Salinity Barriers to Manage Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Zone Aquifers During Global Climate Change: A Review and New Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Climate Change and Saltwater Intrusion
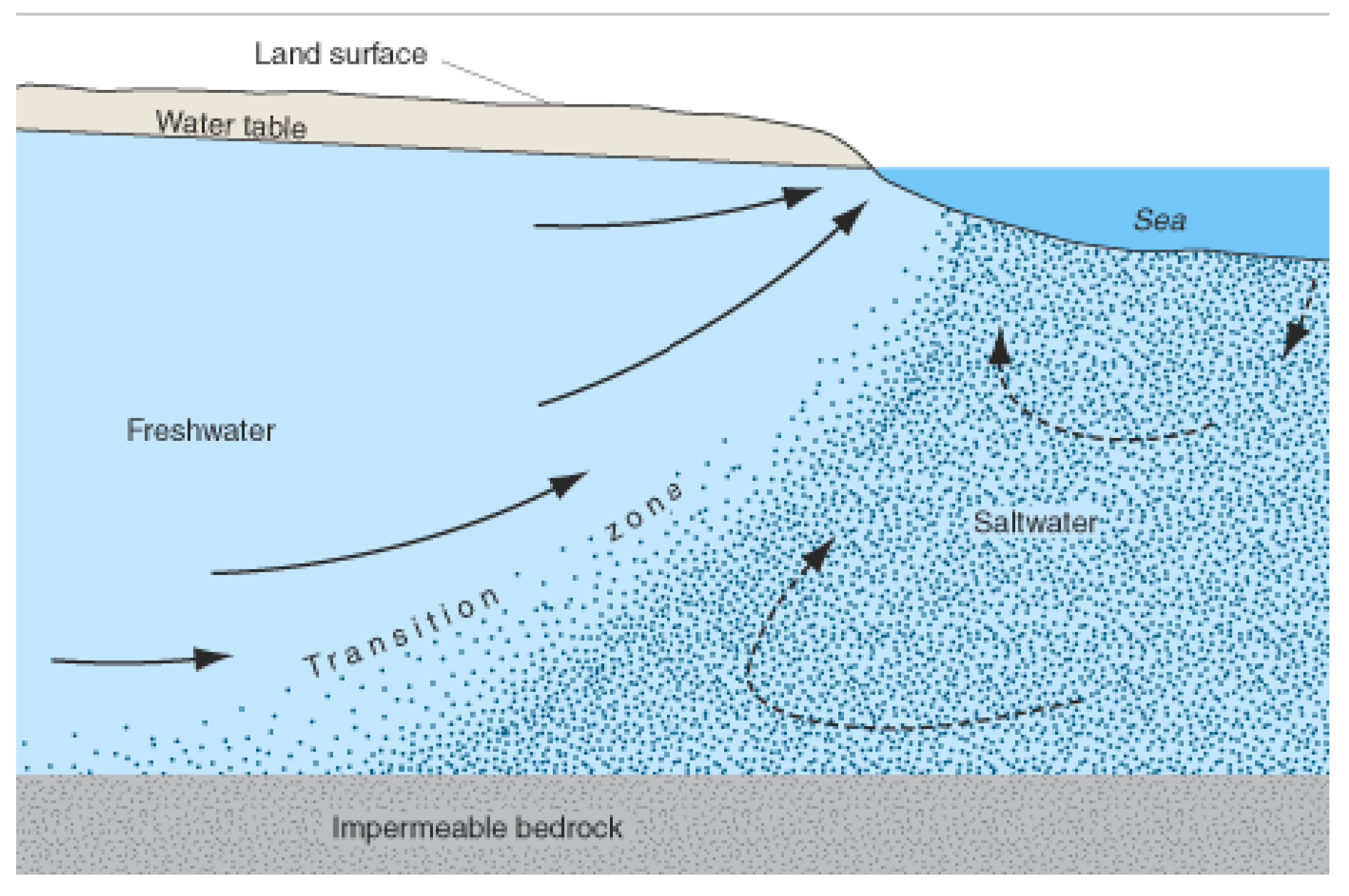
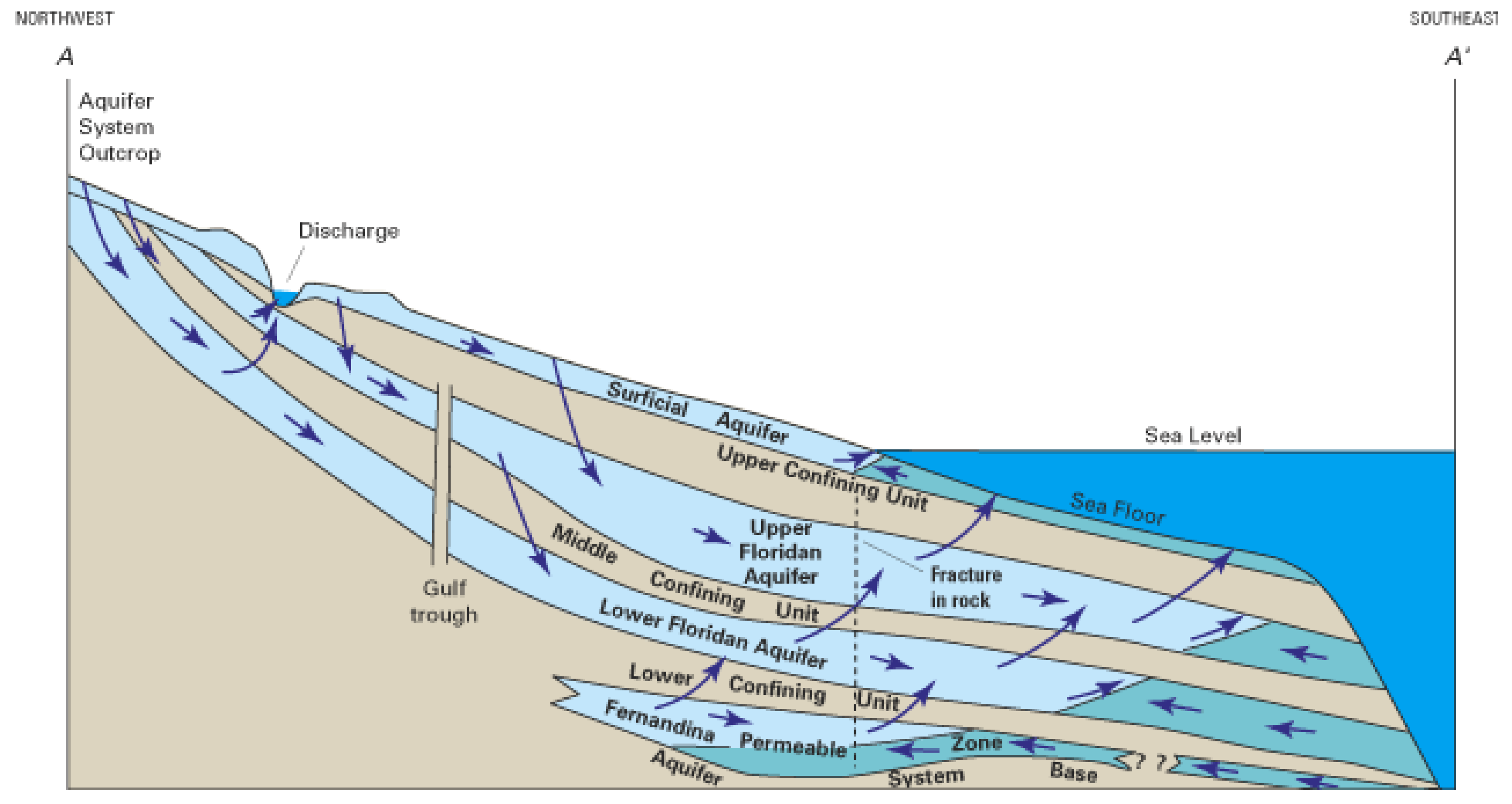
2.1. Fundamental Aspects of Saltwater Intrusion
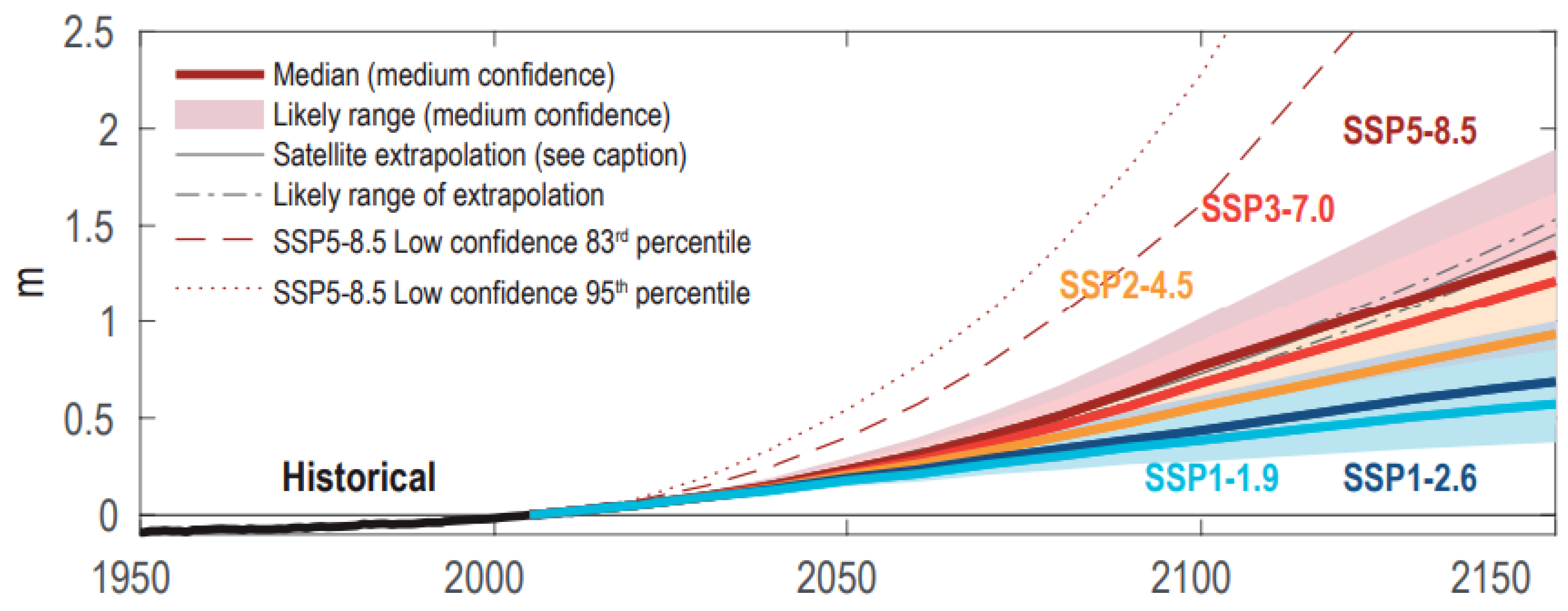
2.2. Projected Sea Level Changes
3. Salinity Barrier Types and Applications
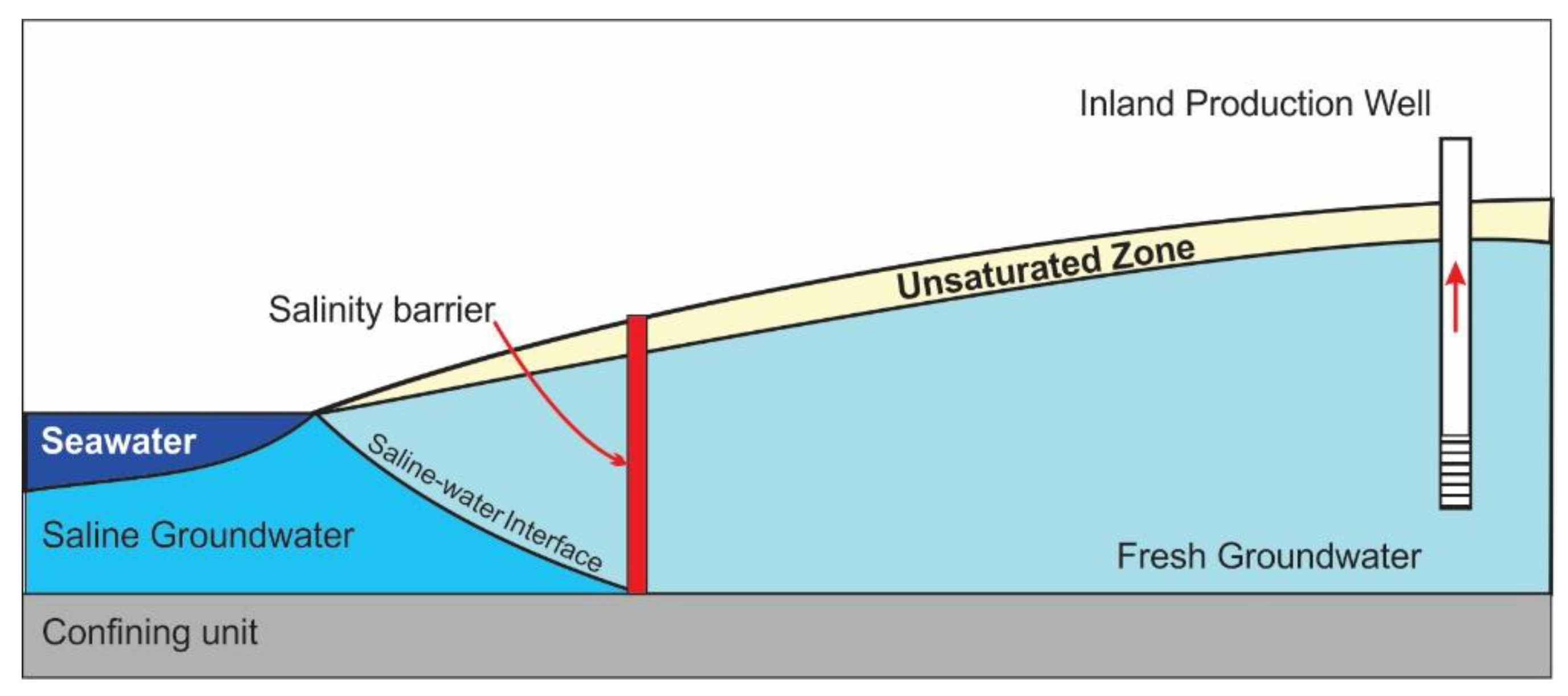
3.1. Physical Vertical Salinity Barriers
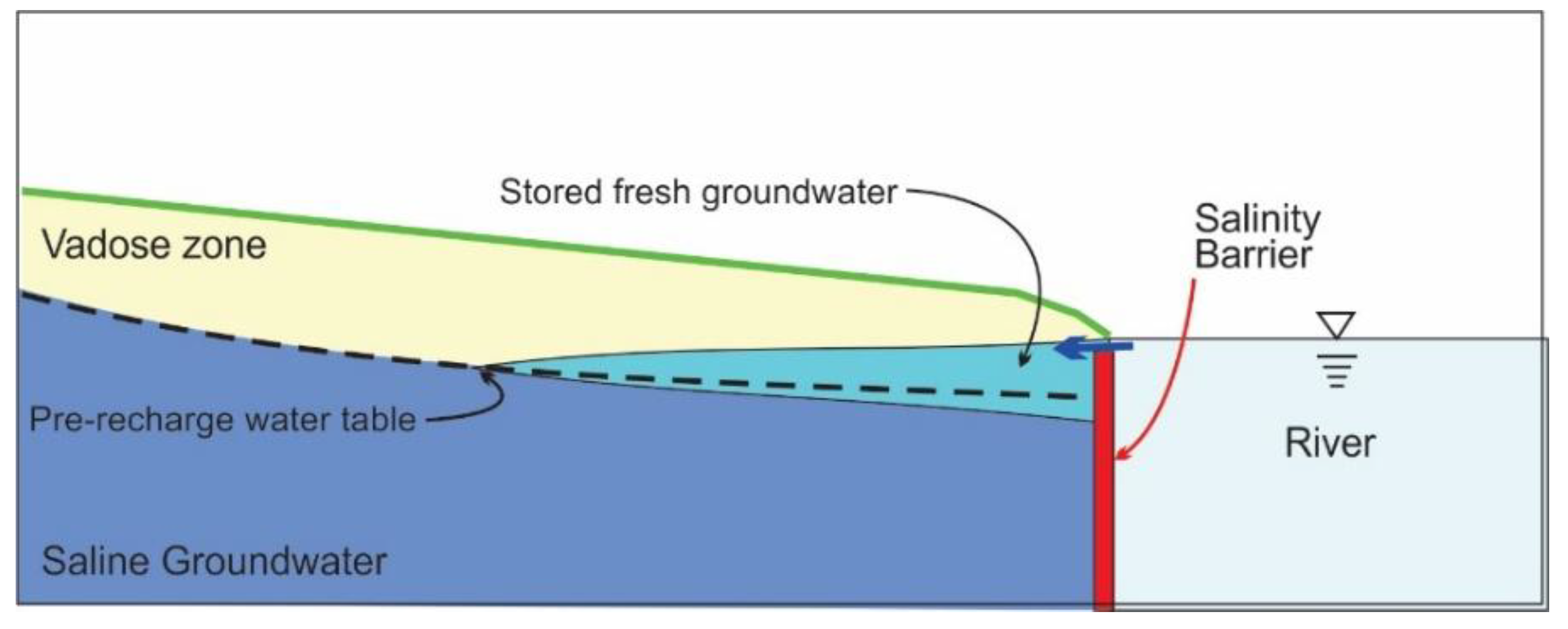
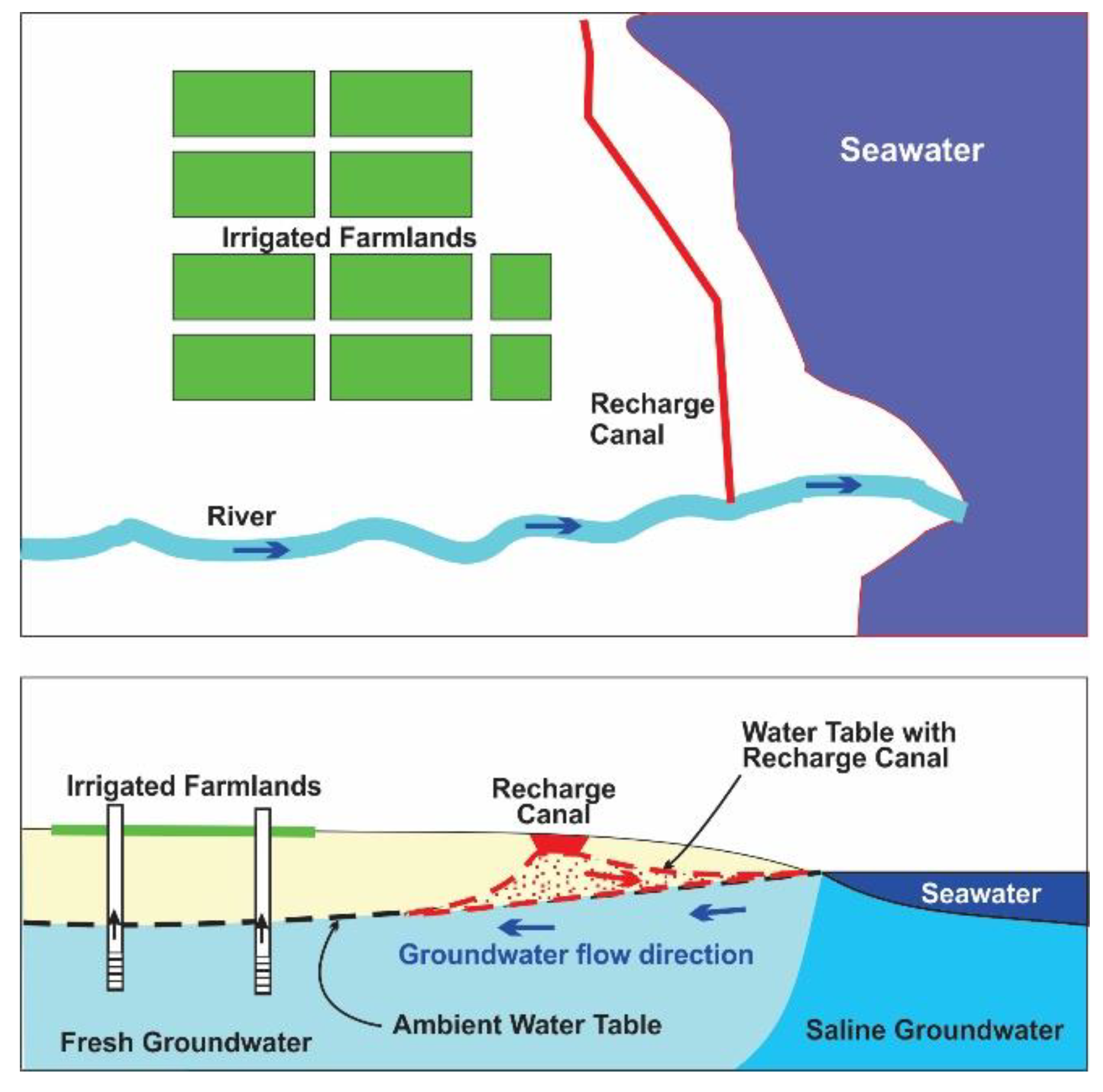
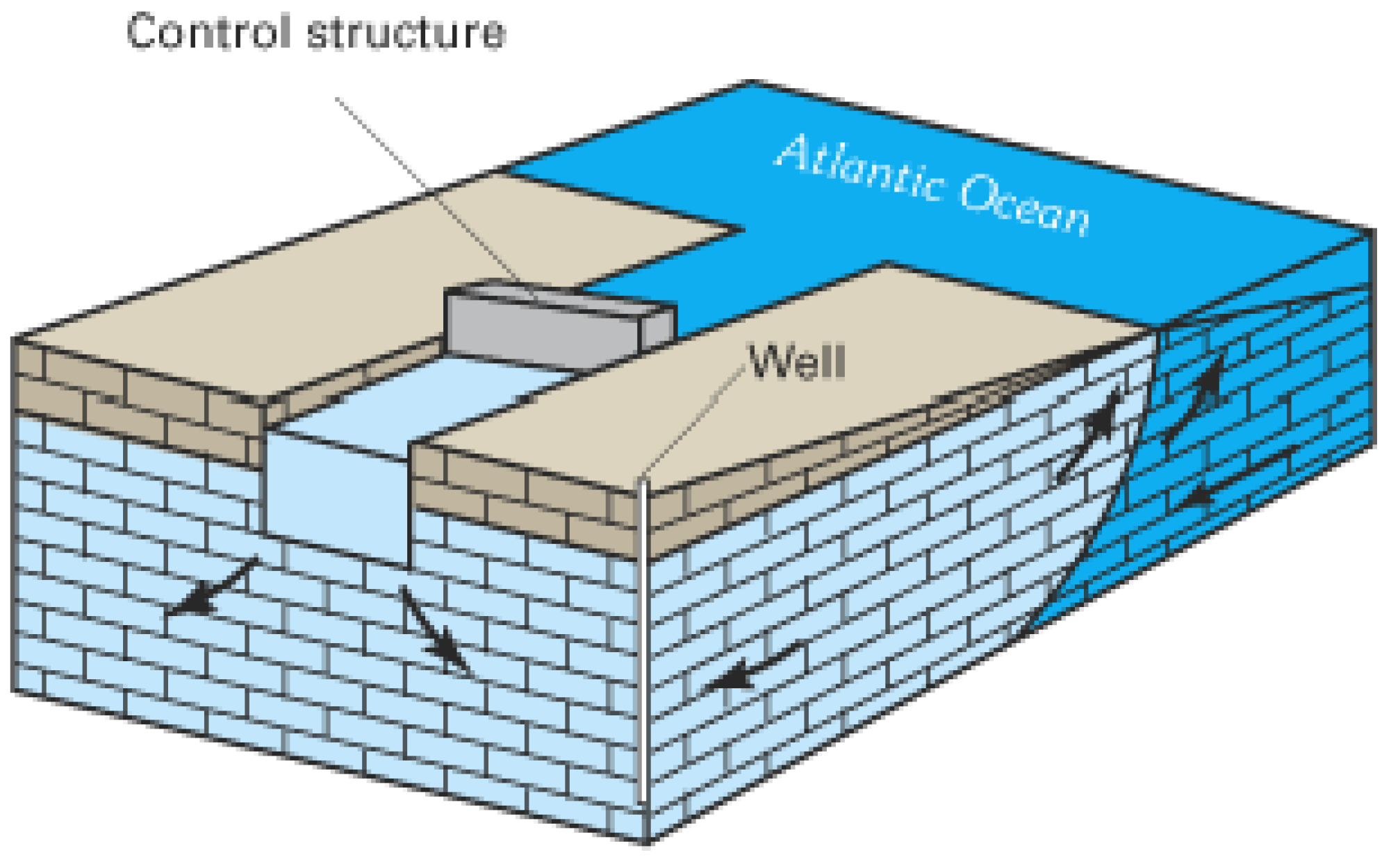
3.2. Salinity Barriers Using Surface Water
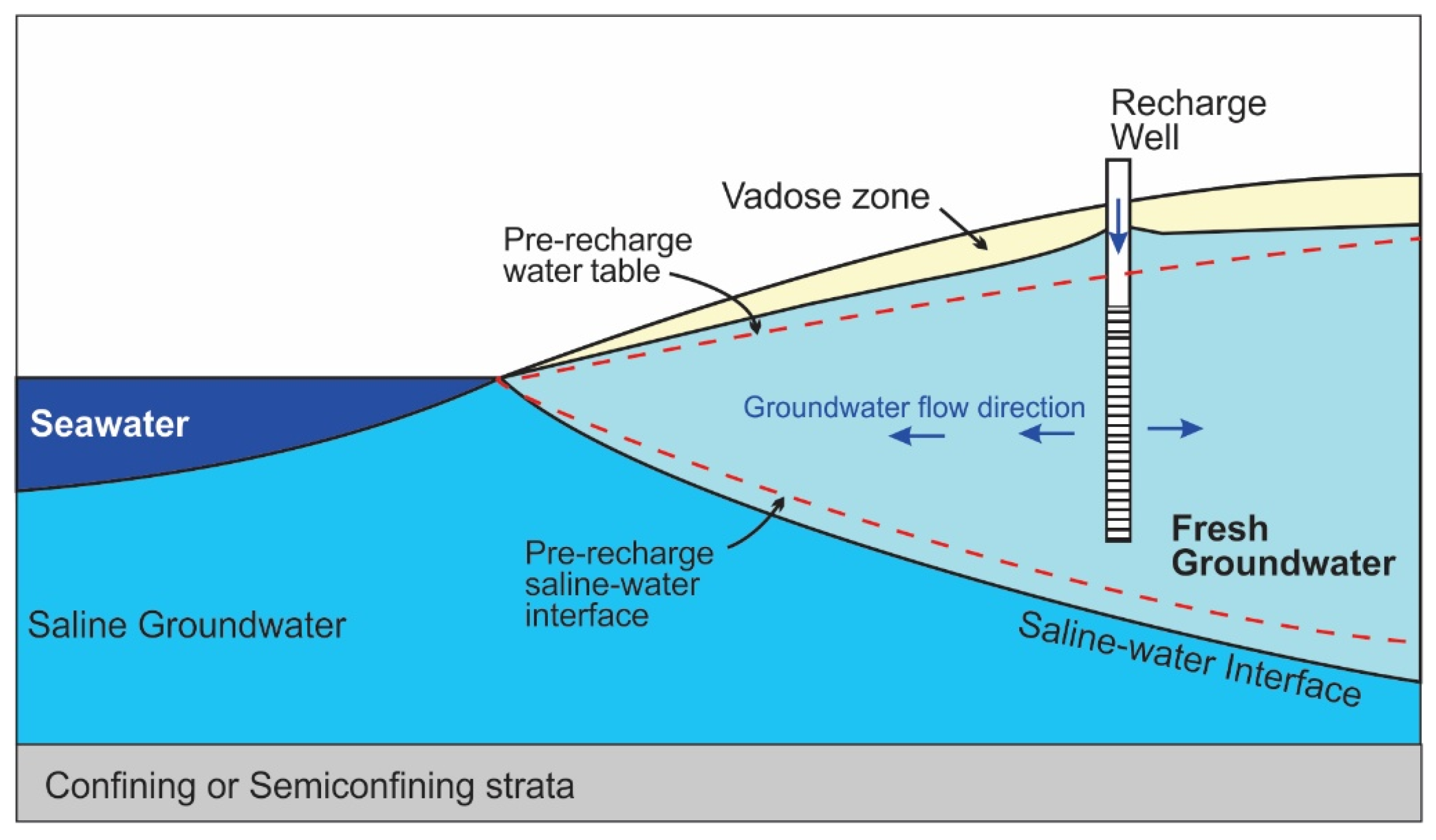
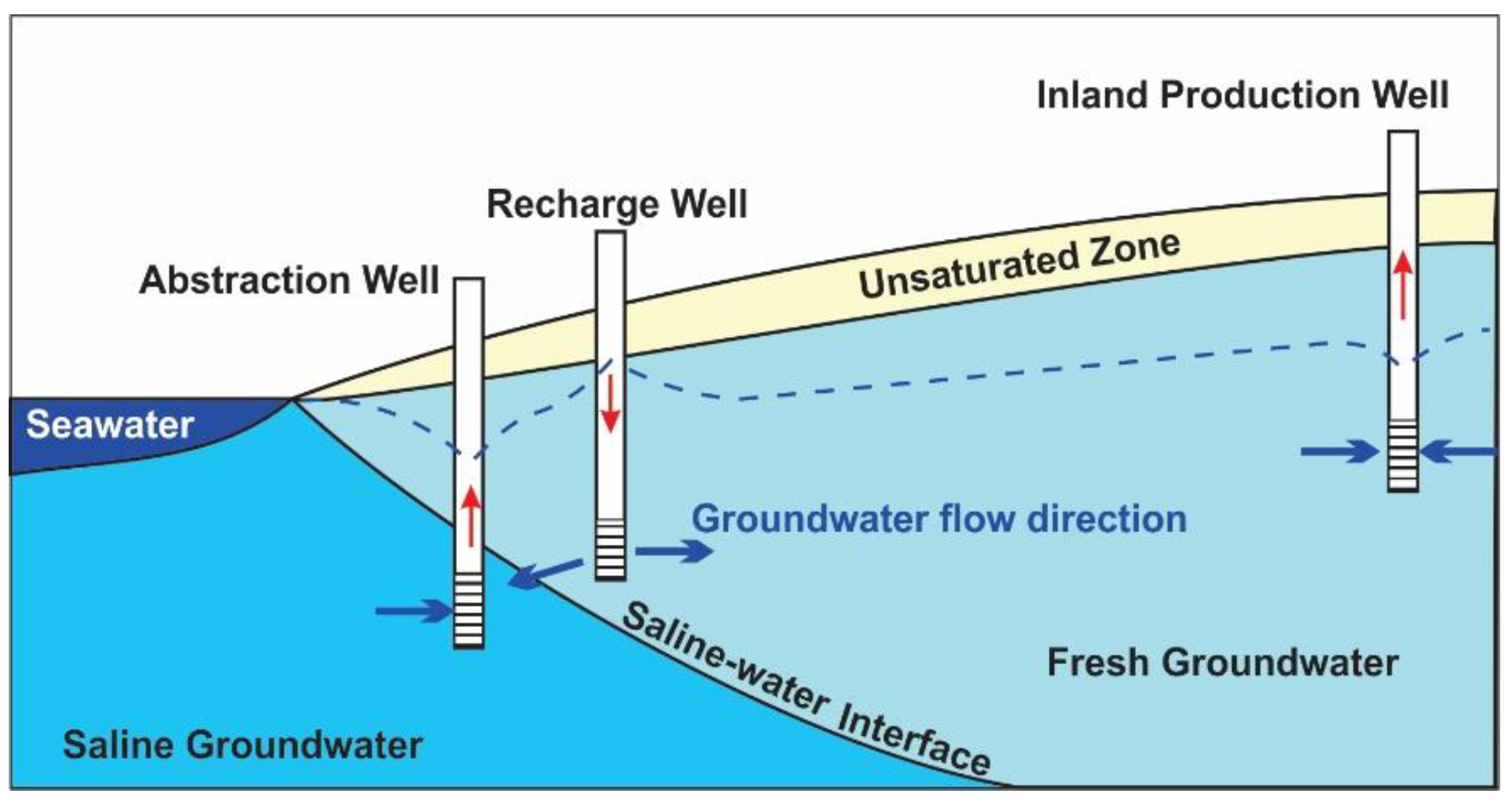
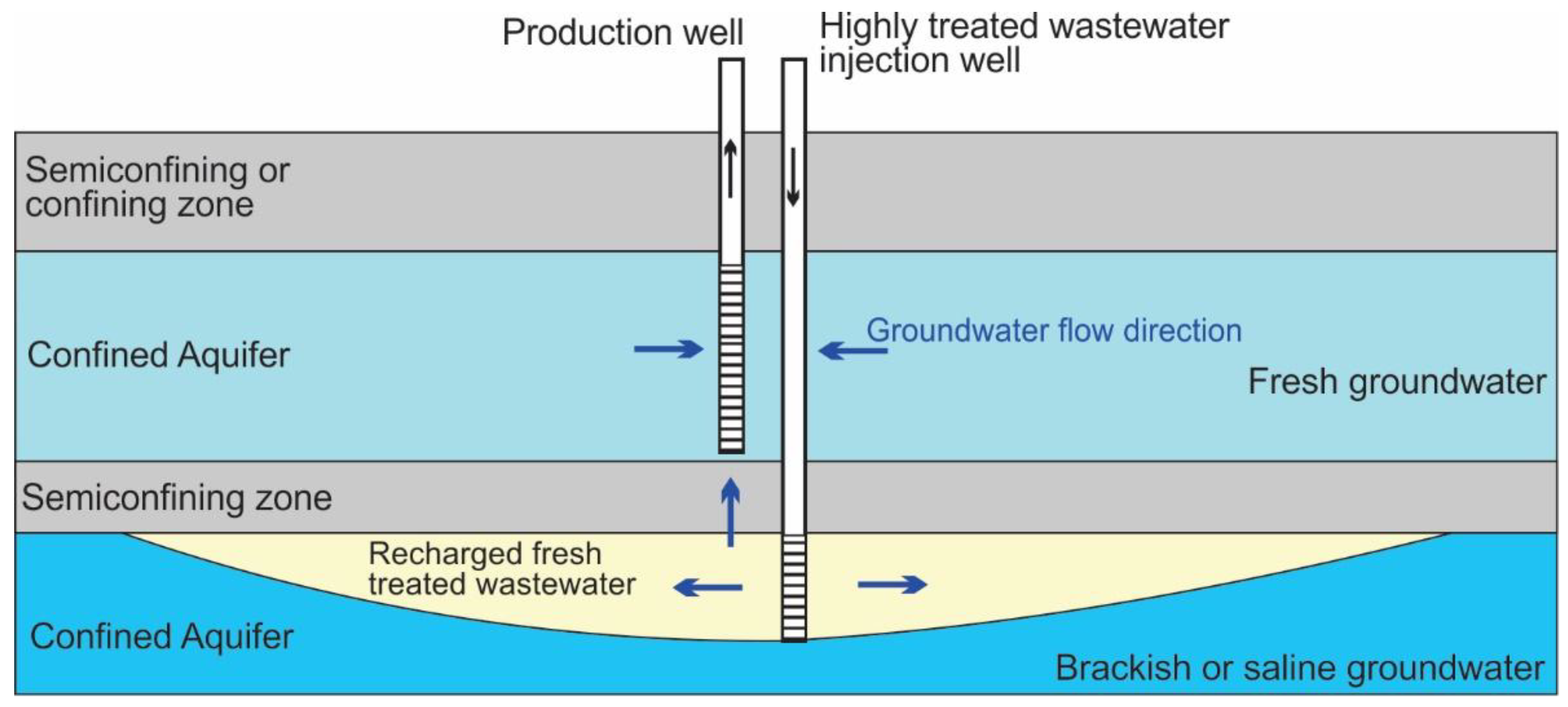
3.3. Horizontal Salinity Barriers Using Injection Wells
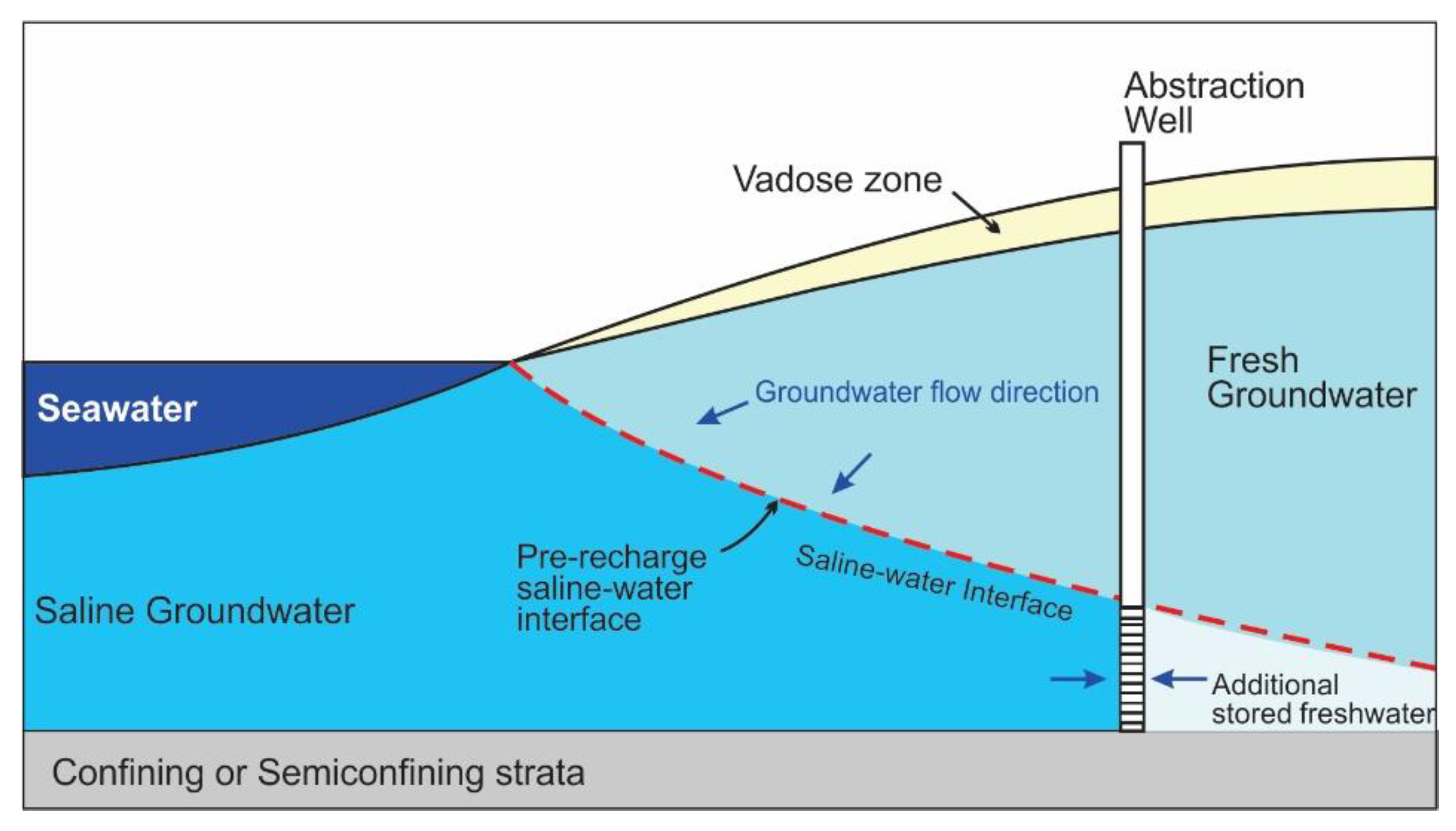
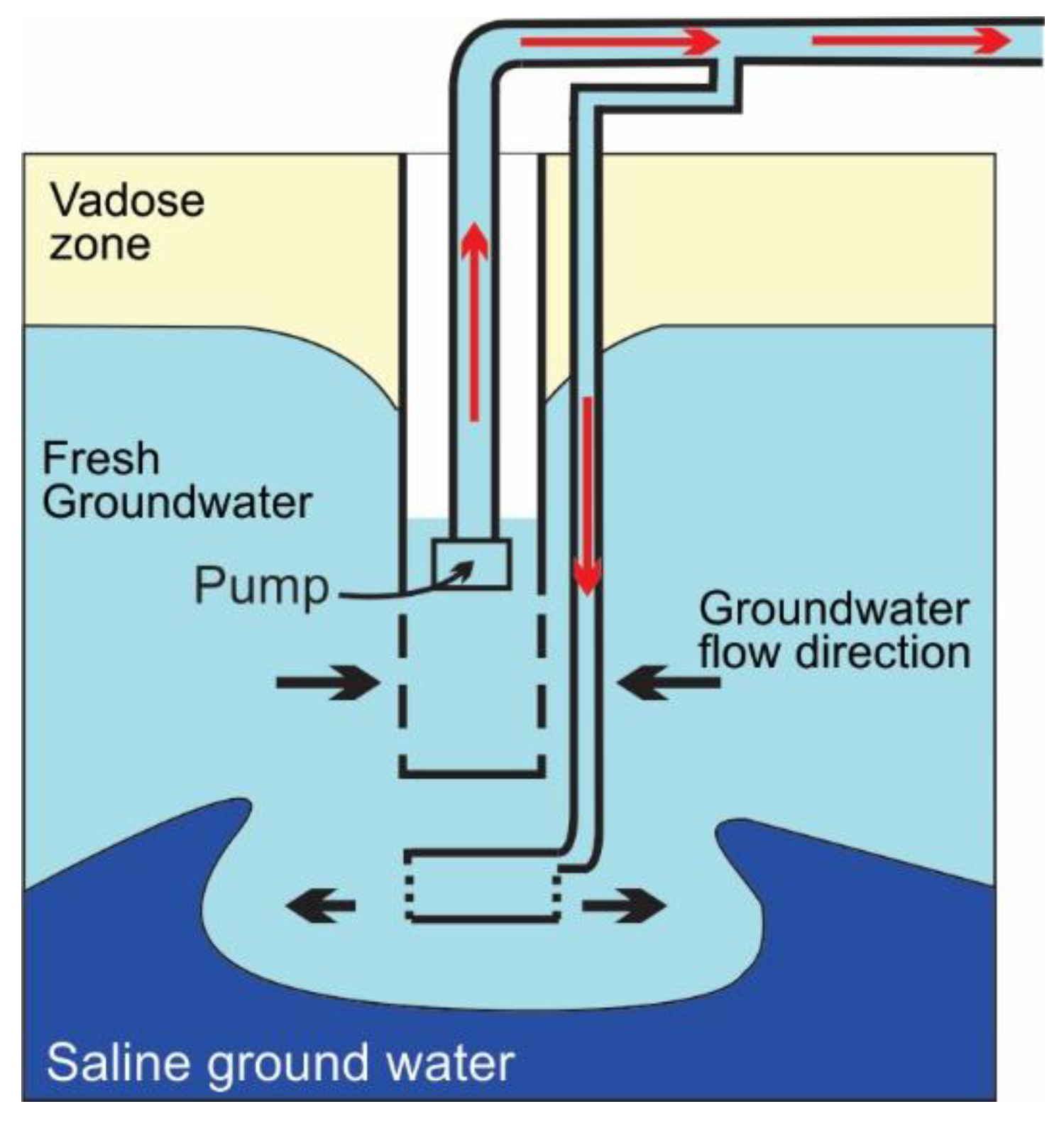
3.4. Horizontal Salinity Barriers Using Pumping Systems
3.5. Concurrently Operated Multi-Barriers or Mixed Barriers
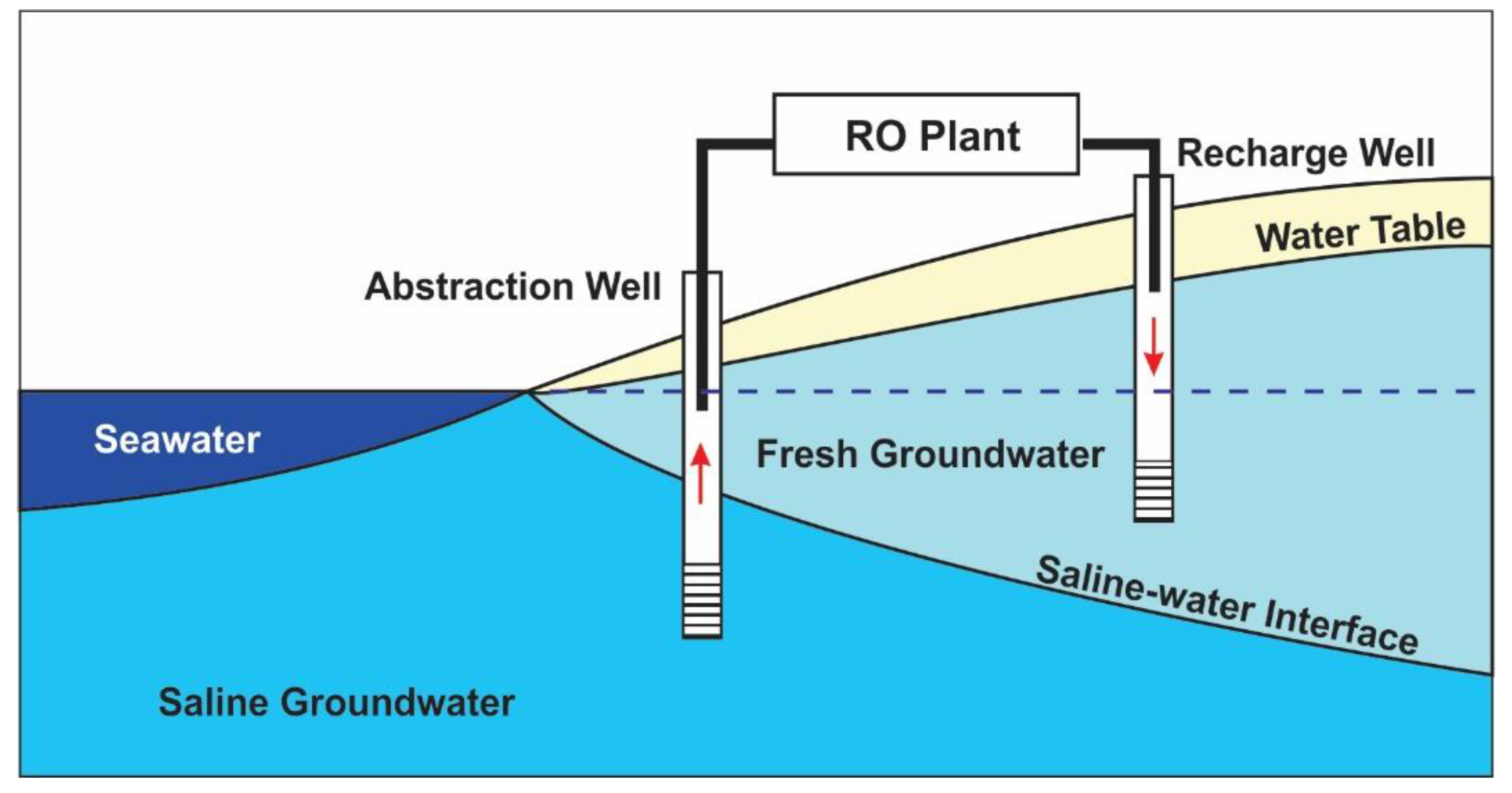
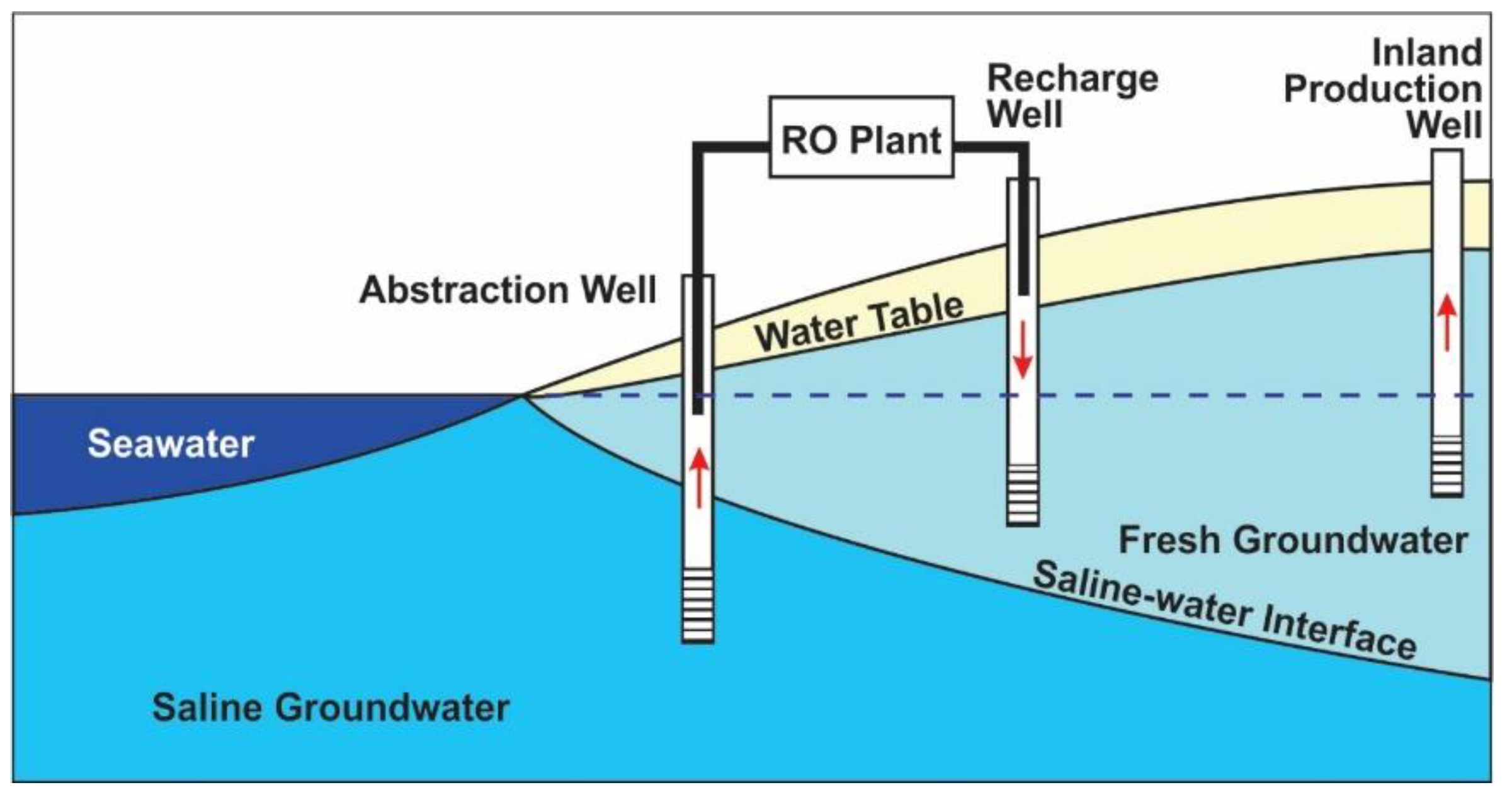
3.6. Abstraction, Desalination, and Recharge (ADR)
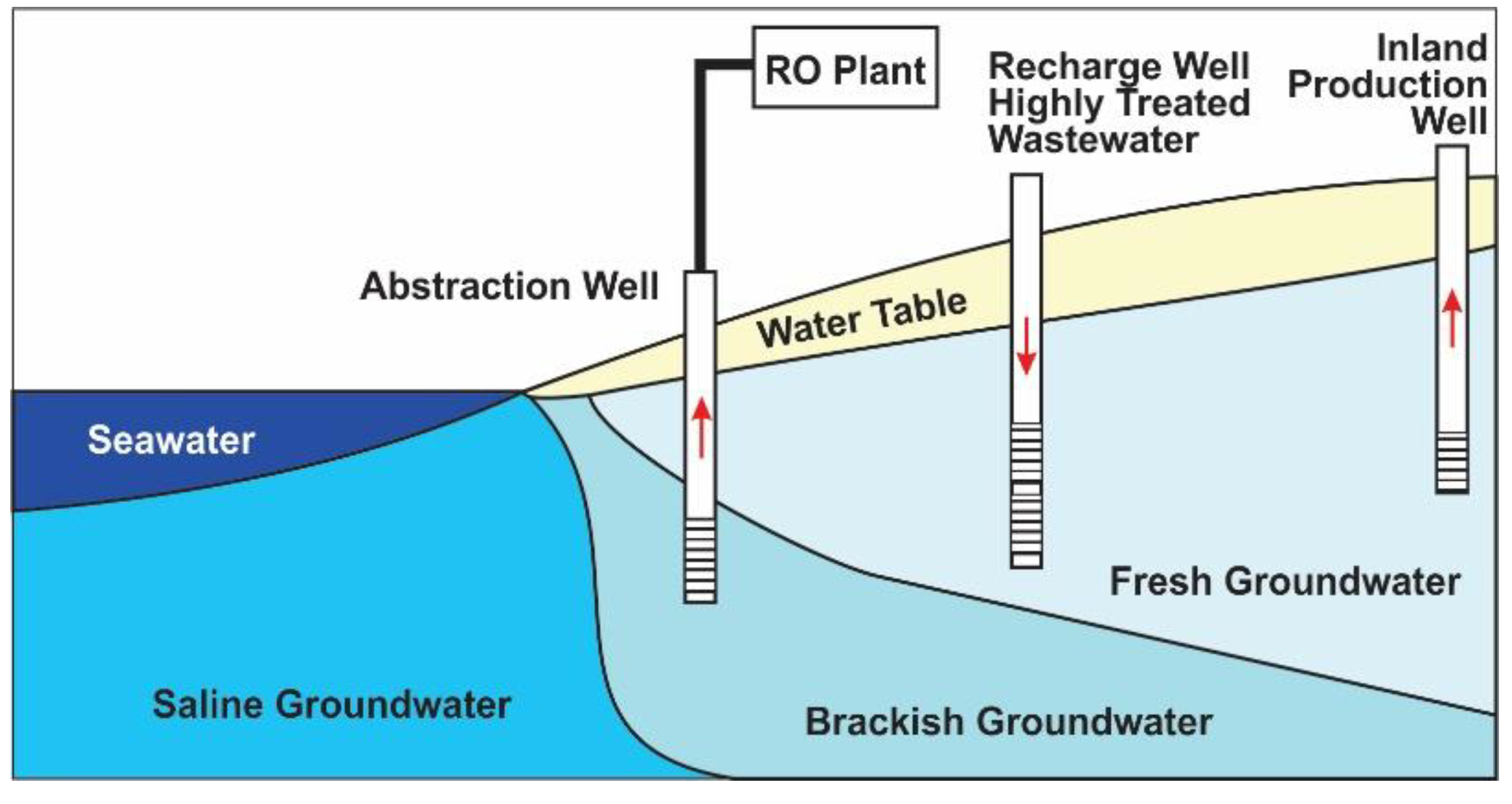
3.7. Evaluation of Hybrid Barrier/Water Treatment Types to Control Saltwater Intrusion
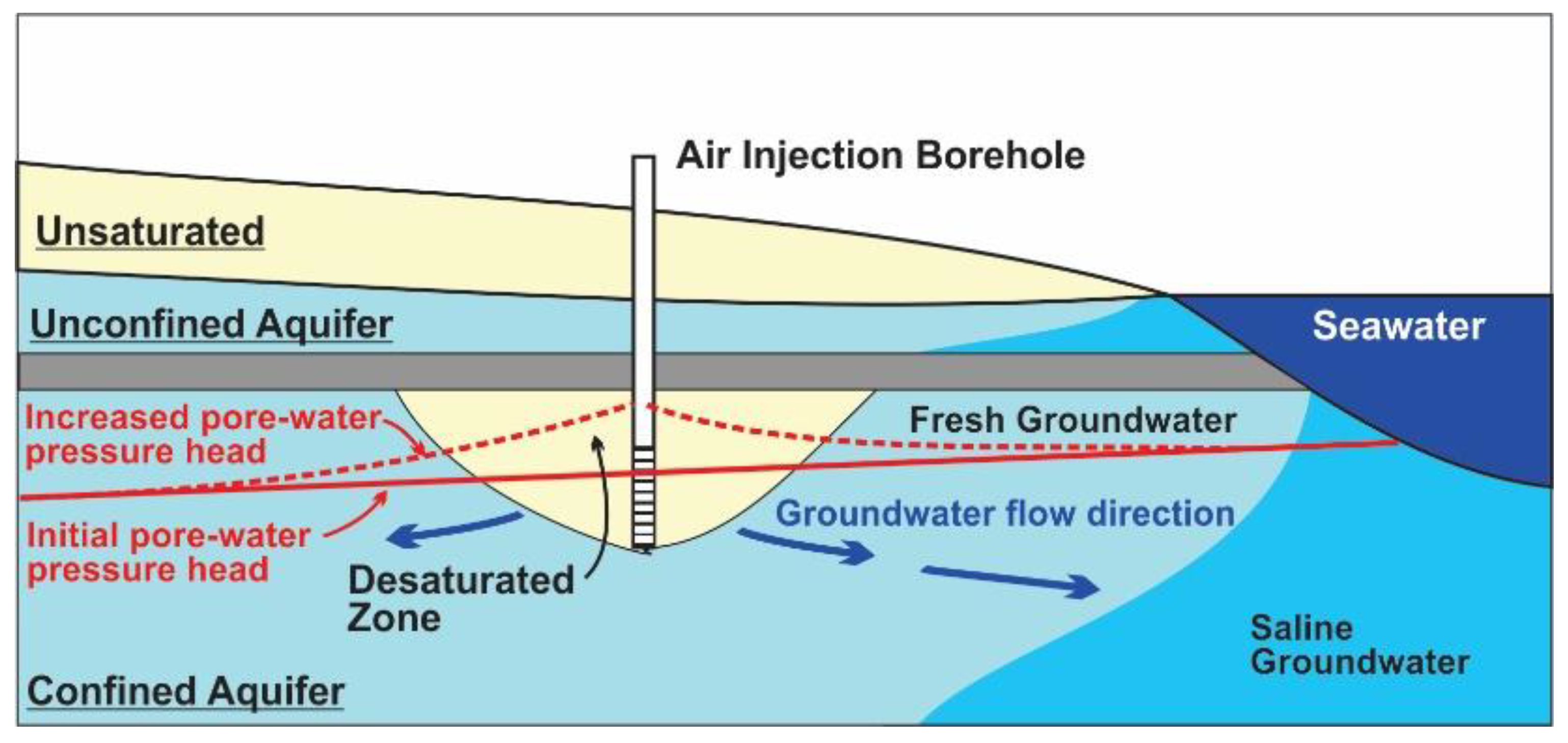
3.8. Pumped Air Barriers
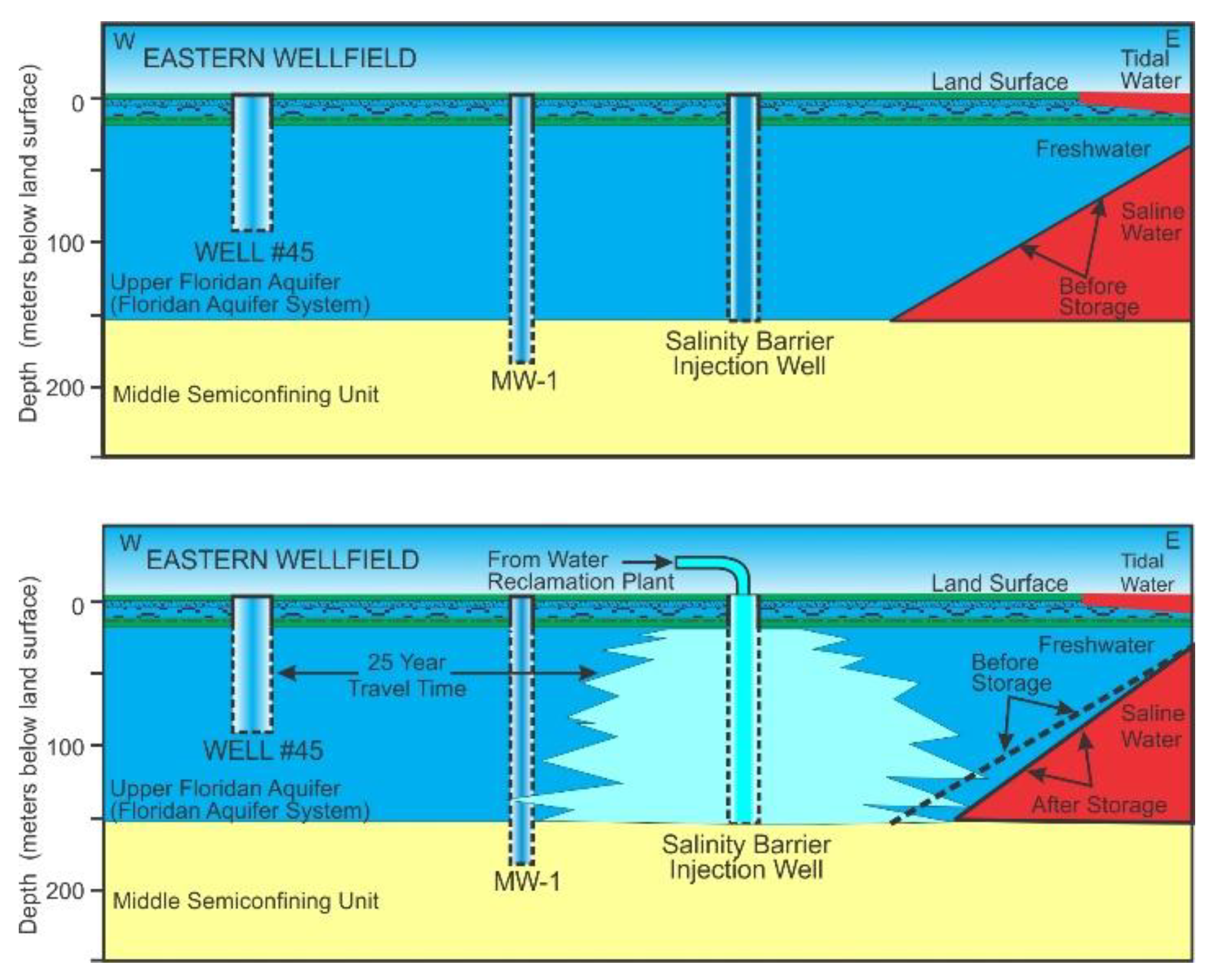
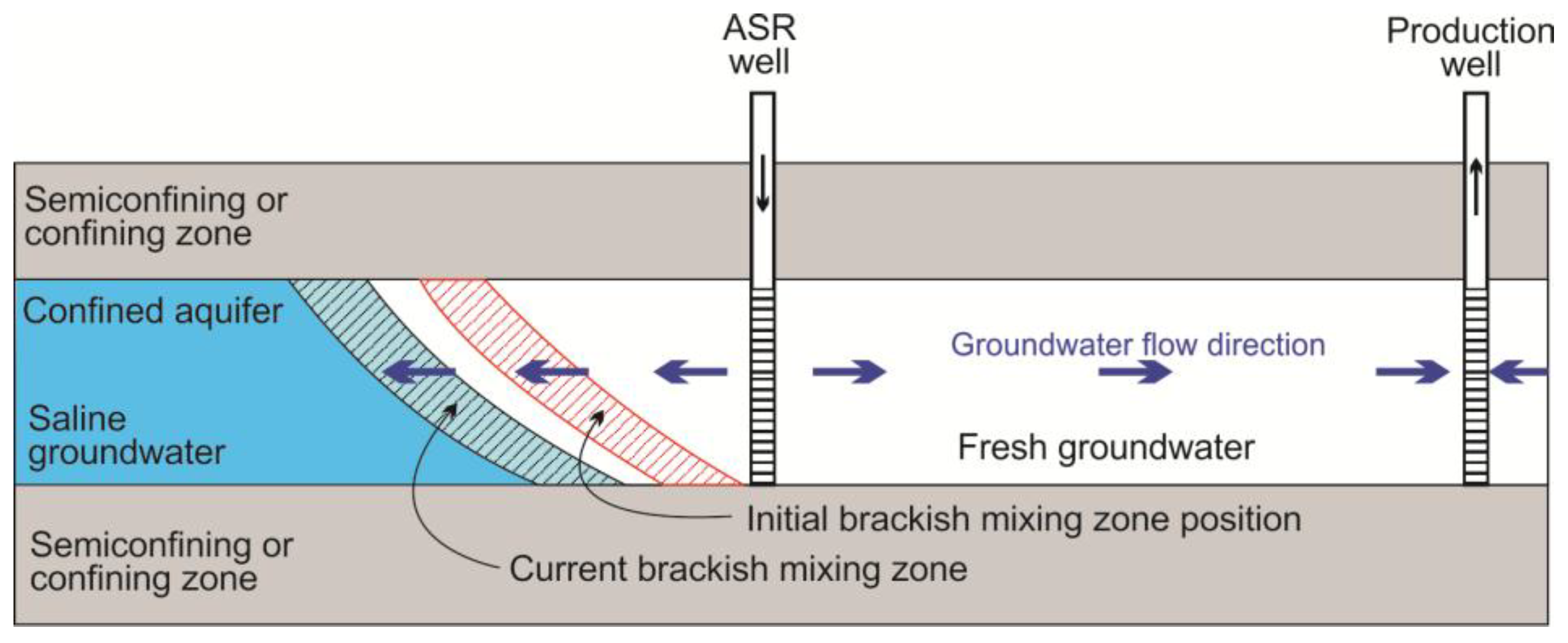
3.9. Management of Saltwater Intrusion Using Aquifer Storage and Recovery
3.10. Biofilm Barriers
3.11. Purposeful Activation of Expanding Clays to Inhibit Saltwater Intrusion
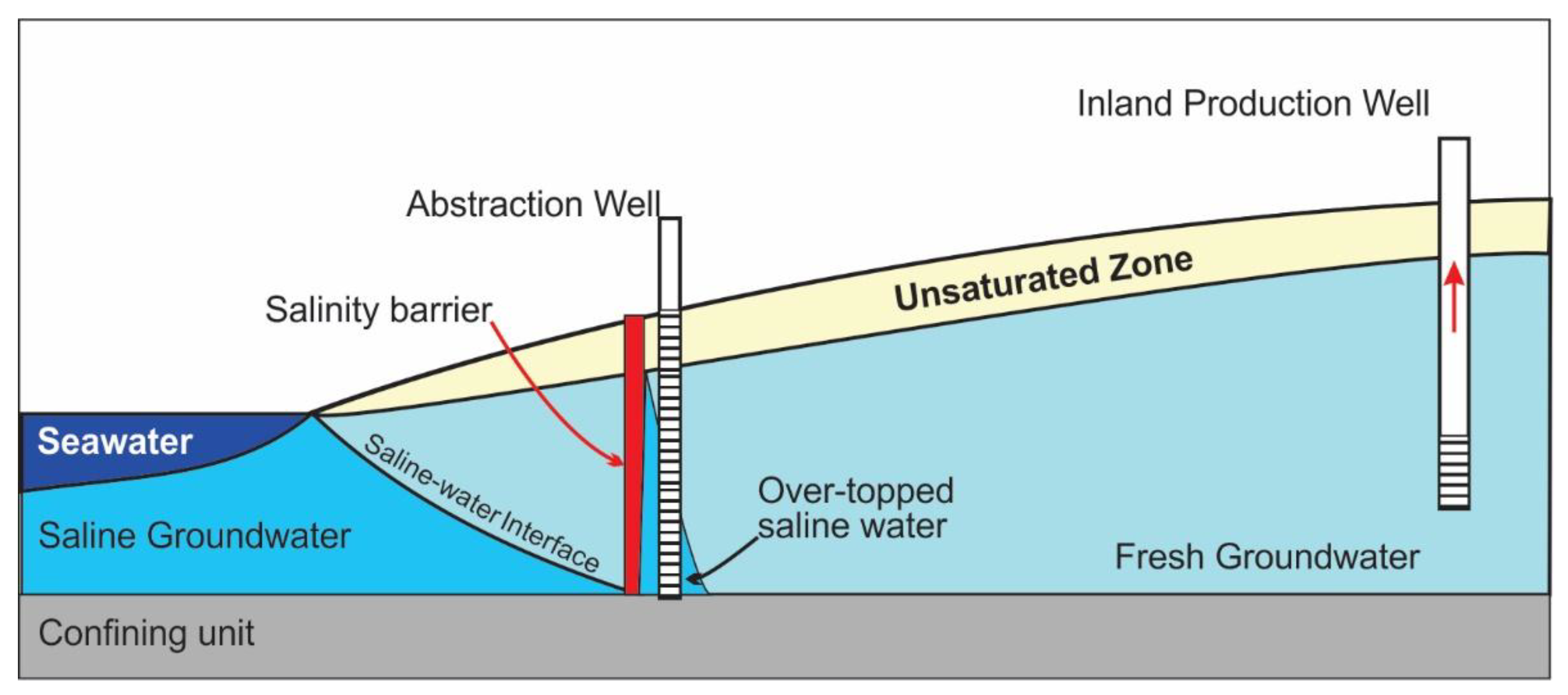
3.12. Vertical Salinity Barriers
4. Current Applications of Salinity Barriers (Examples)
4.1. Salalah, Oman Salinity Barrier
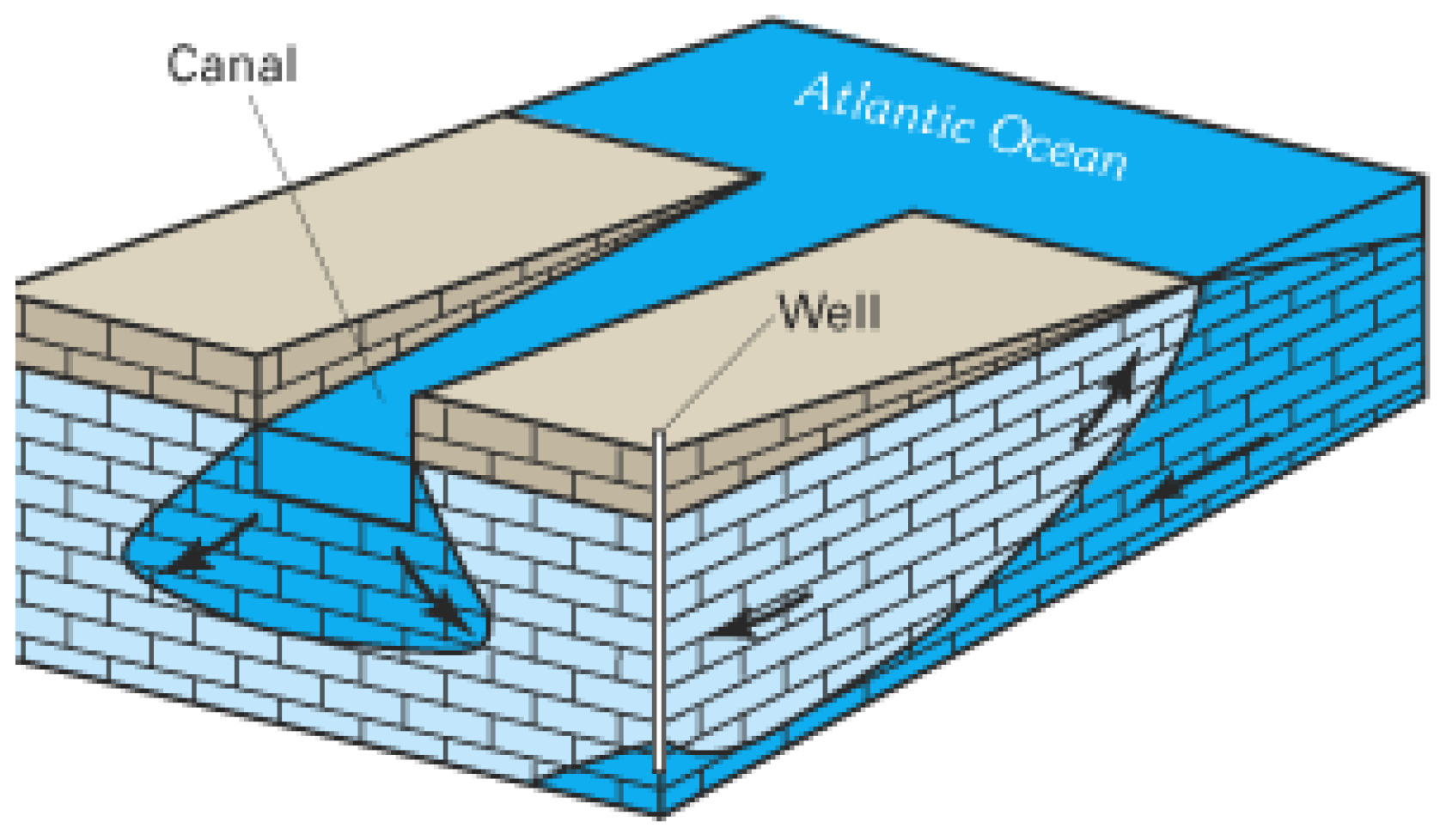
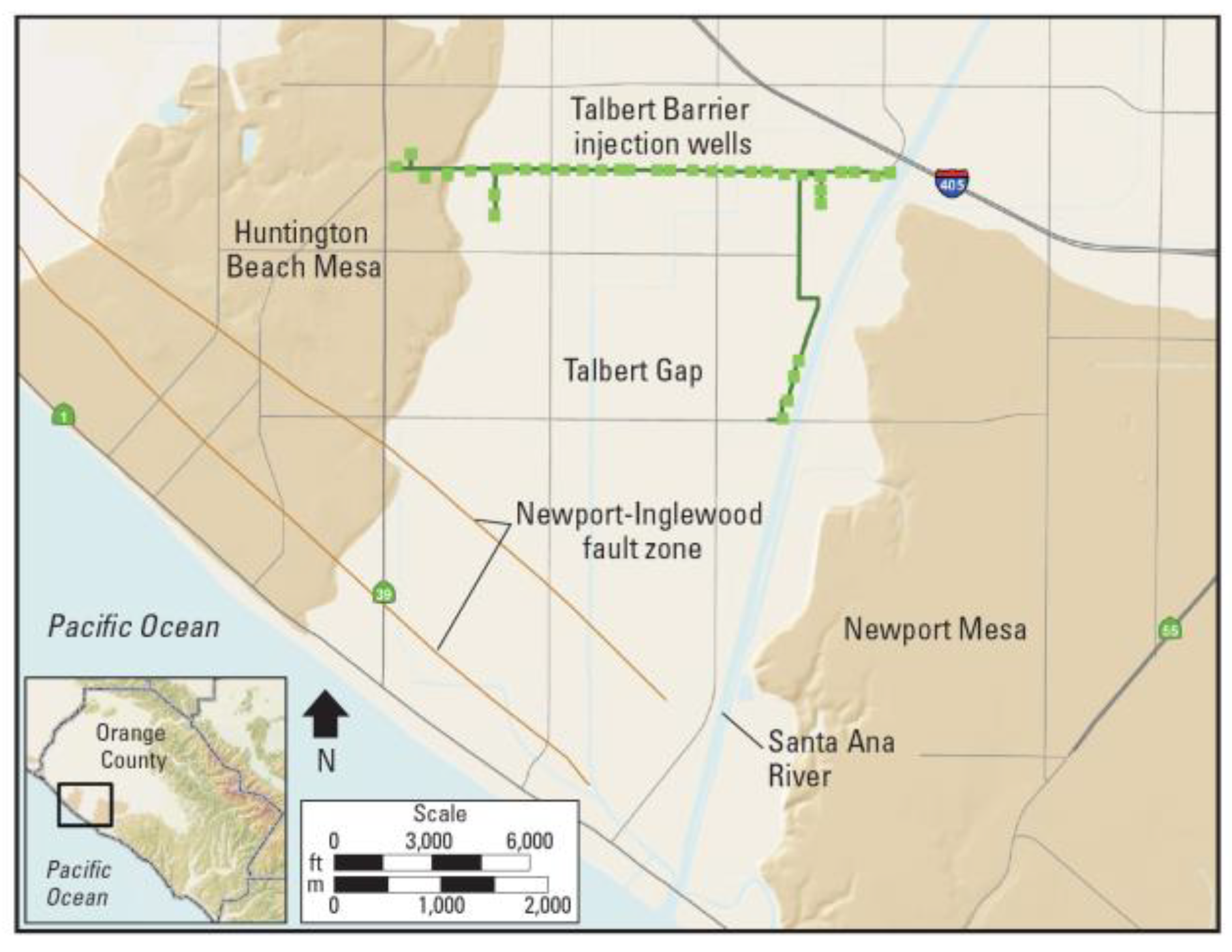
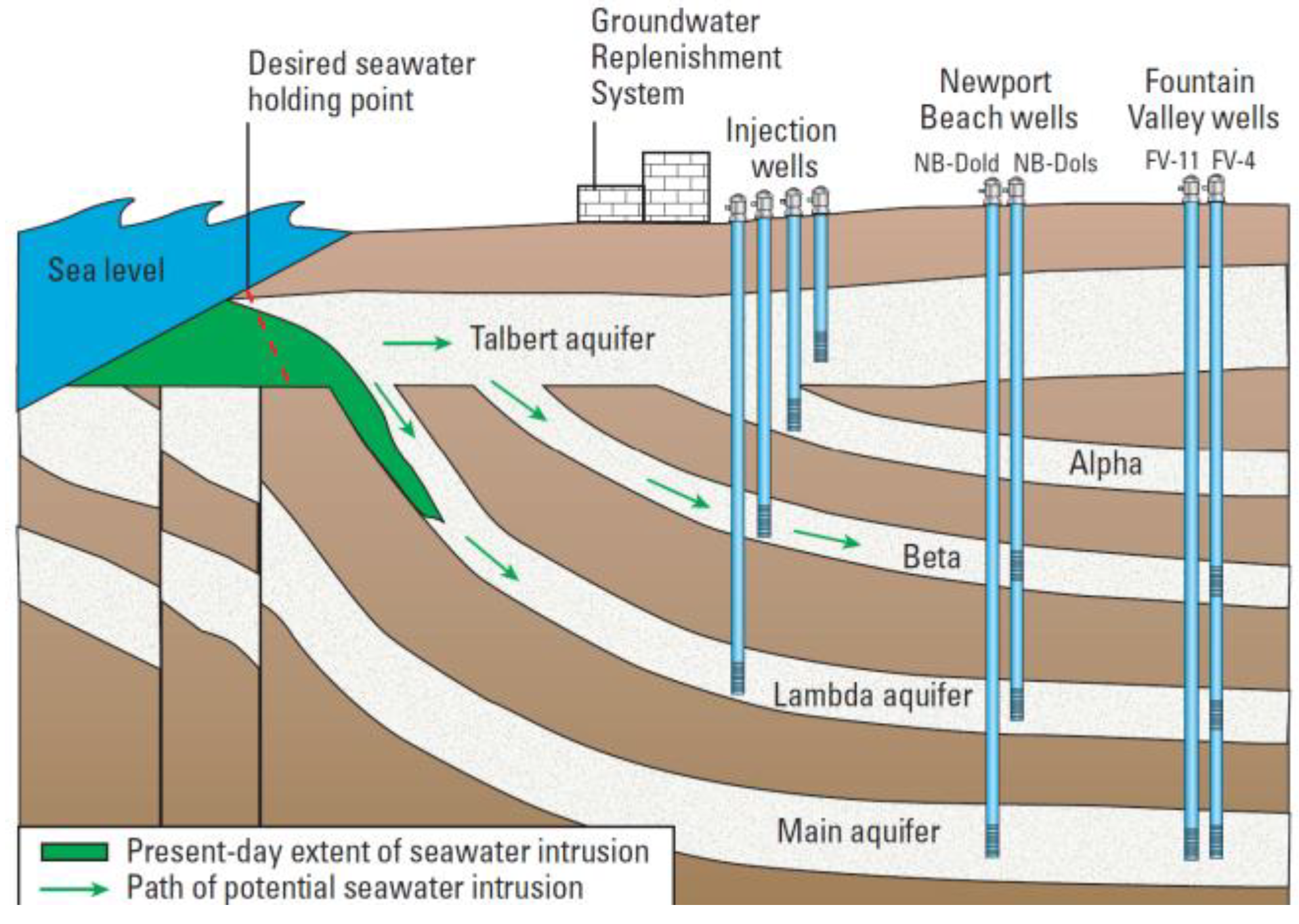
4.2. Talbert Seawater Intrusion Barrier
4.3. Proposed Innovative MAR Project to Prevent Future Saltwater Intrusion
5. An Assessment of Salinity Barriers to Mitigate the Impacts of Sea Level Rise in Coastal Aquifers
5.1. Technology
5.2. Environmental Issues
5.3. Regulatory Issues
5.4. Capital Costs
5.5. Operating Costs
5.6. Long-Term Effectiveness
5.7. A Discussion on the Results Reported in the Evaluation Matrix
6. Limits on Use of Salinity Barriers
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cosby, A.G.; Lebakula, V.; Smith, C.N.; Wanik, D.W.; Bergene, K.; Rose, A.N.; Swanson, D.; Bloom, D.E. Accelerating growth of human coastal populations at the global and continental levels: 2000–2018. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, G.G. Salt-water encroachment in Southern Florida. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1945, 37, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K. Sea-water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1953, 4, 749–754. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.K. Salt water intrusion of coastal aquifers in the United States. Internat. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Publ. 1960, 52, 452–461. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.K. Salt water intrusion and its control. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1974, 66, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980; 535p. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, H.R. Salt intrusion into freshwater aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. 1959, 64, 1911–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, F.A. Cyclic flow of saltwater in the Biscayne Aquifer of southeastern, Florida. J. Geophys. Res. 1960, 65, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.; Dagan, G. Moving interface in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1964, 90, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.H., Jr.; Kohout, F.A.; Henry, H.R.; Glover, R.E. Sea Water in Coastal Aquifers; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1613-C; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; 84p.
- Kashef, A.I. On the management of ground water in coastal aquifers. Ground Water 1971, 9, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmat, Y.; Chetboun, G. Seawater Encroachment in the Coastal Plain of Isreal During the Period 1958–1971; Isreal Hydrological Service Report 2/74; Israel Hydrological Service: TelAviv, Israel, 1974; 52p. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-H.; Cheng, R.T. On seawater water encroachment in coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newport, B.D. Salt Water Intrusion in the United States; Report EPA-600/8-77-011; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Ada, OK, USA, 1977; 30p. [Google Scholar]
- Frind, E.O. Seawater intrusion in continuous coastal aquifer aquitard system. Adv. Water Resour. 1982, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, H.; Waller, B.G. Synopsis of Saltwater Intrusion in Dade County, Florida, Through 1984; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 85-4101; U.S. Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1985.
- Magaritz, M.; Luzier, J.F. Water-rock interactions and seawater-freshwater mixing effects in the coastal dunes aquifer, Coos Bay, Oregon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.; Vacher, H.L. Hydrogeology of an atoll island: A conceptual model from a detailed study of Micronesian example. Ground Water 1986, 24, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cant, R.V.; Weech, P.S. A review of the factors affecting the development of Ghyben-Herzberg lenses in the Bahamas. J. Hydrol. 1986, 84, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, L.D.; Bredehoeft, J.D. Origins of sweater intrusion in a coastal aquifer: A case study of Pajaro Valley. J. Hydrol. 1987, 92, 363–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, W.R.; Voss, C.I. Analysis of an anisotropic coastal aquifer system using variable-density flow and solute transport simulation. J. Hydrol. 1987, 92, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, P.W. Simulation of Saltwater Movement in the Floridan Aquifer System, Hilton Head Island, South Carolina; U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 2331; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DD, USA, 1958; 19p. [Google Scholar]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Geirnart, W. Processes accompanying the intrusion of salt water. In Hydrogeology of Salt Water Intrusion—A Selection of SWIMM Papers, II; A A Balkema Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 291–304. [Google Scholar]
- Vacher, H.L.; Wallis, T.N.; Stewart, M. Hydrogeology of a fresh-water lens beneath a Holocene strandplain, Great Exuma Island, Bahamas. J. Hydrol. 1991, 125, 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Appleyard, S. The impact of urban development on recharge and groundwater supply in a coastal aquifer near Perth, western Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 1995, 3, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, S.; Das Grupta, A. Simulation of salt water encroachment in a multi-layer groundwater system, Bangkok, Thailand. Hydrogeol. J. 1995, 3, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszalka, E.J. Delineation of Saltwater Intrusion on the Biscayne Aquifer, Eastern Broward County, Florida; U.S. Geological Survey Water Resources Investigation 93-4164; U.S. Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, A.; Sherif, M.M. An Integrated Study of Seawater Intrusion in the Nile River Delta Aquifer; Working Paper Series for SHP; NWRC_MPWWR: Cairo, Egypt, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein, R.S. Delineation and Extent of Saltwater Intrusion in the Biscayne Aquifer, Eastern Dade County, Florida; U.S. Geological Survey Water Resources Investigation Report 96-4285; U.S. Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1997.
- Bear, J.; Cheng, A.H.-D.; Sorek, S.; Ouazar, D.; Herrera, I. (Eds.) Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers-Concepts, Methods and Practices; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Konikow, L.F.; Reilly, T.E. Seawater intrusion in the United States. In Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers—Concepts, Methods and Practices; Bear, J., Cheng, A.H.D., Sorek, S., Ouazar, D., Herrera, I., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 463–506. [Google Scholar]
- Qahman, K.; Larabi, A. Evaluation and numerical modeling of seawater intrusion in the Gaza aquifer (Palestine). Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, M.I.; Jacks, G. Seawater intrusion in the Salalah plain aquifer, Oman. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.D.; Biella, G.; Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Lozej, A.; Chiozzotto, B.; Giada, M.; Rizzetto, F.; Claude, C.; Mayer, A. Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy). J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.M. Groundwater Water in Freshwater-Saltwater Environments of the Atlantic Coast; U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1262; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003; 113p.
- Sanford, W.E.; Pope, J.P. Current challenges using models to forecast seawater intrusion: Lessons from the eastern shore of Virginia, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussis, A.D.; Mazi, K.; Riou, F.; Destouni, G. A correction for Dupuit-Forchheimer interface flow models of seawater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 525, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciopinto, C. Management of aquifer recharge in Lebanon by removing seawater intrusion from coastal aquifers. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 130, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.H.; Liu, J.P. Present situation and treatment of seawater intrusion in Dalian City. Water Resour. Hydropower Northeast China 2014, 32, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q. Groundwater resources protection and sea water intrusion in Ganjingzi District of Dalian City. Groundwater 2014, 36, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp, M.; Mtoni, Y.; Mjemah, I.C.; Bakundukize, C.; Walraevens, K. Investigating seawater intrusion due to groundwater pumping with schematic model simulations: The example of the Dar es Salaam coastal aquifer in Tanzania. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 96, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappa, G.; Ergul, S.; Ferranti, F.; Sweya, L.N.; Luciani, G. Effects of seasonal change and seawater intrusion on water quality for drinking and irrigation purposes, in coastal aquifers of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.M.; Klassen, J. Assessing the risk of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 730–745. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, T.H.T.; Babu, T.S.A.; Zander, P.; Muller, K. Paddy in saline water: Analysing variety-specific effects of saline water intrusion on the technical efficiency of rice production in Vietnam. SAGE J. Outlook Agric. 2019, 48, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Javadi, A.A.; Sherif, M.M. Management of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: A review. Water 2019, 11, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polemio, M.; Zuffianò, L.E. Review of utilization management of groundwater at risk of salinization. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 2020, 146, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.M.; Reichard, E.G. Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Robinson, G.; Hamill, G.; Etsias, G. Seawater intrusion in extremely heterogeneous laboratory-scale aquifer: Steady-state results. Water 2022, 14, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, E.; Gleeson, T.; Moosdorf, N. Fresh groundwater discharge insignificant for the world’s oceans but important for coastal ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, E. Effects of human activities on salt–fresh water relationships in coastal aquifers. In Ground Problems in Coastal Areas; Custodio, E., Bruggeman, G.A., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1987; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.A.; Gelhar, L.W. Seawater intrusion in layers aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetter, C.W. Position of the saline water interface beneath oceanic islands. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, G.; Zeitoun, D.G. Seawater-freshwater interface in a stratified aquifer of random permeability distribution. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1998, 29, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Breuk, W. (Ed.) Hydrogeology of Saltwater Intrusion—A Selection of SWIMM Papers; International Contributions to Hydrogeology, IAH, II; Verlag Heins Heise GambH: Hanover, Germany, 1991; 422p. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Graf, T.; Herold, M.; Ptak, T. Modelling the effects of tides and storm surges on coastal aquifers using a coupled surface-subsurface approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 149, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Graf, T.; Ptak, T. Sea level rise and storm surge effects in a coastal heterogeneous aquifer: A 2D modelling study in northern Germany. Grundwasser 2015, 20, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Graf, T.; Koneshloo, M.; O’Neal, M.A.; Michael, H.A. Impact of topography on groundwater salinization due to ocean surge inundation. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 5794–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tokunaga, T. Future risks of tsunami-induced seawater intrusion into unconfined coastal aquifers: Insights from numerical simulations at Niijima island, Japan. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 10082–10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, W.K.; Jin, G.Q.; Xin, P.; Robinson, C.; Gibbes, B.; Li, L. Tidal influence on seawater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, P.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Goncear, G.; Hinsby, K. Assessing impacts of climate change, sea level rise, and drainage canals on saltwater intrusion on coastal aquifer. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.Q.; Xie, T.Y.; Kuan, W. 2015. Effects of tide on salt intrusion: Experimental setup and methods. Res. Explor. Lab. 2015, 34, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Karamouz, M. Influence of coastal flooding on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress; Dunn, C.N., Van Weele, B., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Sacramento, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Brun, P.; Buri, P.; Gessler, A.; McCarthy, M.J.; Pellicciotti, F.; Stocker, B.; Karger, D.N. Global increases in the occurrence and impact of multiyear droughts. Science 2025, 287, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussis, A.D.; Mazi, K.; Riou, F.; Destouni, G. Analytical single potential, sharp-interface solutions for regional seawater intrusion in sloping unconfined coastal aquifers, with pumping and recharge. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, S.; Rapaglia, J.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Kruse, E. Impact of sea-level rise on saltwater intrusion length into the coastal aquifer, Partido de La Costa, Argentina. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 61–62, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Essink, G.H.P. Impact of sea level rise in the Netherlands, Chapter 14. In Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers—Concepts, Methods and Practices; Bear, J., Cheng, A.H.-D., Sorek, S., Ouazar, D., Herrera, I., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 507–529. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T. Impact of sea-level rise on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Groundwater 2009, 47, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T. Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Hanson, S.E.; Lowe, J.A.; Warrick, R.A.; Lu, X.; Long, A.J. Sea-level scenarios for evaluating coastal impacts. Weirs Clim. Change 2014, 5, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, H.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B. Evolutionary algorithms for the optimal management of coastal groundwater: A comparative study toward future challenges. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.V.; Lee, S.I. Assessment of seawater intrusion potential from sea-level rise and groundwater extraction in a coastal aquifer. Desalin. Water Treat. 1999, 53, 2324–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Javadi, A.A. Assessing impacts of sea level rise on seawater intrusion in a coastal aquifer with sloped shoreline boundary. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 11, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazan-Benitéz, B.d.R.; Esteller-Alberich, M.V.; Renau-Pruñonosa, A.; Expósito-Castillo, J.L. Simulation of seawater intrusion and upconing processes in Mediterranean aquifer in response to climate change (Pana de Castellón, Spain). Hydrology 2024, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.M.; Singh, V.P. Effect of climate change on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, H.; Groen, J.; Leijnse, A. Modes of seawater intrusion during transgressions. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3581–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feseker, T. Numerical studies on saltwater intrusion in a coastal aquifer northwestern Germany. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambastiani, B.; Antonellini, M.; Oude Essink, G.H.; Stuurman, R.J. Saltwater intrusion in an unconfined coastal aquifer of Ravenna (Italy): A numerical model. J. Hydrol. 2007, 340, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.F.; Boughriba, M.; Correla, A.; Zarhloule, Y.; Rimi, A.; El Houadi, R. Evaluation of climate change effects in a coastal aquifer in Morocco using a density-dependent numerical model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Essink, G.H.P.; Van Baaren, E.S.; De Louw, P.G.B. Effects of climate change on coastal groundwater systems: A modeling study in the Netherlands. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W00F04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T. Transience of seawater intrusion in response to sea level rise. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yechieli, Y.; Shaley, E.; Wollman, S.; Kiro, Y.; Kafri, U. Response of the Mediterranean and Dead Sea coastal aquifers to sea level variations. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Clement, T.P.; Simpson, M.J.; Lee, K.K. Does sea level rise have an impact on saltwater intrusion? Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.D.; Howard, K.W. Modeling the transient response of saline intrusion to rising sea levels. Groundwater 2011, 49, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiciga, H.A.; Pingel, T.J.; Garcia, E.S. Seawater intrusion by sea-level rise: Scenarios for the 21st century. Groundwater 2012, 50, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Change, S.W.; Clement, T.P. Experimental and numerical investigation of saltwater intrusion dynamics in flux-controlled groundwater systems. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W09527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Ward, J.D.; Morgan, L.K.; Simmons, C.T.; Robinson, N.I.; Teubner, M.D. Vulnerability indicators of sea water intrusion. Groundwater 2012, 50, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T.; Morgan, L.K.; Lu, C. How important is the impact of land-surface inundation on seawater intrusion caused by sea-level rise? Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laattoe, T.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T. Seawater intrusion under current sea-level rise: Processes accompanying coastline transgression. In Groundwater in the Coastal Zone of Asia-Pacific Coastal Research Library; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 7, pp. 295–313. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, L.K.; Stoecki, L.; Werner, A.D.; Post, V.E.A. An assessment of seawater intrusion overshoot using physical and numerical modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6522–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.A.; Russoniello, C.J.; Byron, L.A. Global assessment of vulnerability to sea-level rise in topography-limited and recharge-limited coastal groundwater systems. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2228–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Werner, A.D. Timescales of seawater intrusion and retreat. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 59, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazi, K.; Koussis, A.D.; Destouni, G. Tipping points for seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers under rising sea level. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazi, K.; Koussis, A.D.; Destouni, G. Intensively exploited Mediterranean aquifers: Proximity to tipping points and control criteria for sea intrusion. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seflnasr, A.; Sherif, M. Impacts of seawater rise on seawater intrusion in the Nile delta aquifer, Egypt. Groundwater 2014, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigter, T.Y.; Nunes, J.P.; Pisani, B.; Fakir, Y.; Hugman, R.; Li, Y.; Tome, S.; Ribero, L.; Samper, J.; Oliveira, J.; et al. Comparative assessment of climate change and its impacts on three coastal aquifers in the Mediterranean. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.; Okkonen, J. Impacts of future climate change and Baltic sea level rise on groundwater recharge, groundwater levels, and surface leakage in the Hanko aquifer in southern Finland. Water 2014, 6, 3671–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.R.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B. An evaluation of the relative importance of the effects of climate change and groundwater extraction on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers in Atlantic Canada. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xin, P.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Seawater intrusion in response to sea-level rise in a coastal aquifer with a general-head inland boundary. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnaux, R. Closed-form analytical solutions for assessing the consequences of sea-level rise on groundwater resources in sloping coastal aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, L.K.; Bakker, M.; Werner, A.D. Occurrence of seawater intrusion overshoot. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, E.C. The equilibrium of rain-fed ground water resting on deeper saline water; the Ghyben-Herzberg lens. J. Soil Sci. 1950, 1, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumer, R.R.; Shiau, J.C. Salt water interface in a layered coastal aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 1968, 4, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Datta, B. Saltwater intrusion management of coastal aquifers. I: Linked simulation-optimization. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, H.; Jahangir, M.S. Influence of aquifer heterogeneity on sea level rise-induced seawater intrusion: A probabilistic approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 236, 103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Tidal effects on sea water intrusion in unconfined aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1999, 216, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.M.; Oumeraci, H. Modelling and management of storm-driven saltwater intrusion in freshwater aquifers: The case of near Bremerhaven, Germany. In Integrating Ecosystem in Coastal Engineering Practice; Silva, R., Chavez, V., Eds.; Cuvillier Verlag: Göttingen, Germany, 2017; pp. 150–168. [Google Scholar]
- Van Biersel, T.P.; Carlson, D.A.; Milner, L.R. Impact of hurricane storm surges on the groundwater resources. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paldor, A.; Michael, H.A. Storm surges cause simultaneous salinization and freshening of coastal aquifers, exacerbated by climate change. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, D.; Medeiros, S.C.; Bilskie, M.V.; Hagen, S.C.; Hall, C.R. Exploration of the effects of storm surge on the extent of saltwater intrusion into the surficial aquifer in coastal east-central Florida (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagan, G.; Bear, J. Solving the problem of local interface upconing in a coastal aquifer. J. Hydraul. Res. 1968, 6, 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmorak, S.; Mercado, A. Upconing of freshwater—Sea water interface below pumping wells, field study. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 1290–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, R.A.; McWhorter, D.B. Upconing of the salt-water-freshwater interface beneath a pumping well. Ground Water 1975, 13, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, T.E.; Frimpter, M.H.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Goodman, A.S. Analysis of steady state seawater upconingat TruroWell Field, Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Ground Water 1987, 25, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K. Ground Water Hydrology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1967; 336p. [Google Scholar]
- Izbicki, J.A. Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal California Aquifer; U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet; U.S. Geological Survey: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996.
- Ghasemizadeh, R.; Hellweger, F.; Butscher, C.; Padilla, I.; Vesper, D.; Field, M.; Alschawabkeh, A. Review: Groundwater flow and transport modeling of karst aquifers, with particular reference to the North Coast Limestone aquifer system of Puerto Rico. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1441–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, H.R. Effects of Dispersion on Salt Encroachment in Coastal Aquifers; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1613-C; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; pp. C71–C84.
- Glover, R.E. The pattern of fresh-water flow in a coastal aquifer. J. Geophys. Res. 1959, 64, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D. On the classification of seawater intrusion. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badon Ghyben, W. Nota in verband met de voorgenomen putoring nabij Amsterdam. Tijdschrift van Koninkijk Instituut van Ingenieurs 1888–1889; Hague; 21p.
- Herzberg, B. Die Wasserversorgung einger Nordseebäder. J. Gasbeleucht. Wasserversorg. 1901, 44, 842–844. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J. Experiment and numerical simulation of seawater intrusion under the influences of tidal fluctuation and ground water exploitation in coastal multi layered aquifers. In Geofluids, Special Issue on Flow, Transport, and Reactions in Coastal Aquifers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paldor, A.; Shalev, E.; Katz, O.; Aharonov, E. Dynamics of saltwater intrusion and submarine groundwater discharge in confined coastal aquifers: A case study in northern Israel. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Lu, C.; Werner, A.D. Assessment of the impact of sea level rise on seawater intrusion in sloping confined coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanic, S.; LeRoux, N.K.; Paldor, A.; Mohammed, A.A.; Michael, H.A.; Kurylyk, B.L. Salywater intrusion into a confined island aquifer driven by erosion, changing recharge, sea-level rise, and coastal flooding. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR03394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, F.A. A hypothesis concerning cyclic flow of saltwater related to geothermal heating in the Floridan aquifer. Trans. N. Y. Acad. Sci. Ser. II 1965, 28, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Climate Change 2007. Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. In Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the International Panel on Climate Change; Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J., Hanson, C.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fox-Kemper, B.; Hewitt, H.T.; Xiao, C.; Aðalgeirsdóttir, G.; Drijfhout, S.S.; Edwards, T.L.; Golledge, N.R.; Hemer, M.; Kopp, R.E.; Krinner, G.; et al. Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1211–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlighem, M.; Williams, C.N.; Rignot, E.; An, L.; Arndt, J.E.; Bamber, J.L.; Catania, G.; Chauché, N.; Dowdewell, J.A.; Dorschel, B.; et al. Bed Machine v3: Complete bed topography and ocean bathymetry mapping of Greenland from multibeam echo sounding combined with mass conservation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11051–11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, A. The case for sea-level change as a dominant causal factor in mass extinction of marine invertebrates. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1989, 325, 437–455. [Google Scholar]
- Post, V. Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: Is our technology ready for the problems ahead? Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesha, A. An overview of control of salt water intrusion in coastal aquifers. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 7, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, E.; Vázquez-Suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; Capino, B.; Gámez, D.; Batlle, F. Optimal design of measures to correct seawater intrusion. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W09415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugio, S.; Nakada, K.; Urish, D.W. Subsurface seawater intrusion barriers analysis. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1987, 113, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Reichard, E.G. Evaluating strategies to manage seawater intrusion. In North American Water and Environmental Congress, Anaheim, CA; Bathala, C.T., Ed.; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, B.; Yeh, W. Improving seawater barrier operation with simulation optimization in southern California. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Siade, A.J.; Reichard, E.G.; Ponti, D.J.; Canales, A.G.; Johnson, T.A. Stratigraphic controls on seawater intrusion and implications for groundwater management, Dominguez Gap area of Los Angeles, California, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1699–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, J.; Datta, B. Multi-objective management of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers using genetic programming and modular neural network based surrogate models. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Optimization modelling for seawater intrusion management. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Hussain, M.; Sherif, M.; Farmani, R. Multi-objective optimization of different management scenarios to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 29, 1843–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.D. Puddled-clay cutoff walls stop sea-water infiltration. Civ. Eng. 1951, 21, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, H.O. The effect of a subsurface barrier on the conservation of freshwater in coastal aquifers. Water Res. 1983, 17, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawa, N.; Miyazaki, K. The analysis of saltwater intrusion through Komesu underground dam and water quality management for salinity. Paddy Water Environ. 2009, 7, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Elango, L. Modelling the impact of a subsurface barrier on groundwater flow in the lower Palar River basin, southern India. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleris, V.K.; Ziogas, A.I. The effect of cutoff walls on saltwater intrusion and groundwater extraction in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2013, 17, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoulhalik, A.; Ahmed, A.A. The effectiveness of cutoff walls to control saltwater intrusion in multi-layerd coastal aquifers: Experimental and numerical study. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 199, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Abdoulhalik, A.; Ahmed, A.; Hamill, G.A. A new physical barrier system for seawater intrusion control. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Shi, W.; Xin, P.; Wu, J.; Werner, A.D. Replenishing an unconfined coastal aquifer to control seawater intrusion: Injection or infiltration? Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 4775–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Q.; Walther, M. Effect of subsurface dams on saltwater intrusion and fresh groundwater discharge. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Cao, H.; Ma, J.; Shi, W.; Rathore, S.S.; Wu, J.; Luo, J. A proof of concept study of using a less permeable slice along the shoreline to increase fresh groundwater storage of oceanic islands: Analytical and experimental validation. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6450–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanuos, A.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M. Underground barrier wall evaluation for controlling saltwater intrusion in sloping unconfined coastal aquifers. Water 2020, 12, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zheng, T.; Chang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Walther, M. Effects of mixed physical barrier on residual saltwater removal and groundwater discharge in coastal aquifers. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, S.R.; Gado, T.A.; Zeidan, B.A.; Armanuos, A.M. Evaluating the impact of inclined cutoff-wall to control seawater intrusion in heterogeneous coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 6021–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, S.R.; Armanus, A.M.; Zeiden, B.A.; Gado, T.A. Numerical investigation of mixed physical barriers for saltwater removal in coastal heterogeneous aquifers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 4826–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missimer, T.M.; Amy, V.; Espinosa, C.; Van Lent, T.; Gleason, P.J.; Hansen, T.J.; Harvey, J.; Higer, A.; Horton, W.; Hunt, W.T.; et al. Seepage Management. Report by the Technical Advisory Committee to the Governor’s Commission for a Sustainable South Florida, September 1997. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5d5179e7e42ca1000117872f/t/621f90d539e4f977972aa8c8/1646235863033/Seepage+Management+9-97.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Berger, D.J.; Tryson, S.O. Approach to designing structural slurry walls. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1999, 125, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.B.; Davidson, R.R.; Cavalli, N.J. Slurry Walls: Design, Construction, and Quality Control; ASTM International: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Daw, G.P.; Pollard, C.A. Grouting for ground water control in underground mining. Int. J. Mine Water 1986, 5, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, P.; Tian, S. Prevention and treatment technologies of railway tunnel water inrush and mud gushing in China. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 5, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, H.R.R.; Khatib, M.M. Back analysis of grout treatment at Sumbar Dam using the joint hydraulic factor. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 2485–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strack, O.D.L.; Stoeckl, L.; Damm, K.; Houben, G.; Ausk, B.K.; de Lange, W.J. Reduction of saltwater intrusion by modifying hydraulic conductivity. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 6978–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lu, C.; Yan, M.; Werner, A.D. Expanding freshwater lenses adjacent to gaining rivers through vertical low-hydraulic conductivity barriers: Analytical and experimental validation. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanuos, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Mahmod, W.E.; Takemura, J.; Yoshimura, C. Analysing the combined effect of barrier wall and freshwater injection countermeasures on controlling saltwater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifer systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motallebian, M.; Ahmadi, H.; Raoof, A.; Cartwright, N. An alternative approach to control saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers using a freshwater surface recharge canal. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 222, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.; Javadi, A.A.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Farmain, R. Mitigating seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Novel approach with treated wastewater injection and groundwater circulation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.L. Saltwater-Barrier Line in Florida: Concepts, Consideration, and Site Examples; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations 79-75; U.S. Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1979.
- Geerts, S.J.; van der Sande, W.M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Geurts, B.J.; Roos, P.C. Sand dunes as a nature-based solution to mitigate salt intrusion in stratified estuaries. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2025, 130, e2024JC021103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesha, A.; Nagaraja, S.H. Effect of natural recharge on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1996, 174, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P. Groundwater-water movement controlled through spreading. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1952, 117, 1024–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P. Experiments with fresh-water barrier to prevent sea water intrusion. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1953, 45, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverty, F.B. Recharging wells expected to stem sea-water intrusion. Civ. Eng. 1952, 22, 313–315. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, H.O.; Richter, R.C. Sea-water intrusion into ground-water basins bordering the California coast and inland bays. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1953, 34, 575–582. [Google Scholar]
- Laverty, F.B.; van der Goot, H.A. Development of a fresh-water barrier in southern California for the prevention of sea water intrusion. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1955, 47, 886–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruington, A.E.; Seares, F.D. Operating a sea water barrier project. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1965, 91, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Department Water Resources. Santa Ana Gap Salinity Barrier, Orange County; California Department of Water Resources Bulletin 147-1; California Department of Water Resources: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1966; 178p.
- Bruington, A.E. Control of salt-water intrusion in a ground-water aquifer. Ground Water 1969, 7, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, E.; Gianimo, A.A.; Sulam, D.J. Design and Operation of Artificial-Recharge Plant at Bay Park, New York; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 751-B; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; 14p.
- Mahesha, A. Transient effect of battery of injection wells on seawater intrusion. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1996, 122, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloetcher, F.; Muniz, A.; Witt, G.M. Groundwater Injection: Modelling, Risks, and Regulations; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005; 337p. [Google Scholar]
- Luyun, R., Jr.; Momii, K.; Nakagawa, K. Effects of recharge wells and flow barriers on seawater intrusion. Groundwater 2011, 49, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, J.; Datta, B. Optimal combined operation of production and barrier wells for the control of saltwater intrusion in coastal groundwater well fields. Desal. Water Treat. 2011, 32, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allow, K.A. The use of injection wells and a subsurface barrier in the prevention of seawater intrusion: A modelling approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2012, 5, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanuos, A.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M. Assessing the effectiveness of using recharge wells for controlling the saltwater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifers with sloping beds: Numerical study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange County (CA) Water District. Talbert Seawater Intrusion Barrier Operations & Maintenance Manual; Orange County Water District: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 2023; 244p, Available online: https://cawaterlibrary.net/document/talbert-seawater-intrusion-barrier-operations-maintenance-manual/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). The Class V Underground Injection Control Study, Volume 20, Salt Water Intrusion Barrier Wells; USEPA Publication EPA/816-R-99-01-014tv; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; 29p.
- Perlmutter, N.M.; Pearson, F.J.; Bennett, G.D. Deep-Well Injection of Treated Wastewater—An Experiment in Re-Use of Ground Water in Western Long Island, New York; New York Geological Association Guidebook, 49th Annual Meeting; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1968; pp. 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchioli, J.; Ku, H.F.H. Preliminary Results of Injecting Highly Treated Sewage-Plant Effluent into a Deep Sand Aquifer at Bay Park, New York; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 751-A; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; 14p. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchioli, J.; Bennett, D.; Preseason, F.J., Jr.; Cerrillo, L.A. Geohydrology of the Artificial-Recharge Site at Bay Park, Long Island, New York; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 751-C; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; 29p. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T. Artificial Recharge of Groundwater; Butterworth Publishers: Stonehan, MA, USA, 1985; 767p. [Google Scholar]
- Wesner, G.M.; Herndon, R.L. Orange County Water District Water Reclamation and Seawater Intrusion Barrier Project; OCWD Engineering Report, Orange County Water District: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Missimer, T.M.; Maliva, R.G.; Tidwell, M. City of Daytona Beach, Florida salinity barrier project: Achieving complete reuse of reclaimed water. In Proceedings of the International Desalination Association Conference on Desalination and Water Reuse, Masplamomas, Gran Canaria, Spain, 21–26 October 2007; Proceedings Paper IDAWC/MP07-094. 12p. [Google Scholar]
- Maliva, R.G.; Missimer, T.M. Aquifer Storage and Recovery and Managed Aquifer Recharge Using Wells: Planning, Hydrogeology, Design, and Operation; Schlumberger: Sugar Land, TX, USA, 2010; 578p. [Google Scholar]
- Botero-Acosta, A.; Donado, L.D. Laboratory scale simulation of hydraulic barriers to seawater intrusion in confined coastal aquifers considering the effects of stratification. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 25, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Comte, J.-C.; Li, F.; Chen, H. Influence of tides on the effectiveness of artificial freshwater injection in mitigating seawater intrusion in an unconfined coastal aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617 Pt B, 129043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Department of Water Resources. Oxnard Basin Experimental Extraction-Type Barrier; California Department of Water Resources Bulletin 147-6; California Department of Water Resources: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1970; 157p.
- Coe, J.J. Seawater intrusion extraction barrier. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1972, 98, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.; Hamza, K.I. Mitigation of seawater intrusion by pumping brackish water. Transp. Porous Media 2001, 43, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyfzand, P.J.; Maas, K.; Kappelhof, J.; Kooiman, J.W. Pumping brackish groundwater to prepare drinking water and keep salinized wells fresh. In Proceedings of the 18th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Cartagena, Spain, 31 May–3 June 2004; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Kacimov, A.; Sherif, M.; Perret, J.S.; Al-Mushikhi, A. Control of sea-water intrusion by salt-water pumping: Coast of Oman. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, M.; Carrera, J. Dynamics of negative hydraulic barriers to prevent seawater intrusion. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, P.; Händel, F.; Walther, M. Potential of mixed hydraulic barriers to remediate seawater intrusion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missimer, T.M.; Ghaffour, N.; Dehwah, A.H.A.; Rachman, R.; Maliva, R.G.; Amy, G.L. Subsurface intakes for seawater reverse osmosis systems: Capacity limitation, water quality improvement, and economics. Desalination 2013, 322, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffour, N.; Missimer, T.M.; Amy, G. Technical review and evaluation of the economics of desalination: Current and future challenges for better supply sustainability. Desalination 2013, 309, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, N.T. Injection/extraction well system—A unique seawater intrusion barrier. Groundwater 1977, 15, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesha, A. Control of seawater intrusion through injection-extraction well system. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1996, 122, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.A.; Adb-Elhamid, H.F.; Farmani, R. A simulation-optimization model to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers using abstract/recharge wells. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2015, 36, 1757–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T.; Robinson, N.I.; Luo, J. Maximizing net extraction using an injection-extraction well pair in a coastal aquifer. Groundwater 2013, 51, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Lu, C.; Ye, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of the performance of multiple-well hydraulic barriers on enhancing groundwater extraction in a coastal aquifer. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 144, 103704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Technical Program Overview: Underground Injection Control Regulations; Office of Water4606, EPA 816-R-02-025, Revised, July 2001; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Saad, S.; Javadi, A.A.; Chugh, T.; Farmani, R. Optimal management of mixed hydraulic barriers in coastal aquifers using multi-objective Baysenian Optimization. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Javadi, A.A. A cost-effective method to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2755–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadra, W.M.; Stuyfzand, P.J.; Khadra, I.M. Mitigation of saltwater intrusion by ‘integrated fresh-keeper’ wells combined with high recovery reverse osmosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jaber, I.; Ahmed, M. Technical and economic evaluation of brackish groundwater desalination by reverse osmosis (RO) process. Desalination 2004, 165, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.L.; Michael, P.; Ghaffour, N.; Missimer, T.M. Economics of brackish-water reverse osmosis desalination: Innovations and impacts of feedwater quality. Membranes 2021, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussis, A.D.; Georgopoulou, E.; Kotronarou, A.; Mazi, K.; Restrepo, P.; Destouni, G.; Prieto, C.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Rodriguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; et al. Cost-efficient management of coastal aquifers via recharge with treated wastewater and desalination of brackish groundwater: Application to the Akrotiri basin and aquifer, Cyprus. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-M.; Semprich, S. Using Compressed Air Injection to Control Seawater Intrusion in a Confined Coastal Aquifer. Transp. Porous Media 2013, 100, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Li, M. Numerical assessment of compressed air injection for mitigating seawater intrusion in a coastal unconfined aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Yu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Shang, C.; Lian, X.; Jia, Y. A simulation-optimization integrated framework for subsurface air barrier strategies to mitigate seawater intrusion in 3D coastal aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, I.; Berkowitz, B.; Gorelick, S.M. Effects of air injection on flow through porous media: Observations and analyses of laboratory-scale processes. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 125964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misut, P.E.; Voss, C.I. Freshwater–saltwater transition zone movement during aquifer storage and recovery cycles in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, USA. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Javadi, A.A.; Sherif, M.M.; Naseri-Karim-Vand, R. Control of saltwater intrusion by aquifer storage and recovery. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Eng. Comput. Mech. 2016, 169, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, W.H., Jr.; Speitel, G. E Dual recharge well for water supply stabilization. In Proceedings of the American Society of Chemical Engineers National Conference on Environmental Engineering, New York, NY, USA, 8–10 July 1980; pp. 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe, P.J. Artificial Recharge of Ground Water by Well Injection for Aquifer Storage and Recovery, Cape May County, New Jersey, 1958–1962; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 96-313; U.S. Geological Survey: New York, NY, USA, 1996; 29p.
- Lacombe, P.J. Artificial recharge of ground water by well Injection for aquifer storage and recovery, Cape May County, New Jersey, 1958–1962. In Conjunctive Use of Water Resources: Aquifer Storage and Recovery; Kendall, D.R., Ed.; Proceedings, American Water Resources Association Symposium: Long Beach, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, G.J. Artificial recharge in New Jersy’s Atlantic Coastal Plain. In Artificial Recharge of Ground Water. II: Proceedings, Second International Symposium on Artificial Recharge of Ground Water; Johnson, A.I., Pyne, R.D.G., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 318–323. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, G. Forty years of maximizing water resources with ASR projects in the Mid-Atlantic area. In Proceedings of the American Groundwater Trust Conference on Aquifer Storage Issues in the Middle Atlantic States, Baltimore, MD, USA, 23 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, T.; Yang, J. A review of recharge and clogging in sandstone aquifer. Geothermics 2020, 87, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Hiebert, R.; Warwood, B.; Cunningham, A. Subsurface biofilm barriers for controlling saltwater intrusion. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers-Monitoring, Modeling, and Management, Essaouira, Morocco, 23–25 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; You, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Lin, L. Characteristics and origin of clogging functional bacteria during managed aquifer recharge: A laboratory study. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xin, J.; Zheng, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, T. Effect of biofilms on the clogging mechanisms of suspended particles in porous media during artificial recharge. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Zhou, D.; Tong, M.; Kim, H. Effect of bacteria on the transport and deposition of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in saturated porous media. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazanpour Esfahani, A.; Batelaan, O.; Hutson, J.L.; Fallowfield, H.J. Transport and retention of graphene oxide nanoparticles in sandy and carbonaceous aquifer sediments: Effect of physicochemical factors and natural biofilm. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wiesner, M.R. Transport and retention of selected engineered nanoparticles by porous media in the presence of a biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wayner, C.C.; Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Ball, W.P.; Preheim, S.P. Effect of strain specific biofilm properties on the retention of colloids in saturated porous media under conditions of stormwater biofiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winneberger, J.H.; Francis, L.; Klein, S.A.; McGauhey, P.H. Biological Aspects of Failure of Septic Tank Percolation Systems; Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Altaner, S.P.; Ylagan, R.F. Comparison of structural models of mixed-layer illite/smectite and reaction mechanisms of smectite illitization. Clays Clay Miner. 1997, 45, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, X.; Flury, M.; Lin, G. Permeability changes during remediation of an aquifer affected by sea-water intrusion: A laboratory column study. J. Hydrol. 2009, 276, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.-J.; Zhan, H.; Li, M.-G.; Xia, X.-H. Aquifer recharge using a partially penetrating well with clogging-induced permeability reduction. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.H.; Rex, R.W. Formation damage in sandstones caused by clay dispersion and migration. In Proceedings, Fourteenth National Conference of Clays and Clay Minerals; Pergamon: Mysia, Turkey, 1966; pp. 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- Mays, D.C. Using the Quick-Schofield diagram to explain environmental colloid dispersion phenomena. J. Nat. Resour. Life Sci. Educ. 2007, 36, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.L.; Silvey, W.D. Underground storage and retrieval of fresh water from a brackish-water aquifer. In Underground Waste Managementand Artificial Recharge. Proceedings, 2nd Internation Symposium, New Orleans, September 1973; Braunstein, J., Ed.; U.S. Geological Survey (Available from the Ground Water Protection Council Library): Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 379–419. [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg, L.C.; Magaritz, M. Experimental investigation on irreversible changes of hydraulic conductivity on the seawater–freshwater interface in coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.A. Feasibility of a Scavenger-Well System as a Solution to the Problem of Vertical Salt-Water Encroachment; Water Resources Pamphlet 15; Louisiana Geological Survey: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1965; 27p. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, M.S.M. A hydraulic management approach for salt water intrusion using two level pumping mechanism. In Proceedings of the 10th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Ghent, Belgium, 16–20 May 1988; Natuurwetenschappelijk Tijdschrift, Ghent, 1989. De Breuck, W., Walschot, L., Eds.; pp. 238–244. [Google Scholar]
- Fil, J.F. Horizontal wells reduce salt-water intrusion in Guam’s water supply. Civ. Eng. 1950, 20, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shammas, M.L. The effectiveness of artificial recharge in combatting saltwater intrusion in Salalah coastal aquifer, Oman. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, M.I. Artificial recharge via injection wells for salinity ingress control of Salalah plain aquifer, Sultanate of Oman. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 263, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, M.I. Water resource management of Salalah Plain Aquifer using a sustainable approach. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovich, T. Operations and maintenance of the OCWD Talbert Barrier Injection Well System. Presentation at the Seawater Injection Barrier Workshop. Operation, Maintenance & Repairs—Lessons Learned in Southern California, AWRA SoCal Section, Loyola Marymount University, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 31 October 2001. 23 Slides. [Google Scholar]
- Herndon, R.; Markus, M. Large-scale aquifer replenishment and seawater intrusion control using recycled water in southern California. Boletín Geológico Y Min. 2014, 125, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Orange County (CA) Water District. Groundwater Replenishment System 2021 Annual Report; Orange County Water District: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://ocwd-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/wp-content/uploads/2021-gwrs-annual-report.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- CH2M. Managed Aquifer Recharge Concept Feasibility Study; Consulting Report Prepared for Anne Arundel County, Maryland, USA; CH2M: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anne Arundel County. Anne Arundel County Integrated Management Plan Draft Executive Summary; Anne Arundel County: Annapolis, MD, USA, 2022; 14p. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.L. Sensitivity of tropical cyclone intensity to sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, L.; Wang, Y.W.; Letchford, C.; Rosowsky, D. Assessing climate change impact on the U.S, East Coast hurricane hazard: Temperature, frequency, and track. Nat. Hazards Rew. 2014, 14, 04014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, T.; Camargo, S.J.; Chan, J.C.L.; Emanuel, K.; Ho, C.; Kossin, J.; Mohapatra, M.; Satoh, M.; Sugi, M.; Walsh, K.; et al. Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change Assessment: Part I. Detection and Attribution. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 1987–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, T.; Camargo, S.J.; Chan, J.C.L.; Emanuel, K.; Ho, C.; Kossin, J.; Mohapatra, M.; Satoh, M.; Sugi, M.; Walsh, K.; et al. Tropical cyclones and climate change assessment: Part II. Projected response to anthropogenic warming. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E303–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, T.L.; Lin, N. Climate change impacts to the coastal flood hazard in the northeastern United States. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2022, 36, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apruv, T.; Sivapalan, M.; Cai, X. Understanding the role of climate characteristics in drought propagation. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 9204–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, F.; Mazdiyansi, O.; Aghakouchak, A. Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, P.; Bakalowicz, M.; de Marsily, G. Submarine sorings and coast karst aquifers: A review. J. Hydrol. 2007, 330, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zektser, I.S.; Dzhamalov, R.G.; Everett, L.G. Submarine Groundwater; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, M.; Scholten, J.; Schmidt, A.; Comanducci, J.F.; Pham, M.K.; Mallast, U.; Knoeller, K. Submarine groundwater discharge at a single spot location: Evaluation of different detection approaches. Water 2014, 6, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, G.; Fallico, C.; Brunetti, G.F.A. Correlation structure of steady state well-type flows through heterogeneous porous media: Results and application. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR036279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriver, R.L.; Lempert, R.J.; Wikman-Svahn, P.; Keller, K. Characterizing uncertain sea-level rise projections to support investment decisions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benahmed, A.; Bessedik, M.; Abdelbaki, C.; Mokhdar, S.A.; Goosen, M.F.A.; Höllerman, B.; Zouhiri, A.; Badr, N. Investigating the long-term economic sustainability and water production costs of desalination plants: A case study from Chatt Hilal in Algeria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2025, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Barrier Type | Technology | Environment Issues | Regulatory Issues | Capital Cost | Operating Cost | Long-Term Effectiveness | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | |||||||
| Grout curtain (unconfined) | 10 | 10 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 0 | 44 |
| Curtain wall (unconfined) with pumping | 10 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 39 |
| Curtain wall (confined) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Grout curtain (unconfined) | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 0 | 43 |
| Grout curtain (unconfined) with pumping | 10 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 37 |
| Grout curtain (confined) | 9 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 10 | 10 | 47 |
| Surface Water (unconfined only) | |||||||
| Canal | 10 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 35 |
| Canal with levees | 10 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 35 |
| Blockage of canal/control structures | 10 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 43 |
| Injection | |||||||
| Injected freshwater (unconfined) | 10 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 42 |
| Injected freshwater (confined) | 10 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 48 |
| Injected treated wastewater (unconfined) | 10 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 32 |
| Injected treated wastewater (confined) | 10 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 10 | 37 |
| Pumping | |||||||
| Brackish to tide (unconfined) | 10 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 42 |
| Seawater to tide (unconfined) | 10 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 42 |
| Brackish to tide (confined) | 10 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 44 |
| Seawater to tide (confined) | 10 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 47 |
| Mixed | |||||||
| Injection and pumping (unconfined) | 10 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 34 |
| Injection and pumping (confined) | 10 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 42 |
| Abstraction, Desalination, Recharge (ADR) | |||||||
| Brackish water pumped, treated (BWRO), and injected (unconfined) | 10 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 37 |
| Brackish water pumped, treated (BWRO), and injected (confined) | 10 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 42 |
| Seawater pumped treated (SWRO) and injected (unconfined) | 10 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 33 |
| Seawater pumped treated
(SWRO) and injected (confined) | 10 | 9 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 39 |
| Brackish water pumped, treated (BWRO), and injected with freshwater use (unconfined) | 10 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 39 |
| Brackish water pumped, treated (BWRO), and injected with freshwater use (confined) | 10 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 44 |
| Seawater pumped, treated (SWRO), and injected with freshwater use (unconfined) | 10 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 39 |
| Seawater pumped, treated (SWRO), and injected with freshwater use (confined) | 10 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 44 |
| ADR with treated wastewater for injection and BWRO use for supply (unconfined) | 10 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 41 |
| ADR with treated wastewater for injection and BWRO use for supply (confined) | 10 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 46 |
| ADR with treated wastewater for injection and SWRO use for supply (unconfined) | 10 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 36 |
| ADR with treated wastewater for injection and SWRO use for supply (confined) | 10 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 44 |
| Pumped compressed air | |||||||
| Unconfined/ semi-unconfined aquifers | 3 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 33 |
| Confined aquifers | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 52 |
| Aquifer Storage and Recovery | |||||||
| Unconfined aquifers | 8 | 9 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 40 |
| Confined aquifers | 10 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 51 |
| Biofilm | |||||||
| Biofilm (unconfined) | 1 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 28 |
| Biofilm (confined) | 1 | 9 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 10 | 40 |
| Clay, swelling or dispersion | |||||||
| Clay, unconfined | 1 | 10 | 9 | 6 | 9 | 0 | 35 |
| Clay, confined | 1 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Missimer, T.M.; Maliva, R.G. Salinity Barriers to Manage Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Zone Aquifers During Global Climate Change: A Review and New Perspective. Water 2025, 17, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111651
Missimer TM, Maliva RG. Salinity Barriers to Manage Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Zone Aquifers During Global Climate Change: A Review and New Perspective. Water. 2025; 17(11):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111651
Chicago/Turabian StyleMissimer, Thomas M., and Robert G. Maliva. 2025. "Salinity Barriers to Manage Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Zone Aquifers During Global Climate Change: A Review and New Perspective" Water 17, no. 11: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111651
APA StyleMissimer, T. M., & Maliva, R. G. (2025). Salinity Barriers to Manage Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Zone Aquifers During Global Climate Change: A Review and New Perspective. Water, 17(11), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111651







