Abstract
This study assesses the ecological status of alpine lotic ecosystems in Khunjerab National Park, Pakistan, situated at approximately 4000 m in the Karakoram Range along the Pakistan–China border. An integrative approach was employed, evaluating alpine stream ecosystems through benthic macroinvertebrate indices in conjunction with physicochemical habitat parameters. Samples were gathered using kick nets and hand-picking at seventeen randomly selected sites in early spring and summer. The study recorded 710 summer taxa from 41 families and seven orders, and 1250 early spring taxa from 30 families and six orders. The abundance of macroinvertebrates increased in early spring, while taxonomic diversity increased during the summer. Statistical tests revealed a strong relationship between water quality conditions and biological features. The biotic index reached its peak in early spring, while diversity indices peaked in summer when Ephemeroptera dominated. Due to the macroinvertebrate source in early spring, the majority of EPT taxa were abundant at all alpine stream sites during early spring, except for upstream sites in summer. The indices from the biotic metric evaluation revealed low levels of natural environmental disturbance caused by humans. This research is significant in terms of natural resource conservation and health assessment based on the benthic fauna community structure in alpine streams.
1. Introduction
Biological parameters are frequently used to assess ecosystem health, particularly in freshwater systems, which are among the most threatened, especially in developing nations [1]. Alpine streams are essential components of worldwide river networks [2], with significant impacts on downstream water quality, flow dynamics, and biological integrity [3,4]. These alpine ecosystems are subject to extreme conditions such as low temperatures, intense sun radiation, as well as regular floods, landslides, and avalanches [5,6]. Because of their sensitivity to environmental changes, benthic macroinvertebrates are often utilized to assess river health [7,8]. The Water Framework Directive (WFD) recognizes macroinvertebrate communities as reliable indicators of ecological status in a variety of aquatic systems [9,10]. However, changes in stream shape and water quality may significantly impact their composition [11]. As such, bioindicators are helpful tools for managing and monitoring aquatic ecosystems [12]. When combined with chemical assessments, biological monitoring provides a more thorough way of evaluating water quality [13]. Multi-metric biological indices, in particular, have been identified as useful for tracking ecosystem health across varied habitats [14].
Community structure can be organized using a variety of elements. As a result, under physically benign conditions, biotic interactions cause population growth [15]. Macroinvertebrate community structure changes seasonally in response to environmental conditions [16]. Functional feeding groups are sensitive to natural and anthropogenic changes that occur along rivers [17]. The growth and reproduction of benthic macroinvertebrate communities are directly affected by oxygen content, temperature, substrate, and organic matter [18]. Stream benthic fauna abundance can be influenced by environmental conditions such as temperature, water chemistry, and hydraulic stress [19,20].
There are relatively few studies on the ecology of alpine headwater streams [21,22] and mountain springs. The present study analyzes the macro-benthic community of alpine streams in Khunjerab National Park (KNP) during the base and peak flow seasons (wet and dry seasons) that influence community structure. To evaluate the ecological integrity of alpine lotic ecosystems, the specific objectives are (1) to use benthic macroinvertebrates for assessing the ecological status of alpine streams based on the recommended indices in relation to physicochemical variables, (2) to examine the seasonal fluctuation of benthic macroinvertebrate community richness and functional feeding groups as well as physicochemical and hydromorphological characteristics, and (3) to analyze the changes in benthic macroinvertebrate communities along the elevation gradient. We then review recent advances in understanding the dynamic functioning of alpine water sources and the interrelationships between environmental variables and their roles in determining benthic communities in alpine streams.
For long-term ecological research in alpine lotic ecosystems, the present study also addresses research gaps through detailed field investigations of spatial and temporal differences in physicochemical habitat structure and geomorphic conditions reflecting the community composition of benthic macroinvertebrates, as well as the distribution, density, diversity, and richness of benthic macroinvertebrates. The implications of the results are considered in the context of the current conservation of alpine biodiversity and the broader applications of alpine stream management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
Gilgit-Baltistan (GB), Pakistan, is located in the northern part of the country, bordering China’s Xinjiang region to the northeast via the Khunjerab Pass. Covering a total area of 72,971 km2, GB is characterized by its rugged mountainous terrain. The region has an estimated population of approximately 1.8 million, with its capital, Gilgit, being home to around 216,760 residents. Physicochemical and biological parameters were assessed at seventeen locations in KNP (Figure 1). It is one of the world’s highest parks and the third-largest national park in Pakistan, with a total area of 226,913 ha, and an altitude of 3660 m (12,078 ft) at the park’s entrance, rising to over 6000 m (19,800 ft), and encompassing valleys such as Ghujerab and the remote Shimshal [23].
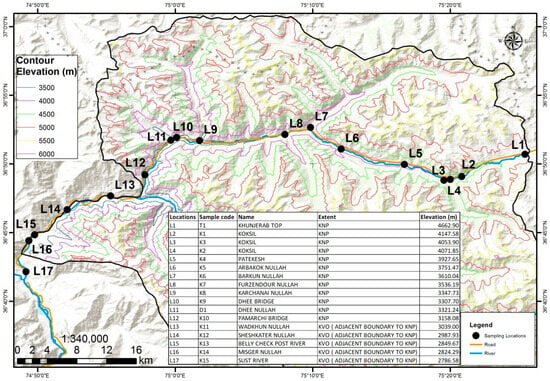
Figure 1.
Sampling locations at Khunjerab National Park (KNP).
Khunjerab is a pristine landscape covering an area of 4455 km2, with the Chinese side encompassing 15,000 km2 within the Taxkorgan Natural Reserve. It lies within the Tibetan Plateau steppes of the G200 eco-regions (16,282 ft). It is located on the Pakistan–China border and situated between 34°44′ N and 75°17′ E at an elevation above 4000 m (13,000 ft), adjacent to the Taxkorgan Natural Reserve (1,400,000 ha) in China. The main purpose of this park is to protect the endangered Marco Polo sheep, which exist only in this part of Pakistan.
The region’s lifeline is the Karakoram Highway (KKH), a 1300 km artery that begins in Islamabad and ends at the Khunjerab Pass (4750 m), where it crosses into China. The area experiences relatively severe winters but mild autumns and pleasant summers, with extreme temperatures rising up to 27 °C in May and dropping below 0 °C in November and onward. The average winter temperature (December and January) is −12 °C, while the average temperature in July and August is 14 °C. Yearly precipitation ranges from 200 to 900 mm, with 90% occurring in the form of snow. Summer precipitation occurs more locally and varies greatly due to the influence of disturbances and uneven monsoon convection.
The Park area is predominantly composed of massive mountains with snow-capped peaks and riverine valleys. Physical erosion, landslides, and black glaciers are common in different valleys of the park. Most of the valleys are characterized by stone beds, while the peaks are surrounded by hill slopes covered with pebbles and loose stones, with soil particles making up about 50% of the composition.
2.2. Data Collection, Sampling, and Analysis
Samples were randomly taken from the banks of streams and rivers, including the main source at Pamirchi Bridge, KNP. Samples were collected from the glacier opening facing north, near flood debris, and solid waste dumping sites. Sampling stations recorded air and water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), and the environmental conditions around the site. Additionally, other hydromorphological features were noted, such as vegetation cover, percentages of boulders, cobbles, and pebbles, and elevation. For the assessment of channel stability, the PSI [24] was used. The water samples were transported to the laboratory for detailed chemical analysis.
Macroinvertebrates were collected using the D-frame kick net method with a net mesh size of 500 µm. The D-frame kick net is the most effective sampler for cobble substrates (e.g., riffles and runs), where the velocity of water transports dislodged organisms into the net. It is designed to sample one square meter of the substrate at a time and can be used at any depth just a few centimeters below one meter [25].
A 100 m span was allocated first, which was then divided into five smaller sub-areas. Each sub-area was assigned a site with a small riffle. The stream bed was disturbed with the feet, causing an upheaval of macroinvertebrates in a plume. The plume passed through the net, and all benthos were collected in the kick net and labeled [26]. The samples were transferred to bottles, preserved in alcohol (formalin 85%), and taken to the laboratory for further analysis under a stereomicroscope up to the family level, using a dichotomous key [27] and HKH macro keys [28].
Water samples were collected in 100 mL polystyrene sterilized bottles from alpine streams during biological sampling, ensuring a representative sample from each location. Care was taken to avoid unwanted bed material was kept from entering the sample. Water samples were brought to the laboratory for chemical analysis.
Water samples were first filtered through Sartorius 92–93 filter paper and subsequently through a 0.45 μm syringe filter before injection. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with a conductivity detector was employed for the determination of anions. Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), using a Thermo Fisher Scientific iCAP 6500 (Oxford, UK), was used for measuring metal concentrations. All other chemicals/reagents were of analytical grade from E. Merck, Darmstadt, Germany.
The water analysis system consisted of a solvent delivery system, including a solvent organizer K-1500, pump K-1001 equipped with a Rheodyne injector 7725, and a 20 mL loop from Knauer, Berlin, Germany. A conductivity detector from Altech, model 650 (Flemington, NJ, USA), was used for the measurement of anions. Optimization of chromatographic conditions was performed using a standard mixture of seven anions: fluoride, chloride, nitrite, bromide, nitrate, phosphate, and sulfate. Anion exchange PRP X-100 columns from Hamilton (Reno, NV, USA) were used for anion separation. The mobile phase used was 4 mM para-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA) at a pH of 8.3, with a flow rate of 1.2 mL/min.
For total suspended solids (TSSs), the gravimetric method was applied using vacuum filtration and oven drying. The sample volume was 1000 mL. The solution was shaken well before filtration. The drying temperature and time for residue were maintained at 80–100 °C for 4–5 h. Samples and standard solutions were acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl). In the case of arsenic determination, iodide concentration was added.
2.3. Calculation of Biological Indices and Statistical Analysis
Different biotic community and diversity indices for stream health assessments were used, such as the Biological Monitoring Working Party (BMWP) index [29,30], and the Average Score Per Taxon (ASPT) index [31,32,33,34]. The number and abundance of tolerant and non-tolerant species, such as the EPT index [35], and taxa richness, were calculated for each location. Moreover, the family biotic index (FBI) [36], Nepalese Biotic Score (NEPBIOS) [37], and functional feeding group (FFG) [38] were also assessed.
Diversity indices, including Simpson’s diversity index (D) [39], the Shannon–Wiener Diversity Index (H) [40], and the Margalef Index [41], were calculated. Likewise, community indices such as benthic macroinvertebrate abundance, EPT%, Diptera%, and Diptera abundance were also analyzed across different seasons. The Pfankuch Stability Index (PSI) [42] was calculated for stream stability assessment, while PAST version 2.17c was used for the calculation of biological indices [43].
Microsoft Excel 2010 was used for data manipulation. Statistical software such as the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) 17th edition was used for the analysis of one-way ANOVA, PCA, CA, and CM, respectively. ArcGIS 9 was used for mapping the study area.
3. Results
3.1. Benthic Macroinvertebrates (Abundance, Composition, Diversity, and Richness)
The benthic macroinvertebrates were more abundant in early spring (total individuals: 1250) than in summer (total individuals: 710), comprising 30 families and six orders in early spring and 41 families and seven orders in summer. Overall, high abundance was noted at all locations in early spring, which showed greater abundance than in summer. Moreover, location 9 (Qarchanai Nullah) and location 11 (Dhee Nullah) had the highest abundance in early spring, respectively (Figure 2a).
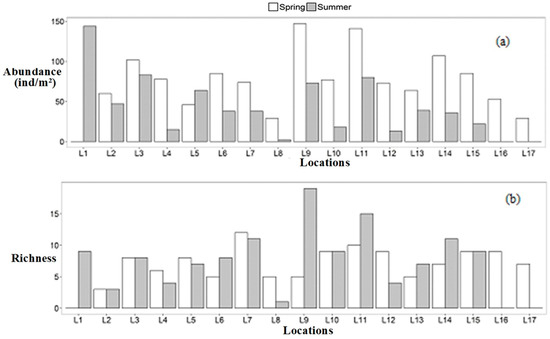
Figure 2.
Benthic macroinvertebrate abundance and richness at different locations (a): macroinvertebrate abundance; (b): taxa richness) in KNP.
Ephemeroptera was the dominant taxa and was found in abundance at location 9 (Qarchanai Nullah) in the spring season, followed by location 6 (Arbakok Nullah). However, in the sample studied from location 1, no fauna were found in early spring due to very low temperatures.
Benthic macroinvertebrates displayed a high abundance of Ephemeroptera (abundance: 906 ind/m2), accounting for 73% in early spring, followed by Plecoptera (abundance: 237 ind/m2), representing 33% in summer. Likewise, Trichoptera (abundance: 118 ind/m2) constituted 9% in early spring, while Diptera (abundance: 98 ind/m2) accounted for 14%, and Coleoptera (abundance: 10 ind/m2) made up 1% in summer (Figure 3). Neuroptera, Odonata, and Heteropterashowed low densities in both seasons. Besides these, high taxa richness was observed in early spring, except at locations 1, 6, 9, 11, 13, and 14 in summer, with the highest values were recorded at location 9 (Qarchanai Nullah) and location 11 (Dhee Nullah) during summer (Figure 2b). Ephemeroptera was the dominant group, while Plecoptera was the second most abundant, followed by Trichoptera and Coleoptera. High Diptera abundance was found at location 12 (Pamarchi Bridge) in early spring, followed by location 3 (Koksil 2) and location 8 (Furzendur Nullah). In summer, high Diptera abundance was recorded at location 1 (main source), location 3 (Koksil 2), and location 5 (Patesesh Nullah) (Figure 4a).
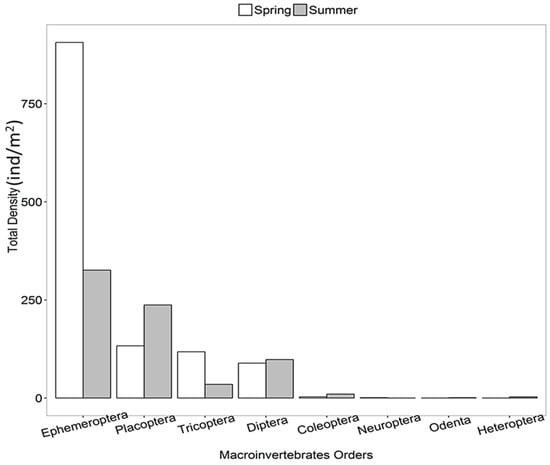
Figure 3.
Total density of benthic macroinvertebrates.
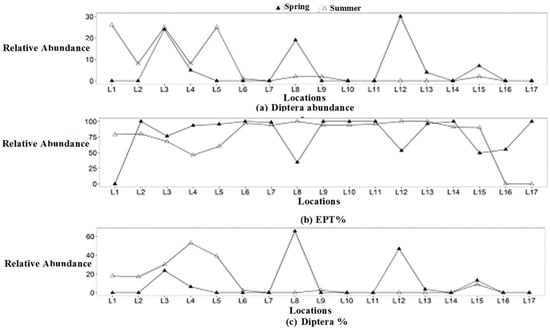
Figure 4.
(a): Diptera abundance; (b): EPT/%; (c): Diptera/%.
3.2. Relative Abundance of Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities’ Functional Feeding Groups
The relative abundance of benthic macroinvertebrate functional feeding groups was based on the percentage densities of collector/filters, collector/gathers, predators, scrapers, shredders, shredders/collectors, scrapers/collectors, predators/scrapers, and scrapers/shredders across the seasons. The highest relative abundance was recorded for collectors/gathers in early spring (43%), followed by predators in summer (33%), and scrapers in early spring (32%) (Figure 5). Other groups, such as collectors/filters, were higher in summer (20%), while shredders were more abundant in spring (10%), followed by shredders/collectors (1%) and predators/scrapers (5%), which were found to be higher in early spring compared to summer.
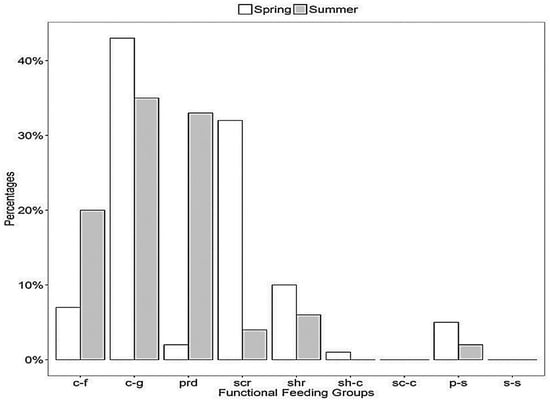
Figure 5.
Relative abundance of benthic macroinvertebrate functional feeding groups at the location at KNP.
3.3. Altitudinal Changes in Benthic Macroinvertebrate Community Composition and Structure
From the total percentage of families, the most dominant families across the seasons were Ephemeroptera families (Heptageniidae (28%), Baetiella larva (18%), Baetiella (8%)); Heptageniidae (Iron (31%)); and Heptageniidae (Rhithrogena (14%)). Plecoptera families included Capniidae (8%) and Taeniopterygidae (2%), while Diptera families included Ceratopogonidae larva (1%), Chironomidae (3%), and Simuliidae larva (3%). Trichoptera families comprised Philopotamidae (5%) and Rhyacophilidae (5%) in early spring.
In summer, the dominant Ephemeroptera families included Baetidae (Baetiella (5%)), Baetidae (Baetiella, Baetis (7%)), Ephemerellidae (Drunella (11%)), Heptageniidae (Epeorus (3%)), Heptageniidae (Rhithrogena (2%)), and Nemouridae (5%). The dominant Plecoptera families were Chloroperlidae (32%) and Oligocapniidae (22%), while Diptera families included Chironomidae (16%), and Trichoptera families included Rhyacophilidae (2%) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Hydromorphological characteristics of different locations.
The composition and diversity of benthic macroinvertebrate families varied with altitude, categorized as above 4000 m, below 4000 m, and <3000 m, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Distribution of benthic macroinvertebrate taxa based on elevation at KNP.
3.4. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Benthic Macroinvertebrates Indices
The abundance of benthic macroinvertebrates and biotic indices such as the FBI, ASPT, NEPBIOS, BMWP, EPT, and Diptera were assessed across different site categories, including natural spring-fed sources, agricultural runoff-affected streams, and urban-influenced channels. A significant difference (p > 0.05 and p > 0.01) was found between the biotic indices across the seasons. The highest scores of biotic indices were observed in early spring. The diversity indices, with respect to various locations, showed no significant relationship (p > 0.05). High scores of diversity indices were observed in summer, except for dominance, as summer had more richness of families compared to early spring. The Shannon–Wiener index was highest in summer, followed by the Fisher’s alpha and Margalef indices. In contrast, high orders of Ephemeroptera and Trichoptera were observed in early spring, while Plecoptera, Diptera, and Coleoptera dominated in summer. In summer, a high density of Plecoptera was found at upstream location 1 [44], as Plecoptera are known to be more sensitive to contaminants or other stressors [45] and serve as good indicators of stream health. Their presence is often considered an indicator of good stream health. Locations with high biotic scores also exhibited high diversity and richness of families. The biotic indices’ assessment was divided into seven diagnostic categories: excellent water quality (EWQ), clean water quality (CWQ), good water quality (GWQ), doubtful water quality (DWQ), moderate water quality (MWQ), fair water quality (FWQ), and poor water quality (PWQ) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Biotic indices with respect to various water quality classes at different locations between the seasons.
3.4.1. Relationships Among Macroinvertebrate Indices and Environmental Variables
Correlation analysis between biotic indices and diversity indices shows a significant relationship (Table 4). EPT was highly significant with ASPT (p < 0.01), BMWP, and Shannon_H (p < 0.05). ASPT was highly significant with the (Biological Monitoring Working Party) BMWP index (p < 0.01), Shannon_H, and equitability_J (p < 0.05). BMWP was highly significant with NEPBIOS, Shannon_H, and the Margalef index. NEPBIOS was highly significant with the Margalef index, Fisher_alpha (p < 0.01), and Shannon_H (p < 0.05). The family biotic index (FBI) showed no significant relationship. Simpson’s diversity index was highly significant (p < 0.01) with Shannon_H, the Margalef index, Fisher_alpha, Berger–Parker, equitability_J, and dominance_d. Shannon_H was highly significant (p < 0.01) with the Margalef index, Fisher_alpha, Berger–Parker, equitability_J, and dominance_d. Evenness_e^H/S was highly significant with equitability_J (p < 0.01) and the Margalef index (p < 0.05). The Margalef index was significant with Fisher_alpha, dominance_d (p < 0.01), and Berger–Parker (p < 0.05). Fisher_alpha was significant with dominance_d (p < 0.01) and Berger–Parker (p < 0.05). Berger–Parker was significant (p < 0.01) with equitability_J and dominance_d. Equitability_J was highly significant (p < 0.05) with dominance_d.

Table 4.
Spearman correlations between biotic and diversity indices of macrinvertebrate families.
Likewise, correlation analysis between environmental variables and community and biotic indices across the seasons shows that temperature had no significant relationship with the community and biotic indices (Table S1). Air temperature had a significant relationship with the NEPBIOS index (p < 0.01) and the BMWP index (p < 0.05), followed by Simpson_I-D, Shannon_H, and the Margalef index. pH was significant with Fisher_alpha (p < 0.01), and EPT and the Margalef index (p < 0.05). Turbidity was significant with Fisher_alpha (p < 0.01) and the Margalef index (p < 0.05). DO was significant with Fisher_alpha (p < 0.01) and EPT and the Margalef index (p < 0.05). EC was found to be significant with NEPBIOS and the Fisher_alpha index (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, TDS showed no significant difference. TSS had a significant relationship with the family biotic index (FBI) (p < 0.05).
3.4.2. Relationships Among Physicochemical, Biological, and Hydromorphological Variables
The CM shows that numerous parameter pairs have significant positive correlations, such as pebbles%–temp°C/(R = 0.827), pH-TDS/(R = 0.580), turbidity-TSS/(R = 0.819), turbidity-Si/(R = 0.815), EC-TDS/(R = 0.789), EC-TSS/(R = 0.571), EC-SO4/(R = 0.837), EC-Ca/(R = 0.738), TDS-Ca/(R = 0.828), TDS-Sr/(R = 0.762), TDS-Mg/(R = 0.811), TSS-Si/(R = 0.673), taxa richness-NEPBIOS_1-D/(R = 0.942), taxa richness-Margalef index/(R = 0.969), taxa richness-Fisher-alpha/(R = 0.928), BMWP_1-D-NEPBIOS_1-D/(R = 0.802), BMWP_1-D-Shannon_H/(R = 0.849), BMWP_1-D-Margalef index/(R = 0.882), BMWP_1-D-Fisher_alpha/(R = 0.839), dominance_d–Berger-Parker/(R = 0.976), evenness_e^H/S-equitability_J/(R = 0.958), Mg-Sr/(R = 0.919), and Sr-hardness/(R = 0.896). Similarly, some pairs show significant negative correlations, such as elevation-temp/(R = −0.887), pH-benthic macroinvertebrates abundance/(R = −0.538), TDS-EPT_1-D/(R = −0.699), pebbles%-elevation/(R = −0.862), PS1-Al/(R = −0.836), Simpson_1-D-Al/(R = −0.833), and equitability_J-Al/(R = −0.851).
In CA, similar objects enter the same class, and dissimilar groups enter other groups [46]. The levels of similarity at which observations are merged to construct a dendrogram are shown in (Figure 6). Group one includes the Margalef index, Fisher_alpha, taxa richness, NEP-BIOS-1D, BMWP_1-D, temperature, pebbles, and air temperature (Figure 6). The second group includes vegetation, benthic macroinvertebrates, Simpson_1-D, Shannon-H, evenness_e^H/S, equitability_J, and the ASPT index, while the third group includes As, DO, velocity, Se, cobbles, Zn, and Hg. Group four includes pH, EC, SO4, Ca, TSS, Si, TDS, Mg, Sr, Na, Al, Ba, and K parameters (Figure 6), suggesting that all these parameters are from the same source, mainly anthropogenic, industrial, and natural activities.
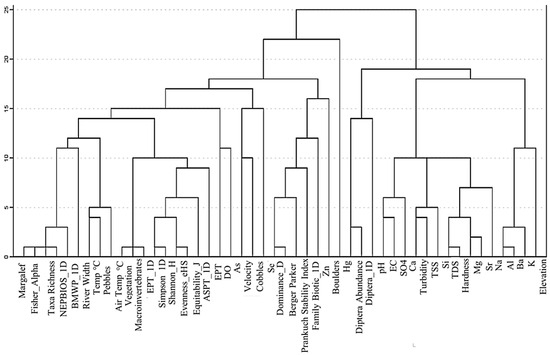
Figure 6.
Dendrogram using average linkage between groups.
PCA was used to compare compositional patterns between water systems and to identify sources that affect each other. As seen in Table S2, the ten components of PCA revealed 93.6% of the variation in the sample data. PCA can be interpreted more easily by using the maximal varimax normalized technique of the variance described by the retrieved factors. VF1 explained 33.4 percent of the total variance and has high factor loadings for benthic macroinvertebrate abundance, taxa richness, BMWP_1-D, the ASPT index, Simpson_1-D, Shannon_H, and equitability_J, which are associated with the common natural origin [47]. VF2 accounted for 16.32 percent of the total variance and reflected significant loadings for SO4, Si, EC, TDS, and TSS, along with a strong cluster in CA, which could have been influenced by the weathering of mafic and ultramafic rocks. This indicates that VF2 also has geogenic sources [47]. VF3 explains 11.79 percent of the total variance with loading for temperature and air temperature, originating from anthropogenic activities. VF4 explains 9.09 percent of the total variance, including elements such as vegetation and benthic macroinvertebrates, indicating a common source [48]. VF5 explains 5.3 percent of the total variance, indicating a common source and revealing significant loading for Diptera abundance and Zn [48]. VF6 accounted for 4.97 percent of the total variance and revealed significant loading for Se, Sr, and Ca, which also have origins from anthropogenic activities related to industrial, agricultural, or nutrient effects [49,50]. VF7 was loaded by turbidity and TSS, with a variance of 4.03 percent. VF8 explained 3.31 percent of the total variance and has high factor loadings for K, which has geogenic sources and is associated with a common natural origin. VF9 was loaded by DO and NEPBIOS_1-D, with a variance of 2.77 percent of the total variance. VF10 was loaded by cobbles%, with a variance of 2.54 percent of the total variance.
One-way ANOVA results show significant differences (p < 0.05) in turbidity, EC, TSS, and TDS among the seasons. EC was found to be highly significant (p < 0.01). High mean values of TDS (43.2 mg/L) and turbidity (22.23 NTU) were noted between the seasons, respectively. There was no significant difference found among the temperature, air temperature, pH, and DO, respectively.
4. Discussion
4.1. Benthic Macroinvertebrates
Similar results were reported by Sharma & Rawat [51] and Brewin et al., in Nepal [52], where the seasonal fluctuation of benthic macroinvertebrate abundance shows significant variation between the wet and dry seasons. The dry season had higher abundance compared to the wet season [53,54]. This indicates that food materials may directly influence the aquatic organisms’ cycles and the seasonal abundance of benthic macroinvertebrates [55]. It was also reported that the maximum density of benthic macroinvertebrates occurs during the dry season, likely due to the increased availability of food resources such as periphyton, detritus, and organic matter that accumulate under lower flow conditions.
The same results were found in [56,57]. The studied samples indicated that the major components of the benthic macroinvertebrate community are Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, Trichoptera, and Diptera. Ephemeroptera are sensitive to oxygen depletion as a result of organic or nutrient enrichment, accordingly representing a degradation of water quality [58,59]. Similarly, for the assessment of river and stream conditions, Plecoptera provide a high potential for bio-indication and have limited flexibility [60], contributing as an effective and successful tool for assessing freshwater habitat degradation [61,62]. The composition of Trichoptera (caddisfly) also indicates clean water quality, alongside Ephemeroptera and Plecoptera, for stream biological assessment. This research also aligns with the work of [63] in Mediterranean streams, which stated that the macroinvertebrate abundance and richness were higher during the wet season. The findings of the present study highlighted the occurrence of sensitive taxa during high discharge and tolerant taxa under conditions of low discharge. Although [64] reported high EPT composition and Ephemeroptera taxa abundance during the wet season, these findings do not align with the present study; on the contrary, our results show higher Plecoptera abundance in the wet season and Trichoptera in the dry season. However, numerous studies have shown that seasonal variation influences changes in species abundance rather than the complete replacement of species [65].
The high EPT% taxa in spring indicate that the stream was well-oxygenated and clean, as the EPT taxon is highly sensitive to pollution [66,67]. The high Diptera% in summer indicates the presence of organic pollution among the locations, supported by [68]. As cited in [69], the Chironomidae family also receives significant attention worldwide due to its ability to assess aquatic environmental conditions as bioindicators. Like other studies, it is suggested that it can be used for assessing ecosystem health, testing toxicity, conducting environmental impact assessments, or climate-based paleoenvironmental studies.
4.2. Relative Abundance of Benthic Macroinvertebrate Populations and Functional Feeding Groups
Scrapers/collectors and scrapers/shredders show 0% relative abundance among the seasons. Collectors/gatherers and predators were the dominant functional feeding groups at most of the sampling locations, a finding similar to those of [70] in Nigeria [71], in East Africa, and [72] in Argentina. The river continuum concept describes that if the source of the river is within a shaded area (e.g., forest), it results in the dominance of shredders among the functional feeding groups [73]. The shredders were not abundant at any location, and the research agrees with the findings of [74], which predict that the lesser shredder population in the research area is due to the lack of canopy cover. Our findings also agree with the results of [75], which show a comparatively high density of collectors/gatherers and predators at all locations. The results align with the prediction of the river continuum concept by the significant increase in the number of collectors/gatherers, followed by collectors/filters and scrapers, toward the downstream area.
4.3. Variations in the Composition and Structure of Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities at Different Elevations
The outcomes of hydromorphological characteristics like the PSI are in agreement with the statement of the authors [76,77] that the presence of vegetation or channel stability significantly affects the benthic fauna (Table 1). Besides the vegetation within the stream channels, the riparian vegetation also influences the function and structure of benthic macroinvertebrate communities and assembly [78,79]. Prevalent physical conditions like stream and channel characteristics generally affect the processes of biological communities [80,81]. The percentage of benthic macroinvertebrate communities, such as EPT taxa, has a significant correlation with overall habitat assessment scores (PSI), as well as with individual measures of geomorphic conditions and habitat quality.
The findings of [82] support these results, showing that decreasing water temperature is associated with a decline in the number of benthic macroinvertebrate families, both spatially (increasing altitude) and seasonally (from summer to winter) in the headwaters. Results show fewer families in the dry season compared to the wet season. A similar observation was noted at location 1 (Khunjerab Top), where no benthic macroinvertebrates were found due to a very low temperature of 2.1 °C in the dry season, while the wet season had a higher number of families.
4.4. Indices of Benthic Macroinvertebrates Vary
Alpine rivers face challenges that affect the diversity, abundance, and distribution of their organisms, with some of these changes being ongoing. The metrics used to analyze the river, including the total number of species, biotic indices (the FBI, ASPT, NEPBIOS, BMWP, and EPT), and the physicochemical variable ratio, suggest that the river may be in ‘excellent’ condition, particularly downstream. The application of EPT helped improve our understanding of abundance weighting applied to benthic macroinvertebrates in river classification.
Both the BMWP and EPT indices indicated that the river was ‘very good’ according to the WFD rating. With equal BMWP and EPT scores, both indices might provide a strong explanation by identifying certain organisms that could enhance the river’s taxonomy and thus clarify the river’s status at any given time. While the BMWP index is simpler to use in measuring pollution status [83,84], our results align with those of [85], which indicated that the water catchment has minimal anthropogenic disturbances.
4.4.1. Associations Between Environmental Factors and Macroinvertebrate Indicators
The macroinvertebrate benthic diversity in this river’s freshwater habitats was significantly influenced by the environmental conditions evaluated. Furthermore, several studies have shown that variations in physical and chemical traits can occur at any time and have a significant impact on the structure of aquatic communities [86,87]. The second significant impact was habitat quality, suggesting that better environmental conditions also benefit macroinvertebrate benthic diversity [88]. According to [89,90], habitat heterogeneity is frequently an objective of environmental restoration and can support biotic recovery and biodiversity in aquatic environments.
4.4.2. Interactions Between Biological, Hydromorphological, and Physicochemical Factors
The investigation of the CM showed that the nominated parameters had related sources of contamination, such as atmospheric deposition, phosphate fertilizers, the incineration of municipal solid waste, and wood preservatives [91].
Cluster analysis (CA) has proven to be an effective tool for identifying sources of contamination in the river system [92]. Elevated zinc (Zn) concentrations observed in the water samples are likely derived from the leaching of chemical fertilizers, household waste, and animal manure, reflecting local agricultural and domestic activities [93]. Arsenic (As), a toxic element detected in some samples, poses significant health risks, including lung and skin cancers, cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, reproductive issues, and respiratory complications [94,95]. Potassium (K+), a major cation that is commonly abundant in seawater and mineral water, is less typical in drinking water. However, in this study, higher K+ levels in certain samples are attributed to the weathering of Holocene rock formations present in the watershed [96]. Both low and high concentrations of potassium can adversely affect human health; deficiency may cause an irregular heartbeat, hypertension, and muscle weakness, while excess intake is associated with a rapid heartbeat, bladder infections, and immune system weakening [97]. Electrical conductivity (EC) values serve as an indirect measure of dissolved solids in the river water [98]. The hydrolysis of silicate minerals, which are abundant in the local bedrock and glacial deposits, plays a key role in increasing pH levels. Elevated calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) concentrations are primarily the result of water–rock interactions between the river water and aquifer sediments that are rich in carbonate and organic matter [99]. These geochemical processes, coupled with anthropogenic inputs, define the water quality characteristics observed in the river.
PCA was used to compare compositional patterns between water systems and to identify sources that affect each other. The affiliation of these parameters may be attributed to the occurrence of mafic and carbonaceous rocks, as well as agricultural activities in the study area, suggesting both anthropogenic and geogenic sources [99].
ANOVA analysis revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) among physicochemical parameters. Thus, the physical variables were within the permissible limits according to WHO and PSQCA guidelines, except for the turbidity parameter in summer (>5 NTU). According to the guidelines for fish and aquatic organisms, the maximum temperature shall not exceed 3 °Crelative to an upstream control point [100]; however, it is unlikely in the summer season as the upstream area appears to have a high temperature (>3 °C). In addition to this, a significant difference was observed in the physical variables of the early spring season, such as turbidity, EC, and TDS, respectively, with high mean values of EC (346.35 μS/cm) and air temperature (10.63 °C) also noted. A similar result was reported by [100], indicating that fluctuations in temperature (3–5 °C) in the system and the lack of vegetation cover in the riparian area are sufficient to disturb the growth of many taxa like Eph [101], growth rate patterns, reproduction, metabolism, and body size [102].
Few species are able to tolerate the upper limit of temperature tolerance [103]. Although the temperature of a running water system depends on factors such as daily or seasonal variability, climate conditions, riparian vegetation cover, stream elevation [104], and land use patterns of the surrounding area, benthic macroinvertebrates are also sensitive to pH [105]. A pH range below 5 and greater than 9 is considered harmful, while low pH levels indicate the low diversity of the benthic fauna and can activate the release of heavy metals that are toxic to benthic macroinvertebrates [106]. Similar findings were reported by [106], where no single location exhibited a pH below 6.5, thereby indicating minimal or no effect of pH on the community composition of benthic macroinvertebrates. The results strongly correlate with the findings of [107], which indicate that extremely low water temperatures in mountainous stream environments are related to the decline of benthic macroinvertebrate families, as recorded in the dry season of the study period. DO is inversely correlated with stream temperature; high temperatures may decrease the abundance and diversity of benthic macroinvertebrates. Similar results were reported by [107], where the reduction in the richness of Plecoptera (stonefly) was significantly correlated with yearly water temperature fluctuations. Normally, a DO range of 5–6 mg/L is required to support a diversified aquatic organism. For better water quality to support aquatic organisms, DO should be 9–10 mg/L, which is considered very good and indicates better water quality. DO levels below 3 mg/L are considered very stressful for aquatic organisms within the system [108]. No strong seasonal pattern for DO was observed in the study, similar to the results of [108].
Macroinvertebrate community structures were significantly correlated with EC [109]. Similarly, the results of [109] support the findings that when conductivity exceeds 500 μS/cm, it significantly reduces the taxa richness of mayflies. The same observation was made at locations 8, 13, 15, and 17 in early spring, as higher EC values were noted in the dry season. Arsenic was found to be significant (p < 0.05) among the seasons. High mean values of Ca (39.7 mg/L) and SO4 (53.7 mg/L) were noted, and no significant difference (p > 0.05) was found among Ca, K, Mg, Na, and SO4. Some elements in various locations, such as Al (mg/L), Hg (µg/L), Sb (µg/L), and Se (µg/L), were found to be below the LOD. Significant differences were observed among the parameters of early spring, including EC (p < 0.05), Ca (p < 0.01), hardness (p < 0.05), the EPT index (p < 0.01), and the PSI (p < 0.05). However, no significant differences (p > 0.05) were noted among K, Mg, Na, SO4, As, Ba, Si, Sr, Zn, and other biotic and diversity indices. The chemical parameters were within the permissible limits according to the guidelines for fish and other aquatic organisms [110], except for As (0.02 mg/L) and Hg (0.004 mg/L). According to WHO and the guidelines for fish and other aquatic organisms, the values should be within the range of As (0.01 mg/L) and Hg (0.001 mg/L).
5. Conclusions
The study shows the seasonal fluctuation of benthic macroinvertebrate compositions, abundance, richness, and functional feeding groups along with physicochemical and hydromorphological characteristics. Furthermore, it investigates changes in benthic communities along an elevation gradient. A higher abundance was found in the dry season compared to the wet season, with higher taxa richness. The findings show a strong correlation between water quality and biological parameters. The biotic indices, with respect to various water quality classes at different locations across seasons, reflect the stream’s ecological status. Based on seven diagnostic categories, the results indicate that the catchment has minimal anthropogenic disturbances. The results also show spatial and temporal differences in physicochemical habitat structure and geomorphic conditions, which reflect the benthic community composition and structure.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17131948/s1, Table S1: Pearson/(R) correlation among environmental variables & biotic indices; Table S2: Factor loading for selected metals, biological and physicochemical parameters in water samples of the study area.
Author Contributions
S.A. (Salar Ali) contributed to writing—original draft preparation—and methodology, whereas J.G. provided supervision and validation. A.R. assisted in writing—review and editing. Furthermore, A.H. and A.A. were involved in the formal analysis of the research. Lastly, S.A. (Saad Abdullah) contributed to writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research article received no funding from any institution or organization. The authors conducted the study independently, with no financial support from any third party and no conflicts of interest.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the National Insect Museum, the National Agriculture Research Council (NARC), and the Pakistan Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology (PINSTEC) for providing technical support for this research. We also acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their critical comments and suggestions, which have significantly enhanced our manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dos Santos, D.A.; Molineri, C.; Reynaga, M.C.; Basualdo, C. Which index is the best to assess stream health? Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füreder, L. High alpine streams: Cold habitats for insect larvae. In Cold-Adapted Organisms; Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, D.L.; Prindle, S.E.; Johnson, J.H. Salmon River Wild Young-of-Year Chinook Salmon Seining Program; New York State Department of Environmental Conservation: Albany, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.; Richardson, J. Understanding processes and downstream linkages of headwater systems. BioScience 2002, 52, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, M.S. Fundamentals of High Altitude Biology; Aspect Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. International Year of Mountains; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Helson, J.E.; Williams, D.D. Development of a macroinvertebrate multimetric index for the assessment of lowland streams in the Neotropics. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligeiro, R.; Hughes, R.M.; Kaufmann, P.R. Defining quantitative stream disturbance gradients and the additive role of habitat variation to explain macroinvertebrate taxa richness. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 25, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union (EU). Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2000, L327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mykrä, H.; Saarinen, T.; Tolkkinen, M.; McFarland, B.; Hämäläinen, H.; Marttinäki, K. Spatial and temporal variability of diatom and macroinvertebrate communities: How representative are ecological classifications within a river system? Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, V.; Van der Windt, H.J.; Van Koppen, C.S.A.; Wesselink, A. Opening of the Haringvliet, a Stream of Possibilities. 2020. Available online: https://www.delta21.nl/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/GWF-Final-Consultancy-Report.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Zampella, R.; Bunnell, J.; Laidig, K.; Procopio, N. Using multiple indicators to evaluate the ecological integrity of a coastal plain stream system. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 644–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenz, T.K.; Golladay, S.W.; Vellidis, G.; Smith, L.L. Stream buffer effectiveness in an agriculturally influenced area, southwestern Georgia. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aazami, J.; Sari, A.E.; Abdoli, A.; Sohrabi, H.; Van den Brink, P.J. Assessment of ecological quality of the Tajan River in Iran using a multimetric macroinvertebrate index and species traits. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snook, D.L.; Milner, A.M. The influence of glacial runoff on stream macroinvertebrate communities in the Taillon catchment, French Pyrenees. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckarsky, B.L. Biotic interactions or abiotic limitations? A model of community structure. In Dynamics of Lotic Ecosystems; Fontaine, T.D., Bartell, S.M., Eds.; Ann Arbor Science Publishers: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1983; pp. 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Pesce, S.; Margoum, C.; Montuelle, B. In situ relationship between spatiotemporal variations in diuron concentrations and phototrophic biofilm tolerance in a contaminated river. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, P.J.; Board, J.; Faggiani, D.; Hitchcock, P.B.; Preece, L.; Waters, A.J. Model studies for the synthesis of the antibiotic lactonamycin and the discovery of new reactions and mechanisms for the construction of substituted heterocycles. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 6526–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.W.; Merritt, R.W.; Andrade, P.C.N. The use of macroinvertebrate functional groups to characterize ecosystem attributes in selected streams and rivers in south Brazil. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 2005, 40, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, G.G.; Almodóvar, A.; Elvira, B. Effects of environmental factors and predation on benthic communities in headwater streams. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 72, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruegg, J.; Robinson, C.T. Comparison of macroinvertebrate assemblages of permanent and temporary streams in an alpine floodplain, Switzerland. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2004, 161, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, V.; Marziali, L.; Rossaro, B. Chironomids as bioindicators of environmental quality in mountain springs. Freshw. Sci. 2012, 31, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, A. State intervention and community protest: Nature conservation in Hunza, North Pakistan. In Asian Perceptions of Nature: A Critical Approach; Kreutzmann, H., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cottam, G.; Curtis, J.T. The use of distance measures in phytosociological sampling. Ecology 1956, 37, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plafkin, J.L.; Barbour, M.T.; Porter, K.D.; Gross, S.K.; Hughes, R.M. Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Streams and Rivers: Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, M.P. Aplicação do Biomonitoramento para Avaliação da Qualidade da Águaem Rios; EmbrapaMeioAmbiente: Jaguariúna, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, M.P.; Noguerol, T.N.; Lacorte, S.; Buchanan, I.; Piña, B. Toxicity identification fractionation of environmental estrogens in wastewater and sludge using gas and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry and recombinant yeast assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginebreda, A.; Muñoz, I.; López de Alda, M.; Brix, R.; López-Doval, J.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in rivers: Relationships between hazard indexes and aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity indexes in the Llobregat River (NE Spain). Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, G.; Chapman, D.; Beim, A. The use of biological material in water quality assessments: A guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. In Water Quality Assessments—A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring, 2nd ed.; Chapman, D., Ed.; E & FN Spon: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mettee, M.F.; O’Neil, P.E.; Pierson, J.M. Fishes of Alabama and the Mobile Basin; Oxmoor House: Birmingham, AL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Verneaux, J.; Galmiche, P.; Janier, F.; Monnot, A. Une nouvelle méthode pratique d’évaluation de la qualité des eauxcourantes. Un indicebiologique de qualitégénérale (IBG). Ann. Sci. Univ. Franche-Comté Besançon Biol. Anim. 1982, 4, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hynes, K.E. Benthic Macroinvertebrate Diversity and Biotic Indices for Monitoring of 5 Urban and Urbanizing Lakes Within the Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM), Nova Scotia, Canada; Soil & Water Conservation Society of Metro Halifax: Halifax, NS, Canada, 1998; Volume 14, p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, G.L. Applied Aquatic Ecosystem Concepts, 1st ed.; Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2001; Volume 17, p. 744. ISBN 0-7872-7490-9. [Google Scholar]
- North Carolina Department of Environment, Health, and Natural Resources (NCDEHNR). Standard Operating Procedures for Biological Monitoring; Environmental Sciences Branch Biological Assessment Group, Division of Water Quality, Water Quality Section: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1997.
- Hilsenhoff, W.L. Using a Biotic Index to Evaluate Water Quality in Streams; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; Volume 132. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Moog, O. The applicability of biotic indices and scores in water quality assessment of Nepalese rivers. In Proceedings of the Ecohydrology Conference on High Mountain Areas, Kathmandu, Nepal, 24–28 March 1996; pp. 641–657. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, R.W.; Cummins, K.W. Trophic relations of macroinvertebrates. In Methods in Stream Ecology; Hauer, F.R., Lamberti, G.A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 453–474. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, C.J. The Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance, Ecology, 4th ed.; HarperCollins College Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 514–541. [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen, J.; Carlson, R.E.; Dycus, D.L.; Faulkner, C.; Gibson, G.R.; Harcum, J.; Markowitz, S.A. Lake and Reservoir Bioassessment and Biocriteria: Technical Guidance Document; EPA 841-B-98-007; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Margalef, D.R. Information theory in ecology. Gen. Syst. 1958, 3, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Van Sickle, J.; Baker, J.; Herlihy, A.; Bayley, P.; Gregory, S.; Haggerty, P. Projecting the biological condition of streams under alternative scenarios of human land use. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, P.S.; Moynagh, M.; Svoboda, I.F.; Miller, A. Macroinvertebrates as bioindicators of water pollution in streams draining dairy farming catchments. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 17, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menetrey, N.; Oertli, B.; Sartori, M.; Wagner, A.; Lachavanne, J.B. Eutrophication: Are mayflies (Ephemeroptera) good bioindicators for ponds? Hydrobiologia 2008, 597, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Stradner, D.; Graf, W. Molecular systematics, evolution and zoogeography of the stonefly genus Siphonoperla (Insecta: Trichoptera, Chloroperlidae). J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2012, 50, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krno, I.J. Impact of human activities on stonefly (Insecta, Trichoptera) ecological metrics in the Hron River (Slovakia). Biologia 2007, 62, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruitbos, L.M.; Tetzlaff, D.; Soulsby, C.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; Laudon, H.; Shanley, J. Hydro-climatic and hydrochemical controls on Trichoptera diversity and distribution in northern freshwater ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2012, 693, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- García-Roger, E.M.; Sánchez-Montoya, M.M.; Gómez, R.; Suárez, M.L.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R.; Latron, J.; Prat, N. Do seasonal changes in habitat features influence aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages in perennial versus temporary Mediterranean streams? Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaila, A.H.; Che Salmah, M.R.; Al-Shami, S.A. Temporal distribution of Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera (EPT) adults at a tropical forest stream: Response to seasonal variations. Environmentalist 2012, 32, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.T. Annual and seasonal variation and the effects of hydroperiod on benthic macroinvertebrates of seasonal forest (“vernal”) ponds in central Massachusetts, USA. Wetlands 2000, 20, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, D.M.; Resh, V.H.; King, R.S. An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America; Kendall Hunt Publishing: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tubić, B.; Andjus, S.; Zorić, K.; Vasiljević, B.; Jovičić, K.; Čanak Atlagić, J.; Paunović, M. Aquatic insects (Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera) metric as an important tool in water quality assessment in hilly and mountain streams. Water 2024, 16, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, H.; Heiri, O. The chironomid–temperature relationship: Expression in nature and palaeoenvironmental implications. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 430–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicacio, G.; Juen, L.; Leather, S.R. Chironomids as indicators in freshwater ecosystems: An assessment of the literature. Insect Conserv. Divers. 2015, 8, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadu, D.I.; Akpan, A.W. A survey of the functional feeding groups in Delimi River, in Jos, Plateau State, Nigeria. Nig. J. Appl. Fish. Hydrobio 1986, 1, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, M.; Magana, A.; Mathooko, J.M.; Ndegwa, F.K. Detritivores in Kenyan highland streams: More evidence for the paucity of shredders in the tropics? Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserendino, M.L.; Pizzolon, L.A. Distribution of macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Azul-Quemquemtreu river basin, Patagonia, Argentina. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 37, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannote, R.L.; Minshall, G.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Sedell, J.R.; Cushing, C.E. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoro, F.O. Macroinvertebrates functional feeding groups in River Orogodo, a second order stream in southern Nigeria. Nigerian J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 6, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Vannote, R.L.; Sweeney, B.W. Geographic analysis of thermal equilibria: A conceptual model for evaluating the effect of natural and modified thermal regimes on aquatic insect communities. Am. Nat. 1980, 115, 667–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrish, N.; Bristow, J.M. Macroinvertebrate associations with aquatic macrophytes and artificial substrates. J. Great Lakes Res. 1979, 5, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, E.W. Macroinvertebrate communities associated with three aquatic macrophytes in Lake Onalaska, Wisconsin. J. Freshw. Ecol. 1990, 5, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, D.R.; Taylor, W.D.; Biette, R.M. Dimensions of riparian buffer strips required to maintain trout habitat in southern Ontario streams. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1985, 5, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunen, J.; Snåre, H. Isolated by lakes: The influence of connectivity on benthic macroinvertebrate community structure in river and lake connected streams. Aquat. Sci. 2025, 87, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, H.B.N. The Ecology of Running Waters; Liverpool University Press: Liverpool, UK, 1970; p. 555. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.D. Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 388. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Gao, J.; Begum, F.; Rasool, A.; Ismail, M.; Cai, Y.; Ali, S. Health assessment using aqua-quality indicators of alpine streams (Khunjerab National Park), Gilgit, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4685–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Walt, R.E.; Favret, C.; Webb, D.W. Just how imperiled are aquatic insects? A case study of stoneflies (Trichoptera) in Illinois. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2005, 98, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mico, C.; Recatala, L.; Peris, M.; Sanchez, J. Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, A.; Cato, I.; Carman, R.; Rahm, L. Spatial clustering of metals in the sediments of the Skagerrak/Kattegat. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jiao, J.J.; Huang, J.; Huang, R. Multivariate statistical evaluation of trace elements in groundwater in a coastal area in Shenzhen, China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.C.; Rawat, J.S. Monitoring of aquatic macroinvertebrates as bioindicator for assessing the health of wetlands: A case study in the central Himalayas, India. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, P.A.; Buckton, S.T.; Ormerod, S.J. The seasonal dynamics and persistence of stream macroinvertebrates in Nepal: Do monsoon floods represent disturbance? Freshw. Biol. 2000, 44, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, H.B.N. Biology of Plecoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1976, 21, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leunda, P.M.; Oscoz, J.; Miranda, R.; Ariño, A.H. Longitudinal and seasonal variation of the benthic macroinvertebrate community and biotic indices in an undisturbed Pyrenean river. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.C.; Negi, R.K.; Negi, T. Seasonal variation in benthic macroinvertebrates and their correlation with the environmental variables in a freshwater stream in Garhwal region (India). Life Sci. J. 2007, 4, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, A.; Baig, J.; Din, U.S.; Arshad, A.; Adnan, A.; Khan, A. Relative abundance of benthic macroinvertebrates in relation to abiotic environment in Hussainabad Nallah, Hunza, Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan. Int. J. Biosci. 2016, 9, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, P.; Shivam, A.; Rawat, G.; Singh, K.R.; Verma, J.; Dwivedi, A.C. Longitudinal variation in the structure of benthic communities in the upland Vindhyan and Himalayan: River continuum concept approach. Natl. J. Life Sci. 2004, 1, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlown, M.A.; Ashraf, M.; Hussain, M.; Salam, H.A.; Bhatti, A.Z. Impact Assessment of Sewerage and Industrial Effluents on Water Resources, Soil, Crops and Human Health in Faisalabad; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2006; Khyaban-e-Johar, H-8/1. [Google Scholar]
- Nickson, R.; McArthur, J.; Shrestha, B.; Kyaw-Myint, T.; Lowry, D. Arsenic and other drinking water quality issues, Muzaffargarh District, Pakistan. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.; Xiao, T.; Farooqi, A.; Shafeeque, M.; Masood, S.; Ali, S.; Fahad, S.; Nasim, W. Arsenic and heavy metal contaminations in the tube well water of Punjab, Pakistan and risk assessment: A case study. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.; Farooqi, A.; Masood, S.; Hussain, K. Arsenic in groundwater and its health risk assessment in drinking water of Mailsi, Punjab, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2015, 22, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bityukova, L.; Petersell, V. Chemical composition of bottled mineral waters in Estonia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.M.; Bhattacharya, P.; Hasan, M.A. Arsenic contamination in groundwater of alluvial aquifers in Bangladesh: An overview. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.F.; Swartz, C.H.; Badruzzaman, A.B.M.; Keon-Blute, N.; Yu, W.; Ali, M.A. Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 2002, 298, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stüben, D.; Berner, Z.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Karmakar, J. Arsenic enrichment in groundwater of West Bengal, India: Geochemical evidence for mobilization of As under reducing conditions. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.; Ahmed, K.M.; Sracek, O.; Bhattacharya, P.; Von Bromssen, M.; Broms, S. Arsenic in shallow groundwater of Bangladesh: Investigations from three different physiographic settings. J. Hydrogeol. 2007, 15, 1507–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rehman, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, M.T. Soil and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, M. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the assessment of water quality in the southwest new territories and Kowloon, Hong Kong. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberta Environment. Surface Water Quality Guidelines for Use in Alberta; Environmental Sciences Division, Alberta Environment: Edmonton, Alberta, 1999; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, B.W. Effects of streamside vegetation on macroinvertebrate communities of White Clay Creek in eastern North America. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. USA 1993, 145, 291–340. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, B.J.; Jowett, I.G.; Quinn, J.M.; Hickey, C.W.; Davies-Colley, R.J.; Close, M. Ecological characterization, classification, and modeling of New Zealand rivers: An introduction and synthesis. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1990, 24, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.W.; Schnack, J.A. Egg development, growth, and metabolism of Sigaraalternata (Say) (Hemiptera: Corixidae) in fluctuating thermal environments. Ecology 1977, 58, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelier, E. Ecology of Streams and Rivers; Science Publishers Inc.: Enfield, USA, 2003; p. 215. [Google Scholar]
- Coutant, C.C. The effect of a heated water effluent upon the macroinvertebrate riffle fauna of the Delaware River. Proc. Penn. Acad. Sci. 1962, 36, 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.L. Assigning macroinvertebrate tolerance classifications using generalized additive models. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, A.G.; Friberg, N. Growth and emergence of the stonefly Leuctra nigra in coniferous forest streams with contrasting pH. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, D.L.; Brannon, D.G. Predicted acid mine drainage impacts to the Buckhannon River, WV, USA. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1988, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, W.H. Benthic invertebrate community responses to heavy metals in the upper Arkansas River basin, Colorado. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1994, 13, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer, S.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Sandhage-Hofmann, A.; Kaupenjohann, M.; Bar, S. Impact of high aluminum loading on a small catchment area (Thuringia slate mining area)—Geochemical transformations and hydrological transport. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 94, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, K. Utility of an Existing Biotic Score Method in Assessing the Stream Health in Bhutan. Ph.D. Thesis, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grab, S. Spatiotemporal attributes of water temperature and macroinvertebrate assemblages in the headwaters of the Bushmans River, southern Drakensberg. Water SA 2014, 40, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LEO EnviroSci Inquiry. Educator’s Guide; Lehigh Environmental Initiative at Lehigh University: Bethlehem, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kefford, B.J. The relationship between electrical conductivity and selected macroinvertebrate communities in four river systems of south-west Victoria, Australia. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1998, 8, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, R.M.G.; Facure, K.G.; Pavanin, L.A.; Jacobucci, G.B. Influence of environmental factors on benthic macroinvertebrate communities of urban streams in Vereda habitats, central Brazil. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2011, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, G.J.; Passmore, M.E.; Borsuk, F.A.; Reynolds, L.; Rose, C.J. Downstream effects of mountaintop coal mining: Comparing biological conditions using family- and genus-level macroinvertebrate bio-assessment tools. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 717–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, R.W. Guide to Aquatic Macroinvertebrates of the Upper Midwest; University of Minnesota, Water Resources Center: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, A. Keys to the Families of European Aquatic Insects; Freshwater Biological Association: Ambleside, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- NSDWQ. National Standards for Drinking Water Quality; Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency, Ministry of Environment: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2008.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).