Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water and Sediment from the Source Reservoir of the Mid-Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Collection and Determination of Water and Sediment Samples
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
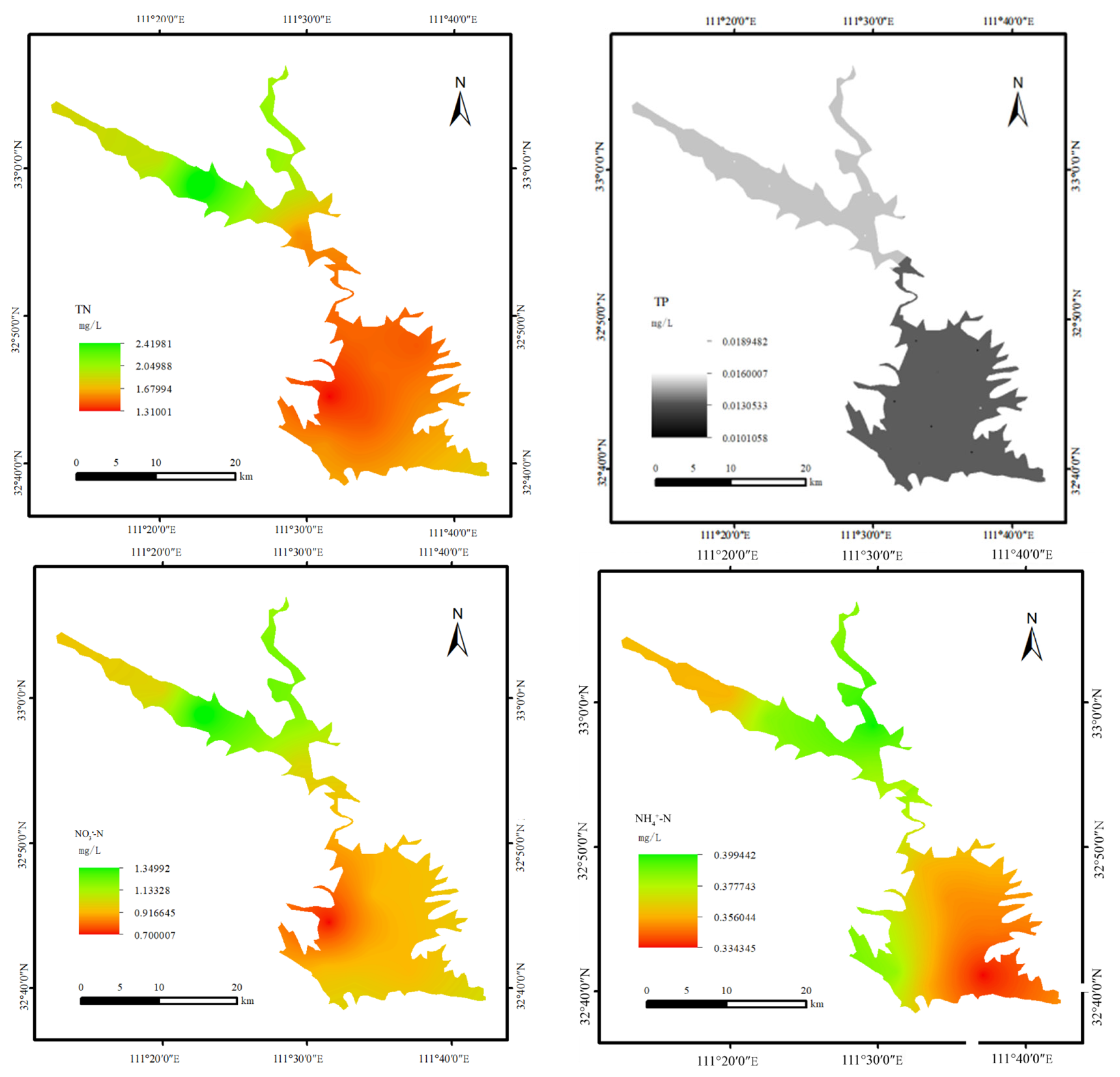
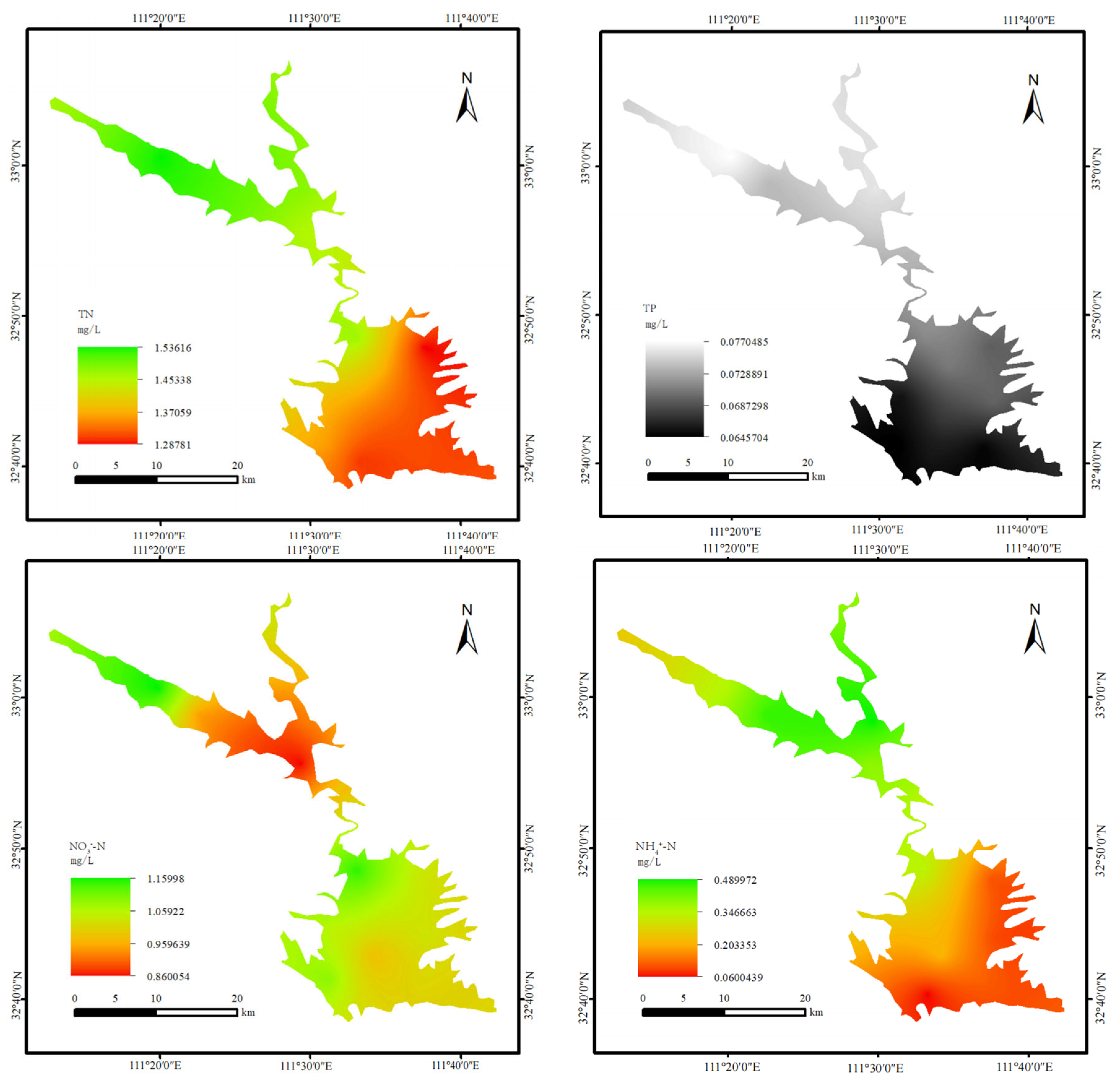
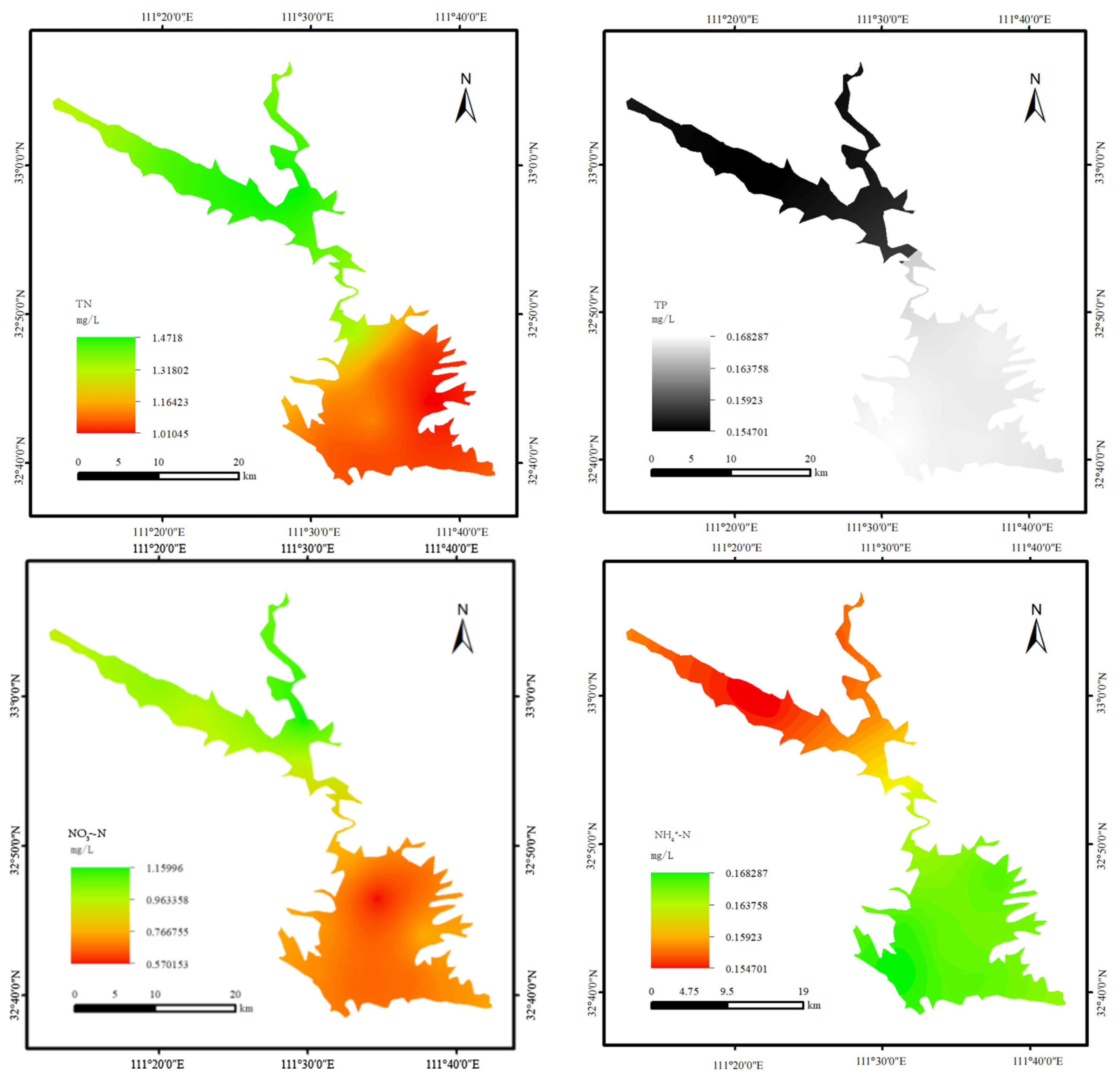
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water
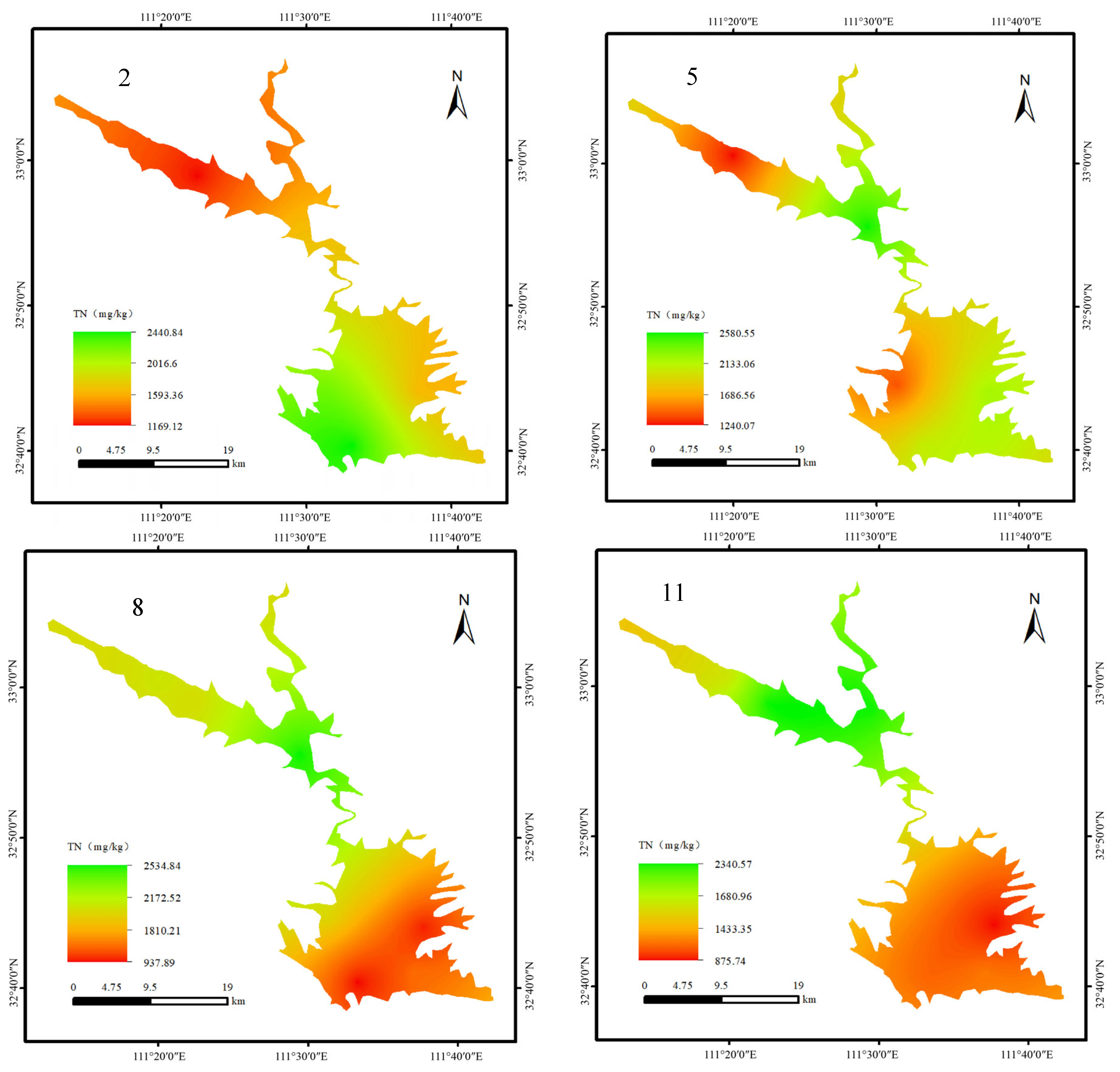
3.2. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Spatiotemporal Characteristics in Sediment
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Characteristics in Water and Sediment
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water of the Dan Reservoir
4.2. Distribution Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Sediment of the Dan Reservoir
4.3. The Interaction Between Water and Sediment in the Dan Reservoir
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seppälä, J.; Knuuttila, S.; Silvo, K. Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems a new method for calculating the potential contributions of nitrogen and phosphorus. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2004, 9, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.B.; Henderson, A.D.; Zelm, R.V.; Jolliet, V.; Huijbregts, M.A. Assessing the importance of spatial variability versus model choices in life cycle impact assessment: The case of freshwater eutrophication in Europe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13565–13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.L.; Gu, X.H.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xu, L.G. Ecological and environmental changes and protection measures of lakes in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2023, 38, 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Chen, K.N.; Gu, X.Z.; Huang, W.; Wei, Z. Occurrence and internal loadings of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediment of Lake Baiyangdian. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.G.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G.M.; Wang, H.J. Research progress on pelease mechanisms of nitrogen and phosphorus of sediments in water bodies and their influencing factors. Wetl. Sci. 2022, 20, 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.L. Study on the Composition and Sedimentary Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water and Sediments of Dianchi Lake. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.Y.; Peng, G.Z.; Xie, Y.N.; Mo, Y.T.; Li, F.F.; Ouyang, M.F.; Huang, D.Z. Characteristics and risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metals pollution in sediments of Dongting Lake. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 2399–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.Y.; Zou, Y.; Chen, J.J.; Li, F.C. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in sediments of Yangcheng Lake. Environ. Monit. Forewarning 2021, 13, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, M.S.; Huang, M.Y. Sediment characteristics of Erhai Lake and its impact on the overlying water. Environ. Sci. Surv. 2023, 42, 5–8+20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.P.; Xu, W.W.; Han, C.; Hu, W.P. Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Chaohu sediments and pollution evaluation. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 699–711. [Google Scholar]
- CCME. Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- GB11894-89; Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 1989.
- GB11893-89; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 1989.
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2002.
- NY/T 53-1987; Method for the Determination of Soil Total Nitrogen (Semi-Micro Kjeldahl Method). Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 1987.
- GB 5009.87-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Phosphorus in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Yin, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Xin, X.K.; Liu, G. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of totalphosphorus in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Yangtze River 2023, 54, 1–7+10. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.Y. Phytoplankton Community Variations in Danku of Danjiangkou Reservoir Under Water Transfer and Driving Factors Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Nanyang Normal University, Nanyang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y. Study on Enhanced Coagulation of South-North Water in Zhengzhou and Water Quality Assement of Danjiang Water. Ph.D. Thesis, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.W.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Cui, N.X.; Cheng, S.P. Water quality assessment of an urban river receiving tail water using the single-factor index and principle component analysis. Water Supply 2019, 19, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am. Sci. 1958, 46, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, A. The Influence of Organisms on the Composition of Sea-Water; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Z.; Wang, H.J.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.N. The Control of Lake Eutrophication: Focusing on Phosphorusabatement, or Reducing both Phosphorus and Nitrogen? Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2020, 44, 938–960. [Google Scholar]
- Naiman, R.J. Animal influences on ecosystem dynamics: Large animals are more than passive components of ecological systems. Bioscience 1988, 38, 750–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peuelas, J. The elemental stoichiometry of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems and its relationships with organismic lifestyle and ecosystem structure and function: A review and perspectives. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhou, J.; Elser, J.J. Water depth underpins the relative roles and fates of nitrogen and phosphorus in lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3191–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Kalff, H. The effect of phosphorus limitation on algal growth rates: Evidence from Alkaline Phosphatase. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 38, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gan, J. Reversing impact of phytoplankton phosphorus limitation on coastal hypoxia due to interacting changes in surface production and shoreward bottom oxygen influx. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Brookes, J.; Qin, B. High probability of nitrogen and phosphorus co-limitation occurring in eutrophic lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Guo, Y. Intensified nutrients removal in constructed wetlands by integrated Tubifex tubifex and mussels: Performance and mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, C.L.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y. The phosphorus release pathways and their mechanisms driven by organic carbon and nitrogen in sediment of eutrophic shallow lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.G.; Qiao, Y.B.; Ma, Q. Effect of Solids Concentration on the Phosphorus Adsorption onto Yellow River Sediments. J. Inn. Mong. Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 39, 50–54+58. [Google Scholar]
- Tammeorg, O.; Nurnberg, G.; Horppila, J.; Haldna, M.; Niemistö, J. Redox-related release of phosphorus from sediment in large and shallow Lake Peipsi: Evidence from sediment studies and long-term monitoring data. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z. Coupling effect of pH and dissolved oxygen in water column on nitrogen release at water–sediment interface of Erhai Lake, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 149, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q. The Release Amount of Carbon and Nitrogen From Soil and Plant Under Inundation in the Water-Level-Fluctuation Zone of the Wujiang Hongjiadu Reservoir. Ph.D. Thesis, Tibet University, Lasa, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.P.; Pan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Analysis on Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Nitrogen in Sediments of Water-fluctuating Zone in Danjiangkou Reservoir Area. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 40, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, X.; Xin, Y.R.; Huang, J.; Guo, S.J.; Bi, S.G.; Hu, L.Q.; Chen, Z.J.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Sediment Nutrients and Heavy Metals of the Danjiangkou Reservoir Before and After Water Division of the Mid-route Project. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 3591–3600. [Google Scholar]
- Blazhchishin, A.I.; Chubarenko, I.P. Sediment-water interactions in the Vistula lagoon-some preiiminary resuits. Sediment. Recycl. Aquat. Ecosyst. 1999, 1, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Holmroos, H.; Hietanen, S.; Niemistö, J.; Horppila, J. Sediment resuspension and denitrification affect the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio of shallow lake waters. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2012, 180, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, J.S.; Pickart, R.S.; Stockwell, D.A.; Lin, P.G.; Charette, M.A. Physical drivers of sediment-water interaction on the Beaufort Sea shelf. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2022, 3, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, M.S.; Yang, J.W.; Ye, F.; Lin, Y. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Deposition and Distribution Characteristics of Sediment in Hongfeng Lake Reservoir. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2008, 36, 15650–15652. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.S. Nutrient Distribution and Its Influencing Factors in Water and Sediment of a Deep-Water Reservoir. Ph.D. Thesis, China West Normal University, Nanchong, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. Spacial and Temporal Variation and Transport of Contaminants Within Water and Up-Layer Sediments in Lake Wuliangsuhai. Ph.D. Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Huhehaote, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]



| Indicators | W-TN | W-TN:TP | W-TP | W-NO3−-N | W-NO2−-N | W-NH4+-N | S-TN | S-TP | S-TN:TP | Water Level | Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-TN | 1 | 0.84852 ** | −0.46695 | 0.5974 * | −0.58204 * | 0.51116 * | −0.6194 * | −0.34814 | −0.55518 | −0.2249 | −0.32965 |
| W-TN:TP | 1 | −0.72515 ** | 0.42564 | −0.87215 ** | 0.40943 | −0.5066 | −0.28435 | −0.45104 | −0.40183 | −0.24211 | |
| W-TP | 1 | −0.29757 | 0.64313 * | −0.24102 | 0.1558 | 0.01542 | 0.18843 | 0.227 | 0.18996 | ||
| W-NO3−-N | 1 | −0.36552 | −0.01952 | −0.47965 | −0.44835 | −0.29456 | −0.38066 | 0.27198 | |||
| W-NO2−-N | 1 | 0.0967 | 0.61357 | 0.42578 | 0.65904 | 0.61829 | 0.175 | ||||
| W-NH4+-N | 1 | −0.06883 | −0.3387 | 0.1341 | −0.17136 | −0.38726 | |||||
| S-TN | 1 | 0.58421 * | 0.83541 ** | 0.21838 | 0.031 | ||||||
| S-TP | 1 | 0.04495 | 0.61653 * | −0.35901 | |||||||
| S-TN:TP | 1 | −0.15583 | 0.29811 | ||||||||
| Water level | 1 | −0.71566 ** | |||||||||
| Rainfall | 1 |
| Indicators | W-TN | W-TN:TP | W-TP | W-NO3−-N | W-NO2−-N | W-NH4+-N | S-TN | S-TP | S-TN:TP | Water Level | Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-TN | 1 | 0.43082 | 0.04151 | −0.12265 | 0.39891 * | −0.64137 ** | 0.59783 * | 0.57219 * | 0.36807 | −0.36189 * | −0.11472 |
| W-TN:TP | 1 | −0.75197 ** | 0.33968 * | 0.35637 | −0.48377 ** | 0.505 | 0.5948 * | 0.13711 | −0.41933 * | −0.1232 | |
| W-TP | 1 | −0.58772 ** | −0.331 | 0.20592 | −0.45696 | −0.54768 * | −0.16085 | 0.36268 * | −0.16354 | ||
| W-NO3−-N | 1 | 0.36698 | −0.03533 | 0.1345 | 0.34825 | −0.20645 | −0.37611 * | 0.50858 ** | |||
| W-NO2−-N | 1 | −0.74744 ** | 0.72793 * | 0.70304 * | 0.64472 | −0.86406 ** | 0.56114 ** | ||||
| W-NH4+-N | 1 | −0.41984 | −0.42412 | −0.20652 | 0.72057 ** | −0.28231 | |||||
| S-TN | 1 | 0.83739 ** | 0.70142 ** | −0.57277 * | 0.27437 | ||||||
| S-TP | 1 | 0.21423 | −0.50783 | 0.21701 | |||||||
| S-TN:TP | 1 | −0.38157 | 0.20858 | ||||||||
| Water level | 1 | −0.71566 ** | |||||||||
| Rainfall | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Gu, K.; Sun, S.; Liu, Q.; Lv, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water and Sediment from the Source Reservoir of the Mid-Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Water 2025, 17, 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121824
Zhang Y, Zhang D, Li Y, Han X, Wang X, Zhang J, Gu K, Sun S, Liu Q, Lv J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water and Sediment from the Source Reservoir of the Mid-Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Water. 2025; 17(12):1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121824
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuanyuan, Donghua Zhang, Yue Li, Xueqing Han, Xinyu Wang, Ji’ao Zhang, Kaidi Gu, Shuaijie Sun, Qigen Liu, and Jun Lv. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water and Sediment from the Source Reservoir of the Mid-Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project" Water 17, no. 12: 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121824
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, D., Li, Y., Han, X., Wang, X., Zhang, J., Gu, K., Sun, S., Liu, Q., & Lv, J. (2025). Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water and Sediment from the Source Reservoir of the Mid-Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Water, 17(12), 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121824






