Waste Natural Pyrite Activation of Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame Potassium: Efficiency, Influencing Factors, Degradation Mechanisms, and Toxicity Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Waste Natural Pyrite
2.3. Experimental Process
2.3.1. Degradation Effect Experiment
2.3.2. Assessment of Application Scope
2.3.3. Free Radical Identification, Quantification, and Quenching Experiments
2.4. Methods for Measuring the Concentration of Target Substances
2.5. Methods for Identification and Toxicity Assessment of Degradation Products
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Research on the Degradation Performance of the Waste Natural Pyrite/PMS System
3.2. Assessment of the Applicable Scope of the Waste Natural Pyrite/PMS System
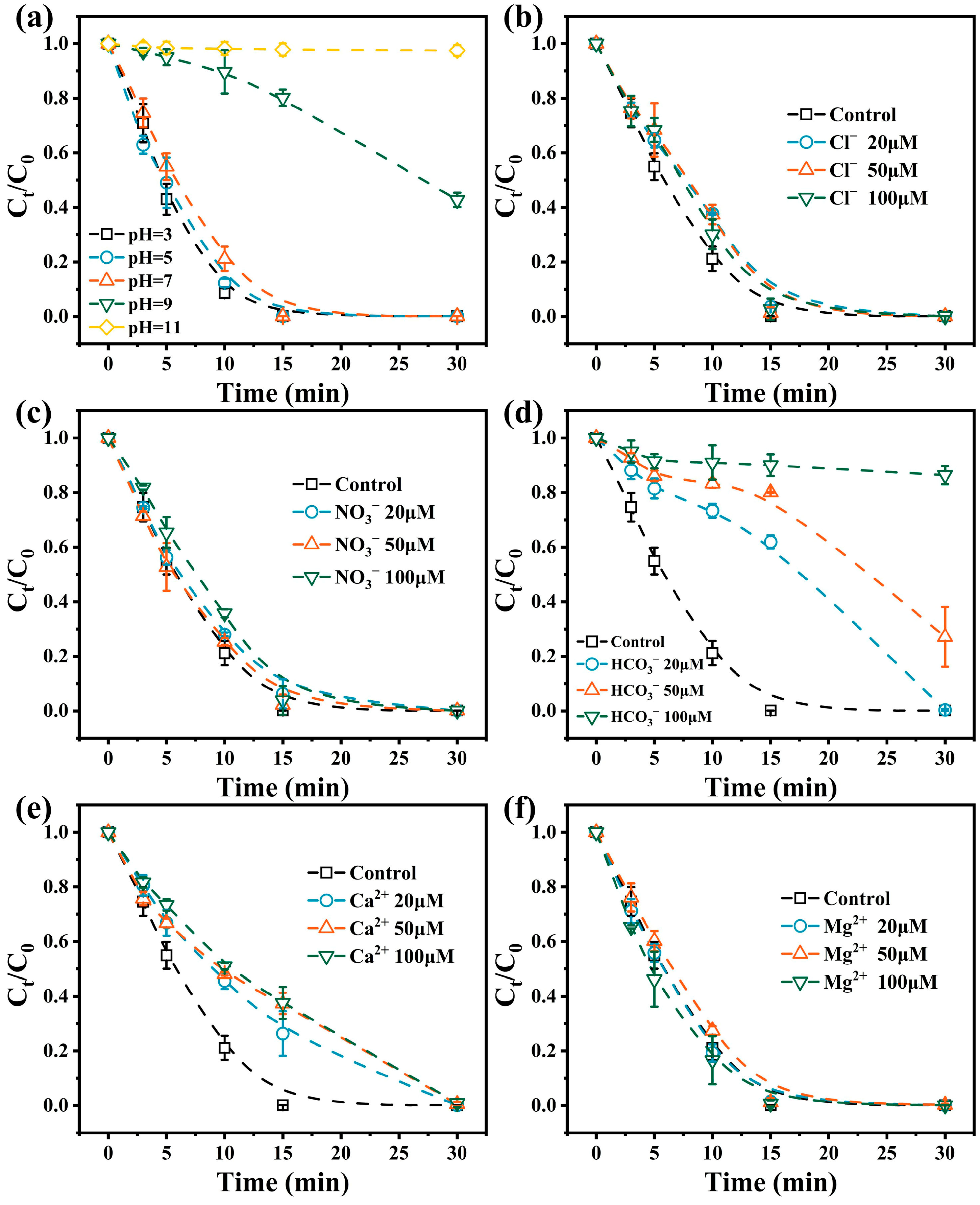
3.2.1. Effect of Solution pH
3.2.2. Effect of Inorganic Anions and Cations
3.3. Reaction Mechanism Exploration
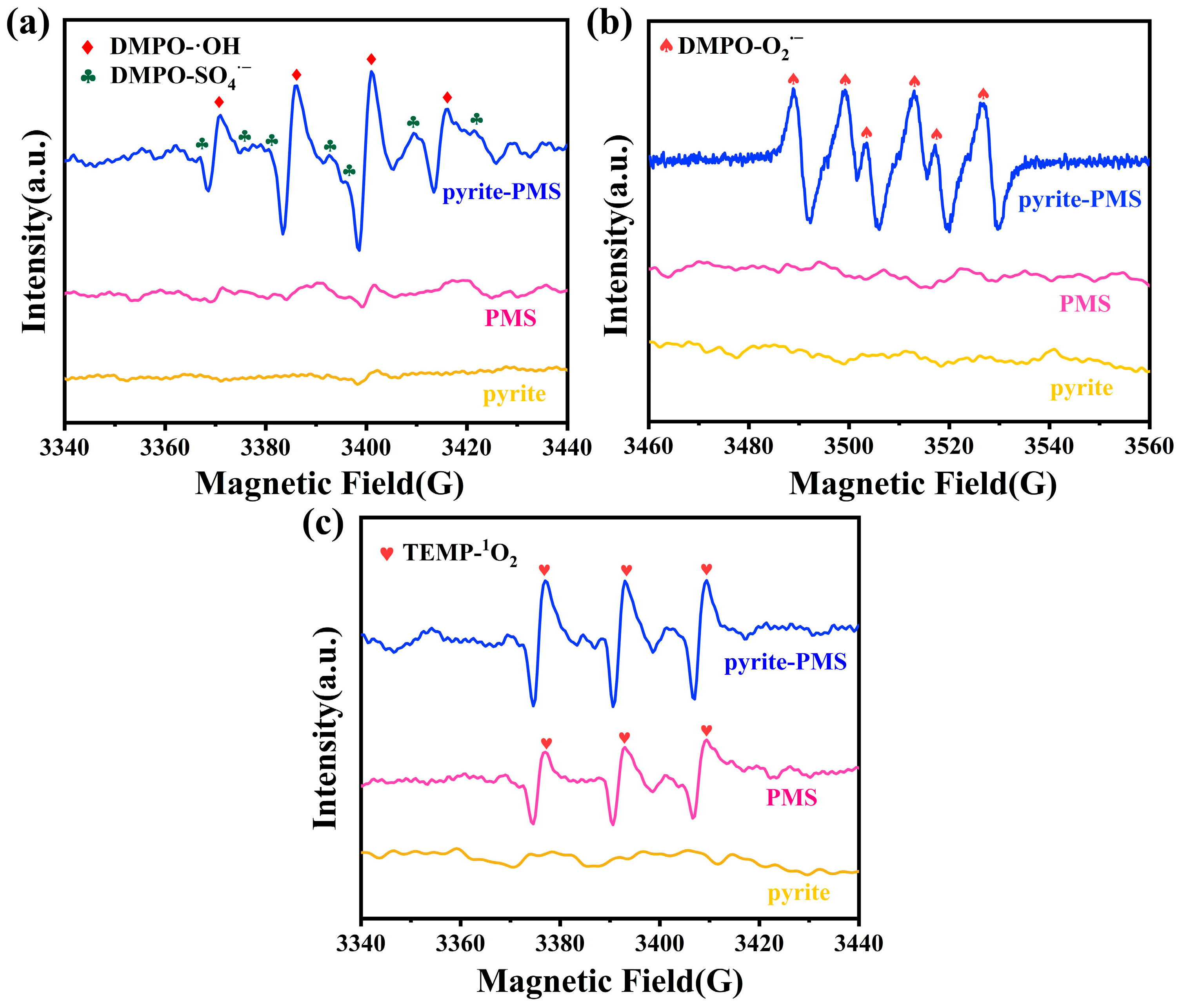
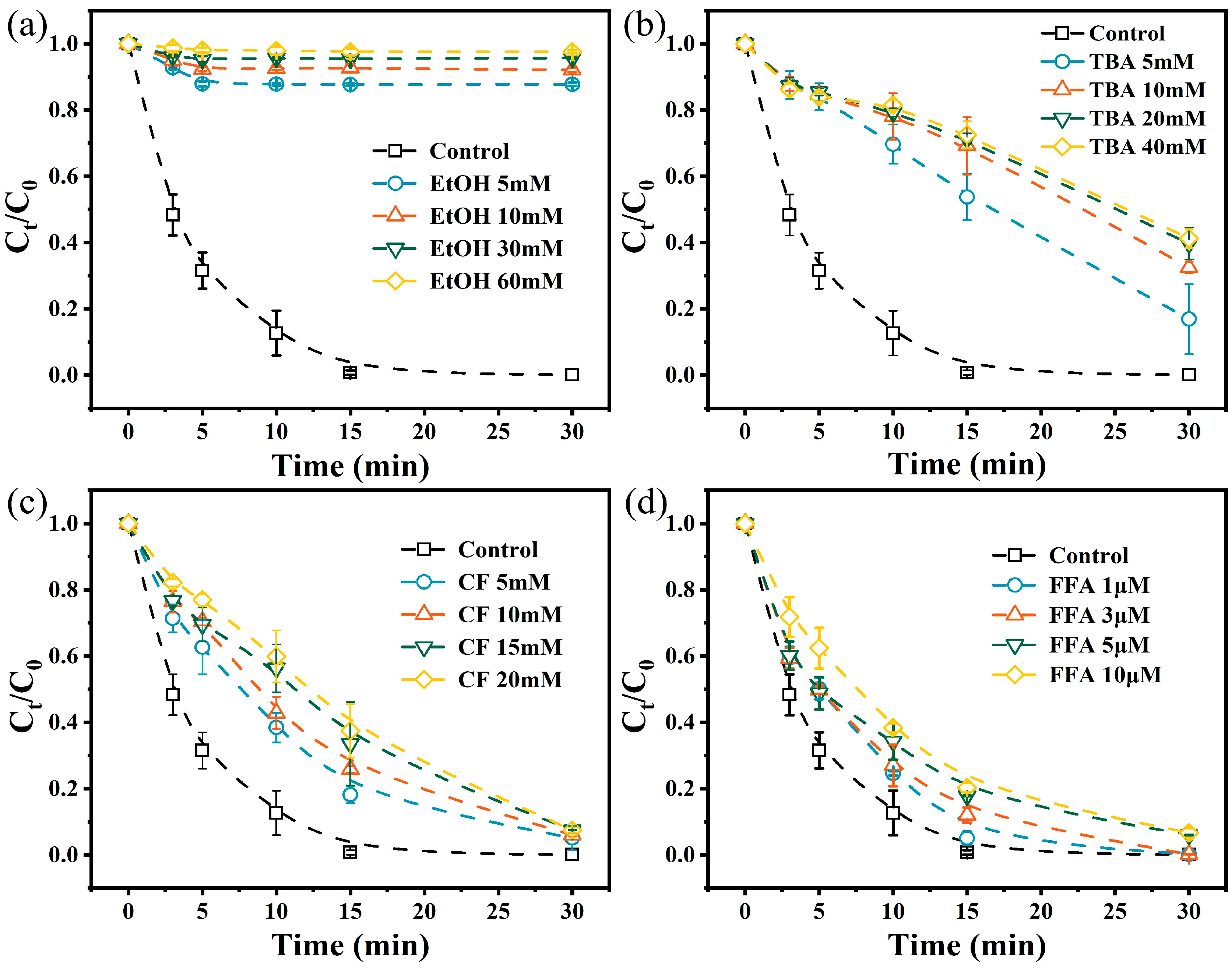
3.3.1. ROS Identification
3.3.2. ROS Contribution Ratios and Concentrations
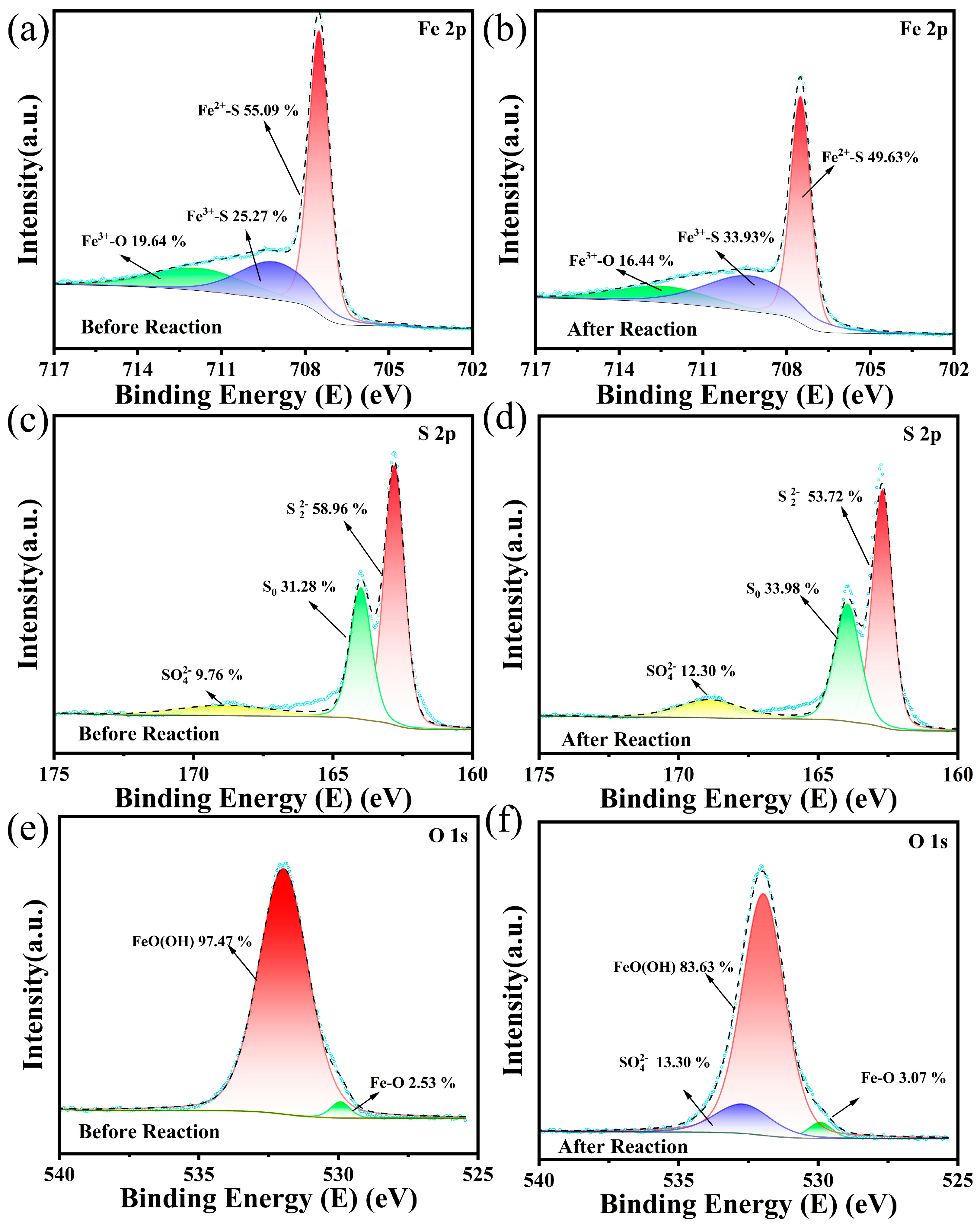
3.3.3. Changes in Waste Natural Pyrite During Reaction
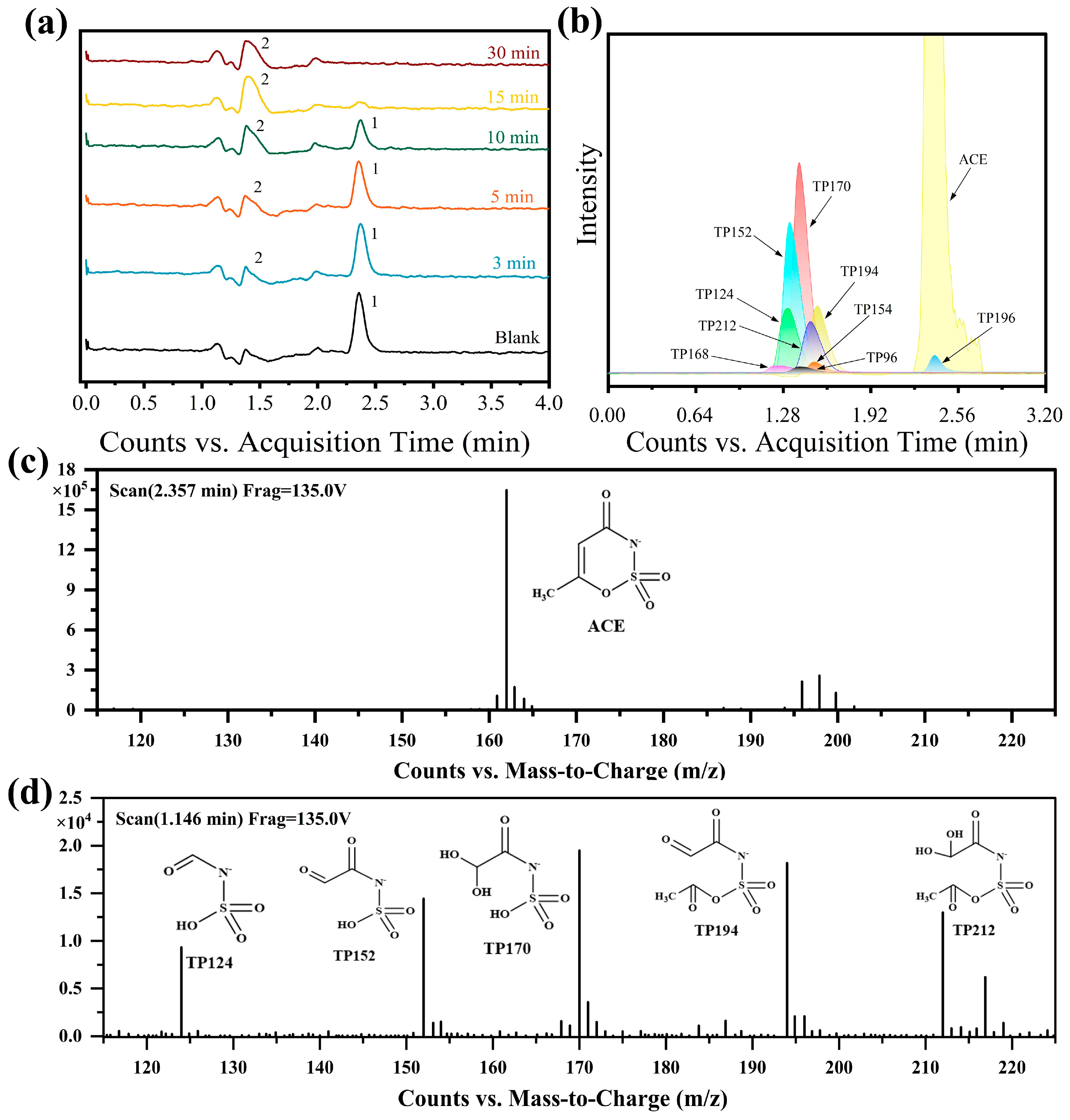
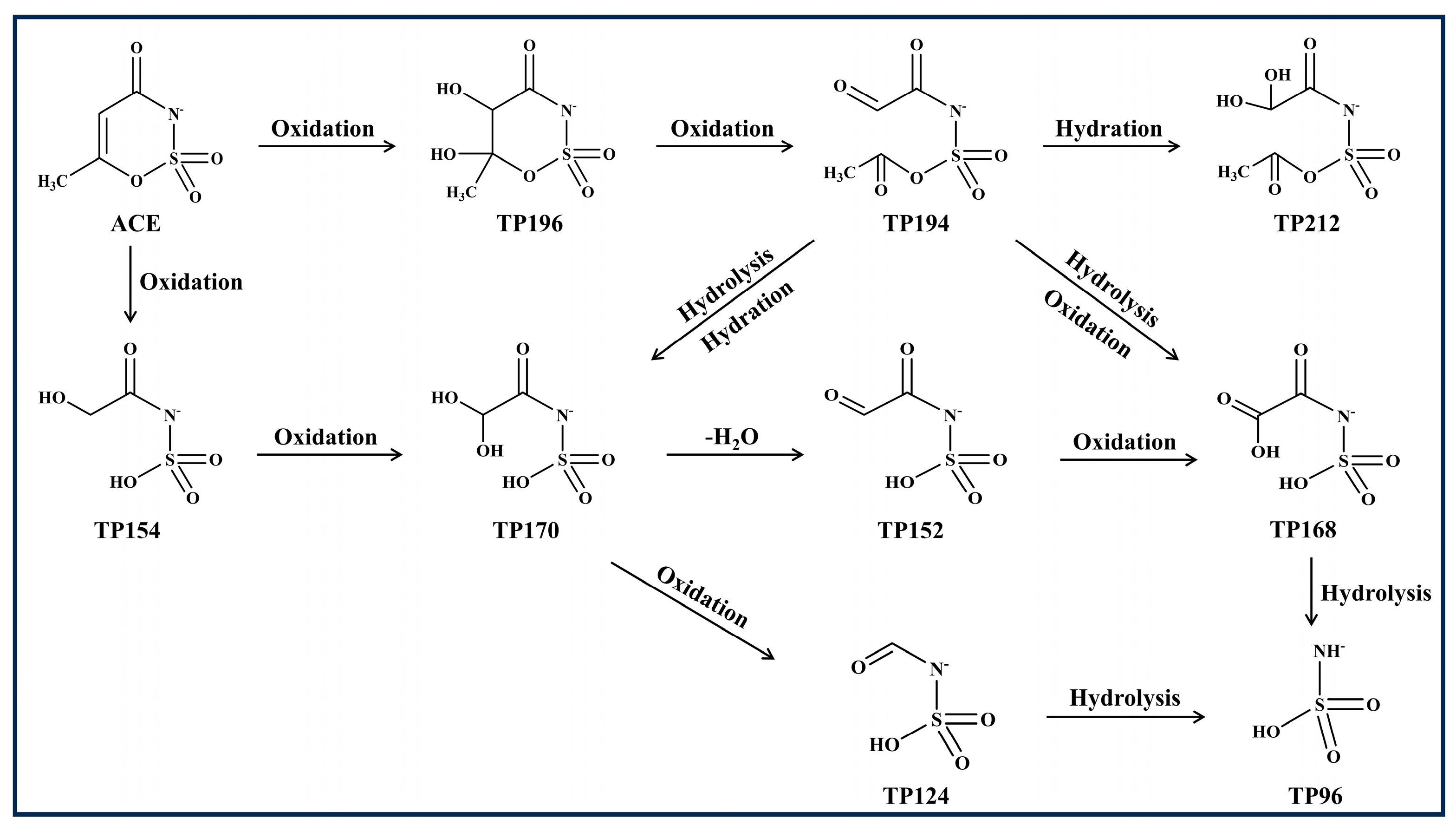
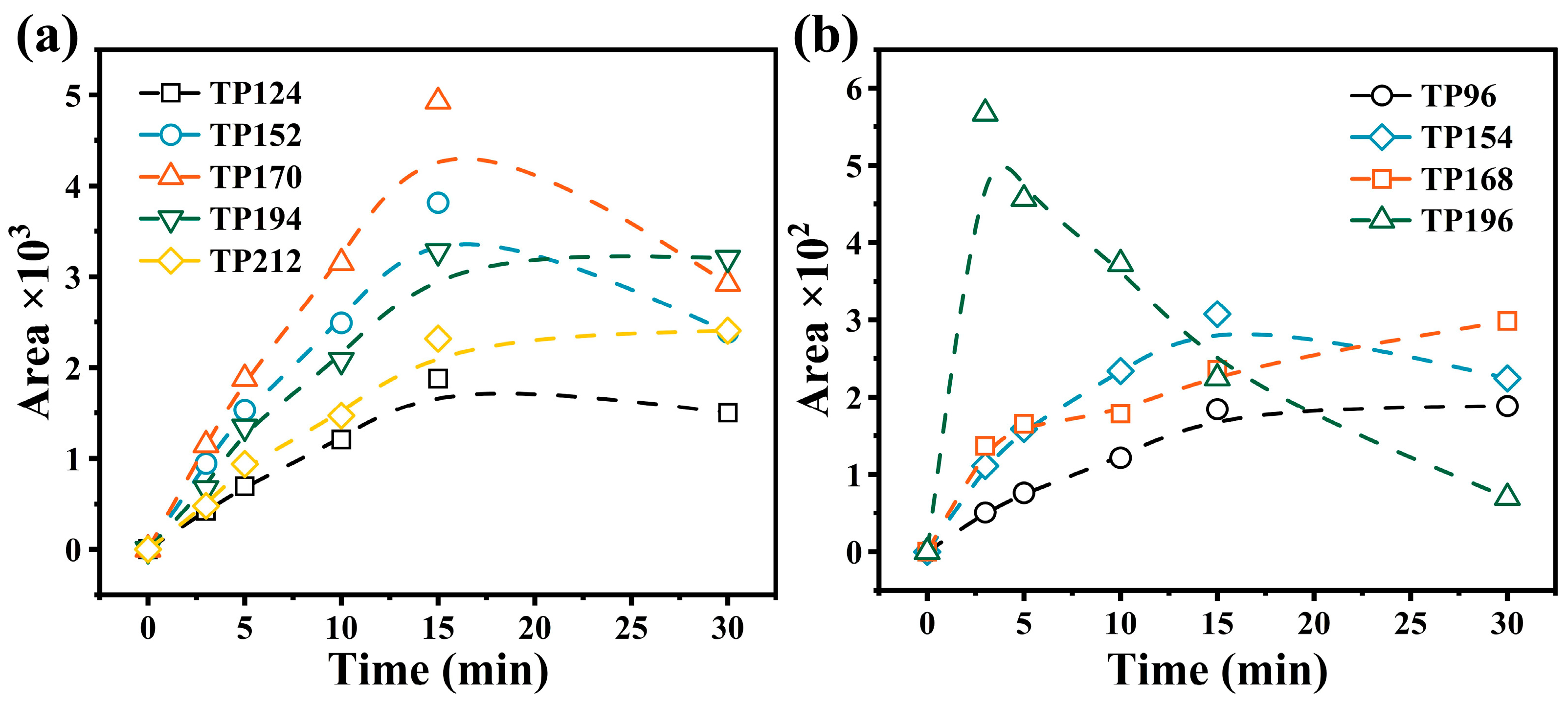
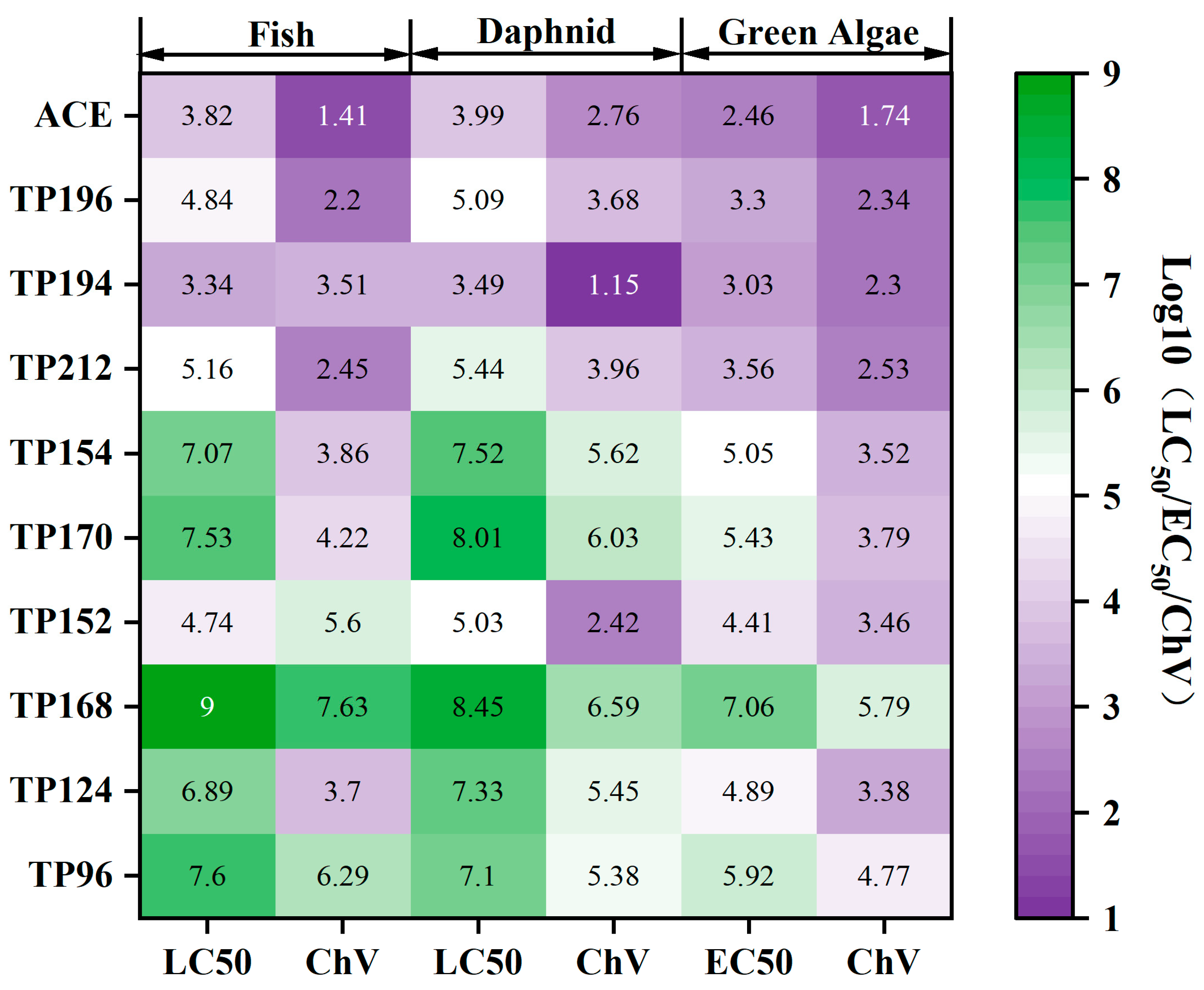
3.4. Identification and Toxicity Assessment of Degradation Products
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, T.; He, Q.; Li, F.; et al. Acesulfame potassium triggers inflammatory bowel disease via the inhibition of focal adhesion pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yao, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Pu, J.; Calderón, R.; Alder, A.; Kannan, K. Artificial Sweeteners in Pig Feed: A Worldwide Survey and Case Study in Pig Farms in Tianjin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4059–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; O’Brien, J.; Tscharke, B.; Choi, P.; Zheng, Q.; Ahmed, F.; Thompson, J.; Li, J.; Mueller, J.; Sun, H.; et al. National wastewater reconnaissance of artificial sweetener consumption and emission in Australia. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.; Poiger, T. Acesulfame: From Sugar Substitute to Wastewater Marker. Chimia 2011, 65, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempvoort, D.; Roy, J.; Brown, S.; Bickerton, G. Artificial sweeteners as potential tracers in groundwater in urban environments. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Qian, Y.; Boyd, J.; Hrudey, S.; Le, C.; Li, X. Direct large volume injection ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of artificial sweeteners sucralose and acesulfame in well water. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, M.; Mueller, M.; Loos, M.; Singer, H. Quantitative target and systematic non-target analysis of polar organic micro-pollutants along the river Rhine using high-resolution mass-spectrometry-Identification of unknown sources and compounds. Water Res. 2015, 87, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Li, X.; Han, G.; Du, L.; Li, M. Zebrafish neuro-behavioral profiles altered by acesulfame (ACE) within the range of “no observed effect concentrations (NOECs)”. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, A.; Giri, A.; Cameron, H.; Sperber, S.; Zickgraf, F.; Haake, V.; Driemert, P.; Walk, T.; Kamp, H.; Rietjens, I.; et al. Investigating the gut microbiome and metabolome following treatment with artificial sweeteners acesulfame potassium and saccharin in young adult Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 165, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, A.; Guo, X.; Gorokhova, E. Cardiotoxic and neurobehavioral effects of sucralose and acesulfame in Daphnia: Toward understanding ecological impacts of artificial sweeteners. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 273, 109733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Guo, F.; Rillig, M.; Chen, C.; Duan, G.; Zhu, Y. Effects of common artificial sweeteners at environmentally relevant concentrations on soil springtails and their gut microbiota. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurer, M.; Storck, F.; Brauch, H.; Lange, F. Performance of conventional multi-barrier drinking water treatment plants for the removal of four artificial sweeteners. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, B.; Kannan, K. Fate of artificial sweeteners in wastewater treatment plants in New York State, U.S.A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13668–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mursaikova, M.; Kuráž, M.; Grasserová, A.; Cajthaml, T.; Hrkal, Z.; Boukalová, Z. Degradation behaviour of the artificial sweetener Acesulfame-K within a riverbank filtration system. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, K.; Schaefer, E.; Guiney, P. A Review of the Environmental Fate and Effects of Acesulfame-Potassium. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2020, 16, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Das, I.; Ghangrekar, M.; Blaney, L. Advanced oxidation processes: Performance, advantages, and scale-up of emerging technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.; Divyapriya, G.; Ezzahra, T.; Hamdani, M. Treatment of textile wastewater by sulfate radical based advanced oxidation processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Tang, H.; Yao, B.; Gao, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y. Activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by spinel ferrite and their composites in degradation of organic pollutants: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Dai, H.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Wang, B. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped watermelon rind as an ordered mesoporous biochar activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for efficient tetracycline degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, S.; Xu, W.; Shang, J.; Yi, M.; Cheng, X. Enhancement of manganese sand activation for PMS degradation of levofloxacin using Co₃O₄ quantum dots: Mechanism and application. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ji, H.; Du, P.; Huang, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, W. Insights into catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate for carbamazepine degradation by MnO2 nanoparticles in-situ anchored titanate nanotubes: Mechanism, ecotoxicity and DFT study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, S.; Yu, M.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y. Lignosulfonate modified zero-valent iron enhanced activation of peroxymonosulfate for sulfamethazine removal: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 159054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, D.; Luther, G. Chemistry of Iron Sulfides. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 514–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y. Evaluation of pyrite cinders from sulfuric acid production as oxygen carrier for chemical looping combustion. Energy 2021, 233, 121079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobal, W.; Pepper, R.; Alarco, J.; Martens, W.; Couperthwaite, S. Production of ferric ammonium sulfate (FAS) dodecahydrate from pyrite (FeS2). Environ. Chall. 2025, 18, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, X. PMS activation by natural pyrite for APAP degradation: Underlying mechanism and long-term removal of APAP. Catal. Commun. 2023, 177, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Zhang, X.; Reinfelder, J. Application of pyrite to water pollutant removal: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helser, J.; Vassilieva, E.; Cappuyns, V. Environmental and human health risk assessment of sulfidic mine waste: Bioaccessibility, leaching and mineralogy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Deric, N.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Peng, W. Facile synthesis of pyrite FeS2 on carbon spheres for high-efficiency Fenton-like reaction. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, F.; Hoek, J.; Royer, S.; Javid, A.; Mashayekh-Salehi, A.; Sani, M. Pyrite nanoparticles derived from mine waste as efficient catalyst for the activation of persulfates for degradation of tetracycline. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, B.; Xue, N.; Du, S.; Wang, Y. Pyrite-activated persulfate to degrade 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl in water: Degradation and Fe release mechanism. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.; Qin, Z.; Nie, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q. Role of surface secondary mineral on tylosin degradation mediated by the pyrite oxidation process. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 5539–5546. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wu, P.; Law, J.; Chow, C.; Postigo, C.; Guo, Y.; Leung, K. Transformation of acesulfame in chlorination: Kinetics study, identification of byproducts, and toxicity assessment. Water Res. 2017, 117, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, Y.; Leung, K. Evaluating the environmental impact of artificial sweeteners: A study of their distributions, photodegradation and toxicities. Water Res. 2014, 52, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, F.; Wu, X.; Pan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J. Degradation of enestroburin in the water-sediment system: Kinetics, transformation products identification and toxicity assessment to aquatic organisms. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, A.; Siciliano, A.; Libralato, G.; Saviano, L.; Guida, M.; Pedatella, S.; Luongo, G.; Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Percarbonate mediated advanced oxidation of irbesartan: A suitable alternative to chlorination? Sci Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Carvalho, R.; António, C.; Comero, S.; Locoro, G.; Tavazzi, S.; Paracchini, B.; Ghiani, M.; Lettieri, T.; Blaha, L.; et al. EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackey, L.; Koomson, J.; Kumi, R.; Hayford, A.; Kayoung, P. Assessing the quality of sewage sludge: CASE study of the Kumasi wastewater treatment plant. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, G.; Geng, J.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Ren, H. Kinetics and modeling of artificial sweeteners degradation in wastewater by the UV/persulfate process. Water Res. 2019, 150, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Gao, Q.; Yang, Q.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y. Hydrochemical compositions characteristics of runoff in Dinghushan forest region under the background of acid deposition. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2368–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, P.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by natural pyrite for effective degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in water: Efficiency, degradation mechanism and toxicity evaluation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, B.; Yang, Z.; Shih, K.; Feng, Y. Acceleration of traces of Fe3+-activated peroxymonosulfate by natural pyrite: A novel cocatalyst for improving Fenton-like processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.; Lin, K.; Chu, W.; Gong, H. Degradation of Triclosan by Recyclable MnFe2O4-Activated PMS: Process Modification for Reduced Toxicity and Enhanced Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 4257–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, N.; Xiao, S.; Chen, J.; Ji, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Revisiting iodide species transformation in peracetic acid oxidation: Unexpected role of radicals in micropollutants decontamination and iodate formation. Water Res. 2024, 265, 122270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, K.; Li, P.; Wu, X.; Yan, K. Visible-light-driven peroxymonosulfate activation by FeS2 nanoplates for simultaneous oxidation of arsenite and organic dyes. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Gong, C.; Zhu, W.; Luo, Y.; Yang, D.; Gao, X. Oxidized pyrite as an efficient Fenton reagent to generate active species for the degradation of carbamazepine in a wide pH range. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 638, 158098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.; Sherman, D.; Purton, J. Surface oxidation of pyrite under ambient atmospheric and aqueous (pH = 2 to 10) conditions: Electronic structure and mineralogy from X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, S.; Liao, S.; Gu, G.; Wang, Y. Effect of oxidized pyrite activating persulfate on the degradation of aniline aerofloat: Mechanism and degradation pathway. Miner. Eng. 2023, 201, 108233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufuß, A.G.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Kartio, I.; Laajalehto, K.; Bancroft, G.M.; Szargan, R. Incipient oxidation of fractured pyrite surfaces in air. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1998, 96, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Liu, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, B. Efficient decontamination of Cr(III)-citrate complex with negligible Cr(VI) accumulation by pyrite-activated peroxymonosulfate process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, N.; Deng, Y.; Chen, F.; Feng, C. Degradation of: P-nitrophenol by nano-pyrite catalyzed Fenton reaction with enhanced peroxide utilization. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15901–15912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C.; Leung, K. Removing acesulfame with the peroxone process: Transformation products, pathways and toxicity. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, P.; Ren, X. Transformation of acesulfame in water under natural sunlight: Joint effect of photolysis and biodegradation. Water Res. 2014, 64, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukarjo; Yustika, R.; Handayani, C.; Dewi, T.; Yustiawati; Yanti, D.; Dariah, A. Risk assessment for non-carcinogenic effect posed by sulfates in water on the health of residents around The Sumpur River, West Sumatra-Indonesia. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Dang, Z.; Shu, X. Waste Natural Pyrite Activation of Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame Potassium: Efficiency, Influencing Factors, Degradation Mechanisms, and Toxicity Evaluation. Water 2025, 17, 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111558
Jiang C, Zeng Z, Jiang L, Dang Z, Shu X. Waste Natural Pyrite Activation of Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame Potassium: Efficiency, Influencing Factors, Degradation Mechanisms, and Toxicity Evaluation. Water. 2025; 17(11):1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111558
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Chengchen, Zehong Zeng, Liwen Jiang, Zhi Dang, and Xiaohua Shu. 2025. "Waste Natural Pyrite Activation of Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame Potassium: Efficiency, Influencing Factors, Degradation Mechanisms, and Toxicity Evaluation" Water 17, no. 11: 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111558
APA StyleJiang, C., Zeng, Z., Jiang, L., Dang, Z., & Shu, X. (2025). Waste Natural Pyrite Activation of Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame Potassium: Efficiency, Influencing Factors, Degradation Mechanisms, and Toxicity Evaluation. Water, 17(11), 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111558





