Feeding Habits of the Invasive Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in Different Habitats of the SE Iberian Peninsula, Spain (Western Mediterranean)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Laboratory Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
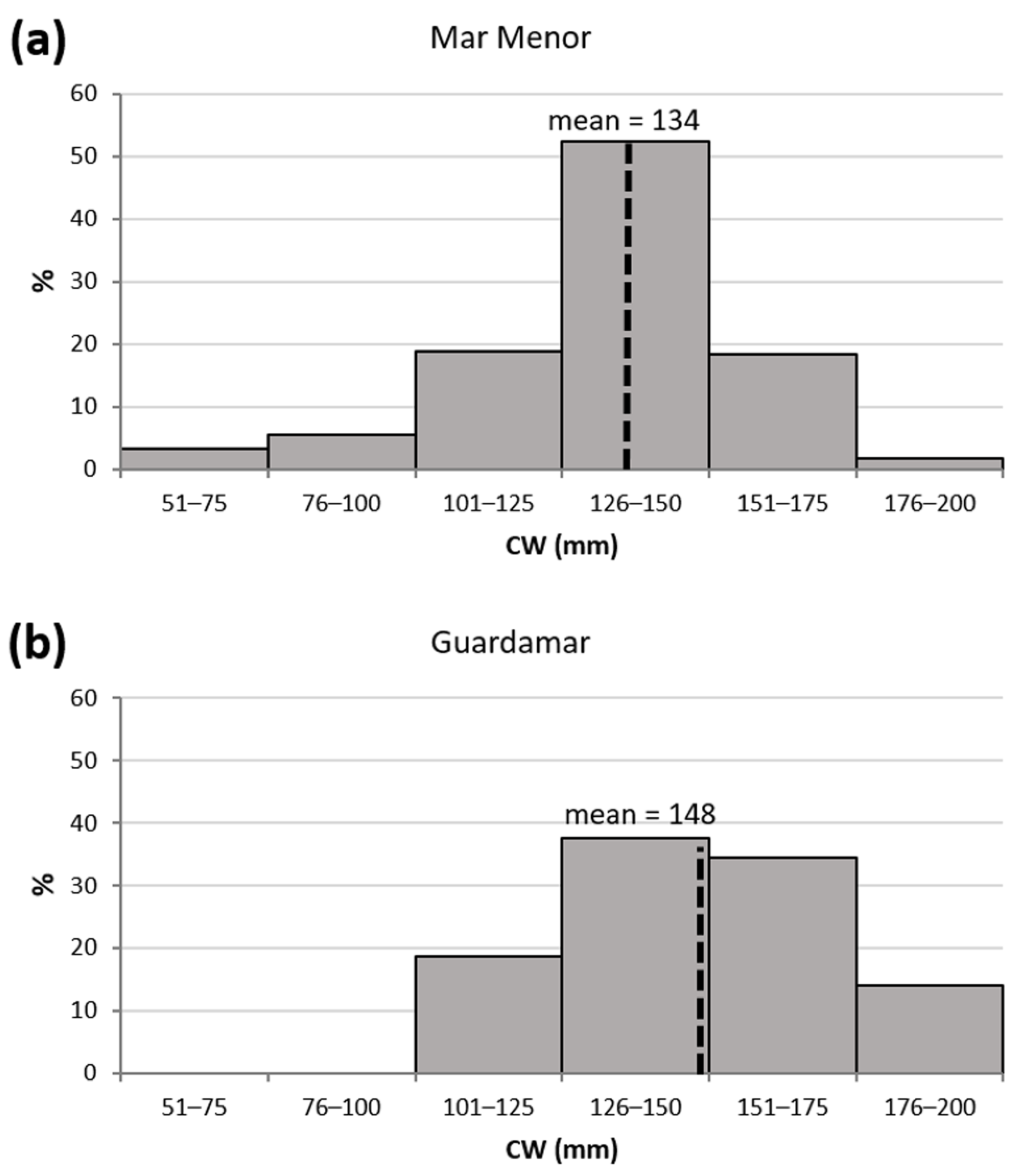
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
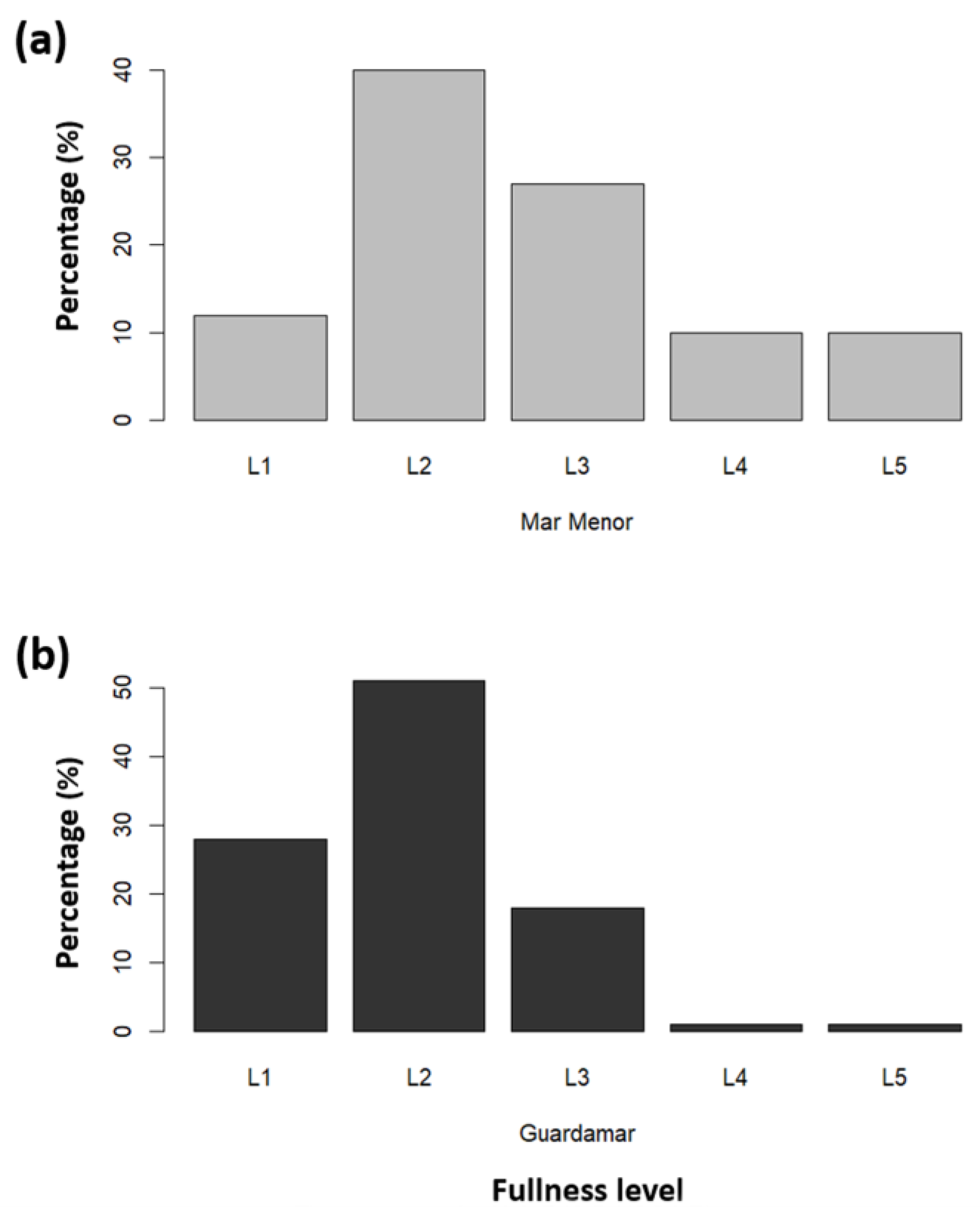
3.2. Stomach Fullness
3.3. Factors That Influenced the Stomach Content Weights
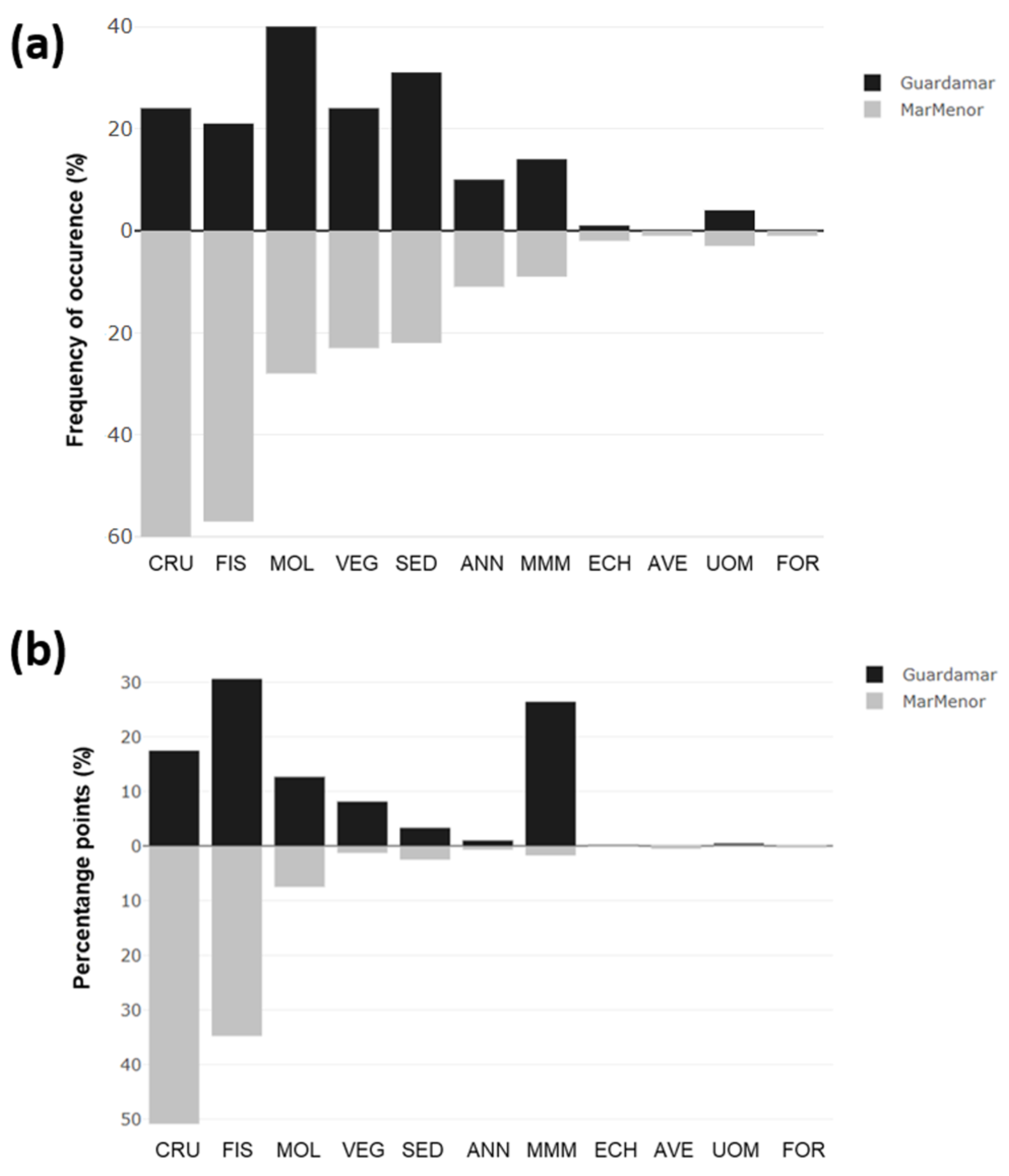
3.4. The Frequency of Occurrence (FO) and the Percentage Points (PPs) of Prey Groups
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GLM | Generalised linear model |
| FO | Frequency of occurrence |
| PP | Percentage points |
| CRU | Crustacea |
| FIS | Fish |
| MOL | Mollusca |
| VEG | Plant/algae |
| SED | Sediment |
| ANN | Annelida |
| MMM | Man-made material |
| ECH | Echinodermata |
| AVE | Aves |
| UOM | Unidentified organic material |
| FOR | Foraminifera |
| CW | Carapace width |
| GU | Guardamar |
| MM | Mar Menor |
Appendix A
| Source | Type III | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wald Chi-Square | df | p Value | |
| (Intercept) | 71.092 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 3.617 | 1 | 0.057 |
| Season | 35.549 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Size group | 7.488 | 2 | 0.024 |
| Parameter | B | Std. Error | 95% Wald Confidence Interval | Hypothesis Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Wald Chi-Square | df | p Value | |||
| (Intercept) | 0.628 | 0.1123 | 0.407 | 0.848 | 31.214 | 1 | <0.001 |
| [sex = female] | −0.174 | 0.0916 | −0.354 | 0.005 | 3.617 | 1 | 0.057 |
| [sex = male] | 0 a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| [season = summer] | 0.016 | 0.1021 | −0.185 | 0.216 | 0.024 | 1 | 0.878 |
| [season = autumn] | 0.563 | 0.1216 | 0.325 | 0.802 | 21.485 | 1 | <0.001 |
| [season = winter] | −0.190 | 0.1345 | −0.454 | 0.074 | 1.991 | 1 | 0.158 |
| [season = spring] | 0 a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| [size_group = 1] | −0.346 | 0.1619 | −0.664 | −0.029 | 4.574 | 1 | 0.032 |
| [size_group = 2] | −0.226 | 0.0971 | −0.416 | −0.035 | 5.407 | 1 | 0.020 |
| [size_group = 3] | 0 a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| (Scale) | 0.243 b | 0.0253 | 0.198 | 0.298 | |||
| Source | Type III | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wald Chi-Square | df | p Value | |
| (Intercept) | 55.491 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.497 | 1 | 0.481 |
| Season | 36.683 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Size group | 16.004 | 2 | <0.001 |
| Sex x season x size group | 28.577 | 11 | 0.003 |
| Source | Type III | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wald Chi-Square | df | p Value | |
| (Intercept) | 19.609 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 4.185 | 1 | 0.041 |
| Season | 5.466 | 1 | 0.019 |
| Size group | 0.683 | 1 | 0.409 |
| Parameter | B | Std. Error | 95% Wald Confidence Interval | Hypothesis Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Wald Chi-Square | df | p Value | |||
| (Intercept) | 0.284 | 0.0951 | 0.097 | 0.470 | 8.888 | 1 | 0.003 |
| [sex = female] | −0.218 | 0.1066 | −0.427 | −0.009 | 4.185 | 1 | 0.041 |
| [sex = male] | 0 a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| [season = summer] | 0.174 | 0.0744 | 0.028 | 0.320 | 5.466 | 1 | 0.019 |
| [season=winter] | 0 a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| [size_group=2] | −0.062 | 0.0752 | −0.210 | 0.085 | 0.683 | 1 | 0.409 |
| [size_group=3] | 0 a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| (Scale) | 0.087 b | 0.0150 | 0.062 | 0.121 | |||
| Source | Type III | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wald Chi-Square | df | p Value | |
| (Intercept) | 13.789 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 2.476 | 1 | 0.116 |
| Season | 4.521 | 1 | 0.033 |
| Size group | 1.670 | 1 | 0.196 |
| Sex x season x size group | 1.195 | 3 | 0.754 |
References
- Dall, W.; Moriarty, D.J.W. Functional aspects of nutrition and digestion. In The Biology of Crustacea, Internal Anatomy and Physiological Regulation; Bliss, D.E., Mantel, L.H., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Josileen, J. Food and feeding of the blue swimmer crab, Portunus pelagicus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Decapoda, Brachyura) along the coast of Mandapam, Tamil Nadu, India. Crustaceana 2011, 84, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.C. Natural diet and feeding habits of the crabs Liocarcinus puber and L. holsatus (Decapoda, Brachyura, Portunidae). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 31, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentu, J.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z. Effects of salinity on survival, feeding behavior and growth of the juvenile swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus (Miers, 1876). Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. Effects of water temperature on growth, feeding and molting of juvenile Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.E. The distribution and behaviour of ovigerous edible crabs (Cancer pagurus), and consequent sampling bias. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1982, 40, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgrad, B.A.; Griffen, B.D. The influence of diet composition on fitness of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, L.; Dick, J.T.; Elwood, R.W. Claw removal and feeding ability in the edible crab, Cancer pagurus: Implications for fishery practice. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 116, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, B.; Marcout, A.; Kopp, D.; Morandeau, F.; Mehault, S.; Mouchet, M.A. Assessing discard consumption dynamic in shallow coastal environment using underwater video. Fish. Res. 2023, 260, 106587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, G.; Chainho, P.; Cilenti, L.; Falco, S.; Kapiris, K.; Katselis, G.; Ribeiro, F. The Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus in southern European coastal waters: Distribution, impact and prospective invasion management strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, G.; Bardelli, R.; Zenetos, A. A global occurrence database of the Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchessaux, G.; Mangano, M.C.; Bizzarri, S.; M’rabet, C.; Principato, E.; Lago, N.; Veyssiere, D.; Garrido, M.; Scyphers, S.B.; Sarà, G. Invasive blue crabs and small-scale fisheries in the Mediterranean sea: Local ecological knowledge, impacts and future management. Mar. Policy 2023, 148, 105461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millikin, M.R. Synopsis of Biological Data on the Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun (No. 138); National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Marine Fisheries Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, M. True Crabs. In The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Atlantic. Volume1: Introdution, Molluscs, Crustaceans, Hagfishes, Sharks, Batoid Fishes, and Chimaeras; Carpenter, K.E., Ed.; FAO Species Identification Guide for Fishery Purposes and American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists Special Publication No. 5; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003; pp. 1–600. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, A.H. Ecology of Juvenile and Adult Blue Crabs. In The Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus; Kennedy, V.S., Cronin, E., Eds.; University of Maryland Sea Grant Press: College Park, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 565–654. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, P.; Ibáñez, C.; Chen, L.; Caiola, N. Feeding habits and short-term mobility patterns of blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, across invaded habitats of the Ebro Delta subjected to contrasting salinity. Estuaries Coast. 2022, 45, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, R.A. Feeding habits of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, in the Apalachicola estuary, Florida. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1982, 32, 807–822. [Google Scholar]
- Stoner, A.W.; Buchanan, B.A. Ontogeny and overlap in the diets of four tropical Callinectes species. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1990, 46, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.E.; Sulkin, S.D.; Lippson, R.L. Composition and seasonal abundance of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, in the Chesapeake and Delaware Canal and adjacent waters. Chesap. Sci. 1975, 16, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramach, S.; Darnell, M.Z.; Avissar, N.; Rittschof, D. Habitat use and population dynamics of blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus, in a high-salinity embayment. J. Shellfish Res. 2009, 28, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, M.D.; Withers, K. Size and Distribution of Blue Crabs (Callinectes sapidus) With Regard to Salinity in the Upper Nueces Estuary, Texas. Gulf Mex. Sci. 2009, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perkins-Visser, E.; Wolcott, T.G.; Wolcott, D.L. Nursery role of seagrass beds: Enhanced growth of juvenile blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 198, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, P.; Gaspar, M.; Garel, E.; Baptista, V.; Cruz, J.; Cerveira, I.; Leitão, F.; Teodosio, M. The Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 expands its non-native distribution into the Ria Formosa lagoon and the Guadiana estuary (SW-Iberian Peninsula, Europe). Bioinvasions Rec. 2019, 8, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öndes, F.; Gökçe, G. Distribution and fishery of the invasive blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) in Turkey based on local ecological knowledge of fishers. J. Anatol. Environ. Anim. Sci. 2021, 6, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortegón, E.; Berger, S.; Encarnação, J.; Chairi, H.; Morais, P.; Teodósio, M.A.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Schubart, C.D.; Cuesta, J.A. Free pass through the pillars of Hercules? Genetic and historical insights into the recent expansion of the Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus to the West and the East of the Strait of Gibraltar. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 918026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampouris, T.E.; Porter, J.S.; Sanderson, W.G. Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 (Brachyura: Portunidae): An assessment on its diet and foraging behaviour, Thermaikos Gulf, NW Aegean Sea, Greece: Evidence for ecological and economic impacts. Crustac. Res. 2019, 48, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, P.; Thebault, E.; Anneville, O.; Duyck, P.F.; Chapuis, E.; Loeuille, N. Impacts of invasive species on food webs: A review of empirical data. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2017, 56, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuven, R.S.; Boggero, A.; Bakker, E.S.; Elgin, A.; Verreycken, H. Invasive species in inland waters: From early detection to innovative management approaches. Aquat. Invasions 2017, 12, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L. Alien species in fresh waters: Ecological effects, interactions with other stressors, and prospects for the future. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Siesa, M.E.; De Bernardi, F.; Padoa-Schioppa, E. Complex impact of an invasive crayfish on freshwater food webs. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 21, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiganova, T.A. Invasion of the Black Sea by the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi and recent changes in pelagic community structure. Fish. Oceanogr. 1998, 7, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kideys, A.E. Fall and rise of the Black Sea ecosystem. Science 2002, 297, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, T.; Fuhrmann, M.M.; Lindstrøm, U.; Nilssen, E.M.; Ivarjord, T.; Ramasco, V.; Jørgensen, L.L.; Sundet, J.H.; Sivertsen, K.; Källgren, E.; et al. Effects of the invasive red king crab on food web structure and ecosystem properties in an Atlantic fjord. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 596, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordone, G.; Galván, D.E.; Momo, F.R. Impacts of an invasion by green crab Carcinus maenas on the intertidal food web of a Patagonian rocky shore, Argentina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2023, 713, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; Franch, N.; Bernardo-Madrid, R.; López, V.; Abelló, P.; Queral, J.M.; Mancinelli, G. Severe, rapid and widespread impacts of an Atlantic blue crab invasion. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryer, C.H. Temporal patterns of feeding by blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) in a tidal-marsh creek and adjacent seagrass meadow in the lower Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 1987, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, C.; Lazaro-Chavez, E.; Bückle-Ramirez, F. Feeding habits and food niche segregation of Callinectes sapidus, C. rathbunae, and C. similis in a subtropical coastal lagoon of the Gulf of Mexico. J. Crust. Biol. 1994, 14, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmuth, J.M.; Roudez, R.; Glover, T.; Weis, J.S. Differences in prey capture behavior in populations of blue crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun) from contaminated and clean estuaries in New Jersey. Estuaries Coast. 2009, 32, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, R.D.; Knick, K.E.; Westphal, M. Diet selectivity of juvenile blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) in Chesapeake Bay. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2011, 51, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.L.; Fehon, M.M.; Cribari, K.J.; Scro, A.K. Blue crab Callinectes sapidus dietary habits and predation on juvenile winter flounder Pseudopleuronectes americanus in southern New England tidal rivers. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 681, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Jiménez, E.; Cuesta, J.A.; Laiz, I.; González-Ortegón, E. Diet of the invasive Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 (Decapoda, Portunidae) in the Guadalquivir estuary (Spain). Estuaries Coast. 2024, 47, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, M.; García-Rodríguez, E.; Muñoz-Vera, A.; Barcala, E.; Guijarro-García, E. Effect of the invasive blue crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896) in a protected coastal lagoon. Estuaries Coast. 2025, 48, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrozzo, L.; Potenza, L.; Carlino, P.; Costantini, M.L.; Rossi, L.; Mancinelli, G. Seasonal abundance and trophic position of the Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun 1896 in a Mediterranean coastal habitat. Rend. Lincei 2014, 25, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, G.; Glamuzina, B.; Petrić, M.; Carrozzo, L.; Glamuzina, L.; Zotti, M.; Raho, D.; Vizzini, S. The trophic position of the Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun 1896 in the food web of Parila Lagoon (South Eastern Adriatic, Croatia): A first assessment using stable isotopes. Medit.Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, H.; Polito, M.J. Trophic ecology of the Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus as an invasive non-native species in the Aegean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Baeta, M.; Mestre, E.; Solis, M.A.; Sanhauja, I.; Gairin, I.; Camps-Castellà, J.; Falco, S.; Ballesteros, M. Trophic role and predatory interactions between the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, and native species in open waters of the Ebro Delta. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2024, 298, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Ruzafa, Á.; Marcos Diego, C.; Gilabert Cervera, F.J.L. The ecology of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon: A fast changing ecosystem under human pressure. In Coastal Lagoons: Ecosystem Processes and Modelling for Sustainable Use and Development; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 392–422. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín, M.Á. Understanding nutrient loads from Catchment and Eutrophication in a salt lagoon: The Mar Menor Case. Water 2023, 15, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez Casalduero, F.; Ramos Espla, A.A.; Izquierdo Muñoz, A.; Gomaríz Castillo, F.; Martínez Hernández, F.J.; González-Carrión, F. Invertebrados Marinos Alóctonos en el Mar Menor. Instituto Español de Oceanografía: Madrid, Spain, 2016; pp. 157–178. Available online: https://rua.ua.es/dspace/handle/10045/61470 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Martínez-Garcia, E.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, V.; Aguado-Giménez, F.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Sanchez-Jerez, P. From paper to practice: An initial approach to implementation of the environmental monitoring plan for fish farming proposed by JACUMAR. Sci. Mar. 2018, 82, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberá, C.; Falco, S.; Prado, P.; Guijarro-García, E.; Barcala, E.; Ramos, A.A. Blue crab catchability of commercial fisheries in different areas of Western Mediterranean Sea. In Proceedings of the IX International Symposium on Marine Sciences, Valencia, Spain, 10–12 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.J. Methods for analysis of natural diet in portunid crabs (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunidae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1981, 52, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, G.R.L.; Negreiros-Fransozo, M.L.; Fransozo, A.; Castilho, A.L. Feeding ecology and niche segregation of the spider crab Libinia ferreirae (Decapoda, Brachyura, Majoidea), a symbiont of Lychnorhiza lucerna (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Seed, R. Ecological implications of cheliped size in crabs: Some data from Carcinus maenas and Liocarcinus holsatus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 84, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegele-Drywa, J.; Normant, M. Feeding ecology of the American crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Crustacea, Decapoda) in the coastal waters of the Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 2009, 51, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- do Vale, J.G.; Barrilli, G.H.C.; Chahad-Ehlers, S.; Branco, J.O. Factors influencing the feeding habits of the ghost crab Ocypode quadrata (Fabricius, 1787) on subtropical sandy beaches. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2022, 269, 107817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach contents analysis—A review of methods and their application. J. Fish Biol. 1980, 17, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraway, J.J. Extending the Linear Model with R: Generalized Linear, Mixed Effects and Nonparametric Regression Models; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; 301p. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in marine communities. In An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Rady, A.; Sallam, W.S.; Abdou, N.E.I.; El-Sayed, A.A.M. Food and feeding habits of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunidae) with special reference to the gastric mill structure. Egypt J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2018, 22, 417–431. [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh, P.W.; McClintock, J.B.; Hopkins, T.S. Comparative study of the diets of the blue crabs Callinectes similis and C. sapidus from a mud-bottom habitat in Mobile Bay, Alabama. J. Crustac. Biol. 1992, 12, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engel, W.A. The blue crab and its fishery in Chesapeake Bay. Part 1. Reproduction, early development, growth and migration. Commer. Fish. Rev. 1958, 20, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Escudero-Lozano, P.; Vivas-Salvador, M.; Barcala-Bellod, E.; Guijarro-García, E. Impact of Callinectes sapidus (Rathbun, 1896) expansion and eutrophic events in Mar Menor small-scale fisheries. In Proceedings of the IX International Symposium on Marine Sciences, Valencia, Spain, 10–12 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Pérez-Flores, R. Seasonal and bathymetric changes in feeding habits of the benthic red crab Pleuroncodes planipes (Decapoda, Anomura, Galatheidae) off the Pacific coast of Baja California Sur, Mexico. Crustaceana 1997, 70, 272–287. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20105861 (accessed on 3 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.I.; Tweedley, J.R.; Johnston, D.J.; Loneragan, N.R. Crab diets differ between adjacent estuaries and habitats within a sheltered marine embayment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 564695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Fernández, A.I.; Marcos, C.; Gilabert, J.; Quispe, J.I.; García-Charton, J.A. Spatial and temporal variations of hydrological conditions, nutrients and chlorophyll a in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, A.H.; Haddon, A.M.; Wiechert, L.A. Guild structure and foraging impact of blue crabs and epibenthic fish in a subestuary of Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 67, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagatz, M.E. Biology of blue crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, in St Johns River, Florida. US. Fish Wildl. Ser. Fish. Bull. 1968, 67, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Renzi, M.; Cilenti, L.; Scirocco, T.; Grazioli, E.; Anselmi, S.; Broccoli, A.; Pauna, V.; Provenza, F.; Specchiulli, A. Litter in alien species of possible commercial interest: The blue crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896) as case study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaie, M. Feeding habits of blue swimming crab Portunus segnis (Forskal, 1775) in the northern coastal waters of Iran. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2016, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albins, M.A.; Hixon, M.A. Invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans reduce recruitment of Atlantic coral-reef fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 367, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.A. (Ed.) Invasive Lionfish: A Guide to Control and Management; Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute Special Publication Series Number 1; Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute: Marathon, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]




| Prey | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Spring | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FO (%) | Content (Mean ± SE) (g) | FO (%) | Content (Mean ± SE) (g) | FO (%) | Content (Mean ± SE) (g) | FO (%) | Content (Mean ± SE) (g) | |
| PLANTS/ALGAE (VEG) | 22 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 7 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 28 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 43 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| POLYCHAETA (ANN) | 14 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 15 | 0.01 ± <0.01 | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 9 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| CRUSTACEA (CRU) | 51 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 74 | 0.57 ± 0.11 | 28 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 89 | 0.17 ± 0.03 |
| Amphipoda | 7 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 2 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 40 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Isopoda | 1 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 2 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 9 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Cirripedia | 4 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 4 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Brachyura | 18 | 0.01 ± <0.01 | 17 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 19 | 0.01 ± <0.01 | 31 | 0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Paguridae | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Panaeus kerathurus | 38 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 59 | 0.40 ± 0.09 | 9 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 66 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| Palaemon sp. | 8 | 0.01 ± <0.01 | 4 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 14 | 0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Other Natantia | 7 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 26 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 17 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| MOLLUSCA (MOL) | 27 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 22 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 22 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 46 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Bivalvia | 25 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 20 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 19 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 46 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Gastropoda | 6 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 2 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - |
| Cephalopoda | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 4 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| ECHINODERMATA (ECH) | 4 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 0 | - | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Asteridae | 4 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Echinoidea | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| FORAMINIFERA (FOR) | 0 | - | 4 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| PISCES (FIS) | 49 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 65 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 47 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 71 | 0.12 ± 0.04 |
| AVES (AVE) | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 6 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| UNIDENDIFIED ORG. (UOM) | 4 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - | 0 | - | 6 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| SEDIMENT (SED) | 22 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 28 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 9 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 26 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| MAN-MADE-MATERIAL (MMM) | 7 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 11 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 9 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 11 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Prey | Summer | Winter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FO (%) | Content (Mean ± SE) (g) | FO (%) | Content (Mean ± SE) (g) | |
| PLANTS/ALGAE (VEG) | 25 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 22 | 0.01 ± <0.01 |
| POLYCHAETA (ANN) | 8 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 11 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| CRUSTACEA (CRU) | 25 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 22 | 0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Amphipoda | 0 | - | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Isopoda | 0 | - | 8 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Cirripedia | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Brachyura | 6 | 0.01 ± <0.01 | 11 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Paguridae | 6 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Panaeus kerathurus | 17 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 8 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Palaemon sp. | 6 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - |
| Other Natantia | 6 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 6 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| MOLLUSCA (MOL) | 42 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 39 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Bivalvia | 36 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 39 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Gastropoda | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 6 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Cephalopoda | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 0 | - |
| ECHINODERMATA (ECH) | 0 | - | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| Asteridae | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Echinoidea | 0 | - | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| FORAMINIFERA (FOR) | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| PISCES (FIS) | 25 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 17 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| AVES (AVE) | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| UNIDENDIFIED ORG. (UOM) | 6 | <0.01 ± <0.01 | 3 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| SEDIMENT (SED) | 36 | 0.01 ± <0.01 | 25 | <0.01 ± <0.01 |
| MAN-MADE-MATERIAL (MMM) | 14 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 14 | 0.04 ± 0.03 |
| Prey | Mean Value (g) (±SE) at Locations | U Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mar Menor (MM) | Guardamar (GU) | |||
| Fish | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 4079 | <0.001 |
| Crustacea | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 3914 | <0.001 |
| Mollusca | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 6129 | 0.201 |
| Polychaeta | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 6594 | 0.724 |
| Plants/Algae | 0.01 ± 0.002 | 0.01 ± 0.004 | 6519 | 0.656 |
| Sediment | 0.01±0.003 | 0.01 ± 0.001 | 6174 | 0.197 |
| Man Made Material | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 6353 | 0.229 |
| Prey | Mean Value (g) (±SE) at Sexes | Uvalue | p Value | |
| ♂ | ♀ | |||
| Fish | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 5588 | <0.001 |
| Crustacea | 0.34 ± 0.06 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 5329 | <0.001 |
| Mollusca | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 7331 | 0.750 |
| Polychaeta | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 7259 | 0.470 |
| Plants/Algae | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.01 ± 0.002 | 6641 | 0.046 |
| Sediment | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.002 | 6533 | 0.027 |
| Man Made Material | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 7374 | 0.725 |
| Source of Variation | R | p |
|---|---|---|
| Location | 0.336 | 0.001 |
| Season | 0.186 | 0.001 |
| Location x Season | 0.308 | 0.001 |
| Pairwise Test MM *, MM+ | 0.271 | 0.001 |
| Pairwise Test MM *, GU * | 0.124 | 0.002 |
| Pairwise Test MM *, GU+ | 0.098 | 0.005 |
| Pairwise Test MM +, GU * | 0.349 | 0.001 |
| Pairwise Test MM +, GU + | 0.343 | 0.001 |
| Pairwise Test GU *, GU + | −0.04 | 0.917 |
| Sex | 0.009 | 0.249 |
| Size Group | 0.103 | 0.001 |
| Pairwise Tests 1–3 | 0.165 | 0.007 |
| Pairwise Tests 1–2 | 0.265 | 0.003 |
| Pairwise Tests 3–2 | 0.056 | 0.029 |
| Size Group (Location x Season) | 0.029 | 0.389 |
| Sex (Location x Season) | 0.25 | 0.114 |
| Contribution of Main Component Diet (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups (% Dissimilarity) | Crust | Fish | Mollusc | Inorg | Algae | Sedim |
| MM * and MM+ (87.8%) | 40.2 | 36.6 | 11.3 | 5.4 | 4.5 | |
| MM * and GU * (87.3%) | 17.8 | 21.1 | 24.9 | 14.6 | 10.2 | 8.1 |
| MM+ and GU * (89.9%) | 39.1 | 29.7 | 12.8 | 6.6 | 5.0 | |
| MM * and GU+ (89.5%) | 22.2 | 25.3 | 15.1 | 12.5 | 9.9 | |
| MM+ and GU+ (87.3%) | 38.7 | 31.8 | 8.6 | 7.8 | 6.9 | |
| GU * and GU+ (86.6%) | 21.9 | 17.7 | 18.9 | 17.1 | 13.9 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Öndes, F.; Esteso, I.; Guijarro-García, E.; Barcala, E.; Giménez-Casalduero, F.; Ramos-Esplá, A.A.; Barberá, C. Feeding Habits of the Invasive Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in Different Habitats of the SE Iberian Peninsula, Spain (Western Mediterranean). Water 2025, 17, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111615
Öndes F, Esteso I, Guijarro-García E, Barcala E, Giménez-Casalduero F, Ramos-Esplá AA, Barberá C. Feeding Habits of the Invasive Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in Different Habitats of the SE Iberian Peninsula, Spain (Western Mediterranean). Water. 2025; 17(11):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111615
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖndes, Fikret, Isabel Esteso, Elena Guijarro-García, Elena Barcala, Francisca Giménez-Casalduero, Alfonso A. Ramos-Esplá, and Carmen Barberá. 2025. "Feeding Habits of the Invasive Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in Different Habitats of the SE Iberian Peninsula, Spain (Western Mediterranean)" Water 17, no. 11: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111615
APA StyleÖndes, F., Esteso, I., Guijarro-García, E., Barcala, E., Giménez-Casalduero, F., Ramos-Esplá, A. A., & Barberá, C. (2025). Feeding Habits of the Invasive Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in Different Habitats of the SE Iberian Peninsula, Spain (Western Mediterranean). Water, 17(11), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111615





