Evolution of the Hydrobiological Communities of a Coastal Lake in the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago (Southern Island, Arctic Russia) in Relation to Climate Change Following the End of the Little Ice Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
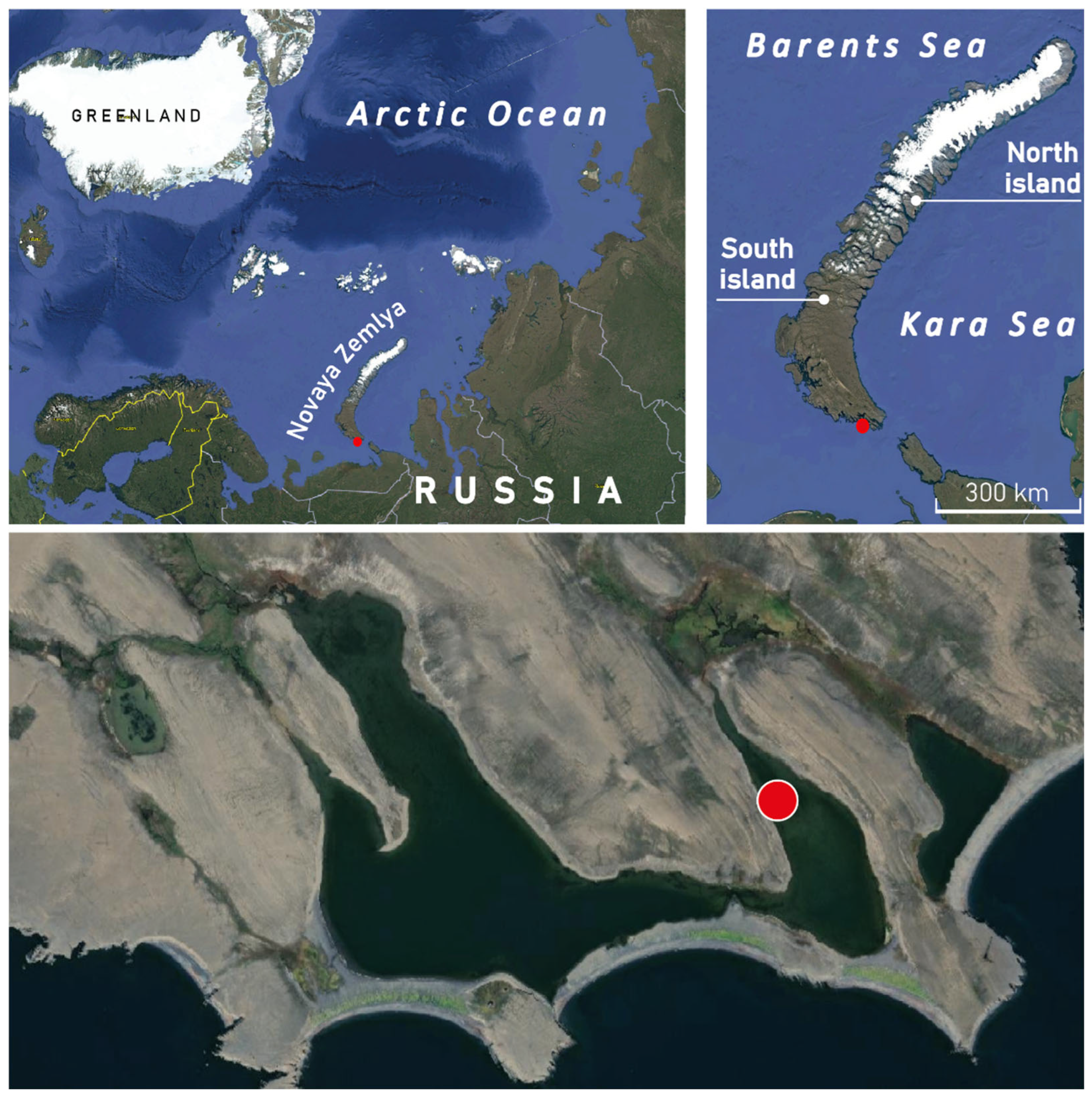
2.1. Regional Settings
2.2. Sampling, Lithology, Geochemistry, and Age Model
2.3. Chironomids
2.4. Diatoms
2.5. Cladocera
2.6. Numerical Analysis
3. Results
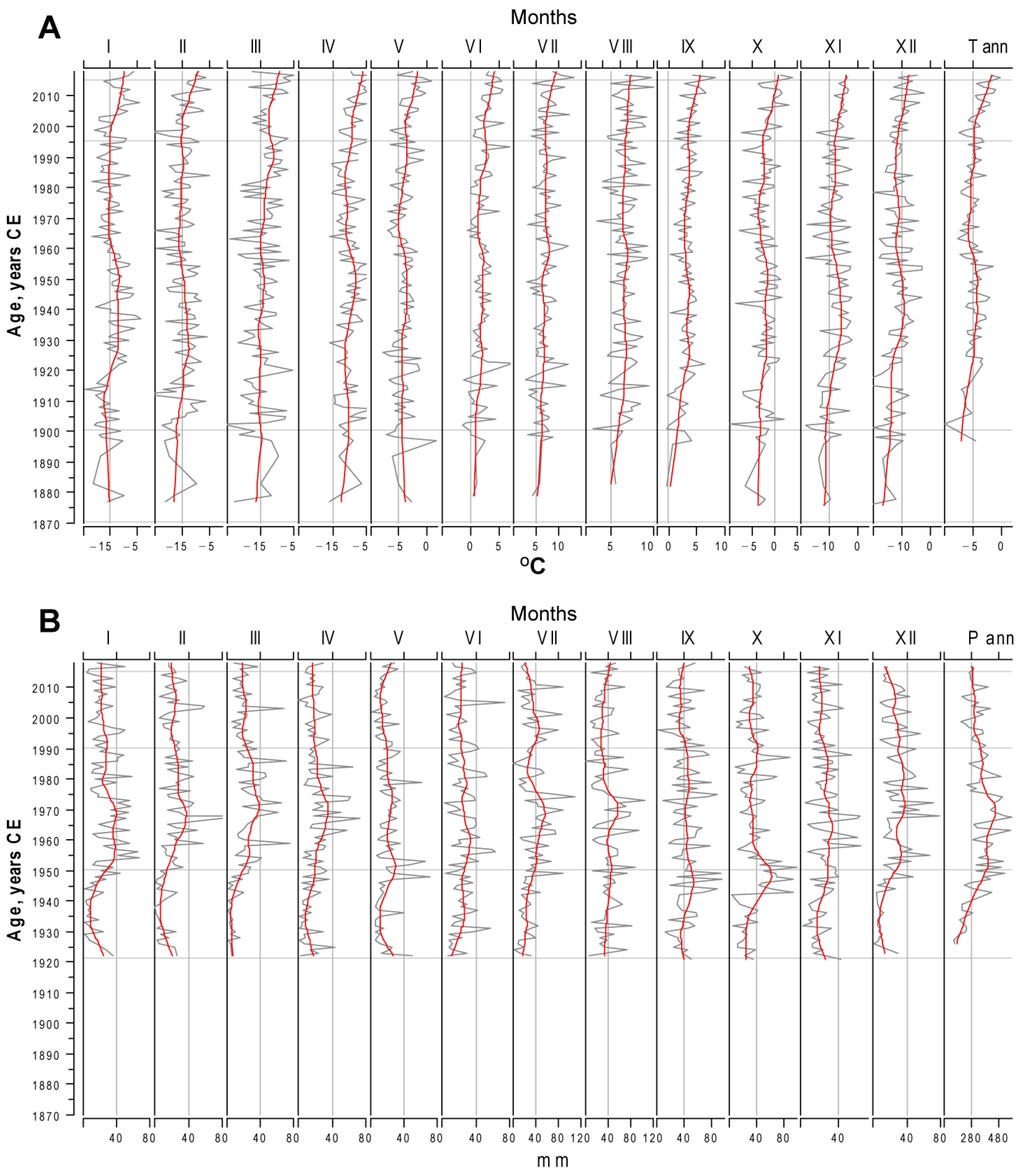
3.1. Climate in Novaya Zemlya Since the Beginning of Observation
3.2. Age Model
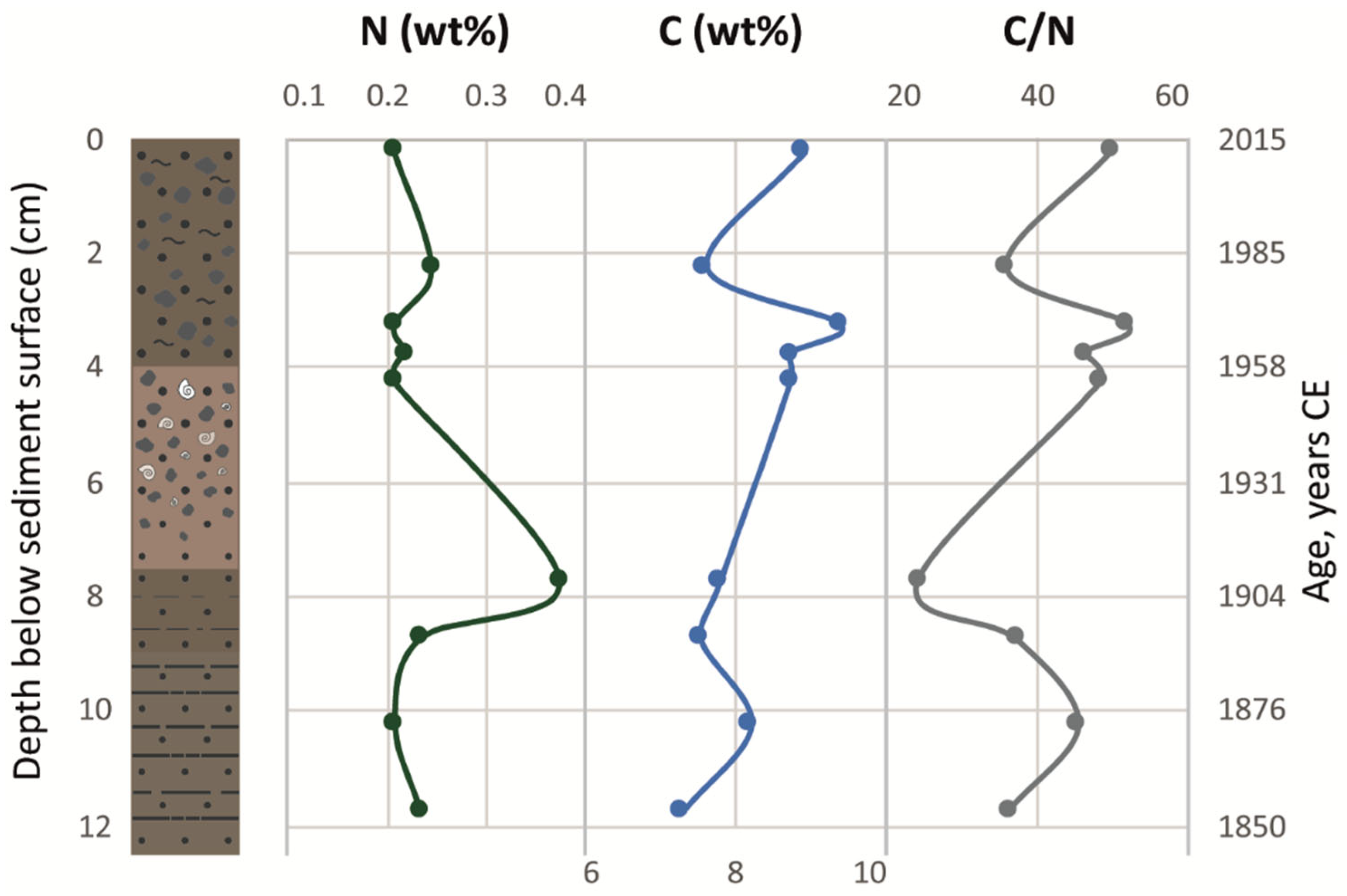
3.3. Lithology and Sediment Organic Chemistry
3.4. Chironomid Stratigraphy
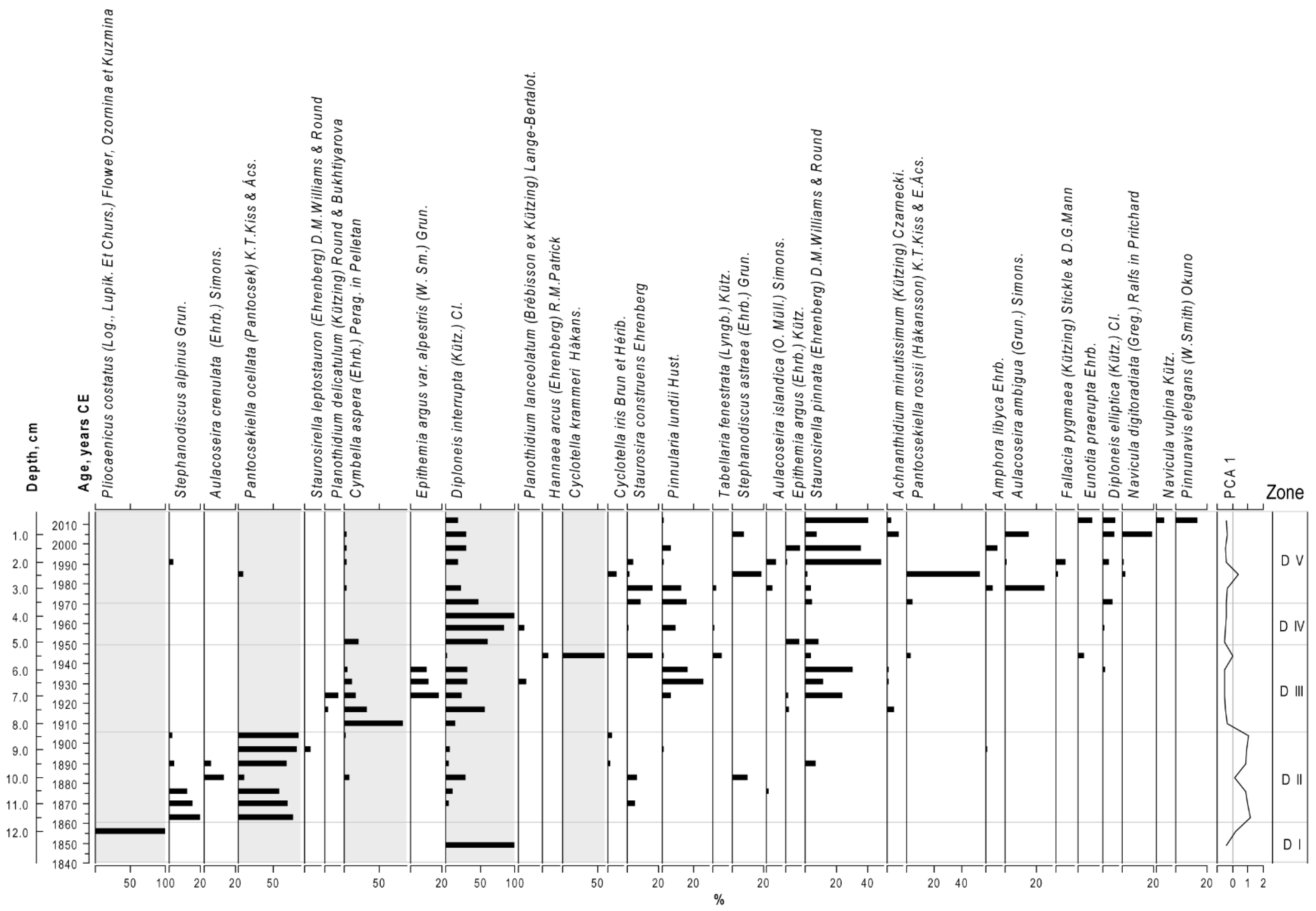
3.5. Diatom Stratigraphy
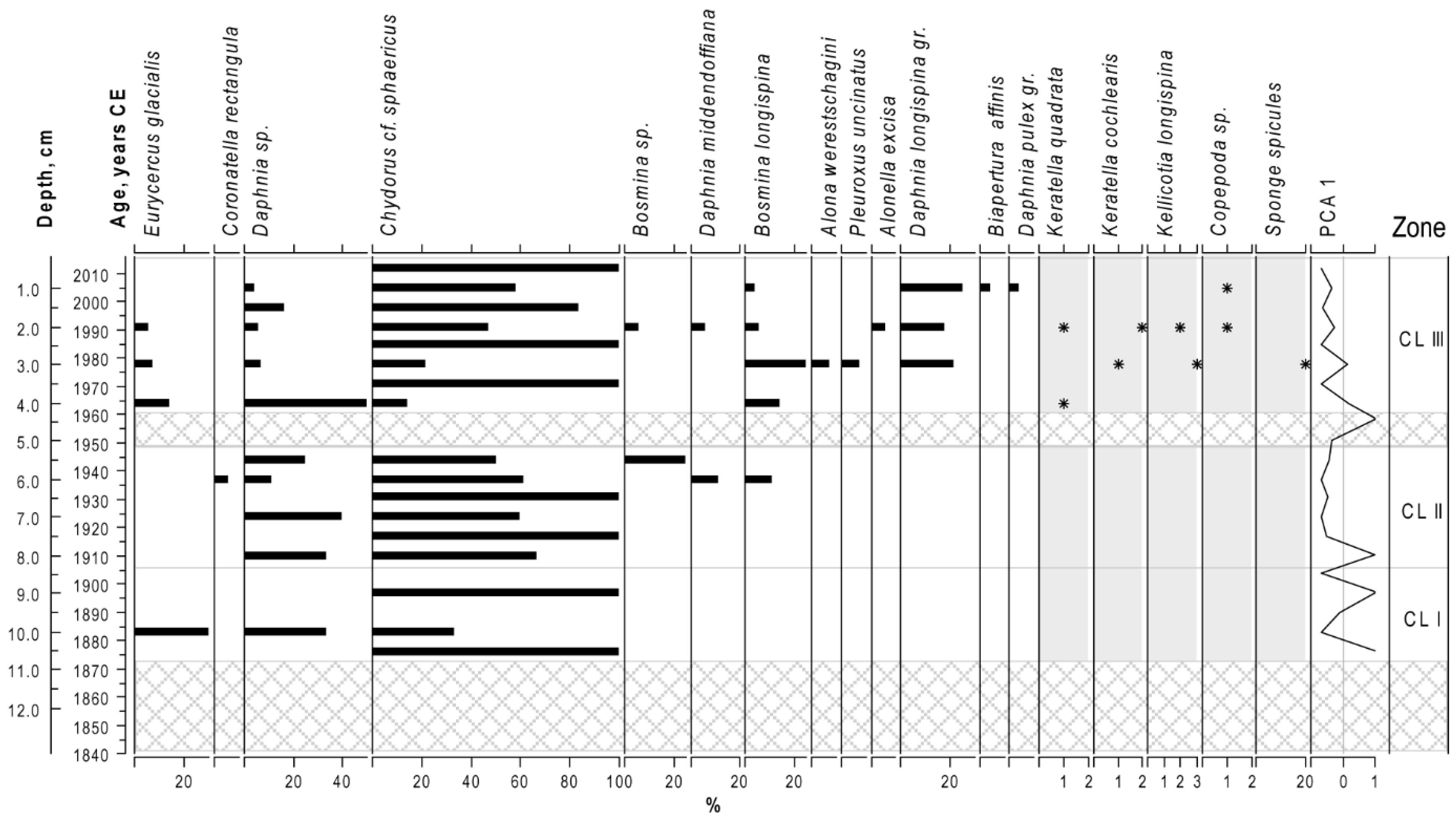
3.6. Cladocera
3.7. Changes in Biological Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Climate and Its Relationship to Biological Indicators
4.2. Chironomids
4.3. Diatoms
4.4. Cladocera
4.5. Diversity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Taxa [36] | Possible Analogue Species in the Modern Fauna | Biotope | Chironomid Zone (Sediment Depth, cm; Age, CE) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (12.5–9.5; 1850–1880) | II (9.5–7.5; 1880–1906) | III (7.5–4.5; 1906–1955) | IV (4.5–2.5; 1955–1975) | V (2.5–0; 1975–2015) | |||
| Chaetocladius type B | Chaetocladius s. str. binotatus | Lo | +++ | + | + | ||
| Chaetocladius piger-type | Chaetocladius s. str. glacialis | Loc | + | ||||
| Chironomus anthracinus-type | Chironomus s. str. albimaculatus | Le | ++ | ++ | |||
| Chironomus plumosus-type | Chironomus s. str. sp. | Le | + | ||||
| Chironomini larvula | - | + | |||||
| Cladotanytarsus mancus-type | Cladotanytarsus sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Corynocera oliveri-type | Corynocera sp. | Le | +++ | ||||
| Corynoneura arctica-type | Corynoneura arctica | Lo/Le | ++ | ||||
| Cricotopus bicinctus-type | Cricotopus gr. bicinctus | Lo | + | ||||
| Cricotopus cylindraceus-type | Cricotopus gr. cylindraceus | Lo/Le | + | + | |||
| Cricotopus intersectus-type | Cricotopus (Isocladius) intersectus | Le | + | ||||
| Cricotopus laricomalis-type | Cricotopus (Isocladius) laricomalis | Le | + | ||||
| Eukiefferiella devonica-type | Tvetenia duodenaria | Lo | ++ | + | + | ++ | |
| Eukiefferiella fittkaui-type | Tvetenia discoloripes | Lo | + | ||||
| Eukiefferiella claripennis-type | Tokunagaia rectangularis | Lo/Le | + | ++ | + | ++++ | |
| Hydrobaenus johannseni-type | Hydrobaenus gr. pilipes | Le | + | ||||
| Hydrobaenus lugubris-type | Hydrobaenus gr. lapponicus | Le | + | ||||
| Limnophyes–Paralimnophyes | Limnophyes sp. | ST | +++++ | ++++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| Metriocnemus eurynotus-type | Metriocnemus sp. | ST | +++++ | +++++ | ++++ | ++ | ++ |
| Oliveridia | Oliveridia tricornis | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Orthocladius oliveri-type | Orthocladius s. str. sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Orthocladius trigonolabris-type | Orthocladius s. str. sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Orthocladius type I | Orthocladius s. str. sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Orthocladius type S | Orthocladius (Eudactylocladius) sp. | ST/Lo/Le | + | ++ | |||
| Paraphaenocladius | Paraphaenocladius sp. | ST/Lo | + | ||||
| Parakiefferiella triquetra-type | Parakiefferiella sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Paratanytarsus austriacus-type | Paratanytarsus austriacus | Lo/Le | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++++ |
| Paratanytarsus | Paratanytarsus kaszabi | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Psectrocladius flavus-type | Psectrocladius (Allopsectrocladius) sp. | Le | + | ||||
| Psectrocladius sordidellus-type | Psectrocladius s. str. sp. | Le | + | ||||
| Pseudosmittia | Allocladius nanseni | ST/Le | +++ | +++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++++ |
| Sergentia coracina-type | Sergentia coracina | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Smittia–Parasmittia | Smittia sp. | ST | ++ | ||||
| Stempellinella–Zavrelia | Chironomus s. str. sp. | Le | + | ||||
| Symposiocladius | Orthocladius (Symposiocladius) sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Stictochironomus | Stictochironomus sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Tanytarsus lugens-type | Tanytarsus sp. | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Tanytarsus no spur | Tanytarsus gracilentus | Lo/Le | + | ||||
| Trissocladius | Hydrobaenus gr. lapponicus | Le | + | ||||
| Zalutschia type A | Zalutschia sp. | Le | + | ||||
| Chironomini undiff. | - | ++ | |||||
| Orthocladiinae undiff. | - | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ||
| Species | Present in the Core | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Allocladius nanseni (Kieffer, 1926) | + |
| 2 | Chaetocladius (Chaetocladius) binotatus (Lundström, 1915) | + |
| 3 | Chaetocladius (Chaetocladius) + (Lundström, 1915) | + |
| 4 | Chironomus s. str. albimaculatus Shobanov, Wülker et Kiknadze, 2002 | + |
| 5 | Corynoneura arctica Kieffer, 1923 | + |
| 6 | Diamesa arctica (Boheman, 1865) | no |
| 7 | Hydrobaenus lapponicus (Brundin, 1956) | + |
| 8 | Limnophyes brachytomus (Kieffer, 1922) | as Limnophyes |
| 9 | Limnophyes minimus (Meigen, 1818) | as Limnophyes |
| 10 | Limnophyes pumilio (Holmgren, 1869) | as Limnophyes |
| 11 | Metriocnemus (Metriocnemus) brusti Saether, 1989 | as Metriocnemus |
| 12 | Metriocnemus (Metriocnemus) sternerectus Makarchenko et Makarchenko, 2013 | as Metriocnemus |
| 13 | Orthocladius (Eudactylocladius) olivaceus (Kieffer, 1911) | no |
| 14 | Orthocladius (Eudactylocladius) subletteorum Cranston, 1999 | no |
| 15 | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) decoratus (Holmgren, 1869) | no |
| 16 | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) glabripennis (Goetghebuer, 1921) | no |
| 17 | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) hazenensis Soponis, 1977 | no |
| 18 | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) oblidens (Walker, 1856) | no |
| 19 | Paraphaenocladius impensus (Walker, 1856) | as Paraphaenocladius |
| 20 | Paraphaenocladius pseudirritus Strenzke, 1950 | as Paraphaenocladius |
| 21 | Paratanytarsus kaszabi Reiss, 1971 | + |
| 22 | Pseudokiefferiella parva (Edwards, 1932) | no |
| 23 | Tanytarsus gracilentus (Holmgren, 1883) | + |
| 24 | Tokunagaia rectangularis (Goetghebuer, 1940) | + |
| 25 | Tvetenia duodenaria Kieffer, 1922 | + |
| Class Centrophyceae | |
| Family Aulacoseiraceae | |
| 1 | Aulacoseira ambigua (Grun.) Simons. |
| 2 | Aulacoseira crenulata (Ehrb.) Simons. * |
| 3 | Aulacoseira islandica (O. Müll.) Simons. * |
| Family Stephanodiscaceae | |
| 4 | Lindavia bodanica (Eulenstein ex Grunow) T.Nakov, Guillory, Julius, Theriot & Alverson * |
| 5 | Cyclotella iris Brun et Hérib. * |
| 6 | Cyclotella krammeri Håkans. * |
| 7 | Pantocsekiella ocellata (Pantocsek) K.T.Kiss & Ács. * |
| 8 | Pantocsekiella rossii (Håkansson) K.T.Kiss & E.Ács. * |
| 9 | Pliocaenicus costatus (Log., Lupik. Et Churs.) Flower, Ozornina et Kuzmina |
| 10 | Stephanodiscus alpinus Grun. * |
| 11 | Stephanodiscus astraea (Ehrb.) Grun. * |
| Class Pennatophyceae | |
| Family Achnanthidiaceae | |
| 12 | Planothidium delicatulum (Kützing) Round & Bukhtiyarova |
| 13 | Planothidium lanceolatum (Brébisson ex Kützing) Lange-Bertalot |
| 14 | Achnanthidium minutissimum (Kützing) Czarnecki |
| Family Bacillariaceae | |
| 15 | Denticula kuetzingii Grun. |
| 16 | Hantzschia amphioxys (Ehrb.) Grun. in Cl. et Grun. |
| Family Cavinulaceae | |
| 17 | Cavinula scutelloides (W.Smith ex W.Gregory) Lange-Bertalot |
| Family Catenulaceae | |
| 18 | Amphora libyca Ehrb. * |
| 19 | Amphora pediculus (Kütz.) Grun. ex A. Schmidt * |
| Family Cocconeidaceae | |
| 20 | Cocconeis lineata Ehrenberg |
| Family Cymbellaceae | |
| 21 | Cymbella aspera (Ehrb.) Perag. in Pelletan |
| 22 | Cymbella cistula (Ehrb.) Kirchn. |
| 23 | Cymbopleura inaequalis (Ehrenberg) Krammer * |
| 24 | Placoneis elginensis (W.Gregory) E.J.Cox |
| 25 | Cymbella sp. |
| Family Diploneidaceae | |
| 26 | Diploneis elliptica (Kütz.) Cl. * |
| 27 | Diploneis interrupta (Kütz.) Cl. |
| Family Encyonemataceae | |
| 28 | Encyonema mesianum (Cholnoky) D.G.Mann * |
| 29 | Encyonema silesiacum (Bleisch) D.G.Mann |
| Family Eunotiaceae | |
| 30 | Eunotia circumborealis Lange-Bert. et Nörp. |
| 31 | Eunotia praerupta Ehrb. |
| 32 | Eunotia subarcuatoides Alles, Norpel et Lange-Bert. |
| Family Fragilariaceae | |
| 33 | Fragilaria capucina Desm. |
| Family Gomphonemataceae | |
| 34 | Gomphonema acuminatum Ehrb. |
| 35 | Gomphonella olivacea (Hornemann) Rabenhorst |
| Family Naviculaceae | |
| 36 | Caloneis silicula (Ehrb.) Cl. |
| 37 | Gyrosigma attenuatum (Kütz.) Rabenh. |
| 38 | Navicula digitoradiata (Greg.) Ralfs in Pritchard |
| 39 | Pinnunavis elegans (W.Smith) Okuno |
| 40 | Navicula vulpina Kütz. |
| 41 | Navicula sp. |
| Family Neidiaceae | |
| 42 | Neidium bisulcatum (Lagerst.) Cleve |
| 43 | Neidium productum (W. Sm.) Cl. * |
| Family Pinnulariaceae | |
| 44 | Pinnularia lata (Bréb.) W. Sm. |
| 45 | Pinnularia lundii Hust. |
| 46 | Pinnularia microstauron (Ehrb.) Cl. |
| 47 | Pinnularia viridis (Nitzsch) Ehrb. |
| Family Rhopalodiaceae | |
| 48 | Epithemia argus (Ehrb.) Kütz. |
| 49 | Epithemia argus var. alpestris (W. Sm.) Grun. |
| Family Sellaphoraceae | |
| 50 | Sellaphora bacillum (Ehrenberg) D.G.Mann |
| 51 | Sellaphora pupula (Kützing) Mereschkovsky |
| 52 | Fallacia pygmaea (Kützing) Stickle & D.G.Mann |
| Family Stauroneidaceae | |
| 53 | Stauroneis anceps Ehrb. |
| 54 | Stauroneis phoenicenteron (Nitzsch) Ehrb. |
| Family Staurosiraceae | |
| 55 | Pseudostaurosira borealis (Foged) M.L.García, E.Morales, Ector & Maidana |
| 56 | Staurosirella leptostauron (Ehrenberg) D.M.Williams & Round |
| 57 | Staurosirella pinnata (Ehrenberg) D.M.Williams & Round |
| 58 | Staurosira construens Ehrenberg |
| Family Tabellariaceae | |
| 59 | Diatoma vulgaris Bory * |
| 60 | Tabellaria fenestrata (Lyngb.) Kütz. * |
| Family Ulnariaceae | |
| 61 | Hannaea arcus (Ehrenberg) R.M.Patrick |
| 62 | Ulnaria ulna (Nitzsch) Compère |
| PAL | [33] | [8] | [129] | [9] | Present Study | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subclass Cladocera | ||||||
| Order Anomopoda | ||||||
| Family Bosminidae | ||||||
| Bosmina (Eubosmina) cf. longispina (O.F. Müller, 1785) | EWS | − | − | − | − | + |
| Bosmina obtusirostris G.O. Sars, 1862 (synonym of Bosmina (Eubosmina) cf. longispina) | EWS | + | + | − | − | − |
| Bosmina sp. | - | − | − | − | − | + |
| Family Eurycercidae | ||||||
| Eurycercus (Teretifrons) glacialis (O.F. Müller, 1776) | ARC (P) | + | + | + | + | + |
| Family Chydoridae | ||||||
| Alona guttata Sars, 1862 | C | + | + | + | − | − |
| * Alona werestschagini (Sinev, 1999) | ARC (P) | − | − | − | − | + |
| * Alonella excisa (Fischer, 1854) | C | − | − | − | − | + |
| * Biapertura affinis (Leydig, 1860) | PAL | − | − | − | − | + |
| Camptocercus fennicus Stenroos, 1898 | ES | + | − | − | − | − |
| Chydorus cf. sphaericus (O.F. Müller, 1785) | C | + | + | + | + | + |
| Coronatella rectangula (Sars, 1862) | C | + | + | + | − | + |
| * Pleuroxus uncinatus (Baird 1850) | PAL | − | − | − | − | + |
| Tretocephala ambigua (Lilljeborg, 1901) | ES | − | + | − | − | − |
| Family Macrothricidae | ||||||
| Macrothrix hirsuticornis Norman & Brady, 1867 | HOL | + | + | + | − | − |
| Family Daphnidae | ||||||
| Daphnia longiremis G. O. Sars, 1862 | HOL | + | + | − | − | − |
| Daphnia longispina gr. O.F. Müller, 1776 | PAL | − | − | − | − | + |
| D. (D.) middendorffiana Fischer, 1851 | ARC (P) | + | + | + | − | + |
| D. (D) pulex Leydig, 1860 | C | + | + | + | − | − |
| D. (D.) pulex gr. | C | − | − | − | − | + |
| D. (D.) pulex tenebrosa (synonym of D. (D.) middendorffiana) | ARC (P) | + | − | − | − | − |
| Daphnia sp. | − | − | − | + | ||
| 11 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 13 | ||
References
- Rantanen, M.; Karpechko, A.Y.; Lipponen, A.; Nordling, K.; Hyvärinen, O.; Ruosteenoja, K.; Vilma, T.; Laaksonen, A. The Arctic has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Core Writing Team. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, S.J.; Convey, P.; Aakra, K.; Aarvik, L.; Ávila-Jiménez, M.L.; Babenko, A.; Biersma, E.M.; Boström, S.; Brittain, J.E.; Carlsson, A.M.; et al. The terrestrial and freshwater invertebrate biodiversity of the archipelagoes of the Barents Sea; Svalbard, Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 440–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, L.B.; Frolova, L.A.; Palagushkina, O.V.; Rudaya, N.A.; Syrykh, L.S.; Grekov, I.M.; Solovieva, N.; Loskutova, O.A. Recent shift in biological communities: A case study from the Eastern European Russian Arctic (Bolshezemelskaya Tundra). Polar Biol. 2021, 44, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stief, P.; Nazarova, L.; De Beer, D. Chimney construction by Chironomus riparius larvae in response to hypoxia: Microbial implications for freshwater sediments. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Grönroos, M.; Ilmonen, J.; Karhu, T.; Niva, M.; Passivirta, L. Environmental heterogeneity and β diversity of stream macroinvertebrate communities at intermediate spatial scales. Freshw. Sci. 2012, 32, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrateva, T.A.; Stepanova, N.; Nikonenkova, T.; Nazarova, L. Influence of Municipal Wastewaters on the zooplankton communities of a small river from the industrial zone of the Middle Volga Region based on the results of long-term observations. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2025, 18, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekhoff, N.V. Invertebrates of inland water bodies (Novaya Zemlya, Arkhangelsk region). Novaya Zemlya. Nature. History. Archaeology. Culture. In Trudy Morskoi Arckticheskoi Kompleksnoi Ekspeditsii; Boyarskiy, P.V., Ed.; Moscow, Russia, 1998; pp. 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bespalaya, Y.; Przhiboro, A.; Aksenova, O.; Berezina, N.; Gofarov, M.; Kondakov, A.; Kurashov, E.; Litvinchuk, L.; Sokolova, S.; Spitsyn, V.; et al. Preliminary study of the benthic fauna in lakes of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago and Vaigach Island (the Russian Arctic). Polar Biol. 2021, 44, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.J. Oversigt over de paa Dijmphna-Togtet indsamlede Krebsdyr. In Dijmphna-Togtets Zoologisk-Botaniske Udbytte; Lütken, C.F., Ed.; Hagerup: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1887; pp. 183–286. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.P. The Craneflies (Superfamily Tipuloidea, Order Diptera). In Report on the scientific results of the Norwegian Expedition to Novaya Zemlya 1921; Holtedahl, O., Ed.; A.W. Brøggers Bogtrykkeri: Oslo, Norway, 1922; Volume 5, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, F.; Thienemann, A. Chironomidenlarven aus Nowaja Semlja. In Report on the scientific results of the Norwegian Expedition to Novaya Zemlya 1921; Holtedahl, O., Ed.; A.W. Brøggers Bogtrykkeri: Oslo, Norway, 1922; Volume 3, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, K.J. Plecoptera. In Report on the Scientific Results of the Norwegian Expedition to Novaya Zemlya 1921; Holtedahl, O., Ed.; A.W. Brøggers Bogtrykkeri: Oslo, Norway, 1923; Volume 16, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Odhner, N.H. Mollusca Pisidium Conventus Clessin. In Report on the Scientific Results of the Norwegian Expedition to Novaya Zemlya 1921; Holtedahl, O., Ed.; A.W. Brøggers Bogtrykkeri: Oslo, Norway, 1923; Volume 6, pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer, G. Ephemeropteren und Trichopteren von Nowaja Semlja. In Report on the Scientific Results of the Norwegian Expedition to Novaya Zemlya 1921; Holtedahl, O., Ed.; A.W. Brøggers Bogtrykkeri: Oslo, Norway, 1925; Volume 29, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sidorov, S.A. The question about freshwater molluscs species Pisidium on Novaya Zemlya. Tr. Plavuchego Morskogo Nauchnogo Instituta 1925, 12, 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbunov, G.P. Preliminary Report of investigations in term Freshand brackish-waters of the Novaya Zemlya in 1923, 1924 and 1925. Tr. Inst. Izutch. Sev. 1929, 40, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren, A.E. Insecta a viris doctissimus Nordenskiöld illun ducem sequentibus in insulis Waigatsch et Novaja Semlia anno 1875 collecta. Diptera Entomol. Tidskr. 1883, 4, 162–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, J.J. Chironomides de la Novuvelle-Zemble. In Report of the Scientific Results of the Norwegian Expedition to Novaya Zemlya; Holtedahl, O., Ed.; A.W. Brøggers Bogtrykkeri: Oslo, Norway, 1922; Volume 2, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, J.J. Nouvelle contribution a l’etude des Chironomides de la Nouvelle-Zemble. In Reports of the Scientific Results of the Norwegian Expedition to Novaya Zemlya 1921; Holtedahl, O., Ed.; A.W. Brøggers Bogtrykkeri: Oslo, Norway, 1923; Volume 9, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Makarchenko, E.A.; Makarchenko, M.A.; Vekhov, N.V. Preliminary data on the chironomid fauna (Diptera, Chironomidae) of the Novaya Zemlya archipelago. Novaya Zemlya Nat. Hist. Archeol. Cult. Mosc. 1998, 1, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zelentsov, N.I. A new genus and a new species of Orthocladiinae (Diptera, Chironomidae) from the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago. Entomol. Rev. 2006, 85, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelentsov, N.I. A new species of the Chironomid genus Chaetocladius (Diptera, Chironomidae) from the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago. Entomol. Rev. 2007, 86, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelentsov, N.I. Fauna of chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) of the Novaya Zemlya and Severnaya Zemlya archipelagos. Inland Water Biol. 2007, 4, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Krasheninnikov, A.B. Preliminary data on fauna and distribution of Chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) from Russian Arctic Islands. Bull. Perm Univ. Biol. 2013, 1, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, V.N. Nuclear Weapon Testing in Arctic; Moskovskie Uchebniki: Moscow, Russia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Khalturin, V.I.; Rautian, T.G.; Richards, P.G.; Leith, W.L. A review of nuclear testing by the Soviet Union at Novaya Zemlya, 1955–1990. Sci. Glob. Secur. 2005, 13, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarsky, P.V.; Gusev, S.V.; Evseev, N.F.; Zakharov, Y.S.; Kalyakin, V.N.; Koryakin, V.S.; Mazurov, Y.L.; Serebryanny, L.R. Concept of Formation of the System of Specially Protected Natural and Historical-Cultural Territories on Novaya Zemlya. In Novaya Zemlya. Proceedings of the Marine Arctic Complex Expedition; Boyarsky, P.V., Ed.; Russian Research Institute of Cultural and Natural Heritage: Moscow, Russia, 1994; Volume IV, pp. 13–37. [Google Scholar]
- Anokhin, V.M. Geological structure. In Novaya Zemlya; Boyarsky, P.V., Ed.; Paulsen: Moscow, Russia, 2009; pp. 257–331. [Google Scholar]
- The Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, 2nd ed.; Boyarsky, P.V., Ed.; Paulsen: Moscow, Russia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Grishchenko, I.V. Climate. In Novaya Zemlya; Paulsen: Moscow, Russia, 2009; pp. 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Zeeberg, J.; Forman, S.L. Changes in glacier extent on north Novaya Zemlya in the twentieth century. Holocene 2001, 11, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekhoff, N.V. Large Branchiopod Crustacea (Anostraca, Notostraca, Spinicaudata) of the Barents Region of Russia. Hydrobiologia 1997, 359, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malye Karmakuly. Novaya Zemlya Archipelago: A Memorial Album; Privalov, V., Ed.; Arkhangelsk, Russia, 2022. Available online: https://porarctic.ru/ru/books/malye-karmakuly/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Vlasov, B.P.; Davydova, N.N.; Druzhinin, G.V.; Subetto, D.A. Sampling of Bottom Sediments. General Patterns of the Emergence and Development of Lakes. Methods of Studying the History of Lakes. In History of lakes of the USSR; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1986; pp. 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.J.; Langdon, P.G.; Heiri, O. Using and Identifying Chironomid Larvae in Palaeoecology; QRA Technical Guide No 10; Quaternary Research Association: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Blaauw, M.; Christen, J.A. Flexible paleoclimate age-depth models using an autoregressive gamma process. Bayesian Anal. 2011, 6, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Meyers, P.A.; Teranes, J.L. Sediment Organic Matter. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments. Physical and Geochemical Methods; Last, W.M., Smol, J.P., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 239–269. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarova, L.B.; Razzjigaeva, N.G.; Golovatuk, L.G.; Biskaborn, B.; Grebennikova, T.A.; Ganzey, L.A.; Mokhova, L.M.; Diekmann, B. Development of ecological conditions in East Prymorje in Holocene. Contemp. Probl. Ecoly. 2021, 14, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederholm, T. Chironomidae of the Holarctic region. Keys and diagnoses. Part 1. Larvae. Entomol. Scand. 1983, 9, 1–457. [Google Scholar]
- Moller Pillot, H.K.M. Chironomidae Larvae. Biology and Ecology of the Chironomini; KNNV Publishing: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller Pillot, H.K.M. Chironomidae Larvae. Biology and Ecology of the Aquatic Orthocladiinae; KNNV Publishing: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, L.; Herzschuh, U.; Wetterich, S.; Kumke, T.; Pestryakova, L. Chironomid-based inference models for estimating mean, I July air temperature and water depth from lakes in Yakutia, northeastern Russia. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 45, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, L.; Self, A.E.; Brooks, S.J.; van Hardenbroek, M.; Herzschuh, U.; Diekmann, B. Northern Russian chironomid-based modern summer temperature data set and inference models. Glob. Planet Change 2015, 134, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, L.B.; Self, A.E.; Brooks, S.J.; Solovieva, N.; Syrykh, L.S.; Dauvalter, V.A. Chironomid fauna of the lakes from the Pechora River basin (east of European part of Russian Arctic): Ecology and reconstruction of recent ecological changes in the region. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2017, 4, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, L.; Syrykh, L.; Grekov, I.; Sapelko, T.; Krasheninnikov, A.B.; Solovieva, N. Chironomid-based modern summer temperature data set and inference model for the Northwest European part of Russia. Water 2023, 15, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battarbee, R.W. Diatom Analysis. In Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology; Berglund, B.E., Ed.; J. Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986; pp. 527–570. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H.B. 1. Part: Naviculaceae: Suesswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Jena, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H.B. 2. Part: Bacillariaceae, Epitemiaceae, Surirellaceae: Suesswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H.B. 3. Part: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae: Suesswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. Algae Base Version 4.2; World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway, UK. 2015. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Glezer, Z.I.; Karaeva, N.I.; Makarova, I.V. Classification of diatoms. In Diatoms of the USSR (Fossil and Modern); Makarova, I.V., Ed.; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1988; Volume 2, pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Genkal, S.I.; Kulikovsky, M.S.; Mikheeva, T.M.; Kuznetsova, I.V.; Lukyanova, E.V. Diatoms of the Plankton of the Svisloch River and Its Reservoirs; Scientific World: Moscow, Russia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase; World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland: Galway, UK, 2019; Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Palagushkina, O.V.; Nazarova, L.B.; Wetterich, S.; Schirrmeister, L. Diatoms of modern bottom sediments in Siberian arctic. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2012, 5, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palagushkina, O.; Wetterich, S.; Biskaborn, B.; Nazarova, L.; Lenz, J.; Schwamborn, G.; Schirrmeister, L.; Grosse, G. Diatom records and tephra mineralogy in pingo deposits of Seward Peninsula, Alaska. Palaeogeogr. Paleocl. 2017, 479, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydova, N.N. Diatoms—Indicators of Natural Conditions of Water Bodies in the Holocene; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, H.; Mertens, A.; Sinkeldam, J.A. Coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from The Netherlands. Aquat. Ecol. 1994, 28, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S.S.; Medvedeva, L.A.; Anisimova, O.V. Biodiversity of Algae-Indicators of the Environment; Pilies Studio: Tel Aviv, Israel, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, D.G. Cladocera Analysis. In Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology; Whiley & Sons.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986; pp. 667–701. [Google Scholar]
- Korhola, A.; Rautio, M. Cladocera and Other Branchiopod Crustaceans. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments. Developments in Paleoenvironmental Research; Smol, J.P., Birks, H.J.B., Last, W.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 4, pp. 125–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeroczyńska, K.; Sarmaja-Korjonen, K. Atlas of Sub Fossil Cladocera from Central and Northern Europe; Friends of the Lower Vistula Society: Swiecie, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kurek, J.; Korosi, J.B.; Jeziorski, A.; Smol, J.P. Establishing reliable minimum count sizes for cladoceran microfossils sampled from lake sediments. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, N.N. Fauna of the USSR. Crustaceans; Nauka, Leningrad: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 1971; Volume 1, p. 353. [Google Scholar]
- Flössner, D. Die Haplopoda und Cladocera (ohne Bosminidae) Mitteleuropas; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sinev, A.Y. A Key to identifying cladocerans of the genus Alona (Anomopoda, Chydoridae) from the Russian European part and Siberia. Zooli. Zh. 2002, 81, 926–939. [Google Scholar]
- Kotov, A.A.; Sinev, A.J.; Glagolev, S.M. Cladocera. In Identification Key of Zooplankton and Zoobenthos of European Russia Freshwater. Zooplankton; Partnership of Scientific Publications KMK: Moscow, Russia, 2010; pp. 151–276. [Google Scholar]
- Korovchinsky, N.M.; Kotov, A.A.; Sinev, A.Y. Cladocera (Crustacea: Cladocera) of Northern Eurasia; Partnership of Scientific Publications KMK: Moscow, Russia, 2021; Volume I–II, pp. 1–544. [Google Scholar]
- Nykänen, M.; Sarmaja-Korjonen, K. Findings of Alona protzi Hartwig 1900 (Branchiopoda: Anomopoda, Chydoridae) in Finland. Stud. Quat. 2007, 24, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme, K.; Elias-Gutiérrez, M.; Dumont, H.J. Three rare European “Alona” taxa (Branchiopoda: Cladocera: Chydoridae), with notes on distribution and taxonomy. Ann. Limnol. Int. Limnol. 2011, 47, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Damme, K.; Nevalainen, L. The most latent cladoceran in the Holarctic revealed—Sinking Unapertura Sarmaja-Korjonen, Hakojirvi & Korhola, 2000 into the genus Rhynchotalona Norman, 1903 (Branchiopoda: Cladocera: Chydoridae. Zootaxa 2019, 4613, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, L.A.; Rybak, J.I. Freshwater Crustacean Zooplankton of Europe; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Juggins, S. C2 Version 1.5 User Guide. In Software for Ecological and Palaeoecological Data Analysis and Visualisation; Newcastle University: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Raan, P.D. PAST: Palaeontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 41, 9. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Prentice, I.C. A theory of gradient analysis. Advan Ecol. Res. 1988, 18, 271–317. [Google Scholar]
- Smol, J.P.; Wolfe, A.P.; Birks, H.J.B.; Douglas, M.S.V.; Jones, V.J.; Korhola, A.; Pienitz, R.; Rühland, K.; Sorvari, S.; Antoniades, D.; et al. Climate-Driven Regime Shifts in the Biological Communities of Arctic Lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4397–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thienpont, J.R.; Rühland, K.M.; Pisaric, M.F.J.; Kokelj, S.V.; Kimpe, L.E.; Blais, J.M.; Smol, J.P. Biological responses to permafrost thaw slumping in Canadian Arctic lakes. Freshwater Biol. 2013, 58, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmeister, L.; Fuchs, M.C.; Opel, T.; Andreev, A.; Kienast, F.; Schneider, A.; Nazarova, L.; Frolova, L.; Kuzmina, S.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Newly dated permafrost deposits and their paleo-ecological inventory reveal a much warmer-than-today Eemian in Arctic Siberia. Clim. Past. 2025. Preprint cp-2024-74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.O. Diversity and Evenness: A unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology 1973, 54, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, N.; Krzywinski, M. Simple linear regression. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 999–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieva, N.; Jones, V.J.; Nazarova, L.; Brooks, S.J.; Birks, H.J.B.; Grytnes, J.-A.; Appleby, P.G.; Kauppila, T.; Kondratenok, B.; Renberg, I.; et al. Paleolimnological evidence for recent climate change in lakes from the Northern Urals, Russia. J. Paleolimnol. 2005, 33, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO for Windows: Software for Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kuptsov, V.M. Absolute Geochronology of Bottom Sediments of Oceans and Seas; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Genkal, S.I.; Vekhov, N.V. Diatoms of Water Bodies of the Russian Arctic. Novaya Zemlya Archipelago and Vaigach Island; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.H.; Geirsdóttir, Á.; Zhong, Y.; Larsen, D.J.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; Holland, M.M.; Bailey, D.A.; Refsnider, K.A.; Lehman, S.J.; Southon, J.R.; et al. Abrupt onset of the Little Ice Age triggered by volcanism and sustained by sea-ice/ocean feedbacks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L02708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M.; Owens, M.; Hawkins, E.; Jones, G.S.; Usoskin, I. Frost fairs, sunspots and the Little Ice Age. Astron. Geophys. 2017, 58, 2.17–2.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W. Response of the Chydorid faunas to rapid climatic change in four alpine lakes at different altitudes. Palaegeogr. Palaeocl. 2000, 159, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, R.J.; Langdon, P.G.; Doncaster, C.P.; Dearing, J.A.; Wang, R.; Nazarova, R.B.; Medeiros, A.S.; Brooks, S.J. Metrics of structural change as indicators of chironomid community stability in high latitude lakes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 249, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, L.; Luoto, T.P. Temperature sensitivity of gamogenesis in littoral cladocerans and its ecological implications. J. Limnol. 2010, 69, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, S.; Medeiros, A.S.; Axford, Y.; Brooks, S.J.; Heiri, O.; Luoto, T.P.; Nazarova, L.; Porinchu, D.F.; Quinlan, R.; Self, A.E. Temperature change as a driver of spatial patterns and long-term trends in chironomid (Insecta: Diptera) diversity. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrykh, L.S.; Nazarova, L.B.; Herzschuh, U.; Subetto, D.A.; Grekov, I.M. Reconstruction of palaeoecological and palaeoclimatic conditions of the Holocene in the south of the Taimyr according to an analysis of lake sediments. Contemp. Probl. Eco. 2017, 4, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterich, S.; Schirrmeister, L.; Nazarova, L.; Palagushkina, O.; Bobrov, A.; Pogosyan, L.; Savelieva, L.; Syrykh, L.; Matthes, H.; Fritz, M.; et al. Holocene thermokarst and pingo development in the Kolyma Lowland (NE Siberia). Permafr. Periglac. 2018, 29, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druzhinina, O.; Kublitskii, J.; Nazarova, L.; Syrykh, L.; Gedmeniene, L.; Uogintas, D.; Skipityte, R.; Arslanov, K.; Vaikutiene, G.; Kulkova, M.; et al. Palaeoenvironmental Conditions in South-Eastern part of the Baltic Region during the Late Pleistocene-Holocene transition (Kaliningrad District, Russia). Boreas 2020, 49, 544–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swadling, K.M.; Pienitz, R.; Nogrady, T. Zooplankton community composition of lakes in the Yukon and Northwest Territories (Canada): Relationship to physical and chemical limnology. Hydrobiologia 2000, 431, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmaja-Korjonen, K.; Nyman, M.; Kultti, S.; Valiranta, M. Palaeolimnological development of Lake Njargajavri, Northern Finnish Lapland, in a changing Holocene climate and environment. J. Paleolimnol. 2006, 35, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, J.N.; Rühland, K.M.; Smol, J.P. Environmental and spatial factors onfluencing the distribution of cladocerans in lakes across the Central Canadian Arctic treeline region. J. Limnol. 2010, 69, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, L.A.; Nazarova, L.B.; Pestryakova, L.A.; Herzschuh, U. Analysis of the effects of climate-dependent factors on the formation of zooplankton communities that inhabit Arctic Lakes in the Anabar River basin. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2013, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, L.; Nazarova, L.; Pestryakova, L.; Herzschuh, U. Subfossil cladoceran remains from sediment in thermokarst lakes in Northeastern Siberia, Russia. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 52, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, L.A.; Ibragimova, A.G.; Ulrich, M.; Wetterich, S. Reconstruction of the history of a thermokarst lake in the Mid-Holocene based on an analysis of subfossil cladocera (Siberia, Central Yakutia). Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2017, 10, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszelewski, W.; Skowron, R. Ice cover as an indicator of winter air temperature changes: Case sudy of the Polish Lowland lakes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Galloway, A.W.E.; Powers, S.M.; Ozersky, T. Ecology under lake ice. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Phytoplankton periodicity: The interactions of form, function and environmental variability. Freshwater Biol. 1984, 14, 111–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. The Development of perceptions of aquatic eutrophication and its control. Int. J. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2003, 3, 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Krylov, A.V.; Kulakov, D.V.; Tsvetkov, A.; Papchenkov, V.G. Effect of atmospheric precipitation and the abundance of semiaquatic bird colonies on zooplankton in the littoral of a small high-trophic lake. Biol. Bull. 2014, 41, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.M.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Van Donk, E.; et al. Lakes as sentinels of climate Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarova, L.; Sachse, D.; Fuchs, H.G.E.; Dirksen, V.; Dirksen, O.; Syrykh, L.; Razjigaeva, N.G.; Rach, O.; Diekmann, B. Holocene evolution of a proglacial lake in southern Kamchatka, Russian Far East. Boreas 2021, 50, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, L.; Grebennikova, T.A.; Razjigaeva, N.G.; Ganzey, L.A.; Belyanina, N.I.; Arslanov, K.A.; Kaistrenko, V.M.; Gorbunov, A.O.; Kharlamov, A.A.; Rudaya, N.; et al. Reconstruction of Holocene environmental changes in Southern Kurils (North-Western Pacific) based on palaeolake sediment proxies from Shikotan Island. Glob. Planet. Change 2017, 159, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douben, K. Characteristics of river floods and flooding: A global overview, 1985–2003. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.J.; Bennett, E.M.; Cassell, K.; Hanes, D.M.; Minor, E.C.; Paerl, H.; Raymond, P.A.; Vargas, R.; Vidon, P.G.; Wollheim, W.; et al. The impact of flooding on aquatic ecosystem services. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaferro, J.; Brooks, S.J. The response of Chironomids to late quaternary climate change in the Taitao Peninsula, Southern Chile. J. Quat. Sci. 2002, 17, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, P.S.; Oliver, D.R.; Saether, O.A. The Larvae of the Orthocladiinae (Diptera: Chiroomidae) of the Holarctic Region. Keys Diagn. Entomol. Scand. Suppl. 1983, 19, 149–291. [Google Scholar]
- Lundström, J.O.; Brodin, Y.; Schäfer, M.I.; Persson Vinnersten, T.Z.; Östman, O. High speed richness of Chironomidae (Diptera) in temporary flooded wetlands associated with high species turn-over rates. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, Y.W. The postglacial history of Lake Flarken, Southern Sweden, interpreted from subfossil insect remains. Int. Rev. Ges. Hydrobio. 1986, 71, 371–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, P.S. A Key to the Larvae of the British Orthocladiinae (Chironomidae). Freshw. Biol. Assoc. Sci. Publ. 1982, 45, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen, K.P.; Odgaard, B.V.; Vestergaard, O.; Anderson, N.J. Chironomid stratigraphy in the shallow and eutrophic lake Søbygaard, Denmark: Chironomid-macrophyte co-occurance. Freshwater Biol. 2001, 46, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, F. Parthenogenetische Stylotanytarsus larven als Bewohner einer Drinkwasserleitung. (Tanytarsus Studien III: Die Gattung Stylotanytarsus. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1941, 38, 214–253. [Google Scholar]
- Klink, A.G. Key to the Dutch Larvae of Paratanytarsus Thienemann and Bause with a Note on the Ecology and the Phenologenetic Relathions; Organ van Hydroboilogisch Adviesburo: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Brundin, L. Chironomiden und andere Bodentiere der südschwedischen Urgebirgsscen. Ein Beitrag zur Kenntnis der bodenfaunistischen Charakterzüge schwedischer oligotropher Seen. Inst. Freshw. Res. Drottningholm. 1949, 30, 1–914. [Google Scholar]
- Thienemann, A. Chironomus. Leben, Verbreitung und Wirtschaftlicher Bedeutung der Chironomiden. Binnengewässer 1954, 20, 1–834. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, J. Die Chironomiden der Fulda. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1971, 37, 466–555. [Google Scholar]
- Kulikovsky, M.S.; Glushchenko, A.M.; Genkal, S.I.; Kuznetsova, I.V. Identifier of diatoms of Russia; Yaroslavl: Filigran, Russia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, R.; Reimer, C.W. The Diatoms of the United States Exclusive of Alaska and Hawaii. Part 1. Entomoneidaceae, Cymbellaceae, Gomphonemaceae, Epithemiaceae; The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1975; pp. 1–213. [Google Scholar]
- Foged, N. Diatoms in Alaska Bibliotheca Phycologica, Band 53; Cramer, J., Ed.; Verlag: Vaduz, Liechtenstain, 1981; 317p, Available online: https://diatoms.org/citations/foged_n-1981-diatoms_in_alaska (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Cox, E. Identification of Freshwater Diatoms from Live Material; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bahls, L. Diatoms of Montana and Western North America: Catalog and Atlas of Species in the Montana Diatom Collection; The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Special Publication: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1–508. [Google Scholar]
- Siver, P.A.; Hamilton, P.B.; Stachura-Suchoples, K.; Kociolek, J.P. Diatoms of North America: The freshwater flora of Cape Cod, Massachusetts, U.S.A. In Iconographia Diatomologica. Annotated Diatom Micrographs; Lange-Bertalot, H., Ed.; A.R.G. Gantner Verlag, K.G.: Nüziders, Austria, 2005; Volume 14, pp. 1–463. [Google Scholar]
- Siver, P.A.; Hamilton, P.B. Diatoms of North America: The freshwater flora of waterbodies on the Atlantic Coastal Plain. In Iconographia Diatomologica. Annotated Diatom Micrographs; Lange-Bertalot, H., Ed.; ARG Gantner Verlag.: Ruggel, Liechtenstein; Nüziders, Austria, 2011; Volume 22, pp. 1–916. [Google Scholar]
- Vekhoff, N.V. Crustaceans of waterbodies from polar deserts of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago. Vestn. Zool. 2000, 34, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Szymanek, M.; Dzierżek, J.; Zawisza, E.; Wasążnik, M.; Viehberg, F.A.; Stańczak, J. First freshwater microcrustacean record in the bottom sediments of Arctic ponds in Bellsund area (SW Spitsbergen). Quat. Int. 2020, 565, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinev, A.Y.; Garibian, P.G.; Kirova, N.; Neplyukhina, A.A. New data on morphology and distribution of Alona Werestschagini Sinev, 1999—the only arcto-alpine species of Chydoridae (Cladocera: Anomopoda) known to date. Zootaxa 2021, 5071, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmaja-Korjonen, K.; Sinev, A.Y. First records of Alona werestschagini Sinev in Finland—Subfossil remains from subarctic lakes. Stud. Quat. 2008, 25, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, M.; Savelieva, L.; Frolova, L.; Cherezova, A.; Moros, M.; Baumer, M.M.; Gromig, R.; Kostromina, N.; Nigmatullin, N.; Kolka, V.; et al. Lateglacial and holocene environmental history of the Central Kola region, Northwestern Russia revealed by a sediment succession from Lake Imandra. Boreas 2021, 50, 76–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, L.; Syrykh, L.S.; Mayfield, R.J.; Frolova, L.A.; Ibragimova, A.G.; Grekov, I.M.; Subetto, D.A. Palaeoecological and palaeoclimatic conditions on the Karelian Isthmus (northwestern Russia) during the Holocene: Multi-proxy analysis of sediments from the Lake Medvedevskoe. Quat. Res. 2020, 95, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Months | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | IX | X | XI | XII | Tann | |
| slope | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.37 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.33 |
| T, °C | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 4.3 | 2.9 | 1.6 | 4.5 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 3.5 |
| Depth, cm | 210 Pb, Bq kg−1 | Pb Ages, Years |
|---|---|---|
| 0–0.5 | 54.05 ± 2.01 | 3.4 ± 0.6 |
| 0.5–1 | 50.17 ± 1.87 | 10.1 ± 1.8 |
| 1–1.5 | 50.17 ± 2.2 | 16.9 ± 3.1 |
| 1.5–2 | 33.23 ± 3.4 | 23.6 ± 4.3 |
| 3–3.5 | 36.35 ± 1.39 | 43.9 ± 6.7 |
| 4–4.5 | 29.22 ± 1.29 | 57.4 ± 9.2 |
| 8.5–9 | 27.3 ± 1.76 | 118.2 ± 20.2 |
| 9–9.5 | 25.67 ± 1.81 | 125.0 ± 21.4 |
| 9.5–10 | 22.89 ± 1.6 | 131.8 ± 23.9 |
| Span | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chironomids | Diatoms | Cladocera | ||
| TJune | 0.5 | 0.37 | 0.26 | 0.14 |
| 0.3 | 0.36 | 0.26 | ns | |
| 0.2 | 0.32 | ns | ns | |
| TJuly | 0.5 | 0.32 | 0.40 | ns |
| 0.3 | 0.33 | 0.26 | ns | |
| 0.2 | 0.28 | ns | ns | |
| TAugust | 0.5 | ns | 0.42 | ns |
| 0.3 | ns | 0.47 | ns | |
| 0.2 | ns | 0.45 | ns | |
| TSeptember | 0.5 | ns | 0.26 | ns |
| 0.3 | ns | 0.28 | ns | |
| 0.2 | ns | 0.31 | ns | |
| Tann | 0.5 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.20 |
| 0.3 | ns | 0.26 | 0.22 | |
| 0.2 | ns | 0.27 | 0.21 | |
| Pann | 0.5 | ns | 0.27 | 0.25 |
| 0.3 | ns | ns | 0.24 | |
| 0.2 | ns | ns | ns | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazarova, L.; Krasheninnikov, A.B.; Frolova, L.A.; Palagushkina, O.V.; Golovatyuk, L.V.; Syrykh, L.S.; Biskaborn, B.K.; Fuchs, H.G.E.; Gavrilo, M.V. Evolution of the Hydrobiological Communities of a Coastal Lake in the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago (Southern Island, Arctic Russia) in Relation to Climate Change Following the End of the Little Ice Age. Water 2025, 17, 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131868
Nazarova L, Krasheninnikov AB, Frolova LA, Palagushkina OV, Golovatyuk LV, Syrykh LS, Biskaborn BK, Fuchs HGE, Gavrilo MV. Evolution of the Hydrobiological Communities of a Coastal Lake in the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago (Southern Island, Arctic Russia) in Relation to Climate Change Following the End of the Little Ice Age. Water. 2025; 17(13):1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131868
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazarova, Larisa, Andrey B. Krasheninnikov, Larisa A. Frolova, Olga V. Palagushkina, Larisa V. Golovatyuk, Liudmila S. Syrykh, Boris K. Biskaborn, Harald G. E. Fuchs, and Maria V. Gavrilo. 2025. "Evolution of the Hydrobiological Communities of a Coastal Lake in the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago (Southern Island, Arctic Russia) in Relation to Climate Change Following the End of the Little Ice Age" Water 17, no. 13: 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131868
APA StyleNazarova, L., Krasheninnikov, A. B., Frolova, L. A., Palagushkina, O. V., Golovatyuk, L. V., Syrykh, L. S., Biskaborn, B. K., Fuchs, H. G. E., & Gavrilo, M. V. (2025). Evolution of the Hydrobiological Communities of a Coastal Lake in the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago (Southern Island, Arctic Russia) in Relation to Climate Change Following the End of the Little Ice Age. Water, 17(13), 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131868







