Abstract
This study evaluated the pollutant removal efficiency of two decentralized wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) located in the high-altitude southern Andes of Ecuador, Acchayacu and Churuguzo, from 2015 to 2024. Acchayacu previously operated using an upflow anaerobic filter (UAF), and from 2021, it transitioned to using vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs). In contrast, Churuguzo employs surface-flow constructed wetlands (SF-CWs). These systems were assessed based on parameters such as the five-day biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total phosphorus, organic nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen, total solids, fecal coliforms (TTCs), and total coliforms (TCs). The data were divided into two subperiods to account for the change in technology in Acchayacu. Statistical analysis was conducted to determine whether significant differences existed between the treatment efficiencies of these technologies, and the SF-CW was found to consistently outperform both the UAF and VSSF-CW in removing organic matter and microbial pollutants. This difference is likely attributed to the longer hydraulic retention time, lower hydraulic loading rate, and vegetation type. The findings highlight the environmental implications of treatment technology selection in WWTPs, particularly regarding the quality of receiving water bodies and their potential applications for public health, proper water resource management, and the design of decentralized systems in high-altitude regions, especially in developing countries.
1. Introduction
Water is a vital natural resource for life, and the growing demand for water due to continuous human development makes it a valuable resource with intrinsic cultural, social, and environmental value [1].
Wastewater is a combination of liquid waste from different origins, including residential, industrial, and institutional. It presents both an environmental risk and reuse opportunities, especially in water-scarce regions [2,3].
Wastewater composition varies depending on the local socioeconomic situation and local customs [4]. Determining the chemical composition of domestic wastewater is essential for evaluating existing treatment methods and selecting the most appropriate facilities [5], as well as determining its impact on the receiving water bodies [6,7]. Water quality analysis also provides information on its potential for reuse after treatment, including applications in agricultural and landscape irrigation, urban uses, and limited residential purposes [8].
Wastewater treatment plays an important role in ensuring the sustainability of water resources, particularly in high-altitude regions where climatic, geographical, and social factors can significantly influence wastewater treatment systems’ efficiency. In this context, applying decentralized systems is important since they are a viable alternative, especially in small and dispersed rural communities [9].
Constructed wetlands are a cost-effective, adaptable, and sustainable solution that have been documented since 1912 according to early records [10]. These systems use methods that harness the natural capacity of substrates, microorganisms, and aquatic macrophytes, which use their roots as a barrier to retain solids and support bacterial growth [11,12]. Pollutant removal occurs through multiple mechanisms, including sedimentation, microbial degradation, absorption, and plant uptake. It integrates microbial activity, oxygen fixation by plants, and a bed composed of gravel, sand, or other inert materials, which function as both a filter and structural support for roots [13].
Two main types of constructed wetlands are recognized: surface-flow constructed wetlands (SF-CWs) and subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (SSF-CWs) [14]. Their performance can vary depending on factors such as the design configuration, vegetation type, climatic conditions, and the operational conditions of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs).
These nature-based solutions have proven effective at reducing energy consumption while efficiently removing organic matter and microbiological contaminants, making them both economically and energetically sustainable [15]. In the case presented by Diaz and Paredes [16], cultivating specific plant species in constructed wetlands created opportunities for production and commercialization, such as biofuel generation.
According to Córdova et al. [17], in Ecuador, although 84.85% of the population has access to safe drinking water and 90.7% has access to sewer systems or septic tanks, proper wastewater management is not always guaranteed, particularly in rural areas where treatment occurs either on-site or is entirely lacking. The state of wastewater treatment in Ecuador reveals that only 26.3% of the total water distributed nationwide undergoes treatment, with the Ecuadorian highlands accounting for 22.8% of this treated volume [18].
Since 1984, the municipal company responsible for water supply and wastewater management, ETAPA-EP, has been working to optimize environmental sanitation within its jurisdiction and to improve the water quality of the rivers flowing through Cuenca City. As part of this effort, several centralized and decentralized wastewater treatment projects have been implemented [19].
Despite their potential, technologies such as UAFs, SF-CWs, and VSSF-CWs are rarely evaluated under comparable conditions, particularly in high-altitude regions. This represents a significant research gap, as performance data may be influenced by climatic characteristics or other external factors. Therefore, evidence-based comparisons are crucial to support better-informed technology selection, particularly in small communities where implementing decentralized systems is essential.
To address these gaps, this study compares pollutant removal efficiencies in two wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) with similar configurations. Both facilities carry out a primary treatment using a sedimentation tank, a secondary treatment consisting of a septic tank, and a tertiary treatment using constructed wetlands. The main difference between them lies in the type of technology used in the tertiary treatment. Acchayacu operated with a UAF system until 2021, after which it transitioned to a VSSF-CW planted with paramo straw (Calamagrostis intermedia). In contrast, the Churuguzo WWTP uses an SF-CW planted with totora (Scirpus californicus). This natural experiment setup provides a valuable opportunity to compare these treatment technologies under consistent climatic and geographic conditions.
Therefore, a hypothesis is proposed suggesting that high-altitude conditions characterized by low temperatures and significant daily climatic variability may significantly affect the pollutant removal performance of wastewater treatment systems. These environmental factors could impact key biological processes such as microbial activity, nitrification, and plant growth under such conditions.
This study evaluates the performances of the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs by analyzing their efficiency in removing various pollutants, using parameters such as the five-day biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total phosphorus (TP), ammonia nitrogen (N_amo), organic nitrogen (N_org), suspended solids (SSs), total solids (TSs), total coliforms (TCs), and fecal coliforms (TTCs). Additionally, it assesses the impact of technology changes and differences in system configuration. The findings offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of constructed wetlands in high-altitude environments, promoting the adequate and sustainable management of water resources in decentralized wastewater treatment systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ubications of WWTPs
This study was conducted at two decentralized wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), Acchayacu and Churuguzo, which are located in the parishes of Tarqui and Victoria of Portete, respectively, in the Azuay province of the southern Ecuadorian Andes (Figure 1). These WWTPs are approximately 14 km apart. Acchayacu is located at 2689 m above sea level (m.a.s.l.), and Churuguzo is at 2628 m.a.s.l.; they experience similar climatic conditions. The effluents from both systems discharge into brooks that flow into the Irquis river, a tributary of the Tarqui river. This water body plays a crucial role in supporting the agricultural and livestock activities of the surrounding communities.
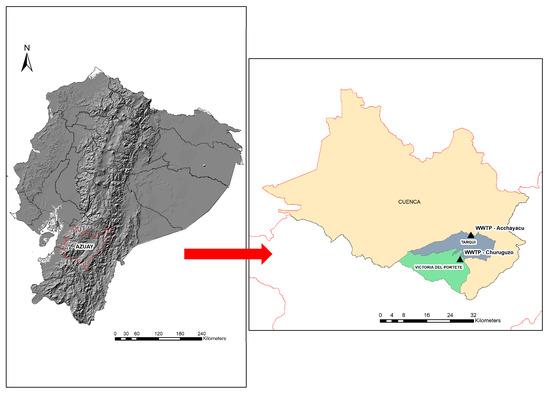
Figure 1.
The locations of the Acchayacu (Tarqui parish) and Churuguzo (Victoria del Portete parish) wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), Azuay, Ecuador.
2.2. Climate Analysis of Study Areas
Studies such as that of Operacz et al. [20] have demonstrated how climatic variability significantly affects the efficiency of constructed wetlands, as an increase in temperature can enhance the removal of parameters such as BOD5 and COD by promoting microbial activity. To account for these climatic influences, temperature and precipitation data were obtained from the “Morascalle” station located in the Tarqui parish and precipitation data from the “Portete” station located in Victoria Portete parish. These stations are part of the meteorological network of the Water and Soil Management Program (PROMAS) at the University of Cuenca. The aforementioned stations are illustrated in Figure A12.
To compare the precipitation data from the Morascalle and Portete stations, a statistical analysis based on hypothesis tests was conducted. At first, descriptive and graphical explorations were performed using box diagrams and a precipitation value graph for each station to assess the differences between the two locations.
Subsequently, the Shapiro–Wilk test was applied to assess the normality of the data. If the data followed a normal distribution, a t-test was applied; otherwise, the Wilcoxon non-parametric test was used. This approach allowed for determining whether there was a significant difference in precipitation between the two sectors.
2.3. Technical Characteristics of the WWTPs
In these communities, the wastewater management system consists solely of a collection network. As previously described, the treatment process includes an inlet sedimentation tank, a septic tank, and the treatment stage, which is the focus of this study. In Acchayacu, this final stage transitioned from an upflow anaerobic filter (UAF) to vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs).
In the case of Churuguzo, the WWTP includes three constructed wetlands, through which the treated water flows before it is collected by a shared outlet pipe. These wetlands are planted with aquatic macrophyte species, specifically totora (Scirpus californicus). In both systems, the wetlands are filled with gravel of varying sizes to prevent clogging at the wastewater inlet.
These systems are decentralized, meaning that domestic wastewater is treated close to its point of origin, without a long sewer network that transports it to a centralized treatment plant. Such systems are particularly effective in small communities where geographic constraints hinder access to large-scale sewer infrastructure. In both WWTPs, the constructed wetlands receive effluent from a pretreatment stage, which comprises a sedimentation tank followed by a septic tank. At Acchayacu, the system includes three vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs) planted with paramo straw (Calamagrostis intermedia), each measuring 5.5 m in length, 5.1 m in width, and 1 m in depth, designed to serve a population of 720 inhabitants. In contrast, Churuguzo features two larger surface-flow constructed wetlands (SF-CWs), each measuring 34.5 m in length, 25 m in width, and 1.5 m in depth, designed to serve a population of 4560 inhabitants.
2.4. Analysis of Operating Parameters in Constructed Wetlands
Hydraulics are an important factor in the performance of a constructed wetland, as they directly influence its treatment capacity. In particular, the hydraulic retention time (HRT) and the hydraulic loading rate (HLR) play fundamental roles in optimizing treatment efficiency.
The HLR is a key factor in designing and operating constructed wetlands. It represents the relationship between the influent flow rate and the available treatment surface area, enabling assessments of the system’s hydraulic capacity and treatment efficiency. The HLR can be calculated using the following formula (Equation (1)):
where the symbols have the following meanings:
HLR = Hydraulic loading rate (m3/(m2 × day));
Q = Design flow or average daily flow (m3/day);
A = Effective surface area of the system (m2).
An adequate HRT (Equation (2)) is crucial to preventing system overloading and ensuring optimal treatment performance. Different types of constructed wetlands have characteristic HRT values. For instance, horizontal-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands operate within a range of 4 to 5 days, while vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands have shorter retention times, ranging from 2 to 6 h [21].
where the symbols have the following meanings:
HRT = Hydraulic retention time;
Q = Design flow or average daily flow (m3/day);
V = Wetland volume (m3).
Although VSSF-CWs are typically operated under unsaturated conditions, those at the Acchayacu WWTP were designed to function under saturated conditions. Consequently, the entire volume of the wetland was considered when calculating the HRT.
The organic loading rate (OLR) (Equation (3)) was calculated to quantify the concentration of organic pollutants entering the system, which is essential for determining its treatment capacity. This parameter provided valuables insights into the performances of constructed wetlands and their efficiency in removing organic contaminants.
where the symbols have the following meanings:
Q = Influent flow rate (m3/day);
C = Pollutant concentration (BOD or COD in kg/m3);
A = Total surface area of the system (m2).
2.5. Sampling and Analyzed Parameters
At the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs, sampling and analyses were conducted by personnel from the public water and sanitation company ETAPA on different dates and under varying climatic conditions. This approach enhanced the representativeness of the analyses, aligning with the requirements of the Ecuadorian Technical Standard NTE INEN 2169:2013 [22]. All analyses were performed in ETAPA’s accredited laboratory, ensuring the reliability and validity of the results obtained.
The wastewater samples were analyzed at the ETAPA-EP’s accredited water laboratory to determine the following parameters: electrical conductivity (Cond), five-day biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total phosphorus (TP), nitrogen ammonia (N_amo), organic nitrogen (N_org), dissolved oxygen (OD), hydrogen potential (pH), suspended solids (SSs), total solids (STs), total coliforms (TCs), and fecal coliforms (TTCs).
2.6. Comparison of Pollutant Removals Between WWTPs
The data were analyzed using R-Studio version 2024.12.1 software (Kousa Dogwood) [23], beginning with data cleaning, which involved an initial review to eliminate outliers (extreme values) and dates with missing records. These entries were excluded as they were not representative and could distort the results when compared to the other data. To determine statistical differences, t-tests were applied for normally distributed data, while Wilcoxon tests were used for non-normal distributions. This analysis aimed to evaluate which of the wastewater treatment technologies implemented at the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs demonstrated a better pollutant removal efficiency. No correction for multiple comparisons was applied due to the exploratory nature of this study.
Efficiency was determined for each analyzed parameter (Equation (4)) by comparing the influent and effluent concentrations at the WWTPs and between the technologies evaluated:
where the symbols have the following meanings:
E = Parameter removal efficiency in the system (mg/L);
CE = Parameter influent concentration analyzed;
CS = Parameter effluent concentration.
In WWTP studies, data often deviate from a normal distribution due to several factors. According to Cantelmo and Ferreira [24], climatic variations in temperature and precipitation significantly affect the measurements. Additionally, biases may arise from outliers, fluctuations in pollutant loads, and the timing of sample collection. For this reason, the Shapiro–Wilk test was applied, which evaluates whether a dataset follows a normal distribution or not [25]. When normality was not found, the Wilcoxon test was used, particularly for comparing related samples to evaluate differences between data groups [26].
Finally, line graphs were used to illustrate the distribution and trends in the removal efficiency for both WWTPs and the analyzed technologies. These visualizations allowed for a comparative assessment of the results, identifying patterns and evaluating the effectiveness between the VSSF-CW with paramo straw, the SF-CW with totora, and the upflow anaerobic filter (UAF).
3. Results
This study compared the efficiency of the depuration of the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs, which are both located in high-altitude regions of the Ecuadorian Andes. The analysis included different wastewater treatment technologies: two types of constructed wetlands and an upflow anaerobic filter (UAF). The results of this analysis are presented in the following sections.
A comparison of these results is presented in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3, which show the removal efficiency as a percentage, indicating the extent of pollutant reduction achieved by each wastewater treatment technology.

Table 1.
A general comparison of treatment efficiency between the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs during 2015–2020.

Table 2.
Comparison of treatment efficiency between WWTP after technology change (vertical sub-superficial flow wetlands and superficial flow wetlands) for 2021–2024.

Table 3.
A comparison of treatment efficiency at the Acchayacu WWTP before and after the transition from UAF to VSSF-CW technology.
3.1. Analysis of Meteorological Parameters
The average precipitation recorded at the Morascalle (737.98 mm/year) and Portete (532.18 mm/year) stations does not show a statistically significant difference, according to the results of the t-test (p = 0.085) and the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test (p = 0.296). Although the mean precipitation at Portete is higher, the confidence intervals for the difference in means include zero values, indicating that the null hypothesis of equality between the stations cannot be rejected. Furthermore, the data distributions of the stations are similar (Figure 2 and Figure 3), suggesting that the observed variations could occur by chance. However, it is important to note that the presence of missing data (10 from Morascalle and 50 from Portete) may have influenced the results.
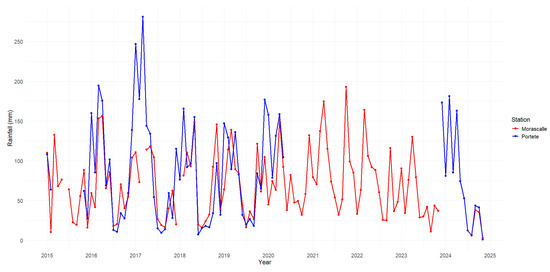
Figure 2.
Comparison of rainfall data from Acchayacu and Churuguzo stations.
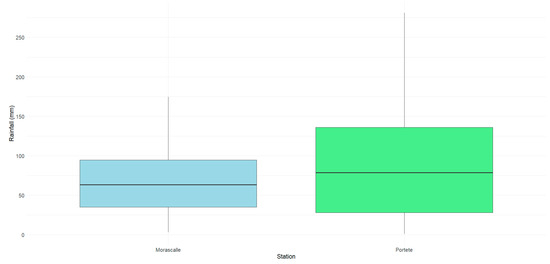
Figure 3.
Precipitation distribution analysis.
The climatic conditions in the study area were evaluated using data from the Morascalle station, which is the only meteorological station in the region. The average daily temperature was 12.6 °C, with maximum and minimum averages of 22.83 °C and 3.16 °C, respectively. During the analyzed period (2015 to 2024), extreme temperatures of 26.7 °C (maximum) and −4.1 °C (minimum) were recorded. The lowest temperatures typically occurred in June, July, and August, fluctuating between −1.4 and 8.2 °C, with July typically being the coldest month. Conversely, the highest temperatures were observed from January to March, fluctuating between 19.3 and 26.7 °C. In 2024, the highest recorded temperature (26.7 °C) occurred in October.
3.2. Comparison of Removal Efficiency Between Treatment Technologies
3.2.1. Efficiency Comparison of the Upflow Anaerobic Filter (UAF) at the Acchayacu WWTP and the Surface Flow Constructed Wetland (SF-CW) at the Churuguzo WWTP During 2015–2020
The statistical analysis of the WWTPs from 2015 to 2020 enabled a comparison of the removal efficiency of different parameters by the UAF reactor of the Acchayacu WWTP and the SF-CW at the WWTP Churuguzo.
The results indicate that the SF-CW at Churuguzo exhibited higher efficiency, achieving superior removal rates across most of the analyzed parameters (Figure A14). These removal efficiencies were calculated based on the influent and effluent concentrations of the different parameters, as presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5. The hydraulic retention time (HRT) of the UAF at Acchayacu ranged from 2.13 to 6.4 h, with an average of 3.19 h, whereas at the SF-CW at Churuguzo, it was 1.13 days. Additionally, the calculated hydraulic loading rate (HLR) was 31.75 cm/day for the SF-CW, while the UAF reactor recorded an HLR of 525 cm/day.
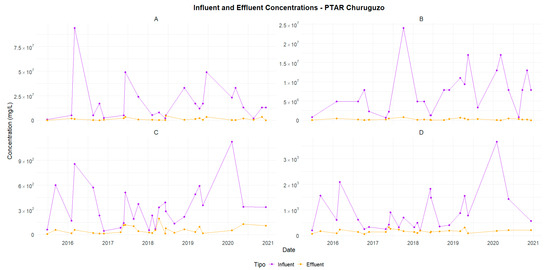
Figure 4.
Churuguzo—Comparison of influent and effluent concentrations (2015–2020): (A) TC, (B) TTC, (C) BOD5, and (D) COD.
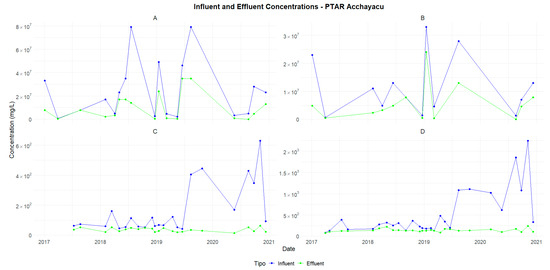
Figure 5.
Acchayacu—Comparison of influent and effluent concentrations (2015–2020): (A) TC, (B) TTC, (C) BOD5, and (D) COD.
Regarding organic matter removal, the BOD5 shows that the Churuguzo WWTP achieved an average efficiency of 74.30%, surpassing that of Acchayacu, which recorded an average of 60.20%. Similarly, the COD removal efficiencies were 68.44% and 48.91% for Churuguzo and Acchayacu, respectively. For SSs, the UAF reactors at Acchayacu showed a removal efficiency of 71.79%, compared with 83.46% obtained for the Churuguzo WWTP. For microbiological pollutants, the SF-CW at Churuguzo exhibited a higher efficiency in removing total coliforms (TCs) (85.24%) and fecal coliforms (TTCs) (92.85%), compared to the UAF reactor at Acchayacu, for which values of 58.65% and 53.18%, respectively, were recorded. Statistical analyses comparing the UAF reactor and the SF-CW for the BOD5, COD, TC, and TTC parameters revealed a significant difference, as indicated by p-values for the Wilcoxon test of 0.024, 0.028, 0.001, and 5.92 × 10−5, respectively.
In contrast to the previously mentioned parameters, smaller differences were found for suspended solids (SSs) (p-value = 0.12) and total phosphorus (TP) (p-value = 0.74) between the two WWTPs. However, the SF-CW at Churuguzo still demonstrated a better overall performance, as shown in Table 1. According to the Wilcoxon test results, there was insufficient statistical evidence to confirm that the removal efficiencies for these parameters were significantly different.
At the Acchayacu WWTP, the UAF reactor presented an ammonia nitrogen (p-value = 0.049) removal efficiency of 20.43%, whereas the SF-CW at Churuguzo demonstrated a higher average efficiency of 33.17%. A similar trend was observed for organic nitrogen (N_org), (p-value = 0.82), with Acchayacu attaining an average removal efficiency of 57.16%, while Churuguzo achieved 68.86%.
The pH results indicate a slight decrease in the influent values compared to the effluent values in Acchayacu, with an average of 6.98, remaining within the neutral range of 6.5 to 8.5 (Figure A1). In contrast, Churuguzo shows a more pronounced pH decline, reaching a minimum of 5.41 (Figure A2). Regarding dissolved oxygen (DO) (p-value = 0.26), the Acchayacu WWTP records an average influent DO concentration of 4.32 mg/L, with peaks of 7.27 mg/L. However, the effluent data show a slight decrease, with an average of 4.94 mg/L, reflecting oxygen consumption due to the aerobic degradation of organic matter (Figure A3). Conversely, Churuguzo exhibits a notable increase in DO levels, with an average influent value of 2.26 mg/L and an effluent average of 4.52 mg/L, reaching a maximum of 6.1 mg/L. This suggests that greater oxygenation occurred in the horizontal subsurface flow wetland (Figure A4).
Figure A13 shows the variability in removal efficiency across different parameters, which may be attributed to fluctuating influent pollutant concentrations that occasionally exceed the treatment capacity of the UAF systems. Moreover, seasonal climate variations and maintenance practices could contribute to this variability.
The organic loading rate (OLR) calculations, based on the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) data from Acchayacu and Churuguzo, indicate that both treatment systems operate under comparable BOD5 loading conditions (0.202 kg/m2·day for Acchayacu and 0.197 kg/m2·day for Churuguzo). However, notable differences were observed in COD loading, with Acchayacu registering 0.762 kg/m2·day compared to 0.620 kg/m2·day in Churuguzo.
3.2.2. Efficiency Comparison of Two Constructed Wetlands Types at the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs During the Period 2021–2024
Before analyzing the removal efficiency of the wetland technologies implemented in the two WWTPs, the corresponding operational parameters, namely the hydraulic loading rate (HLR) and hydraulic retention time (HRT), are presented. Thus, the calculated HLR of the VSSF-CW at Acchayacu was 88.29 cm/day compared to 31.75 cm/day for the SF-CW at Churuguzo. Regarding HRT, each wetland unit in Acchayacu exhibited an HRT of 0.38 days, totaling 1.13 days across the three wetlands in series, compared to 4.72 days and 2.36 per wetland in Churuguzo.
However, the SF-CW in Churuguzo consistently demonstrated better performance in pollutant removal (Figure 6). The removal efficiencies were calculated based on the concentrations of the different parameters, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Both wetland systems achieved a high removal efficiency for parameters such as SSs, with values exceeding 95% (Table 2).
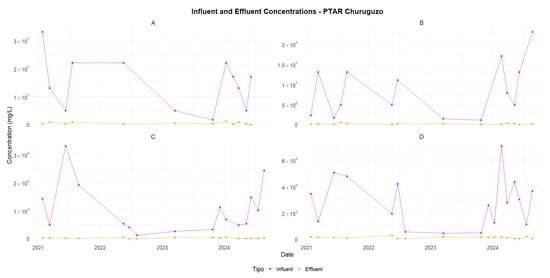
Figure 6.
Churuguzo—Comparison of influent and effluent concentrations (2021–2024): (A) TC, (B) TTC, (C) BOD5, and (D) COD.
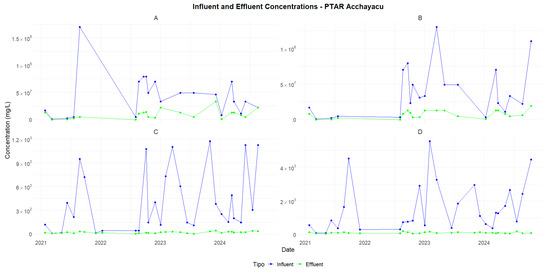
Figure 7.
Acchayacu—Comparison of influent and effluent concentrations (2021–2024): (A) TC, (B) TTC, (C) BOD5, and (D) COD.
Although both systems are effective in treating wastewater, the results suggest that the Churuguzo SF-CW is more efficient in removing organic matter and microorganisms.
The SF-CW in Churuguzo showed a higher efficiency in key parameters such as TC and TTC, with removal rates of 94.71% and 96.33%, respectively, compared to 69.18% and 75.06% for the VSSF-CW in Acchayacu. In terms of organic matter, Churuguzo also outperformed Acchayacu, reaching removal efficiencies of 95.56% for BOD5 (p-value = 0.001) and 89.41% in COD (p-value = 0.12), exceeding the figures of 83.90% and 82.81%, respectively, recorded in Acchayacu. These differences were confirmed using the Wilcoxon test, which showed that the p-values for BOD5 and COD indicated statistically significant differences between the two WWTPs, suggesting a variation in the removal efficiency. Likewise, microbiological parameters, such as TC and TTC, also revealed significant differences between both treatment plants, with p-values of 0.0013 and 3.19 × 10−50, respectively. In contrast, for suspended solids (SSs), both plants have a p-value of 0.064, indicating no statistically significant difference between the plants for this parameter.
Regarding SSs and TSs, although the differences were minor, the SF-CW in Churuguzo showed a slightly better performance. However, the differences were not statistically significant, with p-values of 0.063 and 0.015, respectively. In terms of nutrient removal, specifically organic nitrogen and TP, both systems showed moderate efficiencies, but the SF-CW in Churuguzo achieved better results, as shown in Table 2. The statistical analysis of the removal efficiencies for organic nitrogen (N_org), ammoniacal nitrogen (N_amo), and total phosphorus (TP) between the two WWTPs indicated non-statistically significant differences, with p-values of 0.566, 0.061, and 0.482, respectively, suggesting a comparable performance between the wetland technologies studied.
The pH in Acchayacu remains within a normal range, with no significant difference between influent and effluent values (7.1–7.4) and only a slight decrease in the effluent (Figure A5). In contrast, Churuguzo exhibits a more noticeable decrease in pH, reaching a minimum effluent value of 5.73; however, this still falls within acceptable limits (Figure A6). For dissolved oxygen, DO (p-value = 0.86), Acchayacu shows an increase from 3.00 mg/L at the inlet to 4.74 mg/L at the effluent, suggesting moderate oxygenation (Figure A7). In comparison, in Churuguzo, the influent oxygen levels were low, reaching a maximum of 6.9 mg/L, indicating a higher degree of oxygenation within the wetland system (Figure A8).
3.2.3. Comparison Between Different Treatment Technologies of of Acchayacu WWTP
The change in the Acchayacu WWTP treatment system from an upflow anaerobic filter (UAF) to vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs) in 2021 resulted in a notable improvement in effluent quality. The removal efficiency of parameters such as BOD5 increased from an average of 60.2% with the UAF reactor to 83.9% after implementing the three VSSF-CWs. Similarly, DO removal improved from 48.91% with the UAF to 82.8% with the VSSF-CW system (Table 3). Moreover, the removal of microbiological parameters such as TTCs and TCs showed significant improvements, reducing the microbiological contamination of the treated wastewater. However, parameters such as TP, N_amo, and N_org continued to show only moderate removal efficiencies (Figure A15). Notably, N_amo exceeded the permissible discharge limits on one occasion, attributed to increased influent concentration recorded at that time (Figure 8). The statistical comparison between the two treatment technologies used in Acchayacu showed significant differences for BOD5 (p = 6.07 × 10−5), COD (p = 7.41 × 10−6), SSs (p = 5.38 × 10−7), and TTCs (p = 0.026). In contrast, no statistically significant differences were observed for TC (p = 0.111), N_amo (p = 0.063), N_org (p = 0.091), DO (p = 0.23), and TP (p = 0.093).
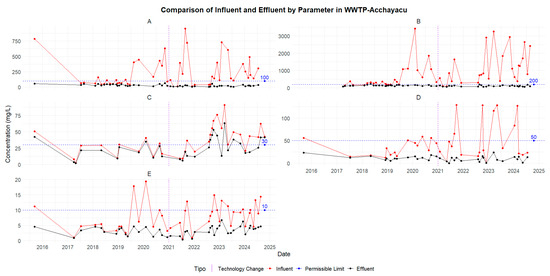
Figure 8.
Concentrations in influent vs. effluent at Acchayacu WWTP: (A) BOD5, (B) COD, (C) N ammonia, (D) N organic, and (E) TP.
Following the change from the UAF reactor to a VSSF-CW, no significant differences in DO and pH levels were initially observed (Figure A9 and Figure A10) between the influent and effluent, likely due to the startup phase of the new system. However, once the VSSF-CW stabilized, the improvement in treatment efficiency was evident. Despite this, pH levels exhibited only minimal variations, which may be attributed to the adaptation of microorganisms and the planted macrophytes (“Calamagrostis intermedia”).
The data show a high removal efficiency values for BOD5 and COD, with significantly lower concentrations observed at the effluent, indicating a superior performance compared to Acchayacu (Figure A11). In contrast, the removal efficiencies for TP, N_amo, and N_org are more variable, with some instances showing lower removal rates. Nonetheless, it is important to highlight that, overall, these parameters demonstrate greater effectiveness in comparison to Acchayacu (Figure A12).
An analysis was conducted to compare the overall removal efficiencies of both WWTPs in the period in which all data were obtained. This comparison focused on the treatment performance of each plant as a whole, without distinguishing between the specific technologies used. However, as illustrated in Figure A15, a noticeable improvement in removal efficiency was observed following the technology upgrade in Acchayacu.
The effluent concentrations in Acchayacu generally complied with permissible limits, except for ammoniacal nitrogen, which, in some cases, exceeded the limit both before and after the technological upgrade implemented in 2021. It is important to highlight that the effluent concentrations of ammoniacal nitrogen in Churuguzo consistently remained below the permissible limit of 30 mg/L (Figure 9).
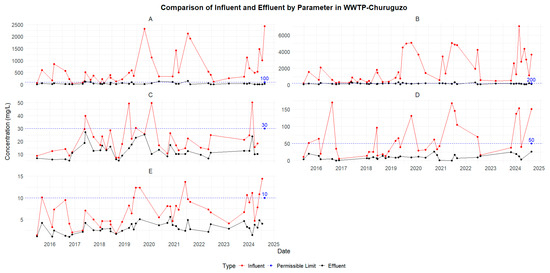
Figure 9.
Concentrations in influent vs. effluent of WWTP Churuguzo: (A) BOD5, (B) COD, (C) N ammonia, (D) N organic, and (E) TP.
For total suspended solids (TSSs), influent levels reached up to 180 mg/L; however, both the Acchayacu and Churuguzo systems effectively reduced TSS levels to below 100 mg/L.
A different trend was observed for total phosphorus (TP). In Acchayacu, influent concentrations ranged from 12 to 18 mg/L (Figure 8), whereas in Churuguzo, they remained below 15 mg/L (Figure 9). Despite these variations, both treatment systems successfully reduced TP levels to below the permissible limit of 10 mg/L.
Regarding fecal coliforms (TTCs), the effluent from Acchayacu consistently exceeded the permissible limit of 1000 MPN/100 mL, with peak values reaching up to 3000 MPN/100 mL. In contrast, the Churuguzo plant demonstrated more effective microbiological control, with effluent TTC concentrations falling below the regulatory threshold on several sampling dates.
4. Discussion
The results of this study highlight both the effectiveness and the limitations of the technologies implemented in the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs, specifically for treating wastewater from small populations using decentralized systems under conditions with a high pollutant load. The comparison of these WWTPs reveals significant differences in several key parameters, underscoring the influence of wetland design and the characteristics of the influent water on treatment performance.
- Analysis of meteorological parameters
The temperature data used in this study were obtained exclusively from the Morascalle weather station, as the Portete station could not be considered due to unavailable records. According to the geographical location data of the two WWTPs, both are situated in the same temperate Andean region, which is characterized by temperate-to-cold temperatures and marked seasonal variability. The Morascalle station is located approximately 3.3 km from the Acchayacu WWTP and 9.2 km from the Churuguzo WWTP, making it possible to determine that both plants are in relatively close proximity. As such, no significant climatic variability between the two sites is expected.
Temperature is a key factor influencing the efficiency of biological processes used in wastewater treatment. In particular, low temperatures can directly affect biological activity. In this case study, the average temperature ranges between 11 and 14 °C, which may impact treatment performance. In addition, in studies such as the one carried out by De La Mora-Orozco et al. [27], it has been shown that the capacity for pollutant removal, in the specific case of ammoniacal nitrogen (NH4+-N), decreases at temperatures below 16 °C. In contrast, water temperatures above 17 °C promote more vigorous and accelerated plant growth, enhancing treatment efficiency. These findings support the conclusion that lower temperatures can lead to reduce nutrient removal efficiency, as observed in the Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs. However, during warmer months such as January to March, when temperatures exceed 19 °C, improved pollutant removal efficiency can be expected due to enhanced biological activity.
Precipitation data were analyzed using records from the Morascalle meteorological station and the Portete rainwater station. Although both stations are located within the same watershed and at similar altitudes, differences were observed in the recorded precipitation values. As noted by Buytaert et al. [28], such variations are common in mountainous regions due to factors such as exposure to prevailing winds, slope orientation, and topographic barriers. However, the differences between the stations studied were not statistically significant, suggesting that the observed variation may be primarily attributed to gaps in the available data from both stations. Therefore, this similarity in precipitation distributions reflects very similar precipitation conditions in both studied areas, which are located only 17 km away from each other.
Although the statistical analysis did not reveal significant differences in precipitation between the Morascalle and Portete stations, it is important to acknowledge that atypical events, such as extreme droughts or heavy rainfall, can introduce variability into the data. For instance, heavy rainfall causes dilution effects, temporarily enhancing treatment efficiency. This effect could be especially relevant in surface flow systems, as observed in the Churuguzo system.
- Analysis of hydraulic parameters
The hydraulic retention time (HRT) plays an important role in the removal efficiency of various wastewater treatment technologies. In general, a longer HRT enhances contaminant removal due to greater interaction between wastewater and microbial communities, thereby improving the system’s ability to eliminate organic matter and nutrients. This relationship is supported by the findings of Navarro et al. [29], who show that higher efficiency is associated with increased HRT values.
The results obtained in this study show that the Churuguzo WWTP has a higher removal efficiency, which could be attributable to its longer HRT, while also acknowledging the influence of vegetation, system configuration, and wetland technology. According to the study conducted by the US EPA [30], an optimal HRT for an SF-CW is approximately three days for preventing algae blooms, a value exceeding that recorded in the SF-CW of Churuguzo. Conversely, for VSSF-CWs, an extensive HRT (greater than 1–3 days) is recommended for nutrient removal [31], a value much higher than that determined in the Acchayacu VSSF-CWs, potentially explaining their comparatively lower performances in nutrient reduction.
For the upflow anaerobic filter (UAF), the HRT suitable for operation is estimated to be between 4 and 10 h. When operating at low temperatures (10–20 °C), the efficiency of a UAF system tends to decrease due to slower reaction rates, which would require a longer HRT to maintain performance [32]. In a previous study conducted by González and Narváez [33], the UAF reactor at Acchayacu would operate at an average HRT below the recommended range, which could have influenced the removal efficiency of this technology.
- Comparative analysis of removal efficiency between SF-CW and VSSF-CW
The following section presents an analysis of the performances of and a comparison between two wetland technologies: the SF-CWs used at the Churuguzo WWTP and the VSSF-CWs implemented at the Acchayacu WWTP.
According to Quintero García et al. [34], a constructed wetland can be considered to function adequately for treating domestic wastewater when the elimination of bioindicators of fecal contamination and the presence of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria responsible for the nitrification and denitrification processes required for nitrogen removal occur.
In general, the analysis of data obtained from the two wetland systems confirms that the Churuguzo WWTP demonstrated a superior performance for removing most of the parameters analyzed, particularly for eliminating organic matter (BOD5 and COD) and microbiological contaminants (total and fecal coliforms). This higher efficiency may be attributed to the enhanced pollutant removal capacity of SF-CWs for pollutants, as reported in studies by Bedoya et al. [35]. The average BOD5 removal efficiency in the SF-CWs at Churuguzo was higher than that of the VSSF-CWs at Acchayacu, supporting the hypothesis that wetlands with a longer HRT and denser vegetation promote more effective wastewater treatment. The difference in hydraulic loading rates (HLRs) between the WWTPs suggests that although Acchayacu has a lower flow rate, its proportionally smaller wetland area limits the interaction time between the wastewater and the treatment system. Furthermore, it should be noted that Churuguzo’s SF-CW technology allows for greater interaction with the atmosphere, enhancing oxygenation and plant development, which in turn contribute to more efficient pollutant removal. These findings highlight Churuguzo’s greater capacity to treat domestic wastewater with high organic and microbiological loads, possibly attributable to its longer HRT. In addition, microbiological parameters such as TCs and TTCs exhibit significant differences between the two WWTPs, underscoring the effectiveness of the Churuguzo SF-CW in mitigating microbiological risks, crucial for protecting both public health and environmental quality.
When comparing the capacity for the removal of nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and suspended solids (SSs), between the VSSF-CWs at Acchayacu, which uses the plant species paramo straw (Calamagrostis intermedia), and the SF-CWs in Churuguzo, the latter demonstrates a higher efficiency. However, these differences were not statistically significant. The variation in performance may be attributed to several factors, including differences in the wetland technology, HLR, HRT, and type of vegetation. This observation is corroborated by Romero-Aguilar et al. [36], who found that a higher HRT in surface-flow constructed wetlands enhances the sedimentation of suspended solids and promotes nutrient uptake by vegetation. Additionally, Zahraeifard and Deng [37] reported that prolonged HRT in subsurface flow wetlands, such as the VSSF-CW at Acchayacu, favors processes such as nitrification and organic matter removal by allowing more time for microbial activity within the filter media. The extended contact between the wastewater, filter media, and microorganisms optimizes key biological processes, including nitrification and denitrification. Conversely, in systems such as the Acchayacu VSSF-CW, where the HRT is shorter, lower removal efficiencies for organic matter and nutrients are observed due to the limited contact time for the treatment process. This reduced retention time increases the risk of diminished performance in biological treatment processes [38]. Regarding vegetation, constructed wetlands may have a greater capacity to remove pollutants such as nutrients (N and P) and organic matter when larger macrophytes such as reeds (Typha) are used. This species improves system oxygenation by transporting oxygen through its roots, in turn stimulating microbial activity within the wetland substrate [39,40].
Considering that paramo straw is a smaller macrophyte species compared to totora, the latter requires more nutrients to sustain its growth. Additionally, the hydraulic loading rate (HLR) of the SF-CW at the Churuguzo WWTP is lower, resulting in a larger treatment area. This expanded surface area promotes greater microbiological development, enhancing the breakdown and removal of organic matter.
This effect could be enhanced with a longer hydraulic retention time (HRT), as observed in the SF-CWs at the Churuguzo WWTP. Considering that paramo straw is a smaller macrophyte species compared to totora, the latter requires a higher nutrient input to sustain its growth. Moreover, the lower hydraulic loading rate (HLR) in the SF-CW at the Churuguzo WWTP results in a larger treatment area, supporting the more extensive microbial development responsible for degrading organic matter. However, neither of the two wetland systems analyzed achieved the complete removal of ammoniacal nitrogen, suggesting the potential need to complement the treatment process with additional systems specifically targeting nutrient removal. These findings are consistent with the previous study conducted by Abdelhakeem et al. [41], which emphasizes the efficiency of subsurface wetlands in enhancing aerobic processes and improving nutrient removal from wastewater. The design of the VSSF-CW, characterized by a smaller effective surface area and higher HLR, may have adversely impacted its treatment performance.
- Influence of technological change
Upflow anaerobic filters (UAFs) have been widely used in wastewater treatment systems as they use a biofilm fixed on a substrate for the removal (primarily) of organic matter under anaerobic conditions [42]. However, these systems have limitations in the removal of nutrients and pathogenic microorganisms, which may require further treatment.
In this study, the UAF exhibits a lower removal efficiency compared to the other technologies evaluated (SF-CW and VSSF-CW), particularly for eliminating ammoniacal nitrogen and fecal coliforms. Furthermore, the variability in treatment performance may be influenced by several factors, including the hydraulic load, stability of anaerobic biomass, and site-specific temperature conditions.
In this comparative analysis, it is necessary to evaluate the period prior to the change in technology at the Acchayacu WWTP—specifically, from 2015 to 2020—when the plant operated using a UAF reactor. The transition in 2021 from the UAF to vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs) led to notable improvements, as reflected in the increased removal efficiency for parameters such as BOD5, COD, SSs, and TTCs compared to the previous system. However, the performance of the Acchayacu VSSF-CW still falls short of the removal efficiencies achieved by the SF-CWs in Churuguzo, particularly for the key parameters such as BOD5, COD, TTC, and TC. This highlights the critical role of wetland design, vegetation selection, adaptation to local environmental conditions, and, in particular, the hydraulic retention time (HRT). A longer HRT not only enhances the removal of organic matter and nutrients but also contributes to eliminating pathogens by allowing the wastewater to have extended contact with the environment and vegetation, thereby facilitating microbial action in the removal process.
A notable decrease in pollutant concentrations, along with an increase in the removal efficiency for several parameters, can be observed following the transition from using UAF reactor technology to VSSF-CW systems. For instance, in the removal of SSs, BOD5, and COD, a peak can be observed, which could be interpreted as an initial decline following the transition from UAF reactor technology to VSSF-CW systems. However, it is important to consider the influence of the wetland’s startup or commissioning phase. As stated by Mosquera [43], for the removal of BOD5, which typically occurs rapidly, treatment efficiency tends to be lower during the first months of the startup process. This phenomenon is closely linked to the development and stabilization of microbial consortia within the system.
Constructed wetlands are typically known for their stability in treatment efficiency once they reach operational equilibrium. However, as shown in Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7, in this case, they exhibit stable behavior in terms of contaminant removal efficiency, even under variations in the load entering the WWTP. This stability can be attributed to their good capacity to absorb peak loads despite the challenges that high-altitude conditions may present. However, it is important to consider factors such as the quality of the effluent and the startup period.
In this study, it was observed that during the first three to six months following the implementation of the new VSSF-CW system, the removal efficiencies for some parameters, particularly those dependent on microbial activity, were relatively low. This trend corresponds to the typical microbial and vegetative stabilization period. Such a startup phase is common in newly constructed wetlands and may influence the results recorded during the initial monitoring period.
The removal of ammoniacal nitrogen (N_amo) across the two evaluated periods improved following the change in technology at the Acchayacu WWTP. However, its efficiency remains lower than that of the Churuguzo WWTP. In contrast, the removal of organic nitrogen (N_org) and N_amo do not exhibit significant variability across different technologies and time periods. Nonetheless, both parameters consistently demonstrate low removal efficiencies. This limited performance may be attributed to several factors, including temperature—an aspect analyzed in previous studies such as that by Zhang et al. [44]. Their study indicates that the removal of these contaminants can fluctuate significantly depending on temperature and seasonal variations, a pattern also observed in both Acchayacu and Churuguzo.
These temperature variations can also significantly impact the efficiency of both constructed wetlands and the UAF reactor, as higher temperatures tend to enhance microbial activity, while lower temperatures can hinder biological processes, thereby reducing the overall treatment performance.
Although the change in technology has enhanced the performance of the Acchayacu WWTP compared to the former UAF system, the HRT may act as a limiting factor, restricting the system from reaching its maximum potential efficiency.
Although the change in technology at the Acchayacu WWTP led to improvements in wastewater treatment, the persistent presence of nutrients such as ammoniacal nitrogen and phosphorus in the effluents from both treatment plants suggests the need to implement complementary treatment strategies.
Considering the case of Acchayacu, additional treatments such as absorbent material filters or anaerobic bioreactors could offer potential solutions for enhanced nutrient removal. Various studies have demonstrated that these systems can effectively reduce elevated nutrient concentrations in effluents by combining physical, chemical, and biological processes across multiple stages. Consequently, future research should explore implementing integrated or hybrid systems to evaluate their performances under high-altitude conditions.
- Implications and limitations
This analysis highlights the positive impacts of integrating nature-based wastewater treatment systems, which offer sustainable and effective solutions, particularly in high-altitude regions. These systems also present strong potential for implementation in areas where the construction of sewer networks and centralized treatment facilities is limited by geographic, economic, or technical constraints. However, several critical factors must be considered when designing and operating constructed wetland-based treatment systems, including the configuration of the WWTP. It is important to note that no wetland treatment system is entirely maintenance-free. One of the most significant operational challenges in horizontal subsurface flow wetlands (HSSF-CWs) is clogging, which occurrs when solids accumulate and block the pore spaces in the media [45]. This reduces treatment efficiency and compromises system performance. Regular maintenance is, therefore, essential to ensure the proper functioning of constructed wetlands. For example, vegetation, such as totora (Scirpus californicus), must be pruned periodically, possibly annually or every two years, depending on the management objectives [46].
Vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs) have been widely studied for their effectiveness in contaminant removal, and they are comparable to other wetland types. However, their distinct structural design presents both advantages and limitations. While their primary advantage lies in restoring aerobic conditions during dry periods, they are limited by their dependence on substrate aeration and their susceptibility to clogging. To mitigate these challenges, VSSF-CWs are typically operated with intermittent loading and controlled organic matter input to prevent system overload [47].
Free-water-surface constructed wetlands (SF-CWs) offer a viable alternative for wastewater treatment, particularly in decentralized systems, as demonstrated in this study. However, their treatment efficiency is closely linked to the hydraulic retention time (HRT). In this study, the Acchayacu system, with an HRT of 1.13 days, exhibited lower removal rates compared to the Churuguzo system, which operated with a longer HRT of 4.72 days. This observation is consistent with findings from previous studies, such as that by Guerra et al. [48], indicating that a longer HRT can enhance nitrification and sedimentation processes.
A notable limitation of SF-CWs is their requirement for more frequent maintenance compared to horizontal flow wetlands (HSSF-CWs). This includes regularly pruning vegetation and periodically removing accumulated substrate material, which can result in higher operational and maintenance costs [49]. In general, surface-flow constructed wetlands (SF-CWs) tend to have lower construction costs due to their simple design and continuous operation, which eliminates the need for intermittent pumping. In contrast, vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs) typically require a higher initial investment. However, operational considerations must also be taken into account. SF-CWs often require more maintenance, particularly for vegetation management, and may present a greater risk of vector proliferation due to the exposed water surface.
Although no visible obstructions were observed in this case and no issues related to reduced flow or wetland overflow were reported, the potential for clogging due to sediment accumulation cannot be ruled out. This underscores the importance of regular and adequate maintenance.
Maintenance activities are managed by ETAPA-EP, which generally prunes vegetation every six months. However, this schedule may vary or adherence may be inconsistent. As such, it is essential to further strengthen the analysis presented in this study by incorporating data related to the frequency and timing of pruning. This would allow for the identification of potential variations in wastewater treatment performance associated with maintenance practices.
An important aspect to consider is that both WWTPs discharge into the Irquis river, which serves as the receiving body for the treated effluent. While the preliminary results indicate improvements in effluent quality, further adjustments may be required to fully comply with discharge standards, particularly in terms of nutrient concentrations. The water quality of the Irquis river has not only environmental significance but also social implications, as local communities rely on this resource for agriculture, domestic use, and other essential activities.
This study did not include an analysis that normalized pollutant loads based on flow rates, which is an acknowledged limitation. However, it is important to emphasize that the comparison was based on removal efficiencies derived from influent and effluent concentrations in the constructed wetlands using actual data provided by the ETAPA-EP, which has been monitoring these decentralized WWTPs. Nevertheless, it is recommended that future studies incorporate flow-based normalization to enable a more comprehensive evaluation of treatment system performance.
It is important to emphasize that the comparisons of treatment technologies were based on influent and effluent concentrations at the wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), expressed in mg/L. Although this study did not include an analysis normalizing pollutant loads based on flow rates—a factor that could be considered a limitation—the primary objective was to compare the efficiency of each technology by assessing the removal capacity of the WWTPs under similar conditions, with the main distinction being the type and characteristics of the treatment technology employed for domestic wastewater. In future research, it is recommended to calculate influent loads to enable a more comprehensive and robust evaluation of system performance.
Although precipitation (P) data were available during the study period, no data on potential evapotranspiration (ETP) were collected. This constitutes a limitation, as it hindered a more comprehensive analysis of the system’s performance. It is recommended that future studies incorporate ETP data to enable a more complete evaluation of the constructed wetlands.
5. Conclusions
The results obtained in this study demonstrate the importance of design, management, and continued research on decentralized wastewater treatment systems in rural and high-altitude regions. In this context, it is essential to consider key operational parameters such as the hydraulic retention time (HRT) and the hydraulic loading rate (HLR). Additionally, selecting endemic vegetation with a high capacity for contaminant removal is crucial to ensuring the effectiveness and sustainability of such systems within the specific environmental conditions of the implementation area.
Regarding public policies, there is evidently a pressing need to strengthen regulatory frameworks and support initiatives that promote the adoption of nature-based sanitation technologies, particularly in areas where access to centralized systems or significant investment in infrastructure is limited or unfeasible. These alternatives offer viable solutions for satisfying water discharge regulations and safeguarding environmental quality, while simultaneously promoting equitable access to essential sanitation services. It is worth noting that constructed wetland systems, such as those analyzed in this study, have demonstrated both efficiency and viability as alternative wastewater treatment solutions, even under the challenging conditions of high-altitude environments and significant daily temperature fluctuations. These characteristics make them particularly well -suited to implementation in such regions as part of a broader strategy for decentralized wastewater management
The technological shift at the Acchayacu WWTP from an upflow anaerobic filter (UAF) to vertical-subsurface-flow constructed wetlands (VSSF-CWs) significantly enhanced pollutant removal, especially for organic matter (BOD5, COD) and microbiological parameters (TCs and TTCs). Nonetheless, the removal efficiency for nutrients such as phosphorus and ammonia nitrogen remains an area requiring improvement.
The comparative analysis between the surface flow constructed wetland (SF-CW) at the Churuguzo WWTP and the VSSF-CW at the Acchayacu WWTP reveals significant differences in the removal efficiency of various contaminants. These differences are likely due to the distinct design characteristics and configurations of each system.
The SF-CW at Churuguzo, with a longer hydraulic retention time (HRT) and a lower hydraulic loading rate (HLR), demonstrated greater efficiency in removing organic matter (BOD5, COD), as well as in microbiological parameters (fecal and total coliforms). This improved performance could be attributed to the greater interaction between the water, filter media, and planted vegetation, with totora (Scirpus californicus) in the SF-CW system and paramo grass (Calamagrostis intermedia) in the VSSF-CW system. Additionally, the SF-CW design enhances oxygenation and microbial activity, further contributing to its higher treatment efficiency.
The findings of this study highlight the significance of the design and configuration of wastewater treatment systems that utilize nature-based technologies in high-altitude regions. The results demonstrated that factors such as the hydraulic retention time (HRT), hydraulic loading rate (HLR), and vegetation type play crucial roles in contaminant removal efficiency. These insights are essential for planning and optimizing more effective and sustainable sanitation strategies. Improving effluent quality has direct implications for enhancing the environmental quality of receiving water bodies, particularly the Tarqui and Irquis rivers and their tributaries, and for protecting public health. These insights are valuable for guiding future designs for sustainable wastewater treatment strategies in high-altitude and decentralized systems.
One limitation of this study is the absence of normalization for the influent contaminant loads; future research should address this issue by conducting analyses based on pollutant loads rather than solely concentrations.
Future research should aim to enhance the existing treatment systems, with a particular focus on nutrient removal. Emphasis should be placed on promoting hybrid technologies, evaluating new endemic vegetation species suitable for constructed wetlands, and incorporating variables such as seasonal fluctuations and potential changes associated with extreme climatic events.
Author Contributions
R.J.-C. contributed to sampling preparation, assisted with field sampling, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. E.M. coordinated and conducted the sampling campaign, contributed to sampling preparation and fieldwork, and also participated in data analysis and manuscript writing. J.F.H.-C., D.M.-S. and H.G.-H. contributed to writing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Vice-Rectorate for Research at the University of Cuenca, research projects 2023.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the municipal water supply and wastewater management company, ETAPA-EP, for providing access to field data collected between 2015 and 2024 at both the Acchayacu and Churuguzo wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
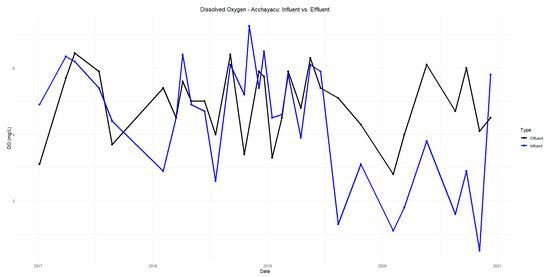
Figure A1.
Dissolved oxygen in Acchayacu influent and effluent in 2015–2020.
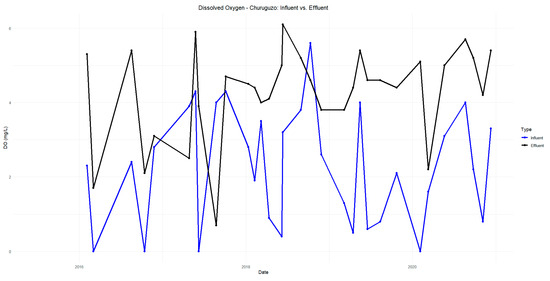
Figure A2.
Dissolved oxygen in Churuguzo influent and effluent in 2015–2020.
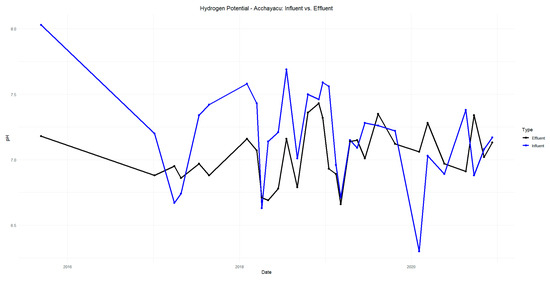
Figure A3.
pH of Acchayacu influent and effluent in 2015–2020.
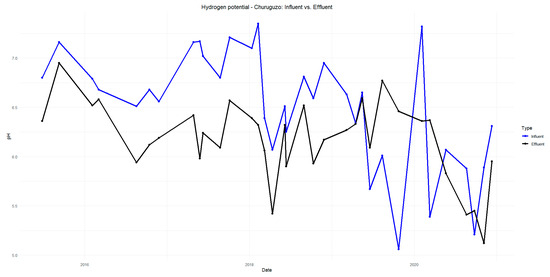
Figure A4.
pH of Churuguzo influent and effluent in 2015–2020.
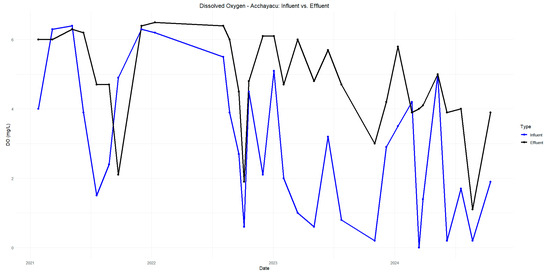
Figure A5.
Dissolved oxygen in Acchayacu influent and effluent in 2021–2024.
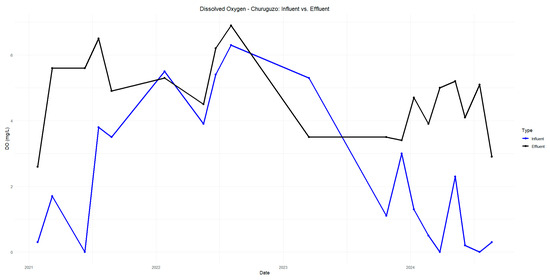
Figure A6.
Dissolved oxygen in Churuguzo influent and effluent in 2021–2024.
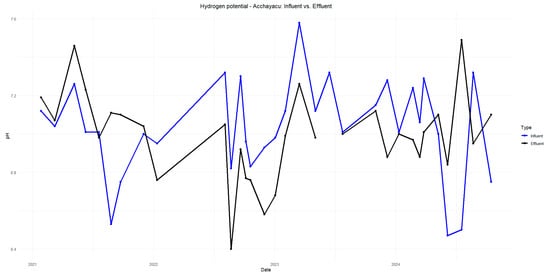
Figure A7.
pH of Acchayacu influent and effluent in 2021–2024.
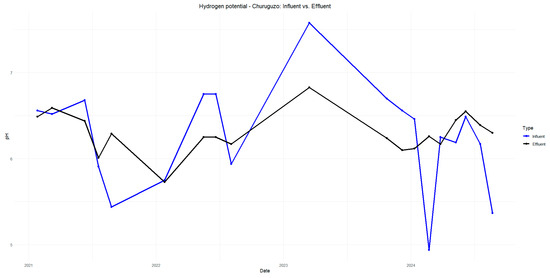
Figure A8.
pH of Churuguzo influent and effluent in 2021–2024.
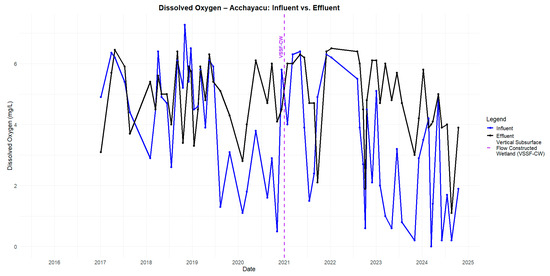
Figure A9.
Dissolved oxygen in Acchayacu.
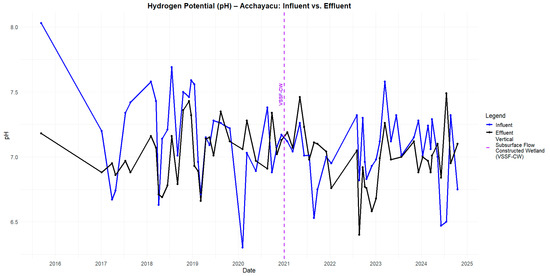
Figure A10.
Hydrogen potential (pH) in Acchayacu.
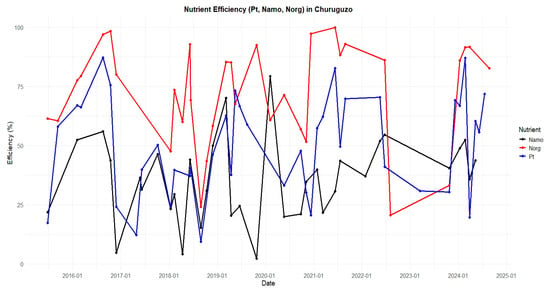
Figure A11.
Removal efficiency—parameters: ammonia nitrogen (N_amo), organic nitrogen (N_org), and total phosphorus (TP) in WWTP Churuguzo.
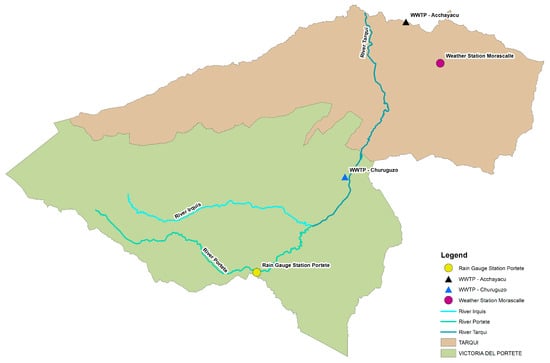
Figure A12.
Locations of Morascalle weather station and Portete rainfall station.
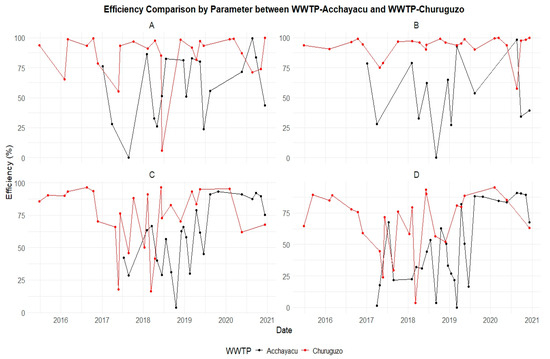
Figure A13.
An efficiency comparison between Acchayacu and Churuguzo WWTPs during the period 2015–2020: (A) total coliforms (TCs), (B) fecal coliforms (TTCs), (C) biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), and (D) chemical oxygen demand (COD).
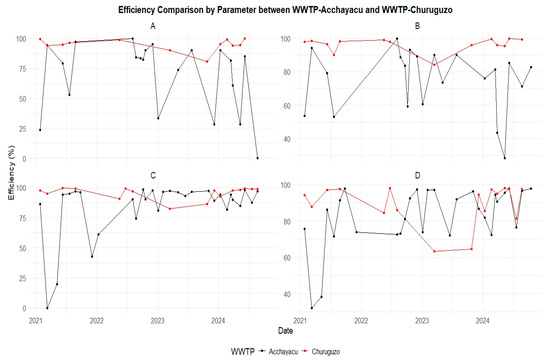
Figure A14.
A comparison of removal efficiency between the VSSF-CW at the Acchayacu WWTP and the SF-CW at the Churuguzo WWTP (2021–2024): (A) TC, (B) TTC, (C) BOD5, and (D) COD.
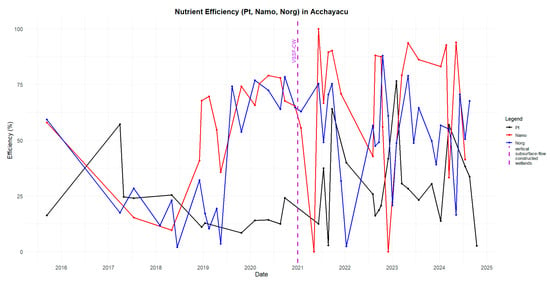
Figure A15.
Removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen (N_amo), organic nitrogen (N_org), and total phosphorus (TP) at the Acchayacu WWTP.
References
- Coello, E.; Burbano, I.; Molina, A. Polluting factors of the San Pablo River in the city of Babahoyo, Ecuador. J. Soc. Dev. Stud. Cuba. Lat. Am. 2023, 11, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, and Reuse, 3rd ed.; Impresos y Revistas, S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 1995; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hanjra, M.A.; Blackwell, J.; Carr, G.; Zhang, F.; Jackson, T.M. Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: Implications for water governance and public policy. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humanante, J.; Moreno, L.; Grijalva, A.; Saldoya, R.; Suárez, J. Removal Efficiency and impact of wastewater treatment system in the urban and rural sector of the Santa Elena Province. Manglar 2022, 19, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, I.M.W.; Soedjono, E.S. Physicochemical Characteristic of Municipal Wastewater in Tropical Area: Case Study of Surabaya City, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 135, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.J.A.R. Wastewater Treatment: Theory and Design Principles, 3rd ed.; Nuevas Ediciones S.A.: Bogotá, Colombia, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jerves-Cobo, R.; Forio, M.A.E.; Lock, K.; Van Butsel, J.; Pauta, G.; Cisneros, F.; Nopens, I.; Goethals, P.L. Biological water quality in tropical rivers during dry and rainy seasons: A model-based analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaza, C.A.A. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Gen. José María Córdova Sci. J. 2005, 3, 40–44. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=476259066011 (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Chung, G.; Lansey, K.; Blowers, P.; Brooks, P.; Ela, W.; Stewart, S.; Wilson, P. A general water supply planning model: Evaluation of decentralized treatment. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llagas, W.; Gómez, E.G. Design of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment at the National University of San Marcos. J. Inst. Res. Fac. Geol. Min. Metall. Geogr. Eng. 2006, 15, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Anil, A.; Sumavalli, K.; Charan, S.; Mounika, M.; Praveen, P.; Gayathri, A.; Ganesh, V.M. Constructed Wetland for Low-Cost Waste Water Treatment. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 10, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizaldi, M.A.; Limantara, L.M. Wetland as revitalization pond at urban area based on the eco hydrology concept. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo, O.; Camacho, A.; Pérez, L.F.; Andrade, M. Wastewater Treatment Through Constructed Wetlands; Antequera, N., Ed.; Andean Center for Water Management and Use (Centro AGUA): Bolivia, Cochabamba, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: A Technology Assessment; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Aguado, R.; Parra, O.; García, L.; Manso, M.; Urkijo, L.; Mijangos, F. Modelling and simulation of subsurface horizontal flow constructed wetlands. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.J.D.-G.; Paredes, P.M.P.-R. Use of treated domestic wastewater through a constructed wetland with Jatropha and sunflower. Knowl. Hub J. 2022, 7, 1478–1495. Available online: https://polodelconocimiento.com/ojs/index.php/es/article/view/3556 (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Córdova, M.; Paz, D.; Santelices, M. Governance for Monitoring Access to Sanitation in Ecuador; Latin American Faculty of Social Sciences—FLACSO: Quito, Ecuador, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terán, C.; Argüello, J.; Cando, C. Technical Bulletin of Environmental Economic Statistics in Municipal Decentralized Autonomous Governments: Drinking Water and Sanitation Management 2022; Agricultural and Environmental Statistics Directorate—DEAGA: Quito, Ecuador, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jerves-Cobo, R.; Benedetti, L.; Amerlinck, Y.; Lock, K.; De Mulder, C.; Van Butsel, J.; Cisneros, F.; Goethals, P.; Nopens, I. Integrated ecological modelling for evidence-based determination of water management interventions in urbanized river basins: Case study in the Cuenca River basin (Ecuador). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operacz, A.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Rodziewicz, J.; Janczukowicz, W.; Bugajski, P. Impact of Climate Conditions on Pollutant Concentrations in the Effluent from a One-Stage Constructed Wetland: A Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.S.; Loaiza, D.C.R.; Asprilla, W.J. Subsurface Constructed Wetlands: Comparison of Design Methodologies for Calculating Surface Area Based on Organic Matter Removal. Ing. USBMed 2022, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTE INEN 2169:2013—Water; Water Quality. Sampling. Handling and Preservation of Samples (First Revision). Ecuadorian Institute for Standardization (INEN): Quito, Ecuador, 2013.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cantelmo, N.F.; Ferreira, D.F. Performance of Multivariate Normality Tests Evaluated by Monte Carlo Simulation. Ciência Agrotecnologia 2007, 31, 1630–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Ahmad, F. Power Comparison of Various Normality Tests. Pak. J. Stat. Oper. Res. 2017, 11, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saculinggan, M.; Balase, E.A. Empirical Power Comparison of Goodness of Fit Tests for Normality in the Presence of Outliers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 435, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Mora-Orozco, C.; Saucedo-Terán, R.A.; González-Acuña, I.J.; Gómez-Rosales, S.; Flores-López, H.E. Effect of Water Temperature on the Reaction Rate Constant of Pollutants in a Constructed Wetland for Swine Wastewater Treatment. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Celleri, R.; Willems, P.; De Bièvre, B.; Wyseure, G. Spatial and temporal rainfall variability in mountainous areas: A case study from the south Ecuadorian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.; Torres, J.; Carlos, R. Review of Groundwater Quality Impacts Generated by Constructed Wetlands in Rural Areas. Desarro. Innovación Ingeniería 2021, 2, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet: Free Water Surface Wetlands; EPA 832-F-00-024; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- EPA. Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet: Subsurface Flow Wetlands; EPA 832-R-00-023; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- CONAGUA. Design of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants: Constructed Wetlands. Manual of Drinking Water, Sewerage and Sanitation (MAPAS); Book 30; National Water Commission (CONAGUA): Mexico City, Mexico, 2015.
- González, T.C.R.; Narváez, T.A.C. Evaluation and Redesign of the Acchayacu Wastewater Treatment Plant; Universidad de Cuenca: Cuenca, Ecuador, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- García, K.L.Q.; Zúñiga, D.P.R.; Duque, M.E.G.; Rojas, J.A.A. Evaluation of Nitrogen and Organic Matter Removal through Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands Coupled with Fixed-Bed Reactors with Microalgae at the Institución Universitaria Colegio Mayor de Antioquia. Ing. Región 2021, 25, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, J.C.; Ardila, A.N.; Reyes, J. Evaluation of a Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland for the Treatment of Wastewater Generated at the Institución Universitaria Colegio Mayor de Antioquia, Colombia. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2014, 3, 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Aguilar, M.; Colin-Cruz, A.; Sanchez-Salinas, E.; Ortiz-Hernandez, M.L. Wastewater treatment by a pilot constructed wetland system: Evaluation of organic load removal. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2009, 25, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Zahraeifard, V.; Deng, Z. Hydraulic residence time computation for constructed wetland design. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 2087–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Miranda, J.P.; Gómez, E.; Garavito, L.; López, F. Comparative study of domestic wastewater treatment using duckweed and water hyacinth in constructed wetlands. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2010, 1, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H. Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xie, H.; Yang, Z. Constructed Wetlands: A Review on the Role of Radial Oxygen Loss in the Rhizosphere by Macrophytes. Water 2018, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhakeem, S.G.; Aboulroos, S.A.; Kamel, M.M. Performance of a vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland under different operational conditions. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Anchundia, B.; Vera-Loor, J.; Loor-Vélez, J. Design of an upflow anaerobic filter for wastewater treatment. INGENIAR Eng. Technol. Res. 2022, 5, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mosquera, Y. Leachate treatment using constructed wetlands. Tumbaga 2012, 1, 73–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Gersberg, R.M.; Liu, Y.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. Application of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in developing countries—A review of recent developments (2000–2013). J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 141, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotro, G.; et al. Constructed Wetlands for Pollution Control; IWA Publishing, Alliance House: London, UK, 2017; Volume 7, SW1H 0QS. [Google Scholar]
- Keyport, S.; Carson, B.D.; Johnson, O.; Lawrence, B.A.; Lishawa, S.C.; Tuchman, N.C.; Kelly, J.J. Effects of experimental harvesting of an invasive hybrid cattail on wetland structure and function. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 27, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Cortez, V.M.; Quevedo-Nolasco, A.; del Valle-Paniagua, D.H.; Castro-Popoca, M.; Bravo-Vinaja, Á.; Ramírez-Zierold, J.A. State of the art: A current review on the mechanisms used by constructed wetlands for nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2019, 10, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, J.D.T.; Vargas, J.S.M.; Aguirre, R.R.P.; Huaranga, M.A.C. Evaluation of the efficiency in wastewater treatment for irrigation using Free Water Surface (FWS) Constructed Wetlands with Cyperus papyrus and Phragmites australis in Carapongo-Lurigancho. Rev. Investig. Cienc. Tecnol. Desarro. 2018, 3, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahora, A. Wastewater purification through constructed wetlands: The Edar de los Gallardos (Almería). Ecol. Manag. Conserv. Wetl. 2003, 49, 99–112. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).