Asymmetric Impacts of Urbanization on Extreme Hourly Precipitation Across the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration During 1978–2012
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
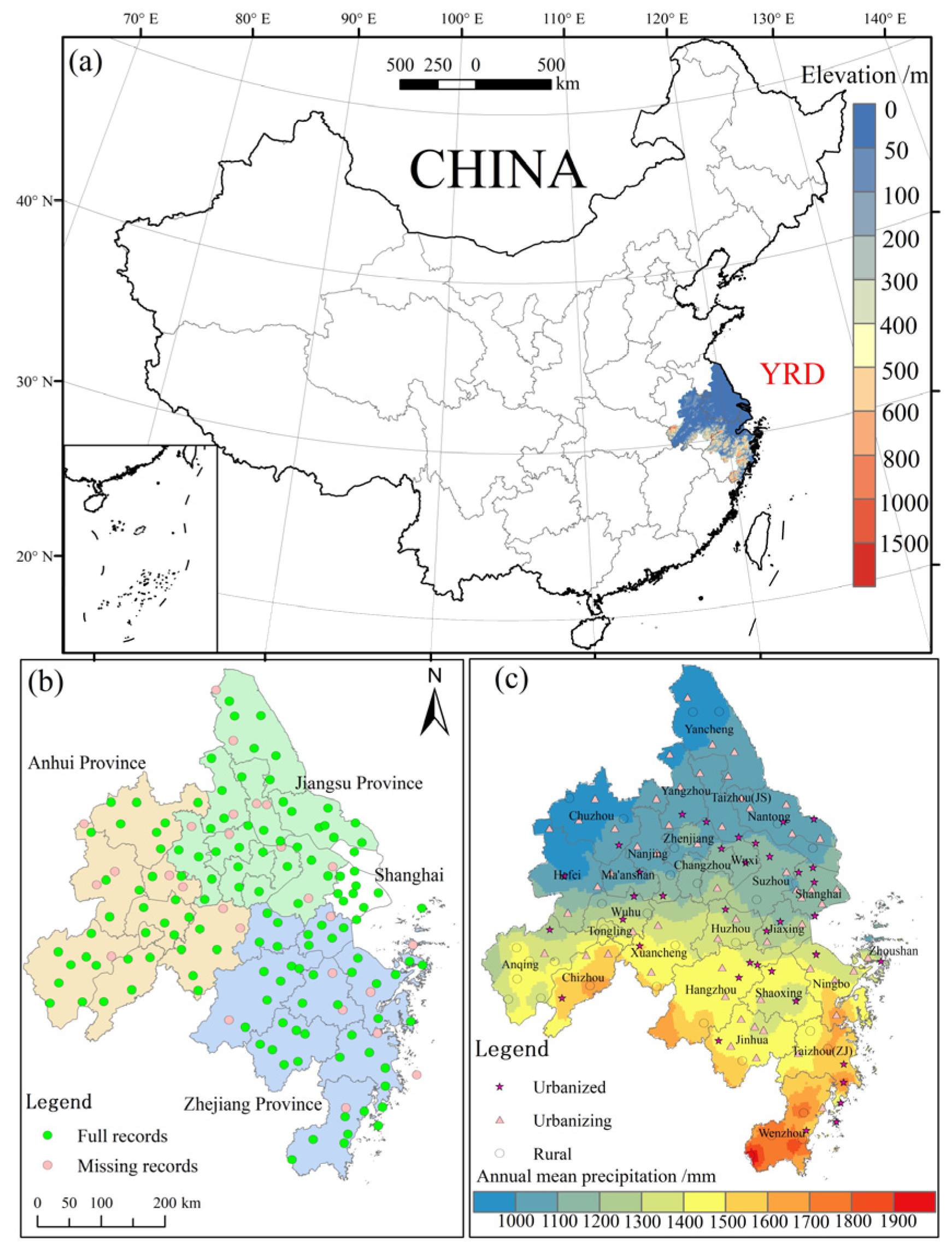
2.1. Study Area
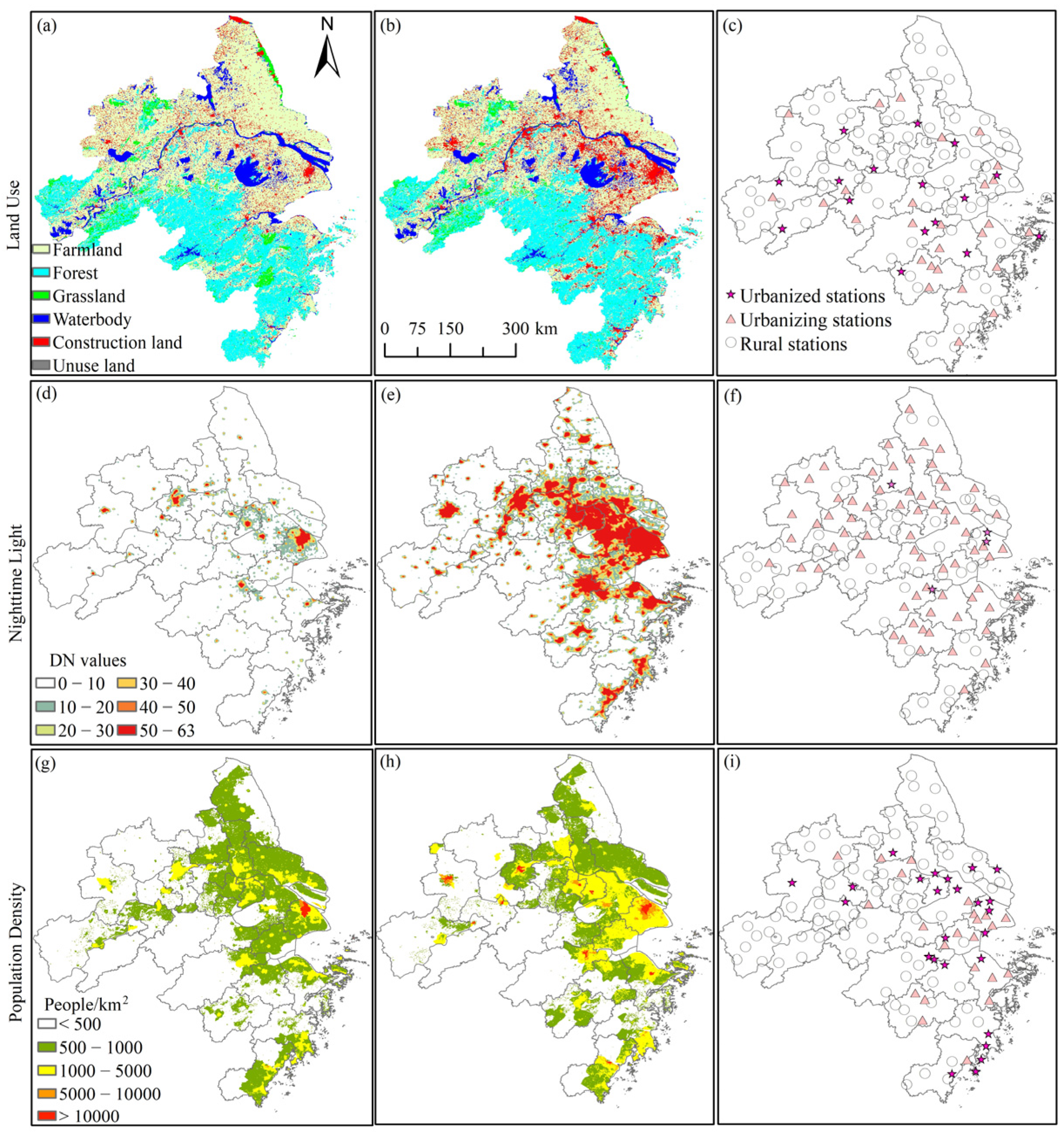
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Definition of the EHP
2.3.2. Characterizing the Stages and Levels of Urbanization
2.3.3. Classification of Urban and Rural Stations
2.3.4. Evaluating the Urbanization Effects on Extreme Precipitation Changes
2.3.5. Regional Variations in Urbanization Effects and Contributions
3. Results
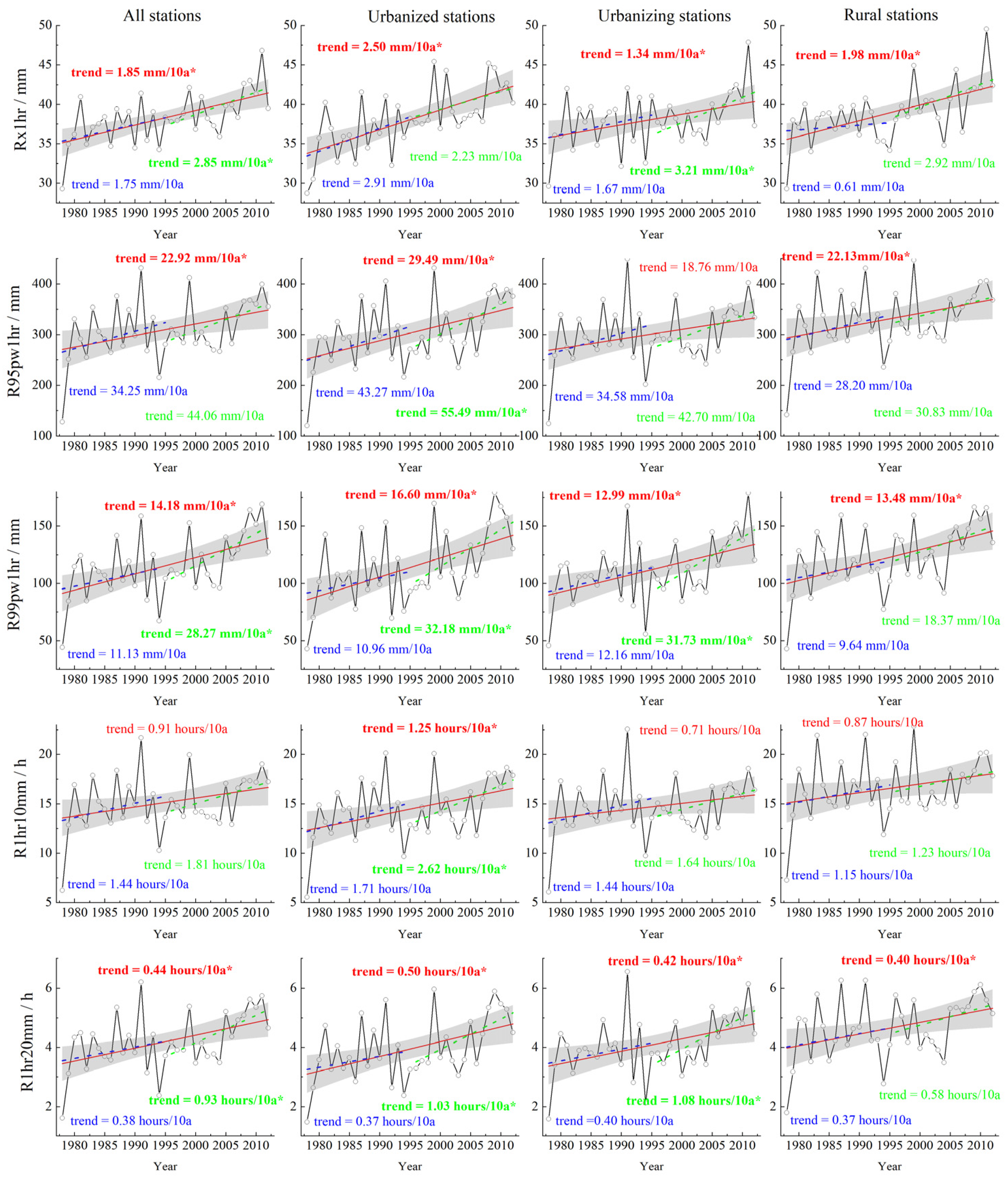
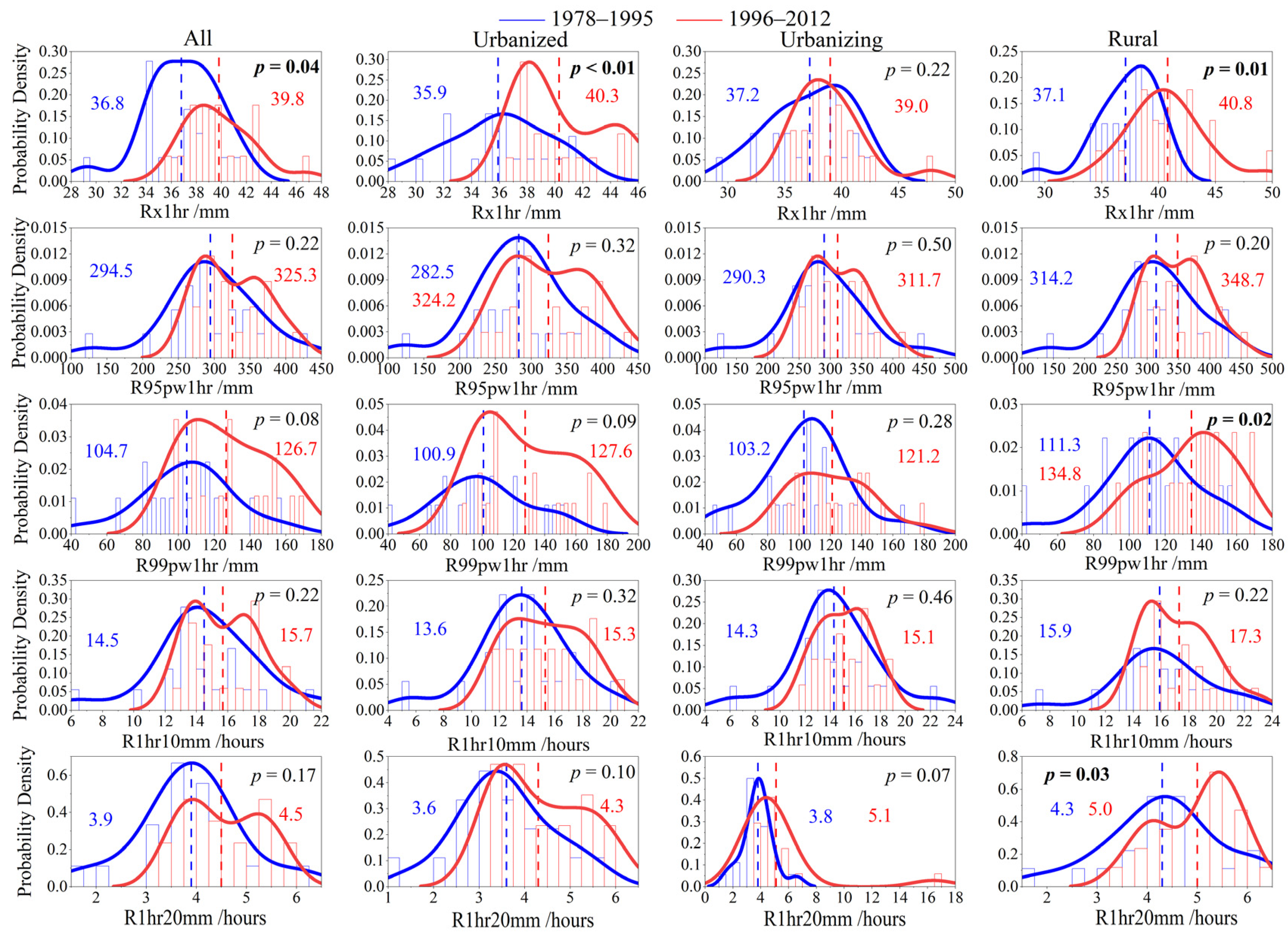
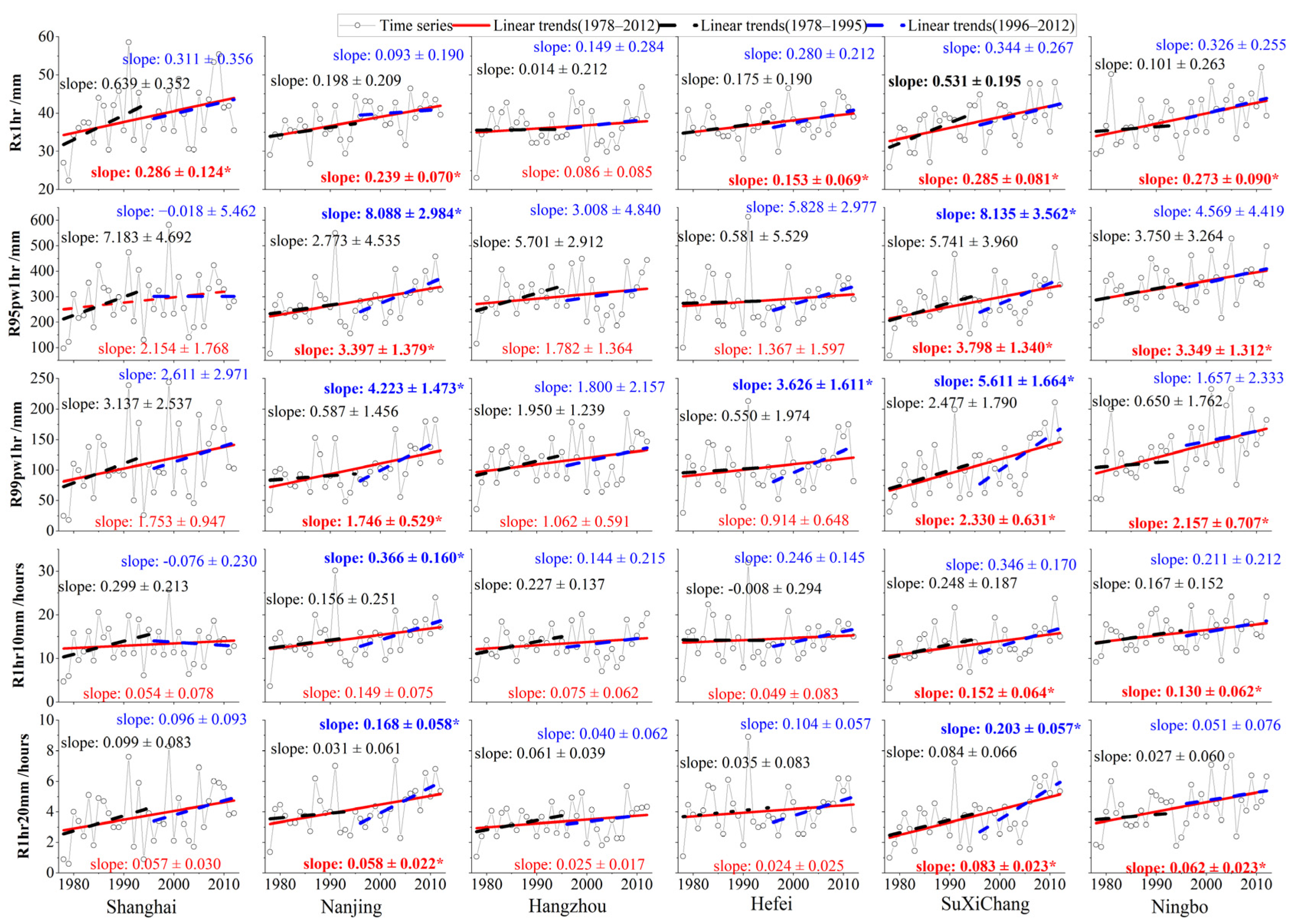
3.1. Changes in the EHP Across YRD
3.1.1. Temporal Variations in the EHP
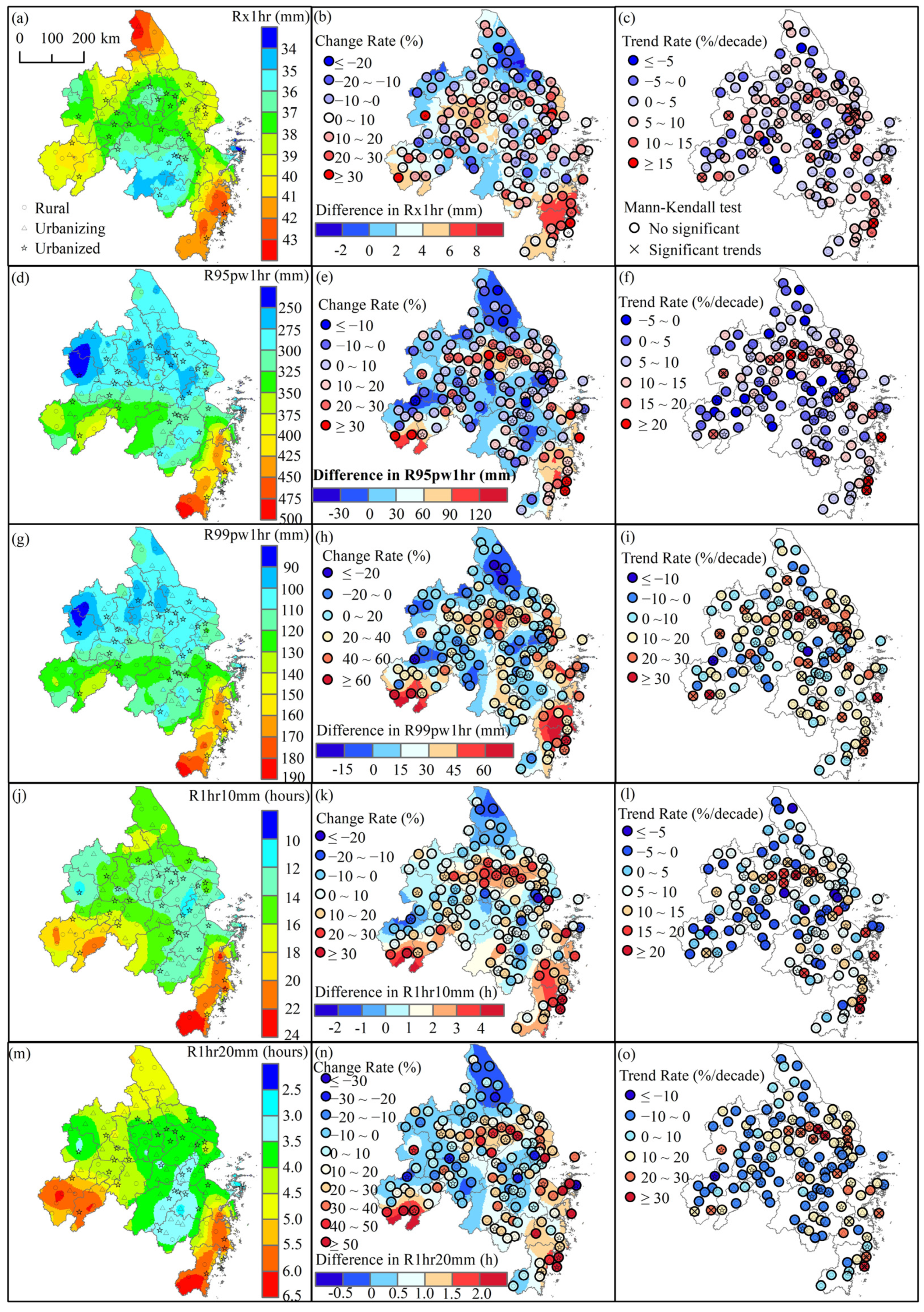
3.1.2. Spatial Patterns of the EHP
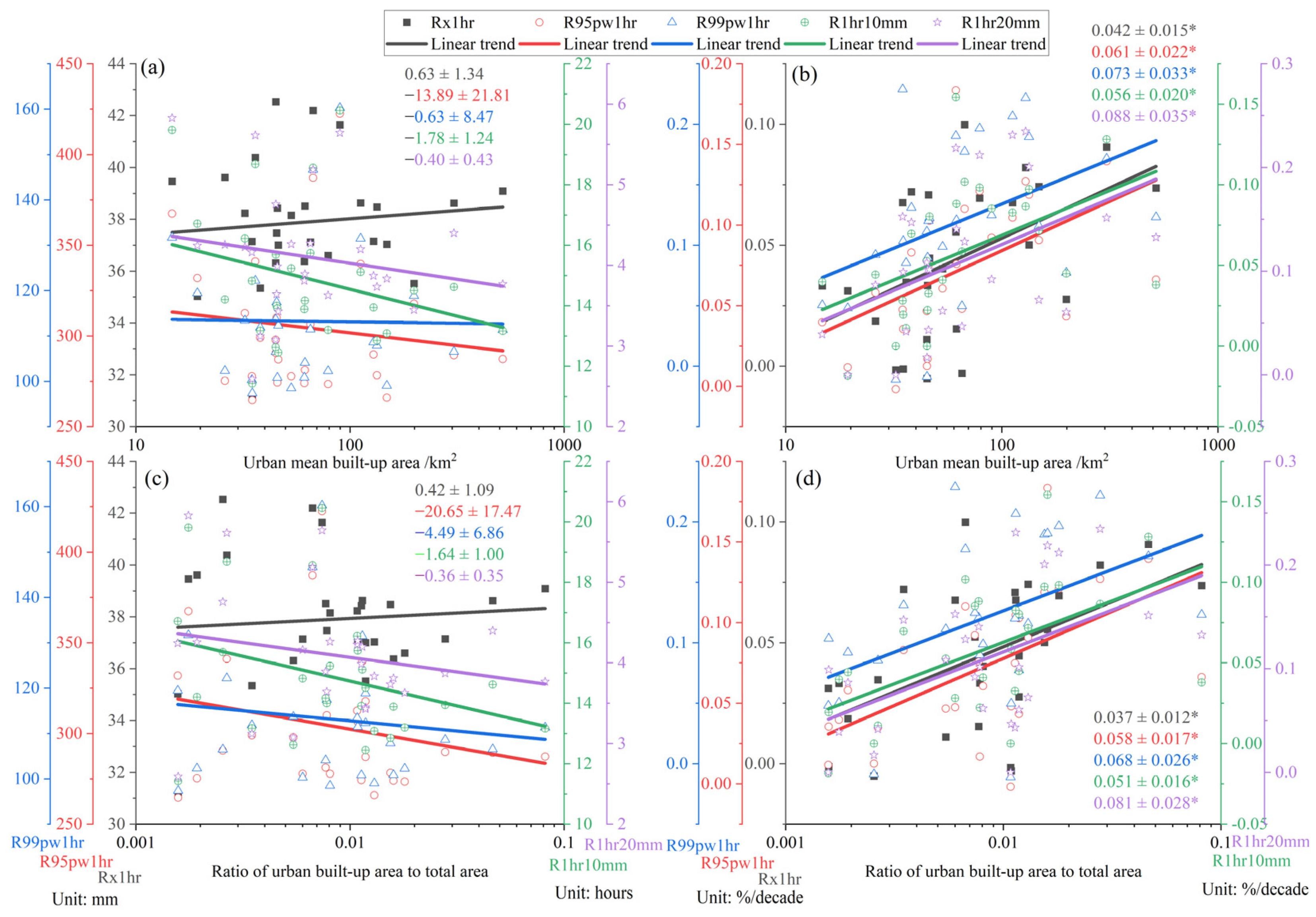
3.2. Relationship Between Urbanization Levels and Extreme Hourly Precipitation
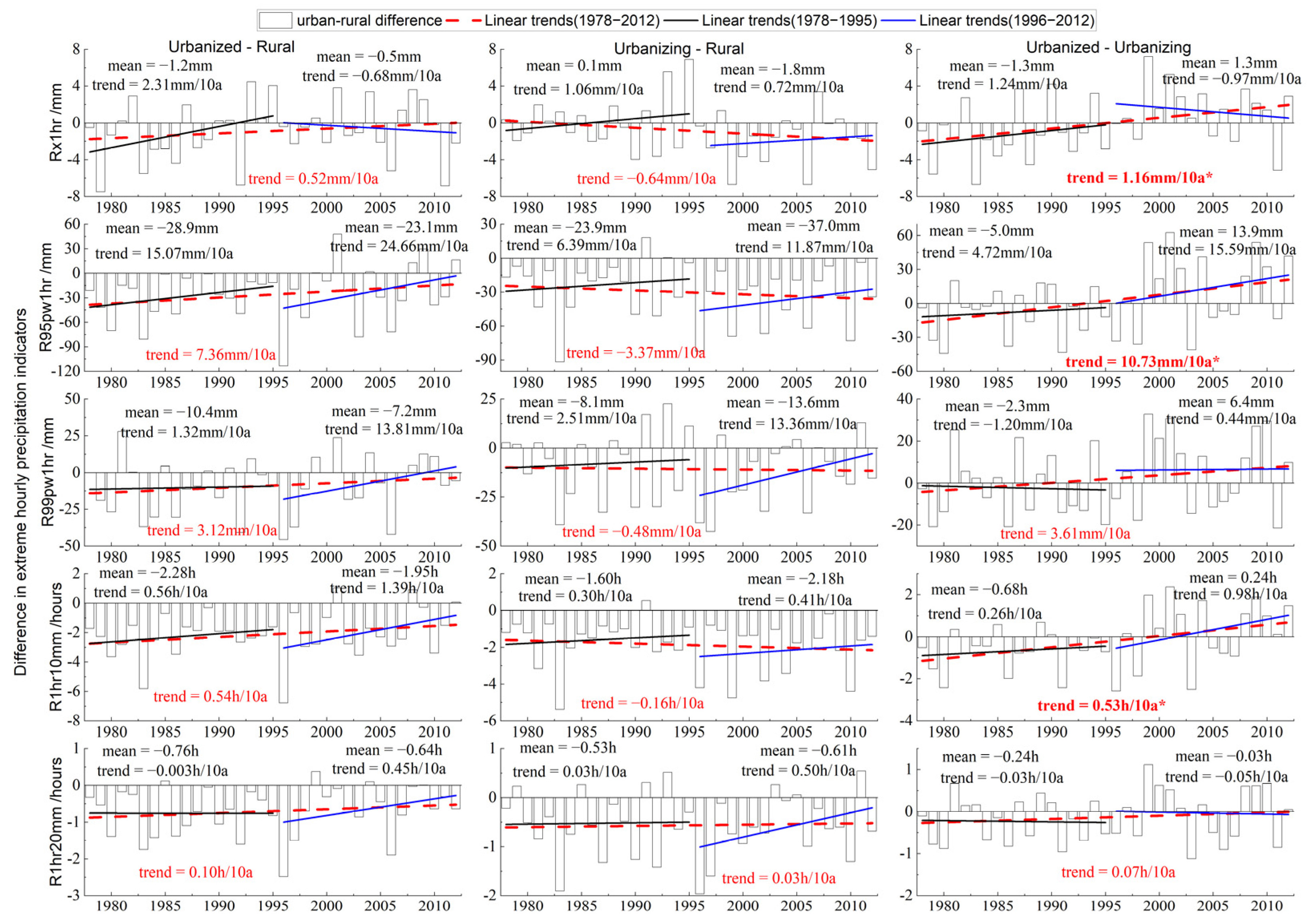
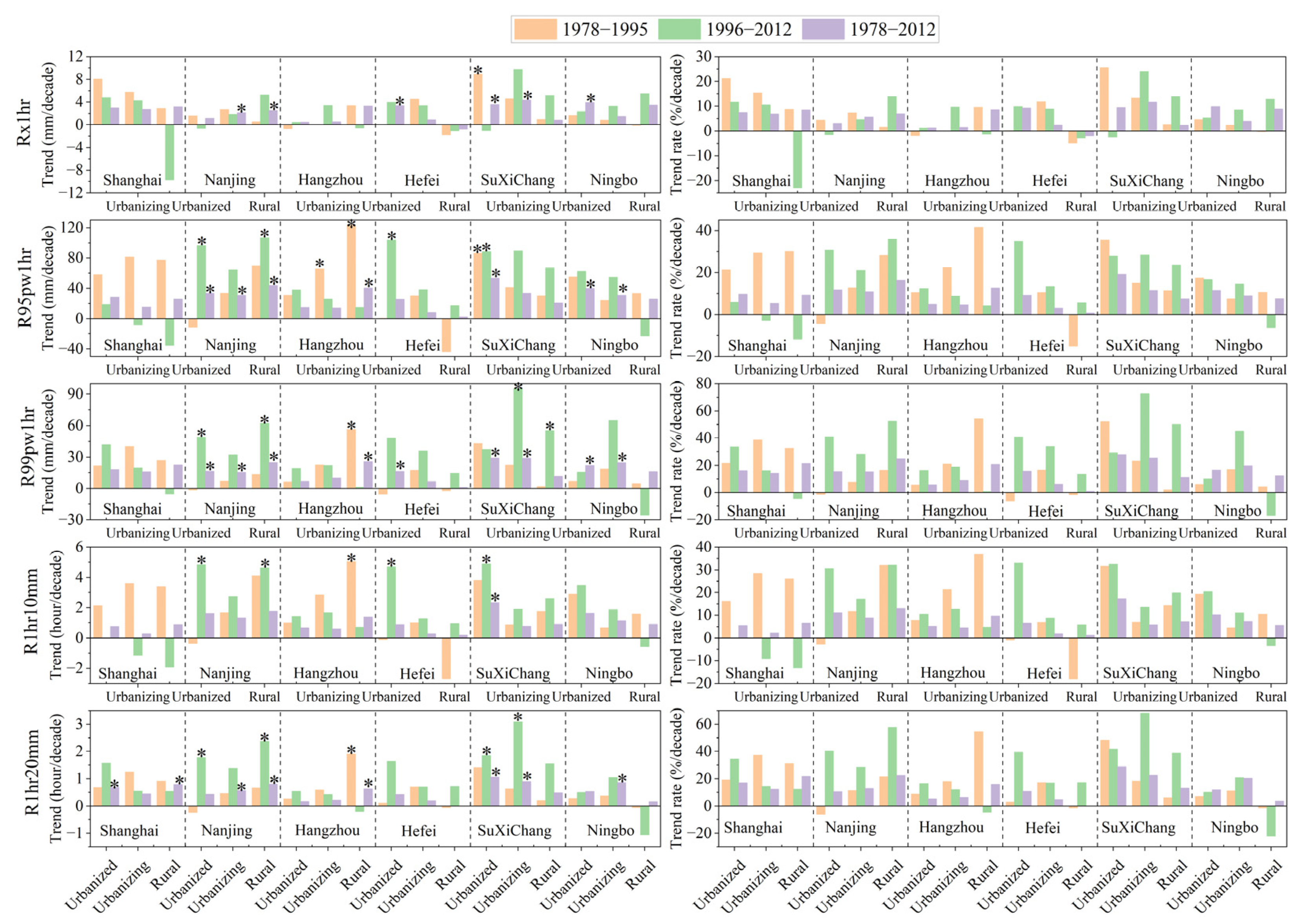
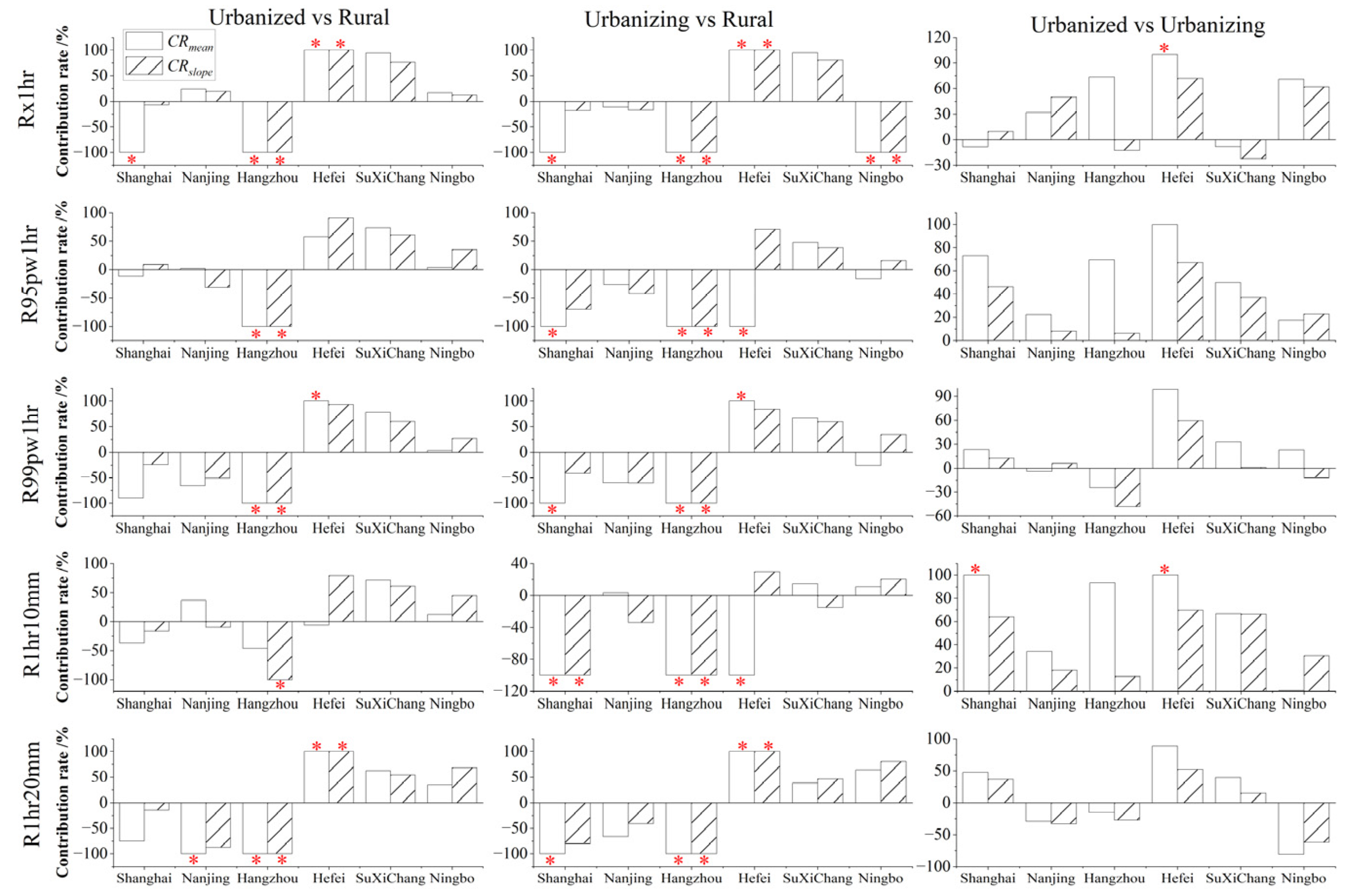
3.3. Impact of Urbanization on the Changes in Extreme Hourly Precipitation
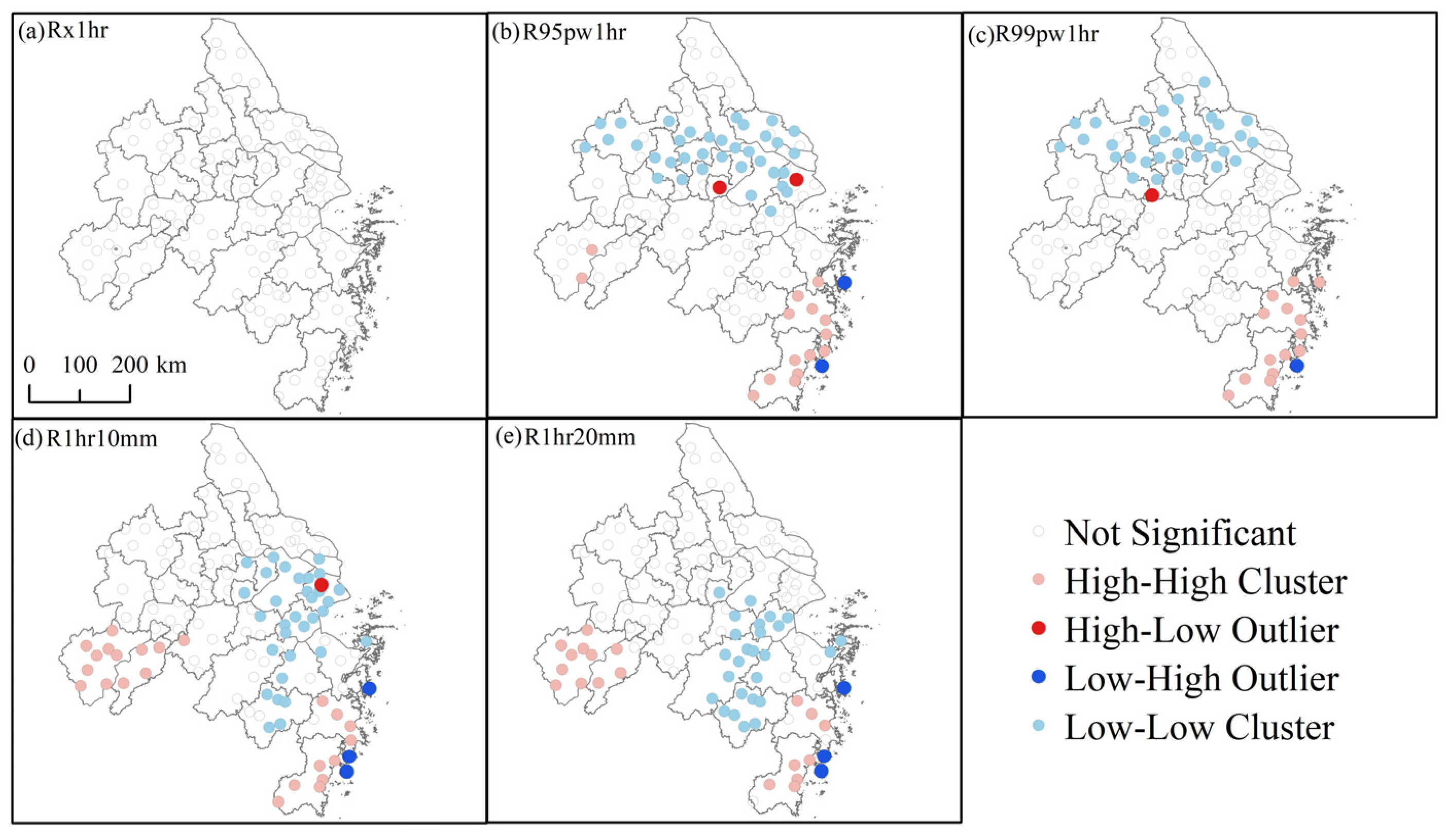
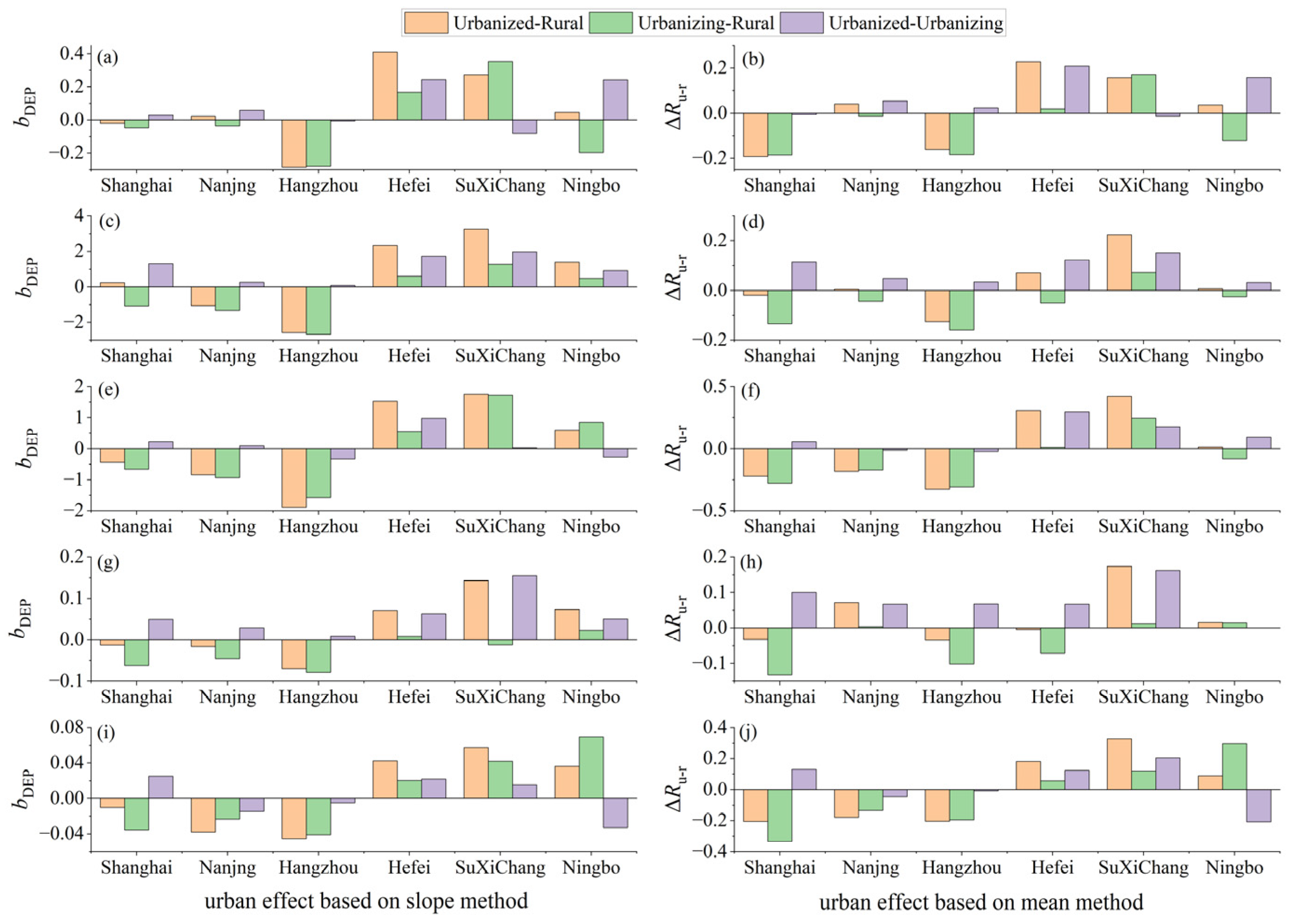
3.4. Spatial Heterogeneity of Urbanization Effects on Extreme Hourly Precipitation
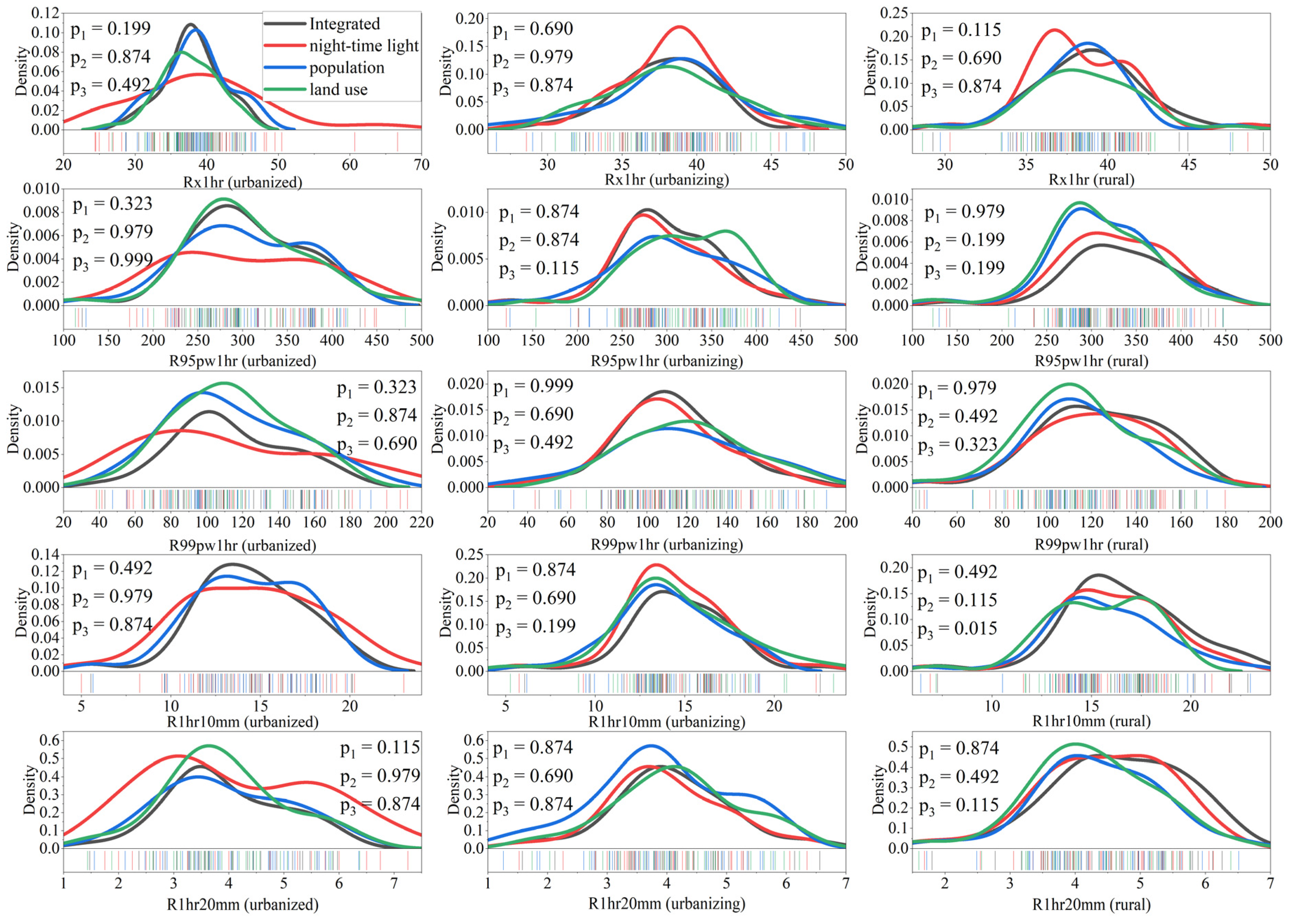
3.5. Uncertainty Analysis of Urbanization Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The YRD urban agglomeration shows a positive trend in all EHP indices during different periods for various types of stations, with higher increases in the urban areas and at the rapid urbanization stage. Spatially, the EHP decreases from the southeastern to the northwestern part of the YRD region, with similar patterns for each index during different periods.
- (2)
- Urbanization significantly enhances the EHP, showing a clear positive relationship. As urbanization levels increase, the frequency and intensity of the EHP are likely to rise. Besides, urbanization increases the positive differences in the EHP between urban and rural areas while decreasing the negative differences. Certainly, the results based on the mean and slope methods indicate that urbanization positively affects changes in the EHP for most cases across different urban–rural scenarios and periods. However, the contributions of urbanization are relatively limited, with most of them being less than 50%.
- (3)
- Urbanization effects and their contributions to the changes in the EHP vary across different sub-regions with obvious spatial heterogeneity. The positive effects are mainly found in the Hefei, SuXiChang, and Ningbo metropolitan areas, but the negative ones are dominantly observed in the Shanghai, Nanjing, and Hangzhou metropolitan areas. The contrasting results reveal that urbanization plays a complex role in the precipitation changes under changing environments.
- (4)
- The urban–rural classification methods directly affect the assessment results about urbanization effects and contributions to the changes in the EHP. Despite larger uncertainties in their results, most cases show positive effects of urbanization on the EHP with varying magnitudes in the urbanization’s contributions.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rummukainen, M. Climate change: Changing means and changing extremes. Clim. Change 2013, 121, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Meehl, G.A.; Parmesan, C.; Changnon, S.A.; Karl, T.R.; Mearns, L.O. Climate extremes: Observations, modeling, and impacts. Science 2000, 289, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.M.; Xu, N.T.; Zhang, J.Y.; He, R.M. Urban flooding in China: Current status, causes and challenges. Adv. Water Sci. 2024, 35, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Gao, X.C.; Zhou, J.J. A Study on the Evolution of Urban Underlying Surfaces and Extreme Rainfall in the Pearl River Delta. Water 2024, 16, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayat, H.; Evans, J.P.; Sherwood, S.C.; Soderholm, J. Intensification of subhourly heavy rainfall. Science 2022, 378, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, M.; Levermann, A.; Wenz, L. The effect of rainfall changes on economic production. Nature 2022, 601, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, A.W.R.; Macias-Fauria, M.; Long, P.R.; Benz, D.; Willis, K.J. Sensitivity of global terrestrial ecosystems to climate variability. Nature 2016, 531, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhan, C.S.; Liu, C.Z. Review for impacts of climate change and human activities on water cycle. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 44, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Kong, F.Z.; Wang, G.Q.; He, R.M.; Zhu, K. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of precipitation extremes in Beijing. Adv. Water Sci. 2017, 28, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V.; Yang, H.; Durre, I.; Vose, R.; Dunn, R.J.H.; Willett, K.M.; Aguilar, E.; Brunet, M.; Caesar, J.; et al. Updated analyses of temperature and precipitation extreme indices since the beginning of the twentieth century: The HadEX2 dataset. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 2098–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H. Climate change impact on flood and extreme precipitation increases with water availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.N.; Wei, W.; Fang, G.H.; Duan, W.L. The increase in extreme precipitation and its proportion over global land. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Huang, Q.X.; Muttarak, R.; Fang, J.Y.; Liu, T.; He, C.Y.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhu, L. Updating global urbanization projections under the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Niyogi, D.; Tewari, M.; Aliaga, D.; Chen, F.; Tian, F.Q.; Ni, G.H. Contrasting impacts of urban forms on the future thermal environment: Example of Beijing metropolitan area. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 034018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Doan, Q.V.; Xu, Y.P. Exploring the effect of urbanization on hourly extreme rainfall over Yangtze River Delta of China. Urban. Clim. 2021, 36, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Smith, J.; Niyogi, D. Urban Impacts on Extreme Monsoon Rainfall and Flooding in Complex Terrain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 5918–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Zheng, G.; Smith, J.; Niyogi, D. Urban development pattern’s influence on extreme rainfall occurrences. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gao, Z.Q.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, Y. Modeling the impact of urbanization on the local and regional climate in Yangtze River Delta, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 102, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Chakraborty, T.C.; Li, J.F.; Li, D.; He, C.L.; Sarangi, C.; Chen, F.; Yang, X.C.; Leung, L.R. Urbanization Impact on Regional Climate and Extreme Weather: Current Understanding, Uncertainties, and Future Research Directions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.Y.; Jiang, S.J.; Mao, Y.N.; Wu, G.C. Urbanization reshapes extreme precipitation metrics in typical urban agglomerations of Eastern China. Atmos. Res. 2024, 300, 107253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, D.; Lei, M.; Kishtawal, C.; Schmid, P.; Shepherd, M. Urbanization Impacts on the Summer Heavy Rainfall Climatology over the Eastern United States. Earth Interact. 2017, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.W.; Luo, Y.L.; Chen, F.; Wong, W.K. Observed Link of Extreme Hourly Precipitation Changes to Urbanization over Coastal South China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 1799–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.D.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.; Singh, V.P.; Shi, P.J.; Song, C.Q. Impact of urbanization on hourly precipitation in Beijing, China: Spatiotemporal patterns and causes. Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 172, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golroudbary, V.R.; Zeng, Y.J.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Su, Z.B. Response of Extreme Precipitation to Urbanization over the Netherlands. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mathew, M.; Devanand, A.; Karmakar, S.; Niyogi, D. Increased Spatial Variability and Intensification of Extreme Monsoon Rainfall due to Urbanization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.L.; Xu, G.R.; Wan, R.; Wang, X.F. Characteristics of summer hourly precipitation under different urbanization background in central China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.W.; Wang, D.S.; Ziegler, A.D.; Liu, X.P.; Zeng, H.; Xu, Z.B.; Zeng, Z.Z. Influence of urbanization on hourly extreme precipitation over China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 044010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.E.; Niyogi, D. Impact of city size on precipitation-modifying potential. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5263–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Yang, J.C.; Yang, L.; Niyogi, D. Impacts of City Shape on Rainfall in Inland and Coastal Environments. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2022EF002654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, M.; Oudin, L.; Bastin, S. Urban effects on precipitation: Do the diversity of research strategies and urban characteristics preclude general conclusions? Urban. Clim. 2023, 51, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.T.; Hu, L.Q.; Xue, L.L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.S. Urban effects on local cloud patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216765120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.G.; Chen, F.; Li, Q.C.; Fan, S.Y. Impacts of Urban Processes and Urbanization on Summer Precipitation: A Case Study of Heavy Rainfall in Beijing on 1 August 2006. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 806–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; AghaKouchak, A.; Sen Roy, S.; Xuan, Y.Q.; Wang, G.Q.; He, R.M.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, C.S. Rapid urbanization and changes in spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation in Beijing metropolitan area. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 11250–11271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhu, L.F.; Zhu, Y. Urban heat island and boundary layer structures under hot weather synoptic conditions: A case study of Suzhou City, China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.D.; Oke, T.R. Local Climate Zones for Urban Temperature Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Li, X.G.; Tian, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, Q.Y.; Yang, M.Q.; Wang, S.B. A novel evaluation method-based effect analysis of urbanization on extreme precipitation in Guangxi, South China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 5957–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Leung, L.R.; Zhao, N.Z.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Hu, K.J.; Liu, X.P.; Chen, B.D. Contribution of urbanization to the increase of extreme heat events in an urban agglomeration in east China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6940–6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.L.; Luo, Y.L.; Zhang, D.L.; Wu, M.W. Urbanization Enhanced Summertime Extreme Hourly Precipitation over the Yangtze River Delta. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 5809–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.Y.; Li, J.; Ren, Y.Y.; Chu, Z.Y.; Zhang, A.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, T. An Integrated Procedure to Determine a Reference Station Network for Evaluating and Adjusting Urban Bias in Surface Air Temperature Data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2015, 54, 1248–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.M.; Mo, Y.C.; Xuan, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.J.; Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zou, X.J. Impacts of urbanization on precipitation patterns in the greater Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region in northern China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 014042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.G.; Yu, Z.H.; Sun, X.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Q.; Han, L.F.; Xu, Y.P. Urbanization effects on intensifying extreme precipitation in the rapidly urbanized Tai Lake Plain in East China. Urban. Clim. 2023, 47, 101399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.X.; Luo, Z.J.; Zong, W.; Hua, J. Impacts of Urbanization on Variations of Extreme Precipitation over the Yangtze River Delta. Water 2021, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Qin, D.J.; Xiao, M.Z.; Lin, K.R. Urbanization Enhances Shorter-Duration Precipitation Intensity in the Yangtze River Delta Region. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2025, 130, e2024JD043300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.L.; Gao, X.Q.; Zhang, W. Evolution characteristics of the precipitation in the Yangtze River delta based on the probability density. Chin. Phys. 2005, 14, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.F.; Xu, Y.P.; Pan, G.B.; Deng, X.J.; Hu, C.S.; Xu, H.L.; Shi, H.Y. Changing properties of precipitation extremes in the urban areas, Yangtze River Delta, China, during 1957–2013. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.M.; Qi, J.C.; Zou, X.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, C.S. Potential Effects of Urbanization on Precipitation Extremes in the Pearl River Delta Region, China. Water 2022, 14, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lin, K.R.; Xiao, M.Z.; Zhou, X.D.; Zhao, G.; Yamazaki, D. How Does Heavy Precipitation of Varying Durations Respond to Urbanization in China? Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.G.; Pan, X.; Xu, N.; Meng, X.J.; Li, Z.Q.; Guluzade, R.; Dai, Y.; Yang, Y.B. Does Urbanization Exacerbate Asymmetrical Changes in Precipitation at Divergent Time Scales in China? Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.P.; Chen, S.F.; Ding, W.Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, P. Fine-scale characteristics of hourly intense rainfall in pre-summer and post-summer rainy seasons in Guangdong Province over coastal South China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 150, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchens, N.M.; Brooks, H.E.; Schumacher, R.S. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Heavy Hourly Rainfall in the United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 4564–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.G.; Yang, Y.B.; Ali, H.; Xie, J.K.; Dai, Y.; LI, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.W.; Pan, X.; Fowler, H. Assessing the consistent and divergent impacts of urbanization on heavy rainfall in Chinese urban agglomerations. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.F.; Wu, X.S.; Villarini, G.; Wang, Z.L.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Lai, C.G. Stronger exacerbation of extreme rainfall at the hourly than daily scale by urbanization in a warming climate. J. Hydrol. 2024, 633, 131025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, S.; Cao, L.J.; Feng, Y. Homogenization of Chinese daily surface air temperatures and analysis of trends in the extreme temperature indices. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 9708–9720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.C.; Song, X.M. Spatiotemporal changes of extreme hourly precipitation in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration during 1978–2012. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2023, 54, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.W.; Qu, Y.G.; Tao, S.W.; Hu, B.K. The application of quality control procedures for real-time data from automatic weather stations. Meteorol. Mon. 2008, 34, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.J.; Zhu, Y.N.; Tang, G.L.; Yuan, F.; Yan, Z.W. Climatic warming in China according to a homogenized data set from 2419 stations. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 4384–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Yu, Y.; Zou, F.L.; Xu, Y. Quality detection of surface historical basic meteorological data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2012, 23, 739–747. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Gong, X.; Shi, Y.; Shi, M.Y.; Yang, D.; Fan, S.H.; Zhou, X.D.; et al. Development of China Ground Climate Normal Value Dataset from 1991 to 2020. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 48, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J.J.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Z.J. Quality assessment of hourly merged precipitation product over China. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 36, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.F.; Yu, X.Q.; Xu, Y.P.; Deng, X.J.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.W.; Lv, D.Q.; Xiao, M. Enhanced Summertime Surface Warming Effects of Long-Term Urbanization in a Humid Urban Agglomeration in China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Bao, H.J.; Zhang, H.D. Climatology and changes in hourly precipitation extremes over China during 1970-2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.S.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, X.G. Spatial and diurnal Diurnal Variations of Summer Hourly Rainfall Over Three Super City Clusters in Eastern China and Their Possible Link to the Urbanization. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2019, 124, 5445–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V.; Fowler, H.J.; Bador, M.; Behrangi, A.; Donat, M.G.; Dunn, R.; Funk, C.; Goldie, J.; Lewis, E.; Rogé, M.; et al. On the use of indices to study extreme precipitation on sub-daily and daily timescales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.L.; Yu, D.L. China’s New Urbanization: Development Paths, Blueprints and Patterns; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.N.; Connor, D.S.; Stuhlmacher, M.; Peng, J.; Yurner, B.L., II. More urbanization, more polarization: Evidence from two decades of urban expansion in China. npj Urban. Sustain. 2024, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Lin, H.X.; Chen, Y.Q.; Blaschke, T.; Luo, L.W.; Xu, Z.H.; Hu, Y.N.; Zhao, M.Y.; Wu, J.S. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban agglomerations in China during 2000–2012: A nighttime light approach. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.L.; Liu, X.P.; Li, D.; Luo, M.; Wang, D.G.; Wang, S.J.; Baldwin, J.; Lin, L.J.; Li, X.; Feng, K.S.; et al. Stronger Contributions of Urbanization to Heat Wave Trends in Wet Climates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11310–11317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.F.; Wang, L.H.; Chen, H.M.; Xu, Y.P.; Sun, F.P.; Reed, K.; Deng, X.J.; Li, W.K. Impacts of Long-Term Urbanization on Summer Rainfall Climatology in Yangtze River Delta Agglomeration of China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briciu, A.E.; Mihaila, D.; Graur, A.; Oprea, D.I.; Prisacariu, A.; Bistricean, P.I. Changes in the Water Temperature of Rivers Impacted by the Urban Heat Island: Case Study of Suceava City. Water 2020, 12, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.C.; Traver, R. Clogging Impacts on Distribution Pipe Delivery of Street Runoff to an Infiltration Bed. Water 2018, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Liu, S.G.; Zhou, Z.Z. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of Short-Duration Extreme Rainfall Events in Megacities in China. Water 2020, 12, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.L.; Gao, X.C.; Yang, Z.Y.; Xu, T.Y.; Feng, J. Variation characteristics and the impact of urbanization of extreme precipitation in Shanghai. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.X.; Yang, Z.L.; Shepherd, M.; Niyogi, D. Global scale assessment of urban precipitation anomalies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2311496121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Lau, N.C. Urban Expansion and Drying Climate in an Urban Agglomeration of East China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6868–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, M.; Liang, X.D.; Xia, R.D.; Gao, Y.Y.; Gao, X.Y.; Yin, J.F. On the Influences of Urbanization on the Extreme Rainfall over Zhengzhou on 20 July 2021: A Convection-Permitting Ensemble Modeling Study. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Wang, N.; Chen, J.Y.; He, T.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.Y.; Han, D.R. Urbanization accelerates urban warming by changing wind speed: Evidence from China based on 2421 meteorological stations from 1978 to 2017. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 102, 107189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Villarini, G.; Vecchi, G.A.; Smith, J.A. Urbanization exacerbated the rainfall and flooding caused by hurricane Harvey in Houston. Nature 2018, 563, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Zou, L.; Xia, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, F.Y. Impact assessment of climate change and urbanization on the nonstationarity of extreme precipitation: A case study in an urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze river. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.P.; Li, S.; Zhao, K.; Wang, T.J.; Xie, M.; Zhuang, B.L.; Li, M.M.; Liu, C. Effects of anthropogenic aerosols and sea salt aerosols during a summer precipitation event in the Yangtze River Delta. Atmos. Res. 2023, 284, 106584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, X.T.; Li, H.Q.; Yue, Q.; Feng, L.; Qu, J.X. Extent of aerosol effect on the precipitation of squall lines: A case study in South China. Atmos. Res. 2023, 292, 106886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.M.; Jiang, B.L.; Shen, X.D.A.; Lin, W.S.; Chen, J.W. Microphysics effects of anthropogenic aerosols on urban heavy precipitation over the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.C.; Yuan, T.A.; Cao, J.H.; Wang, Z.K.; Zhi, R.; Hu, Z.Y.; Huang, J.P. The influence of dust on extreme precipitation at a large city in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.N.; Wang, W.W.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.M. Impacts of urbanization on extreme precipitation in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area. Urban. Clim. 2021, 38, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.; Watson, J.E.M.; Salazar, A.; Thatcher, M.; McAlpine, C.A. The impact of urbanization and climate change on urban temperatures: A systematic review. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.J.; Gao, T.; Luo, M.; Ge, E.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Ning, G.C. Contribution of urbanization to the changes in extreme climate events in urban agglomerations across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Index | Method | Definition | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rx1hr | Maximum value | Maximum 1 h precipitation | mm |
| R95pw1hr | Percentile-based threshold | Total precipitation for hourly precipitation greater than the 95th percentile of the hourly precipitation series | mm |
| R99pw1hr | Total precipitation for hourly precipitation greater than the 99th percentile of the hourly precipitation series | mm | |
| R1hr10mm | Fixed threshold | Number of hours with hourly precipitation greater than 10 mm | hours |
| R1hr20mm | Number of hours with hourly precipitation greater than 20 mm | hours |
| Rx1hr | R95pw1hr | R99pw1hr | R1hr10mm | R1hr20mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full period | 0.406 | 0.048 * | 0.172 | 0.004 * | 0.005 * |
| First part | 0.423 | 0.324 | 0.508 | 0.121 | 0.106 |
| Second part | 0.181 | 0.066 | 0.214 | 0.012 * | 0.026 * |
| Mean | Standard Deviation | CV | Global Moran’s Index | Z-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rx1hr | 38.28 | 3.36 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 6.00 |
| R95pw1hr | 309.46 | 48.53 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 10.08 |
| R99pw1hr | 115.42 | 18.60 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 9.75 |
| R1hr10mm | 15.12 | 2.86 | 0.19 | 0.52 | 10.94 |
| R1hr20mm | 4.19 | 1.02 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 9.63 |
| Urban Mean Built-Up Area | Ratio of Urban Built-up Area to Total Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean values in 1978–2012 | Rx1hr | 0.102 | −0.056 |
| R95pw1hr | −0.090 | −0.297 | |
| R99pw1hr | −0.034 | −0.203 | |
| R1hr10mm | −0.237 | −0.374 | |
| R1hr20mm | −0.140 | −0.267 | |
| Change rates per decade | Rx1hr | 0.523 * | 0.540 * |
| R95pw1hr | 0.659 * | 0.676 * | |
| R99pw1hr | 0.473 * | 0.508 * | |
| R1hr10mm | 0.640 * | 0.582 * | |
| R1hr20mm | 0.487 * | 0.528 * |
| Contribution Rate | CRmean/% | CRslope/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1978–1995 | 1996–2012 | 1978–2012 | |||
| Scenario I: urbanized–rural | Rx1hr | 18.21 | 79.31 | −31.82 | 20.00 |
| R95pw1hr | 25.74 | 28.24 | 47.08 | 26.09 | |
| R99pw1hr | 20.16 | 12.73 | 42.86 | 18.67 | |
| R1hr10mm | 31.27 | 35.29 | 53.85 | 33.33 | |
| R1hr20mm | 28.05 | −0.75 | 40.00 | 20.00 | |
| Scenario II: urbanizing–rural | Rx1hr | −109.67 | 64.71 | 9.38 | −46.15 |
| R95pw1hr | −48.66 | 18.50 | 27.87 | −17.55 | |
| R99pw1hr | −20.98 | 21.31 | 41.96 | −3.85 | |
| R1hr10mm | −58.64 | 21.43 | 25.00 | −28.57 | |
| R1hr20mm | 10.56 | 7.50 | 45.45 | 7.50 | |
| Scenario III: urbanized–urbanizing | Rx1hr | 60.99 | 41.38 | −31.82 | 48.00 |
| R95pw1hr | 50.04 | 11.96 | 26.63 | 37.12 | |
| R99pw1hr | 34.01 | −10.91 | 1.55 | 21.69 | |
| R1hr10mm | 56.68 | 17.65 | 38.46 | 41.67 | |
| R1hr20mm | 19.55 | −7.50 | −5.00 | 20.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Wei, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Asymmetric Impacts of Urbanization on Extreme Hourly Precipitation Across the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration During 1978–2012. Water 2025, 17, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101531
Song X, Wei J, Qi J, Zhang J, Wang X. Asymmetric Impacts of Urbanization on Extreme Hourly Precipitation Across the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration During 1978–2012. Water. 2025; 17(10):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101531
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xiaomeng, Jinjiang Wei, Jiachen Qi, Jianyun Zhang, and Xiaojun Wang. 2025. "Asymmetric Impacts of Urbanization on Extreme Hourly Precipitation Across the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration During 1978–2012" Water 17, no. 10: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101531
APA StyleSong, X., Wei, J., Qi, J., Zhang, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Asymmetric Impacts of Urbanization on Extreme Hourly Precipitation Across the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration During 1978–2012. Water, 17(10), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101531








