Mainstream Wastewater Treatment Process Based on Multi-Nitrogen Removal Under New Anaerobic–Swing–Anoxic–Oxic Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactor Start-Up and Operation
2.2. Wastewater and Inoculated Sludge
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Analysis of Microbial Composition
2.5. Performance Detection of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) and Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria (NOB)
2.6. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Long-Term Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Effects
3.2. Typical Periodic Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Effects
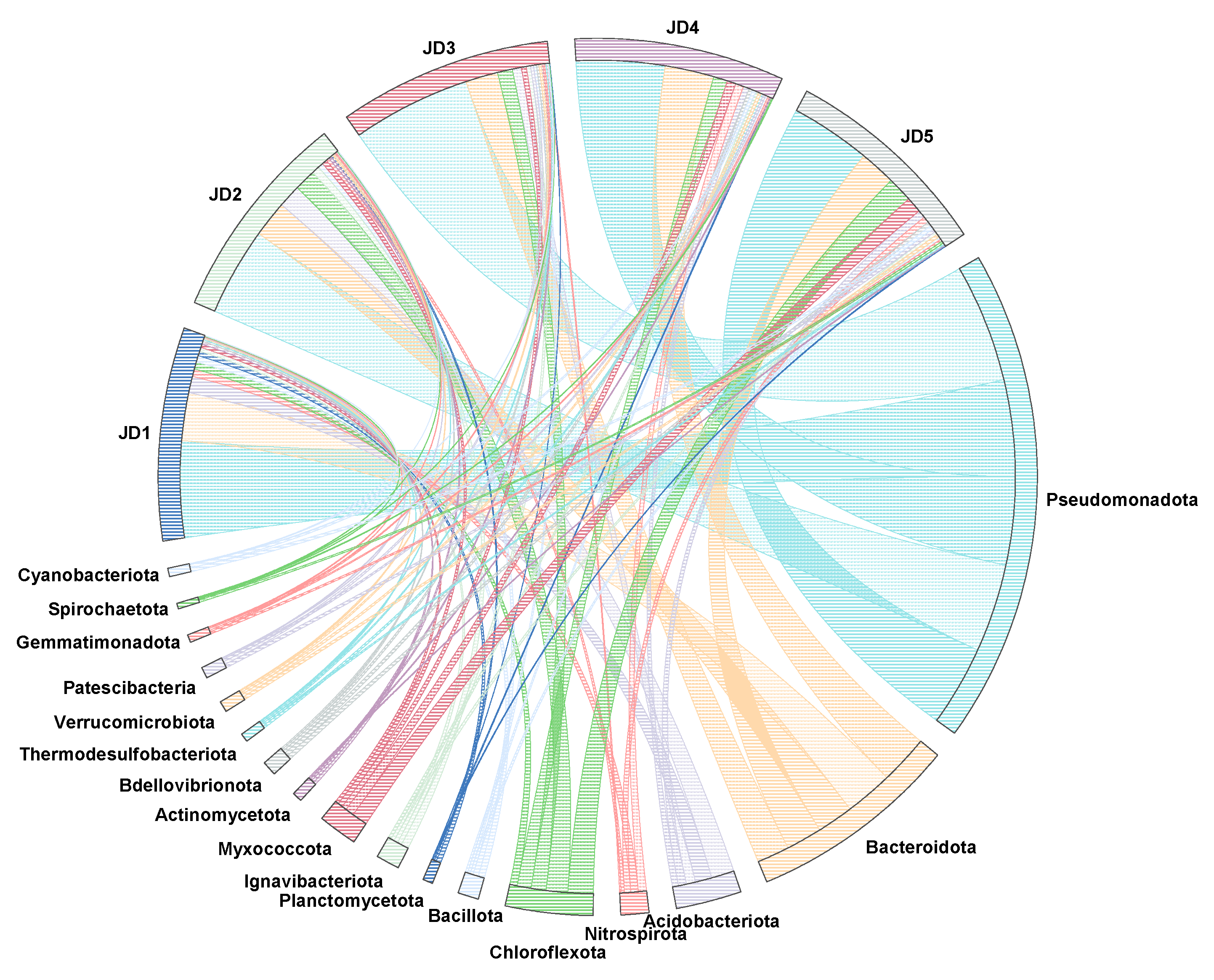
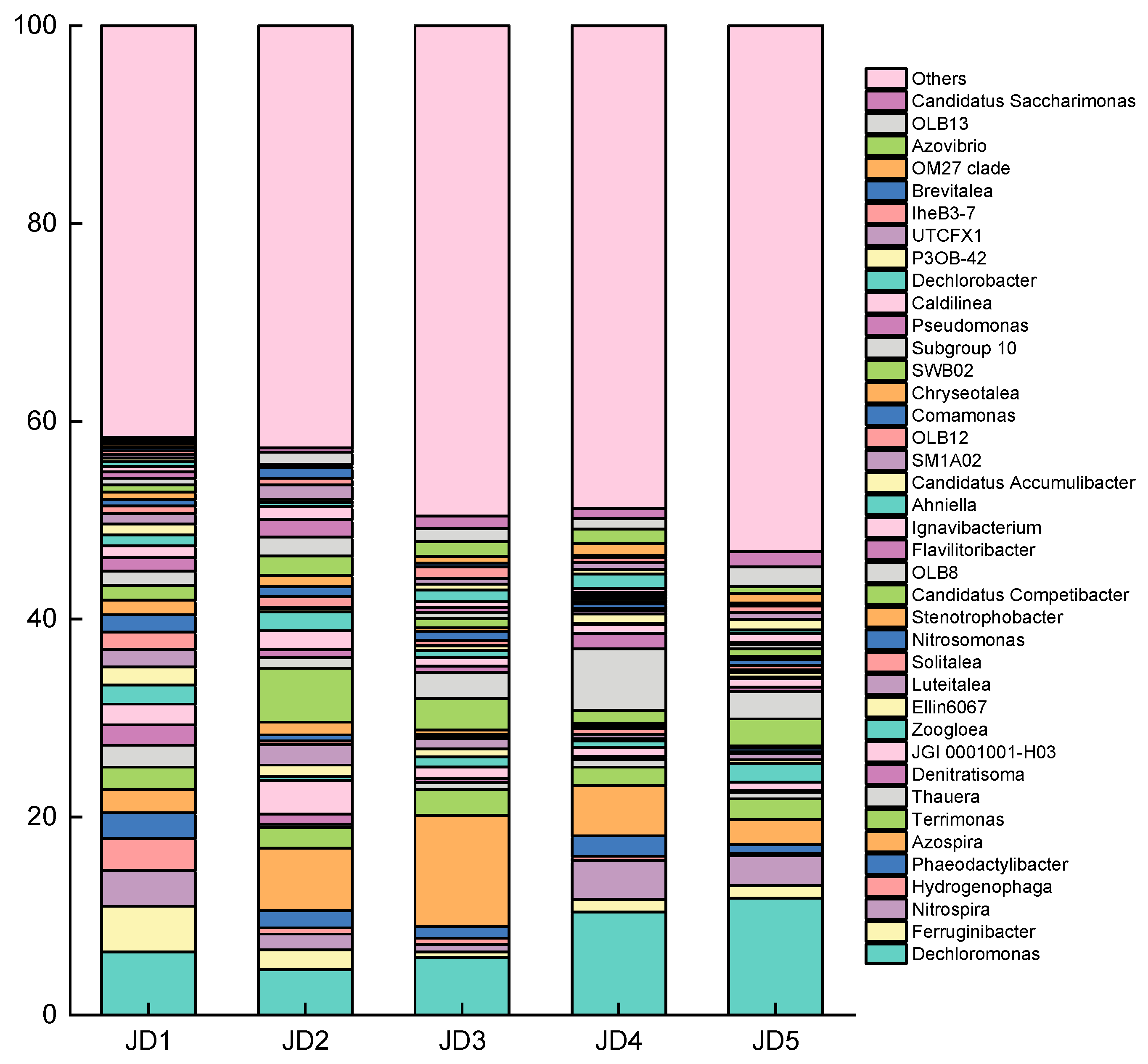
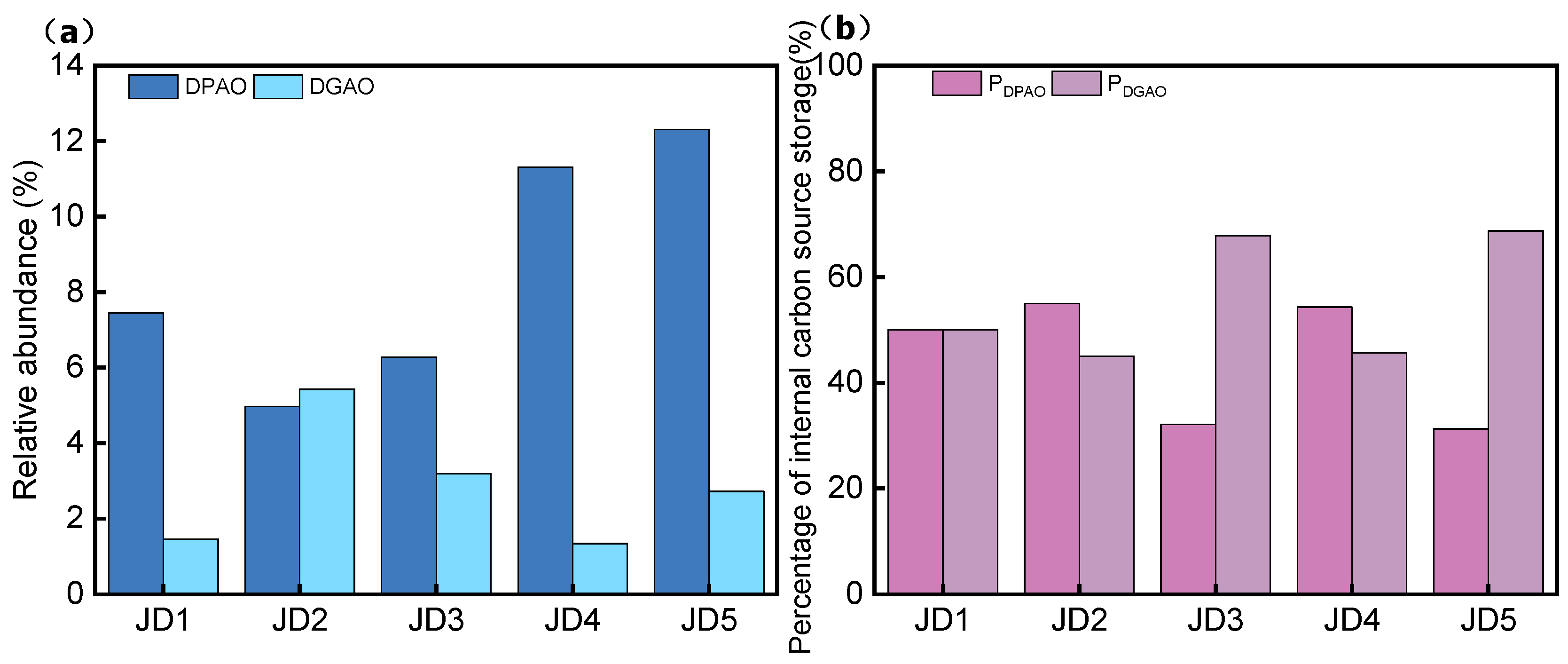
3.3. Changes in the Microbial Community Structure of the ASAO System
4. Conclusions and Prospects
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ASAO | Anaerobic–Swing–Anoxic–Oxic |
| AOA | Anaerobic–Oxic–Anoxic |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| TIN | Total inorganic nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| NOB | Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoates |
| Gly | Glycogen |
| SND | Simultaneous nitrification–denitrification |
| ANAMMOX | Anaerobic ammonium oxidation |
| ED | Endogenous denitrification |
| DPR | Denitrifying phosphorus removal |
| A/O | Anaerobic–Oxic |
| AAO | Anaerobic–Anoxic–Oxic |
| DPAOs | Denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating organisms |
| DGAOs | Denitrifying glycogen-accumulating organisms |
| AnAOB | Anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria |
| EPD | Endogenous partial denitrification |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| PN | Partial nitrification |
| PHB | Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate |
| PHV | Poly-3-hydroxyvalerate |
| MLSS | Mixed-liquor suspended solids |
| MLVSS | Mixed-liquor volatile suspended solids |
| AOB | Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria |
| NAR | Nitrite accumulation rate |
| NRE | Nitrogen removal efficiency |
| SVI | Sludge Volume Index |
| HNAD | Heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification |
| PAOs | Phosphate-accumulating organisms |
| GAOs | Glycogen-accumulating organisms |
| COMAMMOX | Complete ammonia oxidizers |
| VFA | Volatile Fatty Acid |
| DNRA | Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium |
| PAM | Polyphosphate accumulation metabolism |
| GAM | Glycogen accumulation metabolism |
References
- Bernat, K.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Dobrzyńska, A. Denitrification with endogenous carbon source at low C/N and its effect on P(3HB) accumulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Peng, Y.; Mai, W.; He, J.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Achieving advanced nitrogen removal from low C/N wastewater by combining endogenous partial denitrification with anammox in mainstream treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Cao, T.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y. Effect of carbon source type on intracellular stored polymers during endogenous denitritation (ED) treating landfill leachate. Water Res. 2016, 100, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L. Enhanced denitrifying phosphorous removal in a novel anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic (AOA) process with the diversion of internal carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10340–10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Hou, Z.; Dong, W.; Peng, Y. Advanced N removal from low C/N sewage via a plug-flow anaerobic/oxic/anoxic (AOA) process: Intensification through partial nitrification, endogenous denitrification, partial denitrification, and anammox (PNEnD/A). Water Res. 2024, 267, 122452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehmen, A.; Zeng, R.J.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J. Anaerobic metabolism of propionate by polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 91, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Yuan, Z.G.; Keller, J. Metabolic model for glycogen-accumulating organisms in anaerobic/aerobic activated sludge systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 81, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Enhanced nutrient removal from mainstream sewage via denitrifying dephosphatation, endogenous denitrification and anammox in a novel continuous flow process. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, D.; Chen, G.; Du, S.; Zhen, J.; Yuan, M. Stable nitrite accumulation and phosphorous removal from nitrate and municipal wastewaters in a combined process of endogenous partial denitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal (EPDPR). Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Dan, Q.; Sui, J.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Advanced nitrogen removal from municipal sewage via partial nitrification-anammox process under two typical operation modes and seasonal ambient temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. Improved performance of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification via nitrite in an oxygen-limited SBR by alternating the DO. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhan, W.; Du, J.; Wang, G.; Pang, J.; Ren, N.; Yang, S. Effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on performance and mechanism of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in integrated fixed-film activated sludge sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriwiriyarat, T.; Ungkurarate, W.; Fongsatitkul, P.; Chinwetkitvanich, S. Effects of dissolved oxygen on biological nitrogen removal in integrated fixed film activated sludge (IFAS) wastewater treatment process. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roots, P.; Wang, Y.; Rosenthal, A.F.; Griffin, J.S.; Sabba, F.; Petrovich, M.; Yang, F.; Kozak, J.A.; Zhang, H.; Wells, G.F. Comammox Nitrospira are the dominant ammonia oxidizers in a mainstream low dissolved oxygen nitrification reactor. Water Res. 2019, 157, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Feng, L.; Yang, G.; Dai, J.; Mu, J. Development of simultaneous nitrification-denitrification (SND) in biofilm reactors with partially coupled a novel biodegradable carrier for nitrogen-rich water purification. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, M.; Li, D.; Pei, H.; Chang, S.; Guo, W. Effect of dissolved oxygen on high C/N wastewater treatment in moving bed biofilm reactors based on heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification: Nitrogen removal performance and potential mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 365, 128147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Z.; Bin, X.; Zhigang, Q.; Zhiqiang, C.; Junwen, L.; Taishi, G.; Wenci, Z.; Jingfeng, W. Denitrifying capability and community dynamics of glycogen accumulating organisms during sludge granulation in an anaerobic-aerobic sequencing batch reactor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Operation mode of a step-feed anoxic/oxic process with distribution of carbon source from anaerobic zone on nutrient removal and microbial properties. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Jia, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, Y. Partial denitrifying phosphorus removal coupling with anammox (PDPRA) enables synergistic removal of C, N, and P nutrients from municipal wastewater: A year-round pilot-scale evaluation. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Qi, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sui, J.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y. Fast start-up and stable operation of mainstream anammox without inoculation in an A2/O process treating low COD/N real municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, T.; Zhu, X.; Gong, X.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y. Efficient nitrogen removal in a total floc sludge system from domestic wastewater with low C/N: High anammox nitrogen removal contribution driven by endogenous partial denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 378, 128995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Ding, J.; An, Z. The successful integration of anammox to enhance the operational stability and nitrogen removal efficiency during municipal wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Li, C.; Xue, B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Ethylmalonyl-CoA pathway involved in polyhydroxyvalerate synthesis in Candidatus Contendobacter. AMB Express 2022, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, F.; Qian, L.; Yu, X.; Huang, F.; Hu, R.; Su, H.; Gu, H.; Yan, Q.; et al. The vertical partitioning between denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium of coastal mangrove sediment microbiomes. Water Res. 2024, 262, 122113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; He, T.; Yuan, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Lei, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, M.; Yang, L.; Zheng, C.; Wang, C. Enhancement of cold-adapted heterotrophic nitrification and denitrification in Pseudomonas sp. NY1 by cupric ions: Performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 414, 131574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Ma, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, C. Total-solids-controlled microbial response and volatile fatty acids production in sludge and chicken manure co-fermentation. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, J.M.; Singleton, C.; Clegg, L.-A.; Petriglieri, F.; Nielsen, P.H. High Diversity and Functional Potential of Undescribed “Acidobacteriota” in Danish Wastewater Treatment Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriglieri, F.; Kondrotaite, Z.; Singleton, C.; Nierychlo, M.; Dueholm, M.K.D.; Nielsen, P.H. A comprehensive overview of the Chloroflexota community in wastewater treatment plants worldwide. mSystems 2023, 8, e0066723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, S.J.; Karst, S.M.; Nierychlo, M.; Dueholm, M.S.; Albertsen, M.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Seviour, R.J.; Nielsen, P.H. Genomic and in situ investigations of the novel uncultured Chloroflexi associated with 0092 morphotype filamentous bulking in activated sludge. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, A.; Vattiringal Jayadradhan, R.K.; Pillai, D.; Prasannan Geetha, P.; Joseph, V.; Isaac Sarojini, B.S. Nitrospira as versatile nitrifiers: Taxonomy, ecophysiology, genome characteristics, growth, and metabolic diversity. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashita, H.; Hatamoto, M.; Tomita, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Narihiro, T.; Kuroda, K. Comprehensive Insights into Potential Metabolic Functions of Myxococcotain Activated Sludge Systems. Microbes Environ. 2024, 39, ME24068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, B.; Oehmen, A.; Carvalho, G.; Seco, A.; Borrás, L.; Barat, R. Metabolic shift of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms with different levels of polyphosphate storage. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Jia, S.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Y. Improvement of partial nitrification endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal system: Balancing competition between phosphorus and glycogen accumulating organisms to enhance nitrogen removal without initiating phosphorus removal deterioration. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Bi, X.; Peng, Y.; Bai, M. Research advances of the phosphorus-accumulating organisms of Candidatus Accumulibacter, Dechloromonas and Tetrasphaera: Metabolic mechanisms, applications and influencing factors. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrotaite, Z.; Valk, L.C.; Petriglieri, F.; Singleton, C.; Nierychlo, M.; Dueholm, M.K.D.; Nielsen, P.H. Diversity and Ecophysiology of the Genus OLB8 and Other Abundant Uncultured Saprospiraceae Genera in Global Wastewater Treatment Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 917553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Ji, Y.; Fu, Z.; Yan, X.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Bi, P.; Zhu, L.; Xu, B.; et al. Performance of anaerobic/oxic/anoxic simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal system overwhelmingly dominated by Candidatus_Competibacter: Effect of aeration time. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, J. Complete nitrogen removal via simultaneous nitrification and denitrification by a novel phosphate accumulating Thauera sp. strain SND5. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Sun, H.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, P.; Yang, H.; et al. Nitrogen removal characteristics and potential application of the heterotrophic nitrifying-aerobic denitrifying bacteria Pseudomonas mendocina S16 and Enterobacter cloacae DS’5 isolated from aquaculture wastewater ponds. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Luo, Y.-H.; Long, X.; Zaidi, A.A.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, D.; Rittmann, B.E. Wastewater treatment for ships experiencing large temperature changes: The activated sludge/membrane-biofilm reactor. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.H. Dormant microbes: Scouting ahead or plodding along? Nature 2009, 458, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, N.; Franks, A.E.; Shentu, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; He, Y. Loss of microbial diversity does not decrease γ-HCH degradation but increases methanogenesis in flooded paddy soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, A.J.; Jenkins, D. Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal from Wastewater by Biomass with Different Phosphorus Contents, Part II: Anaerobic Adenosine Triphosphate Utilization and Acetate Uptake Rates. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Zeng, W.; Wang, B.; Fan, Z.; Peng, Y. New insights in the competition of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms and glycogen-accumulating organisms under glycogen accumulating metabolism with trace Poly-P using flow cytometry. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Peng, Y. Optimization of the intermittent aeration to improve the stability and flexibility of a mainstream hybrid partial nitrification-anammox system. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
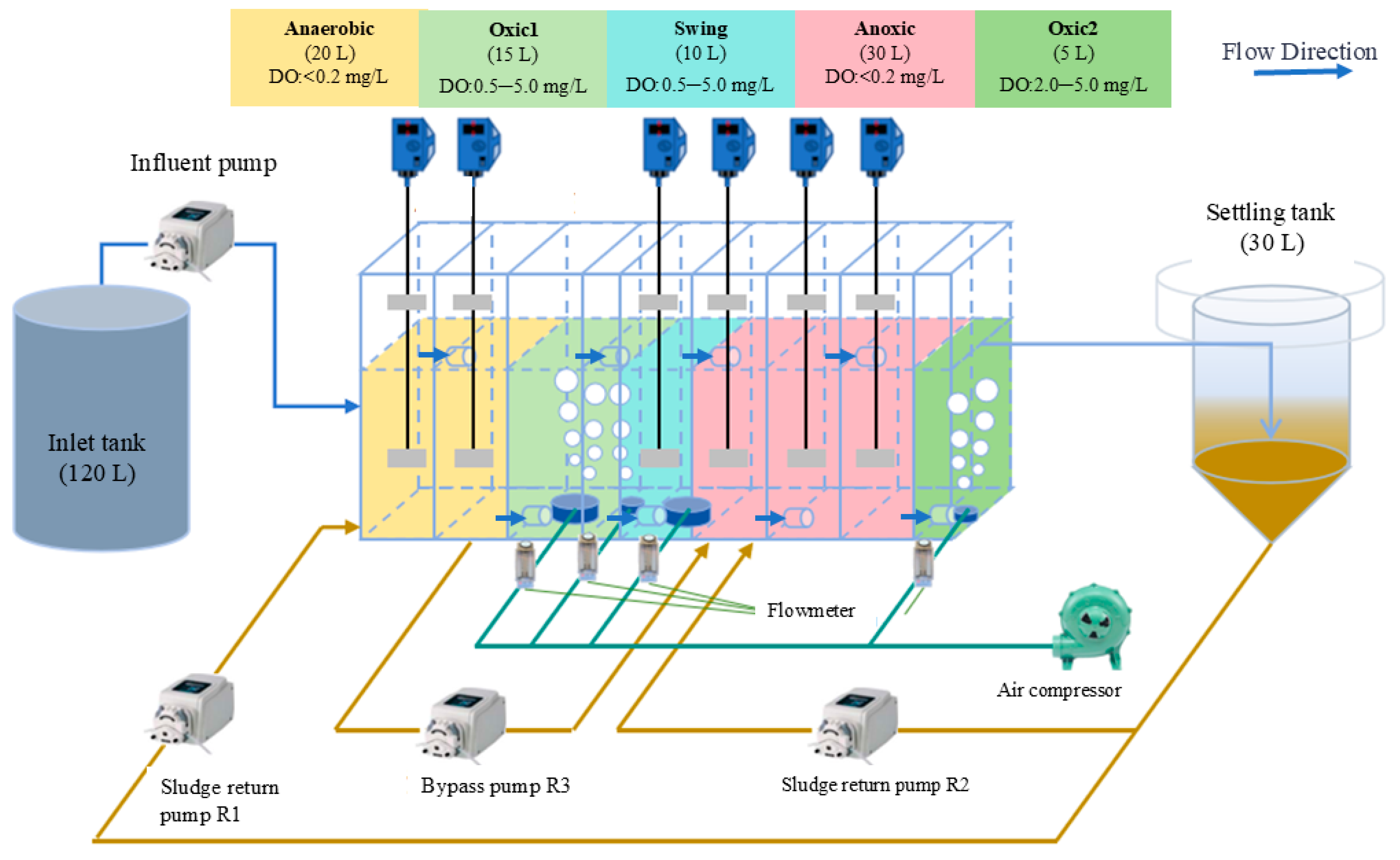
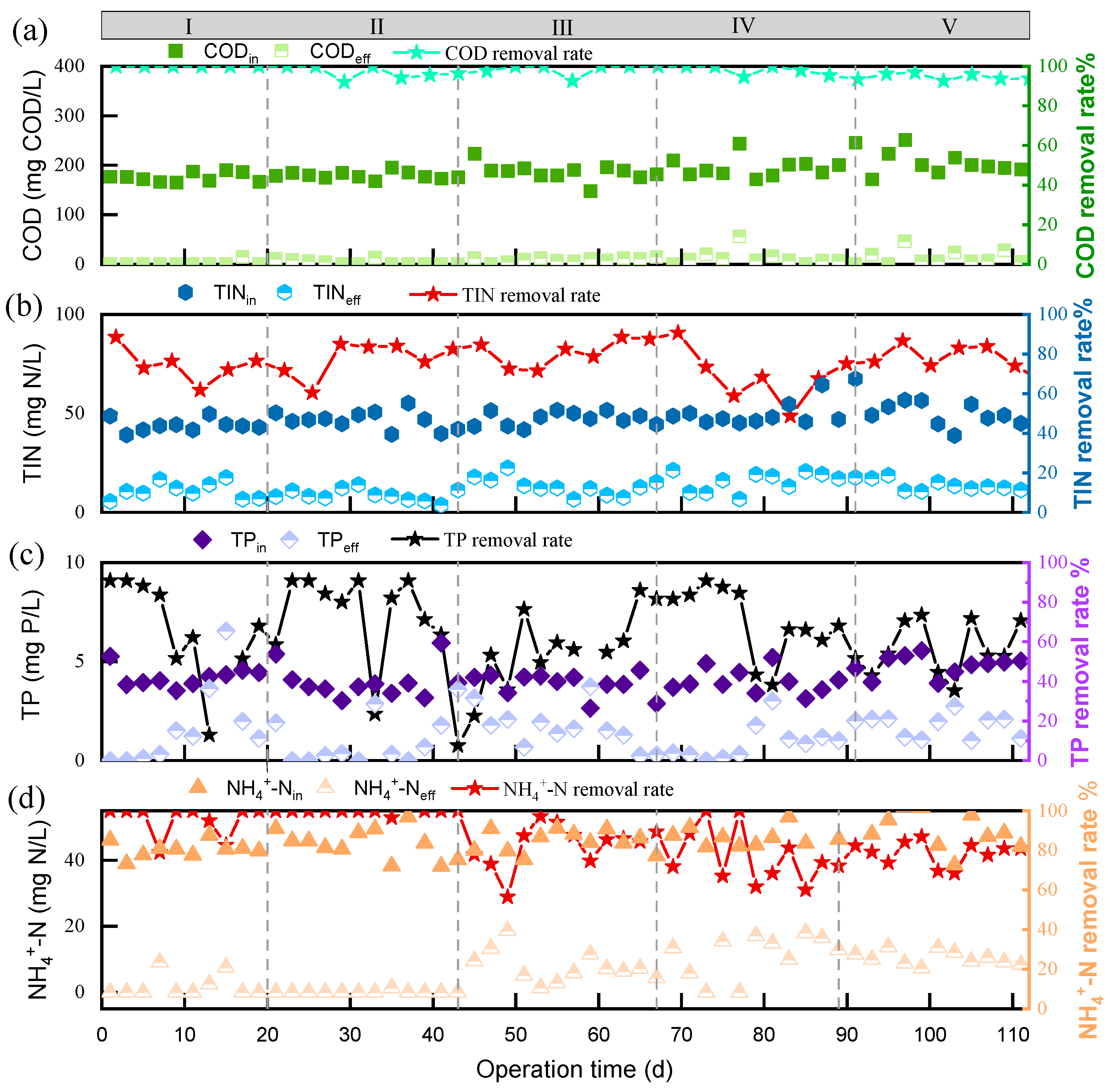
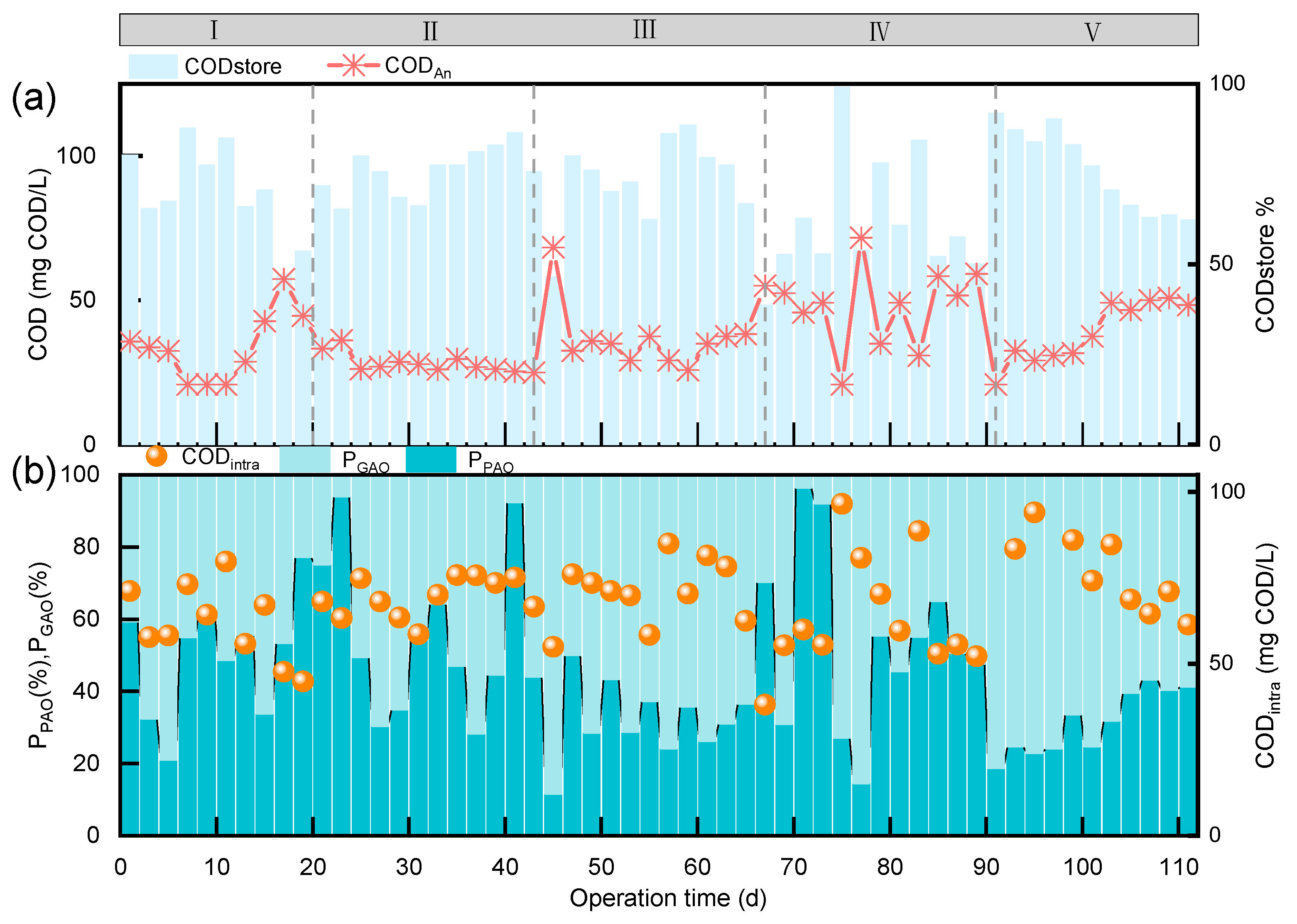
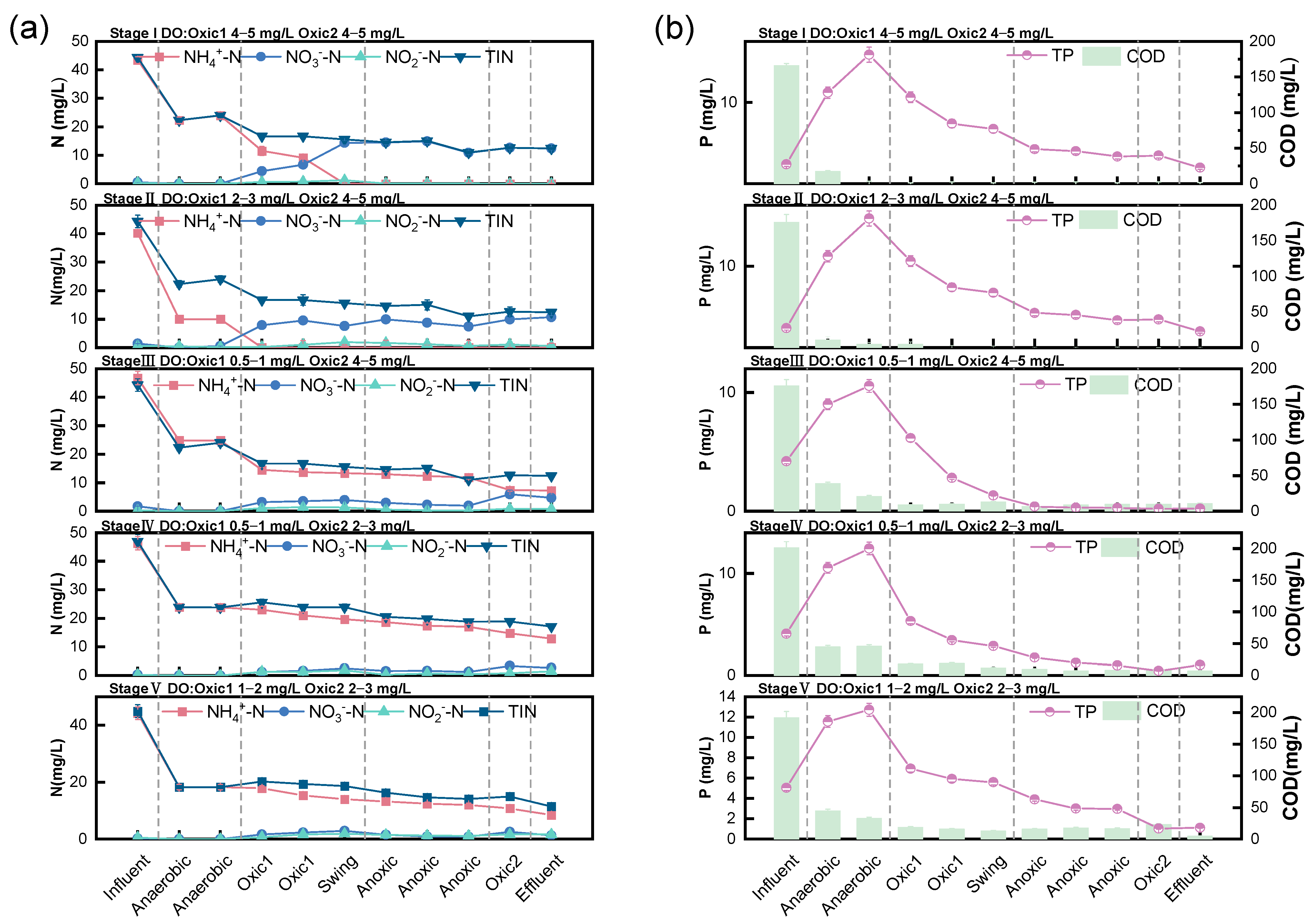



| Oxic1 DO (mg/L) | Swing (Aerobic) DO (mg/L) | Oxic2 DO (mg/L) | HRT (h) | Operating Days (d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 16 | 1–21 |
| II | 2–3 | 2–3 | 4–5 | 16 | 21–43 |
| III | 0.5–1 | 0.5–1 | 4–5 | 16 | 44–65 |
| IV | 0.5–1 | 0.5–1 | 2–3 | 16 | 66–89 |
| V | 1–2 | 1–2 | 2–3 | 16 | 90–112 |
| Main Components | Concentration (mg/L) | Trace Elements | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH3COONa (Shanghai, China) | 256.41 (200 mg COD/L) | FeCl3·6H2O (Shanghai, China) | 1500 |
| MgSO4 (Shanghai, China) | 90 | CuSO4 (Shanghai, China) | 50 |
| CaCl2 (Shanghai, China) | 14 | KI (Shanghai, China) | 150 |
| NH4Cl (Shanghai, China) | 153 (40 mg N/L) | MnCl·4H2O (Shanghai, China) | 110 |
| KH2PO4 (Shanghai, China) | 17.5 (4 mg P/L) | NaMoO4·2H2O (Shanghai, China) | 60 |
| KHCO3 (Shanghai, China) | 200 | H3BO3 (Shanghai, China) | 150 |
| CoCl2·6H2O (Shanghai, China) | 150 | ||
| ZnSO4·7H2O (Shanghai, China) | 120 |
| Indicator | Detection Method | Instrument Employed |
|---|---|---|
| COD | Rapid-digestion spectrophotometry | UV spectrophotometer (PHILES UV2600, Shanghai, China) |
| NH4+-N | Nessler’s reagent photometry | UV spectrophotometer (PHILES UV2600, Shanghai, China) |
| NO2−-N | Ultraviolet spectrophotometry | UV spectrophotometer (PHILES UV2600, Shanghai, China) |
| NO3−-N | Ultraviolet spectrophotometry | UV spectrophotometer (PHILES UV2600, Shanghai, China) |
| TN | Ultraviolet spectrophotometry | UV spectrophotometer (PHILES UV2600, Shanghai, China) |
| TP | Ultraviolet spectrophotometry | UV spectrophotometer (PHILES UV2600, Shanghai, China) |
| SV30 | Natural sedimentation for 30 min | Graduated cylinder (Nanjing, China) |
| pH | Portable sensor | Shanghai Bolv Instrument, Shanghai, China |
| PHA | Gas chromatography | Gas chromatograph (Agilent 7820A, Santa Clara, CA, USA) |
| Gly | Anthrone spectrophotometry | UV spectrophotometer (PHILES UV2600, Shanghai, China) |
| DO | Portable sensor | Shanghai Bolv Instrument, Shanghai, China |
| MLSS | Drying and weighing | Oven, Shanghai, China |
| MLVSS | Drying and weighing | Muffle furnace, Shanghai, China |
| Mainstream Sewage Treatment Processes | Aerobic Zone HRT | TIN Removal Efficiency | Important Pathways for Denitrification | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A/O | 5.8 h | 50.8% | Conventional nitrification and denitrification | [18] |
| AAO | 2 h | 77.1% | Partial denitrifying phosphorus removal coupled with anammox | [19] |
| AAO | 5.7 h | 73.1% | Partial denitrification/anammox (PD/A) | [20] |
| AOA | 4 h | 83.5% | Nitrification–endogenous partial denitrification and anammox | [21] |
| AOA | 4 h | Temperature decreased: 70.7 ± 4.2 % Temperature increased: 87.1 ± 2.6% | Partial denitrification/anammox (PD/A) | [22] |
| ASAO | 3–5 h | 88.18% | SND, DPR, ANAMMOX | This article |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, R. Mainstream Wastewater Treatment Process Based on Multi-Nitrogen Removal Under New Anaerobic–Swing–Anoxic–Oxic Model. Water 2025, 17, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101548
Cao J, Wang J, Xu R. Mainstream Wastewater Treatment Process Based on Multi-Nitrogen Removal Under New Anaerobic–Swing–Anoxic–Oxic Model. Water. 2025; 17(10):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101548
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jiashun, Jinyu Wang, and Runze Xu. 2025. "Mainstream Wastewater Treatment Process Based on Multi-Nitrogen Removal Under New Anaerobic–Swing–Anoxic–Oxic Model" Water 17, no. 10: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101548
APA StyleCao, J., Wang, J., & Xu, R. (2025). Mainstream Wastewater Treatment Process Based on Multi-Nitrogen Removal Under New Anaerobic–Swing–Anoxic–Oxic Model. Water, 17(10), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101548






