Abstract
As emerging contaminants increasingly detected in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, environmental estrogens (EEs) pose significant ecological risks to marine ecosystems, particularly affecting photosynthetic microorganisms occupying fundamental roles in marine food webs. This review summarizes the current knowledge on the toxicological effects of EEs in marine microalgae through a systematic analysis of dose-dependent physiological, biochemical, and molecular responses. Experimental evidence reveals a biphasic response pattern characterized by growth promotion and photosynthetic enhancement in microalgae under low-concentration EE exposure (0.1–10 μg/L), while marked inhibition of both growth and photosynthetic activity was observed at elevated EE concentrations (>50 μg/L). Notably, sustained EE exposure induces metabolic reprogramming, manifested through reduced protein and polysaccharide biosynthesis concurrent with accelerated lipid accumulation. Cellular stress responses include significant ultrastructural alterations such as chloroplast membrane disruption, cell wall thickening, and the formation of multicellular aggregates. The study further elucidates the concentration-dependent modulation of toxin metabolism, with sublethal doses stimulating intracellular microcystin synthesis (1.5–2.3-fold increase), while acute exposure triggers toxin release through membrane permeabilization. At molecular levels, transcriptomic analyses identify the up-regulation of heat shock proteins (HSP70/90) and the differential expression of genes governing cell cycle progression (cyclin-D), apoptotic pathways (caspase-3), photosynthetic electron transport (psbA), and oxidative stress responses (SOD, CAT). These findings demonstrate that EEs exert multilevel impacts on microalgal physiology through interference with fundamental metabolic processes, potentially disrupting marine primary productivity and biogeochemical cycles. The identified response mechanisms provide critical insights for environmental risk assessment and establish a conceptual framework for investigating estrogenic pollutant effects in aquatic ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Environmental endocrine disruptors, i.e., so-called environmental estrogens (EEs), were first defined by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Advisory Committee on Screening and Testing of Environmental Endocrine Disruptors as exogenous chemicals that are capable of altering the structure or function of the endocrine system of organisms and adversely affecting them at the levels of individual, offspring, population, and subpopulation on the basis of scientific rationale, data, and precautionary principle. EEs are classified as exogenous chemical substances that disrupt endocrine functions. Specifically, they interfere with hormonal processes—including synthesis, release, transport, receptor binding, biological action, and metabolic elimination—which are essential for regulating organismal reproductive behaviors and developmental pathways [1,2,3].
EEs can be primarily categorized into natural estrogens and synthetic estrogens (Figure 1). Natural estrogens, derived from humans and livestock, are excreted into the environment following metabolic processes in organisms. Representative natural estrogens—including estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2), and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2)—exhibit high lipophilicity and serve as essential substances for maintaining normal physiological functions, typically acting on target cells and organs to regulate diverse biological processes [4]. Synthetic estrogens are more widely utilized, encompassing chemically synthesized pesticides, industrial raw materials, products, and pharmaceuticals. Notable examples include insulating oils, ether compounds, and phthalates, all of which possess estrogenic properties. Among these, phenolic compounds have garnered significant attention due to their extensive applications in paper manufacturing, pigment synthesis, petroleum refinement, and plastic processing. Notably, their metabolites and degradation byproducts also exhibit bioaccumulation potential and endocrine-disrupting effects [5,6,7,8].
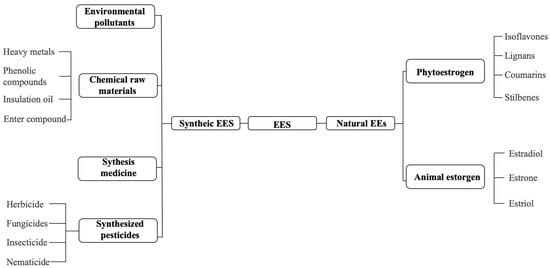
Figure 1.
Classification of substances with estrogenic effects.
EEs, ubiquitous in various sources such as contraceptives, industrial additives, and pesticides, are introduced into the environment primarily through livestock waste, medical effluents, and domestic sewage (Figure 2). Despite typically existing at low concentrations (mostly in the ng/L range), EEs have been detected in eutrophic lakes, rivers, surface seawaters, and bays in many countries. EEs pose acute toxicity, with adverse effects on the reproductive system of organisms even at very low concentrations (1 μg/L), leading to an abnormal expression of traits and indirect impacts on the endocrine, nervous, and reproductive systems of organisms. Synthetic estrogens, in particular, exacerbate these effects due to their slow degradation in water, leading to continuous accumulation in the environment [5,6,7,8,9,10].
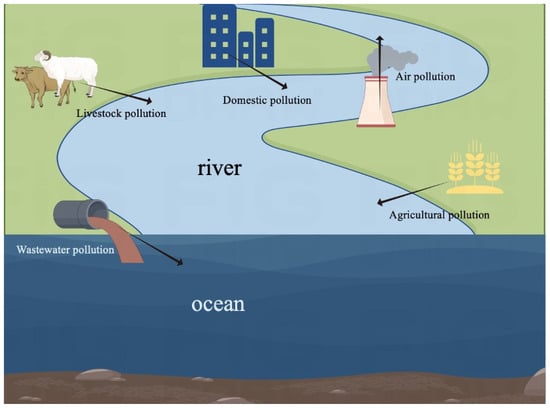
Figure 2.
Sources of EEs in the ocean.
Microalgae may be pioneers in sensing the toxic effects of pollutants in aquatic ecosystems. Unfortunately, existing studies have predominantly focused on freshwater microalgae, demonstrating that EEs may affect various physiological functions and toxicity production in microalgae [11]. As a whole, research on the impact of environmental estrogens on marine microalgae is still in its infant stage. Current research on the impact of EEs on marine microalgae is mainly limited to non-toxic microalgae like Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella salina. Compared to freshwater habitats, oceanic environments possess a much higher diversity of toxin-producing microalgae, encompassing over 100 species known to produce toxins, including dinoflagellates, diatoms, and cyanobacteria. There are several studies on the effects of EEs on the toxin-producing microalgae such as Prorocentrum minimum and Alexandrium pacificum; these primarily focus on general physiological parameters, and the effects of EEs on the toxicity of toxin-producing marine microalgae are rarely investigated. Marine microalgae, as the most crucial primary producers in marine ecosystems, are the indispensable foundation of the marine aquatic food chain, maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems by the production of nutrients and oxygen through photosynthesis. Marine microalgae in marine ecosystems have a large biomass and are highly sensitive to changes in the aquatic environment. Consequently, marine microalgae can serve as model organisms in ecotoxicological studies to indicate pollution levels in the ocean [12,13]. For this reason, this paper mainly summarizes the toxicological effects of EEs on marine microalgae, the toxicity-producing properties of toxin-producing microalgae, and the molecular mechanisms of marine microalgae in response to EEs by reviewing the related literature. The goal of the review is to provide a reference for research in this field and to outline directions for future related studies.
2. Pollution by EEs in the Ocean
Accompanied with the rapid development of industry, EEs have become widespread in water bodies in both freshwater and marine ecosystems, posing significant risks to human health [14]. Up to now, current research has predominantly focused on EE contamination in freshwater systems, encompassing rivers, estuaries, and deltaic regions. In striking contrast, investigations into environmental estrogen pollution in pelagic marine zones remain virtually nonexistent. The possible reason for this may be due to challenges in sampling and the comparatively low levels of contamination in remote waters [14,15].
Numerous studies have indicated that human activities may be the primary source of EEs in marine waters [16], mainly including the discharge of inadequately treated wastewater from sewage treatment plants and the direct release of effluents from livestock farming, agriculture, and other anthropogenic sources (Figure 1) [17]. Thus, understanding and exploring the riverine transport of EEs into marine ecosystems is rather crucial [18]. Atkinson et al. [19] demonstrated that the concentrations of EEs varied from non-detectable levels (<40 pg/L) in open ocean waters to nearly 2000 pg/L in offshore bays. Xu et al. [20] verified the contamination of EEs in the Pearl River Delta and its coastal regions and found the existence of all of the selected target EEs, including as 4-nonylphenol (NP), bisphenol A (BPA), 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2), estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3) in seawater with the concentrations ranging from 45 ng/L to 1050 ng/L (Table 1). Jang et al. [21] identified the widespread presence of the flame retardant hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) across marine waters in 12 countries within the Asia–Pacific region. Natural estrogens and alkylphenol concentrations in all environmental waters in Nagasaki and Tokyo were detected in Song et al.’s 2020 study [22]. Gong et al. [23] investigated the concentrations of eight EEs, including 4-tert-octylphenol (OP), NP, BPA, diethylstilbestrol (DES), E1, E2, EE2, and E3 in the water of the Pearl River Delta. The results showed high concentrations of EEs were usually detected in river estuaries and coastal zones near large cities, among which the contamination of NP and BPA is the most severe, exhibiting significant impacts on aquatic environments. As a result, it may be concluded that human activities are the primary drivers of the presence of EEs in the ocean, with sewage sources being a major contributor. Lu et al. [24] analyzed natural and synthetic estrogens in 255 water samples from the southern part of the Bohai Sea. The total estrogen concentrations in seawater ranged from 1.98 to 99.7 ng/L, primarily dominated by BPA and EE2. Additionally, high concentrations of EEs near sewage sources may seep into the ocean through groundwater, resulting in a gradual attenuation that could be observed from estuaries to the open sea.

Table 1.
Status of EE pollution in the ocean.
3. Toxicological Effects of EEs on Marine Microalgae
3.1. Effects of EEs on the Growth of Marine Microalgae
The most pronounced effects of EEs on microalgae manifest as significant alterations in growth rate inhibition and cell density modulation. Changes in the growth rates and biomass of microalgae are direct outcomes of exposure to EEs, which can be easily quantified. Such effects are typically evaluated by determining the no-observed-effect concentration (NOEC) and the median effect concentration (EC50) or the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) related to microalgal cell growth [32]. Among them, the NOEC denotes the highest concentration of a toxicant that causes no visible or discernible effect on the target organism, while the EC50/IC50 signifies the concentration causing a 50% observed effect or 50% growth inhibition of test organisms. EEs often exhibit an EC50 at or below the mg L−1 level (Table 2), which is comparable to that of emerging contaminants, such as microplastics, antibiotics, and oxidants [33,34]. For instance, Li et al. [35] demonstrated that the 96 h EC50 of bisphenol A (BPA) for Stephanodiscus hantzschii spanned from 3 mg L−1 to 12 mg L−1. Similarly, Ebenezer and Ki [36] showed that the EC50 of Aroclor 1016 [a polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) compound] for three marine microalgae, i.e., Tetraselmis suecica, Ditylum brightwellii, and Prorocentrum minimum, ranged from 0.002 mg L−1 to 3.960 mg L−1. As a whole, the effects of EEs on microalgae growth exhibit a significant dose–effect relationship, namely that growth inhibition escalates with increasing concentrations within a specific range. This inhibitory effect on growth may stem from oxidative damage inflicted by high concentrations of EEs, disrupting cellular repair and protective functions. However, most typical EEs like BPA and NP exhibit stimulative effects on microalgae, promoting the growth of microalgae even at a very low concentration. For example, Belhaj et al. [37] observed that the growth of Dunaliella salina was enhanced when exposed to EE2 at a concentration of 10 ng/L. They also concluded that the inferred reason for this is that the degradation of EEs produces some organic matter that can stimulate the growth of microalgae. In contrast, the growth of D. salina was inhibited by EE2 at higher concentrations of 100 ng/L and 1000 ng/L. Li et al. [38] reported that the growth of Cyclotella caspia was inhibited when exposed to 4–12 mg L−1 of BPA for 4 days, 8 days, and 16 days. In contrast, the biomass and cell density of C. caspia that was exposed to a lower concentration (4 and 6 mg L−1) were significantly higher compared to other treatment groups. They concurred with Belhaj et al. [37] regarding the hypothesis that the degradation of EEs may yield organic matter capable of stimulating the growth of microalgae. Notably, due to the fact that the degradation of EEs occurs gradually, the growth-promoting effect of EEs at a low concentration on microalgae may not be significant in a short period of time. For example, M’Rabet et al. [39] observed that BPA and di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), whether alone or in combination, could inhibit the growth of Alexandrium pacificum. However, the inhibited growth of the algal cells exposed to a low concentration of these EEs can recover to a normal level within 72 h. In addition, the growth-promoting effect of low EEs on microalgae may be attributed to the estrogen-induced up-regulation of genes involved in energy release, cellular transport, and nucleotide transport, thereby expediting material transport for cell growth and energy release [40].

Table 2.
Effect of EEs on the growth of marine microalgae.
Several studies have demonstrated that the effects of the same environmental estrogen on the growth of different microalgal species are different, indicating that the effects of EEs may be species-specific. For instance, the EC50 of three marine microalgae—T. suecica, D. brightwellii, and P. minimum—exposed to Aroclor 1016 ranged from 0.002 mg L−1 to 3.960 mg L−1 [34]. On the other hand, variations exist in the effects of different estrogens on the same microalgae. For example, Liu et al. [41] illustrated that the EC50 of NP and EE2 on Navicula incerta were 0.2 mg L−1 and 3.21 mg L−1, respectively. Additionally, Aroclor 1016 exhibited a greater toxicity for D. brightwellii compared to BPA [34]. Furthermore, diatoms are generally more sensitive to EEs compared to other marine microalgae like dinoflagellate [34]. Accordingly, diatoms may be selected as preferable algal species for investigating the ecotoxicity of estrogen in the marine environment.
Additionally, the duration of exposure significantly influences the measured effects of EEs on the growth toxicity of microalgae. The results from both Li et al. [38] and M’Rabet et al. [39] indicated that EEs exerted the most pronounced growth inhibitory effects on microalgae during the initial growth stage. However, after 4 days post-exposure, this inhibitory effect gradually diminished, exhibiting a gradually increased EC50. The studies conducted in [42,43,44] proposed that there are two possible reasons for the increase in EC50 due to prolonged exposure time. One reason is that algal cells will deactivate EEs through adsorption. Another one is that the degradation of EEs might occur during algal culture. However, different from the above-mentioned view, some researchers argued that the inhibitory effect of EEs on microalgae intensifies with prolonged treatment time due to the resultant toxic substances from the degradation or conversion of EEs by microalgae [45]. It is worth noting that most studies examining the effects of EEs on the growth of microalgae are short-term experiments (1–7 days). However, long-term exposure (>30 days) to EEs may be closer to the actual situation of the natural environment. Unfortunately, the investigations on the effect of EEs on microalgae upon long-term exposure remains relatively scarce [33,38,46,47]. Therefore, prioritizing research into the prolonged growth-inhibitory impacts of EEs on marine microalgae represents a crucial future direction.
3.2. Effects of EEs on the Photosynthesis of Marine Microalgae
Photosynthetic pigments serve as the cornerstone of photosynthesis, enabling microalgae to harness light energy and convert it into chemical energy that is essential for their growth and as producers of organic compounds for higher consumers [48]. Variations in chlorophyll levels offer valuable insights into the growth and development states of an organism across its lifecycle, serving as a pivotal metric for evaluating microalgae biomass. Furthermore, photosynthesis, by liberating oxygen through water decomposition, fuels cellular aerobic respiration and various vital cellular processes [49]. Marine microalgae as primary producers play a crucial role in marine ecosystems, where optimal levels of photosynthetic pigments are indispensable for the normal functioning of marine ecosystems. However, EEs can jeopardize the photosynthetic performance of marine microalgae by impairing their photosynthetic pigments [50,51], consequently disrupting the growth of preliminary producers and potentially destroying the ecological equilibrium of the entire marine ecosystem. Thus, assessing photosynthetic pigment levels offers a means to gauge the toxicity of EEs on microalgae [51,52,53] (Table 3). As the concentration of EEs increases, the trend in changes in cellular chlorophyll content is similar to that of changes in cell density, that is, it generally decreases. In a BPA-induced test with A. pacificum conducted by M’Rabet et al. [39], the chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) content was monitored at a 24 h interval. The results revealed a significant decrease in Chl-a content within 7 days in the water samples containing 2 μg/L of BPA, dropping to a level below 50% of the control. A study suggested that 72 h BPA exposure led to reduced Chl-a content in Chlorella pyrenoidosa, and the decrease in Chl-a content might be not the direct impact of EEs but may be due to methodological differences arising from variations in microalgal biomass [54]. While few researchers have incorporated biomass as a variable when assessing chlorophyll content, there exists experimental evidence supporting the aforementioned point. For instance, a study investigating the impact of BPA on S. hantzschii by Li et al. [35] showed that both low (0.01–1.00 mg L−1) and high (>1.00 mg L−1) concentrations of BPA could lead to decreased Chl-a content and cell density over time, displaying the same change trend with the increased treatment time. In addition, the authors argued that the decrease in Chl-a content is caused by the BPA-induced degradation of chloroplasts and chlorophyll molecules. Similarly, another study by Belhaj et al. [37], focusing on the effects of EE2 on D. salina, found that a significant reduction in Chl-a and Chl-b occurred with the test algal species exposed to an EE2 concentration of 100 ng/L and 1000 ng/L. The authors concluded that EEs inhibited the synthesis of chlorophyll by targeting thylakoids. It should be pointed out that algal biomass was not taken into account when analyzing the chlorophyll content in their study. Overall, the precise mechanism by which EEs influence microalgae chlorophyll content needs to be further explored, and whether EEs can directly act on chlorophyll molecules also needs to be verified in the future. In particular, when assessing the impact of EEs on the chlorophyll content of microalgae, it is advisable to take into account the biomass of algal cells, that is, utilizing the ratio of chlorophyll content to cell number as a testing parameter.
In addition to the content of photosynthetic pigments, photosynthetic efficiency is also a widely used parameter for evaluating the impact of EEs on microalgae [55]. In recent years, fast chlorophyll fluorescence induction kinetics (OJIP test) has emerged as a fundamental technique for investigating photosynthetic processes and has been extensively applied in studies of environmental stress responses and ecotoxicological effects [56,57,58]. For instance, in Zhang et al.’s experimental study [55], the OJIP analysis of Chlorella vulgaris photosynthesis was employed to elucidate the mechanistic action of glyphosate, an environmental estrogenic pollutant, on microalgal physiological systems. Currently, the photosynthetic efficiency of microalgae is predominantly determined by the analysis of changes in photochemical properties using Chl-a fluorescence measurement devices [39,51]. The key chlorophyll fluorescence parameters include the relative electron transport rate (rETR), photosynthetic quotient (Qp), non-photochemical quenching (NPQ), and the maximum quantum yield of photosystem II (PS II) (Fv/Fm). Among them, Fv/Fm could reflect both the maximum quantum yield of PS II when all reactive centers of the photosynthetic system are open and the effective quantum yield of PS II. Given that damage or inactivation of PS II might be the primary cause of environmental estrogen-induced harm to algal photosynthesis [58,59,60], Fv/Fm stands out as a crucial and widely accepted parameter for assessing photosynthetic efficiency [53,61]. Additionally, rETR, Qp, and NPQ, representing the relative electron transfer rate, light-to-chemical energy conversion ability, and the ability to dissipate excess light energy into heat, respectively, offer valuable insights into photosynthetic status [53,62]. For instance, both Fv/Fm and rETR decreased in A. pacificum exposed to BPA with a much higher concentration [39].

Table 3.
Effect of EEs on the photosynthesis of marine microalgae.
Table 3.
Effect of EEs on the photosynthesis of marine microalgae.
| Algal Species | Taxonomy | Types of EEs | Concentration of EEs | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorella pyrenoidosa | Chlorophyta | BPA | 10 mg/L | Chl-a levels decreased significantly. | [52] |
| Dunaliella salina | Chlorophyta | EE2 | 100 ng/L; 1000 ng/L | Chl-a and Chl-b levels decreased significantly. | [35] |
| Skeletonema hantzschii | Diatom | BPA | 0.01–1.00 mg/L; >1.00 mg/L | Chl-a levels decreased significantly. | [63] |
| Alexandrium pacificum | Dinoflagellate | BPA | 2 μg/L; 20 μg/L | Chl-a levels decreased significantly. | [39] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Chlorophyta | Glyphosate | 0, 1, 10, 20, and 40 mmol/L | Inhibited photosynthetic activity and reduced pigment content. | [57] |
3.3. Effect of EEs on the Respiration of Marine Microalgae
Cellular respiration, as a process by which cells convert organic matter into energy, is one of the most important and fundamental physiological activities of cells [64]. Among the process, the key reactions such as glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and electron transport are essential for sustaining normal cellular activities, and any disruption to these reactions may result in cell death. The enzymes involved in oxidative phosphorylation and electron transport, such as cytochrome c oxidase, pyruvate kinase, phosphofructokinase, hexokinase, and isocitrate dehydrogenase, play crucial roles in regulating cellular respiration. EEs have been shown to influence the activity of these enzymes, thereby impacting the intensity and efficiency of respiration. Reduced enzyme activity may also affect other cellular functions, such as cell proliferation [38,65]. The effects of EEs on the activity of enzymes involved in respiration may be dose-dependent, i.e., the enzyme activity may be up-regulated and inhibited in response to a low dose and high dose, respectively. For instance, in a test of impacts of BPA and DEHP on the respiration of A. pacificum lasting for 7 days, M’Rabet et al. [39] observed that either of the EEs alone had a significant impact on the respiration of algae, while the combined effect was more significant. In addition, the respiration rate of the test algal species gradually increased over time, and the differences between the experimental group and the control group became more significant, particularly 72 h post-exposure to the EEs. In summary, the adverse effects of EEs on the respiration of microalgae may stem not only from interference with enzyme activity but also from other pathways, and the degree of impact may vary with the concentration of EEs and exposure time. Overall, however, research on this topic remains limited. Accordingly, further investigation is required to provide comprehensive knowledge about the full scope and mechanisms of the impacts of EEs on the crucial cellular process of marine microalgae.
3.4. Effect of EEs on the Content of Macromolecular Compounds in Marine Microalgae
Intracellular macromolecular compounds, such as proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids, play pivotal roles in cellular functions [66]. EEs can influence protein levels, including the types and quantity of enzymes in marine microalgae. The enzymes involved in cellular respiration mentioned earlier are a good example. Moreover, EEs may impact the formation of microalgal cell walls, which are mainly composed of polysaccharides, thus affecting polysaccharide content within algal cells [41,67]. The effects of EEs on the content of proteins and polysaccharides in microalgal cells correlate with their exposure concentrations. For instance, Liu et al. [41] demonstrated that the contents of polysaccharide and total protein in N. incerta cells remained relatively stable when exposed to 0.1 mg L−1 NPs, 1 mg L−1 BPA, 2 mg L−1 EE2, and 8 mg L−1 E2. These findings also suggest that EEs at an environmental concentration below 0.1 mg L−1 may not affect the levels of macromolecular compounds in marine microalgae. Similarly, Yang et al. [67] found that the intracellular total protein content of Skeletonema costatum in response to 2, 4-Dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) at a concentration less than 3 mg L−1 showed no significant change. By comparison, as the concentration of EEs (NPs, BPA, EE2, and E2) increased, the total protein content of N. incerta decreased by 32.6% (NPs), 43.1% (BPA), 46.7% (EE2), and 17.7% (E2), respectively, compared to the control group [41]. Similarly, the polysaccharide content decreased by 79.1% (NPs), 70.0% (BPA), 63.3% (EE2), and 29.7% (E2), respectively, showing a similar trend to the total protein content [41]. In contrast to proteins and polysaccharides, the lipid content in marine microalgal cells exhibited a positive correlation with the concentration of EEs. As the concentration of EEs increased, the lipid content in algal cells increased by 157.7% (NPs), 134.4% (BPA), 101.1% (EE2), and 32.6% (E2), respectively, compared to the control [41]. In addition, Yang et al. [67] observed a significant increase in the lipid content of S. costatum exposed to 6 mg L−1 2,4-DCP. Taken together, these findings suggest that lipid content may be served as an indicator to evaluate the adverse effects of EEs on marine microalgae.
3.5. Effect of EEs on the Cell Morphology of Marine Microalgae
Changes in morphological characteristics are generally considered as adaptive responses of organisms to an ambient environment. EEs at specific concentrations may induce morphological alterations of microalgal cells, breaking the structure of organelles and impairing the normal physiological functions of cells [62] (Table 4). Thus, the changes in morphological characteristics may be one important clue to indicate the effect of EEs on microalgal species. The current evidence indicated that EEs mainly affect the cell morphology of microalgae by modifying the cell wall, membrane, and cytoskeleton. Krüger and Eloff [68] proposed that morphological changes can signal environmental stress, with increased cell size reflecting elevated stress levels. Li et al. [35] drew a similar conclusion. After exploring effects of different concentrations of BPA (4 mg L−1, 6 mg L−1, 8 mg L−1, 10 mg L−1, and 12 mg L−1) on the morphology of C. caspia, they found that enlarged microalgal cells, damaged organelles, introduced abnormal substances, and the inhibition of cell division could be detected with C. caspia that was exposed to a concentration of BPA exceeding 6 mg L−1. The inhibition of cell division and structural damage may be attributed to the breakdown and reorganization of the intracellular cytoskeleton by BPA. Additionally, cell enlargement may result from inhibited cell division that leads to increased intracellular organelle numbers and sizes. In addition, the cell aggregation of 2–4 cells were observed in two freshwater microalgae, i.e., Desmodesmus subspicatus and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, which were exposed to different concentrations of E2 [42]. Unfortunately, research on the effects of EEs on the morphology of marine microalgae is still scarce. Moreover, the molecular mechanism of unicellular aggregation due to EE stress also needs to be clarified. In addition, it is worth noting that while EEs are supposed to induce a change in microalgal morphology, their small size and susceptibility to ambient environmental factors make a morphological examination challenging. As a consequence, distinguishing morphological alterations may require considerable expertise and sometimes may produce significant identification errors.

Table 4.
Effect of EEs on the cell morphology of marine microalgae.
3.6. Effect of EEs on Antioxidant Responses in Marine Microalgae
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a collective term for peroxides related to oxygen metabolism, oxygen-containing free radicals, and peroxides that are prone to forming free radicals in living organisms, including peroxides, superoxides, and hydroxyl radicals. ROS are primarily produced in the inner membrane of mitochondria through aerobic respiration and play crucial roles in cellular signaling and maintaining homeostasis. In general, ROS with a normal level in cells are not detrimental. However, the balance of ROS within cells will be disrupted when experiencing abiotic stresses, leading to excessive production of ROS that can have adverse effects on living systems [69]. For example, excessive ROS can attack the unsaturated fatty acids in lipid membranes. As a result, this may cause the degradation of lipid membranes, including cell membranes and organelle membranes, thereby affecting the function and metabolic processes of algal cells.
Many EEs like BPA and NP are hydrophobic compounds that can accumulate in the lipid membranes of microalgal cells. This accumulation can lead to lipid peroxidation and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [51,70,71,72], ultimately resulting in the degradation of lipid membranes. Since the degradation of lipid membranes can produce malondialdehyde (MDA), MDA is a commonly used indicator for evaluating the degree of oxidative damage. The content of MDA is usually measured by the thiobarbituric acid method [50,73]. However, it is recommended to simultaneously measure both the intracellular concentration of ROS and the activity of antioxidant enzymes to obtain a comprehensive understanding of oxidative damage in cells [51,58,74].
In general, the activities of the antioxidant enzymes of microalgae in response to oxidative stress will increase, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and glutathione-S-transferase (GST) [75]. These enzymes play a crucial role in cell protection by reducing lipid peroxidation via scavenging ROS. In response to EEs, including NP, BPA, EE2, and E2, the activities of SOD and GST in N. incerta were positively correlated with the concentrations of these EEs [41]. At the highest test concentrations of these EEs, the activities of SOD/GST increased by 55.6%/62.5%, 52.5%/37.1%, 62.3%/59.9%, and 29.3%/30.7%, respectively, compared to the control group. These results indicate that EEs can induce antioxidant responses in marine microalgae. The measurement of antioxidant enzyme activities in microalgae has gained popularity due to its rapidity and accuracy. Consequently, it has been employed as a valuable indicator for assessing the impact of EEs on microalgae [68].
The antioxidant response of marine microalgae to environmental estrogen exposure is influenced by multiple factors, leading to complex outcomes. Variations among microalgae species in producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in response to identical EEs highlight this complexity. Additionally, the physicochemical conditions of their environment can impact how these microalgae manage oxidative stress. Consequently, there is a need for more comprehensive research to understand the varied antioxidant defense strategies of microalgae when faced with EEs under differing conditions.
3.7. Effects of EEs on the Toxin-Producing Performance of Marine Microalgae
In both marine and freshwater environments, some microalgae can produce and release highly toxic active substances known as phycotoxins as a defense mechanism against environmental stressors. When coping with adverse conditions, these microalgae deploy phycotoxins, potentially aiding in the adaptation of the microalgal cells to the challenging environment [76,77]. Consequently, an escalation in toxin production by microalgae serves as a defense mechanism against environmental pressures to some degree [78]. EEs, acting as stressors, may influence the toxin production of microalgae. The current research on the impact of EEs on microalgal toxicity has primarily concentrated on freshwater cyanobacteria because they are the most harmful microalgae in freshwater ecosystems. The obtained data have demonstrated a dose–response relationship between EEs and algal toxins overall. In particular, low concentrations of EEs have been shown to significantly promote microalgal toxin production [79] (Figure 3). The exposure of NP to Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7820 showed that the toxin content in algal cells increased significantly (p < 0.05) at a concentration range of 0.05–0.50 mg L−1. In addition, the content of toxins in cells was highest when the NP concentration was 0.20 mg L−1, which was 75% higher than the control group [80] (Table 5). One possible reason for these results is that low doses of EEs can promote the growth and reproduction of microalgae, thereby increasing the production of toxins. Another possible reason is that EEs up-regulate the transcriptional levels of genes related to microcystin synthesis (such as mcyA and mcyH) in M. aeruginosa, leading to a significant increase in the enzyme activity associated with these genes, thereby promoting the toxin production of algal cells [81,82,83]. In addition, the impact of EEs on the toxin-producing capacity of microalgae may have species or strain specificity. For example, no significant effect (p > 0.05) of NP on the toxin-producing capacity was detected with another strain of M. aeruginosa (M. aeruginosa 562), i.e., even the maximum toxin production of the NP exposure groups treated with the concentration range of 0.05–0.5 mg L−1 was only 10% higher than that of the control group [81]. Furthermore, a much higher concentration of EEs can cause lipid peroxidation in algal cells, leading to the rupture of the cell membrane and the release of cellular contents like toxins that can rapidly release into the extracellular environment [84]. This also explains why higher concentrations of toxins can be detected outside the cells when algal species are exposed to EEs at higher concentrations [85].
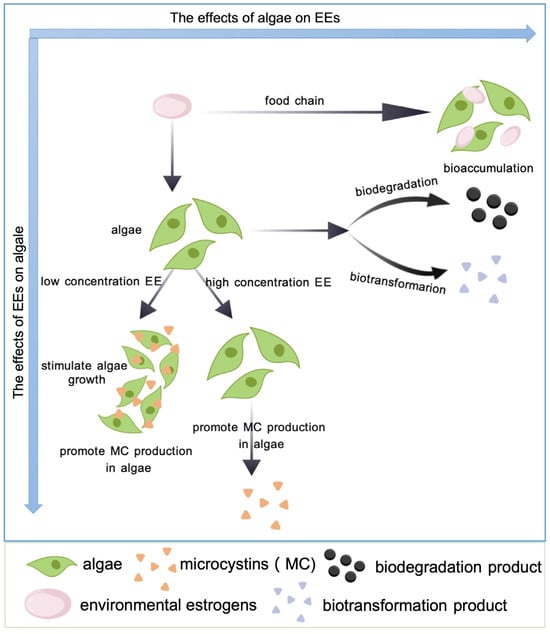
Figure 3.
Effects of different concentrations of EEs on the growth and toxin production of microalgae.

Table 5.
Effect of EEs on the toxin-producing performance of microalgae.
In particular, microalgal toxins could accumulate in the body across the food chain, beginning from the consumption of the toxic microalgae by mollusks and fish. One of the most important adverse impacts of red tides largely stem from microalgal toxins [86]. Compared to freshwater habitats, oceanic environments possess a much higher diversity of toxin-producing microalgae, encompassing over 100 species known to produce toxins, including dinoflagellates, diatoms, and cyanobacteria [87]. The diversity of toxic microalgae in the ocean may correspond to the diversity of marine microalgal toxins. According to poisoning symptoms, these toxins can be classified into paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs), diarrhetic shellfish toxins (DSTs), neurotoxic shellfish toxins (NSTs), amnesic shellfish toxins (ASTs), ciguatera fish toxins (CFTs), and others. Also, they can be categorized into eight groups based on their chemical structures, i.e., saxitoxin (STX), domoic acid (DA), okadaic acid (OA), azaspiracid (AZA), brevetoxin (BTX), pecenotoxin (PTX), yessotoxin (YTX), and cyclic imine (CI).
Environmental factors like temperature and salinity may significantly influence the toxicity of marine toxin-producing microalgae. Shin et al. [88] explored the impact of different temperatures and salinities on the toxin production of the harmful flagellate Centrodinium punctatum. The results showed that no toxin could be detected with the treatment at 5 °C, while the toxin contents ranged from 210 fmol cell/ to 288 fmol/cell with the treatment at 10 °C−25 °C, peaking at 15 °C. Salinity also significantly affected the toxin content, with the highest (276 fmol/cell) and lowest (111 fmol/cell) level observed with salinities of 27.5 and 40, respectively. Additionally, the acidity (pH) of seawater and climatic change are also important factors affecting the toxin production of marine microalgae. For instance, climatic change has led to reoccurring red tides in areas where no red tide was recorded [88]. Brandenburg et al. [89] claimed that there are at least a total of 26 marine toxin-producing algae that may exhibit increased toxin production in response to elevated CO2 levels. In addition, all kinds of pollutants like polyaluminum chloride-modified clay (PAC-MC) have been verified to influence the toxicity of marine microalgae. Song et al. [90] observed a significant decrease in the production of PSTs and toxicity of A. pacificum that was exposed to PAC-MC. Similar phenomena were detected with both Karenia brevis and Prymnesium parvum [91,92]. The increasing global prevalence of algal blooms has raised concerns about microalgal toxin release during microalgal growth [93]. Compromised cellular integrity can lead to a significant liberation of these toxins, underscoring the critical need for appropriate algal growth inhibitors in managing toxigenic algal species. While copper sulfate remains the most widely used algicide [94], its application poses risks of heavy metal contamination [95], adversely affecting aquatic ecosystems and human health [96]. Notably, recent studies have identified natural compounds—including polyphenols and their derivatives, as well as terpenoids—as effective and environmentally friendly alternatives for microalgal control [97,98]. These phytochemicals demonstrate potent algicidal activity while minimizing ecological collateral damage [99]. Tea polyphenols (TPs), as a natural product with antibacterial and antioxidant properties, has also been shown to inhibit toxin release from microalgae like M. aeruginosa, reducing the risk of toxin exposure [100]. Taken together, these findings suggest that environmental pollutants like EEs may similarly impact the production and release of phycotoxins.
Unfortunately, current research on the impact of EEs on marine microalgae is mainly limited to non-toxic microalgae like Chlorella vulgaris and D. salina. Despite the fact that there are several studies on the effects of EEs on toxin-producing microalgae such as P. minimum and A. pacificum, these primarily focus on general physiological parameters like cell density, chlorophyll content, photosynthetic efficiency, and enzyme activity. By contrast, the effects of EEs on the toxicity of toxin-producing marine microalgae are rarely investigated. Therefore, more attention should be paid to explore the influence of EEs on the toxicity of marine toxigenic microalgae and elucidate the underlying mechanisms in the future.
4. Molecular Response of Marine Microalgae to EEs
In addition to cellular response at an epigenetic level, molecular responses are supposed to occur with marine microalgae that are exposed to EEs. Molecular responses are often explored by omics techniques [101]. As for the response at a proteomics level, heat shock proteins (HSPs) have been considered as one of the important markers of interest. HSPs are a class of proteins that are usually up-regulated in response to external stresses, abnormal conditions, or pathological states. They play a crucial role in the defense mechanisms of organisms, protecting against temperature changes, oxidative stress, and exposure to chemical toxicants [102]. Guo et al. [103] examined the stress response of marine microalgae, namely P. minimum, to bisphenol A (BPA) and copper ions (Cu2+), mainly focusing on the changes in transcriptional level and expression profiles of HSP 70. The results showed that the expression of HSP 70 gradually increased with the increased concentration of BPA. At different concentrations of BPA (0.1 mg L−1 and 0.2 mg L−1), the expression of HSP 70 in P. minimum was similar at 12 h post-exposure but up-regulated at 24 h exposure (p < 0.05). Additionally, the expression of HSP 70 increased by 2–7-fold (p < 0.001) with increased concentrations of Cu2+ compared to the control group. These findings suggest that HSP 70 extensively contributes to the response of P. minimum to BPA and Cu2+ stress. Similarly, Kobiyama et al. [104] explored the effect of temperature on the expression of HSP 70 in A. tamarense and found that a high temperature (37 °C) could induce increased expression and accumulation of HSP 70. Taken together, these results imply that HSP 70 is likely to play a positive role in the response of marine microalgae to environmental stressors such as EEs and heavy metals.
Transcriptomics enables the analysis of differential expression of genes and can provide a comprehensive overview of the gene expression patterns of an organism [105]. As for marine microalgae, transcriptomic analysis has been successfully performed on A. pacificum [106,107]. Wang et al. [107] utilized a 6.0 K microarray to uncover transcriptional differences in P. minimum exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and investigated the gene regulatory mechanisms and metabolic pathways in response to stress using bioinformatics tools. The results showed that there is a total of 5981 deferentially expressed genes, among which 609 genes exhibited over 2-fold changes in expression at 12, 24, and 48 h post exposure. In detail, 39, 76, and 176 genes were up-regulated by more than 2-fold, while 195, 207, and 300 genes were down-regulated by more than 2-fold at each time point, respectively. In addition to EEs, Song et al. [90] explored the effects of PAC-MC on the marine microalgae, with A. pacificum at the molecular level by transcriptional analysis. The results showed that several deferentially expressed genes could be detected in the test algal species compared to the control, among which 6646 genes were down-regulated and 4405 genes were up-regulated. These findings are consistent with those from Guo et al. [108] and share similarities with the results from Guo et al. [109]. In general, the identified deferentially expressed genes in response to EEs primarily are those involved in regulating cell growth and death, photosynthesis, antioxidant effects, and signal transduction and transport pathways. Thus, it can be concluded that EEs may disrupt the normal physiological activities of marine microalgae. In addition, Wang et al. [107] further analyzed the transcriptome sequencing data using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and found that both genes and proteins related to cell cycle regulation were up-regulated, and cyclin-dependent kinases were down-regulated in A. pacificum exposed to PCB (Figure 4). These results suggest that PCB could potentially impact the cell cycle and growth by inhibiting the expression of genes involved in these processes, which is consistent with the effects of Aroclor 1016 on the growth of P. minimum [34]. Furthermore, the expression of most apoptosis-related genes was down-regulated, implying that EEs might influence the programmed cell death of P. minimum. Interestingly, the genes related to photosynthesis were not notably affected by PCB, and only few antioxidant genes showed differential expression in combination with less production of ROS. Significantly different from M’Rabet et al. [39], these results may be possibly due to differences in the algal species and EEs examined. Additionally, the expression of genes involved in signaling pathways could also be affected by EEs, such as those encoding calmodulin, calreticulin, and calcium-dependent protein kinase, all of which could be up-regulated in response to copper exposure and temperature stress [110,111]. In conclusion, EEs generally appear to influence the expression of genes related to cell growth and apoptosis, photosynthesis, antioxidation, and signal transduction.
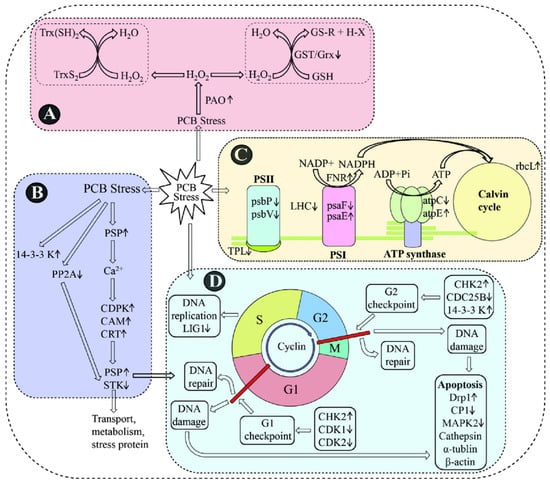
Figure 4.
A schematic representation of PCB-responsive genes and proteins [108]. A schematic representation of PCB responsive genes and proteins involved in ROS producing and scavenging system (A), signal transduction (B), photosystem (C) and cell cycle and apoptosis (D). Trx: thioredoxin; GST: glutathione S-transferase; PAO: polyamine oxidase; PP2A: protein phosphatase 2A; PSP: serine/threonine protein phosphatase; CDPK: calcium-dependent protein kinase; CAM: calmodulin; CRT: calreticulin; STK: serine/threonine-protein kinase; psbP: oxygen evolving enhancer 1 precursor; psbV: cytochrome c550; psaF: chloroplast photosystem I, subunit III; FNR: ferredoxin-NADPþ reductase; atpC: chloroplast ATP synthase subunit C; atpE: ATP synthase CF1 epsilon subunit; rbcL: ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase form II; LIG1: DNA ligase I; CHK2: checkpoint kinase 2; CDK1: cyclin-dependent kinase 1; CDK2: cyclin-dependent kinase 2; Drp1: dynamin-related protein 1; CP1: cysteine protease 1; MAPK2: mitogen-activated protein kinase 2.
5. Conclusions
Current research on the effects of EEs on marine microalgae remains nascent, with critical challenges and solutions identified as follows:
Key Challenges: (1) overemphasis on chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) while neglecting differential responses of other photosynthetic pigments (e.g., carotenoids); (2) discrepancy between laboratory-based high concentration, short-term exposure, and environmentally relevant low dose in chronic scenarios; (3) limited integration of environmental variables (light, temperature) modulating EE toxicity; (4) oversimplified single-pollutant models failing to reflect real-world complex pollution scenarios involving microplastics and heavy metals; and (5) superficial mechanistic insights reliant on macroscopic endpoints (growth, chlorophyll content).
Strategic Solutions: (1) given that different pigments may play different roles in response to EEs, other photosynthetic pigments besides Chl-a should be considered when evaluating the effects of EEs on the photosynthesis of marine microalgae in the future; (2) future studies should focus on restoring the natural conditions to explore the effects of EEs on marine microalgae under a low concentration and long-time exposure conditions by integrating field investigation with laboratory simulation; (3) future studies should attempt to investigate the effects of EEs on marine microalgae by controlling different environmental factors; (4) based on the existing studies on the effects of single EEs, further emphasis should be placed on considering the synergistic effects of EEs in combination with other pollutants, such as microplastics and heavy metal ions; and (5) deciphering molecular toxicological networks using transcriptomic–proteomic–metabolomic multiomics integration. Furthermore, urgent attention is needed to unravel how EEs regulate toxin biosynthesis pathways in marine toxigenic species, leveraging omics technologies to advance ecological and human health risk assessments of harmful algal blooms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C. and L.G.; methodology, L.G.; writing—review and editing, L.G. and W.C.; supervision, G.C., C.Z. and Y.W.; funding acquisition, G.C. and C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (no. 42377422); the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (no. ZR202204170002, no. ZR2020MD081); the HIT Scientific Research Innovation Fund (no. 2022KYCXJJ07); and the Double First Class Discipline Construction Foundation of HIT (no. 2023SYLHY06).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zheng, N.; Lin, X.; Huang, P.; Liu, Y.; Bartlam, M.; Wang, Y. Tea Polyphenols Inhibit Blooms Caused by Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Algae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 265, 115531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, Â.; Silva, M.G.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Freitas, R. Concentrations Levels and Effects of 17alpha-Ethinylestradiol in Freshwater and Marine Waters and Bivalves: A Review. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Hazards of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure: A Systematic Review of Plant Toxicology Studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Fredj, S.; Nobbs, J.; Tizaoui, C.; Monser, L. Removal of Estrone (E1), 17β-Estradiol (E2), and 17α-Ethinylestradiol (EE2) from Wastewater by Liquid–Liquid Extraction. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Rizwan, K.; Adeel, M.; Barceló, D.; Awad, Y.A.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Robust Strategies to Eliminate Endocrine Disruptive Estrogens in Water Resources. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.K.; Taylor, J.A.; Sommerfeld-Sager, J.; Tillitt, D.E.; Ricke, W.A.; Vom Saal, F.S. Estrogen Receptor 1 Expression and Methylation of Esr1 Promoter in Mouse Fetal Prostate Mesenchymal Cells Induced by Gestational Exposure to Bisphenol A or Ethinylestradiol. Environ. Epigenet. 2019, 5, dvz012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Barceló, D.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Occurrence, Environmental Fate, Ecological Issues, and Redefining of Endocrine Disruptive Estrogens in Water Resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Wong, C.K.C.; Zheng, J.S.; Bouwman, H.; Barra, R.; Wahlström, B.; Neretin, L.; Wong, M.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A Review of Sources, Environmental Levels, and Potential Human Health Impacts. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Das, M.K.; Duttaroy, A.K. Plastics Derived Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds and Their Effects on Early Development. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 1308–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-R.; Wei, S.T.-S.; Wang, P.-H.; Wu, P.-H.; Yu, C.-P. Microbial Degradation of Steroid Sex Hormones: Implications for Environmental and Ecological Studies. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 926–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, W.; Tang, T.; Li, Z.; Dai, R. Environmental Estrogens in Surface Water and Their Interaction with Microalgae: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naselli-Flores, L.; Padisák, J. Ecosystem Services Provided by Marine and Freshwater Phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2691–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.L.; Lepère, C.; Scanlan, D.J.; Vaulot, D. Plastid 16S rRNA Gene Diversity among Eukaryotic Picophytoplankton Sorted by Flow Cytometry from the South Pacific Ocean. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Pan, H.-Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Lin, C.-Y. Pollution Characteristics and Mixture Risk Prediction of Phenolic Environmental Estrogens in Rivers of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-C.; Jiang, L.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Hung, C.-F.; Tien, C.-J. Characteristics of Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A Accumulation by Fish and Implications for Ecological and Human Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human Health and Ocean Pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.B.R.; Fernandes, P.A.A.; Bottrel, S.E.C.; Brandt, E.M.F.; Pereira, R.D.O. Fate, Occurrence, and Removal of Estrogens in Livestock Wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 814–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Noguera-Oviedo, K.; Kaushal, S.S.; Rosenfeldt, E.J.; Aga, D.S.; Murthy, S. Evidence That Watershed Nutrient Management Practices Effectively Reduce Estrogens in Environmental Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.; Atkinson, M.J.; Tarrant, A.M. Estrogens from Sewage in Coastal Marine Environments. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yan, W.; Huang, W.; Miao, L.; Zhong, L. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in the Pearl River Delta and Coastal Environment: Sources, Transfer, and Implications. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Shim, W.J.; Han, G.M.; Rani, M.; Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H. Widespread Detection of a Brominated Flame Retardant, Hexabromocyclododecane, in Expanded Polystyrene Marine Debris and Microplastics from South Korea and the Asia-Pacific Coastal Region. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Nagae, M.; Takao, Y.; Soyano, K. Field Survey of Environmental Estrogen Pollution in the Coastal Area of Tokyo Bay and Nagasaki City Using the Japanese Common Goby Acanthogobius flavimanus. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Yang, K.-X.; Lin, C.-Y.; Li, Q.; Han, C.; Tao, W.; Huang, Y.; Lin, W.-Q.; Wu, C.-Q.; Zhang, S.-H.; et al. Prevalence, Distribution, Accumulation, and Risk of Environmental Corticosteroids and Estrogens in Biofilms from the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Xin, M.; Lin, C.; Gu, X.; Lian, M.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations and Risk Assessment of Estrogens in the Water of the Southern Bohai Sea: A Comprehensive Investigation Spanning Three Years. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysman, S.; Van Meulebroek, L.; Vanryckeghem, F.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K.; Vanhaecke, L. Development and Validation of an Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatographic High Resolution Q-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometric Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Steroidal Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Aquatic Matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 984, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial and Seasonal Distributions of Estrogens and Bisphenol A in the Yangtze River Estuary and the Adjacent East China Sea. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, J.; Imai, S.; Fujii, K.; Kawai, S.; Yap, C.K.; Ismail, A. Pollution by Estrogens in River and Estuarine Waters around Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, and Their Effects on the Estuarine Java-Medaka, Oryzias Javanicus. 2006. J. Jpn. Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 9, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, I.-C.; Bruhn, R.; Gandrass, J.; Ruck, W. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Estrogenic Compounds in Coastal Surface Water of the Baltic Sea. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1090, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Remberger, M.; Kaj, L.; Schlabach, M.; Jörundsdóttir, H.Ó.; Vester, J.; Arnórsson, M.; Mortensen, I.; Schwartson, R.; Dam, M. A First Screening and Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals and Additives in Personal Care Products in Waste Water, Sludge, Recipient Water and Sediment from Faroe Islands, Iceland and Greenland. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wen, T.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H.; Lin, Y.; Lien, G. Determining Estrogenic Steroids in Taipei Waters and Removal in Drinking Water Treatment Using High-Flow Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 378, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, F.; Pal, A.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Reinhard, M. Occurrence of Emerging Organic Contaminants in a Tropical Urban Catchment in Singapore. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; Fox, D.R.; Negri, A.P.; van Dam, J.; Flores, F.; Koppel, D. Methods for Estimating No-Effect Toxicity Concentrations in Ecotoxicology. Integr. Environ. Assess. 2024, 20, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Andrés, J.; Romero-Martínez, L.; Seoane, S.; Acevedo-Merino, A.; Moreno-Garrido, I.; Nebot, E. Evaluation of Algaecide Effectiveness of Five Different Oxidants Applied on Harmful Phytoplankton. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Ma, R.; Barrett, H.; Wang, B.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.; Wang, W.; Peng, G.; Yu, G. How Microplastics Affect Chiral Illicit Drug Methamphetamine in Aquatic Food Chain? From Green Alga (Chlorella pyrenoidosa) to Freshwater Snail (Cipangopaludian cathayensis). Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Chen, G.-Z.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Luan, T.-G.; Shin, P.K.S.; Cheung, S.G.; Liu, Y. Toxicity of Bisphenol A and Its Bioaccumulation and Removal by a Marine Microalga Stephanodiscus hantzschii. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, V.; Ki, J.-S. Toxic Effects of Aroclor 1016 and Bisphenol A on Marine Green Algae Tetraselmis suecica, Diatom Ditylum brightwellii and Dinoflagellate prorocentrum Minimum. J. Microbiol. 2016, 52, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaj, D.; Athmouni, K.; Frikha, D.; Kallel, M.; El Feki, A.; Maalej, S.; Zhou, J.L.; Ayadi, H. Biochemical and Physiological Responses of Halophilic Nanophytoplankton (Dunaliella salina) from Exposure to Xeno-Estrogen 17α-Ethinylestradiol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7392–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Shin, P.K.S.; Cheung, S.G.; Luan, T. Physiological Responses of the Alga Cyclotella caspia to Bisphenol A Exposure. Bot. Mar. 2008, 51, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Rabet, C.; Pringault, O.; Zmerli-Triki, H.; Ben Gharbia, H.; Couet, D.; Kéfi-Daly Yahia, O. Impact of Two Plastic-Derived Chemicals, the Bisphenol A and the Di-2-Ethylhexyl Phthalate, Exposure on the Marine Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum. Mar. Pollut. 2018, 126, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B. Proteomic Mechanisms for the Combined Stimulatory Effects of Glyphosate and Antibiotic Contaminants on Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Zhu, W. Cellular Responses, Biodegradation and Bioaccumulation of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Marine Diatom Navicula incerta. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lürling, M. Effect Of Grazing-Associated Infochemicals on Growth and Morphological Development in Scenedesmus acutus (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 1998, 34, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, L.; Rousseau, D.P.L.; Lens, P.N.L. Removal of Estrone, 17α-Ethinylestradiol, and 17ß-Estradiol in Algae and Duckweed-Based Wastewater Treatment Systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2010, 17, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomão, A.L.D.S.; Soroldoni, S.; Marques, M.; Hogland, W.; Bila, D.M. Effects of Single and Mixed Estrogens on Single and Combined Cultures of D. subspicatus and P. subcapitata. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Tang, J.; He, H.; Gu, L.; Pan, X. Ecotoxicological Effects and Removal of 17β-Estradiol in Chlorella Algae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.-K.; Kabra, A.N.; Choi, J.; Hwang, J.-H.; Kim, J.R.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.I.; Oh, Y.-K.; Jeon, B.-H. Biodegradation of Bisphenol A by the Freshwater Microalgae Chlamydomonas mexicana and Chlorella vulgaris. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiong, B.; Sun, W.-F.; An, S.; Lin, K.-F.; Guo, M.-J.; Cui, X.-H. Acute and Chronic Toxic Effects of Bisphenol a on Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus: Acute and Chronic Toxic Effects of Bisphenol a on Two Algae. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, A.J.; Kapoor, L.; Doss, C.G.P.; Hofmann, T.A.; Lawson, T.; Ramamoorthy, S. The Role of Photosynthesis Related Pigments in Light Harvesting, Photoprotection and Enhancement of Photosynthetic Yield in Planta. Photosynth. Res. 2022, 152, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, R.; van Amerongen, H. Light Harvesting in Oxygenic Photosynthesis: Structural Biology Meets Spectroscopy. Science 2020, 369, eaay2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizullah, A.; Khan, S.; Gao, G.; Gao, K. The Interplay between Bisphenol A and Algae—A Review. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizullah, A.; Richter, P.; Häder, D.-P. Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments in the Flagellate euglena Gracilis—As Sensitive Endpoints for Toxicity Evaluation of Liquid Detergents. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 133, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahira, S.; Khan, S.; Samrana, S.; Shahi, L.; Ali, I.; Murad, W.; Rehman, Z.U.; Azizullah, A. Bio-Assessment and Remediation of Arsenic (Arsenite As-III) in Water by Euglena gracilis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Liu, B.; Farooq, M.A.; Islam, F.; Azizullah, A.; Yu, C.; Su, W.; Gan, Y. Toxicological Effects of Bisphenol A on Growth and Antioxidant Defense System in Oryza sativa as Revealed by Ultrastructure Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Chen, Q.; Duan, S. Transcriptional Analysis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa Exposed to Bisphenol A. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, G. Photosynthesis Responses of Tibetan Freshwater Algae Chlorella vulgaris to Herbicide glyphosate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz De Carvalho, R.; Feijão, E.; Matos, A.R.; Cabrita, M.T.; Utkin, A.B.; Novais, S.C.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Caçador, I.; Marques, J.C.; Reis-Santos, P.; et al. Effects of Glyphosate-Based Herbicide on Primary Production and Physiological Fitness of the Macroalgae Ulva lactuca. Toxics 2022, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, R.J.; Tsimilli-Michael, M.; Srivastava, A. Analysis of the Chlorophyll a Fluorescence Transient. In Chlorophyll a Fluorescence; Papageorgiou, G.C., Govindjee, Eds.; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 19, pp. 321–362. ISBN 978-1-4020-3217-2. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Shao, H.; Pan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D. Herbicidal Effects of Harmaline from Peganum harmala on Photosynthesis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa: Probed by Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Thermoluminescence. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2014, 115, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ouada, S.; Ben Ali, R.; Leboulanger, C.; Zaghden, H.; Choura, S.; Ben Ouada, H.; Sayadi, S. Effect and Removal of Bisphenol A by Two Extremophilic Microalgal Strains (Chlorophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Shi, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, C.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. The Effect of Bisphenol A on Growth, Morphology, Lipid Peroxidation, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, and PS II in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 74, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chee, C.W.; Goh, C.J. ‘Photoinhibition’ of Heliconia under Natural Tropical Conditions: The Importance of Leaf Orientation for Light Interception and Leaf Temperature. Plant Cell Environ. 1996, 19, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattullo, C.E.; Bährs, H.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Loffredo, E. Removal of Bisphenol A by the Freshwater Green Alga Monoraphidium braunii and the Role of Natural Organic Matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruban, A.V. Nonphotochemical Chlorophyll Fluorescence Quenching: Mechanism and Effectiveness in Protecting Plants from Photodamage. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.H.; Millar, A.H. The Diversity of Substrates for Plant Respiration and How to Optimize Their Use. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 2133–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.P.; Penjweini, R.; Ma, J.; Alspaugh, G.; Andreoni, A.; Kim, Y.-C.; Wang, P.; Knutson, J.R.; Hwang, P.M. Mitochondrial Respiration Reduces Exposure of the Nucleus to Oxygen. JBC 2023, 299, 103018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Saxena, A.; Kapoor, N.; Singh, K.J.; Saldarriaga-Hernández, S.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Therapeutic Attributes and Applied Aspects of Biological Macromolecules (Polypeptides, Fucoxanthin, Sterols, Fatty Acids, Polysaccharides, and Polyphenols) from Diatoms—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wu, R.S.S.; Kong, R.Y.C. Biodegradation and Enzymatic Responses in the Marine Diatom Skeletonema costatum upon Exposure to 2,4-Dichlorophenol. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 59, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, G.H.J.; Eloff, J.N. The Effect of Physico-Chemical Factors on Growth Relevant to the Mass Culture of Axenic Microcystis. In The Water Environment; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1981; pp. 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, B. Heavy Metal–Induced Stress in Eukaryotic Algae—Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Toxicity and Tolerance with Particular Emphasis on Oxidative Stress in Exposed Cells and the Role of Antioxidant Response. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16860–16911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassman, N.R. Induction of Oxidative Stress by Bisphenol A and Its Pleiotropic Effects. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Gao, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, Z. Oxidative Stress and Immunotoxic Effects of Bisphenol A on the Larvae of Rare Minnow Gobiocypris rarus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Han, R.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Effects of Bisphenol A on Antioxidant System in Soybean Seedling Roots. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakar, C.; Djilianov, D.; Bartels, D. Photosynthesis in Desiccation Tolerant Plants: Energy Metabolism and Antioxidative Stress Defense. Plant Sci. 2012, 182, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakir, S.K.; Irfan, S.; Akhtar, B.; Rehman, S.U.; Daud, M.K.; Taimur, N.; Azizullah, A. Pesticide-Induced Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Responses in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Seedlings. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, E.; Scarano, G. Copper-Induced Changes of Non-Protein Thiols and Antioxidant Enzymes in the Marine Microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Cheng, C.; Gu, Y.; Shu, X.; Xie, L.; Zhao, Y. Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Microcystin-LR and Phenanthrene Alone or in Combination to the Cladoceran (Daphnia magna). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilliges, Y.; Kehr, J.-C.; Meissner, S.; Ishida, K.; Mikkat, S.; Hagemann, M.; Kaplan, A.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. The Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxin Microcystin Binds to Proteins and Increases the Fitness of Microcystis under Oxidative Stress Conditions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y. Synergistic Toxicity to the Toxigenic Microcystis and Enhanced Microcystin Release Exposed to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Mixtures. Toxicon 2022, 210, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, N.; Zaytseva, T.; Kuzikova, I. Cellular Responses and Bioremoval of Nonylphenol by the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacterium Planktothrix agardhii 1113. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 171, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, P.; Guo, N. Effects of Nonylphenol on the Growth and Microcystin Production of Microcystis Strains. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, L.; Lin, Y.; Pan, B.; Li, M. Micrometer Scale Polystyrene Plastics of Varying Concentrations and Particle Sizes Inhibit Growth and Upregulate Microcystin-Related Gene Expression in Microcystis Aeruginosa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Tao, J.; Li, S.; Hao, S.; Zhu, X.; Hong, Y. PAHs Would Alter Cyanobacterial Blooms by Affecting the Microcystin Production and Physiological Characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, C.; Lu, C.; Zhao, M. Effects of Glufosinate on the Growth of and Microcystin Production by Microcystis aeruginosa at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X. Effects of Limonene Stress on the Growth of and Microcystin Release by the Freshwater Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 105, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svendsen, M.B.S.; Andersen, N.R.; Hansen, P.J.; Steffensen, J.F. Effects of Harmful Algal Blooms on Fish: Insights from Prymnesium parvum. Fishes 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdalet, E.; Fleming, L.E.; Gowen, R.; Davidson, K.; Hess, P.; Backer, L.C.; Moore, S.K.; Hoagland, P.; Enevoldsen, H. Marine Harmful Algal Blooms, Human Health and Wellbeing: Challenges and Opportunities in the 21st Century. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2016, 96, 61–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.W.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful Algal Blooms: A Climate Change Co-Stressor in Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Li, Z.; Réveillon, D.; Savar, V.; Hess, P.; Mertens, K.N.; Youn, J.Y.; Shin, K.; Lee, J.; Shin, A.-Y.; et al. Toxic Dinoflagellate Centrodinium punctatum (Cleve) F.J.R. Taylor: An Examination on the Responses in Growth and Toxin Contents to Drastic Changes of Temperature and Salinity. Harmful Algae 2024, 131, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, K.M.; Velthuis, M.; Van De Waal, D.B. Meta-Analysis Reveals Enhanced Growth of Marine Harmful Algae from Temperate Regions with Warming and Elevated CO2 Levels. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Song, X.; Cheng, R.; Chi, L.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z. Uncovering the Regulation Effect of Modified Clay on Toxin Production in Alexandrium Pacificum: From Physiological Insights. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengco, M.R.; Hagström, J.A.; Granéli, E.; Anderson, D.M. Removal of Prymnesium parvum (Haptophyceae) and Its Toxins Using Clay Minerals. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.H.; Henry, M.S.; Higham, C.J.; Blum, P.; Sengco, M.R.; Anderson, D.M. Removal of Harmful Algal Cells (Karenia brevis) and Toxins from Seawater Culture by Clay Flocculation. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, H.; Shutes, B.; Wang, X. Salt-Alkalization May Potentially Promote Microcystis Aeruginosa Blooms and the Production of Microcystin-LR. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 118971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebenezer, V.; Lim, W.A.; Ki, J.-S. Effects of the Algicides CuSO4 and NaOCl on Various Physiological Parameters in the Harmful Dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuez, M.; González-Fernández, C.; Ballesteros, M. Algicidal Microorganisms and Secreted Algicides: New Tools to Induce Microalgal Cell Disruption. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Qiao, J.; Ou, H.; Deng, J. Effects of Different Algaecides on the Photosynthetic Capacity, Cell Integrity and Microcystin-LR Release of Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zheng, T.; Ye, C.; Huannixi, W.; Yakefu, Z.; Meng, Y.; Peng, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. Algicidal Properties of Extracts from Cinnamomum Camphora Fresh Leaves and Their Main Compounds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dao, G.; Tao, Y.; Zhan, X.; Hu, H. A Review on Control of Harmful Algal Blooms by Plant-Derived Allelochemicals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Thiazole Amides, A Novel Class of Algaecides against Freshwater Harmful Algae. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Xiao, T. Environmental Estrogens Shape Disease Susceptibility. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 249, 114125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Ji, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Du, X.; Chung, A.C.K.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cai, Z. Integrative Chemical Proteomics-Metabolomics Approach Reveals Acaca/Acacb as Direct Molecular Targets of PFOA. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11092–11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagymasi, A.T.; Dempsey, J.P.; Srivastava, P.K. Heat-Shock Proteins. Curr. Protoc. 2022, 2, e592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Ebenezer, V.; Ki, J.-S. Transcriptional Responses of Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70) to Thermal, Bisphenol A, and Copper Stresses in the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobiyama, A.; Tanaka, S.; Kaneko, Y.; Lim, P.-T.; Ogata, T. Temperature Tolerance and Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.J.; Gobler, C.J. Global Transcriptional Responses of the Toxic Cyanobacterium, Microcystis Aeruginosa, to Nitrogen Stress, Phosphorus Stress, and Growth on Organic Matter. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeckisch, N.; Yang, I.; Wohlrab, S.; Glöckner, G.; Kroymann, J.; Vogel, H.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Comparative Genomic and Transcriptomic Characterization of the Toxigenic Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, R.; Ki, J.-S. 6.0 K Microarray Reveals Differential Transcriptomic Responses in the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum Exposed to Polychlorinated Biphenyl (PCB). Chemosphere 2018, 195, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Electrochemical Determination of Tetracycline Using the Synergy of a Molybdenum (IV) Sulfide-Thionine Nanocomposite with an Aptamer by Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV). Anal. Lett. 2024, 57, 2364–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Lim, W.-A.; Ki, J.-S. Genome-Wide Analysis of Transcription and Photosynthesis Inhibition in the Harmful Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum in Response to the Biocide Copper Sulfate. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Suh, Y.S.; Ki, J.-S. Transcriptomic Profiles Reveal the Genome-Wide Responses of the Harmful Dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides When Exposed to the Algicide Copper Sulfate. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Sui, Z.; Bao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C. Isolation and Characterization of Calmodulin Gene of Alexandrium catenella (Dinoflagellate) and Its Performance in Cell Growth and Heat Stress. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 13, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).