Intelligent Parameter Fusion for Distributed Flood Modeling in Parallel Ridge–Valley Landscapes
Abstract
1. Introduction
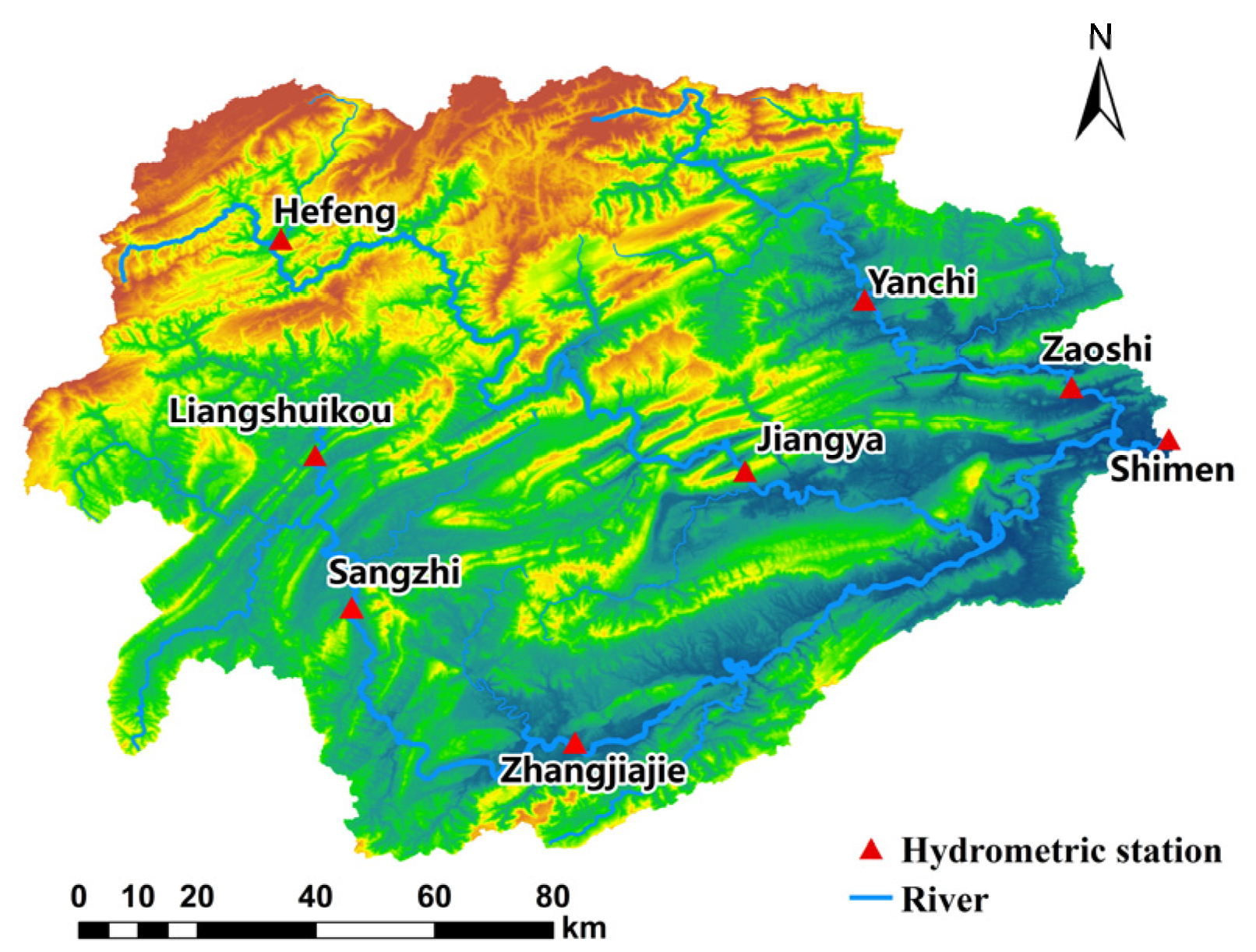
2. The Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
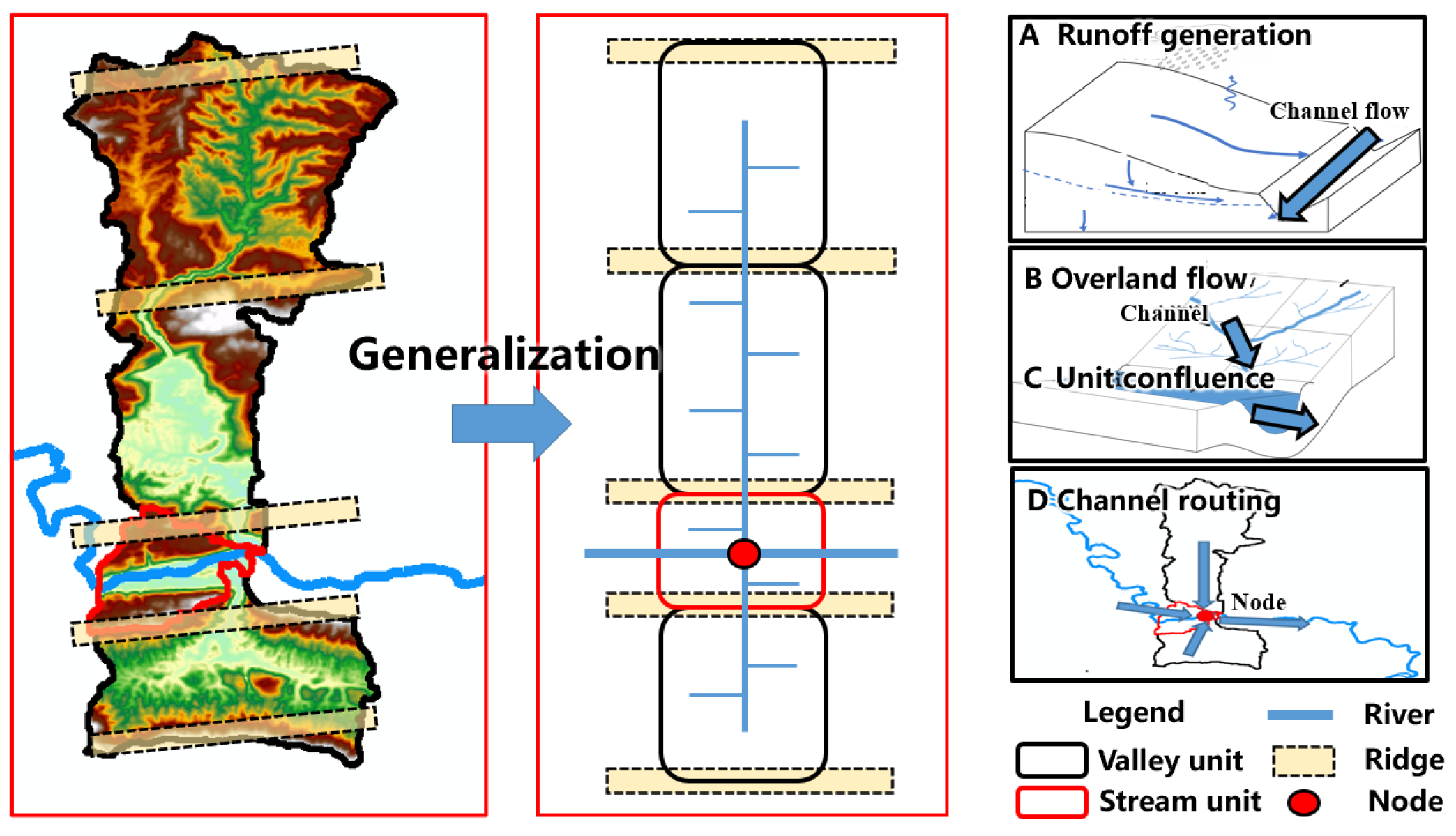
3.2.1. Generalization of Catchment Unit Applicable to Folded Mountainous Areas
3.2.2. Calculation of Production and Sink Flow in Folded Mountainous Areas
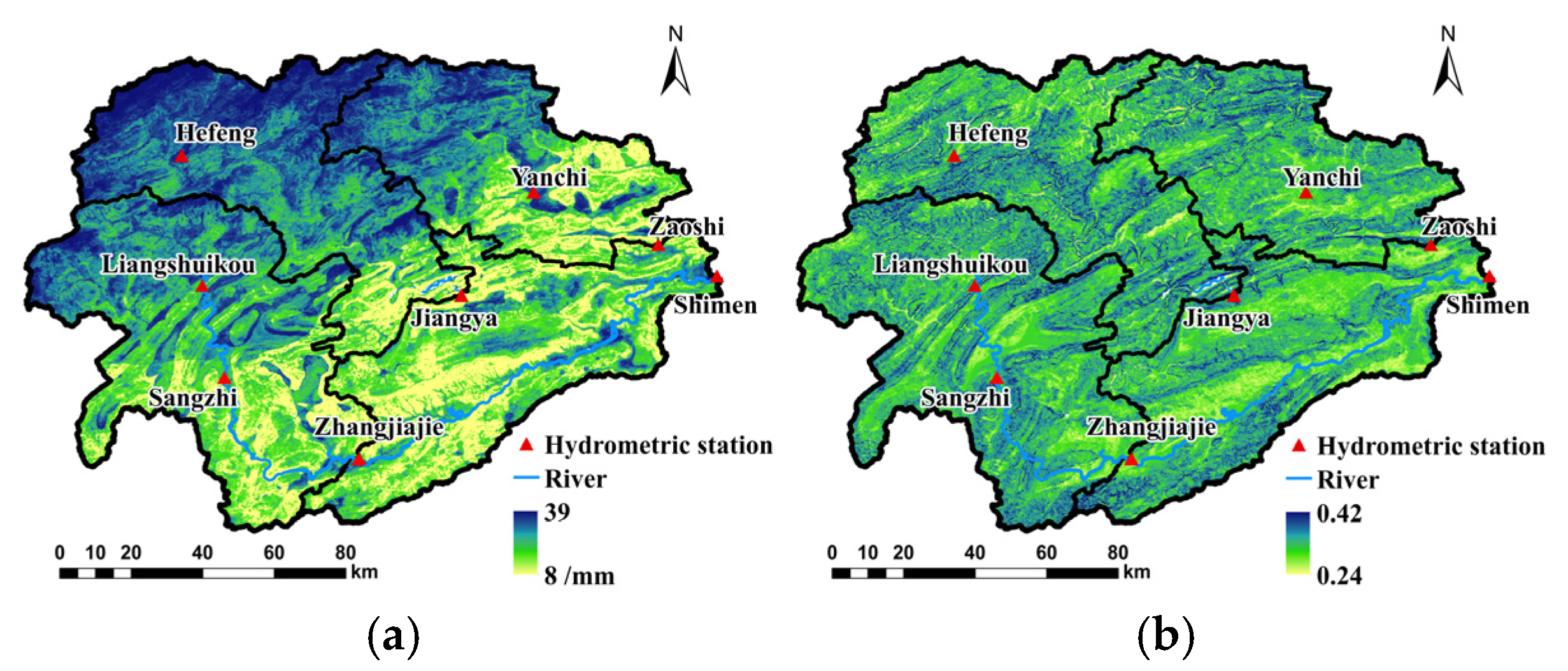
3.2.3. A Priori Estimation of Model Parameters Considering Spatial Differentiation of Watershed Subsurface
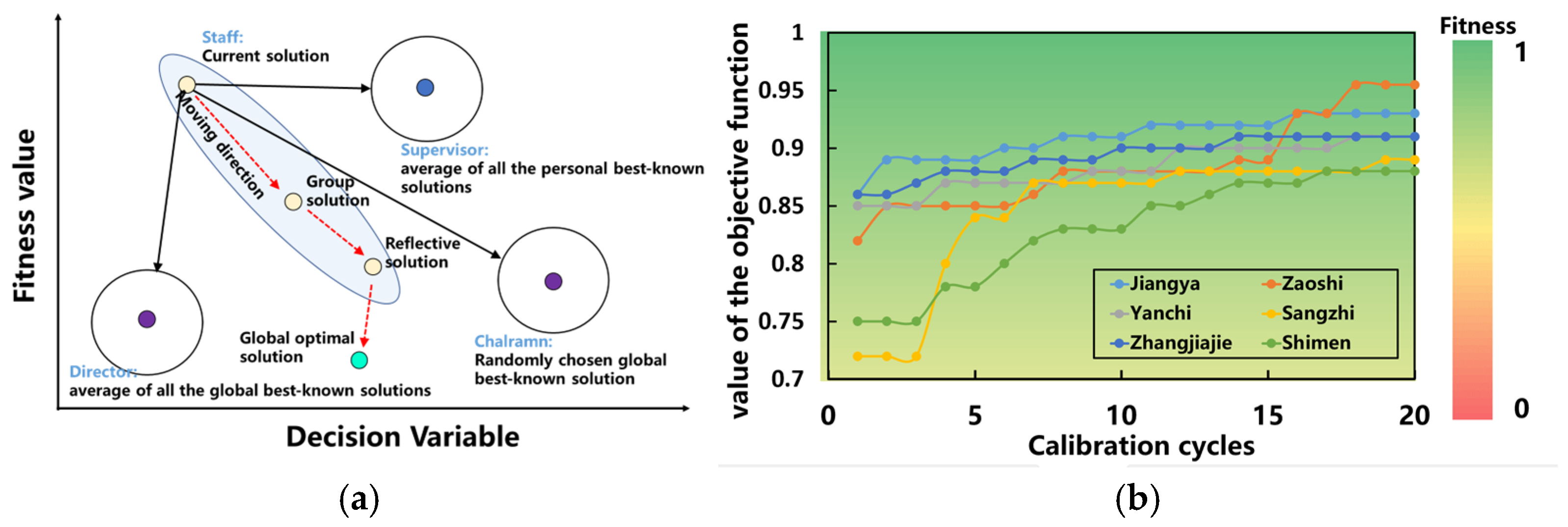
3.2.4. Optimized Rate Determination of Model Parameters with Level-by-Level Nesting in Combination with Intelligent Algorithms
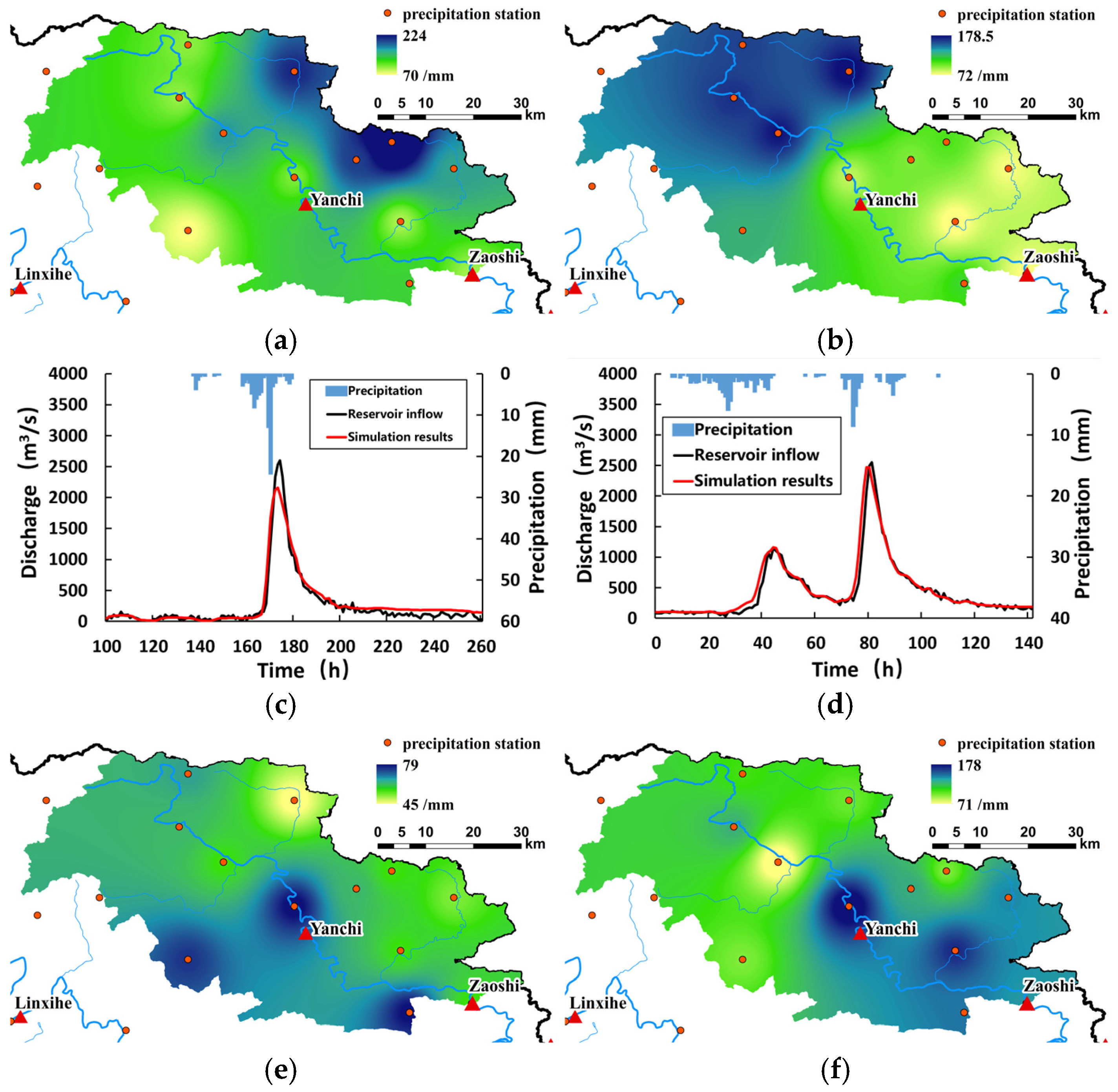
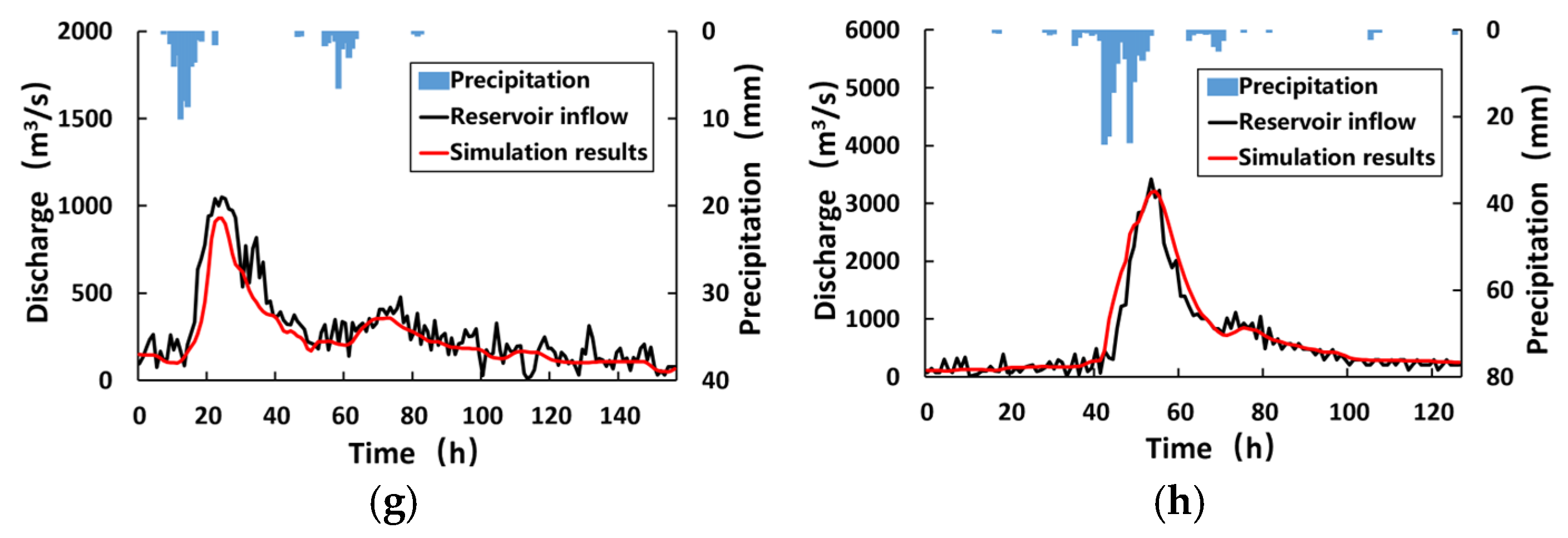
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulation of Watershed Runoff Process
4.2. Simulation Analysis of Typical Flood Process
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, X.; Ma, M.G.; Zhao, W.; Wen, J.G.; OuYang, X.Y. Analysis of driving mechanism of temporal and spatial distribution of surface temperature in parallel Ridge-Valley of East Sichuan. Remote Sens. Inf. 2021, 36, 47–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.H.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, P.; Bing-Qing, L.U.; Xie, S.Y.; Kuang, Y.L. A methodological research on the identification of a typical karst aquifer media in the paralleled Ridge-Valley of East Sichuan—A case study of Qingmuguan karst groundwater system, Chongqing. J. Southwest Univ. 2016, 38, 90–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Lai, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X. Future sea level rise exacerbates compound floods induced by rainstorm and storm tide during super typhoon events: A case study from Zhuhai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 911, 168799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hou, J.; Glade, T. Hazard assessment of rainstorm-geohazard disaster chain based on multiple scenarios. Nat. Hazards 2023, 118, 589–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Song, D.F. East Asian summer monsoon moisture transport belt and its impact on heavy rainfalls and floods in China. Adv. Water Sci. 2020, 31, 629–643. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Ahn, K.H. Self-training approach to improve the predictability of data-driven rainfall-runoff model in hydrological data-sparse regions. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Sela, S.; Dorman, M.; Svoray, T. Runoff generation in a semiarid environment: The role of rainstorm intra-event temporal variability and antecedent soil moisture. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 188, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, P.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, Y.-T.; He, Z. A GPU-accelerated and LTS-based 2D hydrodynamic model for the simulation of rainfall-runoff processes. J. Hydrol. 2023, 623, 129735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, A.; Singh, R. Improving rainfall-runoff model reliability under nonstationarity of model parameters: A hypothesis testing based framework. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2022WR032273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.B.; Zhou, Q.; Sheng, Y.X.; Liu, G. Review on hydrological and hydrodynamic coupling models for flood forecasting in mountains watershed. Shuili Xuebao 2021, 52, 1137–1150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.Q.; Jiang, X.Y.; Liao, M.Y.; Ren, L.; Zhu, Q.; Jin, J.; Jiang, S. Spatio-temporal characteristics of global flood disasters during 1980-2020. Adv. Water Sci. 2024, 35, 197–207. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.T.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, X. Research progresses and prospects of catchment hydrological forecasting driven by global climate forecasts. Adv. Water Sci. 2024, 35, 156–166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, S. Effect analysis on dynamic operation and control of operating water level of Jiangya Reservoir in flood season. Yangtze River 2020, 51, 203–208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, J. Drainage morphometry of the Lishui catchment in the middle Yangtze basin, China: Morphologic and tectonic implications. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X. Principle of Hydrology; Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C.; Alvarez, P.; Anache, J.A.A.; Baartman, J.; Ballabio, C.; Bezak, N.; Biddoccu, M.; Cerdà, A.; Chalise, D.; et al. Soil erosion modelling: A global review and statistical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Sun, J.; Ahmad, N.; Wei, J.J. Comparative CFD modeling of a bubbling bed using a Eulerian-Eulerian two-fluid model (TFM) and a Eulerian-Lagrangian dense discrete phase model (DDPM). Powder Technol. 2021, 383, 418–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Taleghani, A.D.; Kang, Y.; Xu, C. A coupled CFD-DEM numerical simulation of formation and evolution of sealing zones. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohi, M.; Soleymani, K.; Salimi, M.; Heidari, M. Numerical evaluation of the general flow hydraulics and estimation of the river plain by solving the Saint-Venant equation. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tiwari, R.K.; Kumar, K.; Rautela, K.S. Prioritization of sub-watersheds for the categorization of surface runoff and sediment production rate based on Geo-spatial Modeling and PCA approach: A case from upper Beas River, Himachal Pradesh, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2023, 99, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Zhu, G.F.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z. Spatial variability of runoff recharge sources and influence mechanisms in an arid mountain flow-producing zone. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14642.1–e14642.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Q.; Gao, H.B.; Wang, G.Q.; Hao, J.; Wang, Z.; Du, T.; Hao, Z. Modeling potential evapotranspiration based on energy balance. Adv. Water Sci. 2022, 33, 794–804. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.F.; Liang, Z.M.; Liu, J.T.; Li, B.; Duan, Y. Variable runoff generation layer distributed hydrological model for hilly regions. Adv. Water Sci. 2022, 33, 429–441. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tong, B.X.; Li, Z.J.; Yao, C. Estimation of distributed Grid-Xin’anjiang Model parameters based on SoilGrids. Adv. Water Sci. 2022, 33, 219–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Batchu, V.; Nearing, G.; Gulshan, V. A Deep Learning Data Fusion Model using Sentinel-1/2, SoilGrids, SMAP-USDA, and GLDAS for Soil Moisture Retrieval. J. Hydrometeorol. 2023, 24, 1789–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadoux, J.C.; Mcbratney, A.B. A global numerical classification of the soil surface layer. Geoderma 2024, 447, 116915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Shi, P.F.; Yang, T.; Niu, W.-J.; Zhou, J.-Z.; Cheng, C.-T. Parallel cooperation search algorithm and artificial intelligence method for streamflow time series forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Xiao, S.; Dai, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, J. Spatial structure might impede cooperation in evolutionary games with reinforcement learning. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C. Phys. Comput. 2022, 33, 2250168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Stations | WUM | SM | KG | KI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangya | 13 | 15 | 0.25 | 0.2 |
| Zaoshi | 12 | 10 | 0.15 | 0.2 |
| Yanchi | 12 | 15 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Sangzhi | 10 | 15 | 0.12 | 0.25 |
| Zhangjiajie | 15 | 15 | 0.3 | 0.25 |
| Shimen | 13 | 15 | 0.25 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, L.; Tong, B.; Bi, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. Intelligent Parameter Fusion for Distributed Flood Modeling in Parallel Ridge–Valley Landscapes. Water 2025, 17, 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131984
Lan L, Tong B, Bi H, Xu Y, Zhang L. Intelligent Parameter Fusion for Distributed Flood Modeling in Parallel Ridge–Valley Landscapes. Water. 2025; 17(13):1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131984
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Lan, Bingxing Tong, Hongwei Bi, Yinshan Xu, and Li Zhang. 2025. "Intelligent Parameter Fusion for Distributed Flood Modeling in Parallel Ridge–Valley Landscapes" Water 17, no. 13: 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131984
APA StyleLan, L., Tong, B., Bi, H., Xu, Y., & Zhang, L. (2025). Intelligent Parameter Fusion for Distributed Flood Modeling in Parallel Ridge–Valley Landscapes. Water, 17(13), 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131984





