Abstract
Industrial activated sludge plants in many sectors, including the dairy industry, face sludge separation problems caused by sludge bulking. Aerobic granular sludge (AGS) could be a solution by forming well-settling granules. The key to successful granulation is the microbial selection of slow-growing glycogen-accumulating organisms (GAOs) by introducing an anaerobic feeding/reaction step. The objective of the current study was to investigate the impact of two slow feeding strategies to achieve granulation in existing sequencing batch reactors treating real dairy wastewater, by microbial selection only. The first strategy consisted of slow 90 min mixed feeding. The second strategy combined 45 min static and 45 min mixed feeding to build up a substrate gradient. The feeding strategies did not affect the effluent quality, but significantly impacted the sludge morphology, settling properties, and microbial community composition. Mixed feeding led to filamentous overgrowth by Thiothrix species, up to 45% abundance, and deteriorating settling, with sludge volume index (SVI) values up to 125 mL/g. In contrast, static feeding yielded densified sludge with SVI values below 45 mL/g and up to 35% GAO abundance. In conclusion, the results show successful granulation when using a simple static slow feeding mode, which could benefit the industrial application of AGS technology.
1. Introduction
Aerated or aerobic granular sludge (AGS) represents an innovative technology for biological wastewater treatment. Under the tradename Nereda, more than 100 full-scale AGS plants have been put into operation and/or construction worldwide (www.royalhaskoningdhv.com/nereda, accessed on 14 March 2025), mostly for treating municipal wastewater. Compared to the conventional activated sludge process, AGS has multiple benefits in energy and chemical use, and footprint reduction. Moreover, it allows simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in a single reactor system [1]. van Dijk et al. (2022) listed several important mechanisms to obtain and improve granulation, such as (1) selective feeding, (2) selective wasting, (3) feast/famine conditions, and (4) the wastewater composition [2]. Regarding the wastewater composition, the authors identify granule-forming substrates such as volatile fatty acids (VFAs), readily biodegradable chemical oxygen demand (COD), and fast hydrolysable COD. In Nereda-type AGS reactors, these substrates are fed from the bottom through a bed of granules, thereby delivering the carbon substrate first to the granular sludge fractions [3,4]. This is referred to as selective feeding, which gives a competitive advantage to the (larger) granules in the reactor. In addition, a physical selection strategy is applied by selectively wasting the slow settling flocculent sludge fraction. Finally, a key driver for granulation is the microbial selection strategy based on the implementation of an anaerobic feast/aerobic famine regime [3,5]. The alternating anaerobic/aerobic process sequence selects for slow-growing substrate-storing micro-organisms that form stable and dense granules [6]. In practice, these micro-organisms can be divided into two distinct groups: polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) and glycogen-accumulating organisms (GAOs). Selection for PAOs has an additional advantage as it allows biological P removal. For PAOs, Candidatus Accumulibacter (hereafter: Accumulibacter), and for GAOs, Candidatus Competibacter (hereafter: Competibacter) are considered model substrate-storing organisms when VFAs represent the main carbon substrate [7]. Under anaerobic conditions, PAOs and GAOs convert VFAs to storage polymers, which are then consumed for growth under aerobic (or anoxic) conditions. For PAOs, the energy required for VFA conversion is obtained from the hydrolysis of intracellular polyphosphate and glycogen. Under aerobic conditions, polyphosphate and glycogen are replenished, leading to net P removal [7].
Two possible anaerobic feeding strategies have been proposed to select for slow-growing PAOs (or GAOs) and to provide sufficient feast/famine conditions for successful and stable granulation [3,8,9]. These feeding strategies are (1) fast pulse feeding followed by an anaerobic mixed reaction phase in conventional sequencing batch reactors (SBRs) and (2) slow plug-flow feeding through a granular sludge bed in Nereda-type SBRs [3,4]. However, since both strategies are difficult to implement in existing conventional SBRs that are typically slowly fed from the top, several authors proposed a simpler approach combining slow feeding and reaction during a mixed anaerobic phase. A potential drawback of this feeding strategy is the absence of a substrate build-up or gradient during anaerobic feeding and reaction, which is considered to be of importance for stable granulation [10]. Nevertheless, when treating highly loaded industrial wastewater, Tsertou et al. (2022) and Caluwé et al. (2022) showed that the build-up of a substrate gradient during the anaerobic feeding step is not necessary to achieve extensive sludge densification and granulation [11,12]. The absence of additional selective pressure mechanisms did, however, result in the formation of hybrid floccular/granular sludge, which, for all practical purposes, is of sufficient quality to significantly improve sludge separation. Other researchers, on the other hand, found that building up a substrate gradient was necessary to avoid excessive growth of filamentous organisms. Stes et al. (2019) therefore proposed an alternative feeding strategy consisting of a truly static slow anaerobic feeding step, followed by an anaerobic mixed reaction step [13]. Static feeding involves feeding wastewater (from the top of the SBR) without mixing, resulting in a build-up of substrate even when feeding slowly.
Industrial biological treatment plants are facing serious challenges with respect to sludge quality, with filamentous sludge bulking as a major cause of sludge separation problems [14]. Sludge densification and/or granulation could represent a solid preventive method to deal with these challenges. The implementation of sludge densification and granulation in existing SBRs would be most successful if based on simple strategies to minimize operational complexities and the associated retrofitting costs. Previous research has shown successful granulation of sludge treating various industrial wastewaters both in lab-scale and full-scale SBRs, using a microbial selection only [12,15,16]. In these studies, granule formation was achieved using different feeding modes. In the current study, we focus on the treatment of dairy wastewater. Dairy processing is considered a significant contributor of wastewater in the food industry, with a strong potential impact on the environment. Treatment of dairy wastewater is therefore necessary, but challenging [17]. Conventional activated sludge treatment of dairy wastewater faces serious filamentous bulking problems, which could be solved by the application of granulation strategies [15]. De Vleeschauwer and Dries (2023) achieved extensive granulation by the application of an anaerobic pulse feeding followed by an anaerobic mixed reaction step in an SBR treating real dairy wastewater [18]. While these results indicate that granulation is feasible for this type of wastewater, the applied strategy is not easily translatable to full-scale implementation as it would require significant pumping capacities. The objective of the current study is, therefore, to investigate the impact of practically applicable slow feeding strategies to achieve granulation by microbial selection only, for the treatment of dairy wastewater.
2. Materials and Methods
The primary aim of the present study was to cultivate AGS in a conventional lab-scale SBR treating wastewater from the dairy industry. The study consisted of two consecutive experimental periods. In period 1, a single SBR was operated using a slow anaerobic mixed feeding strategy (the specific SBR cycle set-up is detailed in the following section). In period 2, two parallel SBRs were operated to compare two different feeding strategies: slow anaerobic mixed feeding vs. a combination of static feeding followed by mixed feeding to increase the substrate build-up during the feeding step. The granulation process, sludge characteristics, microbial population dynamics, and nutrient removal rates were monitored throughout the reactor operation.
2.1. Reactor Set-Up and Operating Conditions
Fully automated lab-scale SBRs were inoculated with biomass originating from a municipal WWTP (Antwerpen-Zuid) and operated at room temperature (18–22 °C). The SBR sequence and all hardware actions (mixer, air pump, feeding pump, and discharge valve) were controlled by a Siemens programmable logic controller (PLC) (Siemen, Beersel, Belgium) (Figure 1). A custom-made LabVIEW (National Instruments, Austin TX, USA) supervision program was used to control and visualize the PLC (sequence) settings and actions. In addition, the SBRs were equipped with multiple online sensors, such as dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, and oxidation reduction potential, directly connected to the PLC and visualized by the LabVIEW supervision programs.
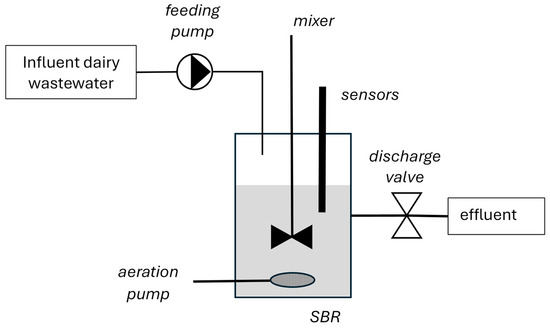
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the laboratory SBR reactor set-up.
During Period 1, a single SBR, referred to as SBR_A, was operated. In period 2, two parallel SBRs using distinct feeding strategies were compared, referred to as SBR_SlowF and SBR_StaticF, respectively. The SBR sequence was identical in all reactors, except for the feeding strategy (Table 1). Each 6 h cycle (Table 1) started with an extended anaerobic feeding step, either mixed or static (90 min, from the top) and a short anaerobic reaction step (15 min), followed by aerobic and anoxic reaction steps, aerobic refresh, settling, and discharge. During aeration, the DO level was controlled between 1.0 and 2.0 mg O2/L. The volume exchange ratio was about 10%, and the SRT was maintained between 25 and 30 days by daily manual wasting of excess sludge from the reactors.

Table 1.
SBR cycle set-up (duration in minutes) in SBR_A and SBR_SlowF (a), and SBR_StaticF (b).
2.2. Analyses
COD samples were analyzed using a standard cuvette test (Hannah Instruments, Temse, Belgium). All other samples were first filtered over a glass microfiber filter (particle retention 1.2 µm), whereafter concentrations of phosphate (Hach Lange, Nazareth, Belgium), ammonium (Hanna Instruments, Temse, Belgium), nitrite (Hach Lange, Nazareth, Belgium), nitrate (Hanna Instruments, Temse, Belgium), VFA (Hach Lange, Nazareth, Belgium), and SCOD (Hanna Instruments, Temse, Belgium) were analyzed with standard cuvette tests. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was analyzed with a laboratory TOC Organic Carbon (TOC) analyzer (Sievers Innovox, Veolia, Aubervilliers, France). Particle size distribution was analyzed using a Malvern Mastersizer 3000 (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK). Microbial community analysis by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing was performed as described previously [12]. Amplicon sequencing was carried out on an Illumina MiSeq system using a MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 (Illumina, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). The obtained paired-end reads were processed with the UPARSE pipeline [19]. As a reference database for taxonomy prediction, MiDAS was used [20].
2.2.1. In Situ Cycle Measurements
To determine the dynamics of DOC uptake and removal, phosphate release and uptake, and nitrogen conversion during the feeding and reaction steps, in situ cycle measurements were carried out. Therefore, samples were taken every 15–60 min (depending on the reactor phase) and analyzed.
2.2.2. Industrial Dairy Wastewater
Real dairy wastewater from a local Flemish company was used. At the dairy company, a chemically enhanced primary treatment step is carried out before the biological treatment to remove suspended solids and fat [17]. The primary treatment involves coagulation flocculation using ferric chloride and solids separation using dissolved air flotation. The pretreated dairy wastewater (Table 2) was sampled about every week. After transportation to the lab, the wastewater was stored at 4 °C before usage.

Table 2.
Average composition of the dairy wastewater during period 1 and period 2 of the study.
The influent total COD ranged from 810 to 2220 mg/L, with soluble COD representing 81% of the total COD. The average VFA concentration in the influent wastewater was 660 mg/L, corresponding to a VFA content of 70% (on a C-basis). Extra phosphate was added when needed to obtain an influent COD/P ratio of approximately 200, to prevent P-limiting conditions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Period 1: Development of AGS Using a Slow Anaerobic Mixed Feeding Strategy
During period 1, a single SBR, SBR_A, was operated for almost 110 days. The reactor used a slow feeding strategy: the dairy wastewater was introduced during a 90 min mixed feeding step under anaerobic conditions (Table 1). During feeding, no build-up of substrate, expressed as DOC, was observed, indicating that the DOC added with the feed was removed instantaneously. Concerning the effluent quality, the average effluent concentrations for COD (51 ± 20 mg/L), NH4-N (0.02 ± 0.04 mg/L), NO3-N (1.7 ± 0.7 mg/L), PO4-P (0.6 ± 0.6 mg/L), and suspended solids (31 ± 12 mg/L) were well below the Flemish legislation standards for COD (125 mg/L), suspended solids (60 mg/L), total N (15 mg/L), and total P (2.5 mg/L). These results confirm that dairy processing wastewater can efficiently be treated using aerobic biological processes for COD and nutrient removal [21].
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the evolution of the biomass parameters and morphology. The inoculum consisted of bad settling open flocs with a high SVI (150–185 mL/gMLSS). The SVI remained high during the first 45 days of operation, and then quickly dropped to values below 50 mL/g, indicative of well-settling sludge. The average particle size (DV50) significantly increased during the same time, from about 110 µm to more than 300 µm (Figure 2).
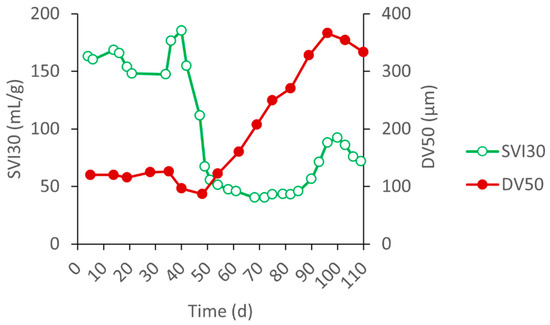
Figure 2.
Evolution of the biomass parameters of SBR_A during period 1: SVI30 (mL/g) and average particle size (DV50, µm).
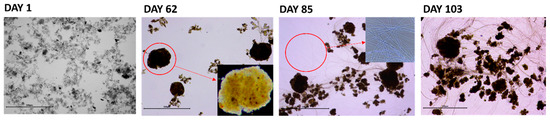
Figure 3.
Evolution of the sludge morphology of SBR_A during period 1 on days 1, 62, 85, and 103 (scale bar = 500 µm).
The sludge morphology also evolved showing the development of dense and spherical particles (Figure 3, day 62). These results indicate successful sludge granulation after approximately 60 days of reactor operation. However, after about 85 days of operation, filamentous (over)growth could be observed (Figure 3, day 85–103), resulting in an increase in SVI30 up to 100 mL/g.
SBR_A used a (slow) anaerobic feeding step to promote the enrichment of carbon-storing slow-growing organisms like PAOs and GAOs [22]. These organisms take up the rapidly biodegradable COD (such as VFA) during anaerobic feeding and convert the COD to storage polymers [3]. After less than 3 weeks of operation, the DOC uptake during the anaerobic step reached 95%, and remained above 90% for the total duration of the experiment, indicating that the enrichment of substrate-storing organisms was successful. Figure 4 shows the corresponding evolution of the microbial community composition, based on 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing.
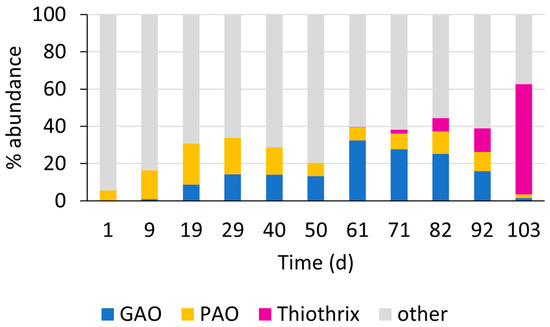
Figure 4.
Evolution of the microbial community composition in SBR_A during period 1, showing the relative read abundance of relevant functional genera such as GAOs, PAOs, and filamentous organisms.
The seed sludge contained a relatively low PAO abundance of approx. 5%. The PAO community consisted mainly of Ca. Accumulibacter (1.7%) and Dechlormononas (2.7%). Both organisms convert VFA to intracellular storage polymers [7]. Initially, the PAO abundance rapidly increased, mainly due to the enrichment of Ca. Accumulibacter, up to 18%. After 20 days of operation, the abundance of GAOs started to increase and reached high numbers after 60 days (Figure 4). The main GAO enriched was Ca. Competibacter, at abundances of up to 30%. The preferred enrichment of Accumulibacter and Competibacter over other PAOs and GAOs is most probably linked to the high proportion of VFAs in the influent wastewater (about 70% on C-basis), as VFAs are the main carbon substrates for these organisms [23]. The selection of PAOs and GAOs is key to the microbial selection strategy to promote aerobic granulation [2]. The enrichment of these organisms accordingly led to the improved sludge settling properties and the morphological changes observed, resulting in granulation (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The average molar P-release to C-uptake ratio during the anaerobic step was about 0.1 molP/molC, indicating a preferential enrichment of GAOs over PAOs [24], which aligns with the low influent P concentrations (Table 2). The adjusted influent COD/P ratio was about 200, favoring GAOs in their competition with PAOs for the substrate. Nevertheless, PAO activity was evident with an average biomass-specific P-release rate of 3.6 mgP/gVSS·h.
From day 71 onwards, corresponding to the increasing filamentous sludge morphology, the filamentous organism Thiothrix was enriched and ultimately became the major genus at the end of period 1 with abundances of up to 60%. At the same time, GAO and PAO abundance decreased and even dropped below 2% at the conclusion of the experiment. Nevertheless, the anaerobic DOC uptake (>90%) and the biomass-specific phosphate release rate (3.95 mgP/gVSS·h) remained constant. The high anaerobic substrate uptake and ongoing P-release observed here correspond to the findings of Rubio-Rincón et al. (2017) [25]. The authors described the specific enrichment of Thiothrix species able to take up and store rapidly biodegradable COD (such as VFAs) under anaerobic conditions. VFA uptake was coupled to phosphorus cycling, comparable to the metabolism of PAOs. To investigate the potential impact of the feeding strategy on the selective enrichment of Thiothrix vs. PAOs and GAOs, a follow-up experiment was set up in period 2.
3.2. Period 2: Comparison of Feeding Strategies for Stable Granulation
In period 2, two parallel SBRs were operated for 80 days to compare two distinct feeding strategies. SBR_SlowF used the same slow mixed anaerobic feeding strategy as SBR_A during period 1 and acted as the reference SBR. SBR_StaticF used a 50/50 combination of static (unmixed) feeding during the first 45 min, followed by slow mixed feeding during the subsequent 45 min (Table 1). The operational impact of the different feeding strategies is best expressed by the active organic loading rate (OLR) during the anaerobic reaction step. This metric takes only the microbially active reaction steps into account, which shows that the sludge was exposed to a significantly higher loading rate during the anaerobic reaction step in SBR_StaticF (Table 3). As in period 1, reactor performance and effluent quality were excellent during the whole study period, for both reactors (Table 3). Moreover, no statistical differences were observed in effluent quality and removal efficiencies between the two SBRs (p > 0.05 for all parameters).

Table 3.
Active OLR during the whole SBR cycle and the anaerobic reaction step, and average effluent quality and removal efficiencies for COD, TN, and PO4-P for SBR_SlowF and SBR_StaticF during period 2. The active OLR only takes the microbially active SBR steps into account (anaerobic mixed feeding, anaerobic, aerobic, and anoxic reaction steps, excluding static feeding, settling, and discharging).
Figure 5 shows the dynamics of the DOC and nutrients at key points during typical cycles for both SBRs. The DOC profiles illustrate the differences between the two reactors with respect to the substrate build-up during feeding. In SBR_StaticF, the DOC increases during static feeding, creating a substrate gradient in the anaerobic step, followed by a rapid decrease due to the uptake under anaerobic mixing conditions (Figure 5B). In SBR_SlowF, no DOC gradient is built up as the substrate is taken up immediately while being fed (at a slow rate) (Figure 5A). The DOC uptake during the anaerobic reaction step was equal for both SBRs and averaged 95.0 ± 2.6%. Both reactors also exhibited the typical P-cycling profile indicative of PAO-like activity: P-release during the anaerobic reaction step, followed by aerobic P-uptake [7]. The average P-release rate was similar in both SBRs at 2.9 ± 1.1 mgP/gVSS·h and 3.3 ± 1.2 mgP/gVSS·h for SBR_SlowF and SBR_StaticF, respectively. The average molar P-release to C-uptake ratio during the anaerobic step was about 0.12 molP/molC, again pointing towards the preferential enrichment of GAOs over PAOs in both reactors [24]. A theoretical ratio of 0.5 is expected for a fully active PAO system when acetate is used as a carbon substrate, while lower values (as observed here) indicate GAO activity as well [7].
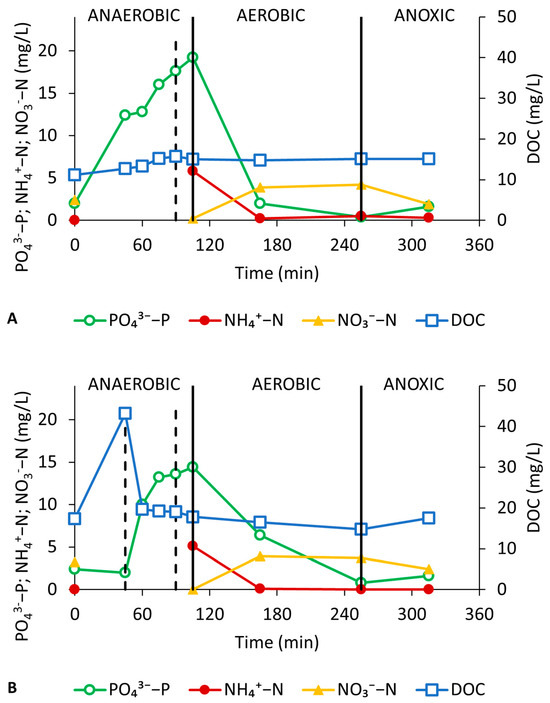
Figure 5.
Concentration profiles for DOC, NH4-N, NO3-N, and PO4-P during a full SBR cycle for SBR_SlowF (A) and SBR_StaticF (B). The vertical dashed lines indicate the end of the static and mixed feeding steps, while the vertical full lines indicate the end of the anaerobic, aerobic, and anoxic reaction steps.
Concerning N-cycling, both reactors showed typical and similar profiles of NH4-N and NO3-N corresponding to full nitrification and (limited) post-denitrification. Nitrite (NO2-N) never accumulated to any appreciable concentrations. Also, no significant simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND) was observed, which can be explained by the small particle size and the moderately high DO levels (1–2 mg/L). All in all, the difference in feeding strategy did not significantly impact the reactor performance or the key microbial activities (P-cycling, N-removal).
Figure 6 shows the evolution of the sludge settling properties during period 2. While the average sludge concentration was comparable in both SBRs (4 ± 1 g/L MLSS), the SVI showed a distinct evolution. The seed sludge SVI was approximately 84 mL/g. For SBR_SlowF, the SVI remained stable until day 50, when it increased to an average value of 125 mL/g at the end of the experiment. For SBR_StaticF, the SVI started decreasing from day 30 onwards and reached low values of 43 mL/g at the end. The feeding strategy thus significantly affected the settling properties of the sludge (p < 0.05).
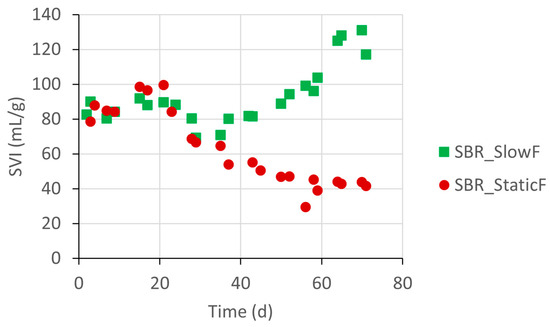
Figure 6.
Evolution of the SVI30 (mL/g) of sludge from SBR_SlowF and SBR_StaticF during period 2.
Concerning the microbial community composition, Figure 7 shows the evolution of the relative abundance of the key functional genera during period 2. The reference reactor, SBR_SlowF, showed a similar evolution as SBR_A during period 1 (Figure 7A). In the first half of the experiment, an enrichment of GAOs up to 25% can be observed, mostly Ca. Competibacter. During the second half (from day 50 onwards), GAO abundance dropped to less than 5%, and a significant increase in the Thiothrix species took place, up to 45% abundance at the end of the experiment. For SBR_StaticF, mostly the GAO Ca. Competibacter was enriched, up to 35%, while the Thiothrix species were barely (<0.5%) found over the entire operational period (Figure 7B). PAO abundance, mostly Ca. Accumulibacter, remained fairly low, below 5% in SBR_StaticF and less than 1% in SBR_SlowF. The preferential selection of GAOs over PAOs corresponds to the low observed molar P-release to C-uptake ratio during the anaerobic step, and the low P availability in the influent wastewater. On the other hand, the observed decreasing GAO and PAO abundance in SBR_SlowF, in combination with the high and stable degree of DOC uptake during the anaerobic step, suggests that other organisms, potentially Thiothrix, played a role in the DOC uptake.
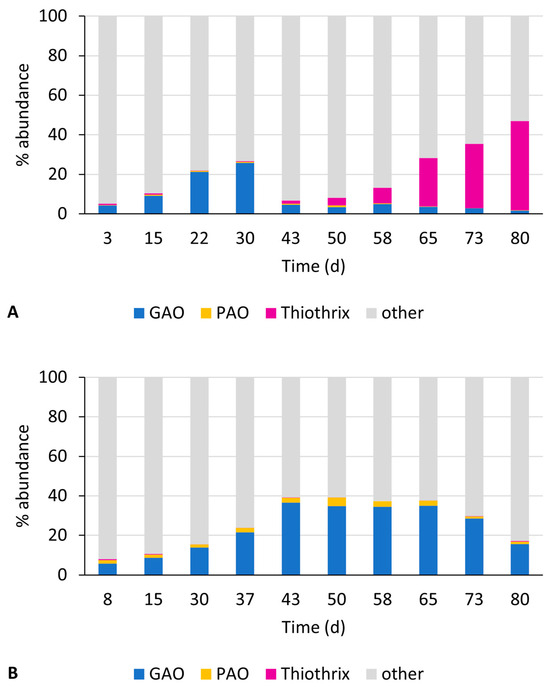
Figure 7.
Evolution of microbial community composition in SBR_SlowF (A) and SBR_StaticF (B) during period 2, showing the relative read abundance of relevant functional genera such as GAOs, PAOs, and filamentous organisms.
3.3. The Potential Role of Thiothrix Species in C- and P-Cycling
The operation of an SBR using a slow anaerobic mixed feeding strategy resulted in similar outcomes in both periods. While PAOs and GAOs were selected initially, the sludge morphology, settling properties, and microbial community composition evolved in the same way, leading to filamentous outgrowth, deteriorated settling, and the significant enrichment of Thiothrix (Figure 2, Figure 4, Figure 6 and Figure 7). At the same time, DOC uptake during the anaerobic reaction step, and the P-cycling dynamics (release and uptake) did not change. These observations suggest that Thiothrix species could be involved in DOC uptake and storage, and PAO-like P-cycling. Several researchers have reported on S-driven enhanced biological P-removal, with Thiothrix species responsible for DOC uptake, and P-release and uptake, driven by intracellular storage of S-granules [25,26,27,28].
High Thiothrix abundance has been reported in several studies involving dairy wastewater treatment, suggesting that this type of wastewater is conductive to Thiothrix enrichment [15,16,23,29]. Many factors could explain the stimulation of Thiothrix species in biological treatment systems, such as the presence of (reduced) sulfur (S) compounds, in combination with nutrient deficiency, low exposure to rapidly biodegradable COD (such as VFA), and/or a low DO level in the aerobic step [30,31,32]. Unfortunately, the presence of S-compounds in the influent wastewater was not measured in the present work. Concerning nutrient and oxygen availability, nutrients were either sufficiently present (N) or added to the influent (P) to meet the sludge growth requirements, while the DO level was controlled between 1 and 2 mg/L during aeration and thus was not limited. The main operational difference between the two SBRs was the feeding strategy, leading to significantly different exposure to the carbon substrate (DOC) during the anaerobic step. PAOs, GAOs, and Thiothrix species have similar metabolic traits, such as VFA uptake and storage, and thus compete for available substrates during the anaerobic step [25,33,34,35]. In the slow-fed SBR, the Thiothrix species outcompeted GAOs and PAOs due to the prolonged exposure of the sludge to low concentrations of short-chained VFAs. Under these conditions, Thiothrix species, with filaments extending into the bulk solution, are favored over GAOs and PAOs [34,36]. This competitive advantage was not present in the statically fed SBR when a substrate buildup was created. It is interesting to note that, in the current study, Thiothrix enrichment negatively impacted the sludge properties, such as the sludge morphology and settling. In contrast, other researchers, using fast pulse feeding or plug-flow feeding, reported a minimal impact of Thiothrix on the sludge granulation/densification process [28,37]. These observations suggest that the feeding strategy also plays a role in the impact of Thiothrix enrichment on the sludge quality.
3.4. Implications for AGS Formation in Industrial Activated Sludge Plants
Many industrial activated sludge plants face serious sludge separation problems, often related to sludge bulking [14]. Sludge densification/granulation strategies have been proposed and applied to solve these issues, and these applications mostly involve the introduction of an anaerobic feeding and reaction step to promote slow-growing PAOs and GAOs [12,15]. The key to this microbial selection strategy is the near-complete uptake of readily biodegradable CODs (such as VFAs) in the anaerobic step, to avoid “leakage” of these substrates in the subsequent aerobic step [18,38]. In most studies, a slow anaerobic feed is applied with the influent entering the reactor from the bottom through the settled granular sludge [10]. This feeding strategy not only creates plug flow anaerobic feast conditions but also ensures that the granule-forming substrates (e.g., VFAs) are selectively delivered to the larger granules at the bottom of the sludge bed [2]. This feeding regime is also successfully applied in full-scale Nereda plants [4]. An alternative feeding mode, often used in lab-scale studies, is the combination of a fast pulse feeding of influent (a few minutes only, from the top) to create plug-flow conditions, followed by a prolonged anaerobic mixed reaction phase to maximize the anaerobic substrate uptake [9,39]. Recent work has shown that both feeding strategies successfully lead to granulation but that the bottom-feed regime favors substrate distribution towards larger granules [3,40].
To be economically significant, the implementation of granulation strategies in industry should be applicable in existing SBRs without major investment or retrofitting costs. Fast feeding of the influent wastewater in a pulse-feeding mode is technically challenging and economically not feasible, as it would require huge pumping capacities. Likewise, the design and introduction of the necessary infrastructure to obtain an adequate substrate distribution when implementing bottom feeding in existing SBRs represent significant added costs and complexity. The most attractive approach would be to simply introduce an anaerobic feeding/reaction step using the existing infrastructure and pumping capacity. Some researchers have shown that a slow anaerobic mixed feeding mode, without significant substrate build-up, indeed leads to a high degree of granulation [11,12]. In contrast, other works, including the present study, show that this simple and easily applicable way of feeding does not always promote the selection of the desired microbial population, and even results in filamentous overgrowth when the conditions for Thiothrix are favorable [13]. In these cases, the build-up of a substrate gradient during the anaerobic feeding step is key to successful sludge densification and granulation [10]. The present study shows that the application of a static feeding mode during (part of) the feed step creates the necessary plug-flow conditions to build up a substrate gradient favoring PAOs and GAOs over Thiothrix.
Previous research reported on the successful upscaling of AGS technology in a two-step approach [12]. First, a lab-scale SBR study showed the possibility of granule formation after about 60 days of operation with an anaerobic feeding strategy. A similar feeding mode was then applied to full-scale, leading to sludge granulation/densification in less than 3 months. These results indicate that a lab-scale SBR test performed under realistic feeding conditions can be translated to full-scale application [11]. The present study proposes to use two parallel SBRs with a distinct feeding mode to assess the feasibility of granulation on the lab-scale before upscaling in a similar integrated test strategy. As such, the present work extends the operational modes available to implement the novel AGS technology in industry [2].
3.5. Outlook and Perspectives in View of a Circular Water Economy
Dairy wastewater contains substantial amounts of organic pollutants and nutrients, requiring treatment before discharge [17]. The current study shows that AGS represents a suitable technology for sustainable dairy wastewater treatment, combining good effluent quality and excellent sludge/liquid separation. In addition, AGS technology also offers many opportunities for innovative resource recovery from wastewater, besides energy recovery via waste sludge digestion, and P-recovery as struvite. Specifically, for AGS, extracellular polymeric substances referred to as Kaumera gum, with valuable gel-forming properties, can be extracted and recovered [41,42,43]. Finally, recent work shows the significant potential impact of the integration of AGS in membrane bioreactor systems (MBRs). The specific properties of the granules (size, composition, hydrophobicity…) positively influence the membrane filtration properties and minimize the fouling potential [44,45,46]. MBR effluent is an excellent starting point for a high-quality water reuse treatment scheme (e.g., as input for reverse osmosis membrane filtration). The implementation of granulation in the dairy wastewater treatment could thus potentially be a significant enabler of sustainable water reuse in industry [21].
4. Conclusions
The present study shows that an alternative and simple feeding strategy consisting of a combined static and mixed anaerobic feeding step creates the necessary substrate build-up for successful granulation when treating dairy wastewater. The static feeding mode thus complements the slow mixed feeding mode and extends the strategies available to implement granulation in existing industrial treatment plants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.D. and J.D.; Methodology, T.D.; Investigation, T.D.; Resources, J.D.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, T.D.; Writing—Review and Editing, T.D., M.F. and J.D.; Visualization, T.D.; Supervision, M.F. and J.D.; Project Administration, T.D.; Funding Acquisition, T.D., M.F. and J.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by VLAIO, the Flanders Innovation and Entrepreneurship Agency, grant number HBC.2017.0525.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Marc Feyaerts was employed by Cre@Aqua BV. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
AGS: aerobic granular sludge; COD: chemical oxygen demand; DOC: dissolved organic carbon; GAOs: glycogen accumulating organisms; OLR: organic loading rate; PAOs: polyphosphate accumulating organisms; S: sulfur; SBR: sequencing batch reactor; SND: simultaneous nitrification denitrification; SVI: sludge volume index; VFAs: volatile fatty acids.
References
- Vydehi, P.; Ravindran, G.; Shyamala, G.; Ramesh, S. Aerobic granular sludge-based wastewater treatment: Current trends, formation, applications, granulation, efficiency, and bottlenecks. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 107075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, E.J.H.; Haaksman, V.A.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pronk, M. On the mechanisms for aerobic granulation—model based evaluation. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaksman, V.A.; Schouteren, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pronk, M. Impact of the anaerobic feeding mode on substrate distribution in aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronk, M.; de Kreuk, M.K.; de Bruin, B.; Kamminga, P.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Full scale performance of the aerobic granular sludge process for sewage treatment. Water Res. 2015, 84, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kreuk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Selection of slow growing organisms as a means for improving aerobic granular sludge stability. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, M.; Abbas, B.; Al-Zuhairy, S.H.K.; Kraan, R.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Effect and behaviour of different substrates in relation to the formation of aerobic granular sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5257–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J.A. A critical review on the effect of different carbon sources on EBPR: Revaluation of performance and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 509, 161083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Liu, Y. Effect of feeding strategy and organic loading rate on the formation and stability of aerobic granular sludge. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 39, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. Effect of different feeding strategies on performance of aerobic granular sludge: From perspective of extracellular polymeric substances and microorganisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 12, 111688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, R.D.G.; Pinheiro, H.M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Lourenço, N.D. Stability of aerobic granules during long-term bioreactor operation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 228–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsertou, E.; Caluwé, M.; Goossens, K.; Dobbeleers, T.; Dockx, L.; Poelmans, S.; Seguel Suazo, K.; Dries, J. Is building up substrate during anaerobic feeding necessary for granulation? Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caluwé, M.; Goossens, K.; Seguel Suazo, K.; Tsertou, E.; Dries, J. Granulation strategies applied to industrial wastewater treatment: From lab to full-scale. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 2761–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stes, H.; Aerts, S.; Caluwe, M.; D'Aes, J.; De Vleesschauwer, F.; Dobbeleers, T.; De Langhe, P.; Kiekens, F.; Dries, J. Influence of mixed feeding rate in a conventional SBR on biological P-removal and granule stability while treating different industrial effluents. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel Suazo, K.; Dobbeleers, T.; Dries, J. Bacterial community and filamentous population of industrial wastewater treatment plants in Belgium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriet, O.; Meunier, C.; Henry, P.; Mahillon, J. Filamentous bulking caused by Thiothrix species is efficiently controlled in full-scale wastewater treatment plants by implementing a sludge densification strategy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, C.; Henriet, O.; Schoonbroodt, B.; Boeur, J.-M.; Mahillon, J.; Henry, P. Influence of feeding pattern and hydraulic selection pressure to control filamentous bulking in biological treatment of dairy wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavov, A.K. Dairy Wastewaters—General Characteristics and Treatment Possibilities—A Review. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 55, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vleeschauwer, F.; Dries, J. Full dynamic control of dairy wastewater treatment by aerobic granular sludge using electric conductivity and oxygen uptake rate. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 2707–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierychlo, M.; Andersen, K.S.; Xu, Y.; Green, N.; Jiang, C.; Albertsen, M.; Dueholm, M.S.; Nielsen, P.H. MiDAS 3: An ecosystem-specific reference database, taxonomy and knowledge platform for activated sludge and anaerobic digesters reveals species-level microbiome composition of activated sludge. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelini, D.B.; Lima, J.P.P.; Borges, A.C.; Aguiar, A. A review on the characteristics and methods of dairy industry wastewater treatment in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszyński, A.; Załęska-Radziwiłł, M. Influence of the bioreactor operating mode and wastewater composition on the structure of microbial communities in activated sludge and abundance and activity of polyphosphate and glycogen accumulating organisms. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 301, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Haddad, L.; Ali, M.; Pronk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Saikaly, P.E. Demystifying polyphosphate-accumulating organisms relevant to wastewater treatment: A review of their phylogeny, metabolism, and detection. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 21, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.; Mackey, B.; Chadalavada, S.; Kainthola, J.; Heck, P.; Goel, R. Enhanced Bio-P removal: Past, present, and future—A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Rincón, F.J.; Welles, L.; Lopez-Vazquez, C.M.; Nierychlo, M.; Abbas, B.; Geleijnse, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Brdjanovic, D. Long-term effects of sulphide on the enhanced biological removal of phosphorus: The symbiotic role of Thiothrix caldifontis. Water Res. 2017, 116, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Cen, S.; Huang, F.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wei, C.; et al. Candidatus Thiothrix phosphatis SCUT-1: A novel polyphosphate-accumulating organism abundant in the enhanced biological phosphorus removal system. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Ekama, G.A.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Biswal, B.K.; Chen, G.; Wu, D. Advances in sulfur conversion-associated enhanced biological phosphorus removal in sulfate-rich wastewater treatment: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel Suazo, K.; Dobbeleers, T.; Dries, J. The impact of reduced sulfur compounds on aerobic granular sludge formation and biological phosphorus removal. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 206, 109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbeck, N.; Borges, J.M.; Wilderer, P.A. Treatment of dairy effluents in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 66, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.; Richard, M.G.; Daigger, G.T. Manual on the Causes and Control of Activated Sludge Bulking, Foaming, and Other Solids Separation Problems, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seviour, R.J.; Nielsen, P.H. Microbial Communities in Activated Sludge Plants. In Microbial Ecology of Activated Sludge; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2010; pp. 95–126. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Xie, Z.; Shi, L.; Yan, X.; Fu, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Xu, B.; He, Q. Distinct responses of aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors to nitrogen and phosphorus deficient conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, N.; Masakke, Y.; Karthikeyan, S.; Kanazawa, S.; Honda, R.; Yamamoto-Ikemoto, R.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Metagenomic insights into the effect of sulfate on enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Zeng, W.; Wang, B.; Fan, Z.; Peng, Y. New insights in the competition of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms and glycogen-accumulating organisms under glycogen accumulating metabolism with trace Poly-P using flow cytometry. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Sun, S.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. Effect of food-to-microorganisms ratio on aerobic granular sludge settleability: Microbial community, potential roles and sequential responses of extracellular proteins and polysaccharides. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.M.P.; Pagilla, K.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Filamentous bulking sludge—A critical review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 793–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaff, D.R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pronk, M. Stable granulation of seawater-adapted aerobic granular sludge with filamentous Thiothrix bacteria. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaksman, V.A.; Mirghorayshi, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pronk, M. Impact of aerobic availability of readily biodegradable COD on morphological stability of aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Ukaigwe, S.; Dang, H.; Liu, Y. Phosphorus Removal from Aerobic Granular Sludge: Proliferation of Polyphosphate-Accumulating Organisms (PAOs) under Different Feeding Strategies. Processes 2022, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wei, M.; Guo, G.; Hu, Q.; Li, B.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Z. Effects of feeding mode on the formation and stability of aerobic granular sludge under combined antibiotic stress. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 145996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areskoug, T.; Mendoza, J.A.; Modin, O.; Lorick, D.; Tumlin, S.; Wilén, B.-M. Sustainable carbon management in aerobic granular sludge for municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 431, 132624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrein, P.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Osseweijer, P.; Posada, J. Exploring resource recovery potentials for the aerobic granular sludge process by mass and energy balances—Energy, biopolymer and phosphorous recovery from municipal wastewater. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2164–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hao, X.; Persiani, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Reinvestigating the Composition of Alginate-Like Exopolymers Extracted from Activated Sludge. ACS ES & T Water 2024, 4, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Cai, Y.-A.; Xiong, X.; Tang, Y.; Shao, S.; Wang, C.; Ng, H.Y. Unraveling the mechanism of fouling mitigation in AGS-MBR system: From AGS properties to foulant interactions. Water Res. 2025, 279, 123403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Jiang, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Bin, L.; Chen, W.; Li, P.; Huang, S.; Tang, B. Insights into the formation and development of membrane fouling in a continuous flow aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsertou, E.; Caluwé, M.; Goossens, K.; Seguel Suazo, K.; Dries, J. Performance of an aerobic granular sludge membrane filtration in a full-scale industrial plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 3002–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).