Abstract
(1) Although lotus ponds exhibit ecological benefits in wetland restoration, their efficacy in water purification and eutrophication mitigation remains unclear. (2) This study utilized Jinluo lotus pond as the experimental group and the adjacent river as the control. Five sampling points were established in each area, with water samples collected in June 2022, April 2025, and May 2025. (3) The pH, BOD, COD, TN, and NH3-N concentrations in Jinluo lotus pond water are higher than those in rivers, while the TP, NO3-N, Chl-a, and algal cell density in rivers are higher. However, there was no significant difference in the nine parameters (p > 0.05) in June 2022. The pH, DO, algal cell density, and algal biomass of the Jinluo lotus pond were significantly higher (p < 0.05 for DO); the concentrations of BOD, COD, TN, TP, NH3-N, NO3-N, PI, and Chl-a in rivers are higher, with significant differences in Chl-a (p < 0.05) in April 2025. The BOD, COD, TP, NO3-N, and PI of the Jinluo lotus pond were relatively high (p < 0.05 for PI); the pH, TN, NH3-N, DO, Chl-a, algal cell density, and algal biomass of rivers are higher, with significant differences in Chl-a (p < 0.05) in May 2025. The results showed that there was no significant difference in the four diversity indicators in June 2022, April 2025, and May 2025. There was no significant difference in the algal diversity indices, including species richness (S), Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H), Simpson diversity index (P), and Pielou evenness index (E) between Jinluo lotus pond and rivers. (4) Conclusions and Recommendations: The Jinluo lotus pond and adjacent rivers suffer from severe nutrient overload, especially with BOD, COD, and TN all being classified as Class 5 water. Expanding natural and constructed reed communities is recommended to enhance nutrient removal. However, given the limited purification capacity of lotus ponds, maintaining or increasing their area may not be justified.
1. Introduction
With the rapid increase in global water demand, a series of water ecological issues caused by eutrophication, such as water quality deterioration and biodiversity loss, have become a global focus of concern [1]. Water eutrophication stands as one of the greatest challenges facing the global water environment, as it undermines the stability and functionality of aquatic ecosystems [2,3]. Water scarcity has emerged as a critical issue threatening sustainability in many regions worldwide [4,5]. Water environment governance constitutes an essential component of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) emphasizing the pivotal role of water governance in addressing sustainable development challenges [6,7].
Selecting appropriate restoration methods is essential for the recovery of aquatic ecosystems [1]. Among these, ecological approaches—known for their cost-effectiveness and efficiency—have emerged as a preferred solution for water quality improvement in diverse aquatic systems [8]. Specifically, aquatic macrophyte-based remediation is widely regarded as one of the most economical, efficient, and environmentally sustainable methods, offering distinct advantages [8]. For instance, constructed wetlands are increasingly utilized for sustainable wastewater treatment, effectively removing organic matter and nutrients while delivering ecosystem services and recreational benefits. Notably, hybrid constructed wetlands represent the most efficient approach for enhancing water quality and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Their performance depends on multiple factors, including plant species, substrate selection, and environmental/hydraulic conditions, with pollutant removal efficiency largely influenced by temperature, hydraulic retention time, and pollutant loading rates [9].
Constructed wetlands composed of diverse aquatic macrophyte species, acknowledged as a convenient, environmentally friendly, low-cost, and efficient phytoremediation technology, have been widely used globally for polluted water treatment [10,11,12]. Artificial water bodies are increasingly becoming prominent features in urban landscapes [13], serving as temporary sanctuaries and phased wetland reserves [14], though most landscape water bodies face risks of pollution and eutrophication.
As a rapidly developing economic powerhouse, China has confronted escalating water pollution challenges resulting from decades of intensive industrialization and urbanization. In response to these pressing environmental concerns, the Chinese government initiated the groundbreaking “Sponge City” program in 2015 as a comprehensive national infrastructure strategy. This innovative approach systematically addresses multiple urban water management challenges, including the following: (1) urban surface water flooding mitigation, (2) stormwater runoff purification, (3) peak flow regulation, and (4) sustainable water resource utilization [15]. Through coordinated efforts led by the State Council and implemented by various governmental departments, sponge city development has been vigorously promoted nationwide. By 2024, the cumulative investment in this initiative had surpassed 60 billion yuan (approximately 8.3 billion USD), facilitating the creation of urban ecosystems with enhanced natural hydrological functions including water retention, infiltration, and purification capacity. However, the effectiveness of natural wetlands in pollution control remains constrained by two fundamental limitations: (1) restricted spatial expansion potential within urban environments and (2) overburdened biogeochemical processing capacities [16]. In this context, constructed wetlands have emerged as strategically important engineered ecosystems, demonstrating a proven efficacy in water quality remediation through controlled biological and physical–chemical processes [17]. Nevertheless, their operational sustainability faces challenges from two primary environmental impacts: (1) greenhouse gas emissions associated with microbial metabolic processes and (2) potential secondary pollution from accumulated contaminants [18].
Constructed wetland systems consistently demonstrate high removal efficiencies (typically 70–90%) for organic pollutants including biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), and suspended solids, although nitrogen removal performance shows a greater variability (30–80%) depending on system configuration [19]. Typical designs incorporate extensive reed beds utilizing either single or mixed plant species to achieve multiple treatment objectives: the physical filtration of suspended solids, biochemical transformation of nutrients, and enhanced sedimentation processes through rhizosphere interactions [20,21]. Selected macrophyte species such as reeds (Phragmites australis), sedges, and other emergent vegetation effectively assimilate nutrients and pollutants through their root systems before translocating them to aerial biomass [22,23]. Particularly high-performing species commonly employed in these systems include Phragmites australis, Nelumbo nucifera, Typha domingensis, T. latifolia, Eichhornia crassipes, Pistia stratiotes, and Vallisneria natans, which are specifically valued for their exceptional nutrient uptake capacities demonstrated in numerous studies [22,23,24,25,26].
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the remarkable treatment efficiency of constructed wetlands across various applications: in Xiantao, a constructed wetland system achieved removal rates of 94% for total nitrogen, 90% for total phosphorus, 68% for COD, and 95% for ammonia nitrogen in municipal wastewater treatment [27]; at Universiti Sains Malaysia, wetlands dominated by Typha angustifolia and Eleocharis variegata effectively reduced nitrites, nitrates, ammonia nitrogen, and phosphates [28]; reed floating beds showed removal efficiencies of 55–60% for total solids, 45–55% for NH3-N, 33–45% for NO3−-N, 45–50% for TKN, and 40–50% for BOD, proving particularly suitable for the in-situ treatment of shallow, slow-flowing water bodies [29]; the Lotus Lake National Wetland Park in Tieling City, featuring Phragmites and Nelumbo nucifera, significantly reduced total phosphorus and ammonia nitrogen concentrations [30]; while lotus pond wetlands demonstrated effectiveness in treating garlic processing wastewater through the substantial removal of organic pollutants and the reduction of COD60 and BOD5 levels [31]. Comparative research has revealed distinct species-specific treatment efficiencies, with Eichhornia crassipes and Phragmites australis exhibiting superior nitrogen removal capabilities, whereas Pistia stratiotes and Nelumbo nucifera show an enhanced phosphorus removal performance [24,32]. Further studies conducted at Wuliangsuhai Lake and Baiyangdian Lake have elucidated Nelumbo nucifera’s dual effects on algal dynamics, demonstrating that low-density plantings can promote algal growth while high-density configurations effectively suppress it, underscoring the critical importance of optimal density management in wetland design [33,34,35].
The Yi River, a major watercourse in the Huai River Basin [36], is located in southern Shandong and northern Jiangsu, with geographical coordinates 34°23′–36°20′ N and 117°25′–118°42′ E. Spanning approximately 574 km, it originates from Yiyuan County in Shandong and flows into the Yellow Sea at Yanwei Port through the Xin-Yi River (Yi River Diversion Channel) from Wu Lou Village in Pi County, Jiangsu [37,38,39]. The Yi River has been listed as a key control and monitoring river in the Huai River Basin Water Pollution Prevention Plan. The Liuqing River, a tributary of the Yi River, suffers from severe excessive nutrient loads in its upper reaches.
Extensive research confirms that aquatic plants play a beneficial role in mitigating water eutrophication [4,10,40]. Common species employed in urban wetlands include reeds and reed ponds [4,41], as well as lotus and lotus ponds [10,32,33,42], all demonstrating ecological benefits for wetland restoration. The study site, Jinluo lotus pond, is situated on the north bank of the Liuqing River in Linyi City, Shandong Province, covering a total area of 7.109 km2 with lotus ponds accounting for 5.5667 km2. This project was designed to utilize lotus roots for regulating nutrient concentrations in wetland waters, alleviating eutrophication, and restoring polluted water bodies. Nevertheless, the actual efficacy of such systems in water quality purification remains questionable, particularly regarding their ability to achieve sustainable eutrophication control without causing secondary ecological impacts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sampling Procedure
In this study, Jinluo lotus pond served as the experimental group, while the adjacent river outside the pond was designated as the control group, with five sampling areas established in each location. Sampling was performed in June 2022, April 2025, and May 2025 using sterilized 4 L sampling buckets to collect water samples for laboratory analysis in Figure 1.
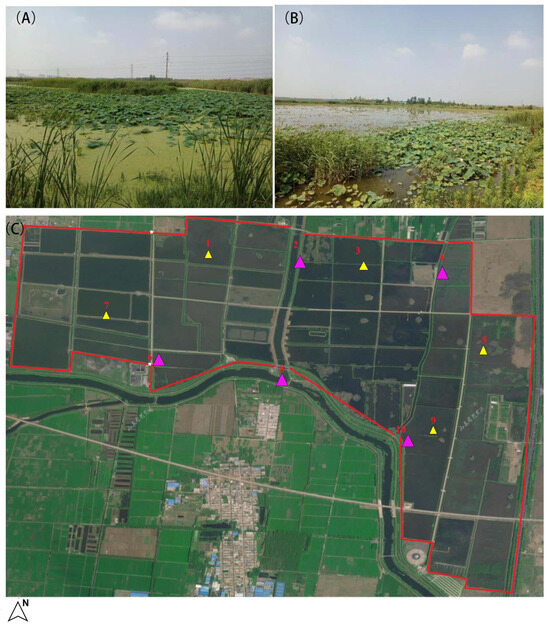
Figure 1.
The sampling point layout of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond. (A,B) show the exterior views of the lotus pond, (C) displays the distribution of sampling points in this study (The red line in the diagram represents the boundary of the lotus pond, yellow triangles indicate the lotus pond area, and pink triangles represent the river outside the lotus pond).
2.2. Analytical Methods
pH, Oxygen Demand (BOD), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Total Nitrogen (TN), Total Phosphorus (TP), Ammonia Nitrogen (NH3-N), Nitrate Nitrogen (NO3−-N), Dissolved Oxygen (DO), Planktonic Index (PI), Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), and algal cell density were studied. These selected parameters served dual purposes: (1) assessing the water purification efficacy of the lotus pond system, and (2) providing scientific basis for developing effective environmental management strategies for the Liuqing River watershed.
pH: Quantify using electrode method (HJ 1147-2020) and ST2100 pH meter (HLJC-243-2) [43]. BOD: Quantified using the standard Dilution and Inoculation Method (HJ 505-2009) with a 25 mL acid burette (Model B193) [44]. COD: Analyzed by the Potassium Dichromate Method (HJ 828-2017) employing a 50 mL acid burette (Model B192) [45]. TN: Determined through Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry (HJ 636-2012) using a UV-1750 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer (Model A11605031003CS) [46]. TP and NH3-N: Measured, respectively, by Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometry (GB 11893-1989) and Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry (HJ 535-2009), with measurements conducted on a DR2008 Visible Spectrophotometer (Serial No. 1429121) [47,48]. NO3−-N: Determined via ion chromatography (HJ 84-2016) using a DIONEX AQUION ion chromatograph (HLJC-231) [49]. DO: Detection using electrochemical probe method (HJ 506-2009) and JPB-607A portable dissolved oxygen analyzer (HLJC-285) [50]. PI: Determination of permanganate index (GB/T 11892-1989) and detection using a 25mL acid burette (B-S-25-2) [51]. Phytoplankton analysis: Species identification and quantification were performed under an optical microscope using standardized counting chambers, with results expressed as cell density (cells/L) and species diversity indices [52,53]. Chl-a: Quantified following Acetone Spectrophotometry (HJ 897-2017) [54].
2.3. Diversity Indices Calculation
Species Richness (S): Total number of identified phytoplankton species per sample.
where Pi denotes the proportion of individuals of the i-th species relative to the total phytoplankton count [55,56,57].
Shannon–Wiener Index (H): H = −∑(Pi × lnPi)
Simpson’s Diversity Index (P): D = 1 − ∑(Pᵢ2)
Pielou’s Evenness Index (E): E = H/lnS
2.4. Statistical and Spatial Analysis
All data were processed using SPSS 19.0 for statistical analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Water Quality Factors
This study conducted a systematic comparison of water quality parameters between the Jinluo lotus pond and its adjacent river system in Figure 2 and Figure 3. Results indicated that while the lotus pond exhibited elevated levels of water pH, BOD, COD, TN, and NH3-N compared to the river, the adjacent river conversely showed higher concentrations of TP, NO3−-N, Chl-a, and algal cell density. Statistical analysis revealed that none of the nine measured parameters demonstrated statistically significant differences (p > 0.05) in June 2022.
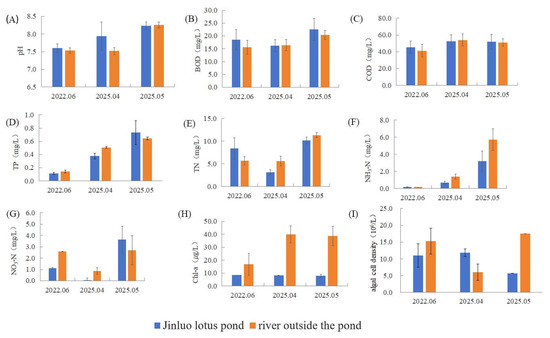
Figure 2.
Differences of (A) pH, (B) BOD, (C) COD, (D) TP, (E) TN, (F) NH3-N, (G) NO3−-N, (H) Chl-a, and (I) algal cell density in the water quality factors of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond.
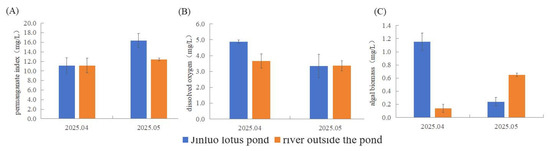
Figure 3.
Differences of (A) PI, (B) DO, and (C) algal biomass in the water quality factors of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond.
Relative to adjacent rivers, the lotus pond exhibited a significantly higher pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), algal cell density, and algal biomass (p < 0.05 for DO). In contrast, river water showed elevated levels of BOD, COD, TN, TP, NH3-N, NO3−-N, planktonic index (PI), and Chl-a, with a statistically significant difference in Chl-a (p < 0.05) in April 2025.
Compared to rivers, the lotus pond had a higher BOD, COD, TP, NO3−-N, and PI, with a significant difference in PI (p < 0.05). Conversely, river samples displayed a greater pH, TN, NH3-N, DO, Chl-a, algal cell density, and algal biomass, with Chl-a showing a significant difference (p < 0.05) in May 2025.
3.2. Water Quality Assessment
In accordance with China’s Surface Water Environmental Quality Standards (GB 3838-2002) [52], we evaluated the water quality of Jinluo lotus pond and its adjacent river using seven key parameters: BOD, COD, TN, TP, NH3-N, PI, and DO (Table 1). The results demonstrated severe exceedances of national standards for BOD, COD, and TN in both systems, reflecting significant organic pollution and nutrient loading. All sampling sites consistently exceeded Class V water quality thresholds—the most polluted classification under GB 3838-2002—indicating critically degraded water conditions throughout the study area.

Table 1.
The water quality assessment of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond.
3.3. The Correlation of Water Quality Factors
As shown in Table 2, BOD and COD exhibited a strong positive correlation (p < 0.01), demonstrating a close relationship between these key organic pollution indicators. A significant positive correlation was also observed between COD and chlorophyll-a (p < 0.05). Among nitrogen components, TN and NH3-N showed a particularly strong positive correlation (p < 0.01), implying shared sources or transformation processes.

Table 2.
The correlation of water quality factors of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond (2022).
The analysis revealed significant linkages between algal dynamics and multiple water quality parameters. Notably, algal cell density showed positive correlations with both NH3-N and Chl-a (all p < 0.05), suggesting a potential coupled biogeochemical cycling of these nutrients within the lotus pond ecosystem.
In Table 3, pH is significantly negatively correlated with COD (p < 0.05). BOD is significantly positively correlated with COD, TN, TP, NH3-N, Permanganate index, and dissolved oxygen (p < 0.01). COD is significantly positively correlated with TP, NH3-N, NO3-N, Permanganate index, dissolved oxygen, Algae cell density, and Algal biomass (p < 0.05). TP is significantly positively correlated with TN and NH3-N (p < 0.01), Permanganate index, and dissolved oxygen (p < 0.05). TN is significantly positively correlated with NH3-N, Permanganate index, and dissolved oxygen (p < 0.01), NO3-N (p < 0.05). NH3-N is significantly positively correlated with dissolved oxygen (p < 0.01). Permanganate index is significantly positively correlated with dissolved oxygen (p < 0.01). Dissolved oxygen is significantly positively correlated with Chl-a (p < 0.05). Algae cell density is significantly positively correlated with Algal biomass (p < 0.01).

Table 3.
The correlation of water quality factors of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond (2025).
3.4. Phytoplankton Diversity
Phytoplankton diversity indices—including species richness (S), Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H), Simpson diversity index (P), and Pielou evenness index (E)—were analyzed for the lotus pond. The results showed that there was no significant difference in the four diversity indicators in June 2022, April 2025, and May 2025 in Figure 4.
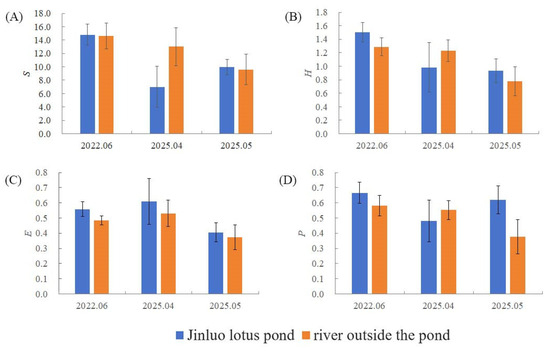
Figure 4.
(A) The Phytoplankton richness index (S), (B) Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H), (C) Simpson diversity index (P), and (D) Pielou evenness index (E) of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond.
There is no significant difference between the Phytoplankton cell density of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond. In order of cell density, the phytoplankton in the Jinluo lotus pond water are Cyclotella meneghiniana, Pseudanabaena sp., and Scenedesmus quadricauda, but in the river outside the pond, the water has P. sp., C. meneghiniana, and S. quadricauda in 2022 in Table 4. The phytoplankton in the Jinluo lotus pond water is Tetrastrum staurogeniaforme, but in the river outside the pond, the water has Tetrastrum staurogeniaforme, Coelastrum microporum, Scenedesmus quadricauda, and Scenedesmus bicaudatus in 2025 in Table 5.

Table 4.
The Phytoplankton cell density of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond (2022).

Table 5.
The Phytoplankton cell density of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond (2025).
4. Discussion
Ecological restoration strategies frequently incorporate three principal phytoremediation approaches: riparian vegetation buffer zones, ecological floating beds, and constructed wetlands, each offering distinct advantages for water quality improvement [58,59,60]. The effectiveness of these phytoremediation systems is primarily determined by two critical design parameters: appropriate plant species selection and optimal planting density, which collectively govern nutrient uptake capacity and treatment performance [61,62,63]. As fundamental elements of ecological engineering solutions, aquatic plants demonstrate marked variations in removal efficiencies depending on pollutant composition, with species-specific responses to different contaminant mixtures [64,65]. Research indicates that under eutrophic conditions, superior nutrient removal performance correlates strongly with three key plant traits: (1) high biomass production capacity, (2) elevated leaf dry matter content (LDMC), and (3) reduced specific leaf area (SLA), suggesting that wetland species exhibiting this combination of characteristics—particularly those with high biomass and LDMC coupled with low SLA values—may represent optimal candidates for nutrient-rich wastewater treatment applications [66]. Notably, engineered sequential wetland systems have proven particularly effective for purifying polluted urban waterways even in challenging cold climate conditions, demonstrating robust year-round treatment capabilities [67].
This study investigates the wastewater treatment capacity of constructed wetlands in the context of livestock effluent, particularly given the upstream location of a globally significant swine slaughtering center that generates substantial volumes of nutrient-rich wastewater containing elevated concentrations of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus compounds. Aquaculture effluents, similarly characterized by high nutrient loads, present significant environmental challenges with nitrogen and phosphorus being primary contributors to ecological degradation [68]. Research demonstrates that constructed wetland systems can reliably achieve total nutrient removal efficiencies exceeding 60% when treating bullfrog aquaculture wastewater [69], while Euryale ferox Salisb-based ecological ponds exhibit exceptional performance in both the in-situ and ex-situ treatment of shrimp aquaculture effluent, showing particularly high removal rates for total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) [70]. Advanced multi-stage treatment systems combining lotus ponds with surface flow wetlands have proven particularly effective for swine wastewater remediation, capable of transforming heavily contaminated influent into lightly polluted effluent through efficient nitrogen and phosphorus removal mechanisms [71], though these systems require careful operational management including seasonal lotus root harvesting during winter–spring periods and periodic sediment dredging to maintain treatment efficacy.
Constructed wetlands have emerged as a highly efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable solution for wastewater treatment, offering distinct advantages over conventional treatment systems in terms of operational simplicity, minimal maintenance requirements, and ecological compatibility [72]. The field has witnessed an evolutionary shift from basic treatment wetlands to sophisticated, multi-functional integrated systems. This transition is exemplified by the Integrated Constructed Wetland (ICW) concept, which adopts a comprehensive design philosophy that systematically incorporates four key dimensions—economic viability, social acceptance, environmental performance, and landscape integration—throughout all project phases from initial planning to long-term operation. Beyond their core treatment functions, these integrated wetland systems provide substantial secondary benefits, particularly in terms of biodiversity enhancement and habitat creation [73,74]. In this context, while performance assessments reveal that the Jinluo lotus pond demonstrates relatively modest water purification capabilities as a standalone treatment system, it nonetheless makes valuable contributions as a constructed wetland through its significant ecological services and exceptional aesthetic qualities that enrich the surrounding landscape.
Derived from Liebig’s Law of the Minimum, this paradigm suggests algal growth in aquatic ecosystems becomes N-limited when the aqueous N:P ratio falls below 16 (molar basis), while P-limitation occurs when ratios exceed 16 [75,76]. Alternative formulations using the TN:TP mass ratio propose N-limitation thresholds at TN:TP < 9 and P-limitation thresholds at TN:TP > 23 [42], with some studies establishing a nitrogen limitation threshold at TN:TP < 25 [77]. Our research shows that from 2022 to 2025, the nitrogen phosphorus ratio in this water area will decrease in Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond in Table 6.

Table 6.
The N:P of Jinluo lotus pond and the river outside the pond.
5. Conclusions
The main findings indicate that Jinluo lotus pond, as a low-density lotus pond artificial wetland system, has not shown significant water quality improvement effects. Based on these findings, we propose the following management recommendations: (1) a strategic expansion of both natural and constructed reed (Phragmites australis) communities along riparian zones, as these demonstrate superior nitrogen removal capabilities, a and (2) discontinuation of current lotus pond maintenance practices and an avoidance of further lotus cultivation area expansion, given their demonstrated tendency to exacerbate nitrogen accumulation in aquatic systems. This integrated approach would optimize nutrient removal efficiency while enhancing the overall ecological functionality of the watershed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L., Y.G., J.Z., Y.W. and J.H.; Methodology, B.L., Y.G., J.Z. and Y.W.; Software, Y.G., J.Z. and J.H.; Validation, Y.G.; Formal analysis, Y.G. and Y.W.; Investigation, Y.G.; Resources, B.L. and Y.G.; Data curation, Y.G. and J.H.; Writing—original draft, B.L., Y.G. and J.Z.; Writing—review & editing, Y.G., J.Z., Y.W. and J.H.; Visualization, Y.G.; Supervision, Y.G.; Project administration, B.L. and Y.G.; Funding acquisition, B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Water and Soil Conservation and Environmental Protection (No. STKF202307), and Shandong Province Youth Innovation and Technology Support Program for Higher Education Institutions (2020KJE009).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, D.; Gan, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Wu, S.; Du, L. Research status on remediation of eutrophic water by submerged macrophytes: A review. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 169, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimma, D.; Devi, O.R.; Laishram, B.; Ramesh, J.V.N.; Boddupalli, S.; Ayyasamy, R.; Tirth, V.; Arabil, A. Implications of climate change on freshwater ecosystems and their biodiversity. Desalination Water Treat. 2025, 321, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Kun, Y.; Sen, P.; Xin-Hua, Z.; Xia, L. Development of a two-dimensional eutrophication model in an urban lake (China) and the application of uncertainty analysis. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, A.A.; El-Hawary, A.M.; Abbas, M.H.H.; Mohamed, I.; Abdelhafez, A.A.; Bassouny, M.A. Reclamation of wastewater in wetlands using reed plants and biochar. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, P.; Kahil, T.; Mochizuki, J.; Schinko, T.; Satoh, Y.; Burek, P.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S.; Burtscher, R.; Langan, S.; et al. Global assessment of water challenges under uncertainty in water scarcity projections. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl-Wostl, C.; Knieper, C.; Lukat, E.; Meergans, F.; Schoderer, M.; Schütze, N.; Schweigatz, D.; Dombrowsky, I.; Lenschow, A.; Stein, U.; et al. Enhancing the capacity of water governance to deal with complex management challenges: A framework of analysis. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 107, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, D. Research on Regional Disparities, Dynamic Evolution, and Influencing Factors of Water Environment Governance Efficiency in China. Water 2025, 17, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.S.; Van Donk, E.; Declerck, S.A.J.; Helmsing, N.R.; Hidding, B.; Nolet, B.A. Effect of macrophyte community composition and nutrient enrichment on plant biomass and algal blooms. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Yan, P.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Guo, Z.; et al. Constructed wetlands for pollution control. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rasid, N.S.; Naim, M.N.; Che Man, H.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Mokhtar, M.N. Evaluation of surface water treated with lotus plant; Nelumbo nucifera. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.M.; Hayder, G. Recent studies on applications of aquatic weed plants in phytoremediation of wastewater: A review article. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Peng, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, J.; Wang, H. Phytoremediation of nutrients and organic carbon from contaminated water by aquatic macrophytes and the physiological response. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Gao, J. Design and Application of an Integrated Landscape Water Purification Device: Long-Term Performance in Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal. Water 2025, 17, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C. Global change refugia could shelter species from multiple threats. Nat. Rev. Biodivers. 2025, 1, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.S.; Griffiths, J.A.; Higgitt, D.; Xu, S.; Zhu, F.; Tang, Y.-T.; Xu, Y.; Thorne, C.R. “Sponge City” in China—A breakthrough of planning and flood risk management in the urban context. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Solomun, M.K.; Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Zhao, W.; Kalantari, Z. Wetlands as nature-based solutions for water management in different environments. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 33, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, N.R.; Fallowfield, H.; Baring, R. Spatial performance assessment of reed bed filtration in a constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, F.; Wu, F.; Bryan, B.A. Costs and benefits of constructed wetlands for meeting new water quality standards from China’s wastewater treatment plants. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ji, B.; Liu, R.; Ren, B.; Wei, T. Constructed treatment wetland: Glance of development and future perspectives. Water Cycle 2020, 1, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, A.; Shebeshe, N.; Kloos, H.; Belay, S. Suitability of nutrients removal from brewery wastewater using a hydroponic technology with Typha latifolia. BMC Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, H.R.; Mufarrege, M.M.; Pinciroli, M.; Di Luca, G.A.; Maine, M.A. Morphological Response of Typha domingensis to an Industrial Effluent Containing Heavy Metals in a Constructed Wetland. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisey, E.; Laffray, X.; Contoz, O.; Cavalli, E.; Mudry, J.; Aleya, L. The Bioaccumulation Performance of Reeds and Cattails in a Constructed Treatment Wetland for Removal of Heavy Metals in Landfill Leachate Treatment (Etueffont, France). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 1723–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, M.; Gennaro, M.C.; Tuttolomondo, T.; Leto, C.; La Bella, S.; Singer, A.C. Research focusing on plant performance in constructed wetlands and agronomic application of treated wastewater—A set of experimental studies in Sicily (Italy). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S. Site test of phytoremediation of an open pond contaminated with domestic sewage using water hyacinth and water lettuce. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Ponraj, M.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Mohamad, S.E.; Din, M.F.M.; Taib, S.M.; Sabbagh, F.; Sairan, F.M. Perspectives of phytoremediation using water hyacinth for removal of heavy metals, organic and inorganic pollutants in wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 163, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Liu, F.; Song, X.; Zou, G. Combined ozonation and aquatic macrophyte (Vallisneria natans) treatment of piggery effluent: Water matrix and antioxidant responses. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, X.; Wu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xiong, R.; Ye, S. The efficiency and risk to groundwater of constructed wetland system for domestic sewage treatment—A case study in Xiantao, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaharuddin, S.; Chan, N.W.; Zakaria, N.A.; Ab Ghani, A.; Chang, C.K.; Roy, R. Constructed Wetlands as a Natural Resource for Water Quality Improvement in Malaysia. Nat. Resour. 2014, 5, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billore, S.K.; Prashant; Sharma, J.K. Treatment performance of artificial floating reed beds in an experimental mesocosm to improve the water quality of river Kshipra. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Meng, H.; Yan, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, X. Wetland Park Planning and Management Based on the Valuation of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Tieling Lotus Lake National Wetland Park (LLNWP), China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, X. Purification and utilization of garlic processing wastewater in lotus pond wetlands. Water Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhao, Y.J.; Gao, Y. Seasonal influence of reed (Phragmites australis) and lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) on urban wetland of Yi river. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 7891–7900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.S.; Meng, F.L.; Meng, R.; Huang, C.H.; Li, Y.W.; Xi, B.D.; Shu, J.M. In Situ Enclosure Experiment on Nelumbo nucifera for Eutrophication Control in Baiyangdian Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2013, 11, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hou, W.-H. Inhibitory effects of liquor cultured with Nelumbo nucifera and Nymphaea tetragona on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.Q.; Gou, M.M. Study on the influence of lotus planting in Wuliangsu of Inner Mongolia on water environment. J. Environ. Health 2018, 35, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y. Influence of the island with grass and the island with trees to water quality in Yihe River, China. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 121, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ci, H.X.; Qi, S.C.; Su, Y.X. Seasonal changes of phytoplankton diversity and assessment of water quality in four tributaries of Yi River. Res. Environ. Sci. 2009, 22, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Qi, S.C.; Su, Y.X. Seasonal changes of phytoplankton diversity and water quality in Yi River and Beng River. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 32, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Su, Y.X.; Qi, S.C. Phytoplankton and evaluation of water quality in Yi River watershed. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 544–548. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J. Water Quality Assessment and Management Strategies for Nishan Reservoir, Sihe River, and Yihe River Based on Scientific Evaluation. Water 2024, 16, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.W.; Fang, S.Y.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Bu, Q.Q.; Xue, Y.H. Analysis of the plant N and P sequestration from common reed and common reed+ cattail communities in wetland soil in Qinhu Lake of northern Jiangsu, China. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guildford, S.J.; Hecky, R.E. Total Nitrogen, Total Phosphorus, and Nutrient Limitation in Lakes and Oceans: Is There A Common Relationship? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 1147-2020; Water Quality-Determination of pH-Electrode Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- HJ 505-2009; Water Quality-Determination of Biochemical Oxygen Demand After 5 Days (BOD5) for Dilution and Seeding Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- HJ 828-2017; Water Quality-Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand-Dichromate Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- HJ 636-2012; Water Quality-Determination of Total Nitrogen-Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality-Determination of Total Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. State Administration of Technical Supervision of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- HJ 535-2009; Water Quality-Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen-Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- HJ 84-2016; Water Quality-Determination of Inorganic Anions (F−, Cl−, NO2−, Br−, NO3−, PO43−, SO32−, SO42−)-Ion Chromatography. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- HJ 506-2009; Water Quality-Determination of Dissolved Oxygen-Electrochemical Probe Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB 11892-89; Water Quality-Determination of Permanganate Index. Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China and General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- HJ 1296-2023; Technical Guidelines for Water Ecological Monitoring-Aquatic Organism Monitoring and Evaluation of Lakes and Reservoirs (on Trial). Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- HJ 897-2017; Water Quality-Determination of Chlorophyll a-Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Borics, G.; Abonyi, A.; Salmaso, N.; Ptacnik, R. Freshwater phytoplankton diversity: Models, drivers and implications for ecosystem properties. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colares, G.S.; Dell’Osbel, N.; Wiesel, P.G.; Oliveira, G.A.; Lemos, P.H.Z.; da Silva, F.P.; Lutterbeck, C.A.; Kist, L.T.; Machado, Ê.L. Floating treatment wetlands: A review and bibliometric analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 714, 136776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Zhao, J.-C. Research and application status of ecological floating bed in eutrophic landscape water restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.-Y.; Wang, W.-H.; Li, H.-M.; Yue, Z.-Q.; Chen, W.; Xue, F.-R. Strengthen the purification of eutrophic water and improve the characteristics of sediment by functional ecological floating bed suspended calcium peroxide and sponge iron jointly. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, J.N.; Montas, H.J. An analysis of performance models for free water surface wetlands. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Liu, S.; Li, R.; Sun, H.; Feng, J.; Cheng, X.; Yao, J. Research on the purification enhancement of ecological ponds: Integrating water cycle optimization and plants layout. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabokrouhiyeh, N.; Bottacin-Busolin, A.; Savickis, J.; Nepf, H.; Marion, A. A numerical study of the effect of wetland shape and inlet-outlet configuration on wetland performance. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 105, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; He, S.; Miao, Y. A comparison of the growth status, rainfall retention and purification effects of four green roof plant species. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.-A.; Uchiyama, K.; Inadama, D.; Ishida, Y.; Yamagiwa, K. Performance evaluation of laboratory scale up-flow constructed wetlands with different designs and emergent plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7239–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenzel, P.; Brunings, O.; Esler, K.J.; le Maitre, D.; Rebelo, A.J. How well do endemic wetland plant species perform in water purification? Wetlands 2024, 44, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, C.; Sheng, L.; Zhuang, J. Purification effect of sequential constructed wetland for the polluted water in Urban River. Water 2020, 12, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Imron, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Said, N.S.M.; Rahim, N.F.M.; Alnawajha, M.M.; Abu Hasan, H.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F. Potential of valuable materials recovery from aquaculture wastewater: An introduction to resource reclamation. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2954–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Gong, S.; Xie, Y. The Performance of a multi-stage surface flow constructed wetland for the treatment of aquaculture wastewater and changes in epiphytic biofilm formation. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, L.; Hua, J.; Rong, H.; Gu, Z. In- situ and ex- situ purification effect of ecological ponds of Euryale ferox Salisb on shrimp aquaculture. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lei, J.; Guo, C. Application studies on purification of piggery waste water by multi-level artificial system of ecological lotus pond-surface flow wetland. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, C.; Scholz, M. Assessment of pre-digested piggery wastewater treatment operations with surface flow integrated constructed wetland systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7713–7723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.; McInnes, R. Integrated Constructed Wetlands (ICW) for livestock wastewater management. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5498–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, M.; Harrington, R.; Carroll, P.; Mustafa, A. The Integrated Constructed Wetlands (ICW) concept. Wetlands 2007, 27, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, F.; Lepori, F. Can we predict nutrient limitation in streams and rivers? Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Jin, W.; Wu, J. Ecosystem N:P stoichiometric ratios determine the catchment surface water N:P ratio through subsurface hydrological processes. CATENA 2020, 194, 104740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, G.; Hipsey, M.; Parparov, A.; Wagner, U.; Makler, V.; Zohary, T. Implementation of ecological modeling as an effective management and investigation tool: Lake Kinneret as a case study. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1697–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).