Unsteady Flow Analysis Inside an Electric Submersible Pump with Impeller Blade Perforation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methodology
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Computational Model
2.3. Mesh Independence Verification
2.4. Numerical Simulation Boundary Conditions
3. Experimental Testing
3.1. Experimental Apparatus
3.2. Experimental Validation
4. Results and Discussions
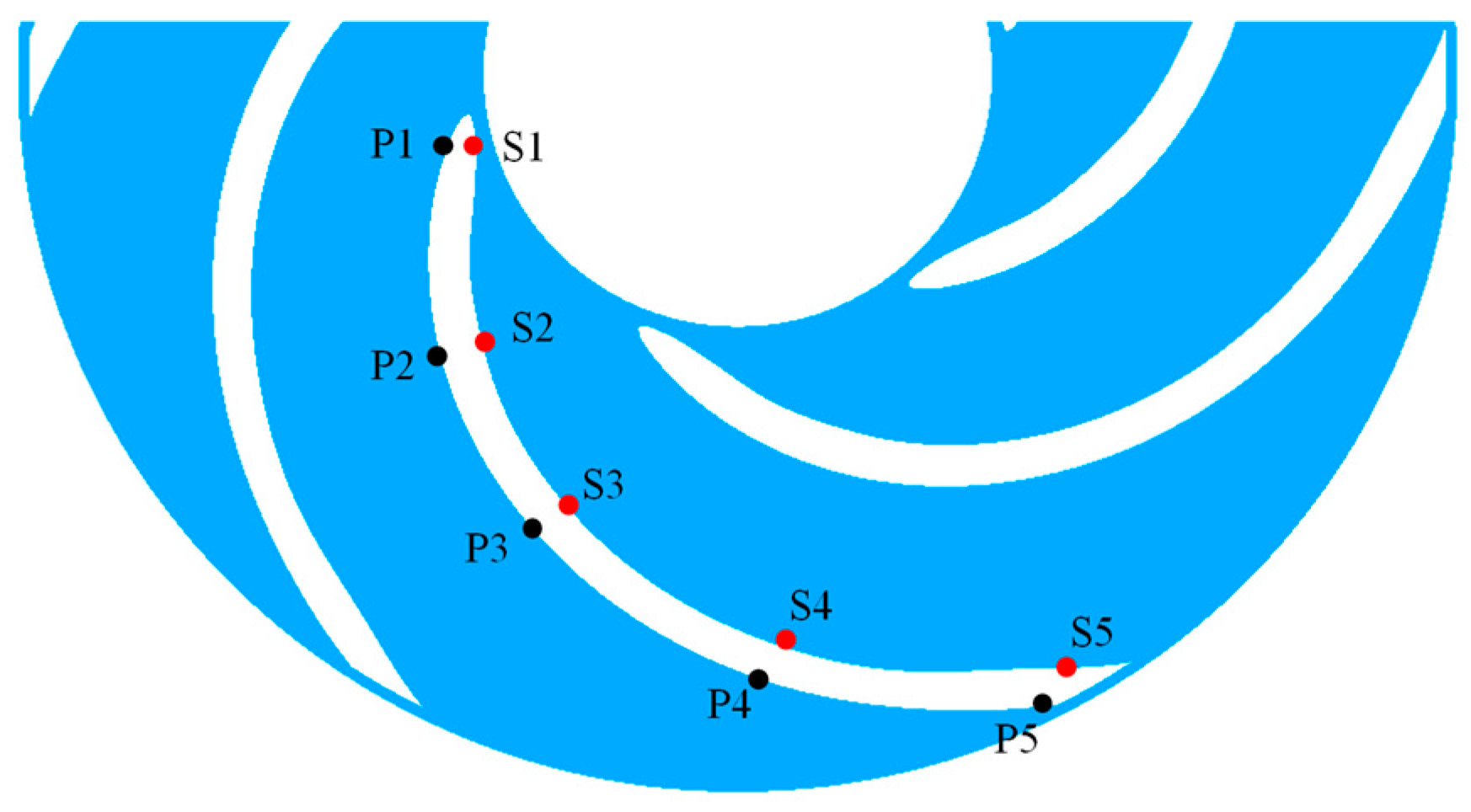
4.1. Pressure Fluctuation Analysis
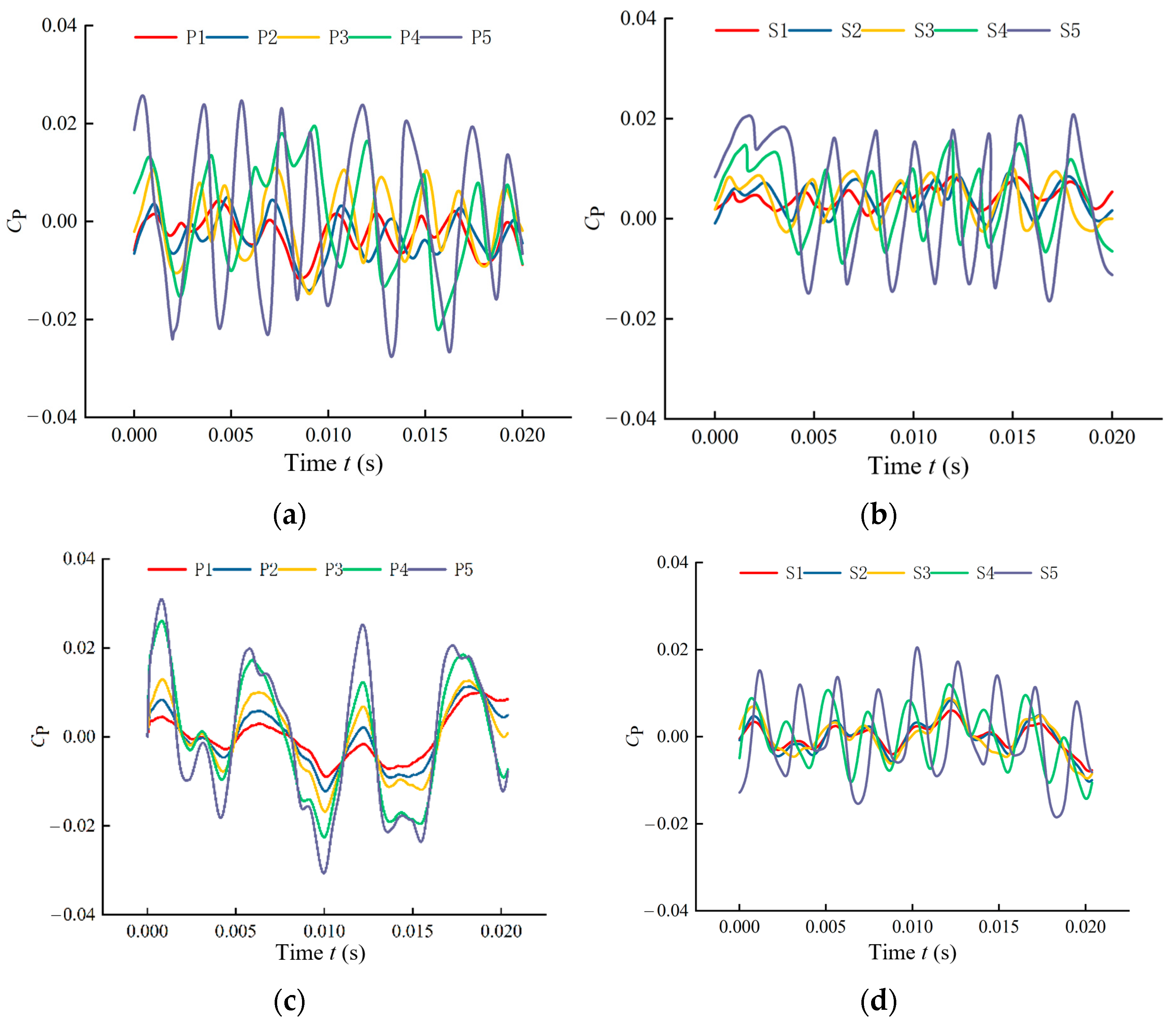
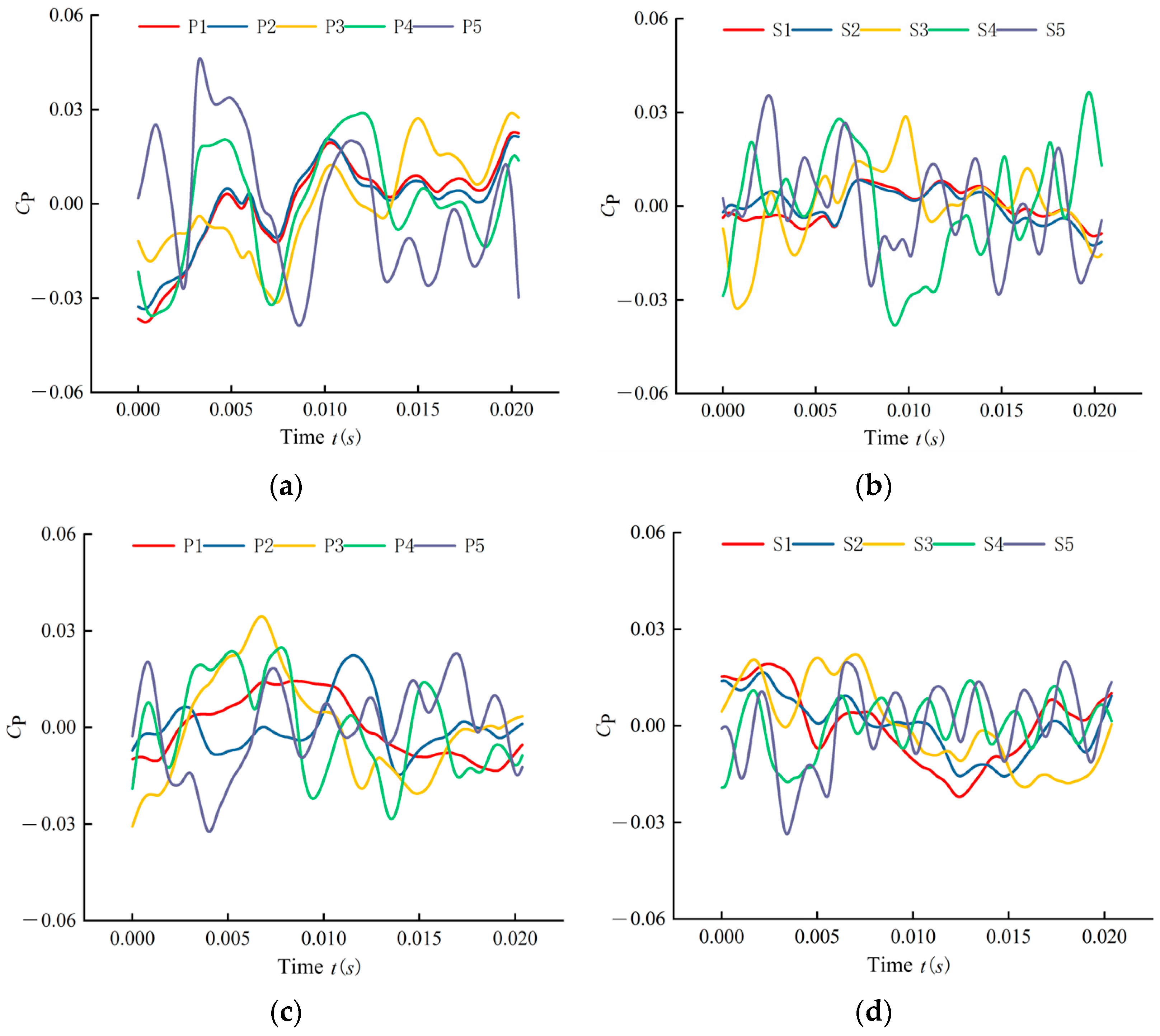
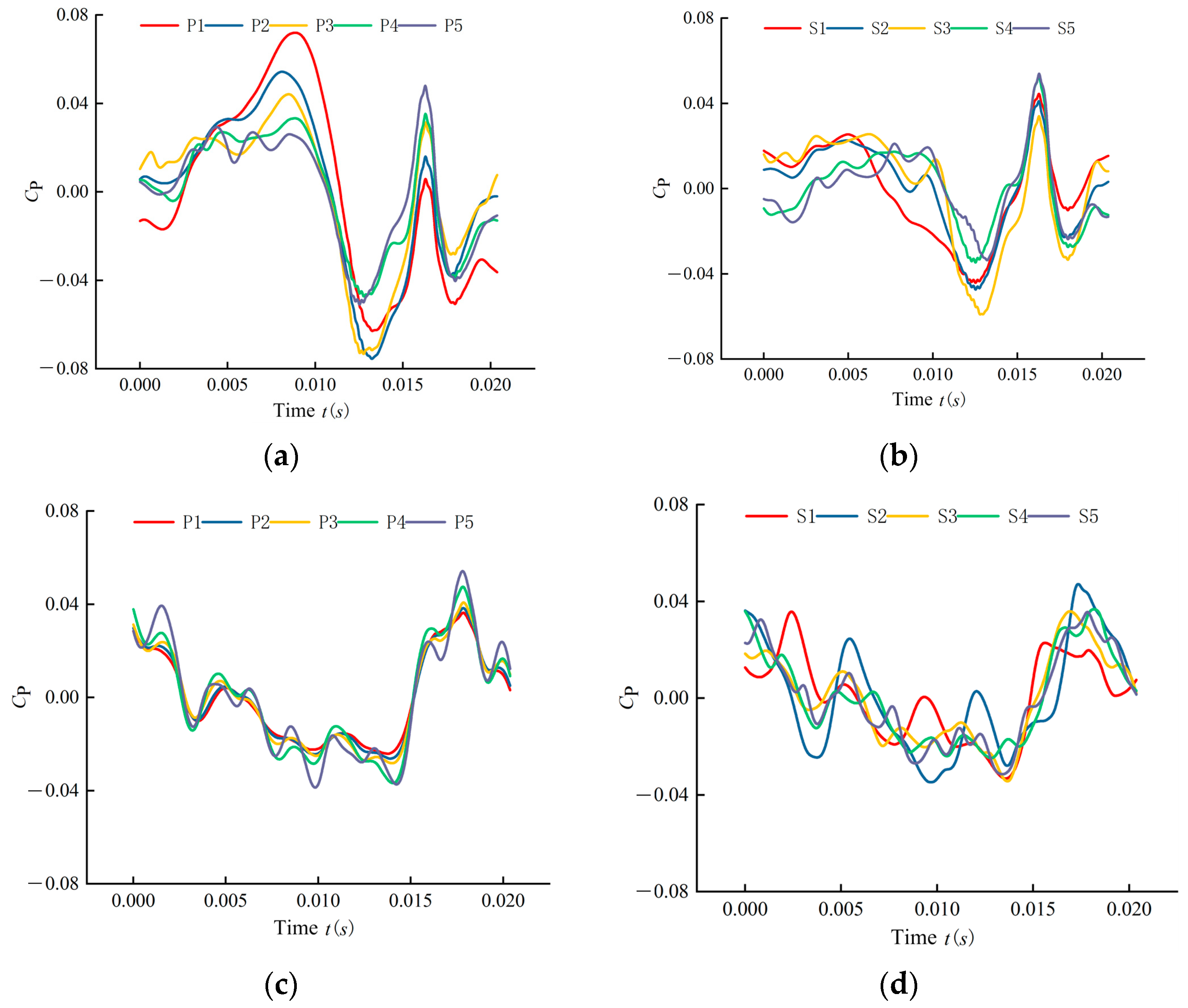
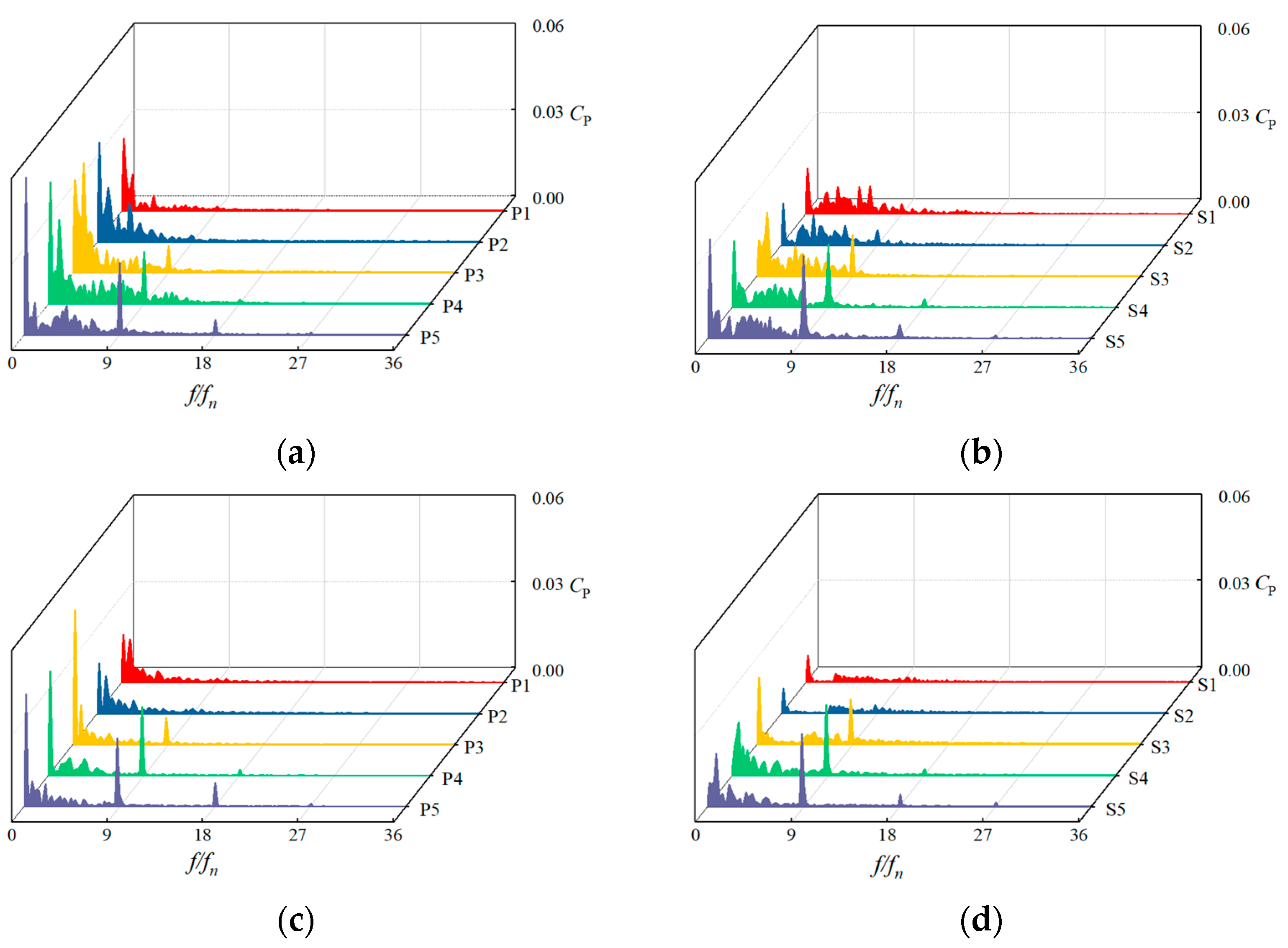
4.1.1. Time-Domain Analysis
4.1.2. Frequency-Domain Analysis
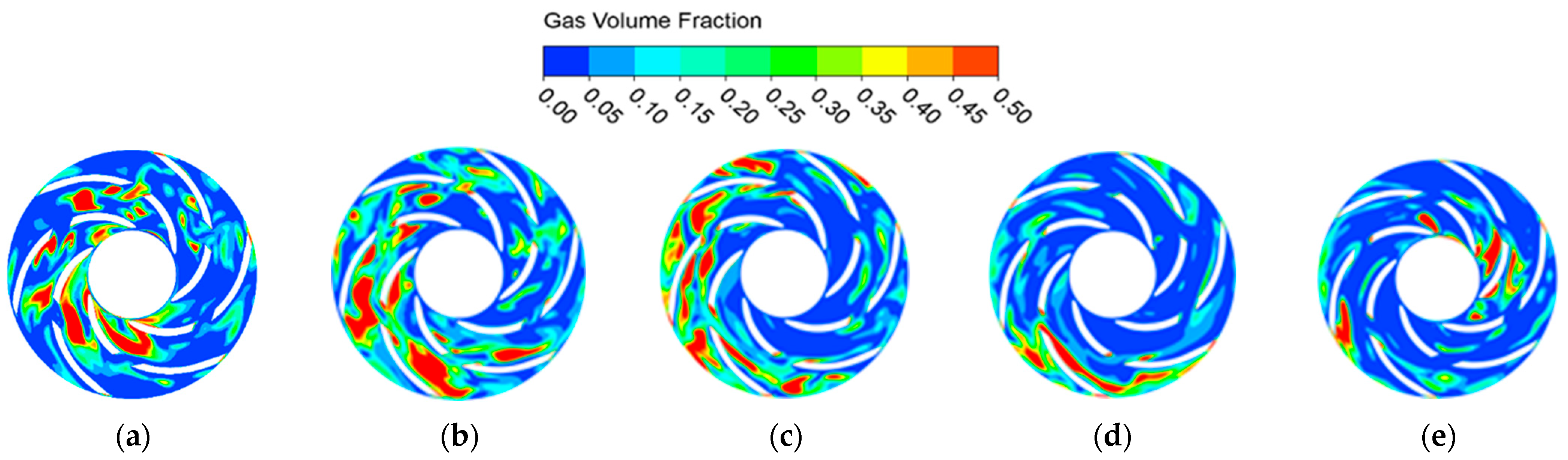
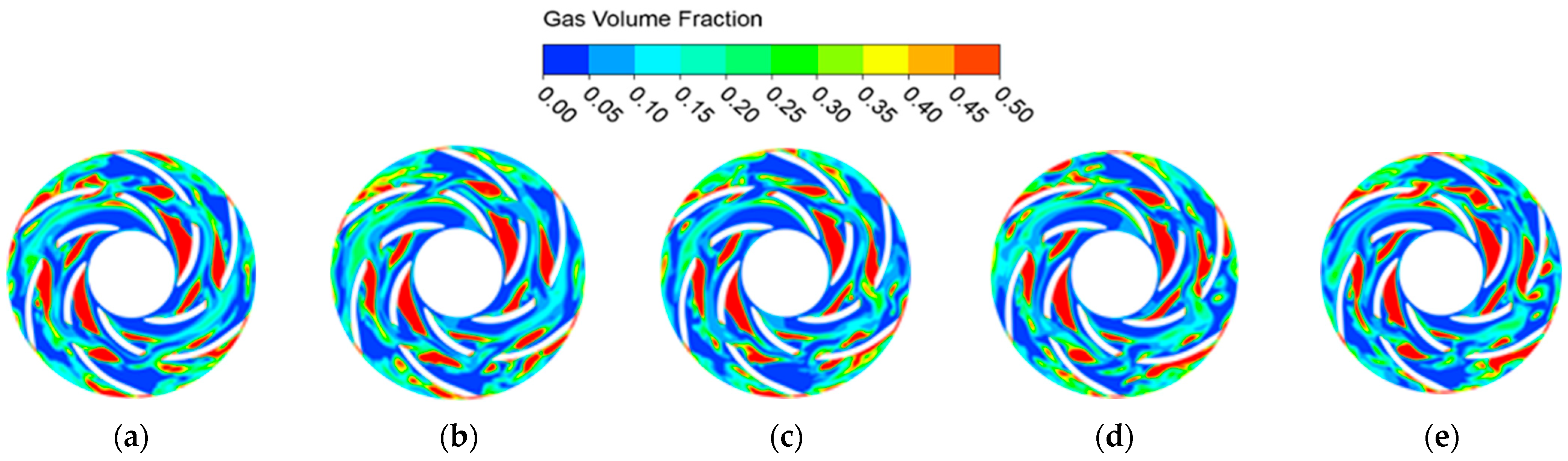
4.2. Unsteady Analysis of the Internal Flow Field
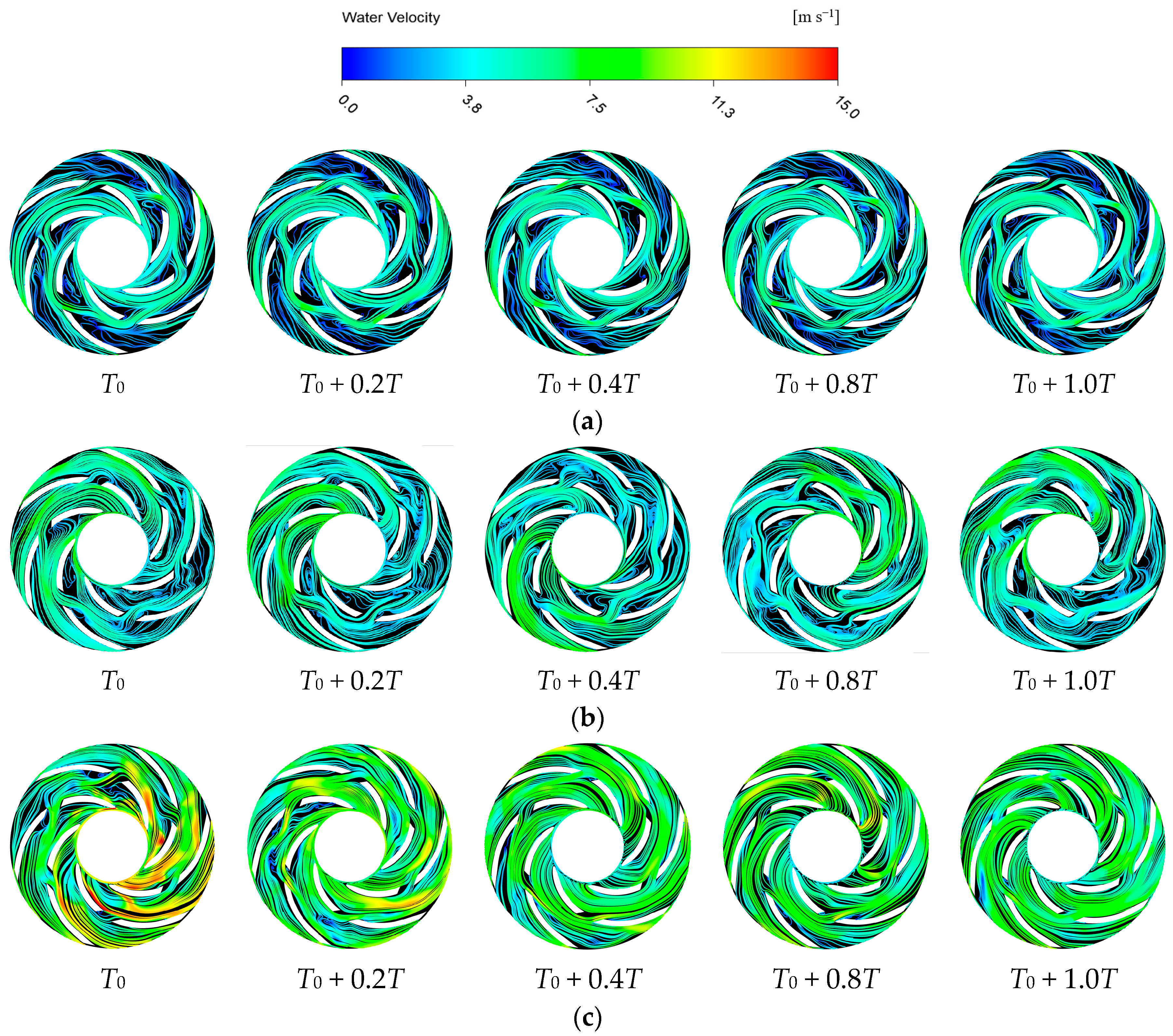
4.3. Unsteady Distribution of Liquid Phase Streamlines
4.4. Unsteady Distribution of Liquid Phase Turbulent Entropy Generation Dissipation Rate
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- This study analyzes and compares the pressure fluctuations at monitoring points on the suction and pressure sides of the impeller blades in open-hole and closed-hole ESPs under three different flow rates. The results show that at off-design flow rates of 0.6 Qdes and 1.4 Qdes, blade perforation reduces the fluctuation amplitude and enhances periodicity, with the maximum fluctuation amplitude on the pressure side decreasing by approximately 34.4% and 42.9%, respectively, and reduces the fluctuations and amplitudes in the low-frequency range. However, at the design flow rate of 1.0 Qdes, blade perforation increases the fluctuation amplitude and causes more chaotic fluctuations in the low-frequency range, with the maximum pressure side fluctuation amplitude increasing by 8.3%.
- (2)
- The study of instantaneous gas phase distribution in the open-channel ESP under three flow conditions reveals that, at the design flow rate, gas concentrates in the middle of the flow passages. At low flow rates, a high gas content region forms near the inlet, with significant gas–liquid separation occurring in the midsection. At high flow rates, the gas accumulation zone shifts from the inlet and midsection toward the outlet over a single cycle.
- (3)
- The study of instantaneous streamline distribution in an open-channel ESP under three flow rates reveals that the effective flow area of the impeller passages is closely related to the degree of gas accumulation. At low and design flow conditions, large-scale low velocity recirculation vortices form near the impeller inlet. However, under high flow conditions, these recirculation vortices disappear, significantly improving the backflow phenomenon.
- (4)
- The analysis of turbulent entropy generation dissipation rates in the open-channel ESP under three flow conditions shows that high entropy generation regions typically coincide with areas of high gas volume fraction. At low flow rates, entropy generation is mainly concentrated near the inlet and midsection of the blade suction side, with little variation over time. Under the design flow rate, high entropy generation appears at the inlet and midsection, with the distribution of high dissipation zones remaining relatively stable across time. At high flow rates, the high entropy generation region shifts progressively from the impeller inlet to the outlet over time.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H. Mechanistic modeling of gas effect on multi–stage Electrical Submersible Pump (ESP) performance with experimental validation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 252, 117288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Fu, J.; Bai, L.; Chen, J. Numerical and experimental study of viscosity effects on an electric submersible pump. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 035162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Bai, L.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, L.; Shi, W.; Agarwal, R. Inter–stage energy characteristics of electrical submersible pump under gassy conditions. Energy 2022, 256, 124624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, H.; Merey, S. Design of Electrical Submersible Pump system in geothermal wells: A case study from West Anatolia, Turkey. Energy 2021, 230, 120891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, N.A.V.; Biazussi, J.L.; Verde, W.M.; Perles, C.E.; de Castro, M.S.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental investigation on the performance of Electrical Submersible Pump (ESP) operating with unstable water/oil emulsions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 197, 107900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, L.; Liang, A.; Yao, Z. Energy performance and unsteady gas-liquid flow characteristics of a multiphase rotodynamic pump: An experiment. Appl. Energy 2024, 375, 124112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, H. A review of trends in the use of sewage irrigation technology from the livestock and poultry breeding industries for farmlands. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Effect of cavitation on energy conversion characteristics of a multiphase pump. Renew. Energy 2021, 177, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.A.; Asuaje, M.; Pereyra, E.; Ratkovich, N. Analysis of two–phase gas–liquid flow in an Electric Submersible Pump using A CFD approach. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 233, 212510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Effect of the inlet gas void fraction on the tip leakage vortex in a multiphase pump. Renew. Energy 2020, 150, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Yuan, J.; Deng, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Si, Q.; Buttar, N.A. Research progress and prospects of multi–stage centrifugal pump capability for handling gas–liquid multiphase flow: Comparison and empirical model validation. Energies 2021, 14, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X. Application of entropy production theory to hydro-turbine hydraulic analysis. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, W.; Biazussi, J.; Sassim, N.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental studyof gas-liquid two-phase flow patterns within centrifugal pumps impellers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2017, 85, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Luo, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Feng, J. Influence of inlet gas volume fraction on energy conversion characteristics of multistage electric submersible pump. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 109164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Minemura, K. Effects of entrained air on the performance of a centrifugal pump: 1st report, performance and flow conditions. Bull. JSME 1974, 17, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Minemura, K. Effects of entrained air on the performance of centrifugal pumps: 2nd report, effects of number of blades. Bull. JSME 1974, 17, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, L. Visualization and Modeling of Multiphase Performance Inside an Electrical Submersible Pump. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cubas, J.; Stel, H.; Ofuchi, E.; Marcelino Neto, M.A.; Morales, R.E.M. Visualization of two–phase gas–liquid flow in a radial centrifugal pump with a vaned diffuser. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 187, 106848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Xie, H.; Feng, J.; Ge, Z.; Zhu, G. Influence of the balance hole on the performance of a gas–liquid two–phase centrifugal pump. Ocean Eng. 2022, 244, 110316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Deng, F.; Wang, C.; Si, Q. Effect of Short Blade Circumferential Position Arrangement on Gas–Liquid Two–Phase Flow Performance of Centrifugal Pump. Processes 2020, 8, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, X. Phase distribution in the tip clearance of a multiphase pump at multiple operating points and its effect on the pressure fluctuation intensity. Processes 2021, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B. Effect of tip clearance on flow behaviors in a multiphase pump. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2022, 40, 332–337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Zhu, B.; Ma, Z. Analysis of phase interaction and gas holdup in a multistage multiphase rotodynamic pump based on a modified Euler two–fluid model. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Ruan, Y.; Wu, B.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, S. Performance evaluation of Hydrodynamic Vortex Separator at different hydraulic retention times applied in Recirculating Biofloc Technology system. Trans. ASABE 2017, 60, 1737–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Emam, M.; Zhou, L.; Omara, A. Predicting the performance of aero-type cyclone separators with different spiral inlets under macroscopic bio-granular flow using CFD-DEM modelling. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 233, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F. Two–equation eddy–viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, L.; Prado, G. Experimental visualization of two-phase flow inside an electrical submersible pump stage. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2009, 133, 042901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J. Flow pattern recognition inside a rotodynamic multiphase pump via developed entropy production diagnostic model. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Li, D.; Kang, C. Visualization of the evolution of bubbles in the spray sheet discharged from the air-induction nozzle. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Dou, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhai, C. Design and Experiment of a Breakpoint Continuous Spraying System for Automatic-Guidance Boom Sprayers. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hang, J.; Bai, L.; Krzemianowski, Z.; El-Emam, M.A.; Yasser, E.; Agarwal, R. Application of entropy production theory for energy losses and other investigation in pumps and turbines: A review. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 119211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Hui, X.; Xing, S. Numerical simulation of the effect of varying dispersion tooth insertion depth on the jet breakup and hydraulic performance. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 239, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Rakibuzzaman, M.; Agarwal, R.; Zhou, L. Numerical and experimental investigations of a double-suction pump with a middle spacer and a staggered impeller. Irrig. Drain. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Han, L.; Wei, X.; Qin, D. Entropy production analysis of hysteresis characteristic of a pump–turbine model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 149, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

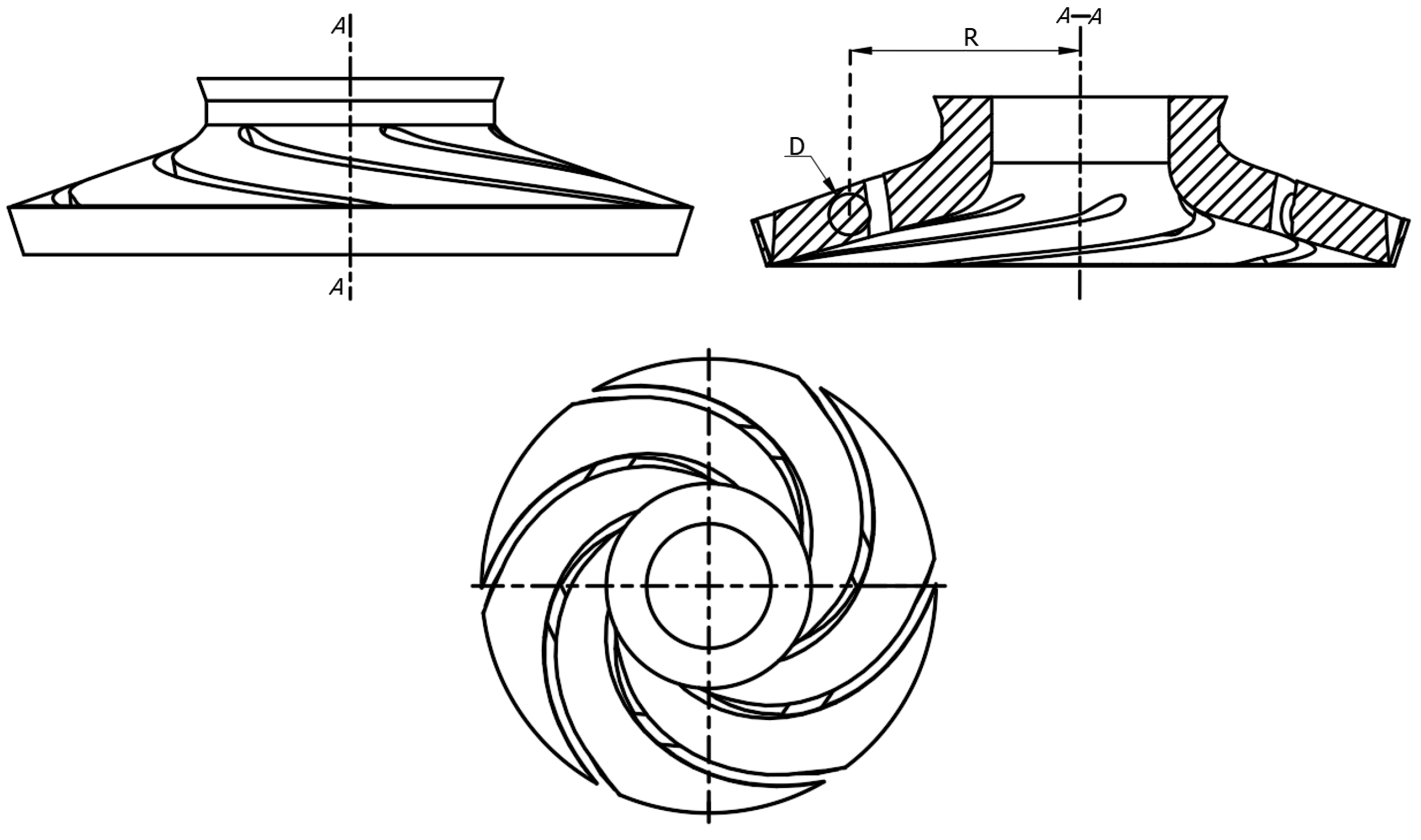
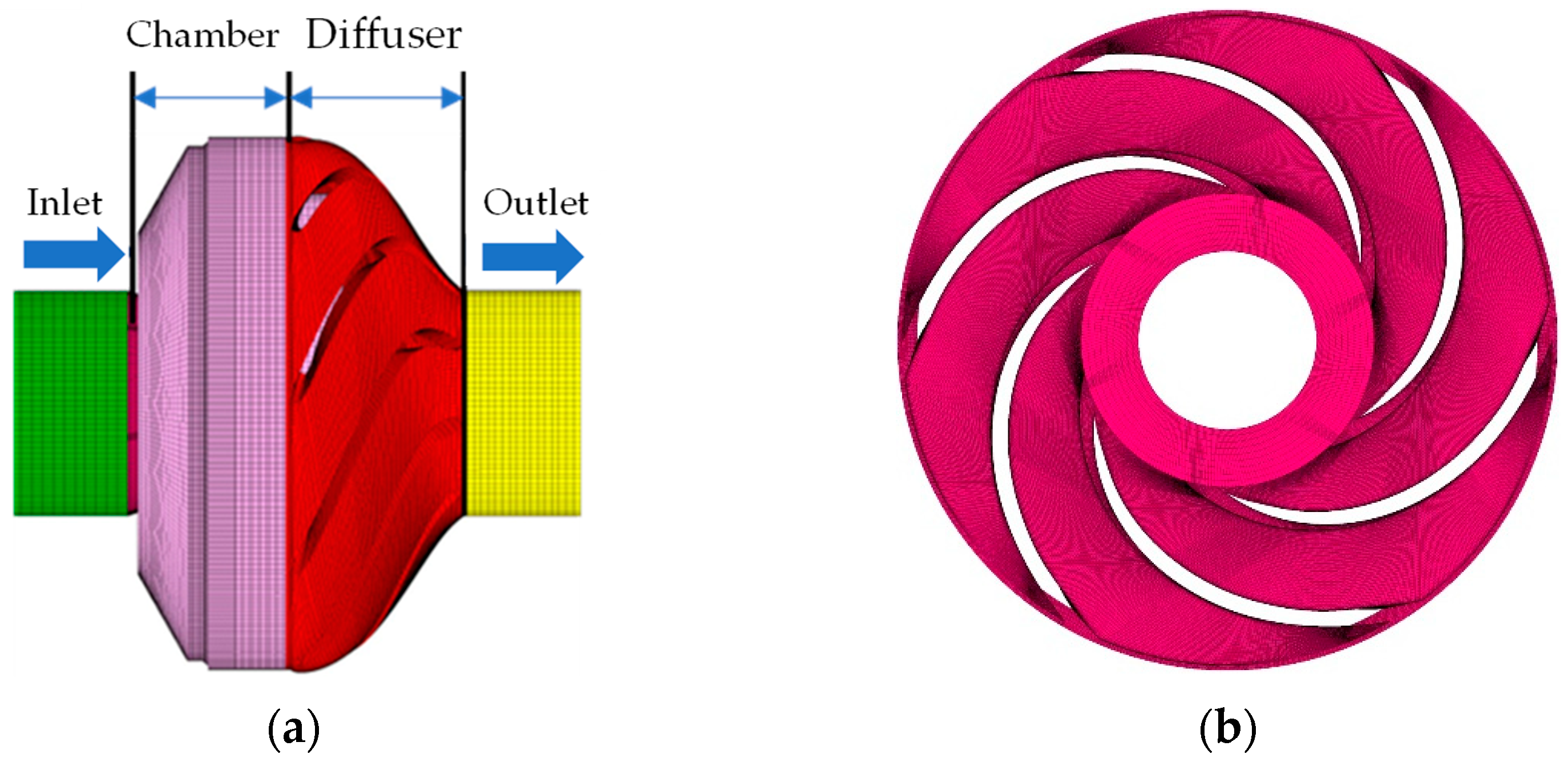

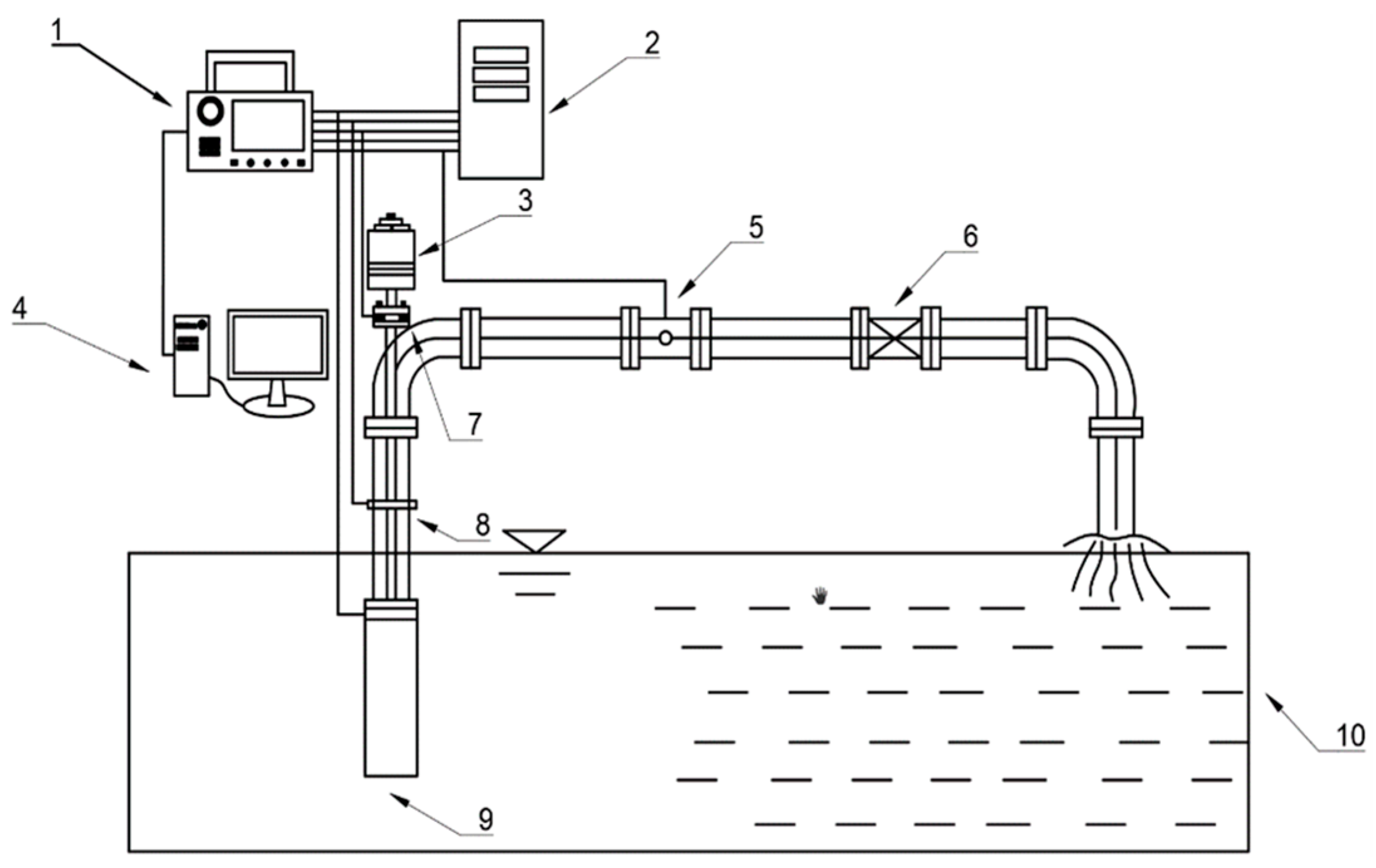
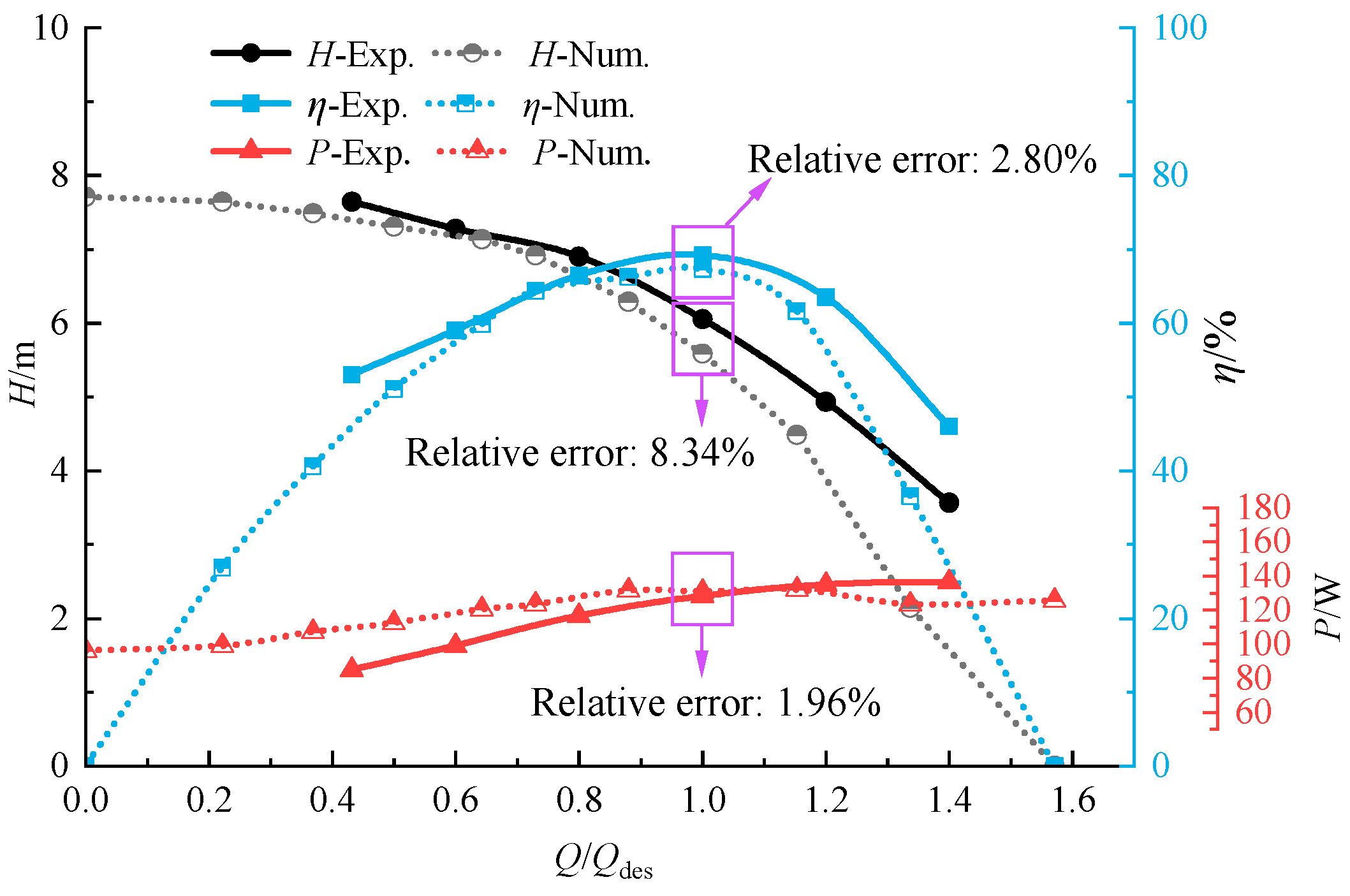




| Impeller | Diffuser | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet inner diameter Dinph1/mm | 22 | Inlet inner diameter Ddifh1/mm | 72 |
| Inlet outer diameter Dinps1/mm | 34 | Inlet outer diameter Ddifs1/mm | 84 |
| Outlet inner Diameter Dinph2/mm | 75 | Outlet inner Diameter Ddifh2/mm | 22 |
| Outlet outer diameter Dinps2/mm | 79 | Outlet outer diameter Ddifs2/mm | 34 |
| Number of blades Zimp/blade | 6 | Number of blades Zdif/blade | 9 |
| Inlet setting angle βimp1/° | 26 | Inlet setting angle βdif1/° | 56 |
| Outlet setting angle βimp2/° | 19 | Outlet setting angle βdif2/° | 37 |
| Wrap angle φimp/° | 62 | Wrap angle φdif/° | 42 |
| Setting Items | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Fluid medium | Liquid phase: water, density ρ = 997 kg/m3 |
| Gas phase: air, density ρ = 1.185 kg/m3 | |
| Inlet boundary conditions | Inlet pressure: atmospheric pressure atm |
| Given the inlet gas phase volume fraction, IGVF | |
| Outlet boundary conditions | Mass flow rate, kg/s |
| Rotational speed | 2917 r/min |
| Convergence precision | 1.0 × 10−4 |
| Turbulence model | Liquid phase: SST k–ω |
| Gas phase: dispersed phase zero equation model |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Dai, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L. Unsteady Flow Analysis Inside an Electric Submersible Pump with Impeller Blade Perforation. Water 2025, 17, 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121790
Li S, Zhang Y, Bai J, Dai J, Zhang H, Wang J, Zhou L. Unsteady Flow Analysis Inside an Electric Submersible Pump with Impeller Blade Perforation. Water. 2025; 17(12):1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121790
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Siyuan, Yang Zhang, Jianhua Bai, Jinming Dai, Hua Zhang, Jian Wang, and Ling Zhou. 2025. "Unsteady Flow Analysis Inside an Electric Submersible Pump with Impeller Blade Perforation" Water 17, no. 12: 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121790
APA StyleLi, S., Zhang, Y., Bai, J., Dai, J., Zhang, H., Wang, J., & Zhou, L. (2025). Unsteady Flow Analysis Inside an Electric Submersible Pump with Impeller Blade Perforation. Water, 17(12), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121790






