Adsorptive Removal of Reactive Black 5 by Longan Peel-Derived Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of LPAC
2.2. LPAC Characterization Study
2.3. Adsorption Study of RB5 onto LPAC
2.4. Kinesitcs Study
2.5. Isotherm Study
2.6. Recyclability Study
2.7. Modeling for the Adsorption Process of RB5 onto LPAC
2.7.1. Multiple Linear Regression
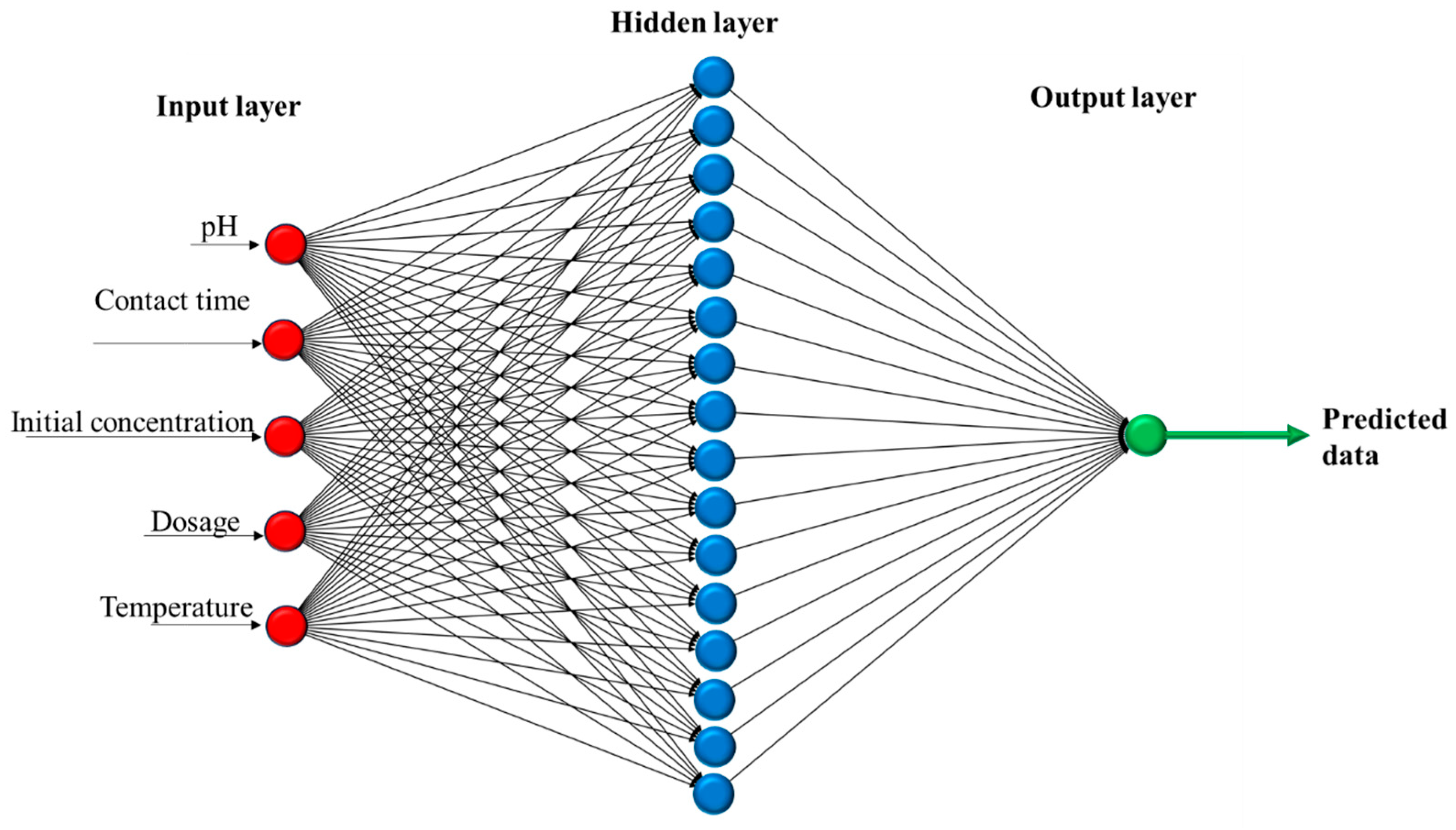
2.7.2. Artificial Neural Network
3. Results and Discussion
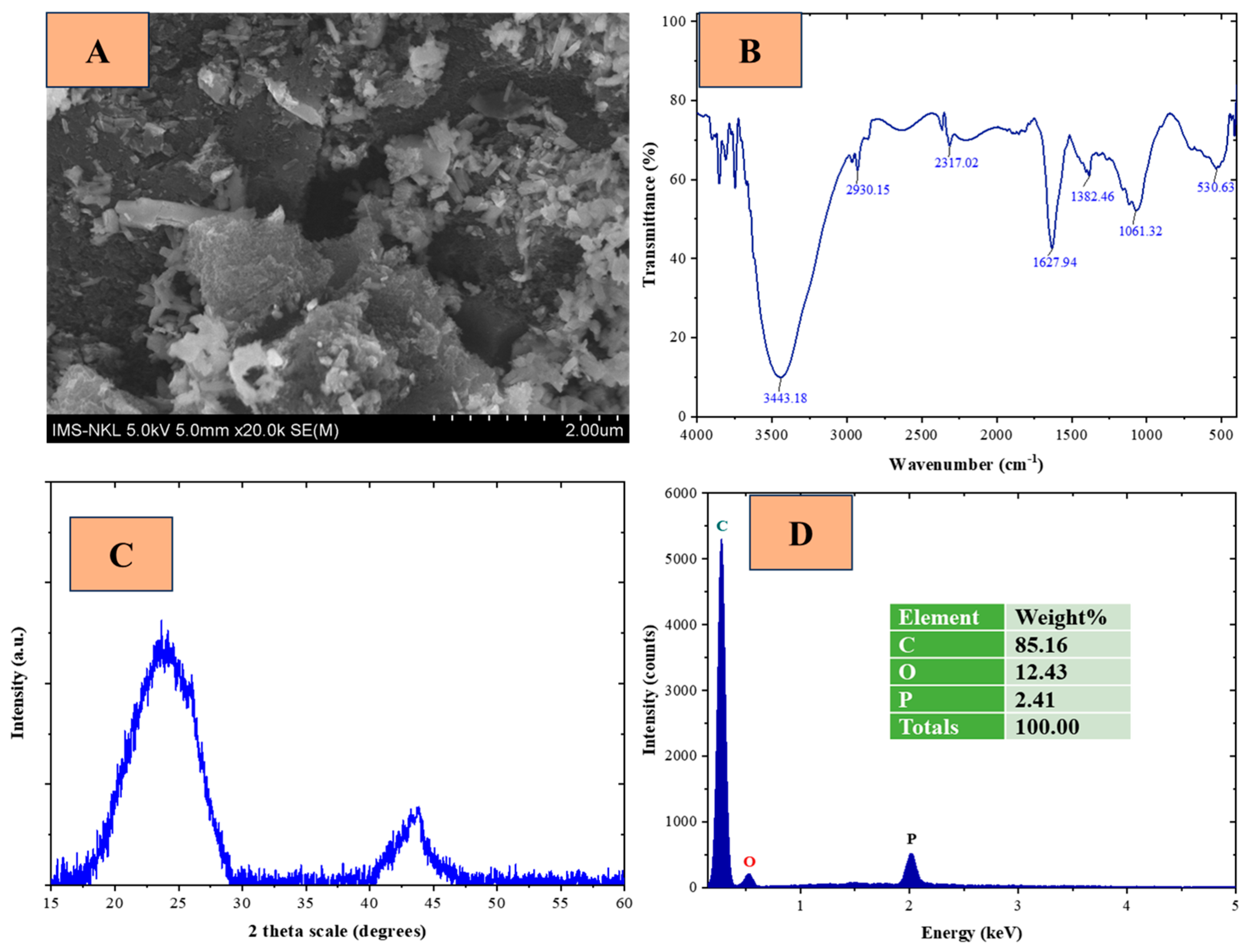
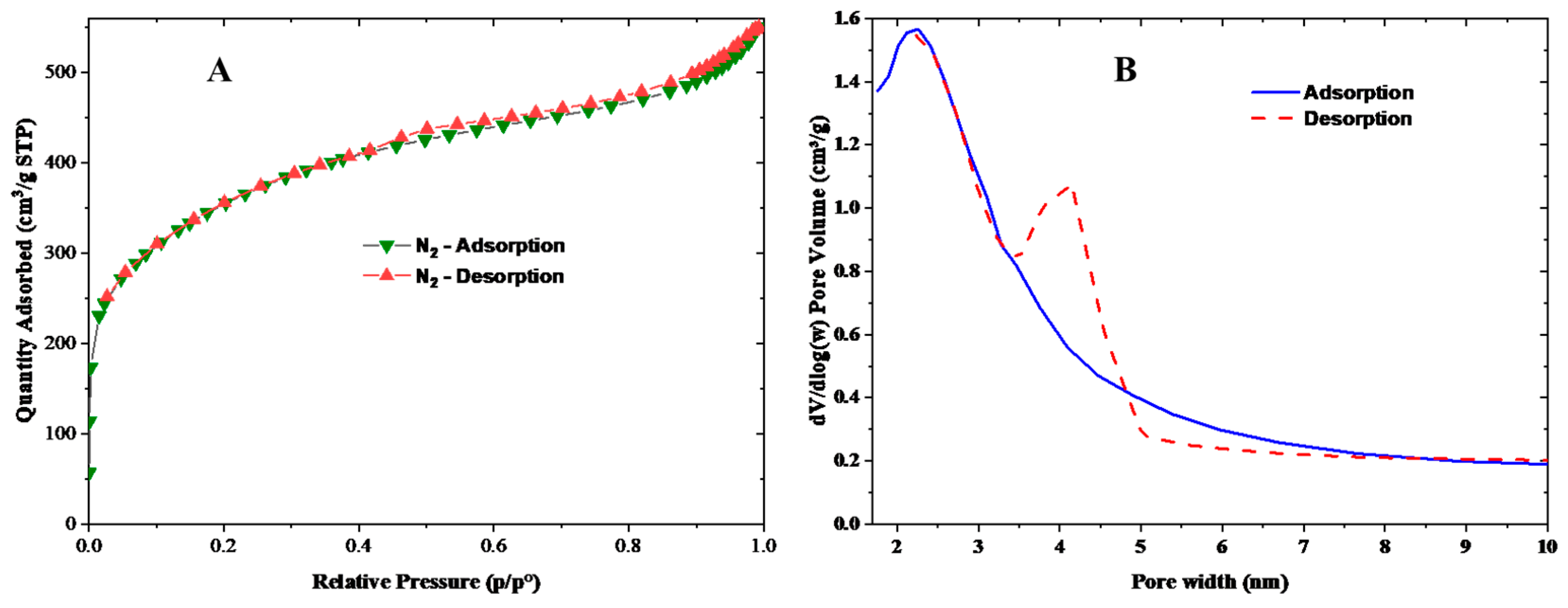
3.1. Chacterization of LPAC
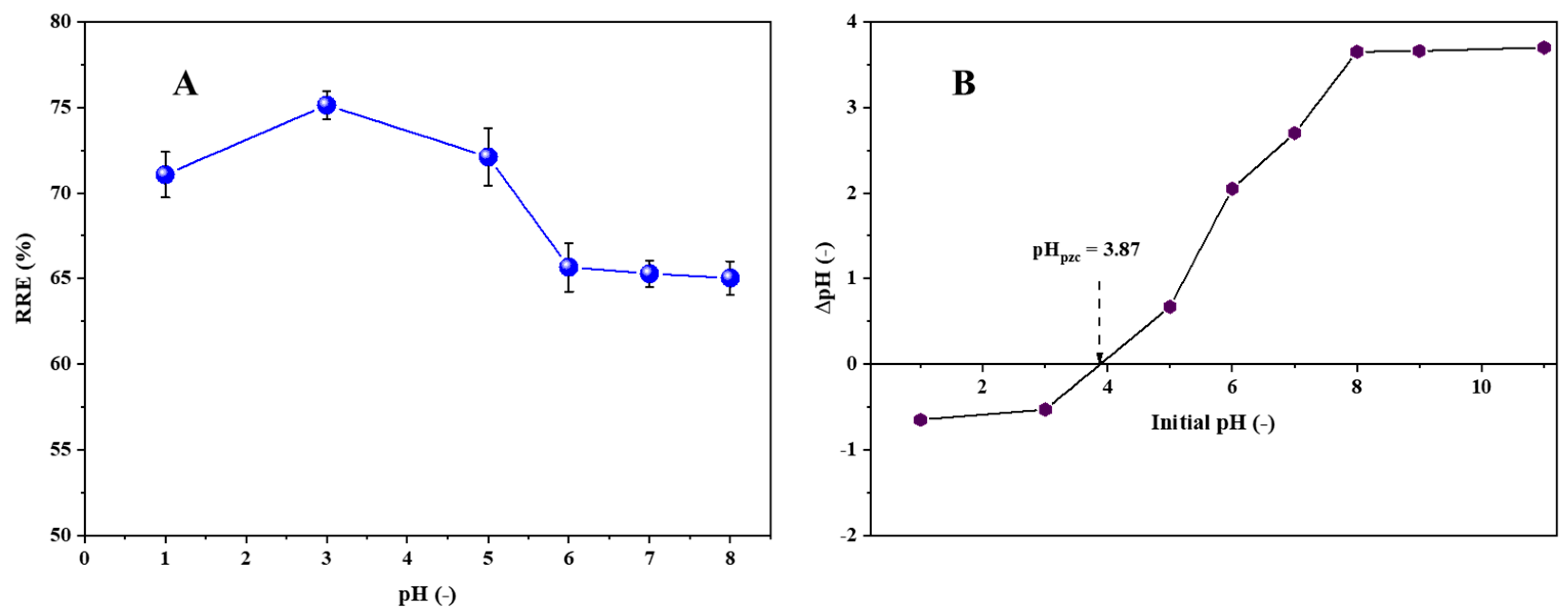
3.2. Effect of pH on the RRE of LPAC
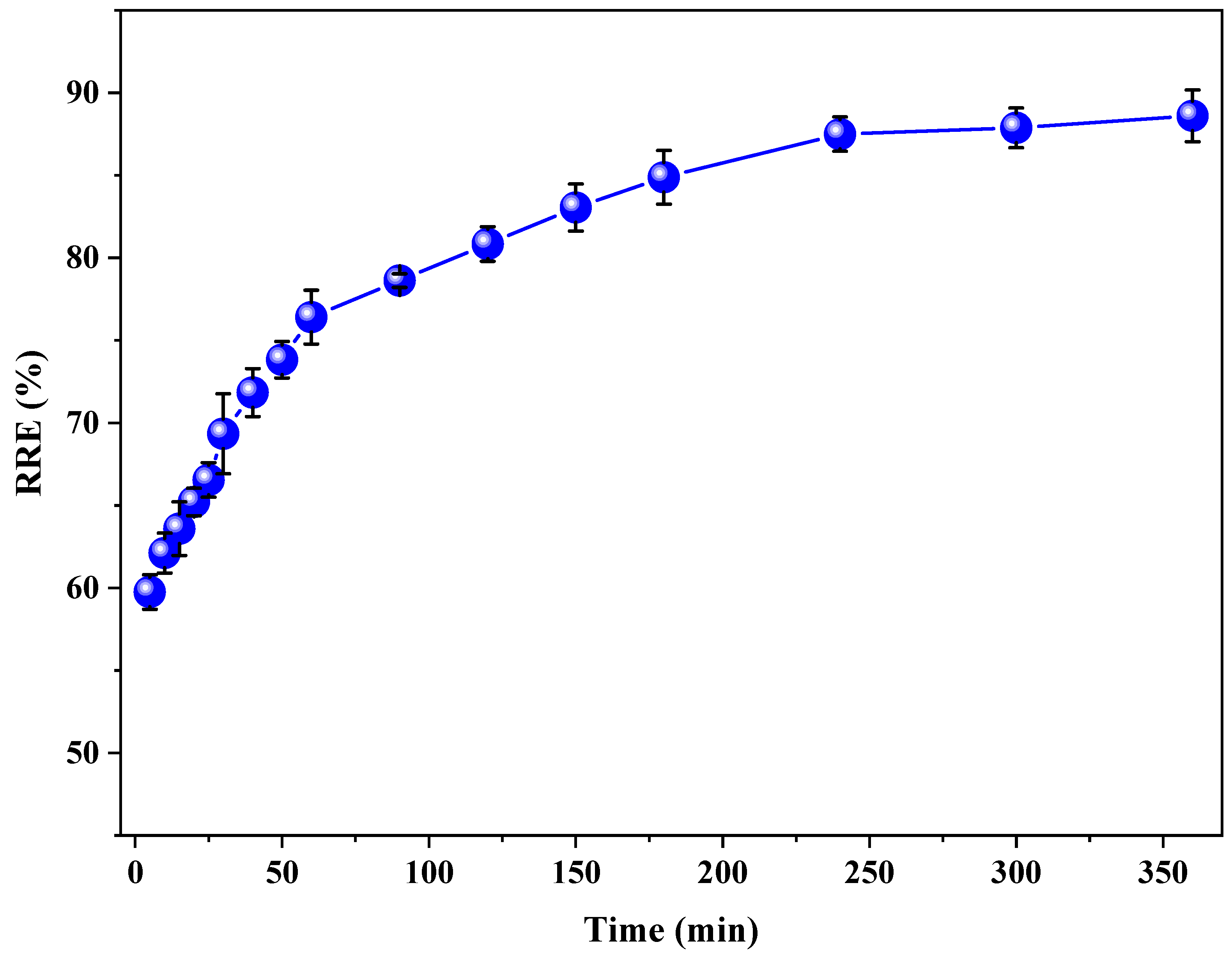
3.3. Effect of Time on the Removal of RB5
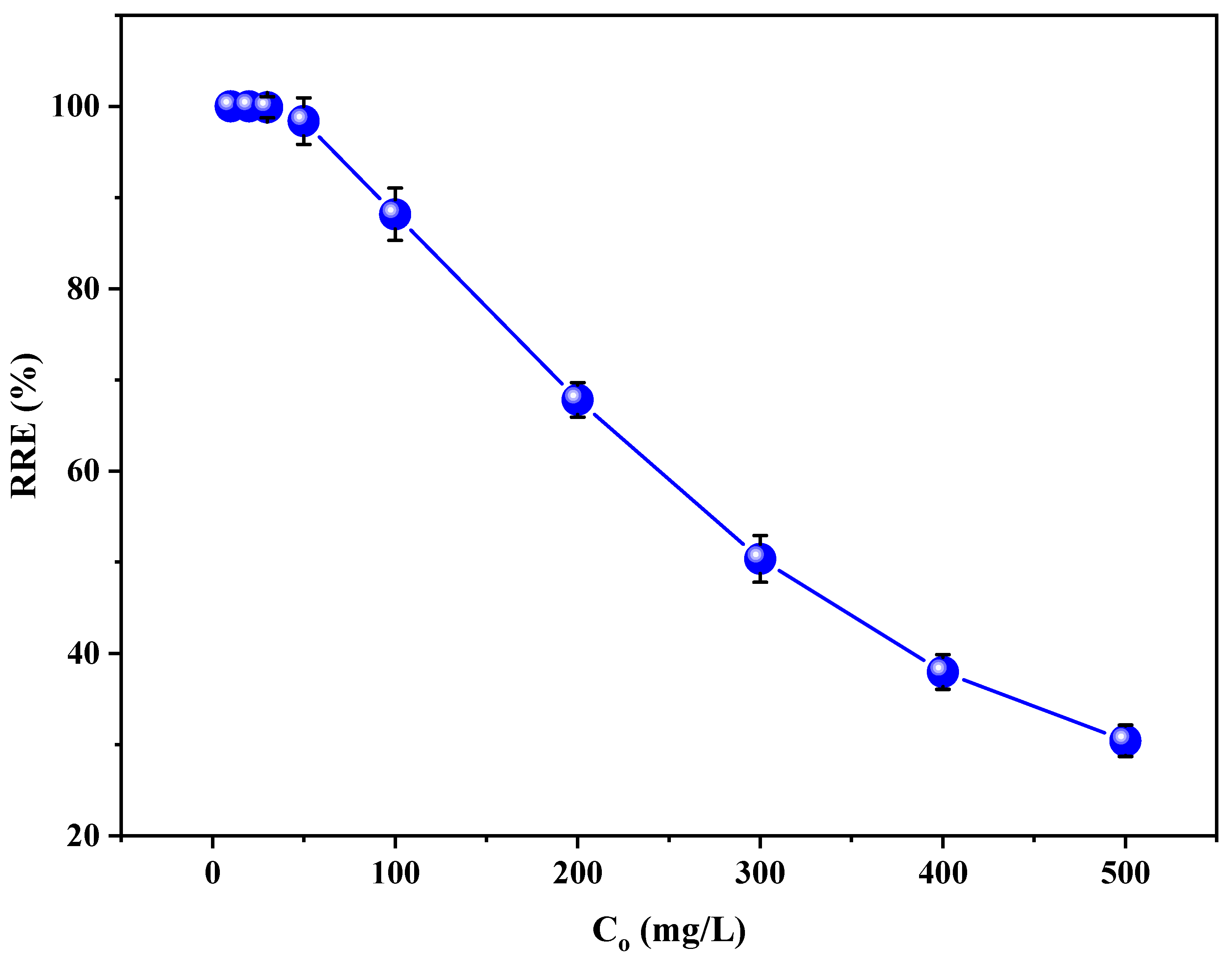
3.4. Effect of Initial RB5 Concentration on the RRE
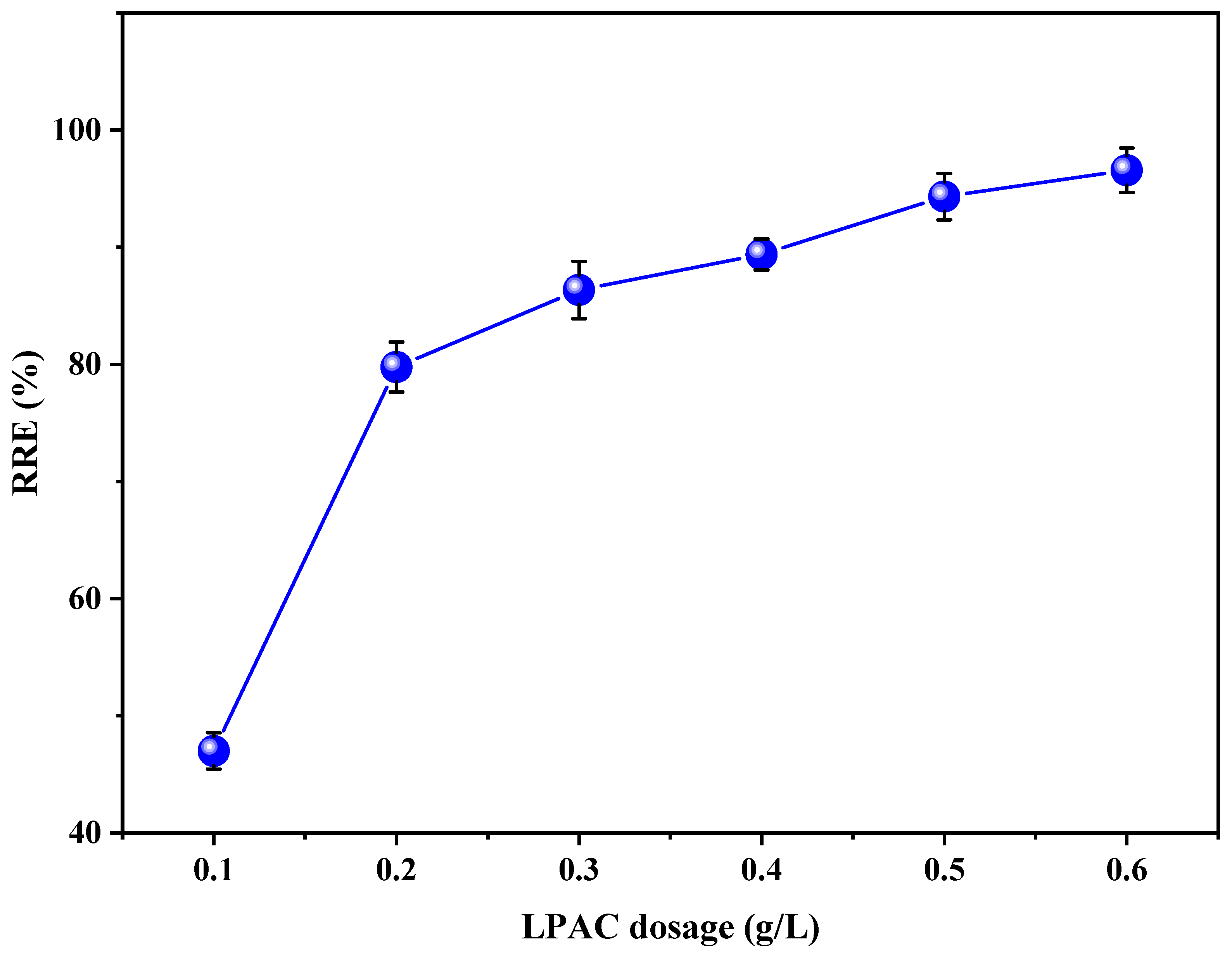
3.5. Effect of LPAC Dosage on the RRE
3.6. Kinetics of the Adsorption of RB5 onto LPAC
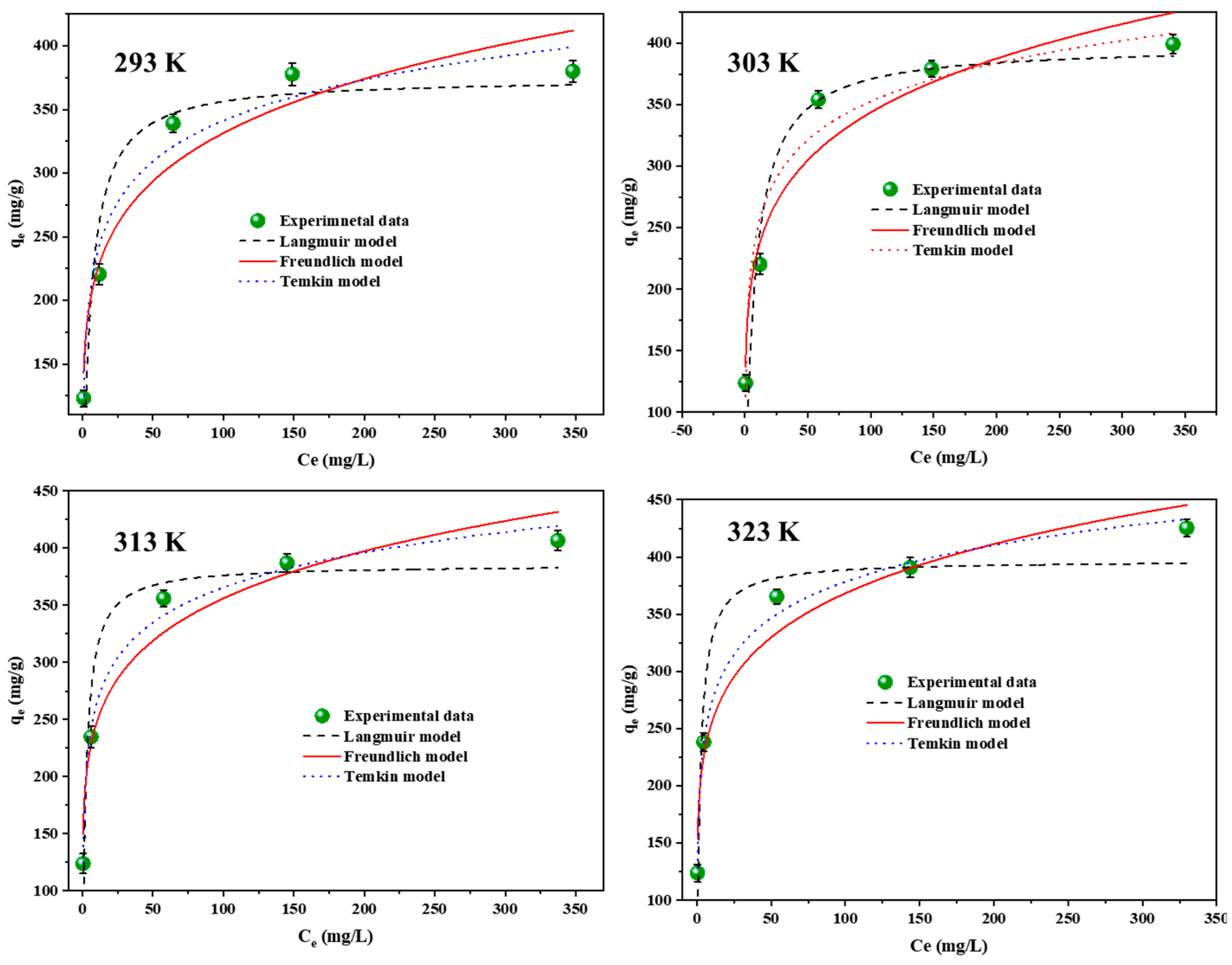
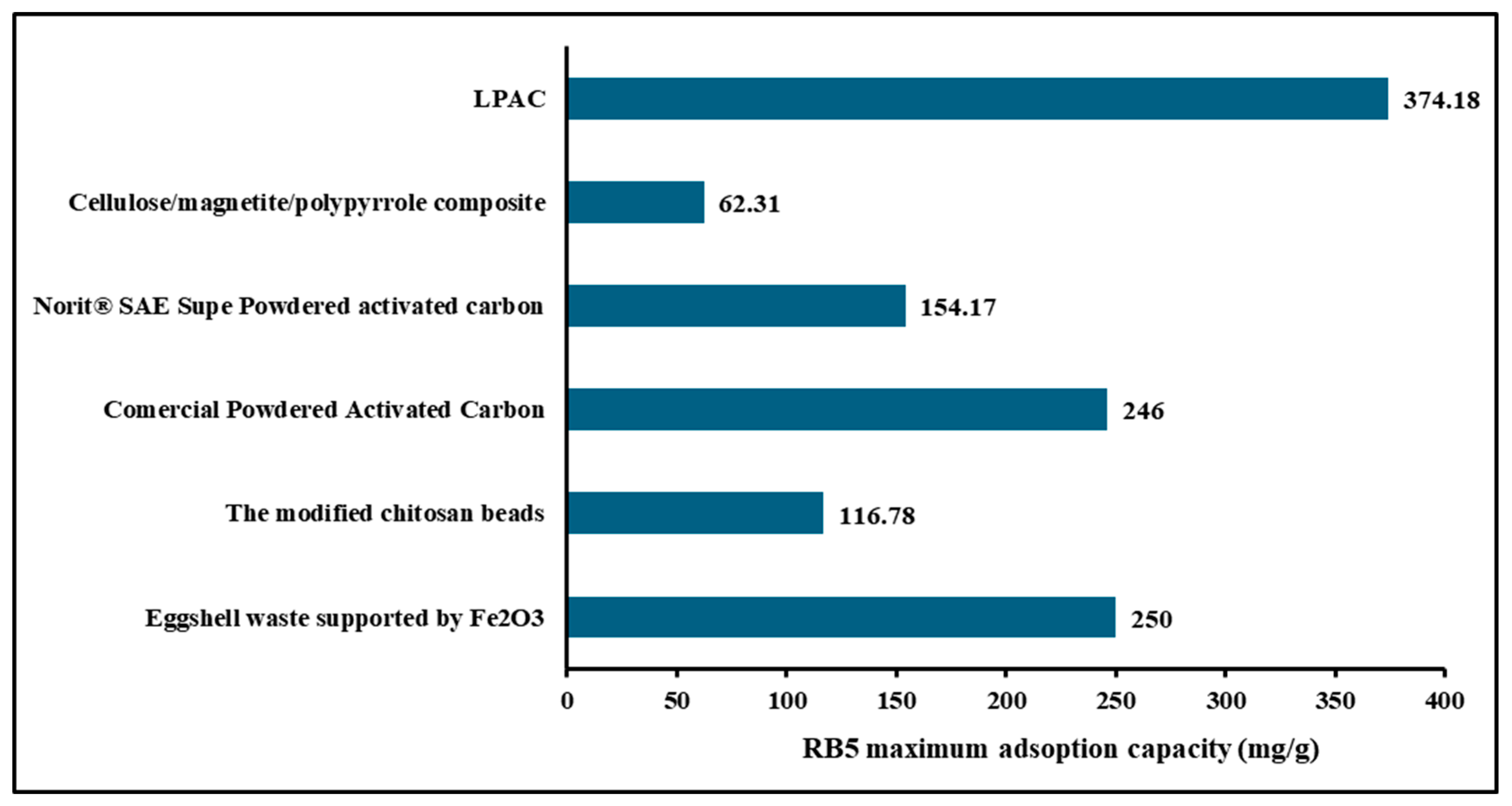
3.7. Isotherms of the Adsorption of RB5 onto LPAC
3.8. Thermodynamics of the Adsorption of RB5 onto LPAC
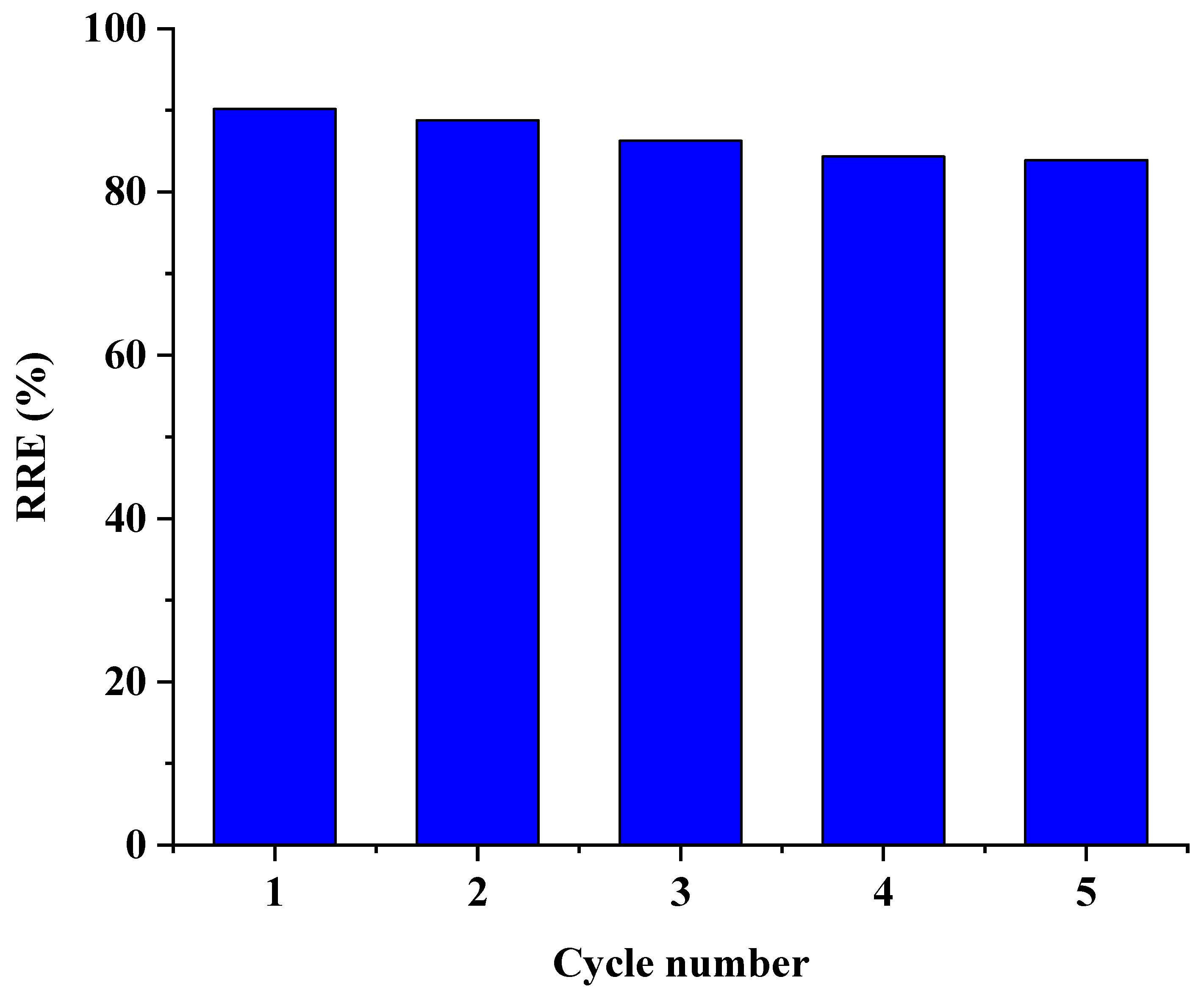
3.9. Recyclability of LPAC
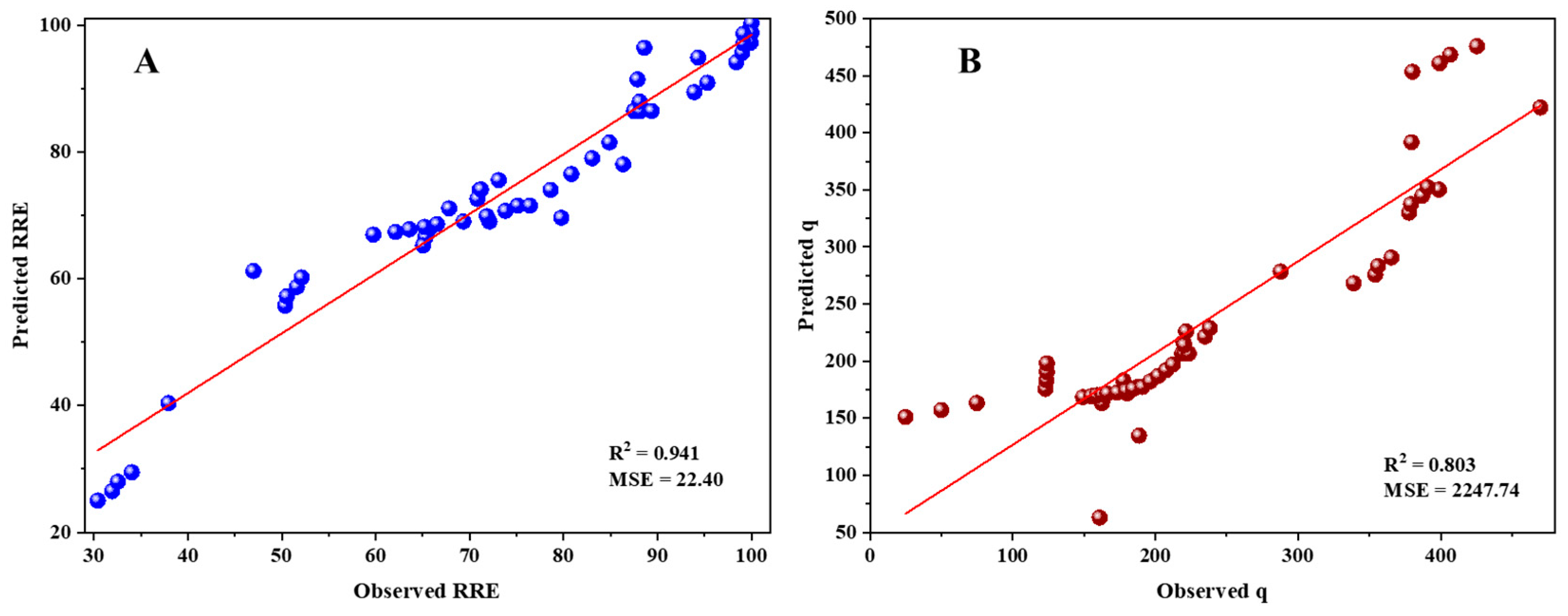
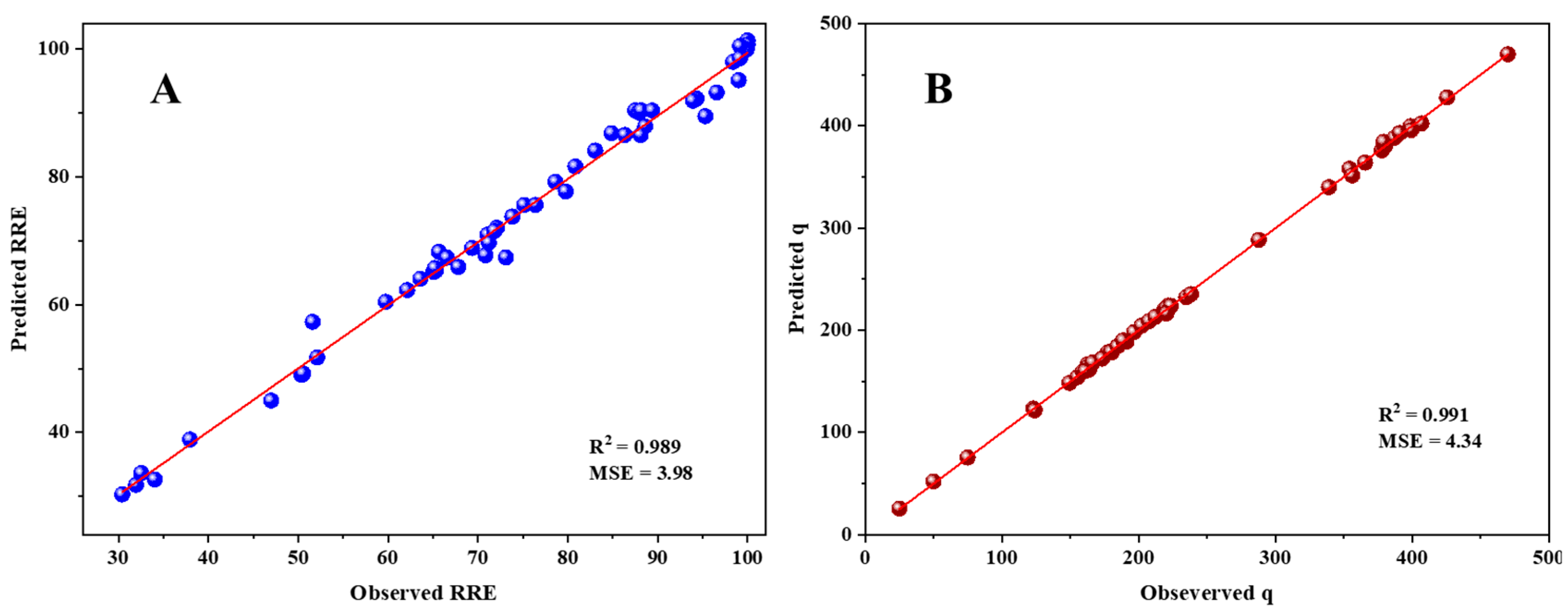
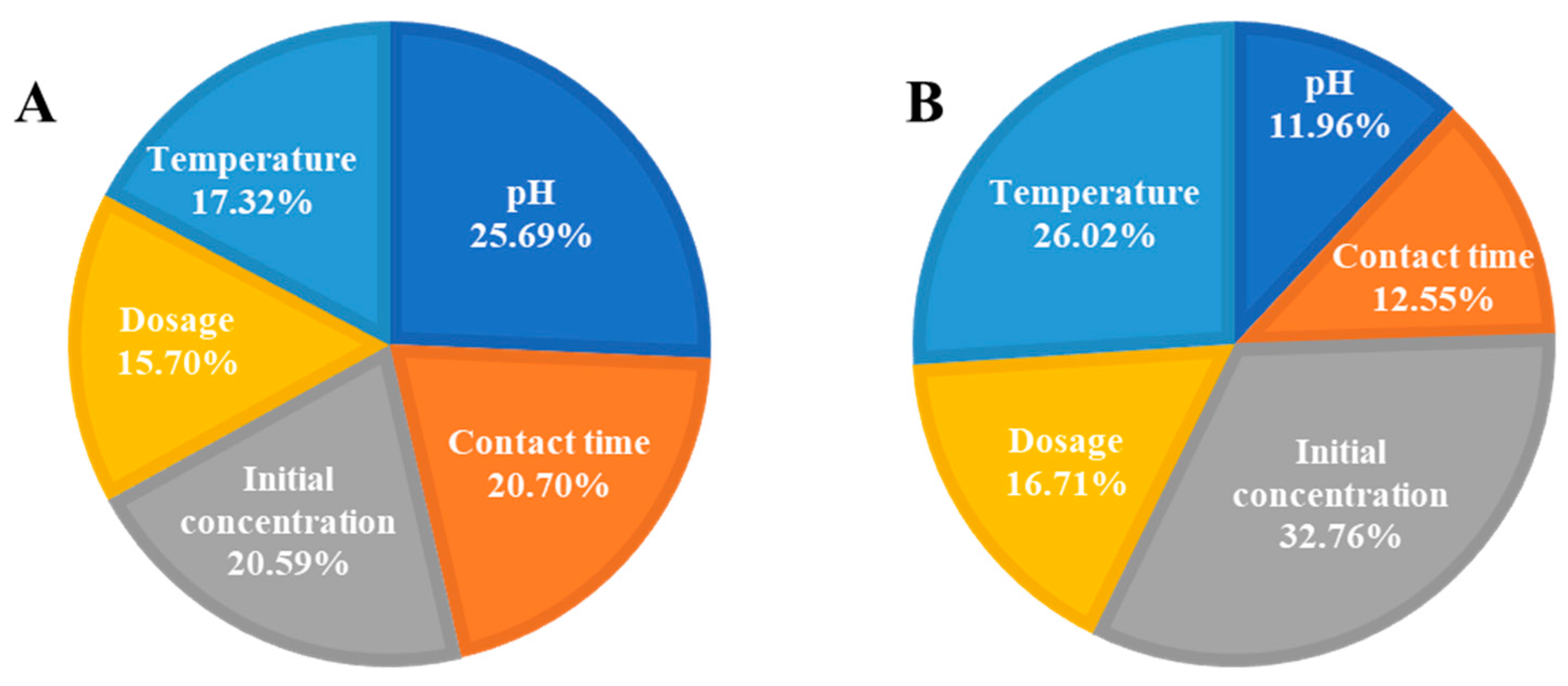
3.10. Multiple Linear Regression and ANN Modeling for Adsorption of RB5 onto LPAC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahu, A.; Poler, J.C. Removal and Degradation of Dyes from Textile Industry Wastewater: Benchmarking Recent Advancements, Toxicity Assessment and Cost Analysis of Treatment Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanjwani, M.F.; Tuzen, M.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Saleh, T.A. Trends in Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dye Pollutants Using Nanoparticles: A Review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 159, 111613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T.; Cen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, Z. A Review on Modified Red Mud-Based Materials in Removing Organic Dyes from Wastewater: Application, Mechanisms and Perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 407, 125171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; Nagy, J.B. Treatment of Water Contaminated with Reactive Black-5 Dye by Carbon Nanotubes. Material 2020, 13, 5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; He, Z.; Qiu, J.; Xu, L.; Chen, J. Ozone Assisted Electrocoagulation for Decolorization of C.I. Reactive Black 5 in Aqueous Solution: An Investigation of the Effect of Operational Parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 55, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, Z.; Salim, S.; Kumar, D. Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Reactive Black 5 by Activated Carbon Derived from Tamarind Seeds. Trop. Aquat. Soil Pollut. 2021, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beluci, N.D.C.L.; Mateus, G.A.P.; Miyashiro, C.S.; Homem, N.C.; Gomes, R.G.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, A.M.S. Hybrid Treatment of Coagulation/Flocculation Process Followed by Ultrafiltration in TIO2-Modified Membranes to Improve the Removal of Reactive Black 5 Dye. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, D.; Kupka, D.; Vaclavikova, M.; Ivanicova, L.; Gallios, G. Degradation of Reactive Black 5 by Electrochemical Oxidation. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiz, L. Removal of Reactive Black 5 from Wastewater by Membrane Filtration. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3047–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouraie, M.; El Din, W.S. Biodegradation of Reactive Black 5 by Aeromonas Hydrophila Strain Isolated from Dye-Contaminated Textile Wastewater. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, Z.; Acar, F.N. Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 from an Aqueous Solution: Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies. Desalination 2006, 194, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelebi, H. The Applicability of Evaluable Wastes for the Adsorption of Reactive Black 5. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushati, A.; Zheng, K.; Haxhari, R.; Zmarzlak, T.; Meng, Y.; Kim, T.; Nitodas, S. Kinetics of the Decomposition of Reactive Black 5 on Carbon Nanostructured Adsorbents. Environ. Adv. 2024, 17, 100590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Mehdi, M.; Otho, A.A.; Tagar, U.; Hakro, R.A.; Hussain, S. Electrospun Silk Nanofibers for Numerous Adsorption-Desorption Cycles on Reactive Black 5 and Reuse Dye for Textile Coloration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mahmodi, A.F.; Atta, M.R.; Munusamy, Y.; Al-dhawi, B.N.S. Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 Dye Using Eggshell Waste Supported by Fe2O3: An Equilibrium Isotherms Study. Chem. Thermodyn. Therm. Anal. 2025, 18, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanday, W.A.; Soon, K.A.; Ahmed, M.J.; Hummadi, E.H. Cross-Linked Chitosan/Pencil Clay Hybrid Beads for the Adsorption of Reactive Black 5. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 285, 138301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojnović, B.; Cetina, M.; Franjković, P.; Sutlović, A. Influence of Initial PH Value on the Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 Dye on Powdered Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Mechanisms, and Thermodynamics. Molecules 2022, 27, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez-Cid, A.A.; Herrera-González, A.M.; Salazar-Villanueva, M.; Bautista-Hernández, A. Elimination of Textile Dyes Using Activated Carbons Prepared from Vegetable Residues and Their Characterization. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, L.C.; de Carvalho, K.Q.; Bassetti, F.J.; Coral, L.A.A. Kinetic, Isothermal and Thermodynamic Studies of Reactive Black 5 Removal Using Rice Husk Ashes and Powdered Activated Carbon. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, P. Activated Carbon from Lignocellulosics Precursors: A Review of the Synthesis Methods, Characterization Techniques and Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1393–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunarbekova, M.; Busquets, R.; Sailaukhanuly, Y.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Toshtay, K.; Kudaibergenov, K.; Azat, S. Carbon Adsorbents for the Uptake of Radioactive Iodine from Contaminated Water Effluents: A Systematic Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.W. An Overview of Heavily Polluted Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Food Waste as an Alternative and Renewable Source of Activated Carbon. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 98, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannavijit, S.; Outama, P.; Le Xuan, C.; Fontana, C.M.; Paolucci, M.; Ahmed Sumon, M.A.; El-Haroun, E.; Van Doan, H. Evaluation of Longan (Dimocarpus longan) Peel Powder as Fruit by-Product Additive in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Feed: Effects on Growth, Immunity, and Immune-Antioxidant Gene Expressions. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Feng, F.; Xu, L.; Ma, X.; Tian, Y. A Comprehensive Evaluation on Thermo-Chemical Potential of Longan Waste for the Production of Chemicals and Carbon Materials. Fuel 2023, 334, 126655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, H.; Fu, N.; Chen, J.; Lan, G.; Qian, W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Han, S. Excellent Electrochemical Properties and Large CO2 Capture of Nitrogen-Doped Activated Porous Carbon Synthesised from Waste Longan Shells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 231, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Fang, Y.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Wu, S.D.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.W.; Cao, Y.; Gao, H.L.; Wang, L.Z.; et al. Nitrogen-Doped Oxygen-Rich Activated Carbon Derived from Longan Shell for Supercapacitors. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 1982–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Yan, S.; Ali, M.; Mahmood, F.; Zheng, Y.; Song, X.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. From Longan Peel Waste to Energy Storage: Porous Activated Carbon as a Cathode Matrix for Advanced Li/Na-Selenium Batteries. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2024, 34, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neme, I.; Gonfa, G.; Masi, C. Activated Carbon from Biomass Precursors Using Phosphoric Acid: A Review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Soluble Substances. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of Heavy Metals from Waters by Means of Natural Zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roginsky, S.; Zeldovich, Y.B. The Catalytic Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide on Manganese Dioxide. Acta Phys. Chem. USSR 1934, 1, 554. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Kapillarchemie, Eine Darstellung Der Chemie Der Kolloide Und Verwandter Gebiete; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.I. Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis on Promoted Iron Catalysts. Acta Physicochim. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, F. Optimizing the Leaching Parameters and Studying the Kinetics of Copper Recovery from Waste Printed Circuit Boards. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 3689–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F. Activated Carbon Activated Carbon; Elsevier Science & Technology BooksElsevier Science & Technology Books; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 6, ISBN 9781583219072. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y. Characterization and Lead Adsorption Properties of Activated Carbons Prepared from Cotton Stalk by One-Step H3PO4 Activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Sen Gupta, B.; Hashim, M.A.; Redzwan, G. Taguchi Optimization Approach for Production of Activated Carbon from Phosphoric Acid Impregnated Palm Kernel Shell by Microwave Heating. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 105, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.S.; Rashidi, N.A.; Yusup, S. Production and Characterization of Bamboo-Based Activated Carbon through Single-Step H3PO4 Activation for CO2 Capture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12434–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baytar, O.; Ceyhan, A.A.; Şahin, Ö. Production of Activated Carbon from Elaeagnus Angustifolia Seeds Using H3PO4 Activator and Methylene Blue and Malachite Green Adsorption. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Simultaneous Adsorptive Desulfurization of Diesel Fuel over Bimetallic Nanoparticles Loaded on Activated Carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Marshall, W.E.; Rao, R.M.; Bansode, R.R.; Losso, J.N. Activated Carbon from Pecan Shell: Process Description and Economic Analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2003, 17, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vunain, E.; Njewa, J.B.; Biswick, T.T.; Ipadeola, A.K. Adsorption of Chromium Ions from Tannery Effluents onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Rice Husk and Potato Peel by H3PO4 Activation. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Flores, P.E.; Guzmán-Álvarez, C.J.; Ovando-Medina, V.M.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, H.; González-Ortega, O. Synthesis of A-Cellulose/Magnetite/Polypyrrole Composite for the Removal of Reactive Black 5 Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 155, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rico, O.; Blanco, L.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Accessible Eco-Friendly Method for Wastewater Removal of the Azo Dye Reactive Black 5 by Reusable Protonated Chitosan-Deep Eutectic Solvent Beads. Molecules 2024, 29, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lim, S.-R.; Woo, S.H. Removal of Reactive Black 5 by Zero-Valent Iron Modified with Various Surfactants. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsa, E.K.; Tolkou, A.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Composite Activated Carbon Modified with AlCl3 for the Effective Removal of Reactive Black 5 Dye from Wastewaters. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Zafar, M.; Prajapati, J.K.; Kumar, S.; Kannepalli, S. Modeling Studies on Simultaneous Adsorption of Phenol and Resorcinol onto Granular Activated Carbon from Simulated Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Lan, R.; He, L.; Liu, H.; Pei, X. A Critical Review of Adsorption Isotherm Models for Aqueous Contaminants: Curve Characteristics, Site Energy Distribution and Common Controversies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Anastopoulos, I. A Critical Review of the Estimation of the Thermodynamic Parameters on Adsorption Equilibria. Wrong Use of Equilibrium Constant in the Van’t Hoof Equation for Calculation of Thermodynamic Parameters of Adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and Inconsistencies Regarding Adsorption of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, A.A.; Khataee, A.; Ahmadpour, E.; Sheydaei, M.; Kakavandi, B.; Alaee, Z. Optimization of Cationic Dye Adsorption on Activated Spent Tea: Equilibrium, Kinetics, Thermodynamic and Artificial Neural Network Modeling. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Bhatnagar, A.; Lima, E.C. Adsorption of Rare Earth Metals: A Review of Recent Literature. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Noureen, S.; Mustaqeem, M.; Saleh, T.A.; Zafar, S. Efficient Adsorbent Derived from Haloxylon Recurvum Plant for the Adsorption of Acid Brown Dye: Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Optimization. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 20, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S. Insight into Adsorption Thermodynamics; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shikuku, V.O.; Zanella, R.; Kowenje, C.O.; Donato, F.F.; Bandeira, N.M.G.; Prestes, O.D. Single and Binary Adsorption of Sulfonamide Antibiotics onto Iron-Modified Clay: Linear and Nonlinear Isotherms, Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Mechanistic Studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyen, H.T.H.; Vranova, V.; Nguyen, L.T.N.; Bui, Q.M.; Khieu, T.T. Artificial Neural Network Modeling for Congo Red Adsorption on Microwave-Synthesized Akaganeite Nanoparticles: Optimization, Kinetics, Mechanism, and Thermodynamics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9133–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, A.M.; Vafaei, A. Applications of Artificial Neural Networks for Adsorption Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solution: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 245, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyet, N.T.; Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyet, N.T.; Balasubramani, R.; Nghia, N.T. Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions using reversal mode electrocoagulation with iron and aluminum electrodes: RSM optimization and ANN modeling. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynel-Ávila, H.E.; Aguayo-Villarreal, I.A.; Diaz-Muñoz, L.L.; Moreno-Pérez, J.; Sánchez-Ruiz, F.J.; Rojas-Mayorga, C.K.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A. A Review of the Modeling of Adsorption of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants from Water Using Artificial Neural Networks. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 9384871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; Wei, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Evaluation of Adsorption Potential of Bamboo Biochar for Metal-Complex Dye: Equilibrium, Kinetics and Artificial Neural Network Modeling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
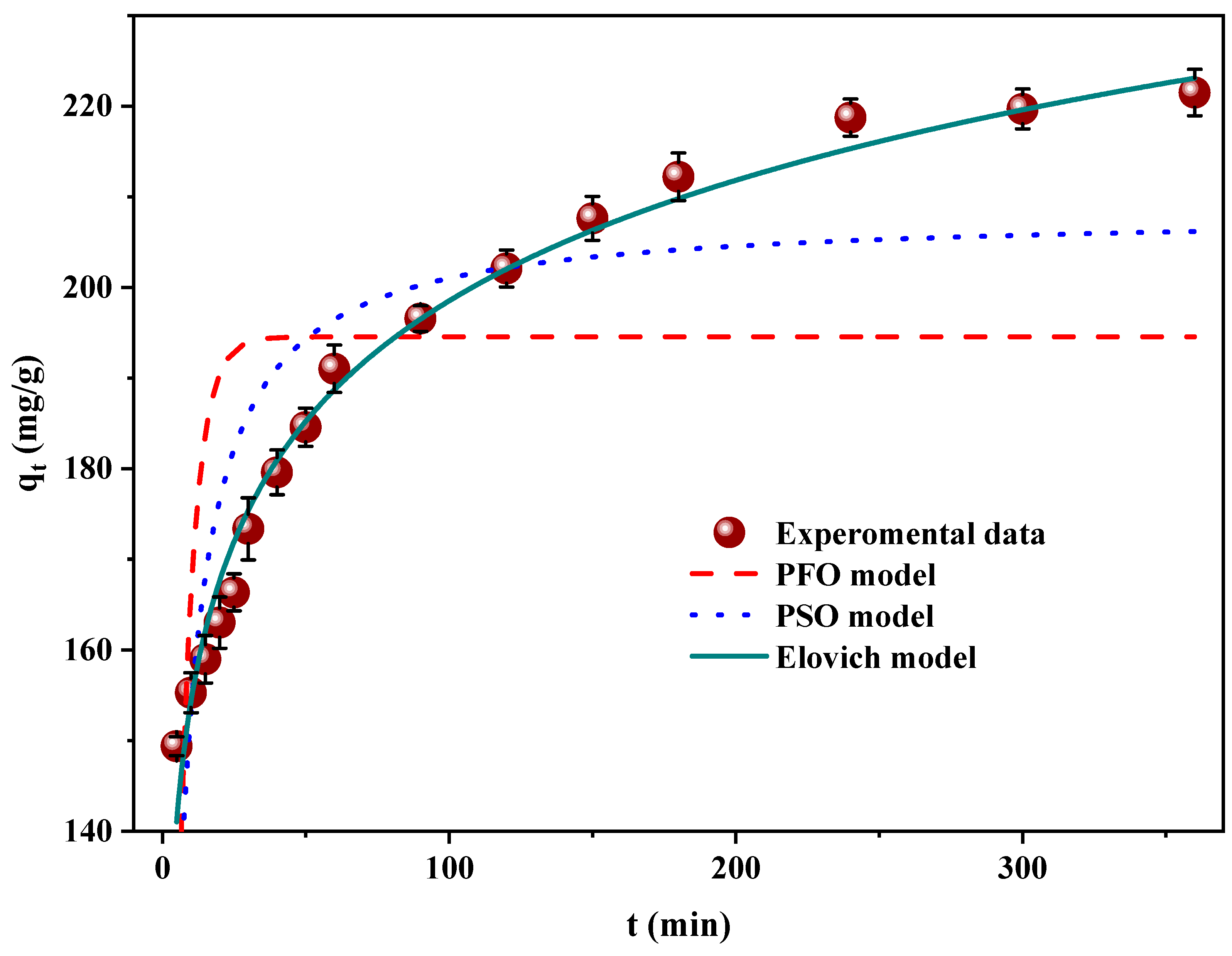
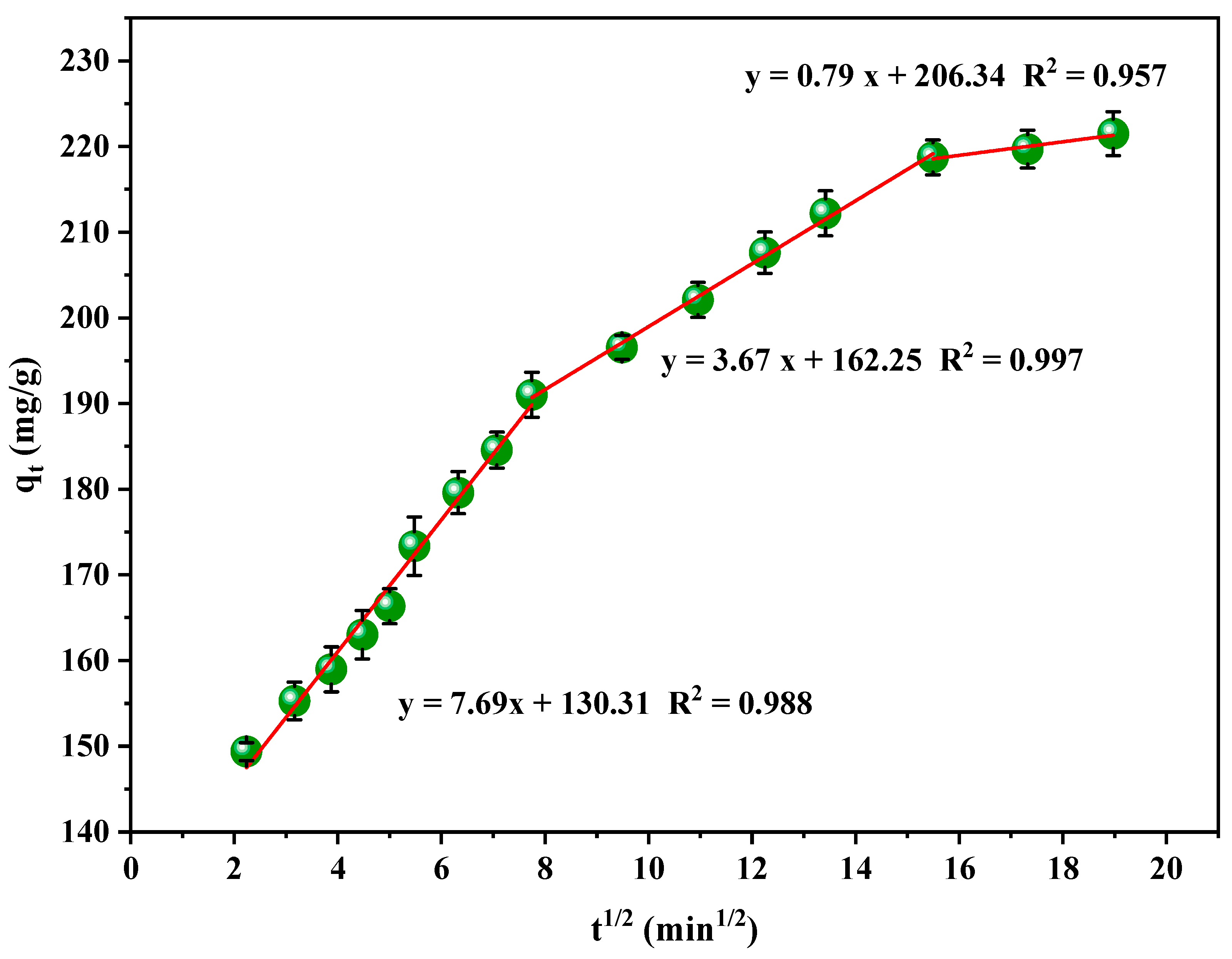
| Model | Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | k1 = 0.192 (1/min) | qe = 194.55 (mg/g) | R2 = 0.311 |
| PSO | k2 = 1.34 × 10−3 (g/mg × min) | qe = 208.21 (mg/g) | R2 = 0.732 |
| Elovich | α = 5.971 × 103 (mg/g × min) | β = 0.052 (g/mg) | R2 = 0.981 |
| Model | 293 K | 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | KL (L/mg) | 0.193 | 0.135 | 0.410 | 0.474 |
| qm (mg/g) | 374.80 | 398.13 | 385.44 | 396.83 | |
| R2 | 0.856 | 0.813 | 0.880 | 0.908 | |
| RL | 1.0 × 10−2 | 1.4 × 10−2 | 4.8 × 10−3 | 4.2 × 10−3 | |
| Freundlich | KF ((mg/g)(L/mg)1/n) | 148.38 | 155.05 | 171.56 | 176.76 |
| n | 0.174 | 0.172 | 0.158 | 0.150 | |
| R2 | 0.941 | 0.947 | 0.960 | 0.961 | |
| Temkin | KT (L/g) | 15.98 | 25.05 | 39.01 | 37.98 |
| B | 46.27 | 45.06 | 44.21 | 45.91 | |
| R2 | 0.970 | 0.959 | 0.980 | 0.987 |
| Temperature (K) | Thermodynamic Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (kJ/mol) | |
| 293 | −23.15 | 14.23 | 0.127 |
| 303 | −24.12 | ||
| 313 | −25.68 | ||
| 323 | −26.88 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoa, N.T.H.; Quynh, N.T.; Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyen, T.N.; Huy, B.Q.; Thanh, N.T.; Loan, H.T.; Hoa, N.T.Q.; Nghia, N.T. Adsorptive Removal of Reactive Black 5 by Longan Peel-Derived Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Modeling. Water 2025, 17, 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111678
Hoa NTH, Quynh NT, Nguyen VD, Nguyen TN, Huy BQ, Thanh NT, Loan HT, Hoa NTQ, Nghia NT. Adsorptive Removal of Reactive Black 5 by Longan Peel-Derived Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Modeling. Water. 2025; 17(11):1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111678
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoa, Nguyen Thi Hong, Ngo Thi Quynh, Vinh Dinh Nguyen, Thi Nguyet Nguyen, Bui Quoc Huy, Nguyen Thi Thanh, Hoang Thi Loan, Nguyen Thi Quynh Hoa, and Nguyen Trong Nghia. 2025. "Adsorptive Removal of Reactive Black 5 by Longan Peel-Derived Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Modeling" Water 17, no. 11: 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111678
APA StyleHoa, N. T. H., Quynh, N. T., Nguyen, V. D., Nguyen, T. N., Huy, B. Q., Thanh, N. T., Loan, H. T., Hoa, N. T. Q., & Nghia, N. T. (2025). Adsorptive Removal of Reactive Black 5 by Longan Peel-Derived Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Modeling. Water, 17(11), 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111678







