Water-Richness Evaluation of Sandstone Aquifer Based on Set Pair Analysis Variable Fuzzy Set Coupling Method: A Case Study on Bayangaole Mine, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
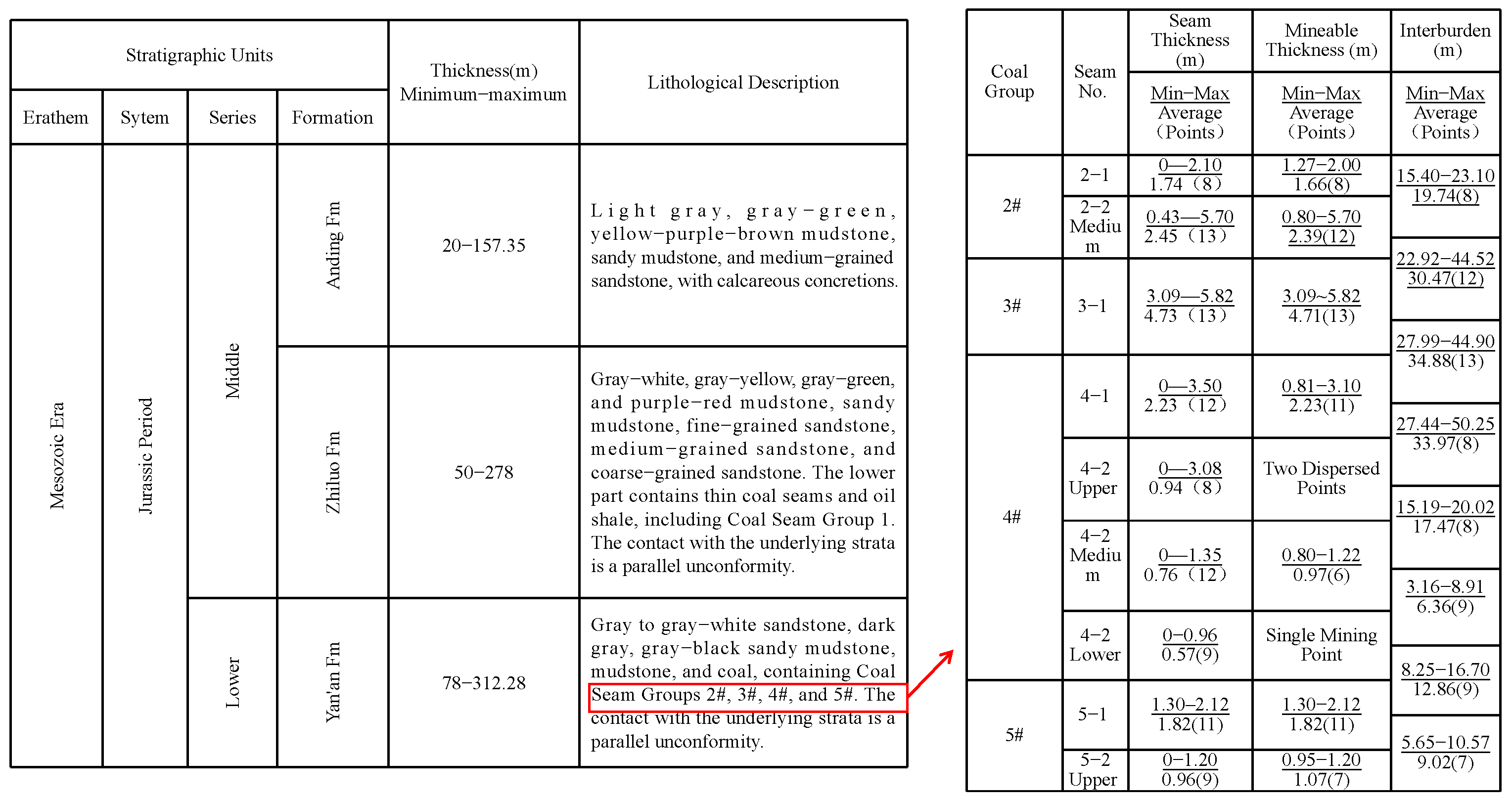
2. Geological Survey of the Study Area
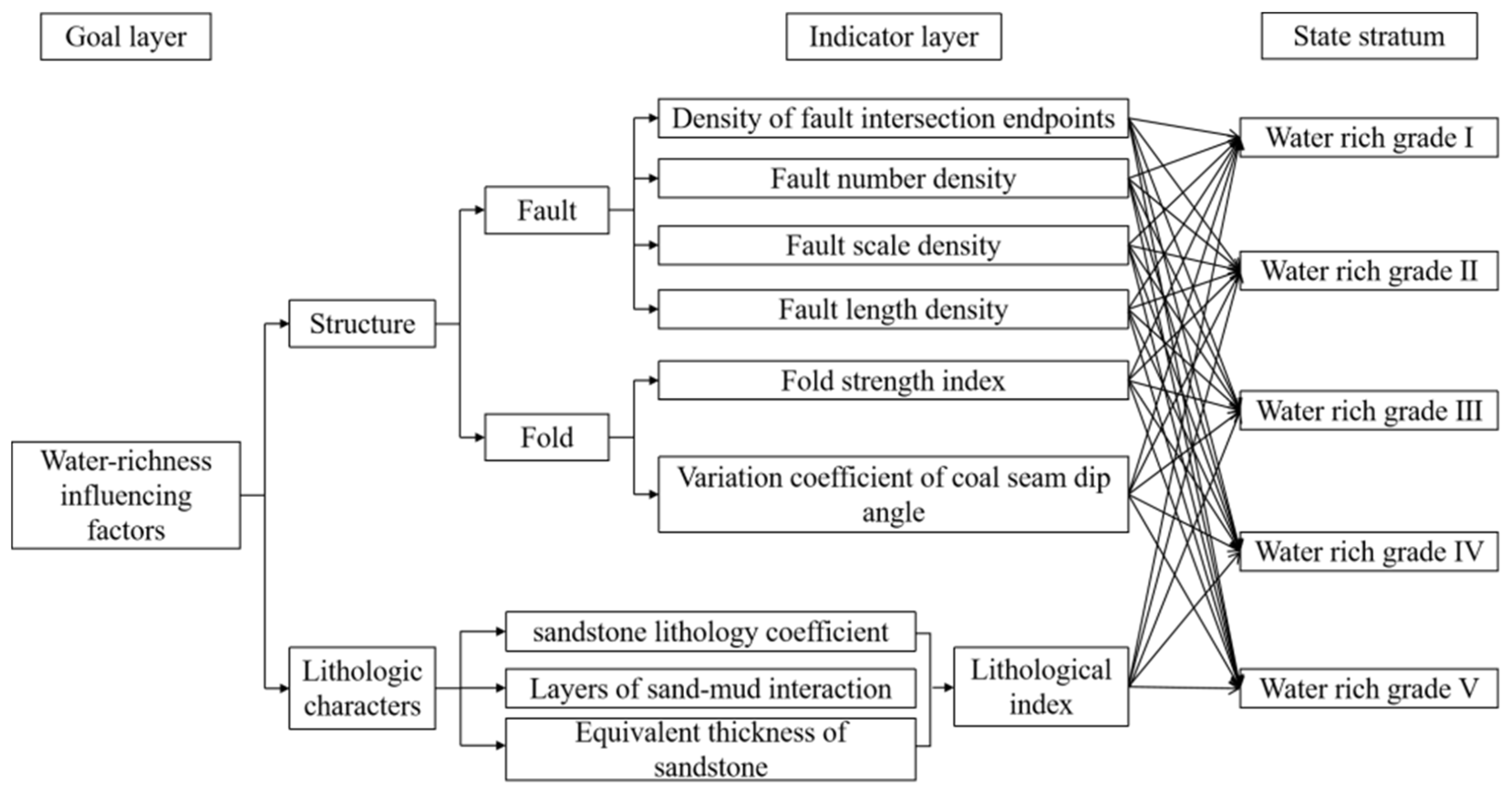
3. Water-Rich Control Factors
3.1. Lithology and Rock Structure
3.2. Structure
3.2.1. Faults
3.2.2. Folds
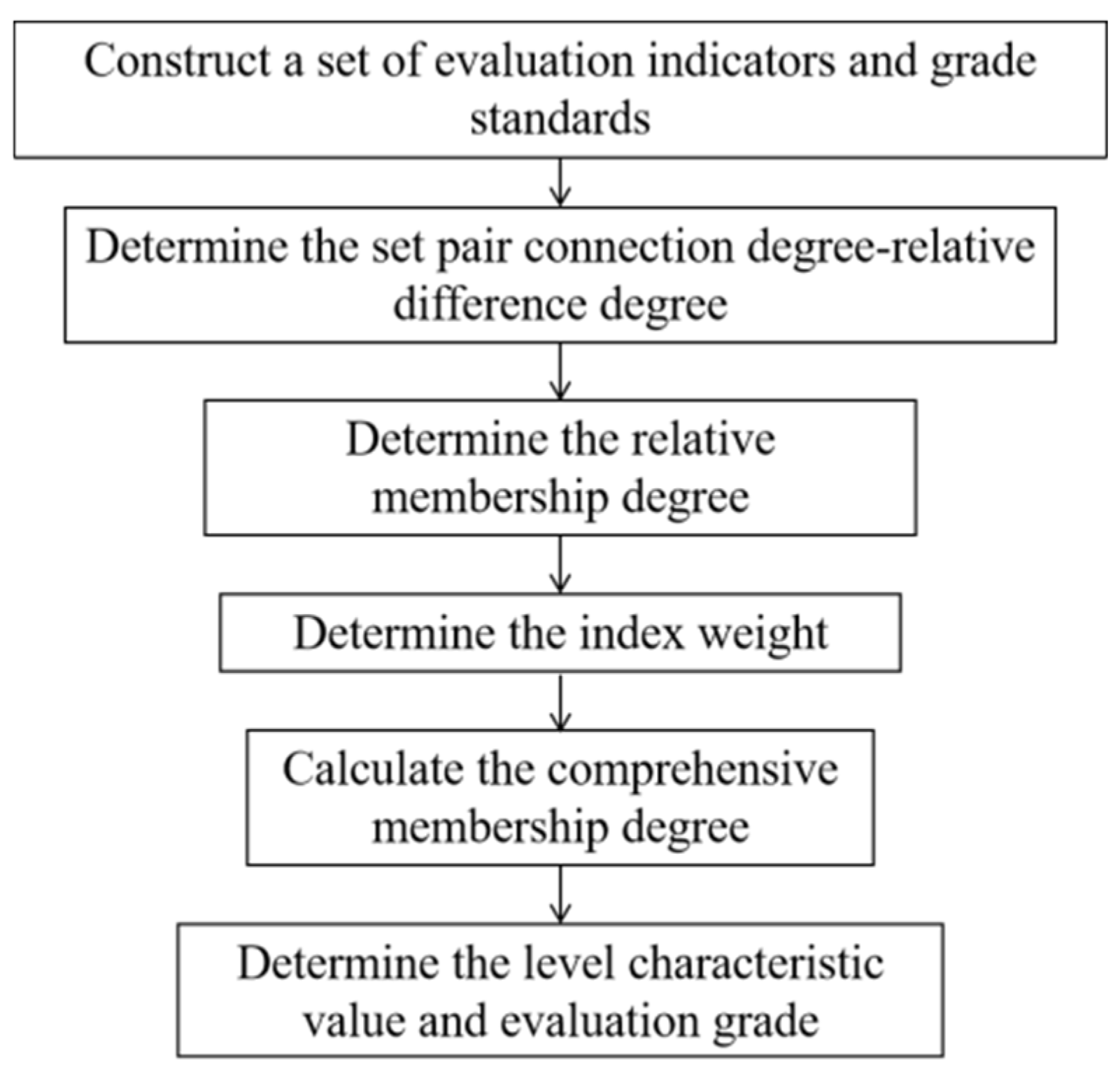
4. Set Pair Analysis—Variable Fuzzy Set Coupling Evaluation Model
4.1. Set Pair Analysis
4.2. Variable Fuzzy Set Theory
4.3. Set Pair Analysis—Variable Fuzzy Set Coupling Evaluation Method
5. Evaluation of Water Abundance of Roof Sandstone Aquifer in Bayangaole 3-1 Coal Field
5.1. Indicator Selection
5.2. Evaluation Index Value Standard
5.3. Determination of the Weight of the Evaluation Index
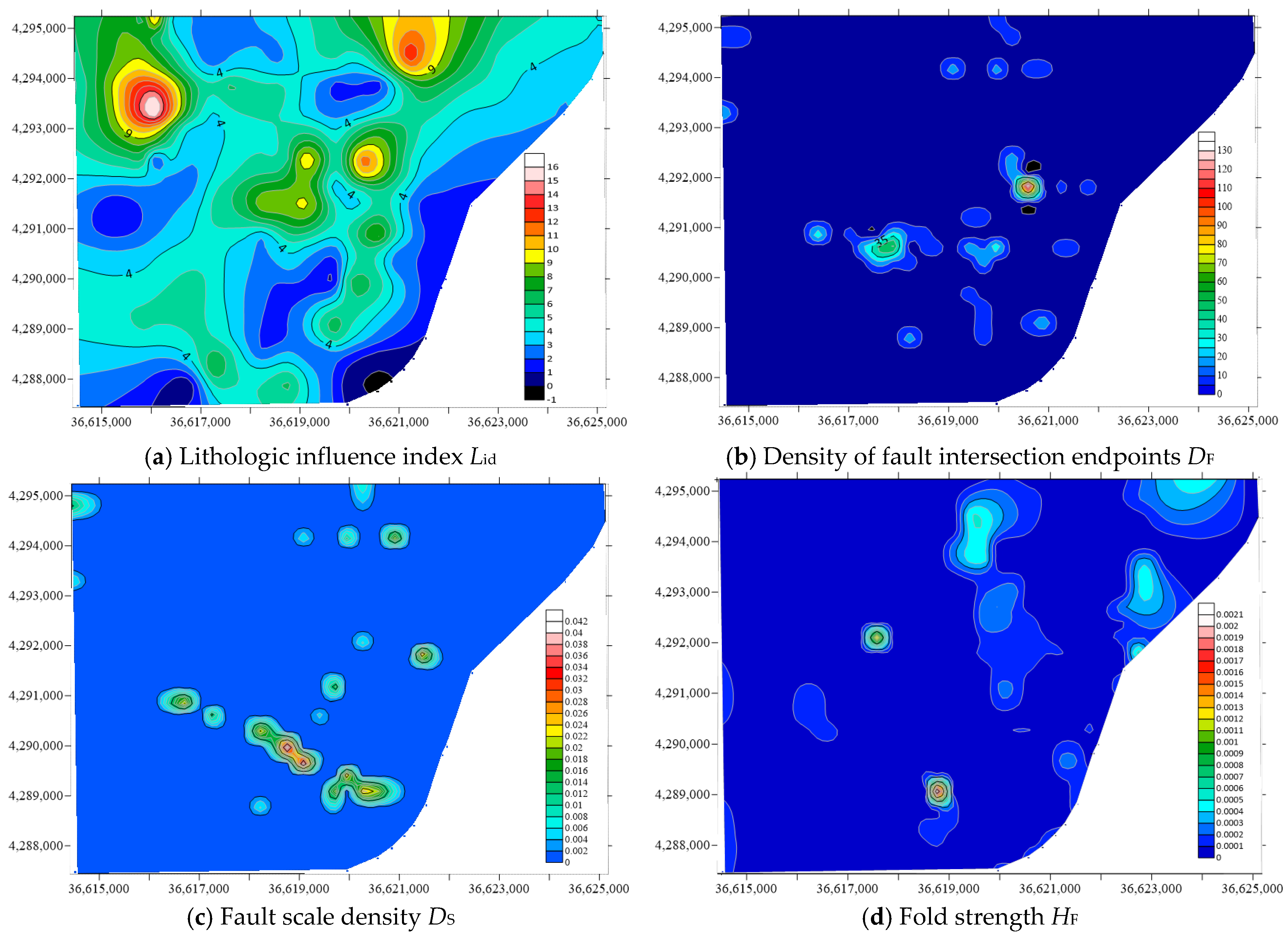
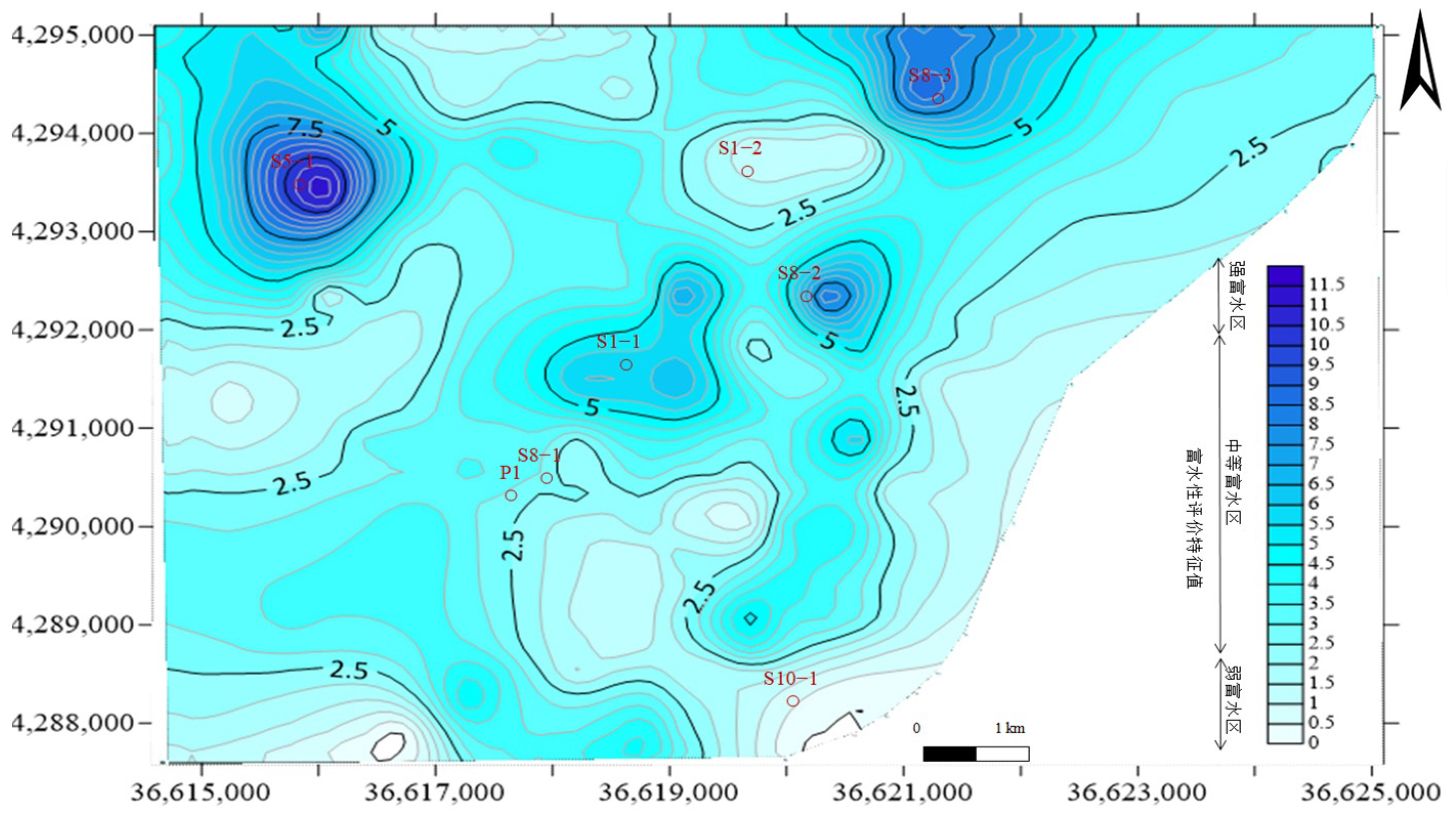
5.4. Water-Richness Evaluation Results and Verification
5.5. Comparison of Methods
6. Conclusions
7. Discussion and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Statement of Novelty
References
- Sun, Y.J.; Chen, G.; Xu, Z.M.; Yuan, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, L.J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.X.; Zheng, J.M. Research progress of water environment, treatment and utilization in coal mining areas of China. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 304–316. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.P.; Bi, Y.L. Strategic consideration and core technology about environmental ecological restoration in coal mine areas in the Yellow River basin of China. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W.S.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, A.H.; Han, N.B.; Rong, M.R. Assessment and remediation model of eco-geo-environmental conditions in arid limestone mining areas. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 217, 107644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Waheed, A.; Kuerban, A.; Muhammad, M.; Aili, A. Dynamic approaches to ecological restoration in China’s mining regions: A scientific review. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 214, 107577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, K.; Zhang, W. Further research on “three maps-two predictions” method for prediction on coal seam roof water bursting risk. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.F.; Wu, Q.; Du, X.; Liu, S.Q.; Zan, J.C.; Dou, G.D.; Wu, Z.T. Further research on “water-richness index method” for evaluation of aquifer water abundance. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, L.H.; Zong, C.J. Prediction and Actual Measurement of Water Flowing Fractured Zone Height in Overburden Strata of Flat Seam. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 44, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, H.; Xu, J.P.; Sui, W.H. Mechanical analysis of relations between water abundance and fatalness of water inrush from underlying aquifers. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2017, 34, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.F.; Yu, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, L.E.; Yin, S.X.; Zhang, B.C.; Liu, Z.Y.; Cui, Y.S.; Kan, X.D.; Huang, H. “Three zones” method for coal mine water hazard control and its significance. J. China Coal Soc. 2024, 49, 3605–3618. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T. Coalbed methane fracturing effectiveness test using bore-hole transient electromagnetic method. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 3195–3207. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.H.; Hou, Z.; Wang, T.Y.; Song, H.W. A new model to predict the water inflow of aquifer. Prog. Geophys. 2012, 27, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Q.Y. Quantitative prediction of water abundance in rock mass by transient electro-magnetic method with LBA-BP neural network. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, G.L.; Yang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, C. Exploration of the water-abundant sandstone geological features of Ningtiaota Ida Nao Luo in Shenfu mining area. J. Saf. Environ. 2016, 16, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Fan, Z.L.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Sun, W.J. Water-richness evaluation method of water-filled aquifer based on the principle of information fusion with GIS: Water-richness index method. J. China Coal Soc. 2011, 36, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, E.K.; Tong, R.J.; Wang, S.J.; Feng, J.; Chen, T. Prediction method for the water enrichment of weathered bedrock based on Fisher model in Northern Shaaxi Jurassic coalfield. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 2312–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Niu, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Du, P.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Liang, X.S. Gushing Water Law and Its Control Factors Analysis of Jinjie Coal Mine. Saf. Coal Mines 2014, 45, 145–147, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. Prediction of Water Abundance of Sandstone Aquifer IN2 Coal Seam Roof and Risk Assessment of Water Inrush in 22 Mining Area of Yingpanhao Coal Mine. Doctoral Dissertation, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.X.; Wei, J.C.; Yin, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. Study on Water Enrichment Prediction of Roof Sandstone Aquifer Based on the Fuzzy Clustering Method: A Case Study on Longgu Coal Mine. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Ang Technol. Nat. Sci. 2011, 30, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Pan, X.H.; Li, G.L.; Tu, J.N. The Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process of water abundance of an aquifer based on GIS and multi-source information fusion techniques. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2012, 39, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.H.; Wei, J.C.; Xie, D.L.; Xu, J.G.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhao, Z.C. Water-richness evaluation of sandstone aquifer based on set pair analysis-variable fuzzy set coupling method: A case from Jurassic Zhiluo formation of Jinjiaqu coal mine in Ningdong mining area. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 2432–2443. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.G.; Wang, D.D.; Shi, L.Q.; Meng, M.M. Water-richness Evaluation Method of Water-filled Aquifer Characteristics Analysis Based on Evaluation Method. Coal Technol. 2016, 35, 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Feng, J.; Hou, E.K.; Huang, K.J.; Xue, W.F.; Duan, H.J. Microscopic pore structure types of sandstone and its effects on aquifer water abundance: Taking in Ningtiaota coal mine as an example. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 3236–3244. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wei, T.; Liu, Z.J. Construction of evaluation index system for water abundance of karst aquifers and risk assessment of water inrush on coal seam roof in Southwest China. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, X.; Gai, G.; Han, Z.; Zhao, J. Water-richness evaluation method and application of clastic rock aquifer in mining seam roof. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.Q. Application overview of set pair analysis in intelligent prediction system. CAAI Trans. Intell. Syst. 2022, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Jia, X.; Xiao, L.; Dong, L.; Qiao, H.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Qian, W. Evaluation of Water Richness in Sandstone Aquifers Based on the CRITIC-TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of the Guojiawan Coal Mine in Fugu Mining Area, Shanxi Province, China. Water 2025, 17, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Hu, H.P. Application of set pair analysis model based on entropy weight to comprehensive evaluation of water quality. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 40, 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Tang, H.Q.; Chen, H.T.; Xu, L. Application of set pair analysis method in the evaluation of groundwater quality. Water Sav. Irrig. 2007, 32, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y. Unified theory and model of variable fuzzy clustering and pattern recognition. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2009, 49, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Xu, X.; Dai, G.; Liu, K.; Xiao, L.; Luo, S.; Qian, W. Evaluation of Water-Richness and Risk Level of the Sandstone Aquifer in the Roof of the No. 3 Coal Seamin Hancheng Mining Area. Water 2025, 17, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, X. Evaluation of Coal-Seam Roof-Water Richness Based on Improved Weight Method: A Case Study in the Dananhu No.7 Coal Mine, China. Water 2024, 16, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K.; Li, W.; Ge, W.; Xu, H.Y. Dam breach environmental impact evaluation based on set pair analysis-variable fuzzy set coupling model. J. Tianjin Univ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.Y.; Jin, J.L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wang, W.S. Set pair analysis-variable fuzzy set assessment model for watershed water resources security. J. Sichuan Univ. Eng. Sci. Ed. 2008, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. Prediction Model of Water Abundance of Weakly Cemented Sandstone Aquifer Based on Principal Component Analysis–Back Propagation Neural Network of Grey Correlation Analysis Decision Making. Water 2024, 16, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, P.; Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Wei, Z. Risk Assessment of Water Inrush of a Coal Seam Floor Based on the Combined Empowerment Method. Water 2022, 14, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.C.; Zhou, Z.C.; Xie, D.L.; Yu, G.Y.S.; Wu, X. Water-abundance evaluation of sandstone aquifer based on lithologic and structural characteristics. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2020, 39, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, E.K.; Ji, Z.C.; Che, X.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Gao, L.J.; Tian, S.X.; Yang, F. Water abundance prediction method of weathered bedrock based on improved AHP and the entropy weight method. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 40, 3164–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L. Application of entropy weight method and analytic hierarchy process in evaluation of water inrush from coal seam floor. Coal Geol. Explor. 2017, 45, 91–95. [Google Scholar]



| Lithology | Sample Porosity/% | Average/% | Equivalent Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No 1. | No 2. | No 3. | No 4. | |||
| Coarse sandstone | 19.05 | 18.01 | 17.65 | 22.97 | 18.92 | 1 |
| Medium sandstone | 15.05 | 15.21 | 14.98 | 15.28 | 15.13 | 0.8 |
| Fine sandstone | 10.96 | 11.27 | 12.09 | 11.08 | 11.35 | 0.6 |
| NO. | Indicator Category | Order of Evaluation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Rich I | Water Rich II | Water Rich III | Water Rich IV | Water Rich V | ||
| 1 | Lithologic influence index (Lid) | [0, 3.6) | [3.6, 6.6) | [6.6, 9.6) | [9.6, 10.8) | [10.8, 15.6] |
| 2 | Density of fault intersection endpoints (DF) | [0, 2.1) | [2.1, 7) | [7, 9.8) | [9.8, 11.9) | [11.9, 18.2] |
| 3 | Fault scale density (DS) | [0, 0.0001) | [0.0001, 0.0097) | [0.0097, 0.0193) | [0.0193, 0.0241) | [0.0241, 0.0418] |
| 4 | Fold strength (HF) | [0, 0.0163) | [0.0163, 0.0326) | [0.0326, 0.0570) | [0.0570, 0.1384) | [0.1384, 0.2117] |
| Index | Lithologic Influence Index (Lid) | Fault Intersection Endpoints Density (DF) | Fault Scale Density (DS) | Fold Strength (HF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.7 | 0.04336 | 0.04342 | 0.21322 |
| Evaluation Index | Lithologic Influence Index (Lid) | Density of Fault Intersection Endpoints (DF) | Fault Scale Density (DS) | Fold Strength (HF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted value | 2.822 | 5 | 0.022485493 | 2.248549333 |
| Evaluation Index | Lithologic Influence Index (Lid) | Density of Fault Intersection Endpoints (DF) | Fault Scale Density (DS) | Fold Strength (HF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 |
| II | 0.96 | 0.81 | 0.38 | 0.76 |
| III | 0.72 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 0.51 |
| IV | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.38 |
| V | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.65 | 0.30 |
| Model Parameter | The Normalized Comprehensive Membership Vector | Water Richness Level Characteristic Value H |
|---|---|---|
| α = 1, p = 1 | [0.2341, 0.2225, 0.2016, 0.1751, 0.1667] | 2.8177 (Weak water-rich area) |
| α = 1, p = 2 | [0.2341, 0.2225, 0.2016, 0.1751, 0.1667] | 2.8238 (Weak water-rich area) |
| α = 2, p = 1 | [0.2159, 0.2141, 0.2066, 0.1864, 0.1770] | 2.8946 (Weak water-rich area) |
| α = 2, p = 2 | [0.2164, 0.2153, 0.2054, 0.1878, 0.1751] | 2.8899 (Weak water-rich area) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, K.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, C.; Xie, D.; Liang, S.; Xi, B. Water-Richness Evaluation of Sandstone Aquifer Based on Set Pair Analysis Variable Fuzzy Set Coupling Method: A Case Study on Bayangaole Mine, China. Water 2025, 17, 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121826
Liang K, Li Y, Bai Y, Zhang W, Han C, Xie D, Liang S, Xi B. Water-Richness Evaluation of Sandstone Aquifer Based on Set Pair Analysis Variable Fuzzy Set Coupling Method: A Case Study on Bayangaole Mine, China. Water. 2025; 17(12):1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121826
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Kaihua, Yueyue Li, Yuanlin Bai, Weijie Zhang, Chenghao Han, Daolei Xie, Shengjian Liang, and Bowen Xi. 2025. "Water-Richness Evaluation of Sandstone Aquifer Based on Set Pair Analysis Variable Fuzzy Set Coupling Method: A Case Study on Bayangaole Mine, China" Water 17, no. 12: 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121826
APA StyleLiang, K., Li, Y., Bai, Y., Zhang, W., Han, C., Xie, D., Liang, S., & Xi, B. (2025). Water-Richness Evaluation of Sandstone Aquifer Based on Set Pair Analysis Variable Fuzzy Set Coupling Method: A Case Study on Bayangaole Mine, China. Water, 17(12), 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121826






