The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution in the Sand River Catchment, Limpopo, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
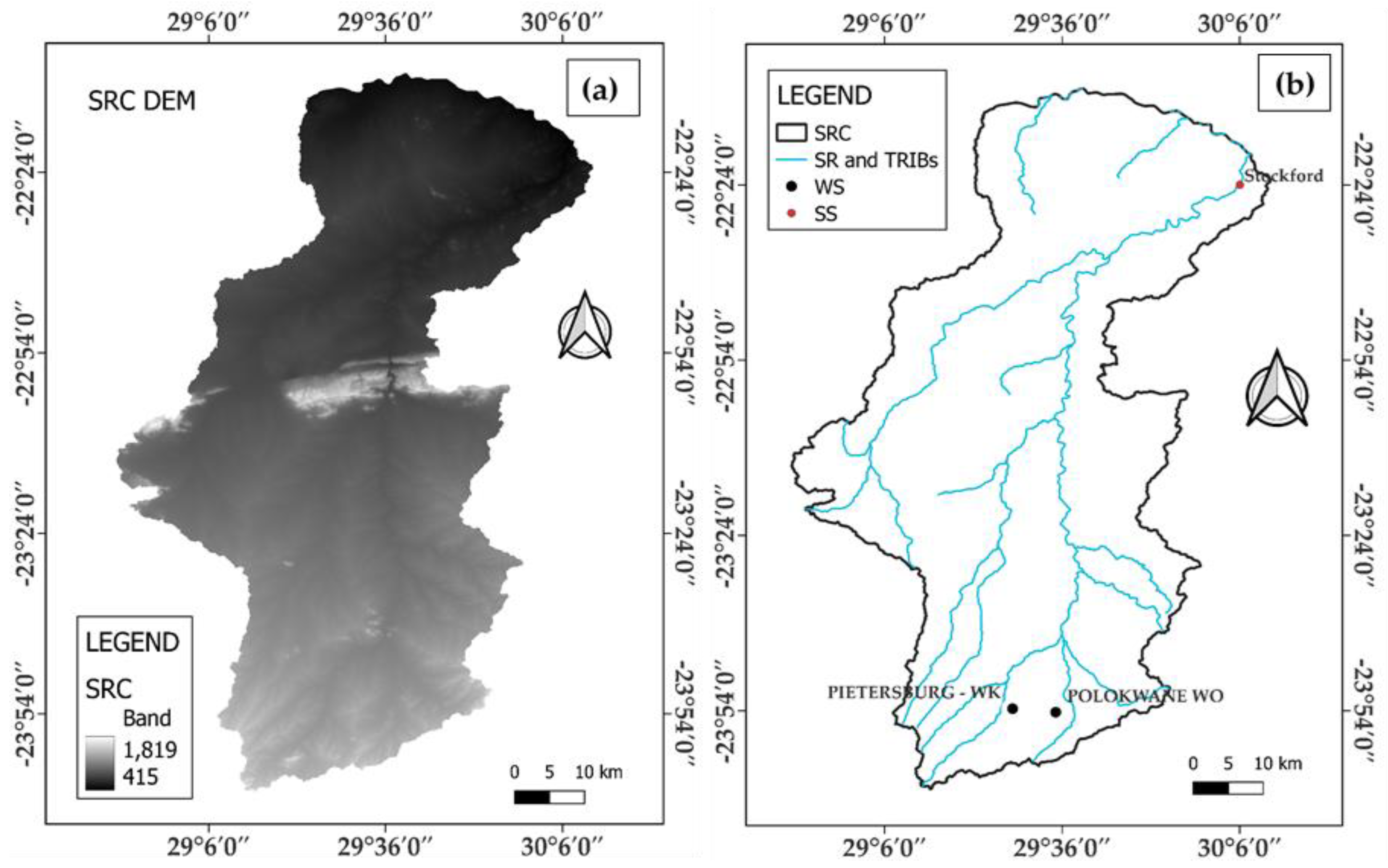
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. SWAT+ Input Data
2.3. SWAT+ Setup and Procedure
2.4. SWAT+ Calibration and Validation
2.5. SWAT+ Application
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
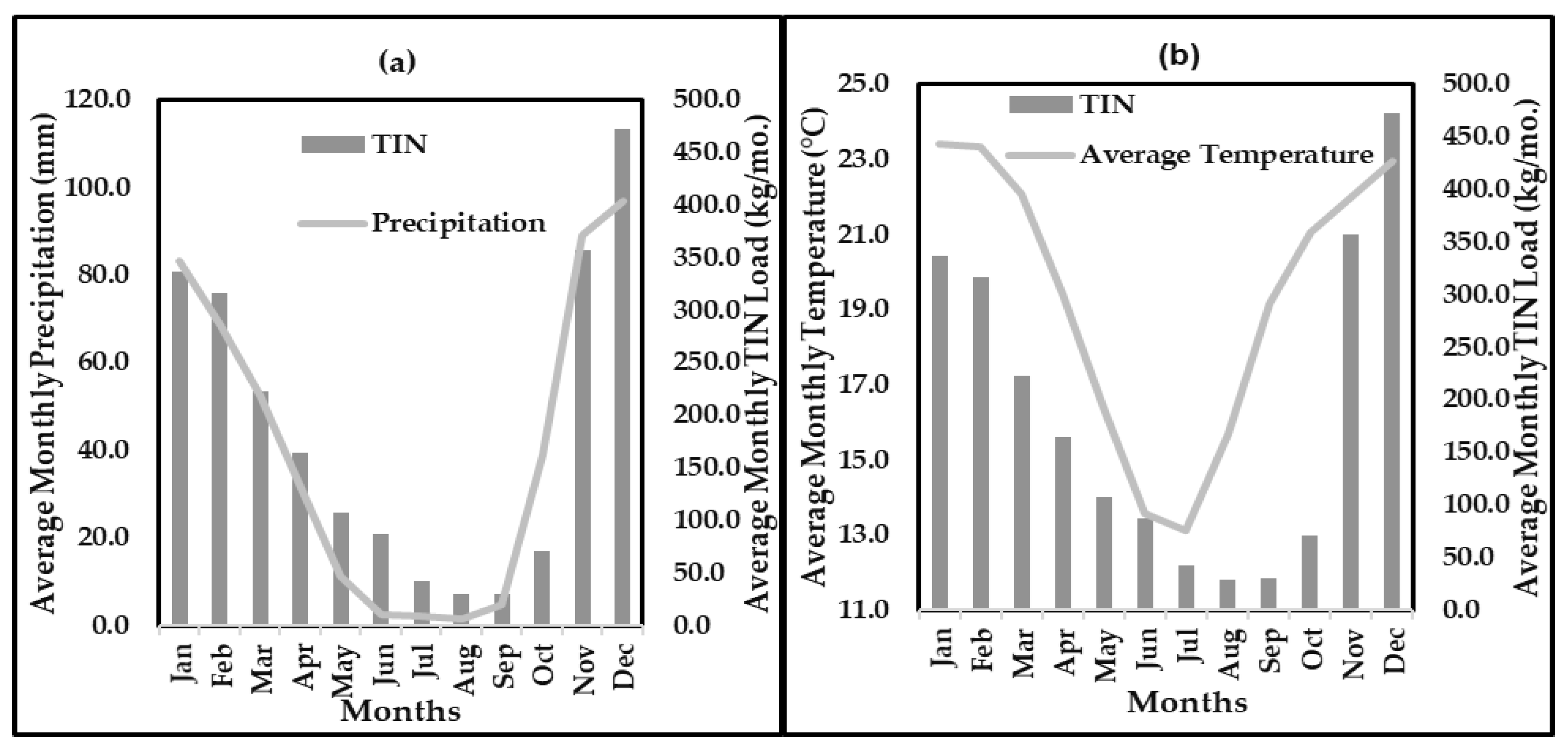
3.1. Impact of Precipitation and Temperature Variation on Monthly Sediment Load
3.2. Impact of Precipitation and Temperature Variation on Monthly TIN Load
3.3. Impact of Precipitation and Temperature Variation on Monthly TIP Load
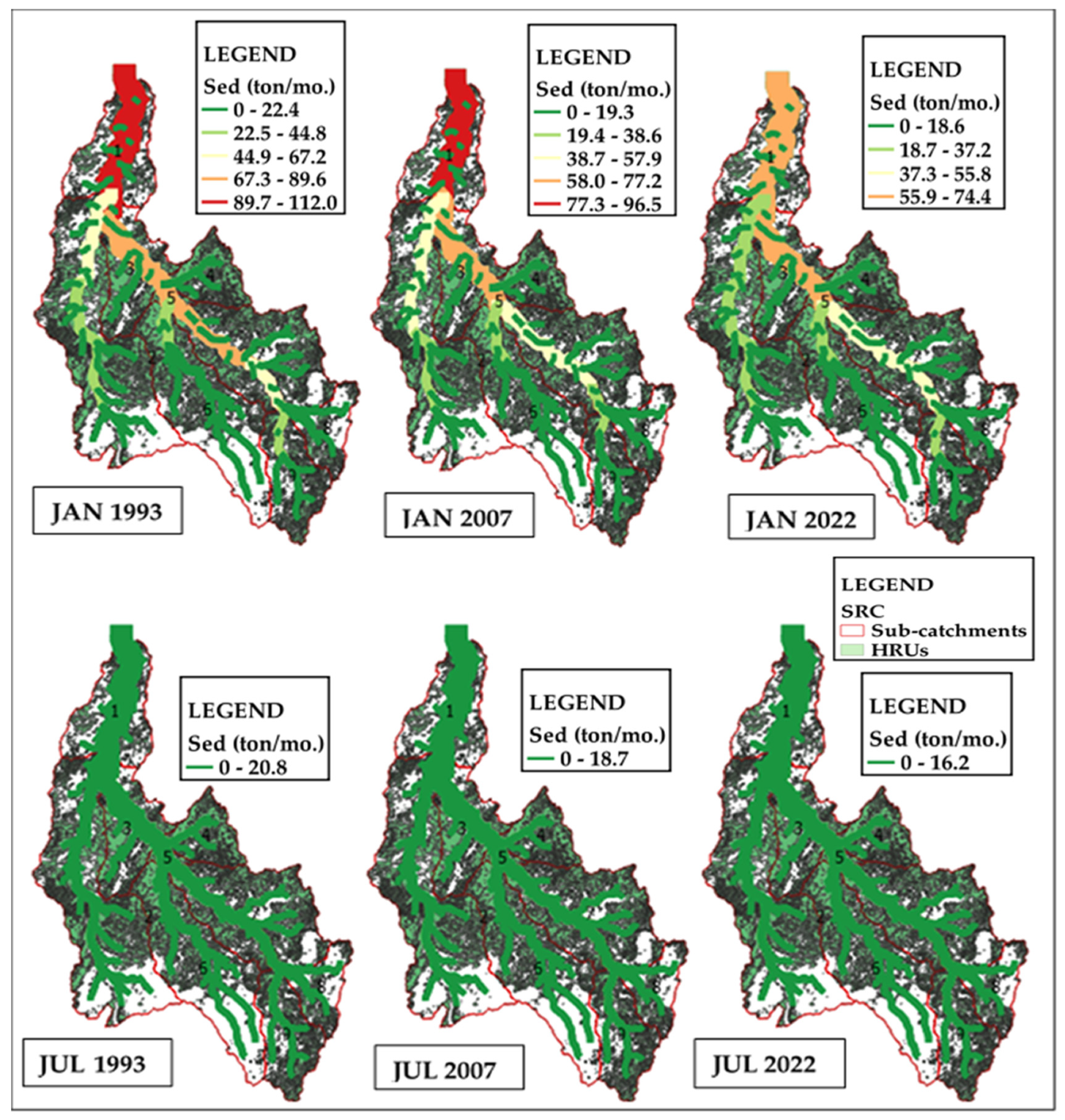
3.4. Long-Term Spatio-Temporal Variability of Sediment, TIN, and TIP Loads During High and Low Peaks of Precipitation and Temperature in the SRC
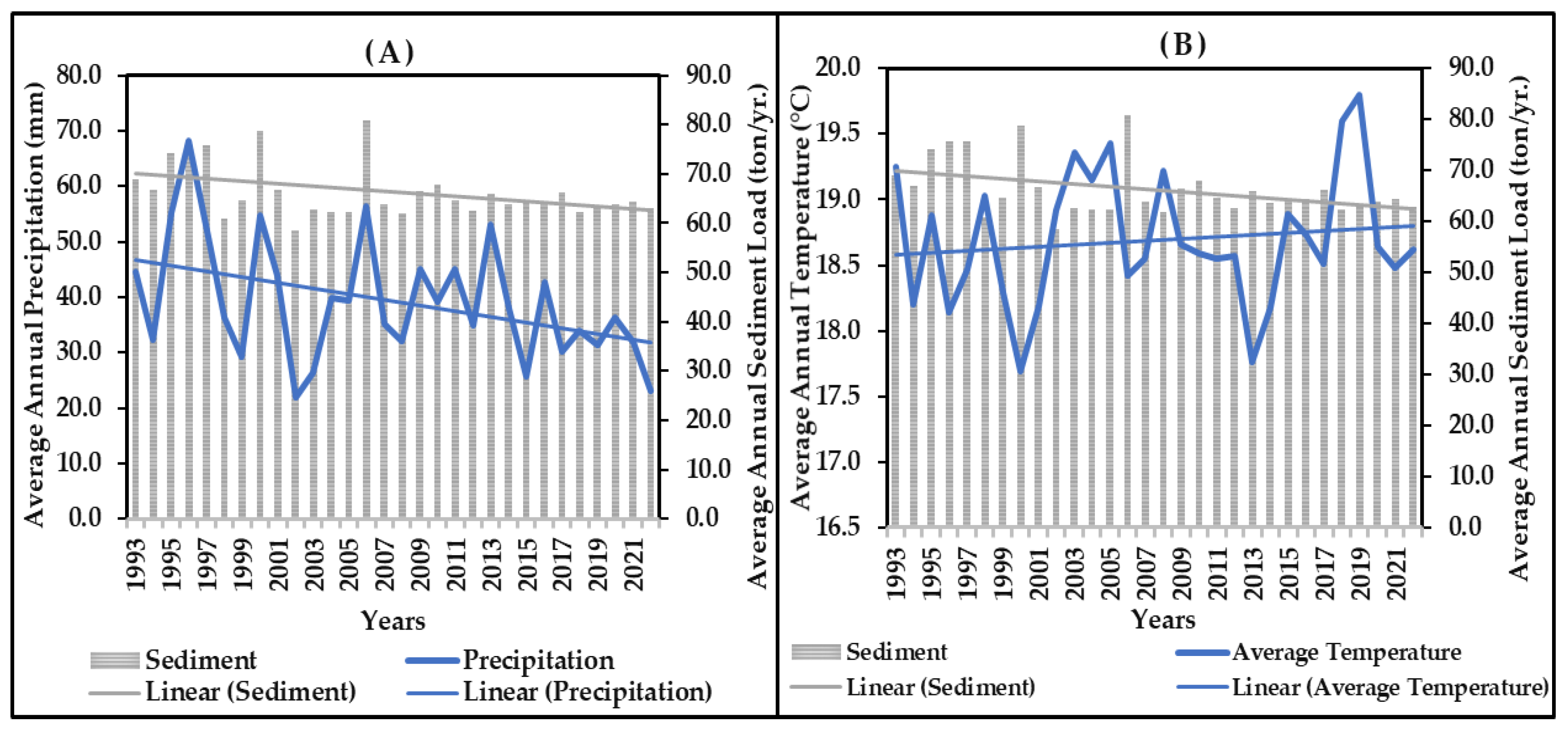
3.5. Inter-Annual Impact of Precipitation and Temperature on Annual Sediment Load
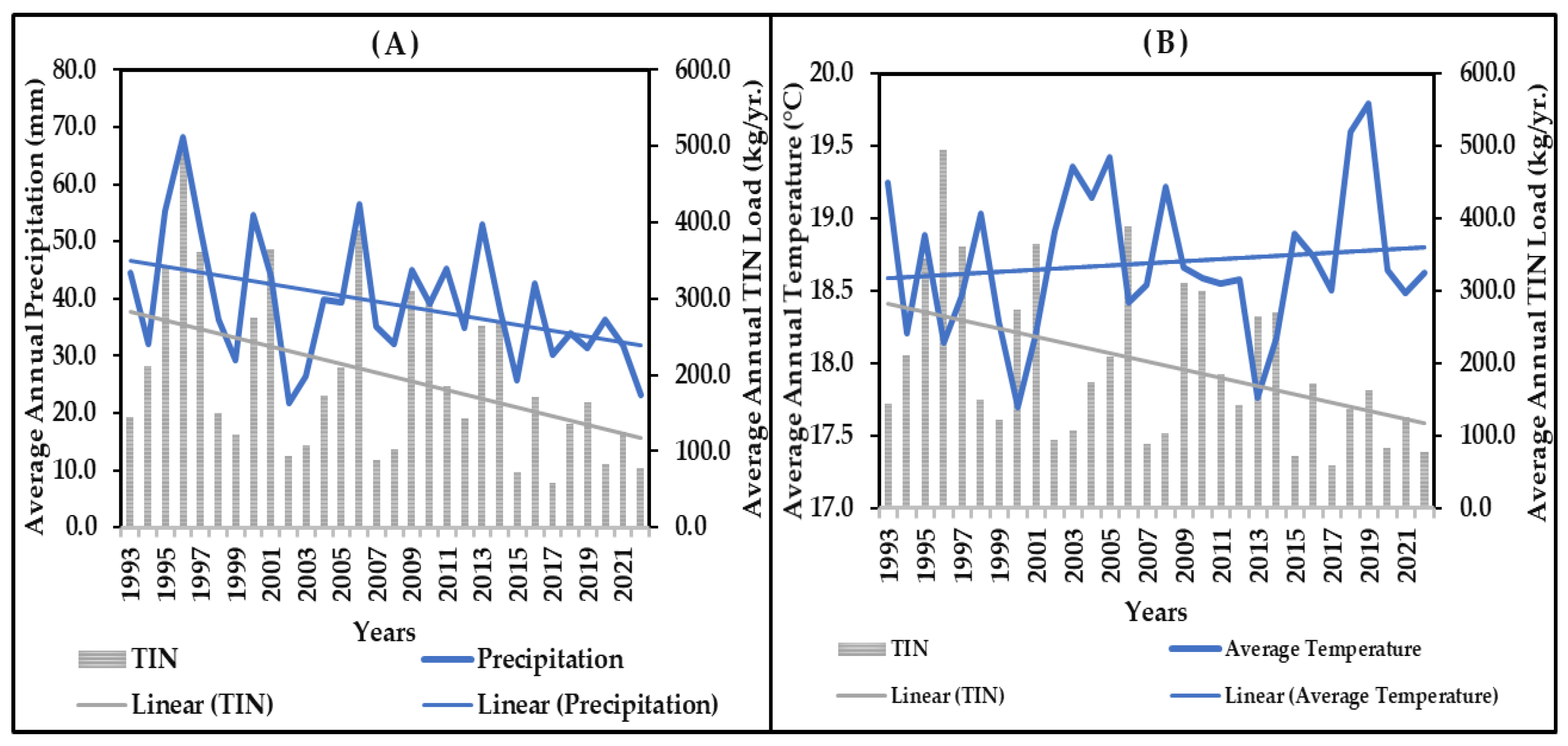
3.6. Inter-Annual Impact of Precipitation and Temperature on Annual TIN Load
3.7. Inter-Annual Impact of Precipitation and Temperature on Annual TIP Load
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Monthly Precipitation and Temperature on Agricultural NPS Pollution
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Sediment, TIN, and TIP Loads During High and Low Precipitation and Temperature Peaks
4.3. Effect of Inter-Annual Variation in Precipitation and Temperature on Agricultural NPS Pollution in the SRC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nimma, D.; Devi, O.R.; Laishram, B.; Ramesh, J.V.N.; Boddupalli, S.; Ayyasamy, R.; Tirth, V.; Arabil, A. Implications of climate change on freshwater ecosystems and their biodiversity. Desalination Water Treat. 2025, 321, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Su, Z.; Liu, C.; Nie, Y.; Cui, L. Climate change, air pollution and chronic respiratory diseases: Understanding risk factors and the need for adaptive strategies. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2025, 30, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.K. Fresh water availability and its global challenge. Br. J. Multidiscip. Adv. Stud. 2023, 4, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/caddis/sediments (accessed on 19 May 2024).
- Ault, T.R. On the essentials of drought in a changing climate. Science 2020, 368, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Shreya, S.; Sarkar, N.; Maitra, A. Time series trend analysis of rainfall and temperature over Kolkata and surrounding region. Atmósfera 2023, 37, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/syr/ (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Center for Climate and Energy Solutions. Available online: https://www.c2es.org/content/drought-and-climate-change/ (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- van der Wiel, K.; Bintanja, R. Contribution of climatic changes in mean and variability to monthly temperature and precipitation extremes. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemeda, D.O.; Sima, A.D. The impacts of climate change on African continent and the way forward. J. Ecol. Nat. Environ. 2015, 7, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kone, S.; Balde, A.; Zahonogo, P.; Sanfo, S. A systematic review of recent estimations of climate change impact on agriculture and adaptation strategies perspectives in Africa. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2024, 29, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remilekun, A.T.; Thando, N.; Nerhene, D.; Archer, E. Integrated assessment of the influence of climate change on current and future intra-annual water availability in the Vaal River catchment. J. Water Clim. Change 2021, 12, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedeke, S.B. Climate change vulnerability and adaptation of crop producers in sub-Saharan Africa: A review on concepts, approaches and methods. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1017–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, B. Agricultural production system in arid and semi-arid regions. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Food Technol. 2021, 7, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Food Programme. Climate Change in Southern Africa—A Position Paper. Available online: https://www.wfp.org/publications/climate-change-southern-africa-position-paper#:~:text=A%20position%20paper%20for%20WFP,highly%20sensitive%20to%20weather%20fluctuations (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- McBride, C.M.; Kruger, A.C.; Johnston, C.; Dyson, L. Projected changes in daily temperature extremes for selected locations over South Africa. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2025, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikhwari, T.; Nethengwe, N.; Sigauke, C.; Chikoore, H. Modelling of extremely high rainfall in Limpopo Province of South Africa. Climate 2022, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pheto, S.M. A Comparative Study of the Impact of Climate Change on Food Security in Limpopo and North West Provinces of South Africa. Ph.D. Dissertation, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mazibuko, S.M.; Mukwada, G.; Moeletsi, M.E. Assessing the frequency of drought/flood severity in the Luvuvhu River catchment, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Water SA 2021, 47, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Water and Sanitation. Available online: https://www.dws.gov.za/iwrp/Limpopo/sa.aspx (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Zhang, H.; Meng, Q.; You, Q.; Huang, T.; Zhang, X. Influence of vegetation filter strip on slope runoff, sediment yield and nutrient loss. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Ye, C.; Li, C.H.; Shi, X.G.; Shao, Y.; Qi, W. The global progress on the non-point source pollution research from 2012 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seanego, K.G.; Moyo, N.A.G. The effect of sewage effluent on the physico-chemical and biological characteristics of the Sand River, Limpopo, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2013, 66, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Kim, G. Impacts of climate change scenarios on non-point source pollution in the Saemangeum watershed, South Korea. Water 2019, 11, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortesa, J.; Latron, J.; García-Comendador, J.; Company, J.; Estrany, J. Runoff and soil moisture as driving factors in suspended sediment transport of a small mid-mountain Mediterranean catchment. Geomorphology 2020, 368, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Royal Society. Available online: https://royalsociety.org/news-resources/projects/climate-change-evidence-causes/basics-of-climate-change/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Sadiqi, S.S.J.; Nam, W.H.; Lim, K.J.; Hong, E. Investigating Nonpoint Source and Pollutant Reduction Effects under Future Climate Scenarios: A SWAT-Based Study in a Highland Agricultural Watershed in Korea. Water 2024, 16, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Yin, Q. Assessing the response of non-point source nitrogen pollution to land use change based on SWAT model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoi, D.N.; Loi, P.T.; Trang, N.T.T.; Vuong, N.D.; Fang, S.; Nhi, P.T.T. The effects of climate variability and land-use change on riverflow and nutrient loadings in the Sesan, Sekong, and Srepok (3S) River Basin of the Lower Mekong Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 29, 7117–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieger, K.; Arnold, J.G.; Rathjens, H.; White, M.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Allen, P.M.; Volk, M.; Srinivasan, R. Introduction to SWAT+, a completely restructured version of the soil and water assessment tool. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapangaziwiri, E.; Kahinda, J.M.; Oosthuizen, N. Towards the Quantification of the Historical and Future Water Resources of the Limpopo River Basin, Pretoria; Report to the Water Research Commission, Council for Scientific and Industrial Research and Rhodes University, South Africa; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vhembe District Municipality. Available online: https://www.vhembe.gov.za/wpfd_file/vhembe-district-municipality-idp-2019-2020-review-old/ (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Xiang, X.; Ao, T.; Xiao, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Bi, Y.; Guo, J. Parameter sensitivity analysis of SWAT modeling in the Upper Heihe River Basin using four typical approaches. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Skutsch, M.; Paneque-Gálvez, J.; Ghilardi, A. Remote sensing of forest degradation: A review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.A.; Bailey, R.T.; White, J.T.; Arnold, J.G.; White, M.J.; Čerkasova, N.; Gao, J. A framework for parameter estimation, sensitivity analysis, and uncertainty analysis for holistic hydrologic modeling using SWAT+. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumsa, B.C.; Kenea, G.; Tola, B. The application of SWAT+ model to quantify the impacts of sensitive LULC changes on water balance in Guder catchment, Oromia, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.G.; do Vasco, A.N.; Soares, C.C.; de Jesus Neves, R.J.; Garcia, C.A.B.; Netto, A.D.O.A. Spatial modeling of nitrogen and phosphorus in an agricultural basin in northeastern Brazil. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e475111537047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.; van Zijl, G.; Riddell, E.; van Tol, J. Model calibration using hydropedological insights to improve the simulation of internal hydrological processes using SWAT+. Hydrol. Process. 2024, 38, e15158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lee, S.; Kang, T.; Kim, Y. A Dynamically Dimensioned Search Allowing a Flexible Search Range and Its Application to Optimize Discrete Hedging Rule Curves. Water 2022, 14, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasper, E.E.; Ajibola, V.O.; Onwuka, J.C. Nonlinear regression analysis of the sorption of crystal violet and methylene blue from aqueous solutions onto an agro-waste derived activated carbon. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K. Understanding one-way ANOVA using conceptual figures. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2017, 70, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Vigneswaran, K.; Dickens, C.; Retief, H.; Andarcia, M.G. A Description of Recent Drought Prevalence in the Limpopo River Basin. 2024. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/158254 (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Botai, C.M.; Botai, J.O.; Zwane, N.N.; Hayombe, P.; Wamiti, E.K.; Makgoale, T.; Murambadoro, M.D.; Adeola, A.M.; Ncongwane, K.P.; de Wit, J.P.; et al. Hydroclimatic extremes in the Limpopo River Basin, South Africa, under changing climate. Water 2022, 12, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, T.K.; Gyedu-Ababio, T.; Mpenyana-Monyatsi, L. Pollution of Sand River by Wastewater Treatment Works in the Bushbuckridge Local Municipality, South Africa. Pollutants 2022, 2, 510–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröbel, R.; Stephens, E.C.; Gorzelak, M.A.; Thivierge, M.N.; Akhter, F.; Nyiraneza, J.; Singer, S.D.; Geddes, C.M.; Glenn, A.J.; Devillers, N.; et al. Making farming more sustainable by helping farmers to decide rather than telling them what to do. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 055033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintern, A.; McPhillips, L.; Winfrey, B.; Duncan, J.; Grady, C. Best management practices for diffuse nutrient pollution: Wicked problems across urban and agricultural watersheds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9159–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhanya, N.Z. Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrological Droughts in the Limpopo River Basin. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.; Sutter, C.; Shepherd, A.; Jarvie, H.; Wilson, H.; Elliott, J.; Liu, J.; Macrae, M. Impact of climate change on catchment nutrient dynamics: Insights from around the world. Environ. Rev. 2022, 31, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Francis, R.A.; Chadwick, M.A. Nutrient dynamics at the sediment-water interface: Influence of wastewater effluents. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 1337–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R.; Zhang, H.; Hamilton, D.; Trancoso, R.; Syktus, J. Impacts of climate change on nutrient and sediment loads from a subtropical catchment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikwambana, S.; Malaza, N.; Shale, K. Impacts of rainfall and temperature changes on smallholder agriculture in the Limpopo Province, South Africa. Water 2021, 13, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Liang, D.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z. How climate change and land-use evolution relates to the non-point source pollution in a typical watershed of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santy, S.; Mujumdar, P.; Bala, G. Potential impacts of climate and land use change on the water quality of Ganga River around the industrialized Kanpur region. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Tao, F.; Chen, Y. Effects of climate change, crop planting structure, and agricultural management on runoff, sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus losses in the Hai-River Basin since the 1980s. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelnour, M.A.; Tank, J.L.; Hamlet, A.F.; Bertassello, L.E.; Ren, D.; Bolster, D. A SWAT model depicts the impact of land use change on hydrology, nutrient, and sediment loads in a Lake Michigan watershed. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveca, P.S.L.; Abi, A.; Stigter, T.Y.; Lukas, E.; Fourie, F. Assessing groundwater dynamics and hydrological processes in the sand river deposits of the Limpopo River, Mozambique. Front. Water 2022, 3, 731642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrea, S.; Chea, R.; Tudesque, L. Spatial patterns of benthic diatom community structure in the largest northwestern river of Cambodia (Sangker River). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2024, 425, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Ren, H.; Qin, J.; Wang, M.; Shi, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, Y. Analysis of pollutant dispersion patterns in rivers under different rainfall based on an integrated water-land model. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Du, S.; Li, M.; Zhao, R.; Mou, Q.; Min, X.; Xu, W. Inter-and intra-annual fluctuations and attribution analysis of runoff and sediment transport in the middle and lower Yangtze River. Hydrol. Process. 2024, 38, e15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Meng, S.; Yang, F.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Dong, Q.; Wang, J. Warming causes variability in SOM decomposition in N-and P-fertiliser-treated soil in a subtropical coniferous forest. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhao, J.; Peng, W.; Chen, Q.; Ma, B. Non-point source pollution simulation and best management practices analysis based on control units in Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

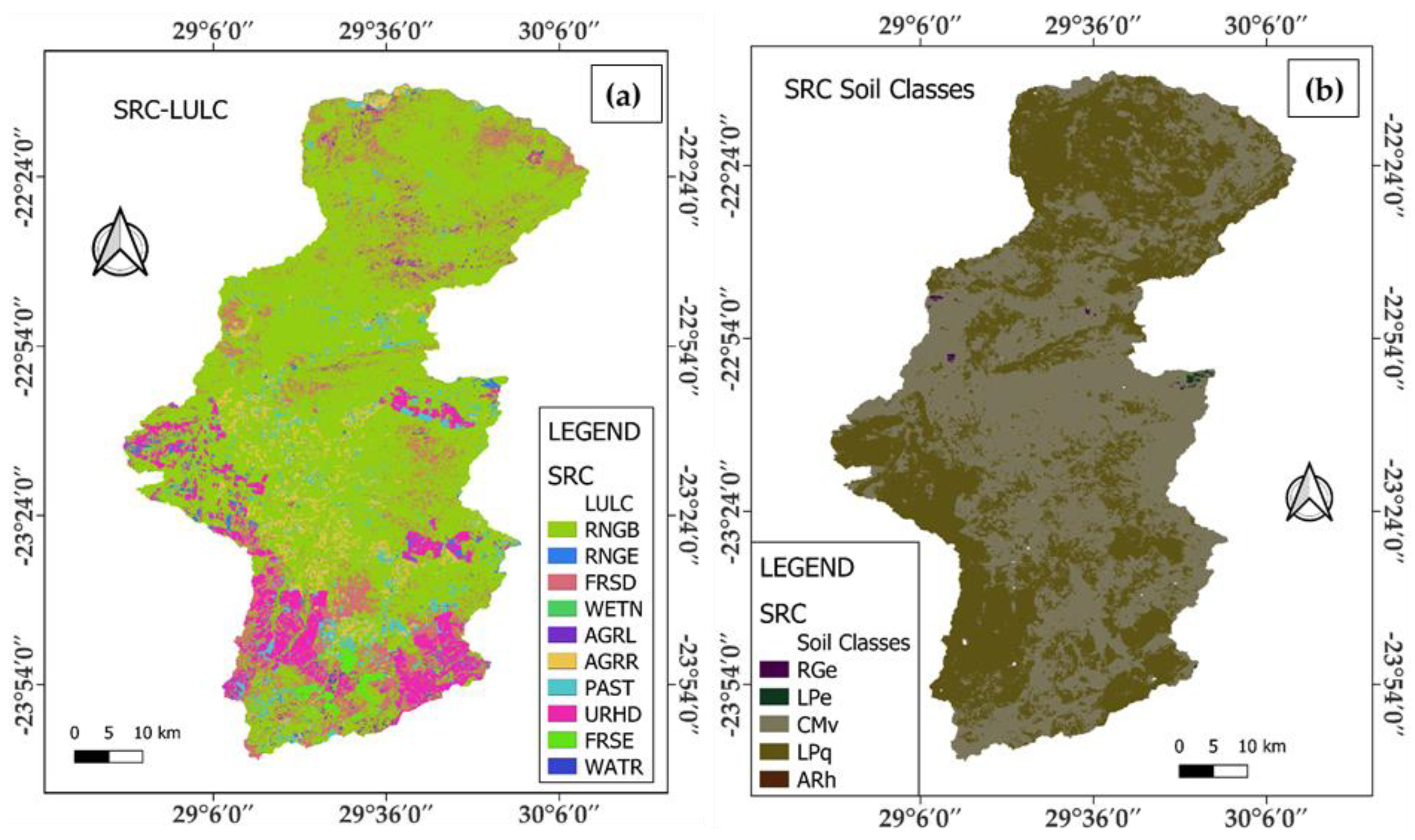






| SANLC LULC Classes | SWAT+ LULC Classes | SWAT+ LULC Description |
|---|---|---|
| Grasslands | RNGE | Grasslands/Herbaceous |
| Shrubland | RNGB | Range Shrubland |
| Buildings (residential, industries, and mines) | URHD | Urban High Density |
| Cultivated land | AGRL | Generic |
| Indigenous forest | FRSE | Evergreen Forest |
| Waterbodies | WATR | Water |
| Pivot irrigated land | AGRR | Row Crops |
| Non-pivot land | PAST | Pasture |
| Planted forest | FRSD | Deciduous Forest |
| Wetlands | WETN | Emergent Wetlands |
| Soil Texture | Name | Soil Code |
|---|---|---|
| Loamy Clay | Lithic Leptosols | LPq |
| Sandy Clay–Loam | Vertic Cambisols | CMv |
| Clay | Calcaric Regosols | RGe |
| Loam | Eutric Leptosols | LPe |
| Loamy Sand | Haplic Arenosols | ARh |
| Variable | Parameter | Definition | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | usle_p | Universal soil loss equation support practice factor | 0.93 |
| usle_k | Universal soil loss equation soil erodibility factor | 0.91 | |
| rock | Rock fragment content (total weight %) | 0.80 | |
| slope | Average slope steepness in HRU (m/m) | 0.69 | |
| TIN (NO3−, NO2−, and NH4+) | anion-excl | Fraction of porosity from which anions are excluded | 0.89 |
| nperco | Nitrogen percolation coefficient | 0.77 | |
| biomix | Biological mixing efficient | 0.12 | |
| TIP | bd | Moist bulk density (Mg/m3) | 0.71 |
| pperco | Phosphorus percolation coefficient | 0.46 | |
| phoskd | Phosphate soil partitioning coefficient | 0.28 |
| Parameters | Object | Change Type | Min-Value | Calibrated Value | Max-Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anion-excl | sol | Percent | 0.1 | 0.69 | 0.90 | |
| Nperco | bsn | Percent | 0 | 0.52 | 1 | |
| Biomix | hru | Percent | 0 | 0.23 | 1 | |
| Bd | sol | Percent | 0.90 | 1.60 | 2.50 | Mg/m3 |
| Pperco | bsn | Percent | 10 | 11.40 | 17.50 | |
| Phoskd | bsn | Percent | 100 | 147 | 200 | |
| usle_p | hru | Percent | 0 | 0.38 | 1 | |
| Rock | sol | Percent | 0 | 48 | 100 | % |
| Slope | hru | Percent | 0.0001 | 0.23 | 0.90 | m/m |
| usle_k | sol | Percent | 0 | 0.51 | 0.65 |
| Variables | R2 | Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > F | p-Value Signification Codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | 0.95 | Model | 1 | 9770 | 9770 | 200 | <0.0001 | *** |
| vs. | Error | 10 | 489 | 49 | ||||
| Sediment | Corrected Total | 11 | 10,260 | |||||
| Temperature | 0.68 | Model | 1 | 7020 | 7020 | 22 | 0.001 | *** |
| vs. | Error | 10 | 3240 | 324 | ||||
| Sediment | Corrected Total | 11 | 10,260 |
| Variables | R2 | Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > F | p-Value Signification Codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | 0.91 | Model | 1 | 229,155 | 229,155 | 105 | <0.0001 | *** |
| vs. | Error | 10 | 21,768 | 2177 | ||||
| TIN | Corrected Total | 11 | 250,923 | |||||
| Temperature | 0.59 | Model | 1 | 146,866 | 146,866 | 14 | 0.004 | ** |
| vs. | Error | 10 | 104,057 | 10,406 | ||||
| TIN | Corrected Total | 11 | 250,923 |
| Variables | R2 | Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > F | p-Value Signification Codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | Model | 1 | 30,388 | 30,388 | 83 | <0.0001 | *** | |
| vs. | 0.89 | Error | 10 | 3658 | 366 | |||
| TIP | Corrected Total | 11 | 34,046 | |||||
| Temperature | Model | 1 | 24,215 | 24,215 | 25 | 0.001 | *** | |
| vs. | 0.71 | Error | 10 | 9831 | 983 | |||
| TIP | Corrected Total | 11 | 34,046 |
| Variables | R2 | Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > F | p-Value Signification Codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | Model | 1 | 545 | 545 | 48 | <0.0001 | *** | |
| vs. | 0.63 | Error | 28 | 316 | 11 | |||
| Sediment | Corrected Total | 29 | 861 | |||||
| Temperature | Model | 1 | 195 | 195 | 8 | 0.008 | ** | |
| vs. | 0.23 | Error | 28 | 666 | 24 | |||
| Sediment | Corrected Total | 29 | 861 |
| Variables | R2 | Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > F | p-ValuesSignification Codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | Model | 1 | 270,052 | 270,052 | 77 | <0.0001 | *** | |
| vs. | 0.73 | Error | 28 | 97,848 | 3495 | |||
| TIN | Corrected Total | 29 | 367,900 | |||||
| Temperature | Model | 1 | 65,367 | 65,367 | 6 | 0.020 | * | |
| vs. | 0.19 | Error | 28 | 302,533 | 10,805 | |||
| TIN | Corrected Total | 29 | 367,900 |
| Variables | R2 | Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > F | p-ValuesSignification Codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | Model | 1 | 2788 | 2788 | 34 | <0.0001 | *** | |
| vs. | 0.55 | Error | 28 | 2301 | 82 | |||
| TIP | Corrected Total | 29 | 5089 | |||||
| Temperature | Model | 1 | 258 | 258 | 1 | 0.232 | ° | |
| vs. | 0.05 | Error | 28 | 4832 | 173 | |||
| TIP | Corrected Total | 29 | 5089 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuene, T.A.; Akanbi, R.T.; Chikoore, H. The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution in the Sand River Catchment, Limpopo, South Africa. Water 2025, 17, 1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121818
Chuene TA, Akanbi RT, Chikoore H. The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution in the Sand River Catchment, Limpopo, South Africa. Water. 2025; 17(12):1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121818
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuene, Tlhogonolofatso A., Remilekun T. Akanbi, and Hector Chikoore. 2025. "The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution in the Sand River Catchment, Limpopo, South Africa" Water 17, no. 12: 1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121818
APA StyleChuene, T. A., Akanbi, R. T., & Chikoore, H. (2025). The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution in the Sand River Catchment, Limpopo, South Africa. Water, 17(12), 1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121818







