Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II) on Green Zn-Mn Ferrite Soft Magnetic Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Manufacturing of the Zn-Mn Ferrite Soft Magnetic Material
2.2. Characterization of the Adsorbent
2.3. Effect of pH on Zn-Mn Ferrite
2.4. Zeta Potential of Zn-Mn Ferrite
2.5. Adsorption of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II)
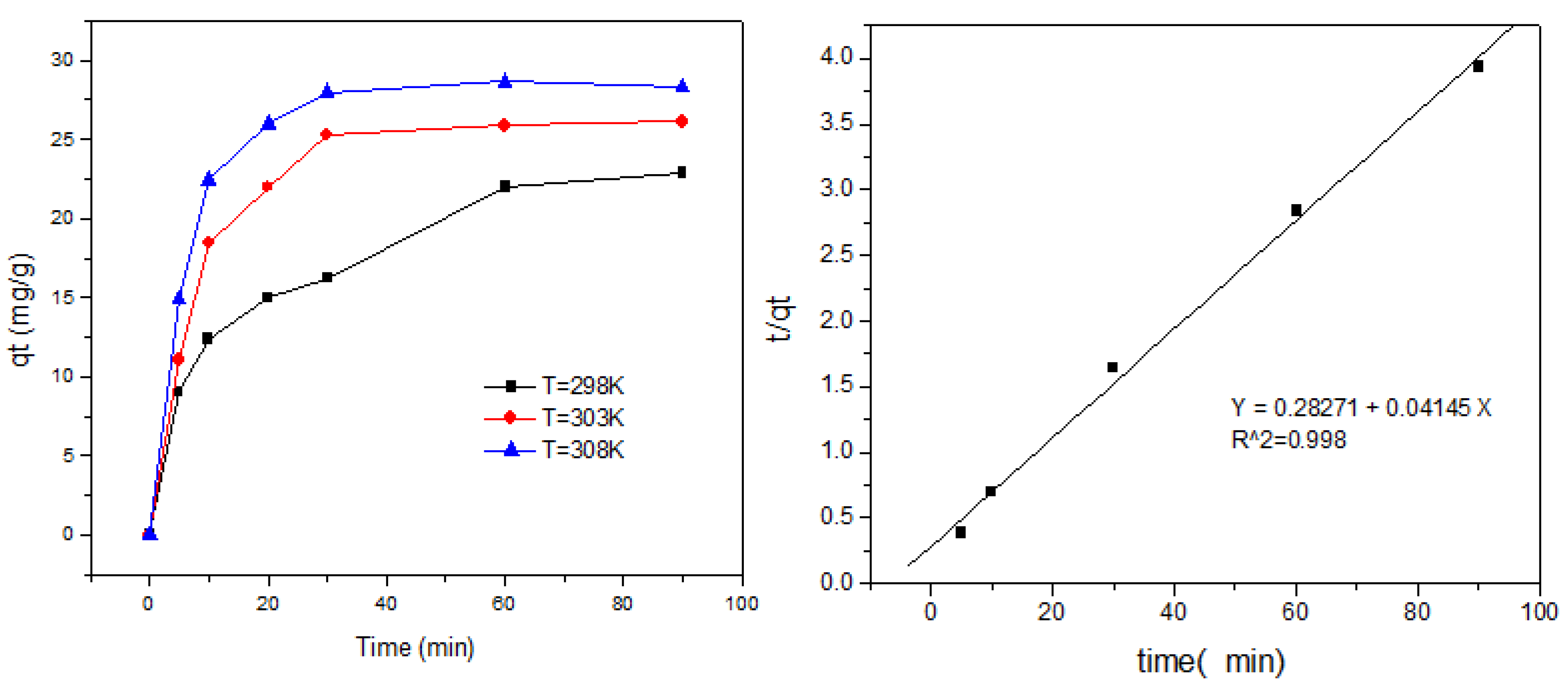
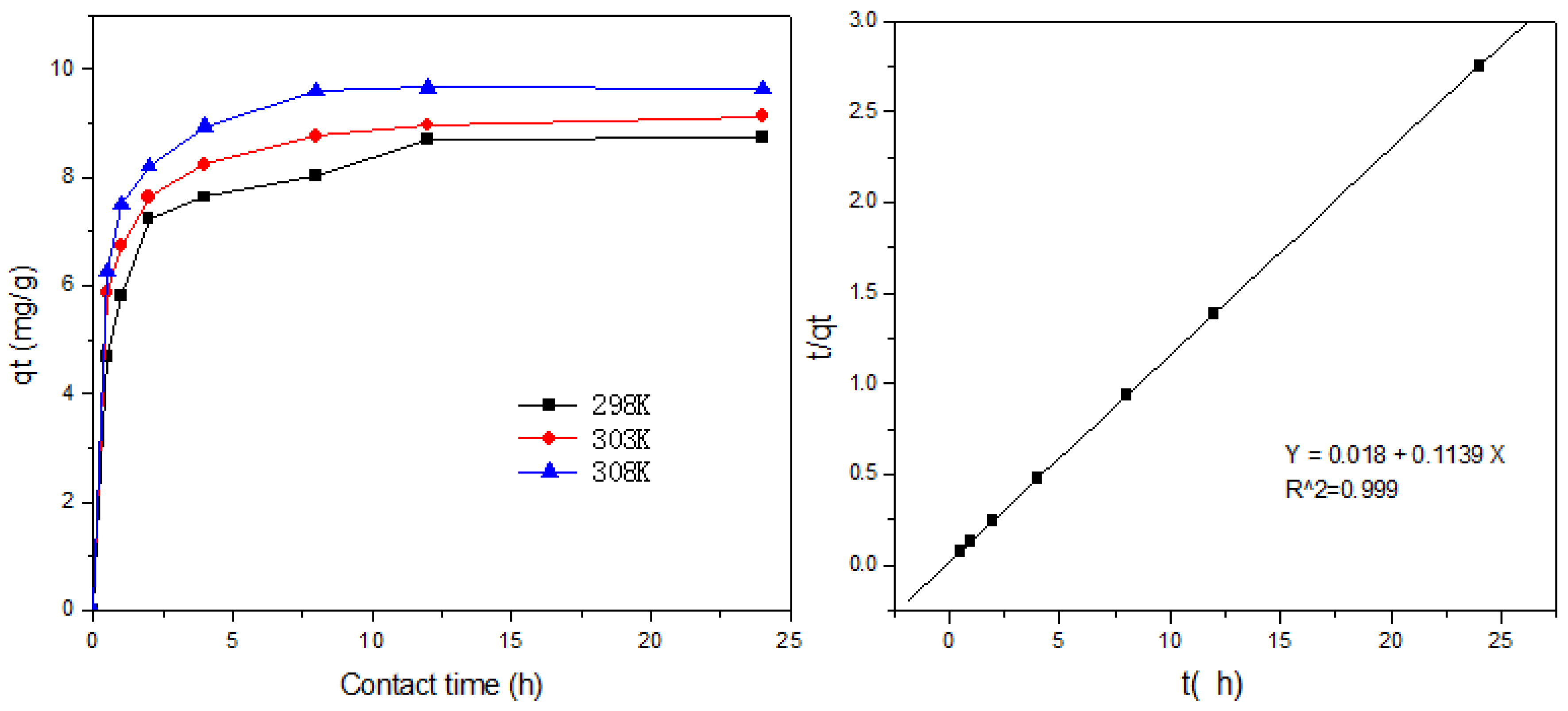
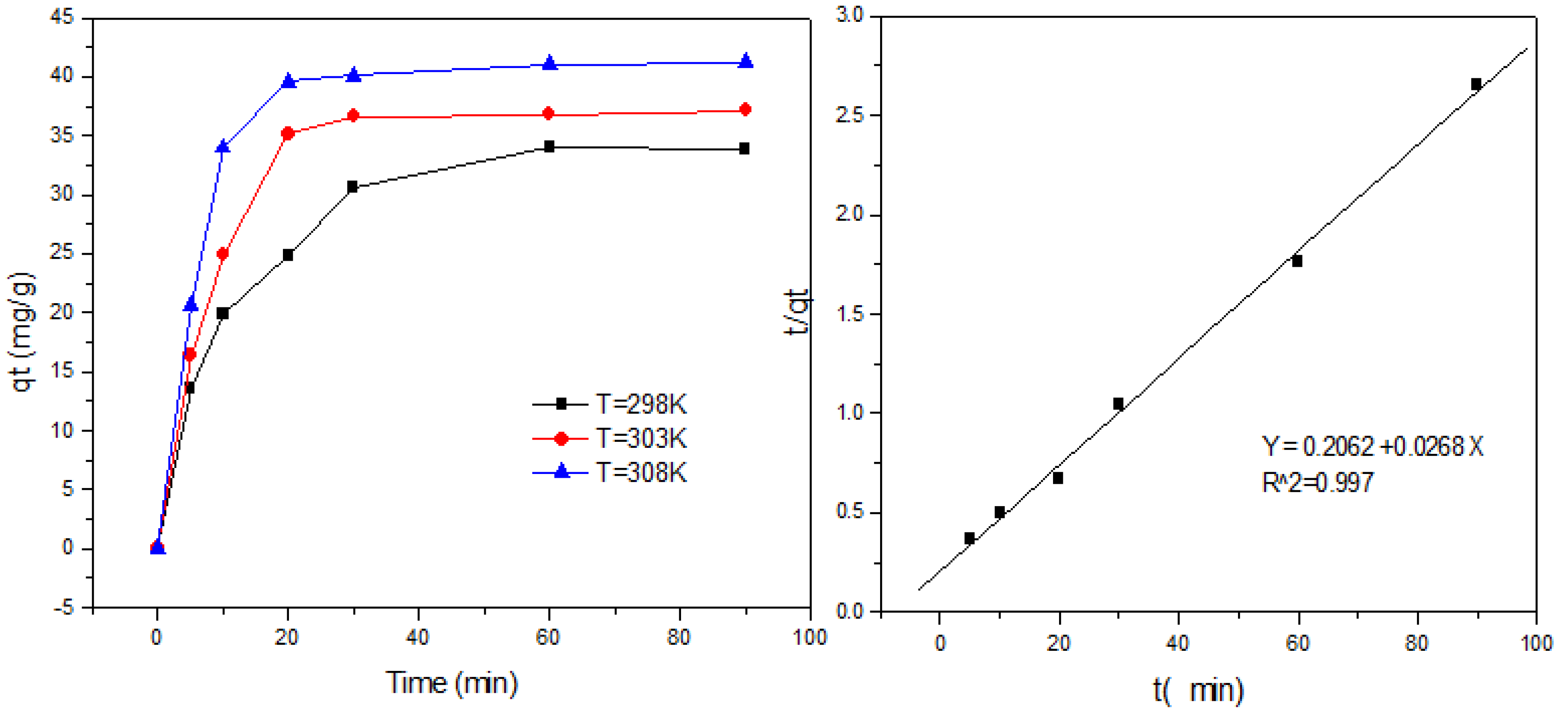
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
2.6.1. The Pseudo-Second-Order Model
2.6.2. Adsorption Reaction Activation Energy
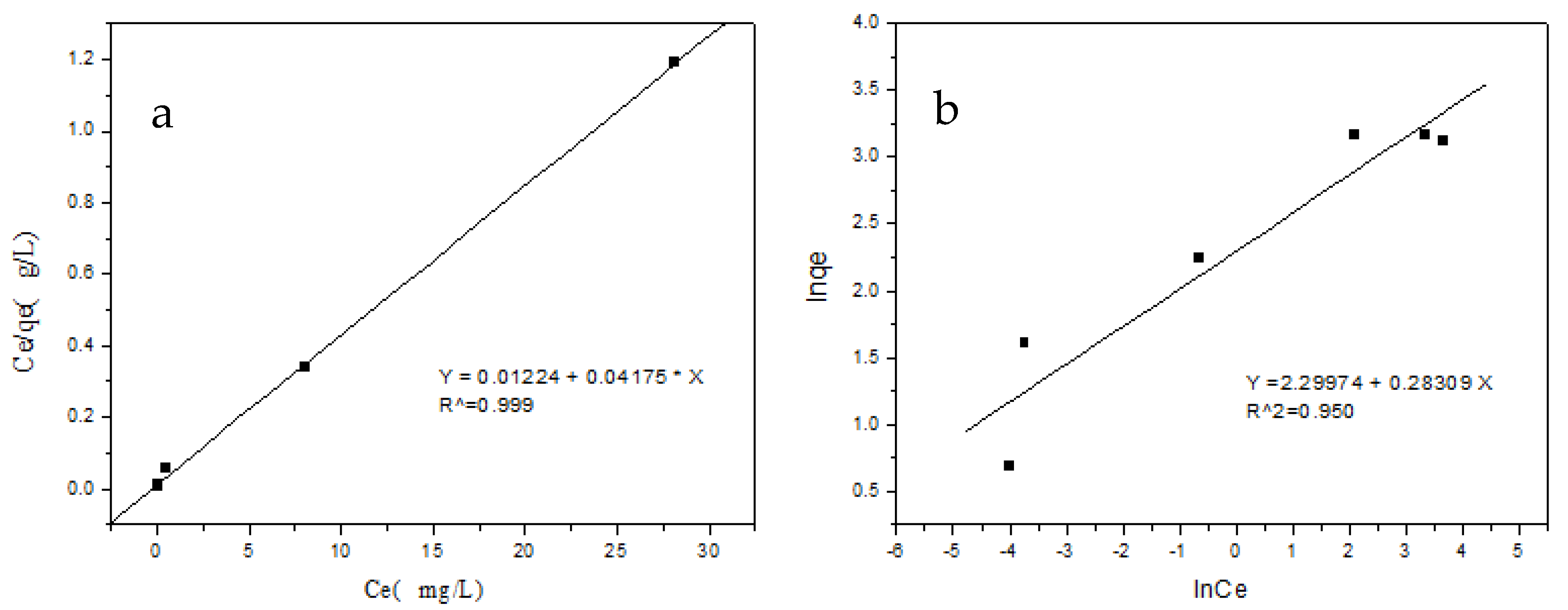
2.7. Adsorption Isotherms
2.7.1. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm Model
2.7.2. Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm Model
2.8. Apparatuses and Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
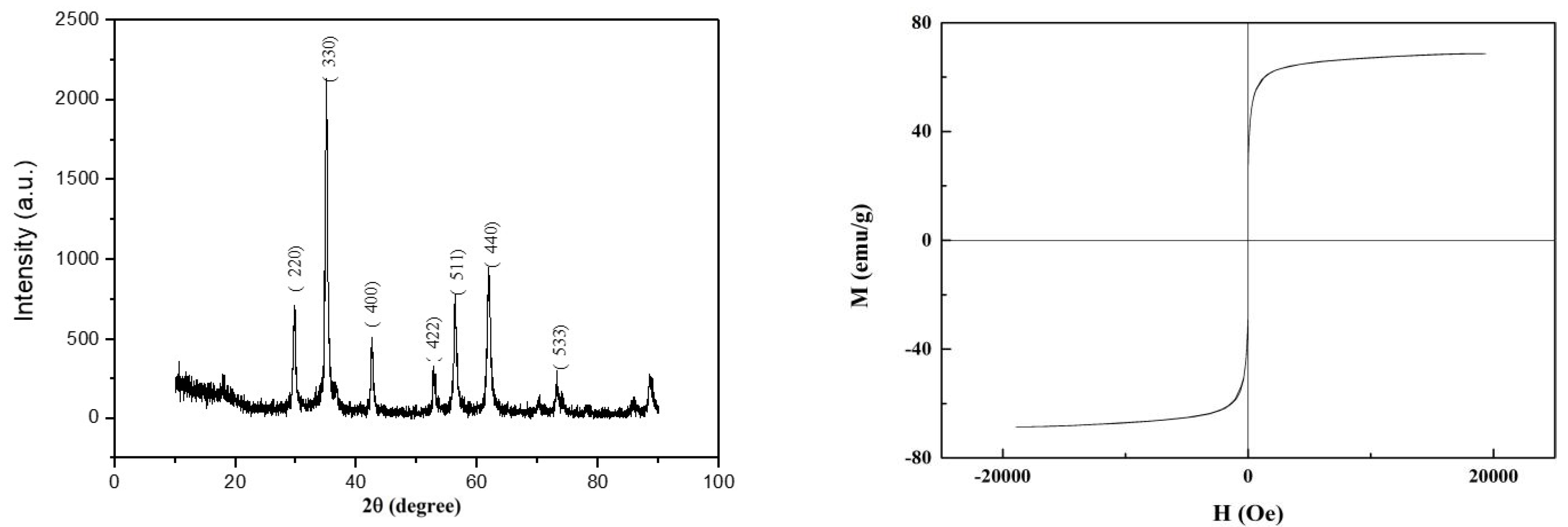
3.1. Adsorbent Characterization
3.2. Effect of pH Level on Zn-Mn Ferrite
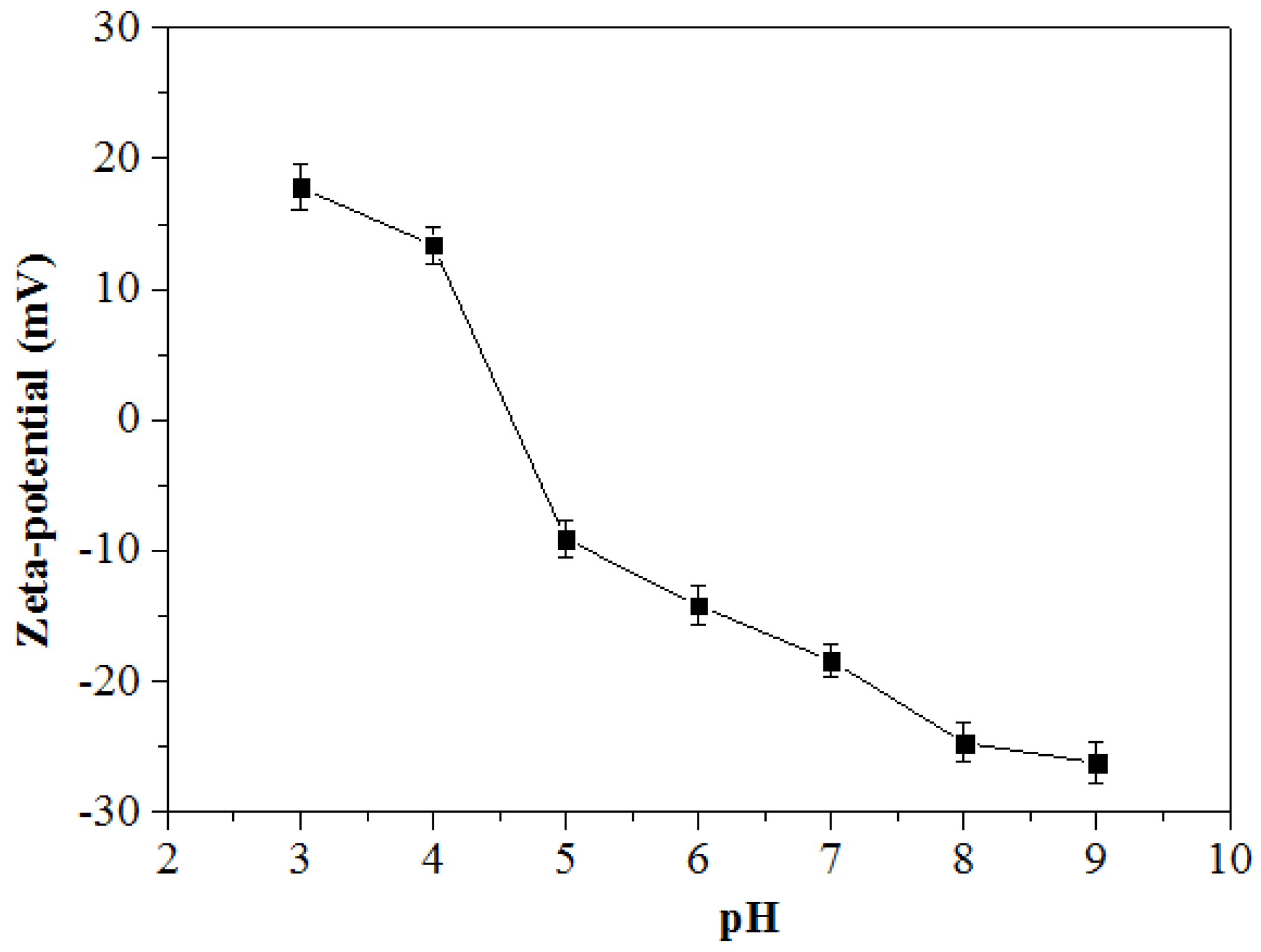
3.3. Zeta Potential of Zn-Mn Ferrite
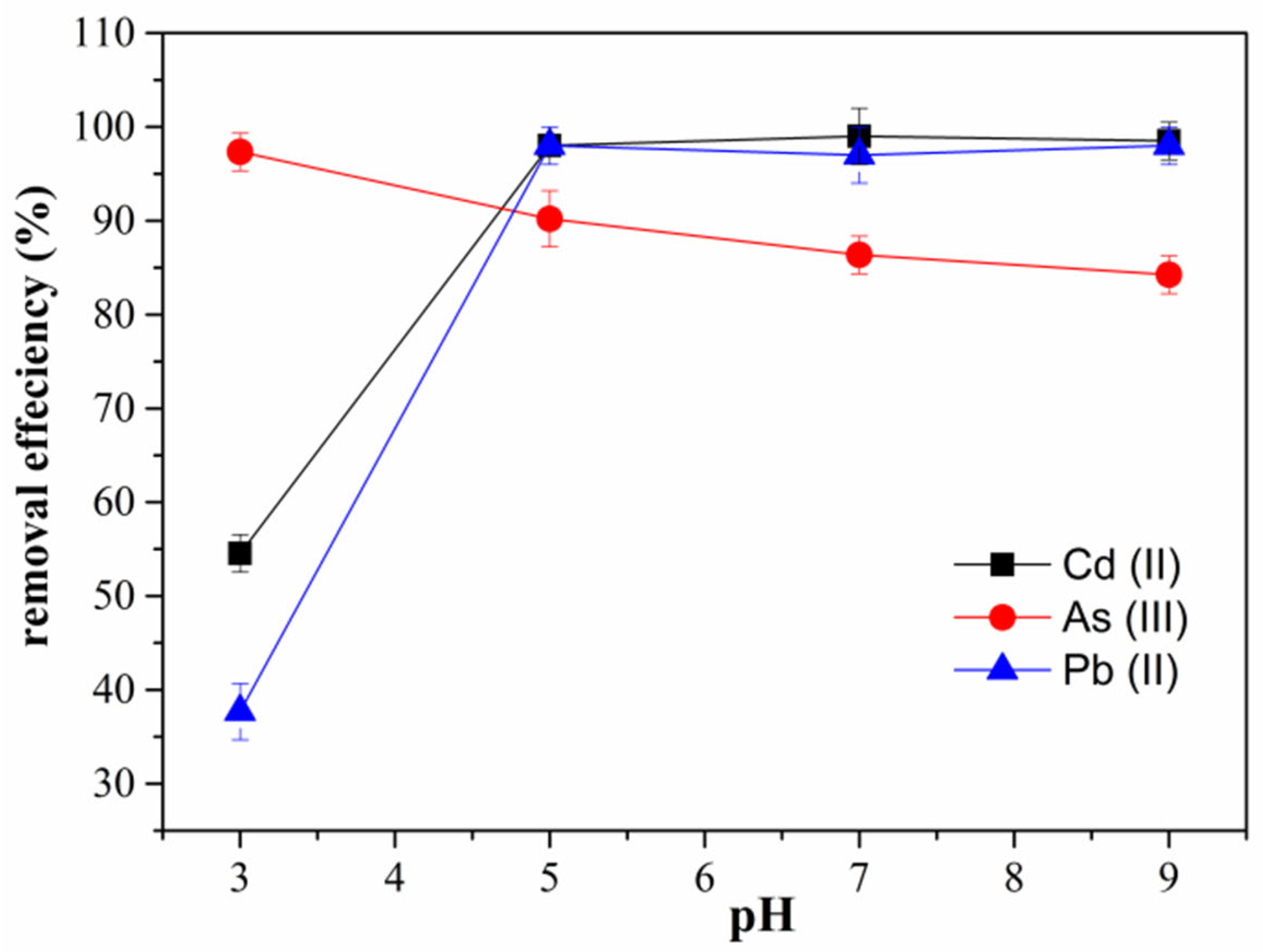
3.4. Effect of pH on Adsorption of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II)
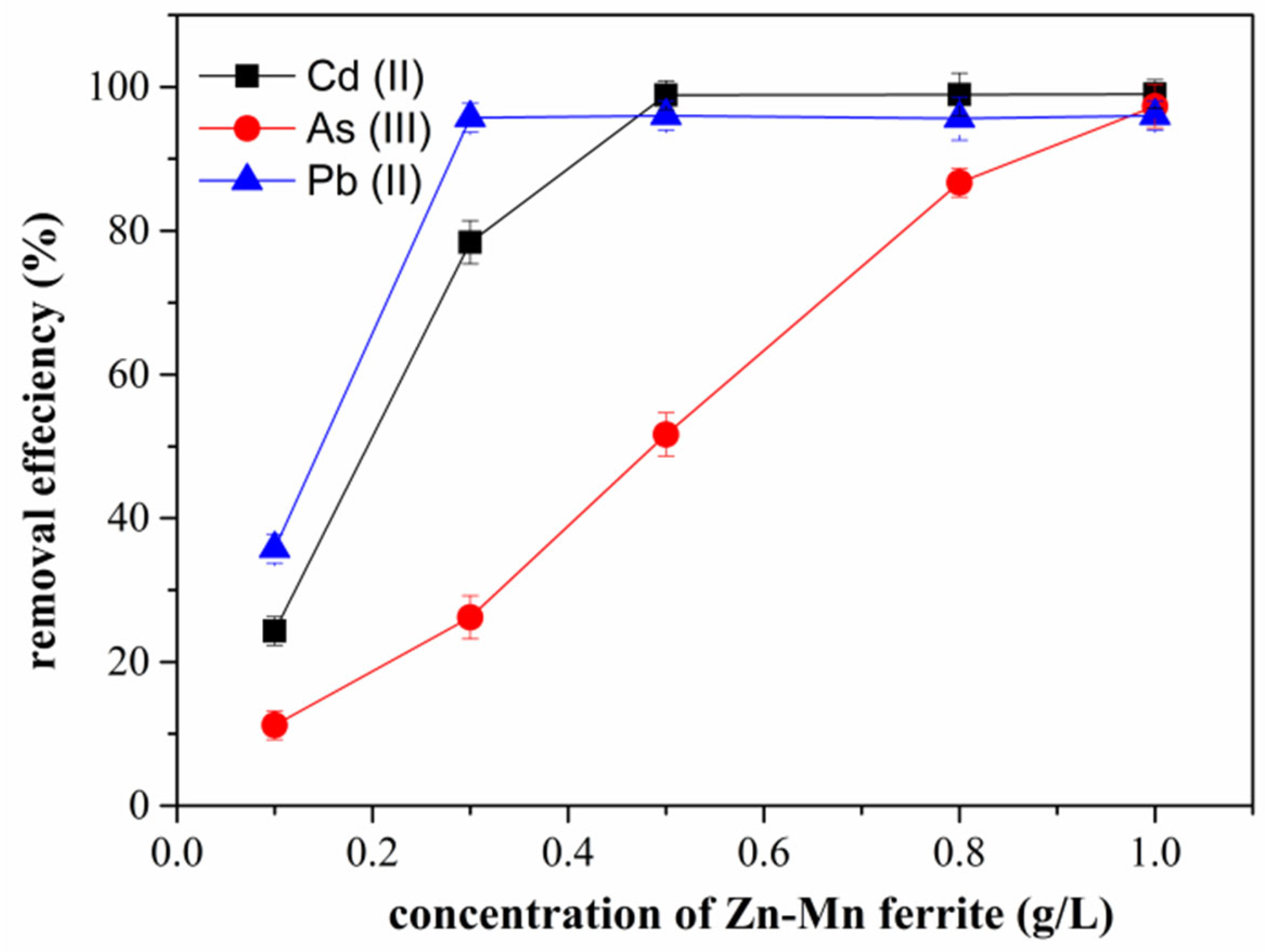
3.5. Effect of Concentration on Adsorption of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II)
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics
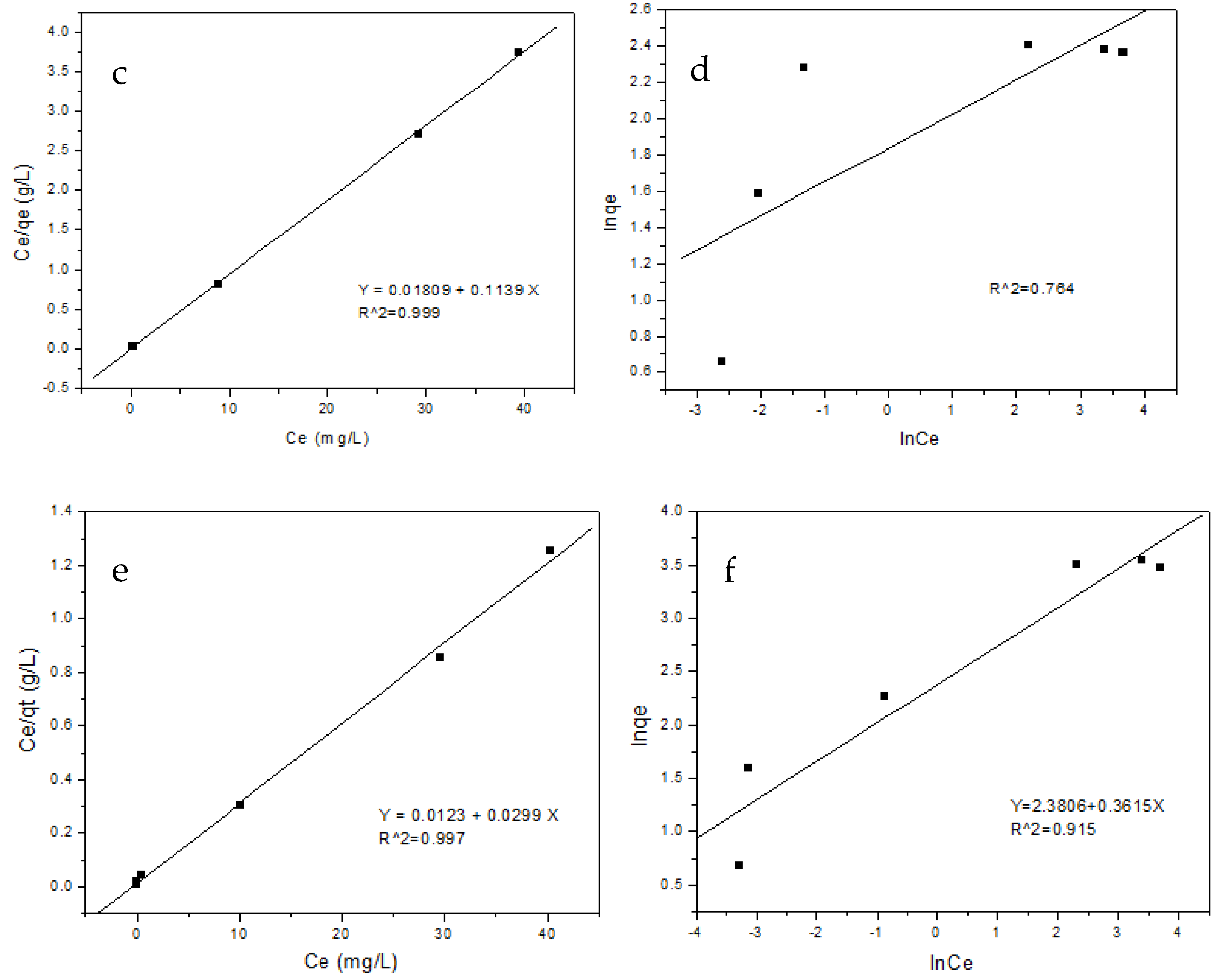
3.7. Adsorption Isotherms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, M.; Yang, X.; Huisingh, D.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y. Consumer behavior and perspectives concerning spent household battery collection and recycling in China: A case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayilgan, E.; Kukrer, T.; Civelekoglu, G.; Ferella, F.; Akcil, A.; Veglio, F.; Kitis, M. A review of technologies for the recovery of metals from spent alkaline and zinc–Carbon batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.P.; Toews, P.; Bouvier, R. Increasing diversion of household hazardous wastes and materials through mandatory retail take-back. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 123, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, Q.; Niu, Z.; Ma, J.; Xin, B.; Chen, S.; Dai, J.; Wang, R. Preparation of Zn–Mn ferrite from spent Zn–Mn batteries using a novel multi-step process of bioleaching and co-precipitation and boiling reflux. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 153, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Plant, J.A.; Voulvoulis, N.; Oates, C.J.; Ihlenfeld, C. Cadmium levels in Europe: Implications for human health. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.F.; Fowler, B.A.; Nordberg, M.; Friberg, L.T. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Marín, A.; Zapata, V.M.; Ortuño, J.; Aguilar, M.; Sáez, J.; Lloréns, M. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto orange waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gode, F.; Pehlivan, E. Removal of chromium(III) from aqueous solutions using Lewatit S 100: The effect of pH, time, metal concentration and temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, H.; Chandra, V.; Jung, S.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, S.B. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal using iron nanoparticle decorated graphene. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3583–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Few—Layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10454–10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wu, W.; Li, S.; Xing, N.; Zhu, N.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Dang, Z. Removal of Cd2+ from aqueous solutions by adsorption using Fe-montmorillonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taty-Costodes, V.; Fauduet, H.; Porte, C.; Delacroix, A. Removal of Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions, from aqueous solutions, by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 105, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pont, N.; Salvadó, V.; Fontàs, C. Selective transport and removal of Cd from chloride solutions by polymer inclusion membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Adlan, M.N.; Ariffin, K.S. Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cu and Cr(VI)) removal from water in Malaysia: Post treatment by high quality limestone. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Wu, Y.; Grigg, R.B. Adsorption and desorption kinetics and equilibrium of calcium lignosulfonate on dolomite porous media. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 13772–13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oter, O.; Akcay, H. Use of natural clinoptilolite to improve, water quality: Sorption and selectivity studies of lead(II), copper(II), zinc(II), and nickel(II). Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhemer, W.K.; Hefne, J.A.; Alandis, N.M.; Aldayel, O.A.; Al-Raddadi, S. Thermodynamics and kinetics of Co (II) adsorption onto natural and treated bentonite. Jordan J. Chem. 2008, 3, 409–423. Available online: https://jjc.yu.edu.jo/index.php/jjc/article/view/427 (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Alex, S.A.; Lomenech, C.; Hurel, C.; Marmier, N. Adsorption of nickel and arsenic from aqueous solution on natural Sepiolite. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 9, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, A.; Baudu, M.; Kankou, M.O.S.O.; Basly, J.-P. Copper and nitrophenol removal by low cost alginate/Mauritanian clay composite beads. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.-A.; Toloman, D.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Cadar, O. Investigation on the formation, structural and photocatalytic properties of mixed Mn-Zn ferrites nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 matrix. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawas, U.; Verenkar, V.; Vader, V.; Jain, A.; Meena, S.S. Effects of sintering temperature on microstructure, initial permeability and electric behaviour of Ni-Mn-Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 275, 125250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefatgol, R.; Gholizadeh, A. The effect of the annealing temperature on the microstructural, magnetic, and spin-dynamical properties of Mn–Mg–Cu–Zn ferrites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2022, 624, 413442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, K.P.; Jain, A.; Loeppert, R.H. Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on ferrihydrite: Kinetics, equilibrium, and adsorption envelopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, J.; Luan, T.; Wen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution on magnetic porous ferrospinel MnFe2O4. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnanelli, F.; Mainelli, S.; Vegliò, F.; Toro, L. Heavy metal removal by olive pomace: Adsorbent characterisation and equilibrium modelling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 4709–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Yasukawa, A.; Kandori, K.; Orii, R. Textures of Tetradecahedron δ-FeOOH Particles and Their Thermal Decomposition Products. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1994, 90, 2567–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Sakata, W.; Yasukawa, A.; Kandori, K. Pore structures of the thermal decomposition products of δ-FeOOH particles doped with Ni(II), Co(II) and Cu(II). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 136, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, L.; Pei, Z.; Li, C.; Lv, J.; Xie, J.; Wen, B.; Zhang, S. Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics of Cr(III) on graphene oxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, B.N.; Suresha, S. NPP–Modified bentonite for adsorption of Ni (II) from aqueous solution and electroplating wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.H.; Zhang, C.Z.; Han, R.P. Removal of copper cation and lead cation from aqueous solution by manganese-oxide-coated-sand. J. Acta Sci. Cireumstantiae 2005, 25, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, M. Adsorption character for removal Cu(II) by magnetic Cu(II) ion imprinted composite adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirtom, V.N.; Dinçer, A.; Becerik, S.; Aydemir, T.; Celik, A. Comparative adsorption of Ni(II) and Cd (II) ions on epichlorohydrin crosslinked chitosan–Clay composite beads in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, A.; Iorio, M.; Capasso, R. Sustainable sorption strategies for removing Cr3+ from tannery process wastewater. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| pH | Mn Dissolution Rate (%) | Zn Dissolution Rate (%) | Fe Dissolution Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 14.23 | 18.82 | 6.72 |
| 1.0 | 6.88 | 12.70 | 2.46 |
| 1.5 | 1.96 | 3.43 | 0.51 |
| 2.0 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Guan, M.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Xin, B. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II) on Green Zn-Mn Ferrite Soft Magnetic Material. Water 2025, 17, 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111630
Wang J, Guan M, Qin Z, Zhang S, Cheng J, Xin B. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II) on Green Zn-Mn Ferrite Soft Magnetic Material. Water. 2025; 17(11):1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111630
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jia, Mengyi Guan, Zijian Qin, Shihao Zhang, Jian Cheng, and Baoping Xin. 2025. "Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II) on Green Zn-Mn Ferrite Soft Magnetic Material" Water 17, no. 11: 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111630
APA StyleWang, J., Guan, M., Qin, Z., Zhang, S., Cheng, J., & Xin, B. (2025). Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Cd (II), As (III), and Pb (II) on Green Zn-Mn Ferrite Soft Magnetic Material. Water, 17(11), 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111630






