Abstract
In recent years, land subsidence in the Northern Anhui Plain has become increasingly pronounced, posing serious risks to infrastructure and groundwater management. However, quantitative assessments of its driving mechanisms remain limited. This study focuses on Bozhou, a typical resource-based city, and employs 186 Sentinel-1 SAR images and SBAS-based interferometric analysis to retrieve the spatiotemporal evolution of land subsidence from 2022 to 2024. Results show that the peak subsidence rate reaches 102 mm/year and has its major distribution in the central and eastern sectors of Bozhou. Temporally, the subsidence pattern shows an initial intensification followed by gradual stabilization. Furthermore, a GeoDetector-based analysis indicates that excessive groundwater extraction and coal mining are the dominant factors, with significant interactive enhancement effects. These findings provide crucial insights for the prevention and mitigation of land subsidence in resource-based cities.
1. Introduction
Land subsidence, also known as ground settlement or surface collapse, is a geological process marked by the gradual lowering of the Earth’s surface elevation. This phenomenon primarily results from the compaction and consolidation of unconsolidated soil and rock layers, triggered by the interplay of natural dynamics and anthropogenic pressures [1,2,3]. The underlying causes of land subsidence can be broadly classified into natural and anthropogenic factors, including hydrogeological conditions, mineral resource extraction, and excessive groundwater withdrawal [4,5,6]. Owing to its complex formation mechanisms and the challenges associated with effective mitigation, land subsidence frequently poses significant risks to public safety, infrastructure integrity, and economic assets [5,6,7].
To enhance the understanding of the mechanisms and spatiotemporal dynamics of land subsidence, extensive research efforts have been undertaken worldwide to advance monitoring technologies and investigate the associated driving forces, leveraging emerging theories and technological innovations [6,8,9,10,11]. Traditional monitoring techniques, including leveling surveys and Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), are constrained by high operational costs and limited spatial coverage, which reduces their effectiveness in capturing large-scale ground deformation patterns [12]. In recent years, Time-Series Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (TS-InSAR) has gained prominence as a robust and efficient tool for surface deformation monitoring, owing to its high measurement precision, frequent revisit intervals, and capability to operate under all-weather, day-and-night conditions [13]. Among the various TS-InSAR techniques, Permanent Scatterer InSAR (PS-InSAR) and Small Baseline Subset InSAR (SBAS-InSAR) are the most widely utilized [14]. PS-InSAR is particularly effective in urban environments or areas with persistent, highly coherent targets (e.g., buildings, bridges, exposed bedrock) [15]; however, its performance significantly deteriorates in regions dominated by dense vegetation or lacking stable scatterers [16]. In contrast, SBAS-InSAR is designed to retrieve deformation signals from pixels exhibiting relatively high coherence over shorter temporal baselines [17]. This makes it more suitable for capturing surface changes across natural landscapes such as grasslands and bare soil, thereby offering broader applicability for regional-scale land subsidence monitoring [18,19,20].
Land subsidence has remained a persistent geohazard in the Northern Anhui Plain [21,22,23]. As a rapidly developing industrial city in Anhui Province, Bozhou has received increasing attention from local governments and relevant agencies for the monitoring and management of urban geological hazards. However, previous work on regional subsidence has largely dealt with refining data analysis procedures and preliminary assessments of potential causative factors, while relatively few have undertaken in-depth quantitative analyses of the driving mechanisms. Identifying and quantifying the predominant forces responsible for subsidence is essential for developing effective disaster prevention strategies and promoting sustainable urban development.
In this study, Bozhou City, located in the northwestern part of Anhui Province, China, was selected as a representative resource-based city that has experienced significant land subsidence in recent years. To capture the spatial and temporal patterns of subsidence with high resolution, a total of 186 Sentinel-1 SAR images acquired between 2022 and 2024 are processed, adopting the SBAS-InSAR framework for surface deformation analysis. Subtle surface movements and their temporal evolution can thus be captured over extended time periods. To further explore the underlying causes and spatial heterogeneity of subsidence, the influence of several candidate driving forces is quantified using the GeoDetector—including geological structure, hydrogeological conditions, anthropogenic engineering activities, and socio-economic development. By integrating advanced remote sensing techniques with geostatistical analysis, this study aims to reveal the mechanisms governing land subsidence in Bozhou and to provide scientific guidance for hazard prevention, groundwater management, and sustainable urban planning in resource-dependent regions.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
Bozhou City is situated at the southern margin of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, straddling the provincial boundary between Anhui and Henan in eastern China [24]. The city governs one district and three counties (Figure 1), encompassing a total area of approximately 8522.58 km2 [24,25]. Geologically, Bozhou is situated within the Huaihe Depression, a subordinate tectonic unit of the North China Platform, where fold structures and fault zones are well developed [26]. The region exhibits a predominantly flat topography, gently sloping from the northwest to the southeast. It is adjacent to alluvial fans deposited by historical breaches of the Yellow River and displays the typical geomorphological features of the Huang-Huai depositional zone [25,26].
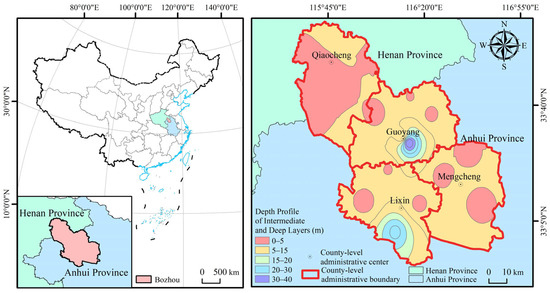
Figure 1.
Study area scope.
Stratigraphically, the region belongs to the Xuhuai stratigraphic subdivision of the North China stratigraphic province [26]. The Quaternary system extensively overlies the bedrock, and the combined thickness of Quaternary and Upper Tertiary unconsolidated sediments reaches approximately 800–1000 m [25]. Bozhou is rich in coal resources [24]. According to the Bozhou Mineral Resources Master Plan (2021–2025), there are 17 identified coal mining sites, primarily located in Guoyang and Mengcheng counties. The proven coal reserves amount to approximately 4.35 billion tons, accounting for 17.17% of Anhui Province’s total coal resources. The major coal-bearing strata are Carboniferous and Permian formations, with coal seams buried at depths of approximately 600–1000 m [27].
Groundwater in Bozhou can be categorized into three types based on lithological characteristics: pore water in unconsolidated sediments, fissure–karst water in carbonate rocks, and fissure water in bedrock formations [24,25]. Depending on aquifer depth and confinement, the groundwater system is further subdivided into four aquifer groups: shallow pore aquifers (within 50 m), intermediate to deep confined aquifers (50–165 m), deep confined pore aquifers (165–660 m), and ultra-deep confined aquifers (660–900 m) [24,26]. According to the 2021 Bozhou Water Resources Bulletin, the total exploitable volume of groundwater resources in the city is approximately 1.567 billion cubic meters. Of this, shallow groundwater accounts for 459 million m3, while intermediate and deep groundwater resources amount to 1.108 billion m3. Currently, nine groundwater overexploitation zones have been identified, covering a total area of about 980.9 km2. Annual groundwater extraction in these zones is estimated at 40 million m3 from shallow aquifers and approximately 138 million m3 from intermediate and deep aquifers.
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Sentinel-1
Sentinel-1, launched under ESA’s Earth observation framework, revisits the same location approximately every twelve days [28] and offers four acquisition modes: IW, EW, WV, and SM [29]. The IW mode is most suitable for land surface studies due to its extensive swath and spatial resolution, and it is thus commonly used in interferometric applications. In this study, we analyzed 186 ascending Sentinel-1 SLC images, acquired in IW mode between 2022 and 2024, to detect and evaluate surface deformation patterns within the target area (Table 1).

Table 1.
Parameters of Sentinel-1 satellite.
2.2.2. SRTM DEM
The SRTM Digital Elevation Model (DEM), developed jointly by NASA and NGA, offers 30 m resolution elevation data with a vertical accuracy of ±16 m and covers around 80% of global land areas [10,30,31]. In this study, it was applied to correct for terrain-induced phase variations in the interferometric workflow.
2.2.3. Other Data
The selection of driving factors was guided by a comprehensive consideration of the geological setting, hydrogeological conditions, human engineering activities, and socio-economic development within the study area [1,2,3]. Eight representative indicators were selected to characterize the potential influences on land subsidence: fluctuation amplitude of deep groundwater levels (X1), fluctuation amplitude of intermediate-deep groundwater levels (X2), burial depth of intermediate-deep groundwater (X3), burial depth of deep groundwater (X4), gross domestic product (GDP) per unit area (X5), thickness of unconsolidated deposits (X6), road density (X7), and population density (X8). All datasets were processed and reclassified using ArcGIS to ensure consistency in spatial resolution and facilitate subsequent driving factor detection using the Geographical Detector model. This preprocessing step enhances the comparability of variables and ensures the robustness of spatial heterogeneity analysis.
3. Methodology and Data Processing
3.1. Land Subsidence Monitoring
3.1.1. Principle of SBAS-InSAR
To monitor ground surface deformation using the SBAS-InSAR technique, an initial co-registration is performed on N + 1 SAR images that span the area of interest. Based on predefined spatial and temporal baseline thresholds, M interferometric pairs are subsequently generated [32], described as follows:
For the i-th interferometric pair (i ∈ 1, 2, …, M), let the acquisition times of the master and slave images be ta and tb, respectively, where tb > ta [33]. After removing non-deformation phase components, the residual interferometric phase can be expressed as:
The deformation phases of the M interferometric pairs can be organized into the following matrix form [34]:
Each interferogram provides one observation equation. By combining Equations (2) and (3), a system of M observation equations with N unknown deformation parameters can be formulated as [35]:
Here, A is an M × N coefficient matrix. If the rank of A (r(A)) is greater than N, the system can be solved using the least squares method [35]:
In practice, however, r(A) is often less than N, making the inverse of ATA unavailable [35]. To resolve this, matrix A is decomposed using singular value decomposition (SVD) as follows:
In this decomposition, U is an M × M orthogonal matrix composed of the eigenvectors of AAT; S is an M-order diagonal matrix; and V is an N × M orthogonal matrix formed from the eigenvectors of ATA.
In Equations (7) and (8), UT denotes the transpose of U, and A+ and S+ represent the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverses of matrices A and S, respectively. Once the time-series deformation φ is obtained, the corresponding surface displacement rate can be quantified by dividing the deformation by the time interval between observations.
3.1.2. Data Processing Workflow
The overall procedure for obtaining ground deformation information primarily comprises two stages: data preprocessing and SBAS-InSAR processing. In this study, Sentinel-1 SAR data were processed using the SARscape module in the ENVI 5.3 platform [36]. SARscape 5.2.1, developed by the Swiss company sarmap, is a professional radar image processing software that has been widely used for various satellite-borne radar datasets, including various SAR missions such as ERS, RADARSAT, ENVISAT, ALOS, and Sentinel-1 [37].
The Sentinel-1 data preprocessing steps were as follows: (1) importing the SAR scenes into the standard SARscape format; (2) mosaicking SAR images acquired on the same date; and (3) cropping the data along the borders of the study domain. The subsequent SBAS-InSAR processing included the following steps: (1) pairing the input scenes using an optimal combination strategy; (2) performing interferometric processing on the selected image pairs; (3) re-flattening all interferograms using control points; (4) removing atmospheric phase artifacts and estimating deformation velocity; and (5) geocoding, which involves projecting the deformation results into a geographic coordinate system.
3.2. Geographical Detector Model
Geographical phenomena inherently exhibit spatial variability. To quantitatively assess the explanatory power of various factors on the spatial distribution pattern of land subsidence, this study adopts the Geographical Detector (GD) model [38]. Proposed by Chinese scholar Jin-Feng Wang [39], the GD model is based on the concept of spatial stratified heterogeneity and has been widely applied in surface process analysis and environmental driver identification. It does not rely on assumptions of linearity, and is well-suited for the analysis of multi-source, non-linear, and non-normally distributed datasets. Therefore, it offers high adaptability in the study of complex geographic problems such as land subsidence.
The GD model quantifies spatial differentiation by measuring how the variance of a dependent variable shifts across categories of an explanatory factor [40]. Specifically, we adopted the “Factor Detector” component to assess the influence of each variable on the configuration of land subsidence in spatial terms. The equation used is:
where q represents the extent to which a factor explains the spatial variation of the dependent variable, with values ranging from 0 to 1—a higher q indicates stronger explanatory ability. h refers to the number of stratified subregions; Nh and σh represent the number of observations and variance within subregion h, respectively; N and σ2 denote the total sample count and the overall variance across the entire study area, respectively.
To ensure rational and scientific stratification, the natural breaks method was applied to discretize continuous variables. Additionally, spatial aggregation rules were employed to standardize the spatial resolution between dependent and independent variables. The model was jointly implemented in ArcGIS 10.7 and the GeoDetector 2015 software platform.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Accuracy Validation
To evaluate the reliability of land subsidence data within the study area, leveling measurements from three benchmark points in Qiaocheng District in 2022 were compared with the corresponding Surface displacement measurements derived from SBAS-InSAR (Table 2). The differences between the SBAS-InSAR and leveling measurements were found to be within 1 mm, demonstrating the high trustworthiness of ground deformation detected via InSAR analysis.

Table 2.
Leveling-based verification of SBAS-InSAR monitoring performance.
Discrepancies between the monitoring data and field measurements can mainly be attributed to various error sources inherent in SAR interferometry, including atmospheric delay, topographic variations, and signal decorrelation. Additionally, leveling data represent discrete point-based elevation changes, whereas SBAS-InSAR provides spatially averaged deformation values over grid cells, which may not perfectly align with individual leveling points.
4.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence
Using SBAS-InSAR technology, the spatiotemporal distribution of land subsidence rates in Bozhou City from 2022 to 2024 was characterized (Figure 2). Spatially, land subsidence exhibited significant heterogeneity. The central area of Guoyang County and its surroundings acted as the primary subsidence center, forming a distinct subsidence funnel, with deformation rates decreasing radially outward from the center. Subsidence in other areas was comparatively mild, with generally lower rates (Figure 3).
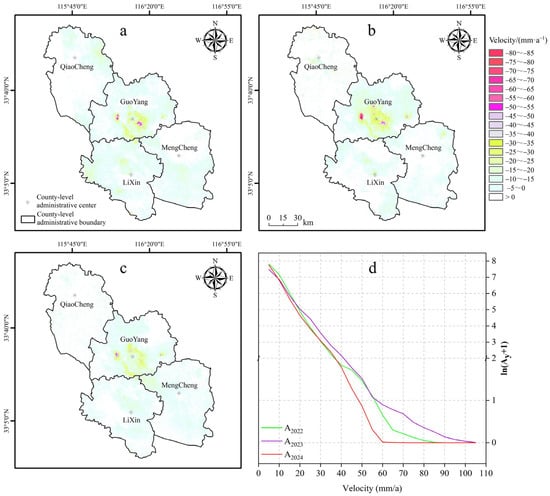
Figure 2.
Geographic pattern of Deformation Rates in Bozhou City from 2022 to 2024: (a–c) show the geographic pattern of land subsidence rates across Bozhou City for 2022, 2023, and 2024, respectively; (d) presents the area variation across different subsidence rate intervals from 2022 to 2024, where Ay represents area (km2), y represents the year).
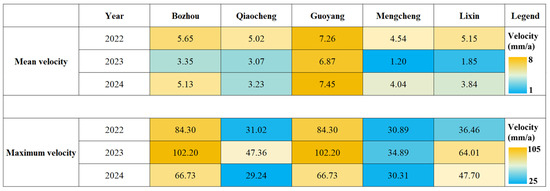
Figure 3.
Variation of Subsidence Rates in Different Districts and Counties of Bozhou City from 2022 to 2024.
Temporally, land subsidence followed a “slow–intensification–mitigation” pattern over the three-year period. In 2022, subsidence was moderate, with Guoyang experiencing the most pronounced deformation, reaching a maximum rate of −84.30 mm/year. In 2023, subsidence intensified markedly, with the peak rate in Guoyang rising to −102.20 mm/year. Significant subsidence also emerged in Qiaocheng, Mengcheng, and other areas, accompanied by the appearance of new high-subsidence zones and rapid expansion of subsidence funnels, representing the peak deformation intensity during the study period. In 2024, although the average subsidence rate in Guoyang increased slightly, the maximum rate declined to −66.73 mm/year. Overall, both the intensity and spatial extent of subsidence showed a decreasing trend, indicating a gradual mitigation phase.
From a spatial distribution perspective, the subsidence rate and affected area exhibited a power-law relationship: zones with higher subsidence rates occupied progressively smaller areas (Figure 3). The extent of high and moderate subsidence zones peaked in 2023, slightly contracted in 2024, but remained above 2022 levels. In summary, land subsidence in Bozhou demonstrated an initial intensification followed by attenuation, with 2023 identified as the most critical year. Despite a slight improvement in 2024, localized subsidence risks remain significant.
4.3. Single-Factor Detection Results of the GeoDetector Model
The GeoDetector results indicate the extent to which each driving factor (X1–X8) contributes to spatial variation on land subsidence in Bozhou during 2022–2024 was quantitatively assessed (Figure 4). Although minor interannual variations were observed, the overall explanatory hierarchy exhibited a clear “strong-to-weak” gradient, underscoring the multifactorial complexity underlying subsidence processes.
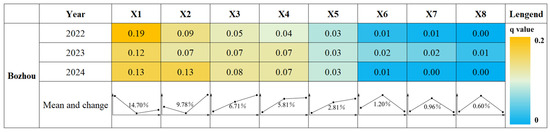
Figure 4.
Univariate Analysis of Driving Factors for Deformation Rates in Bozhou City.
Among all factors, X1 (deep groundwater level variation) consistently demonstrated the highest explanatory power, with an average q-value of 14.70%, highlighting it as the primary driver of land subsidence. This was followed by X2 (intermediate-deep groundwater level variation) and X3 (intermediate-deep groundwater depth), with q-values of 9.78% and 6.71%, respectively, confirming the pivotal role of groundwater dynamics in controlling subsidence. X4 (deep groundwater depth) showed a moderate influence with a q-value of 5.81%.
Regarding geological factors, X6 (thickness of the unconsolidated layer) contributed marginally to subsidence, with a q-value of 1.20%. Anthropogenic factors exhibited relatively weak explanatory power: X5 (GDP per unit area), X8 (population density), and X7 (road density) yielded q-values of 2.81%, 0.60%, and 0.96%, respectively, suggesting limited impact of human-induced urban growth on subsidence patterns within the study area.
In summary, groundwater fluctuations dominate land subsidence in Bozhou, while geological conditions and human activities serve as secondary but non-negligible contributors, collectively forming a complex multi-factor coupling mechanism.
4.4. Interaction Detection Outcomes of the GeoDetector-Based Investigation
To further elucidate the synergistic mechanisms among driving factors, this study utilized the interaction detector module of the Geographical Detector to assess the pairwise interactions of factors influencing land subsidence (Figure 5). The interaction of driving factors indicates that multiple factors influencing land subsidence do not simply have additive effects; rather, they synergistically enhance each other’s impact, resulting in a combined effect that exceeds the sum of their individual influences. This nonlinear interaction reflects the multifaceted drivers responsible for land subsidence and highlights the critical role of integrating multiple contributing elements in a comprehensive manner. The results demonstrated that most factor pairs exhibited a “synergistic nonlinear enhancement” effect, indicating that the combined impact of two variables on subsidence surpasses the simple sum of their individual effects.
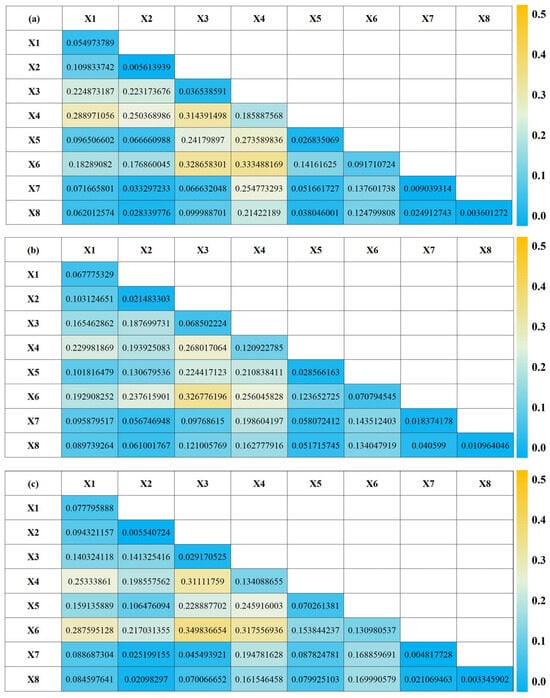
Figure 5.
Interaction Analysis of Driving Factors for Deformation Rates in Bozhou City ((a–c) represent 2022, 2023, and 2024, respectively).
Notably, the interaction between X3 (intermediate-deep groundwater depth) and X6 (thickness of the unconsolidated layer) consistently yielded the highest explanatory power throughout the study period (q > 0.32), underscoring the amplifying influence of stratigraphic structure on groundwater-induced subsidence. In 2024, the interaction between X4 (deep groundwater depth) and X6 reached the peak q-value of 0.3757, highlighting an intensified compaction effect within the deep geological layers.
Interactions between natural and anthropogenic factors, such as X3 (intermediate-deep groundwater depth) with X5 (GDP per unit area), and X4 (deep groundwater depth) with X7 (road density), also exhibited enhanced explanatory power. This suggests that socioeconomic activities may indirectly affect land subsidence by modifying groundwater conditions.
Overall, the coupling between groundwater dynamics and geological structure constitutes the primary mechanism driving land subsidence, while socioeconomic factors act as important amplifiers or modulators within this complex system.
5. Discussion
5.1. Synergistic Effects of the Groundwater System and Geological Setting
Grounded in the observed spatiotemporal dynamics of subsidence derived from SBAS-InSAR analysis, combined with factor detection using the GeoDetector model, this study confirms that the groundwater system serves as the predominant control mechanism governing subsidence. Among all examined variables, fluctuations in deep and mid-deep groundwater levels exhibited the highest explanatory power (Figure 5), corroborating former analyses performed in areas including the North China Plain and Mexico City [2,41]. In these areas, overexploitation of deep groundwater has been identified as a direct physical driver of large-scale land subsidence through aquitard compaction.
While the thickness of unconsolidated sediments showed relatively low explanatory power in the univariate factor detection (q-values), its interaction with groundwater-related factors revealed a pronounced synergistic nonlinear enhancement effect (Figure 5). This suggests that the geological media in Bozhou function as an “amplifier” within the subsidence process. Specifically, thicker unconsolidated strata tend to possess greater compressibility; once the hydrostatic support from groundwater diminishes, these layers become more susceptible to intensified compaction [42,43,44,45]. Consequently, sediment thickness effectively modulates the regional sensitivity to land subsidence. This finding underscores the crucial role of geological conditions in shaping the spatial heterogeneity of subsidence by influencing the compaction response threshold, highlighting the coupled and complex mechanisms underlying subsidence development.
5.2. Coupled Feedback Mechanisms Between Urbanization and Subsurface Systems
While excessive groundwater withdrawal has long been recognized as the primary driver of land subsidence, this study further elucidates the critical yet indirect role of urban construction factors—such as road density and GDP per unit area. Although these factors individually exhibit limited explanatory power, their interaction with groundwater variables significantly amplifies their influence on subsidence dynamics. This underscores how urbanization can profoundly alter the regional hydrogeological equilibrium.
Rapid urban expansion typically entails intensive infrastructure development, which is often accompanied by localized groundwater overextraction, increased surface loading, and disturbances to subsurface utility networks. These latent anthropogenic interventions, frequently overlooked in conventional groundwater management frameworks, act synergistically to exacerbate land subsidence in urban environments. Consequently, addressing urbanization-driven impacts is essential for comprehensive subsidence mitigation strategies.
5.3. Limitations and Perspectives on Groundwater-Induced Land Subsidence
Despite the integrated application of SBAS-InSAR technology and the GeoDetector model to systematically elucidate the spatiotemporal dynamics and driving mechanisms of land subsidence in Bozhou, several limitations persist. First, the temporal resolution and revisit interval of Sentinel-1 imagery constrain the capacity to detect short-term or abrupt deformation events, thereby limiting the ability to capture rapid subsidence responses triggered by sudden disturbances. Second, although the GeoDetector model quantitatively assesses the explanatory power of individual factors, its reliance on variable discretization may influence the precision and robustness of the results. Third, socioeconomic indicators—such as groundwater extraction volumes, industrial structure, and land-use patterns—exhibit pronounced spatial heterogeneity that may not be fully captured, consequently restricting the accuracy of causal inferences.
Future research should prioritize the integration of higher-resolution datasets, including continuous groundwater monitoring well records and detailed water usage statistics. Moreover, the incorporation of multi-source remote sensing data and Internet of Things (IoT)-based environmental monitoring networks will facilitate multi-scale coupled modeling and empirical validation of subsidence drivers.
Thematically, this study concentrates on land subsidence in resource-dependent cities predominantly driven by groundwater overexploitation, sharing numerous parallels with investigations in the North China Plain (e.g., Beijing, Cangzhou) [46,47], the Yangtze River Delta (e.g., Suzhou, Wuxi) [48], and international contexts such as Mexico City and California’s Central Valley [37,49]. Common characteristics across these regions include prolonged deep groundwater depletion coupled with the compaction of unconsolidated sediments, resulting in subsidence driven by the interplay between hydrogeological conditions and anthropogenic activities. However, Bozhou exhibits a more complex subsidence pattern due to the additional influence of intensive coal mining activities, which contribute further spatial variability and uncertainty to the deformation processes.
Therefore, future studies should aim to develop comprehensive response models that integrate the triple coupling of hydrological, geological, and mining factors, while advancing more dynamic and fine-grained assessments of environmental carrying capacity to inform sustainable policy and management frameworks.
6. Conclusions
This study integrated SBAS-InSAR technology with the GeoDetector model to analyze the spatial-temporal evolution and driving mechanisms of land subsidence in Bozhou, a representative resource-dependent city in the northern Anhui Plain. The major findings are summarized below.
Spatiotemporal Characteristics: From 2022 to 2024, land subsidence in Bozhou was significant and spatially heterogeneous. The most severe deformation occurred in the central and eastern regions, particularly in Guoyang County, where the maximum subsidence rate reached 102 mm/year. Temporally, subsidence followed a clear pattern of intensification in 2023 and subsequent mitigation in 2024, although local risks remained. Primary Driving Forces: Quantitative analysis showed that excessive groundwater extraction—especially from deep and intermediate-deep aquifers—was the dominant factor, followed by intensive coal mining. Together, these factors accounted for more than 80% of the spatial variation in land subsidence across the study area. Interaction Effects: Strong nonlinear interactions were identified between hydrogeological and geological factors. Notably, the interaction between groundwater depth and the thickness of unconsolidated sediments significantly amplified the risk of subsidence. Interactions between natural and socioeconomic variables (e.g., GDP per unit area, road density) further highlighted the compounded effects of urbanization on subsidence dynamics. Implications: These findings confirm that land subsidence in Bozhou results from a complex coupling of natural and anthropogenic forces, with groundwater depletion and geological susceptibility playing central roles. The study emphasizes the necessity of integrated groundwater management and stricter regulation of mining activities to mitigate future subsidence hazards.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.H.; methodology, Z.Z. and Q.H.; software, Q.H.; validation, H.L. and L.W.; formal analysis, H.L. and Q.H.; investigation, Q.H. and H.L.; resources, L.W. and Z.Z.; data curation, Q.H., L.W. and H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.H.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z., Q.H. and L.W.; visualization, H.L.; supervision, Z.Z.; project administration, L.W. and Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Open Fund of Hebei Cangzhou Groundwater and Land Subsidence National Observation and Research Station (No. CGLOS-2024-08); Strategic Research and Consulting Project of Anhui Research Institute of Engineering and Technological Development Strategy, Chinese Academy of Engineering (2023-02).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data underlying the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the European Space Agency (ESA) for providing free access to Sentinel-1 SAR data, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for the SRTM DEM data, and the developers of the ENVI SARscape software used for SBAS-InSAR processing. We also thank the developers of the Geographical Detector model for making the tool publicly available. The authors appreciate the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions that helped improve the quality of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-García, G.; Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; López-Vinielles, J.; Rossi, M.; Mateos, R.M.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Lambert, J.; Teatini, P.; et al. Mapping the global threat of land subsidence. Science 2021, 371, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.L.; Xu, Y.S. Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 48, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater extraction, land subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Jin, M.Q.; Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Sun, W.; Wei, J.Q.; Chen, Y. Monitoring Land Subsidence in Wuhan City (China) using the SBAS-InSAR Method with Radarsat-2 Imagery Data. Sensors 2019, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Miranda, S.; Tuxpan-Vargas, J.; Ramos-Leal, J.A.; Hernández-Madrigal, V.M.; Villaseñor-Reyes, C.I. Land subsidence by groundwater over-exploitation from aquifers in tectonic valleys of Central Mexico: A review. Eng. Geol. 2018, 246, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, S.; Tessitore, S.; Bonì, R.; Di Martire, D.; Achilli, V.; Borgstrom, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Floris, M.; Meisina, C.; Ramondini, M.; et al. From ERS-1/2 to Sentinel-1: Two decades of subsidence monitored through A-DInSAR techniques in the Ravenna area (Italy). GISci. Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Zhu, L.; Dai, Z.X.; Gong, H.L.; Guo, T.; Guo, G.X.; Wang, J.B.; Teatini, P. Spatiotemporal modeling of land subsidence using a geographically weighted deep learning method based on PS-InSAR. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Wang, G.Y.; Huang, M.; Song, J.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Ji, W.Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.L.; Wei, C.W.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence and Driving Factors Analysis in Shenzhen. Water 2024, 16, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.M.; Hou, C.H. Unveiling the driving factors of urban land subsidence in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Gao, Z.; Xiao, R.; Luo, H.; Jia, D.; Zhang, Z. Application and prospect of the integration of InSAR and BDS/GNSS for land surface deformation monitoring. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1338–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Hu, J.; Feng, G.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; et al. Partial geoscience parameters inversion from InSAR observation. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1458–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perski, Z.; Wojciechowski, T.; Borkowski, A. Persistent Scatterer Sar Interferometry Applications on Landslides in Carpathians (Southern Poland). Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2010, 7, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Samsonov, S.; Tiampo, K. Polarization Phase Difference Analysis for Selection of Persistent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, J. Research Progress and Methods of InSAR for Deformation Monitoring. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, Z.H.; Guo, S.F.; Xia, J. Land Subsidence Monitoring Method in Regions of Variable Radar Reflection Characteristics by Integrating PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR Techniques. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.L.; Yuan, Y.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Cui, J.; Zhang, D.J.; Zhang, R.R.; Cao, Q.Z.R.; Li, J.; Dai, W.H.; Bao, H.M.; et al. Large-Scale Land Subsidence Monitoring and Prediction Based on SBAS-InSAR Technology with Time-Series Sentinel-1A Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.X.; Chen, Z.W.; Wang, S.Y.; Cui, H.; Zheng, Y.Z. Predictable Condition Analysis and Prediction Method of SBAS-InSAR Coal Mining Subsidence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5232914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wei, L.; Cai, P.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Z. Risk assessment of land subsidence based on GIS in the Yongqiao area, Suzhou City, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.M.; Chen, Z.X.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.J.; Zhou, C.K.; Shu, Y.; Wu, J.D.; Chen, L.J. Spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Fuyang: Time series InSAR monitoring and analysis of impacting factors. Earth Sci. Inform. 2025, 18, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.A.; Jin, S.G.; Zhang, J.X.; Chen, J.Y.; He, J.J. Subsidence Characteristics in North Anhui Coal Mining Areas Using Space-Air-Ground Collaborative Observations. Sensors 2024, 24, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N. Bozhou Extent of Groundwater Exploitation and Evaluation of the Effect of Limiting Mining Forecast. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Environmental Hydrogeochemical Characteristies of Groundwater in Loose Bed of the Huaibei Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T. Geological Calamity Assessment and Engineering Countermeasureon Bozhou City Economic and Technological Development Zone. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X. The Research of Scheme in Preventing Flood of Bozhou City. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiei, F.; Gharechelou, S.; Golian, S.; Johnson, B.A. Aquifer and Land Subsidence Interaction Assessment Using Sentinel-1 Data and DInSAR Technique. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, E.A.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Solano-Rojas, D.; Salazar-Tlaczani, L.; Gárcia-Venegas, J.; Marquez-Azúa, B.; Graham, S.; Villarnobo-Gonzalez, K.M. Country-scale assessment of urban areas, population, and households exposed to land subsidence using Sentinel-1 InSAR, and GPS time series. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 1577–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.Y.; Xie, F.M.; Ding, J.; Li, G.L.; Su, H.R. Quantifying Spatiotemporal Changes in Supraglacial Debris Cover in Eastern Pamir from 1994 to 2024 Based on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, G.F.; Zhao, H.H.; Wang, J.Z.; Qiao, B.J. Estimation of Lake Storage Based on the Surrounding Topography around the Lake from the SRTM DEM. Water 2023, 15, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Feng, T.; Feng, H.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhou, X.X. Deformation Monitoring and Potential Risk Detection of In-Construction Dams Utilizing SBAS-InSAR Technology-A Case Study on the Datengxia Water Conservancy Hub. Water 2024, 16, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Z.W.; Feng, G.C.; Wang, Q.J.; Hu, J. Monitoring surface deformation over permafrost with an improved SBAS-InSAR algorithm: With emphasis on climatic factors modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface deformation of Long Valley Caldera and Mono Basin, California, investigated with the SBAS-InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.C.; Samsonov, S.; Yin, H.W.; Ye, S.J.; Cao, Y.R. Time-series analysis of subsidence associated with rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China measured with SBAS InSAR method. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Li, B.Q.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Chen, C.; Jin, G.Y.; Liu, H.Y. Surface Subsidence over a Coastal City Using SBAS-InSAR with Sentinel-1A Data: A Case of Nansha District, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Garfias, J.; Martel, R.; Brouard, C.; Rivera, A. InSAR to support sustainable urbanization over compacting aquifers: The case of Toluca Valley, Mexico. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 63, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.J.; Meng, J.J.; Zhu, L.K. Applying GeoDetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. GeoDetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shanguan, D.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Ding, Y.J. Evaluation and Hydrological Simulation of CMADS and CFSR Reanalysis Datasets in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water 2018, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.L.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.Q.; Li, X.J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, H.G.; Zhou, C.F. Long-term groundwater storage changes and land subsidence development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, W.B. Geologic Factors Affecting Compaction of Deposits in a Land-Subsidence Area. GSA Bull. 1973, 84, 3783–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.G.; Majumdar, S. Groundwater Storage Loss Associated With Land Subsidence in Western United States Mapped Using Machine Learning. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, X. Measuring Spatiotemporal Features of Land Subsidence, Groundwater Drawdown, and Compressible Layer Thickness in Beijing Plain, China. Water 2017, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faunt, C.C.; Traum, J.A.; Boyce, S.E.; Seymour, W.A.; Jachens, E.R.; Brandt, J.T.; Sneed, M.; Bond, S.; Marcelli, M.F. Groundwater Sustainability and Land Subsidence in California’s Central Valley. Water 2024, 16, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gong, H.L.; Li, X.J.; Wang, R.; Chen, B.B.; Dai, Z.X.; Teatini, P. Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in the northern Beijing plain, China. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Jiao, J.J. Groundwater-derived land subsidence in the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.C.; Shi, X.Q.; Xue, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.X.; Yu, J. The development and control of the land subsidence in the Yangtze Delta, China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, C.; Shirzaei, M.; Werth, S.; Argus, D.F.; Farr, T.G. Sustained Groundwater Loss in California’s Central Valley Exacerbated by Intense Drought Periods. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 4449–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).