Planktonic Pro- and Microeukaryotes of the Kuibyshev Reservoir and Its Bays During the Cyanobacterial Bloom Period
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
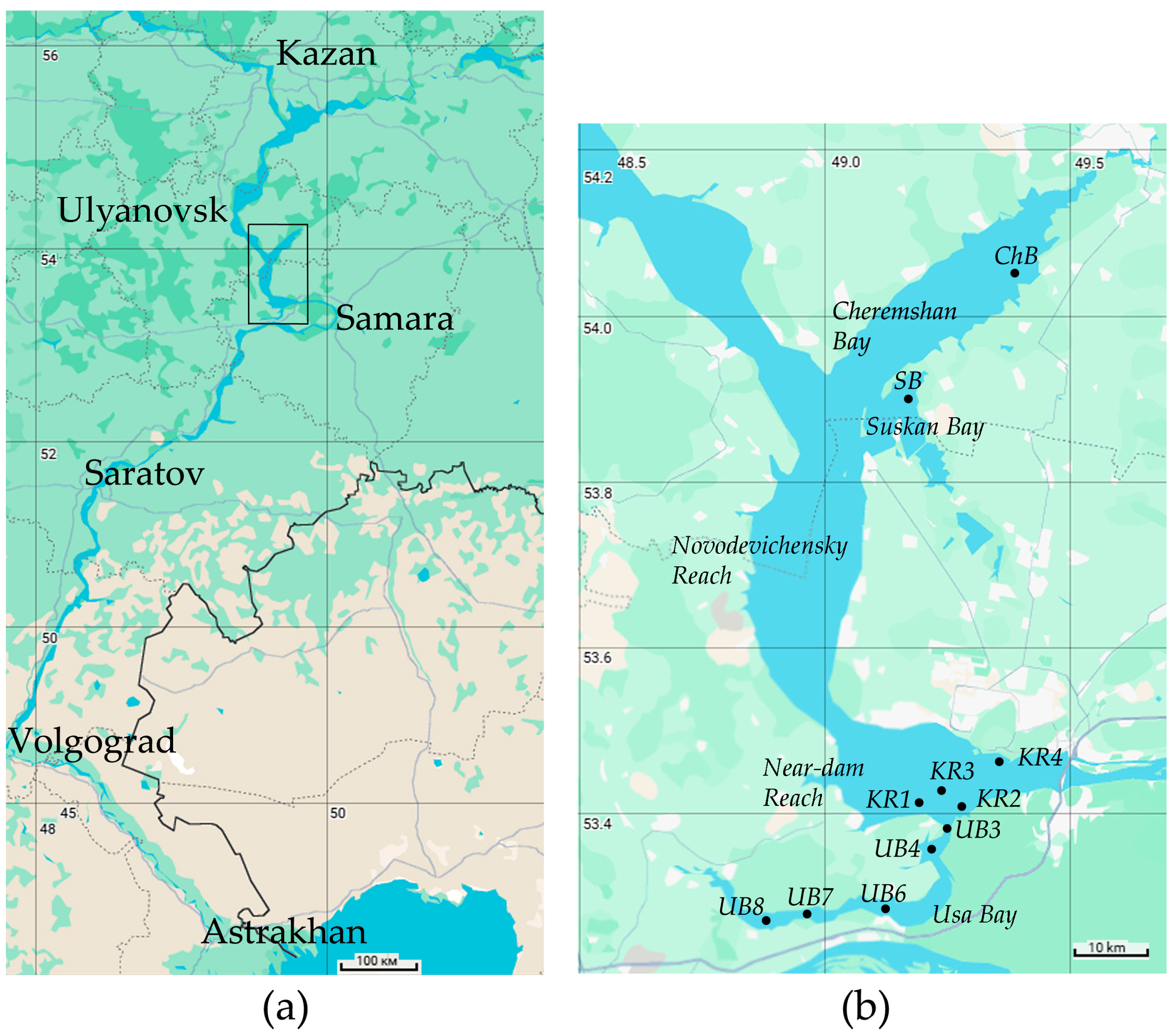
2.1. Study Site and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction, 16S and 18S rRNA Gene Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Abiotic Conditions and Chlorophyll a
3.2. Microbial Gene Diversity of the Lower Part of the Kuibyshev Reservoir
3.3. Community Structure and Composition of Phototrophic Cyanobacteria
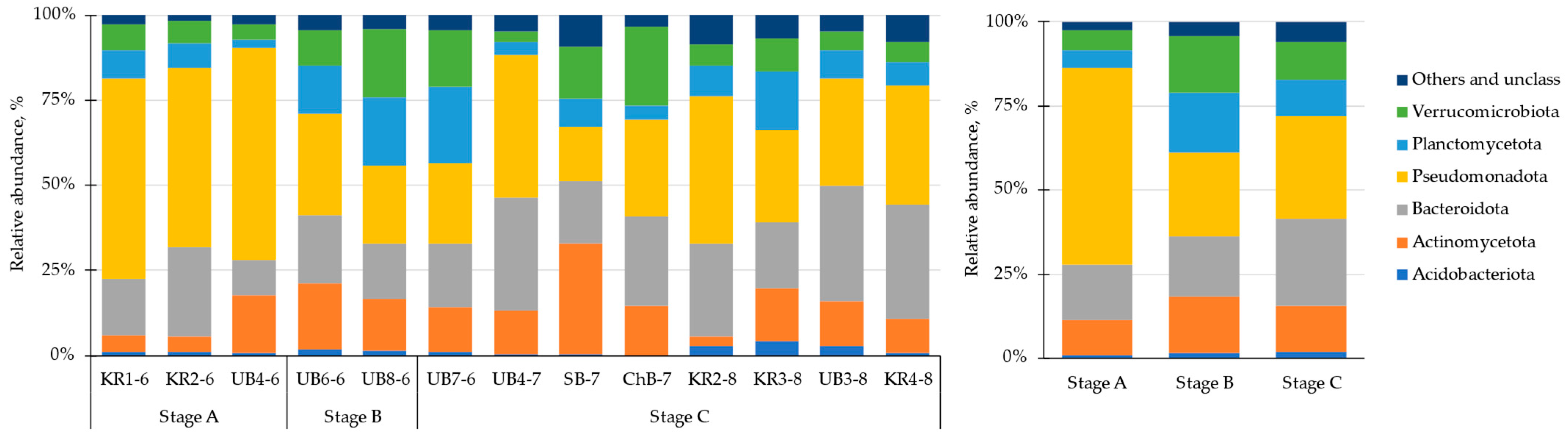
3.4. Heterotrophic Bacteria Community Structure and Composition in Different Parts of the Reservoir
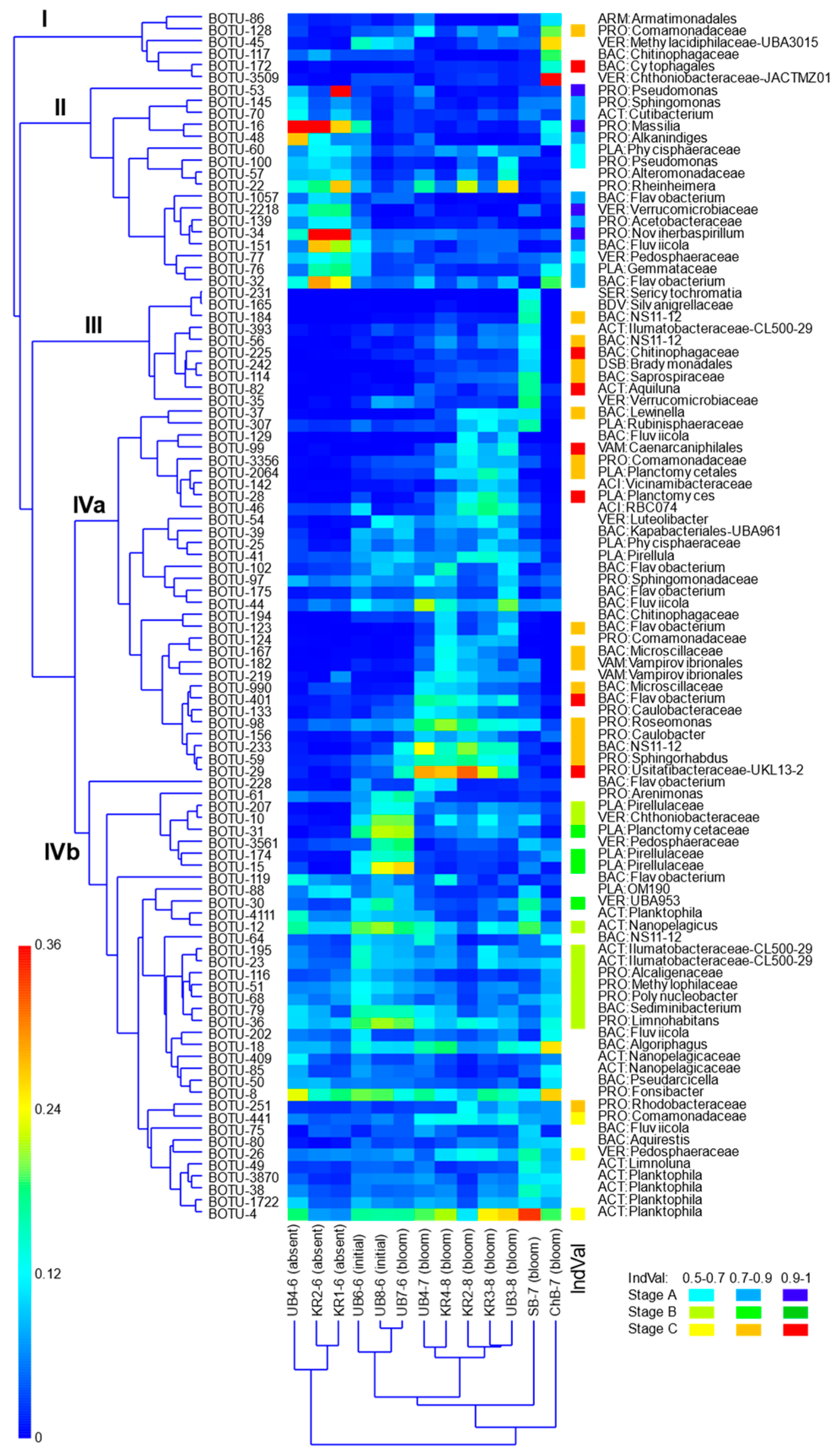
3.5. Protist Community Structure and Composition in Different Parts of the Reservoir
3.6. Microscopic Determination of Phytoplankton, Planktonic Ciliates, and Heterotrophic Bacteria in the Lower Part of the Kuibyshev Reservoir
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havens, K.E. Cyanobacteria blooms: Effects on aquatic ecosystems. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. WIREs Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Huszar, V.; Kruk, C.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Melo, S. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padisák, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Naselli-Flores, L. Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: A critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 2009, 621, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, I.; Lee, J.W.; Jeon, C.O.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Cho, J.C. Heme auxotrophy in abundant aquatic microbial lineages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102750118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Sommer, U. Effects of harmful blooms of large-sized and colonial cyanobacteria on aquatic food webs. Water 2020, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneva, L.G.; Solovyeva, V.V. Dynamics of morphofuncitonal groups of phytoplankton in the Rybinsk reservoir and assessment of the reservoir water quality by the community index. Water Resour. 2021, 48, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylov, A.I.; Kosolapov, D.B.; Mikryakova, I.S. Long-term dynamics of heterotrophic bacterioplankton in a large eutrophic reservoir. Inland Water Biol. 2020, 13, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Pei, H. Cyanobacterial bloom intensities determine planktonic eukaryote community structure and stability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiba, J.; Wilk-Woźniak, E.; Krztoń, W. The effect of potentially toxic cyanobacteria on ciliates (Ciliophora). Hydrobiologia 2019, 827, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirjaková, E.; Krajčovičová, K.; Illyová, M.; Vďačný, P. Interaction of ciliate communities with cyanobacterial water bloom in a shallow, hypertrophic reservoir. Acta Protozool. 2016, 55, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, V.A.; Bykova, S.V.; Umanskaya, M.V.; Tarasova, N.G. Free-living ciliates during the period of the greatest cyanobacterial water bloom in the Usinsky bay (Kuibyshev reservoir). Proc. Samara Sci. Center RAS 2021, 23, 127–133. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louati, I.; Pascault, N.; Debroas, D.; Bernard, C.; Humbert, J.F.; Leloup, J. Structural diversity of bacterial communities associated with bloom-forming freshwater cyanobacteria differs according to the cyanobacterial genus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zancarini, A.; Louati, I.; De Cesare, S.; Duval, C.; Tambosco, K.; Bernard, C.; Debroas, D.; Song, L.; Leloup, J.; et al. Bacterial communities associated with four cyanobacterial genera display structural and functional differences: Evidence from an experimental approach. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, G.S.; Vykhristyuk, L.A. (Eds.) Kuibyshev Reservoir (Scientific-Information Handbook); IEVB RAS: Tolyatti, Russia, 2008; 123p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivatin, A.V. Bacterioplankton and Bacteriobenthos of the Kuibyshev Reservoir; Kassandra: Tolyatti, Russia, 2012; 183p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pautova, V.N.; Nomokonova, V.I. Dynamics of Phytoplankton of the Lower Volga—From the River to the Cascade of Reservoirs; IEVB RAS: Tolyatti, Russia, 1994; 188p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tarasova, N.G. Phytoplankton Composition, Seasonal Dynamics and Invasive Species of the Kuibyshev Reservoir. Ph.D. Thesis, IEVB RAS, Tolyatti, Russia, 2005; 146p. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Konovalov, S.M.; Pautova, V.N. (Eds.) Phytoplankton Ecology of Kuibyshev Reservoir; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1989; 304p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zharikov, V.V. Inventory of Free-Living Ciliates in the Volga Reservoirs; IEVB RAS: Togliatti, Russia, 1996. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bykova, S.V. Structure and Spatial Distribution of Planktonic Ciliates from the Middle and Lower Volga Reservoirs. Inland Water Biol. 2021, 14, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotova, A.V.; Serkebaeva, Y.M.; Sorokin, V.V.; Dedysh, S.N. Filterable microbial forms in the Rybinsk water reservoir. Microbiology 2013, 82, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, E.V.; Sukhanova, E.V.; Kosolapov, D.B. Taxonomic Diversity and Size-Morphological Structure of Bacterioplankton of the Rybinsk Reservoir. Microbiology 2021, 90, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umanskaya, M.V.; Gorbunov, M.Y.; Bykova, S.V.; Tarasova, N.G. Diversity and Transformation of the Community of Planktonic Freshwater Protists in the Estuarine Tributary Zone of a Large Plainland Reservoir: Metabarcoding of the 18S Ribosomal RNA Gene. Biol. Bull. 2023, 50, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umanskaya, M.V.; Gorbunov, M.Y. Phylogenetic Structure of Bacterioplankton in Water Bodies of the Kuibyshev Reservoir Basin during Cyanobacterial Bloom. Microbiology 2013, 93, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, Y.Y. (Ed.) Unified Methods of Analysis of Waters; Khimija: Moscow, Russia, 1973; 376p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Solorzano, L. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, Y.V.; Lastochkina, K.O.; Boldina, Z.N. Methods of Studying the Quality of Water in Reservoirs; Medicine: Moscow, Russia, 1990; 400p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Humfrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for deter-mining chlorophylls a, b, c, and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phyto-plankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, C.J. Determination of chlorophyll and pheo-pigments: Spectro-photometric equations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1967, 12, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordukhai-Boltovskoy, F.D. (Ed.) Methodology for Studying Biogeocenoses of Inland Water Bodies; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1975; 240p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bereczky, M.C. Fixations-und Färbungsschnellverfahren bei quantitativen ökologischen Untersuchungen von Protozoen in Binnengewässern. Arch. Protistenkd. 1985, 129, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.G.; Feig, Y.S. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting of aquatic microflora. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every base matters: Assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apprill, A.; McNally, S.; Parsons, R.; Weber, L. Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugerth, L.W.; Muller, E.E.; Hu, Y.O.; Lebrun, L.A.; Roume, H.; Lundin, D.; Wilmes, P.; Andersson, A.F. Systematic design of 18S rRNA gene primers for determining eukaryotic diversity in microbial consortia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A. DADA2 Formatted 16S rRNA Gene Sequences for Both Bacteria & Archaea (4.4). Zenodo 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. SINTAX: A simple non-Bayesian taxonomy classifier for 16S and ITS sequences. Biorxiv 2016, 074161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruesse, E.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrêne, M.; Legendre, P. Species assemblages and indicator species: The need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A. Past: Paleontological statistics software package for educaton and data anlysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, T.A.; Vepritskiy, A.A.; Gouliamova, D.E.; Nierzwicki-Bauer, S.A. The molecular diversity of freshwater picoeukaryotes from an oligotrophic lake reveals diverse, distinctive and globally dispersed lineages. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthers, I.M.; Richardson, A.J.; Rissik, D. The importance of plankton. In Plankton: A Guide to Their Ecology and Monitoring for Water Quality; Suthers, I., Rissik, D., Richardson, A., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2019; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Matveev, V.F.; Matveeva, L.K. Seasonal succession and long-term stability of pelagic community in a productive reservoir. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 56, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottingham, K.L.; Weathers, K.C.; Ewing, H.A.; Greer, M.L.; Carey, C.C. Predicting the effects of climate change on freshwater cyanobacterial blooms requires consideration of the complete cyanobacterial life cycle. J. Plankton Res. 2021, 43, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Phytoplankton periodicity: The interactions of form, function and environmental variability. Freshw. Biol. 1984, 14, 111–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, N.E.; Heffernan, J.B.; Ross, M.R.V.; Doyle, M. A simple metric for predicting the timing of river phytoplankton blooms. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, M.C.; Hrycik, A.R.; Costello, A.; Bai, Y.; Rose, K.C.; Relyea, R.; Dordick, J.S. Spatiotemporal dynamics of microbial communities and cyanobacteria blooms in two North American Lakes using long-read 16S rRNA sequencing. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isles, P.D.; Giles, C.D.; Gearhart, T.A.; Xu, Y.; Druschel, G.K.; Schroth, A.W. Dynamic internal drivers of a historically severe cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Champlain revealed through comprehensive monitoring. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiling, R.M.; Givens, C.E.; Baker, A.C.; Kiesling, R.L.; Dantoin, E.D.; Perner, P.M.; Sterner, S.P.; Gierke, K.J.; Reneau, P.C. Role of tributary cyanobacterial and nutrient transport and sediment processes on cyanobacterial bloom initiation in Lake Superior nearshore. J. Great Lakes Res. 2025, 51, 102409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota 1. Teil: Chroococcales. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 19/1; Ettl, H., Gärtner, G., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany; Stuttgart, Germany; Lübeck, Germany; Ulm, Germany, 1998; 548p. [Google Scholar]
- Griese, M.; Lange, C.; Soppa, J. Ploidy in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 323, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, N.D.; Pöckl, M.; Weisse, T. Dispersal and phylogenetic diversity of nonmarine picocyanobacteria, inferred from 16S rRNA gene and cpcBA-intergenic spacer sequence analyses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003 69, 5716–5721. [CrossRef]
- Jezbera, J.; Sharma, A.K.; Brandt, U.; Doolittle, W.F.; Hahn, M.W. ‘Candidatus Planktophila limnetica’, an actinobacterium representing one of the most numerically important taxa in freshwater bacterioplankton. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2864–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Neuenschwander, S.M.; Ghai, R.; Pernthaler, J.; Salcher, M.M. Microdiversification in genome-streamlined ubiquitous freshwater Actinobacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W. Description of seven candidate species affiliated with the phylum Actinobacteria, representing planktonic freshwater bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipko, I.A.; Belykh, O.I. Environmental Features of Freshwater Planktonic Actinobacteria. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2021, 14, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, M.C.; Haber, M.; Salcher, M.M. Adaptive genetic traits in pelagic freshwater microbes. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 606–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimek, K.; Mukherjee, I.; Szöke-Nagy, T.; Haber, M.; Salcher, M.M.; Ghai, R. Cryptic and ubiquitous aplastidic cryptophytes are key freshwater flagellated bacterivores. ISME J. 2023, 17, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Hameed, A.; Arun, A.B.; Liu, Y.C.; Hsu, Y.H.; Lai, W.A.; Rekha, P.D.; Young, C.C. Description of Noviherbaspirillum malthae gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from an oil-contaminated soil, and proposal to reclassify Herbaspirillum soli, Herbaspirillum aurantiacum, Herbaspirillum canariense and Herbaspirillum psychrotolerans as Noviherbaspirillum soli comb. nov., Noviherbaspirillum aurantiacum comb. nov., Noviherbaspirillum canariense comb. nov. and Noviherbaspirillum psychrotolerans comb. nov. based on polyphasic analysis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 4100–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, D.K.; Dahal, R.H.; Hong, Y. Noviherbaspirillum pedocola sp. nov., isolated from oil-contaminated experimental soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jin, C.Z.; Jin, F.J.; Li, T.; Sung, Y.J.; Oh, H.M.; Lee, H.G.; Jin, L. Lacisediminimonas profundi gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Oxalobacteraceae isolated from freshwater sediment. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holochová, P.; Mašlaňová, I.; Sedláček, I.; Švec, P.; Králová, S.; Kovařovic, V.; Busse, H.-J.; Stanková, E.; Barták, M.; Pantůček, R. Description of Massilia rubra sp. nov., Massilia aquatica sp. nov., Massilia mucilaginosa sp. nov., Massilia frigida sp. nov., and one Massilia genomospecies isolated from Antarctic streams, lakes and regoliths. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Spitz, S.R.; Goetz, G.W.; McLellan, S.L. Temporal and spatial variability in nearshore bacterioplankton communities of Lake Michigan. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneva, L.G. Phytoplankton of Volga River Basin Reservoirs; Kostroma Printing House: Kostroma, Russia, 2015; 284p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sakharova, E.G.; Korneva, L.G. Phytoplankton in the littoral and pelagial zones of the Rybinsk Reservoir in years with different temperature and water-level regimes. Inland Water Biol. 2018, 11, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalch-Schuler, M.; Bassin, B.; Andrei, A.S.; Dirren-Pitsch, G.; Waller, K.; Hofer, C.; Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T. The planktonic freshwater ciliate Balanion planctonicum (Ciliophora, Prostomatea): A cryptic species complex or a “complex species”? J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2025, 72, e13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautova, V.N.; Nomokonova, V.I.; Gorbunov, M.Y. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton in the Kuibyshev Reservoir. Inn. Water Biol. 2001, 3, 29–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hill, D.R. Chroomonas and other blue-green cryptomonads. J. Phycol. 1991, 27, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javornicky, P. Taxonomic notes on some freshwater planktonic Cryptophyceae based on light microscopy. Hydrobiologia 2003, 502, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastepa, A.; Comte, J.; Crevecoeur, S. Prevalence and ecological features of deep chlorophyll layers in Lake of the Woods, a complex hydrological system with strong trophic, physical, and chemical gradients. J. Great Lakes Res. 2023, 49, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.B.; Otten, T.G.; Brown, N.M.; Dreher, T.W. Towards long-read metagenomics: Complete assembly of three novel genomes from bacteria dependent on a diazotrophic cyanobacterium in a freshwater lake co-culture. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2017, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parulekar, N.N.; Kolekar, P.; Jenkins, A.; Kleiven, S.; Utkilen, H.; Johansen, A.; Sawant, S.; Kulkarni-Kale, U.; Kale, M.; Sæbø, M. Characterization of bacterial community associated with phytoplankton bloom in a eutrophic lake in South Norway using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequence analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reignier, O.; Bormans, M.; Hervé, F.; Robert, E.; Savar, V.; Tanniou, S.; Amzil, Z.; Noel, C.; Briand, E. Spatio-temporal connectivity of a toxic cyanobacterial community and its associated microbiome along a freshwater-marine continuum. Harmful Algae 2024, 134, 102627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, J.R.; Rosen, B.H. Associations of Species of Vorticella (Peritrichida) and Planktonic Algae. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1983, 102, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wichelen, J.; D’hondt, S.; Claeys, M.; Vyverman, W.; Berney, C.; Bass, D.; Vanormelingen, P. A hotspot of amoebae diversity: 8 new naked amoebae associated with the planktonic bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis. Acta Protozool. 2016, 55, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobard, M.; Wawrzyniak, I.; Bronner, G.; Marie, D.; Vellet, A.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Debroas, D.; Lepère, C. Freshwater Perkinsea: Diversity, ecology and genomic information. J. Plankton Res. 2020, 42, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerphagnon, M.; Macarthur, D.J.; Latour, D.; Gachon, C.M.; Van Ogtrop, F.; Gleason, F.H.; Sime-Ngando, T. Microbial players involved in the decline of filamentous and colonial cyanobacterial blooms with a focus on fungal parasitism. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2573–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groult, B.; St-Jean, V.; Lazar, C.S. Linking Groundwater to Surface Discharge Ecosystems: Archaeal, Bacterial, and Eukaryotic Community Diversity and Structure in Quebec (Canada). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, C.; Xie, W. Deterministic processes dominate archaeal community assembly from the Pearl River to the northern South China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1185436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Castelle, C.J.; Probst, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Banfield, J.F.; Gu, J.D. Insights into the ecology, evolution, and metabolism of the widespread Woesearchaeotal lineages. Microbiome 2018, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomakina, A.; Bukin, S.; Shubenkova, O.; Pogodaeva, T.; Ivanov, V.; Bukin, Y.; Zemskaya, T. Microbial Communities in Ferromanganese Sediments from the Northern Basin of Lake Baikal (Russia). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hambright, K.D.; Bowen, H.G.; Trammell, M.A.; Grossart, H.P.; Burford, M.A.; Hamilton, D.P.; Jiang, H.; Latour, D.; Meyer, E.I.; et al. Global co-occurrence of methanogenic archaea and methanotrophic bacteria in Microcystis aggregates. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6503–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


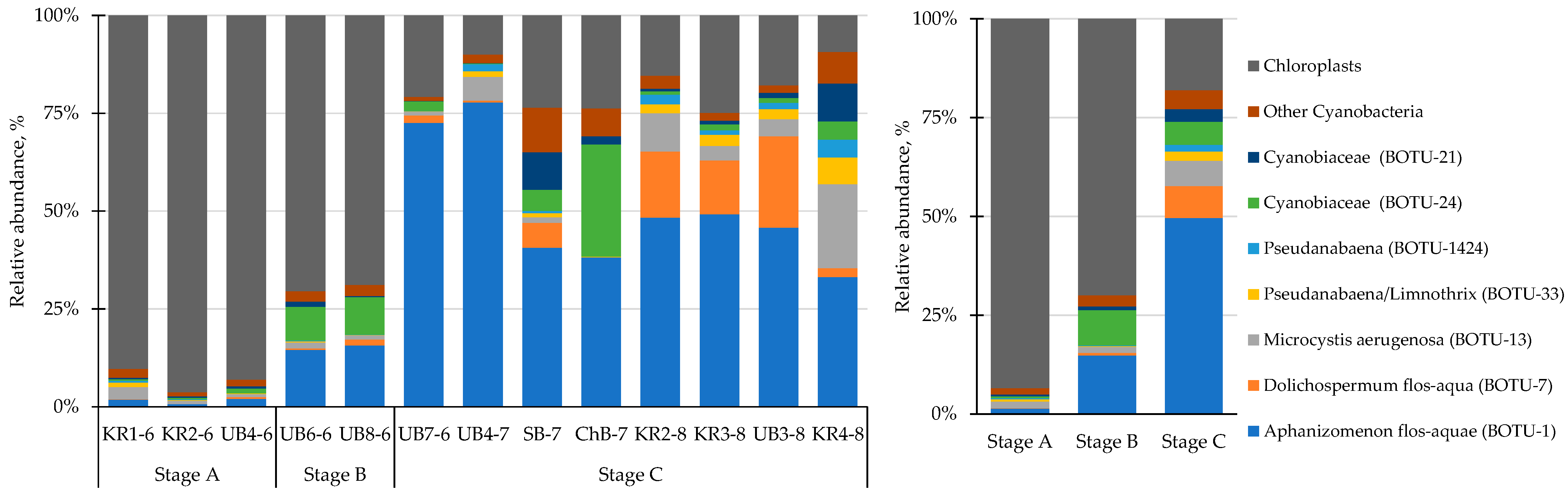
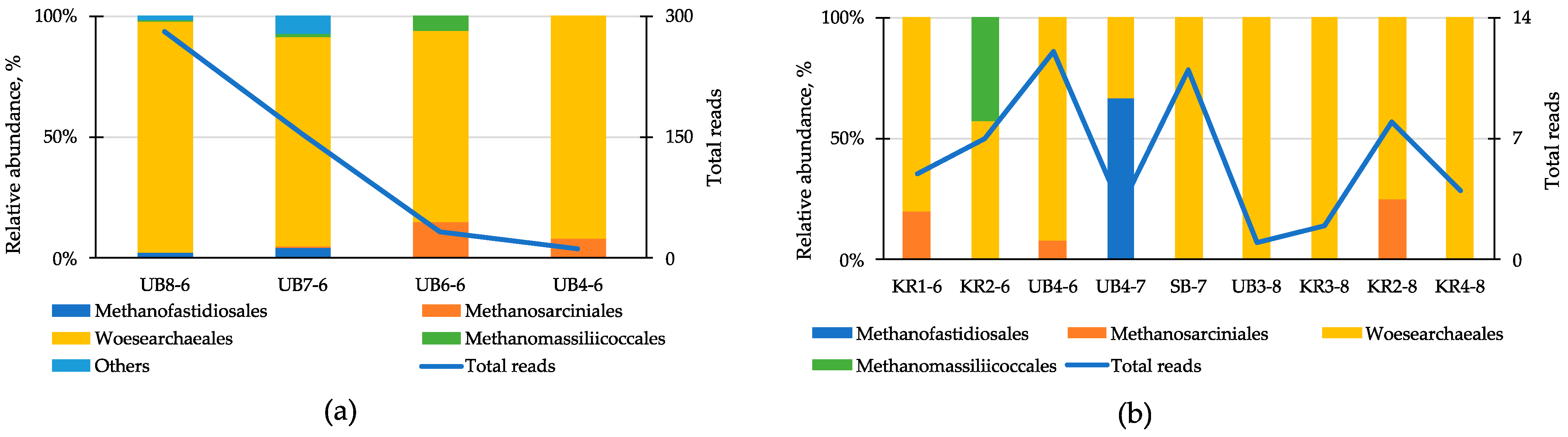


| Parameters | The Whole Period | June | July | August |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 13 | 6 | 3 | 4 |
| Transparency, m | 1.05 ± 0.54 | 1.41 ± 0.55 | 0.87 ± 0.15 | 0.72 ± 0.40 |
| Temperature, °C | 22.8 ± 3.9 | 19.1 ± 0.7 | 26.1 ± 3.0 | 26.0 ± 0.7 |
| Conductivity, µS cm−1 | 374 ± 20 | 381 ± 16 | 388 ± 20 | 353 ± 2 |
| pH | 8.51 ± 0.74 | 7.77 ± 0.08 | 9.12 ± 0.28 | 9.18 ± 0.23 |
| Dissolved oxygen, mg L−1 | 12.14 ± 4.06 | nd 1 | 8.91 ± 1.18 | 15.36 ± 2.95 |
| Dissolved oxygen, % | 152 ± 51 | nd | 112 ± 17 | 192 ± 38 |
| Water color, °Pt | 61 ± 11 | 59 ± 13 | 56 ± 3 | 68 ± 6 |
| SO4, mg L−1 | 41 ± 9 | 33 ± 2 | 51 ± 6 | 46 ± 5 |
| HCO3, mg L−1 | 203 ± 54 | 252 ± 18 | 181 ± 51 | 147 ± 1 |
| N-NH4, mg L−1 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.05 |
| Ptot, mg L−1 | 0.10 ± 0.21 | 0.16 ± 0.31 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Si, mg L−1 | 3.28 ± 1.26 | 3.70 ± 1.82 | 3.03 ± 0.48 | 2.85 ± 0.11 |
| Fetot, mg L−1 | 0.32 ± 0.08 | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 0.35 ± 0.11 | 0.28 ± 0.07 |
| Chl a, µg L−1 | 42.0 ± 48.7 | 14.5 ± 10.0 | 35.2 ± 13.7 | 88.3 ± 69.0 |
| Sample | Prokaryotes and Chloroplasts | Protists and Fungi | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | B-P | 1-D | 1/D | H2 | E | N | B-P | 1-D | 1/D | H2 | E | |
| KR2-8 | 1096 | 0.27 | 0.91 | 11.0 | 5.62 | 0.56 | 481 | 0.18 | 0.95 | 19.2 | 5.80 | 0.65 |
| KR3-8 | 963 | 0.29 | 0.90 | 9.9 | 5.53 | 0.56 | 507 | 0.08 | 0.97 | 29.8 | 6.02 | 0.67 |
| UB3-8 | 850 | 0.20 | 0.94 | 17.2 | 6.03 | 0.62 | 468 | 0.15 | 0.96 | 22.5 | 5.76 | 0.65 |
| KR4-8 | 925 | 0.20 | 0.92 | 13.2 | 5.55 | 0.56 | 433 | 0.13 | 0.96 | 23.7 | 5.75 | 0.66 |
| KR1-6 | 851 | 0.21 | 0.92 | 12.0 | 5.07 | 0.52 | 347 | 0.14 | 0.94 | 17.3 | 5.16 | 0.61 |
| KR2-6 | 826 | 0.25 | 0.90 | 9.8 | 4.77 | 0.49 | 335 | 0.15 | 0.94 | 16.5 | 5.10 | 0.61 |
| UB6-6 | 1432 | 0.13 | 0.97 | 29.6 | 6.59 | 0.63 | 467 | 0.19 | 0.95 | 18.7 | 5.77 | 0.65 |
| UB7-6 | 1736 | 0.25 | 0.93 | 13.4 | 6.25 | 0.58 | 523 | 0.26 | 0.91 | 11.1 | 5.25 | 0.58 |
| UB4-6 | 858 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 12.5 | 5.60 | 0.57 | 275 | 0.22 | 0.93 | 13.9 | 5.28 | 0.65 |
| UB8-6 | 1919 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 51.6 | 7.21 | 0.66 | 322 | 0.28 | 0.88 | 8.1 | 4.47 | 0.54 |
| SB-7 | 883 | 0.23 | 0.93 | 13.7 | 5.61 | 0.57 | 412 | 0.08 | 0.97 | 30.0 | 5.66 | 0.65 |
| UB4-7 | 972 | 0.51 | 0.74 | 3.8 | 4.24 | 0.43 | 532 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 12.4 | 5.45 | 0.60 |
| ChB-7 | 735 | 0.21 | 0.92 | 12.8 | 5.32 | 0.56 | 337 | 0.18 | 0.94 | 16.3 | 5.11 | 0.61 |
| Sum | 2990 | 0.18 | 0.96 | 23.3 | 6.71 | 0.58 | 1131 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 34.9 | 6.72 | 0.66 |
| Samples without Cyanobacterial Blooms | Samples with Cyanobacterial Blooms | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Period | Main Period | ||||||||||||
| Stage A | Stage B | Stage C | |||||||||||
| KR2-6 | UB4-6 | KR1-6 | UB8-6 | UB6-6 | KR3-8 | ChB-7 | SB-7 | UB7-6 | UB3-8 | KR2-8 | UB4-7 | KR4-8 | |
| Cya/(Cya + Chl), % | 3.7 | 7.0 | 9.7 | 31.2 | 29.5 | 75.1 | 76.2 | 76.4 | 79.2 | 82.2 | 84.6 | 90.0 | 90.6 |
| Cya/Bac,% | 4.0 | 1.6 | 8.8 | 5.5 | 20.3 | 52.1 | 47.5 | 51.1 | 30.0 | 38.6 | 51.2 | 62.9 | 58.5 |
| Chl a, μg L−1 | 22.4 | 3.9 | 12.6 | 9.2 | 8.3 | 33.4 | 31.3 | 23.9 | 30.4 | 63.8 | 189.3 | 50.4 | 66.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorbunov, M.Y.; Bykova, S.V.; Tarasova, N.G.; Krasnova, E.S.; Umanskaya, M.V. Planktonic Pro- and Microeukaryotes of the Kuibyshev Reservoir and Its Bays During the Cyanobacterial Bloom Period. Water 2025, 17, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111602
Gorbunov MY, Bykova SV, Tarasova NG, Krasnova ES, Umanskaya MV. Planktonic Pro- and Microeukaryotes of the Kuibyshev Reservoir and Its Bays During the Cyanobacterial Bloom Period. Water. 2025; 17(11):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111602
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorbunov, Mikhail Yu., Svetlana V. Bykova, Natalia G. Tarasova, Ekaterina S. Krasnova, and Marina V. Umanskaya. 2025. "Planktonic Pro- and Microeukaryotes of the Kuibyshev Reservoir and Its Bays During the Cyanobacterial Bloom Period" Water 17, no. 11: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111602
APA StyleGorbunov, M. Y., Bykova, S. V., Tarasova, N. G., Krasnova, E. S., & Umanskaya, M. V. (2025). Planktonic Pro- and Microeukaryotes of the Kuibyshev Reservoir and Its Bays During the Cyanobacterial Bloom Period. Water, 17(11), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111602






