T. Groundwater Quality Assessment Based on Water Quality Index in Northern Cyprus. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2022, 12, 8435–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpek, C.; Türker, U. Geospatial based groundwater resources susceptibility and contamination risk mapping for Yeşilköy aquifer, Cyprus. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, G.P.; Andersen, D.F. Teamwork in group model building. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1995, 11, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, B. The strategic forum: Aligning objectives, strategy and process. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1997, 13, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.C. Diagramming conventions in system dynamics. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2000, 51, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.F.; Vennix, J.A.; Richardson, G.P.; Rouwette, E.A. Group model building: Problem structuring, policy simulation and decision support. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2007, 58, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, G.P. Concept models in group model building. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2013, 29, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.F.; Richardson, G.P. Scripts for group model building. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1997, 13, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Reyes, L.F.; Martinez-Moyano, I.J.; Pardo, T.A.; Cresswell, A.M.; Andersen, D.F.; Richardson, G.P. Anatomy of a group model-building intervention: Building dynamic theory from case study research. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2006, 22, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, F.; Andersen, D.F.; Eden, C.; Richardson, G.P. ScriptsMap: A tool for designing multi-method policy-making workshops. Omega 2011, 39, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovmand, P.S.; Andersen, D.F.; Rouwette, E.; Richardson, G.P.; Rux, K.; Calhoun, A. Group model-building ‘scripts’ as a collaborative planning tool. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2012, 29, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinov, A.A. Participatory modeling for sustainability. In Encyclopedia of Sustainable Technologies; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Vennix, J.A.M. Group Model Building: Facilitating Team Learning Using System Dynamics; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J.D. All Models Are Wrong: Reflections on Becoming a Systems Scientist. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2002, 18, 501–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.S.; Graves, A.; Dandy, N.; Posthumus, H.; Hubacek, K.; Morris, J.; Prell, C.; Quinn, C.H.; Stringer, L.C. Who’s in and Why? A Typology of Stakeholder Analysis Methods for Natural Resource Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1933–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-samarraie, H.; Hurmuzan, S. A Review of Brainstorming Techniques in Higher Education. Think. Ski. Creat. 2017, 27, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, P.E.; Robins, G.L.; Snijders, T.A.B.; Wang, P. Conditional Estimation of Exponential Random Graph Models from Snowball Sampling Designs. J. Math. Psychol. 2013, 57, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J.D. Bussiness Dynamics. Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Shelstad, J.J., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanzadeh, E.; Elshorbagy, A.; Wheater, H.; Gober, P. Managing Water in Complex Systems: An Integrated Water Resources Model for Saskatchewan, Canada. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 58, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monat, J.P.; Gannon, T.F. What is systems thinking? A review of selected literature plus recommendations. Am. J. Syst. Sci. 2015, 4, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H. Analysis and effects of high school students’ systems thinking using iceberg (IB) model. J. Korean Assoc. Sci. Educ. 2017, 37, 611–624. [Google Scholar]
- Gejl, R.N.; Rygaard, M.; Henriksen, H.J.; Rasmussen, J.; Bjerg, P.L. Understanding the impacts of groundwater abstraction through long-term trends in water quality. Water Res. 2019, 156, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taftazani, R.; Kazama, S.; Takizawa, S. Spatial analysis of groundwater abstraction and land subsidence for planning the piped water supply in Jakarta, Indonesia. Water 2022, 14, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.S. The interdependence of groundwater and urbanisation in rapidly developing cities. Urban Water 2001, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, I.E.M.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Wada, Y.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Dynamic attribution of global water demand to surface water and groundwater resources: Effects of abstractions and return flows on river discharges. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 64, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizer, H.; Hagendorf, U. Microbial contamination as an indicator of sewer leakage. Water Res. 1991, 25, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y.; Tong, L.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J. Characterization of microbial communities in urban subway: Connotation for indoor environment quality and public health. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2024, 17, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, W.A.; Vaux, H.J., Jr. The emerging global water crisis: Managing scarcity and conflict between water users. Adv. Agron. 2007, 95, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Curry, L.L. Consumer Attitudes Toward Public Water Supply Quality: Dissatisfaction and Alternative Water Sources; Illinois State Water Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, W.E.; Lowery, D. Citizen responses to dissatisfaction in urban communities: A partial test of a general model. J. Politics 1989, 51, 841–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.L.; Perrone, D. Local groundwater withdrawal permitting laws in the south-western US: California in comparative context. Groundwater 2016, 54, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tójar-Hurtado, J.C.; Mena-Rodríguez, E.; Fernández-Jiménez, M.Á. Spanish agriculture and water: Educational implications of water culture and consumption from the farmers’ perspective. Water 2017, 9, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, T.T.; Luan, X.B.; Yin, Y.L.; Wu, P.T.; Wang, Y.B.; Sun, S.K. Determinants of agricultural water demand in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorogbona, A.O.; Denner, F.D.; Managa, L.R.; Khosa, T.B.; Maduwa, K.; Adebola, P.O.; Amoo, S.O.; Ngobeni, H.M.; Macevele, S. Water quality impacts on agricultural productivity and environment. Sustain. Agric. Rev. 2018, 27, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashrafi, S. Land subsidence: A global challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.W.; Gerbens-Leenes, P.W.; Vaca-Jiménez, S.D. Freshwater competition among agricultural, industrial, and municipal sectors in a water-scarce country. Lessons of Pakistan’s fifty-year development of freshwater consumption for other water-scarce countries. Water Resour. Ind. 2023, 29, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzepek, K.; Boehlert, B. Competition for water for the food system. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2927–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucx, T.H.M.; Van Ruiten, C.J.M.; Erkens, G.; De Lange, G. An integrated assessment framework for land subsidence in delta cities. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Hou, R.; Wang, H. Does urbanization improve industrial water consumption efficiency? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Vashisht, B.B.; Jalota, S.K.; Jyolsna, T.; Singh, S.P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, G. Improving Water efficiencies in rural agriculture for sustainability of water resources: A review. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 3505–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, E. Identifying leverage points for shifting Water-Energy-Food nexus cases towards sustainability through the Networks of Action Situations approach combined with systems thinking. Sustain. Sci. 2023, 18, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Riechers, M. A leverage points perspective on sustainability. People Nat. 2019, 1, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolouri, F.; Gökçekuş, H.; Nourani, V.; Kassem, Y. Groundwater Management Modeling in the Güzelyurt Region (Northern Cyprus): A Group Model Building Approach. Water 2025, 17, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132004
Bolouri F, Gökçekuş H, Nourani V, Kassem Y. Groundwater Management Modeling in the Güzelyurt Region (Northern Cyprus): A Group Model Building Approach. Water. 2025; 17(13):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132004
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolouri, Farhad, Hüseyin Gökçekuş, Vahid Nourani, and Youssef Kassem. 2025. "Groundwater Management Modeling in the Güzelyurt Region (Northern Cyprus): A Group Model Building Approach" Water 17, no. 13: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132004
APA StyleBolouri, F., Gökçekuş, H., Nourani, V., & Kassem, Y. (2025). Groundwater Management Modeling in the Güzelyurt Region (Northern Cyprus): A Group Model Building Approach. Water, 17(13), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132004












