Multi-Scale Impacts of Land Use Change on River Water Quality in the Xinxian River, Yangtze River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
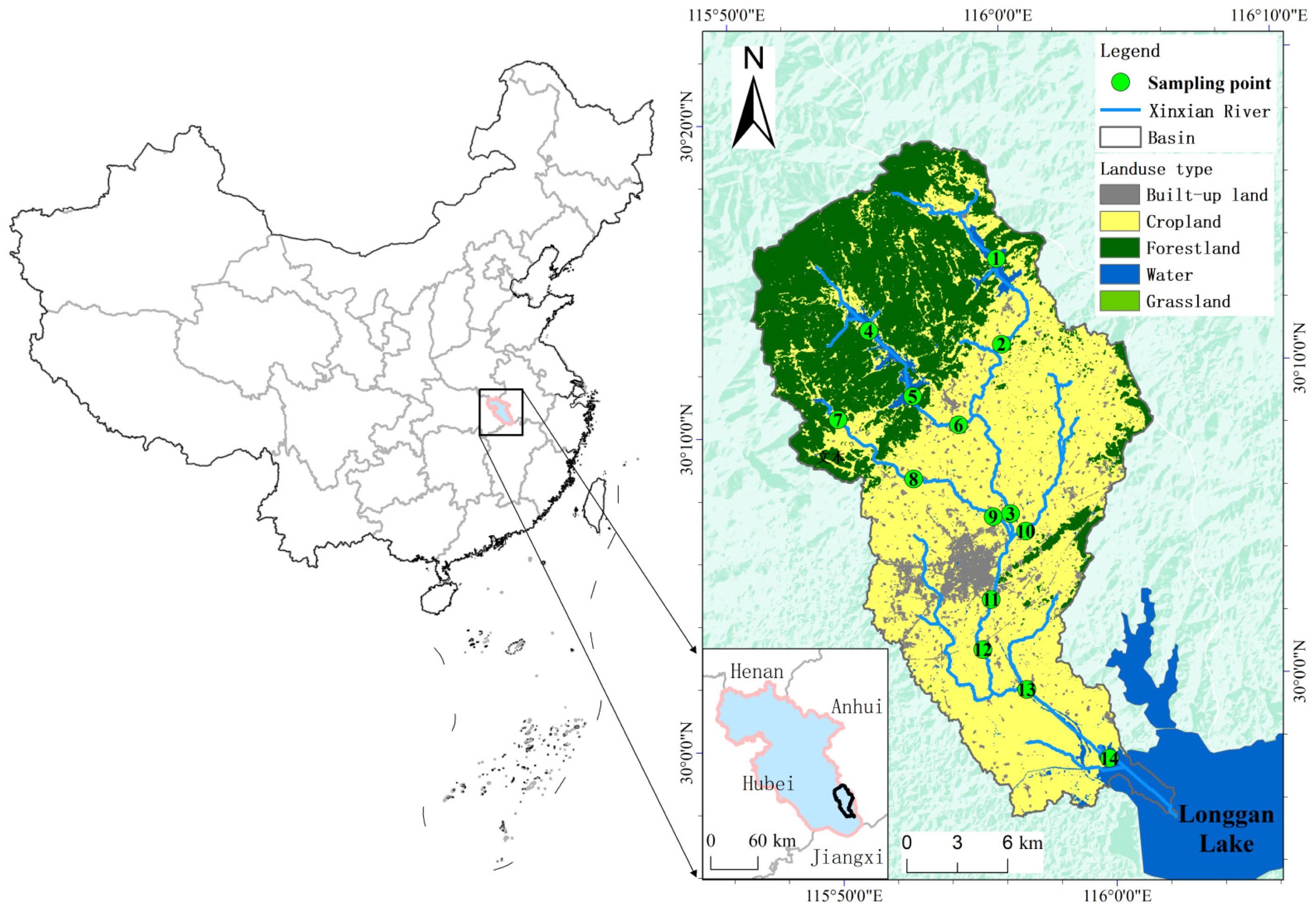
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.1.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.1.2. Land Use Data Sources and Data Processing
2.1.3. Water Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Determining the Size of the Buffer Zone
2.2.2. Calculation of Land Use Pattern Change
2.2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
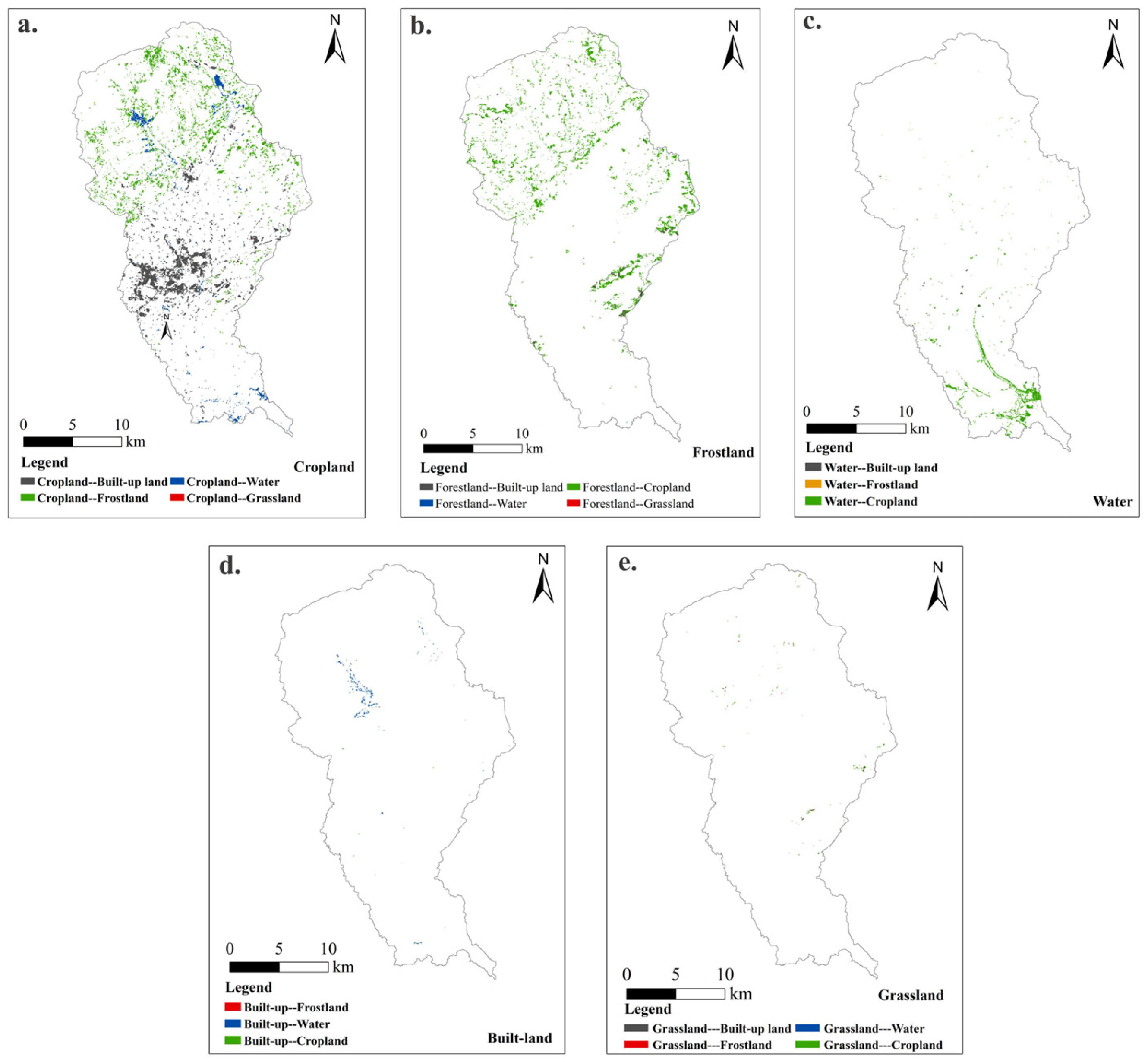
3.1. Characteristics of Land Use Type Changes
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of River Water Quality
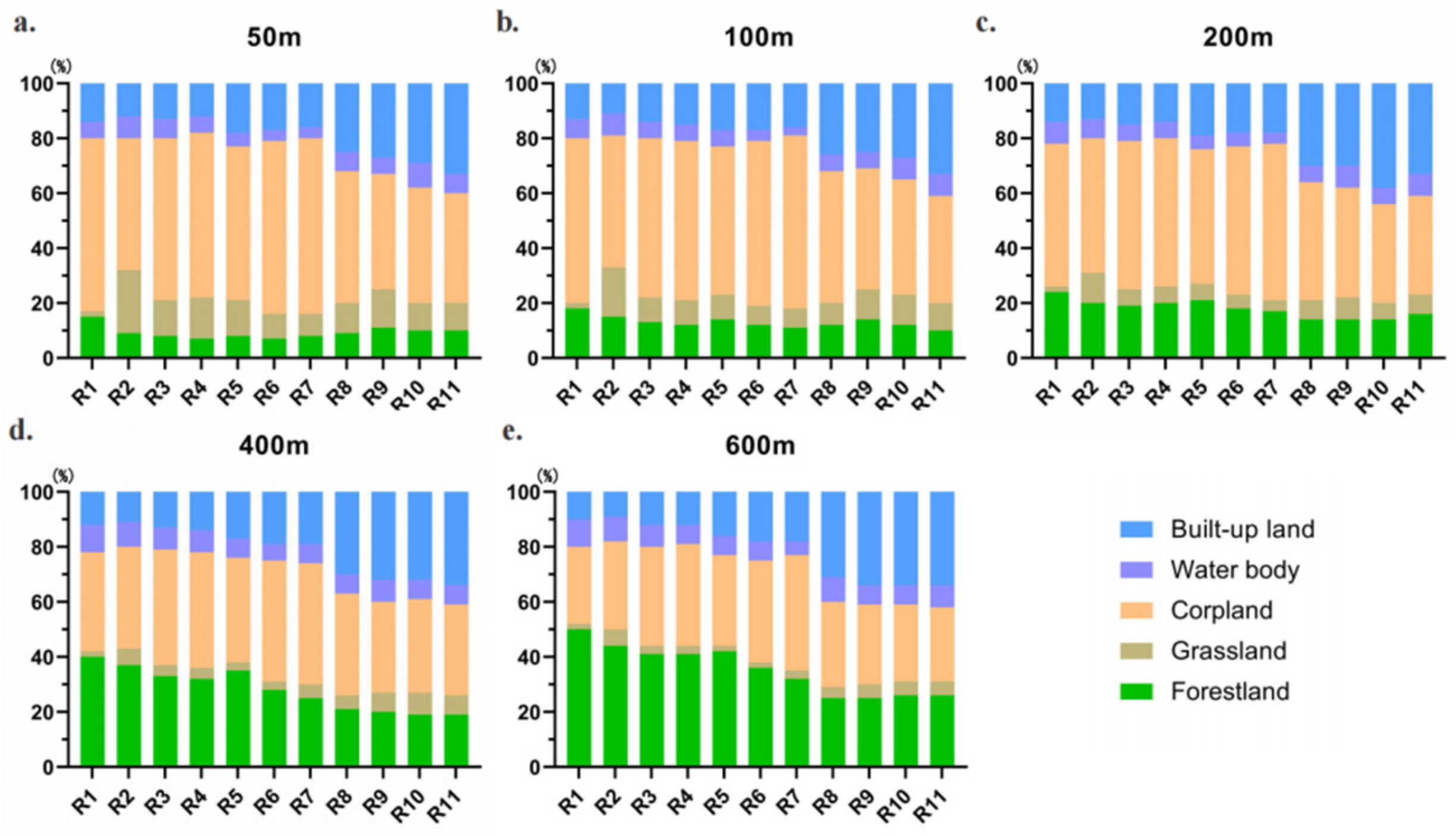
3.3. Spatial Heterogeneity of Land Use in Buffer Zones
3.4. Impact of Land Use on River Water Quality
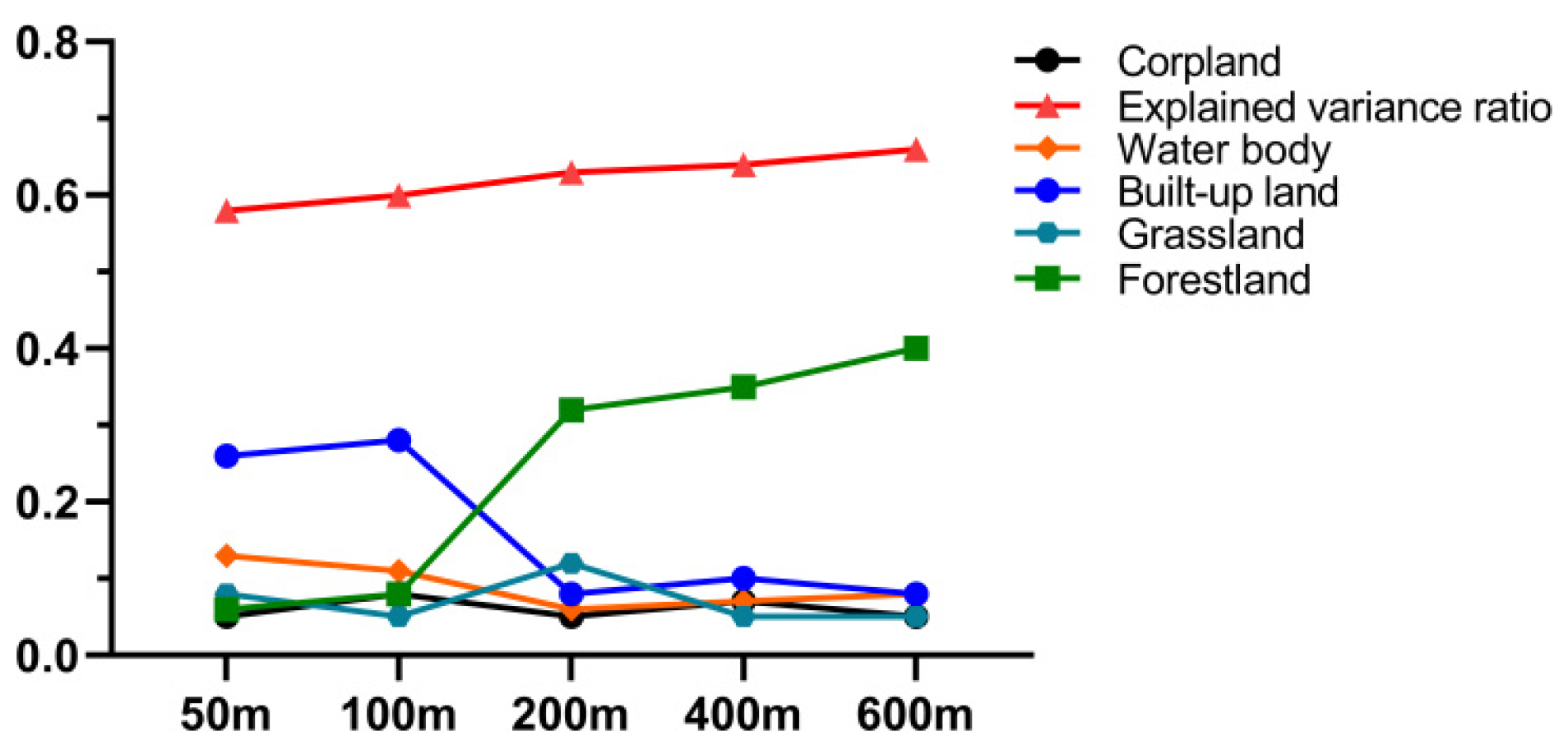
3.5. Scale Dependence
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of Economic Development on Land Use Types
4.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of River Water Quality and Land Use Types in Buffer Zones
4.3. Scale Effect of Land Use on Water Quality
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; An, C.; Tan, Q.; Tian, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y. Spatiotemporal analysis of land use pattern and stream water quality in southern Alberta, Canada. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 242, 103852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Huang, J.; Prell, C.; Bryan, B.A. Changes in supply and demand mediate the effects of land-use change on freshwater ecosystem services flows. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervinia, A.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J. Coupled effects of climate variability and land use pattern on surface water quality: An elasticity perspective and watershed health indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wang, C.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, X.; Chi, Y. Impacts of Land Use on Surface Water Quality Using Self-Organizing Map in Middle Region of the Yellow River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Multi-scale analysis of relationship between landscape pattern and urban river water quality in different seasons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, M.; Yackulic, C.B.; Lim, Y.; Arce-Nazario, J.A. Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: A multi-scale analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, S.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Q. Water quality in the upper Han River basin, China: The impacts of land use/land cover in riparian buffer zone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewane, E.B. Assessing land use and landscape factors as determinants of water quality trends in Nyong River basin, Cameroon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, T.C.; MCaldwell, P.V.; Martin, K.L.; Vose, J.M.; Baker, J.S.; Warziniack, T.W.; Costanza, J.K.; Frey, G.E.; Nehra, A.; Mihiar, C.M. Forested watersheds provide the highest water quality among all land cover types, but the benefit of this ecosystem service depends on landscape context. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L. The evolution of habitat quality and its response to land use change in the coastal China, 1985–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Wu, X.; Ge, X.; Lin, G.; Feng, L.; Ma, W.; Xu, D. Study on the Water Quality Characteristics of the Baoan Lake Basin in China under Different Land Use and Landscape Pattern Distributions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaraj, A.; Honnasiddaiah, R. Multi-spatial-scale land/use land cover influences on seasonally dominant water quality along Middle Ganga Basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Bai, H.; Tong, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, S. Scale effects of land use on river water quality: A case study of the Tuojiang River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 48002–48020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, K.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of multiple spatial scale characterization of land use on water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 7106–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 636-2012; Water Quality-Determination of Total Nitrogen-Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- HJ 535-2009; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen—Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB 11892-89; Water Quality—Determination of Permanganate Index. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- HJ 897-2017; Water Quality—Determination of Chlorophyll A—Spectrophotometric Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Dai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, L. Influence of spatial variation in land-use patterns and topography on water quality of the rivers inflowing to Fuxian Lake, a large deep lake in the plateau of southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaria, D.; Moksia, F.; Tchobsala; Pierre, K.; Tezore Bakary, P. Dynamic of land use and vegetation change in the eastern bank of Bénoué (North Cameroon). Bot. Stud. 2024, 65, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qian, Y. An integration method to predict the impact of urban land use change on green space connectivity under different development scenarios using a case study of Nanjing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 85243–85256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufebo, B.; Elias, E. Land Use/Land Cover Change and Its Driving Forces in Shenkolla Watershed, South Central Ethiopia. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 9470918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lei, Z.; Tong, X.; Gao, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Spatially-explicit modeling and intensity analysis of China’s land use change 2000–2050. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yen, H.; Lei, Q.; Qiu, W.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Qin, L.; Zhai, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; et al. Impact of human activities on phosphorus flows on an early eutrophic plateau: A case study in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; McConkey, K.R.; Tran, L.P.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Wu, G. Scientific concept and practices of life community of mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes, grasslands, and deserts in China. Ambio 2023, 52, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Ye, S.; Gao, P.; Ren, S.; Liu, C.; Song, C. Analyzing spatial patterns and driving factors of cropland change in China’s National Protected Areas for sustainable management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Jiang, G.; Wang, M. The Allocation Change of Rural Land Consolidation Type Structure under the Influence Factors of Different Geographical and Economic Development of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Zhan, C. Land use/land cover prediction and analysis of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River under different scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X. Forecast of policy-driven land use change and its impact on ecosystem services in China: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, J. Spillover effects of urban form on urban land use efficiency: Evidence from a comparison between the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 125816–125831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y. Can improving law enforcement effectively curb illegal land use in China? PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Towards a protocol on fair compensation in cases of legitimate land tenure changes: Input document for a participatory process. J. Chin. Gov. 2017, 3, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tong, X.; Chen, L. Evaluating land ecological security and examining its relationships with driving factors using GIS and generalized additive model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, H.; Lian, K.; Yu, Z. Comprehensive Evaluation of Cultivated Land Quality at County Scale: A Case Study of Shengzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalburgi, P.B.; Jha, R.; Ojha, C.S.; Deshannavar, U.B. Evaluation of re-aeration equations for river Ghataprabha, Karnataka, India and development of refined equation. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayele, H.S.; Atlabachew, M. Review of characterization, factors, impacts, and solutions of Lake eutrophication: Lesson for lake Tana, Ethiopia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 14233–14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, W.; Luo, L. What will the water quality of the Yangtze River be in the future? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857 Pt 3, 159714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungenge, C.P.; Wasserman, R.J.; Dondofema, F.; Keates, C.; Masina, F.M.; Dalu, T. Assessing chlorophyll-a and water quality dynamics in arid-zone temporary pan systems along a disturbance gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, J.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Hong, H. New insight into the correlations between land use and water quality in a coastal watershed of China: Does point source pollution weaken it? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543 Pt A, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Luo, Y. Dynamical changes of land use/land cover and their impacts on ecological quality during China’s reform periods: A case study of Quanzhou city, China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhou, X.; Guo, M.; Wei, W. Land use change and its effects on water quality in typical inland lake of arid area in China. J. Environ. Biol. 2016, 37, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Pakoksung, K.; Inseeyong, N.; Chawaloesphonsiya, N.; Punyapalakul, P.; Chaiwiwatworakul, P.; Xu, M.; Chuenchum, P. Seasonal dynamics of water quality in response to land use changes in the Chi and Mun River Basins Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Kung, H.T. What is the relationship between land use and surface water quality? A review and prospects from remote sensing perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 56887–56907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaggio, M.; Siikamäki, J. The value of forest water purification ecosystem services in Costa Rica. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Shen, Z.; Wei, G.; Wang, G.; Xie, H.; Lv, G. A systematic assessment of watershed-scale nonpoint source pollution during rainfall-runoff events in the Miyun Reservoir watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 25, 6514–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrić, S.; Leonhardt, G.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Processes improving urban stormwater quality in grass swales and filter strips: A review of research findings. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M.; Hale, R.; Parris, K.M.; Swearer, S.E. Impacts of human-induced environmental change in wetlands on aquatic animals. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 529–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, N.; Habte, L.; Waleed, M. Land use dynamics and their impact on hydrology and water quality of a river catchment: A comprehensive analysis and future scenario. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2025, 32, 4124–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Guerra, E.; Ghimire, U.; Nandimandalam, H.; Norris, A.; Gude, V.G. Wetlands for environmental protection. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1677–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Cui, Z. Effects of land use and slope on water quality at multi-spatial scales: A case study of the Weihe River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 57599–57616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Water Quality Indicators | Detection Methods | Implementation Standards |
|---|---|---|
| TN | Alkaline potassium persulfate digestion UV spectrophotometry | HJ 636-2012 [16] |
| TP | Molybdate spectrophotometry | GB 11893-89 [17] |
| NH3-N | Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry | HJ 535-2009 [18] |
| CODMn | Determination of permanganate index | GB 11892-89 [19] |
| Chl-a | Spectrophotometry | HJ 897-2017 [20] |
| Type of Land Use | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2000~2010 | 2010~2020 | 2000~2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio (%) | Ratio (%) | Ratio (%) | K | K | K | |
| Grassland | 0.073 | 0.075 | 0.071 | 0.256 | −0.591 | −0.175 |
| Cropland | 61.2 | 59.1 | 58.4 | −0.345 | −0.116 | −0.228 |
| Built-up land | 2.99 | 4.14 | 6.09 | 3.834 | 4.697 | 5.166 |
| Forestland | 32.1 | 33.5 | 31.9 | 0.430 | −0.462 | −0.027 |
| Water body | 3.59 | 3.18 | 3.48 | −1.165 | 0.961 | −0.157 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2000 | 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grassland | Cropland | Built-Up Land | Forestland | Water Body | Total | ||
| Grassland | Transfer rate (%) | 46.10 | 29.10 | 17.20 | 7.00 | 0.60 | 100 |
| Cropland | Transfer rate (%) | 0.02 | 90.07 | 5.02 | 3.91 | 0.98 | 100 |
| Built-up land | Transfer rate (%) | 0.00 | 0.30 | 96.20 | 0.00 | 3.50 | 100 |
| Forestland | Transfer rate (%) | 0.07 | 7.79 | 0.40 | 91.74 | 0.00 | 100 |
| Water body | Transfer rate (%) | 0.08 | 21.44 | 0.38 | 0.80 | 77.30 | 100 |
| Monitoring Points | Monitoring Point Coordinates | Surrounding Conditions | Main Pollution Sources | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 30.210955° N | 115.991872° E | Farmland and villages | Ground source pollution |
| R2 | 30.143537° N | 115.960534° E | Farmland and villages | Ground source pollution |
| R3 | 30.156726° N | 115.931034° E | Farmland and villages | Rural domestic sewage |
| R4 | 30.168153° N | 115.868749° E | Farmland and vegetable fields | Agricultural pollution |
| R5 | 30.164087° N | 115.963161° E | Villages and vegetable fields | Rural domestic sewage |
| R6 | 30.089987° N | 115.968701° E | Villages, roads and ponds | Livestock and Poultry Farming |
| R7 | 30.163456° N | 115.923303° E | Villages, forests and farmlands | Livestock and Poultry Farming |
| R8 | 30.137921° N | 115.900476° E | Farmland | Agricultural pollution |
| R9 | 30.125004° N | 115.930469° E | Towns and farmland | Urban domestic sewage |
| R10 | 30.086437° N | 115.958231° E | Urban areas and roads | Urban domestic sewage |
| R11 | 30.069171° N | 115.952148° E | Urban areas and roads | Urban domestic sewage |
| R12 | 30.058221° N | 115.948246° E | Villages and farmland | Agricultural pollution |
| R13 | 30.039928° N | 115.949029° E | Villages and farmland | Agricultural pollution |
| R14 | 30.008812° N | 115.961683° E | Farmland and fish ponds | Fishery wastewater |
| Monitoring Points | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | CODMn (mg/L) | Chl-a (mg/m3) | DO (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream | R1 | 0.56 | 0.042 | 0.08 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 9.6 |
| R4 | 0.45 | 0.028 | 0.06 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 10.6 | |
| R5 | 0.75 | 0.056 | 0.11 | 3.8 | 4.6 | 8.8 | |
| R7 | 0.68 | 0.052 | 0.18 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 9.2 | |
| Midstream | R2 | 0.72 | 0.060 | 0.16 | 5.1 | 2.8 | 7.2 |
| R3 | 0.81 | 0.062 | 0.21 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 6.8 | |
| R6 | 0.96 | 0.072 | 0.28 | 5.6 | 5.2 | 7.6 | |
| R8 | 1.06 | 0.078 | 0.36 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 7.8 | |
| R9 | 1.12 | 0.086 | 0.42 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 5.9 | |
| R10 | 1.46 | 0.098 | 0.64 | 7.8 | 8.2 | 6.1 | |
| R11 | 1.94 | 0.127 | 0.73 | 10.2 | 12.2 | 4.6 | |
| Downstream | R12 | 1.46 | 0.102 | 0.58 | 8.2 | 11.4 | 5.2 |
| R13 | 1.36 | 0.094 | 0.49 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 5.6 | |
| R14 | 1.42 | 0.092 | 0.48 | 5.9 | 8.6 | 6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, X.; Liu, X.; Liao, H. Multi-Scale Impacts of Land Use Change on River Water Quality in the Xinxian River, Yangtze River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101541
Guo Y, Liu Y, Li W, Cai X, Liu X, Liao H. Multi-Scale Impacts of Land Use Change on River Water Quality in the Xinxian River, Yangtze River Basin. Water. 2025; 17(10):1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101541
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yongsheng, Ying Liu, Weilin Li, Xiting Cai, Xinyi Liu, and Haikuo Liao. 2025. "Multi-Scale Impacts of Land Use Change on River Water Quality in the Xinxian River, Yangtze River Basin" Water 17, no. 10: 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101541
APA StyleGuo, Y., Liu, Y., Li, W., Cai, X., Liu, X., & Liao, H. (2025). Multi-Scale Impacts of Land Use Change on River Water Quality in the Xinxian River, Yangtze River Basin. Water, 17(10), 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101541






