Valorization of Golden Mussel Shells for Sustainable Phosphorus Recovery in Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. GMS Collection and Preparation
2.2. Wastewater Collection
2.3. GMS Characterization
2.4. Batch P Recovery Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of the Shells
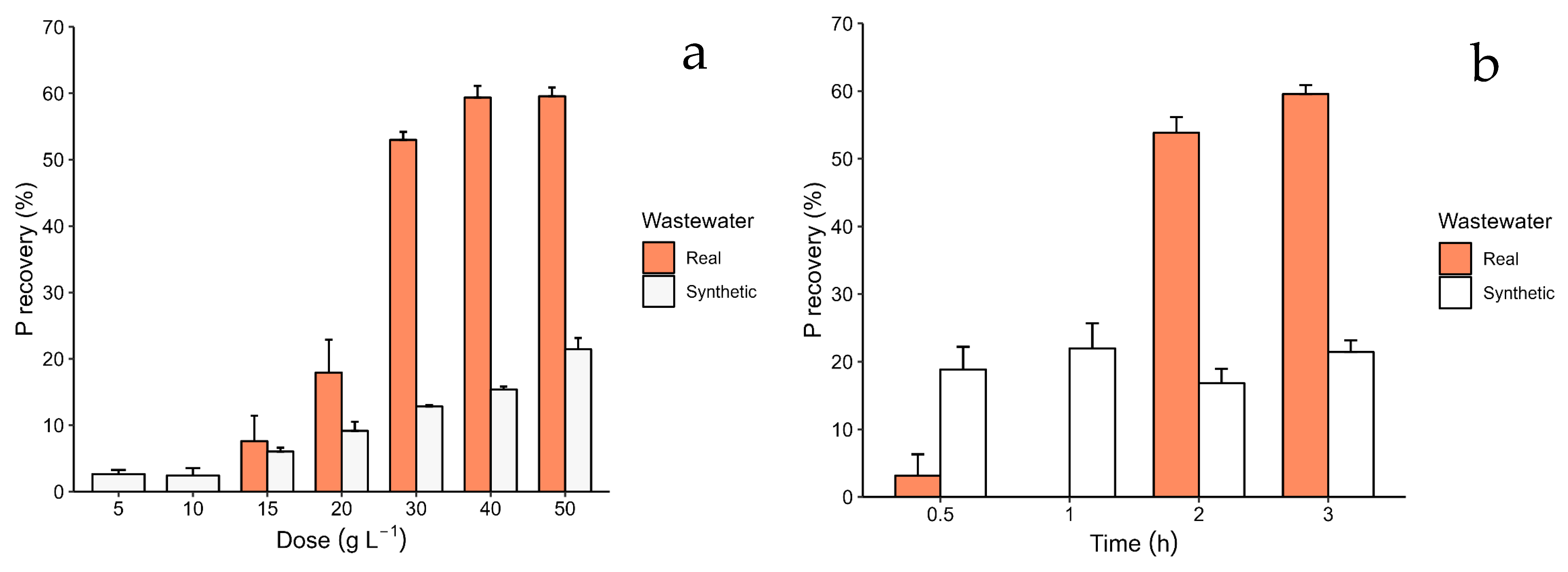
3.2. Recovery Kinetics, and Efficiency
3.3. Recovery Isotherms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boltovskoy, D.; Paolucci, E.; MacIsaac, H.J.; Zhan, A.; Xia, Z.; Correa, N. What we know and don’t know about the invasive golden mussel Limnoperna fortune. Hydrobiologia 2025, 852, 1275–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessotto, M.A.; Nogueira, M.G. More than two decades after the introduction of Limnoperna fortunei (Dunker 1857) in La Plata Basin. Braz. J. Biol. 2018, 78, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marengoni, N.G.; Klosowski, E.S.; Oliveira, K.P.; Chambo, A.P.S.; Gonçalves Junior, A.C. Bioacumulação de metais pesados e nutrientes no mexilhão dourado do reservatório da usina hidrelétrica de Itaipu Binacional (Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and nutrients in the golden mussel of the reservoir of the Itaipu Binational Hydroelectric power plant). Química Nova 2013, 36, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Vieira, J. Space-time variation of the relative abundance of Limnoperna fortunei in deep zones of São Gonçalo Channel, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Iheringia Série Zool. 2012, 102, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, X.; Hou, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, E.; Chu, W. Limnoperna fortunei as an invasive biofouling bivalve species in freshwater: A review of its occurrence, biological traits, risks, and control strategies. AQUA Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2022, 71, 1364–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.R.; Soares, B.M.; Vieira, J.P.; Mai, A.C.G.; Picoloto, R.S.; Muller, E.I.; Flores, E.M.M.; Duarte, F.A. Assessment of inorganic contaminants in golden mussel (Limnoperna fortunei) in Southern Brazil. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tao, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, A. Real-Time Quantification of Activated Sludge Concentration and Viscosity through Deep Learning of Microscopic Images. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 24, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Gu, C. Aerobic Granular Sludge Treating Tannery Wastewater and Particle Size Control. AIP Adv. 2025, 15, 25128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.H.; Liom, S.L.; Zainudin, A.H.; Huzil, M.A.I.; Yaacob, M.S.S.; Salim, N.A.A.; Kaamin, M.; Talaiekhozani, A. Waste mussel shells as an adsorbent for phosphate removal in solution: Kinetic and isotherm model. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2022, 15, 25–36. Available online: https://ijneam.unimap.edu.my/images/PDF/ISSTE2022/Vol_15_SI_March_2022_25-36.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Cataldo, D.; O’Farrell, I.; Paolucci, E.; Sylvester, F.; Boltovskoy, D. Impact of the invasive golden mussel (Limnoperna fortunei) on phytoplankton and nutrient cycling. Aquat. Invasions 2012, 7, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.D.; Chottitisupawong, T.; Vu, H.H.T.; Ahn, J.W.; Kim, G.M. Removal of phosphorus from an aqueous solution by nanocalcium hydroxide derived from waste bivalve seashells: Mechanism and kinetics. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12290–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, D.K.; Ali, M.A.; Kim, P.J. Effects of oyster shell on soil chemical and biological properties and cabbage productivity as a liming materials. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.H.; Polprasert, C. Roles of oyster shells in an integrated constructed wetland system designed for P removal. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Lopes, D.V.; Alvarenga, P.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M.; Quina, M.J. Phosphorus removal from urban wastewater through adsorption using biogenic calcium carbonate. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroneze, M.M.; Zepka, L.Q.; Vieira, J.G.; Queiroz, M.I.; Jacob-Lopes, E. A tecnologia de remoção de fósforo: Gerenciamento do elemento em resíduos industriais (Phosphorus removal technology: Management of the element in industrial waste). Rev. Ambiente Água 2014, 9, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nobaharan, K.; Novair, S.B.; Lajayer, B.A.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Phosphorus removal from wastewater: The potential use of biochar and the key controlling factors. Water 2021, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.O.; Aturagaba, G.; Ntale, M.; Nyakairu, G.W. A review of adsorption techniques for removal of phosphates from wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 3113–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Yuan, J.; Li, Q.; Qi, L.; Wang, H. Performance and mechanism of phosphorus adsorption removal from wastewater by a Ce-Zr-Al composite adsorbent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 79258–79268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.C.; Matos, M.T.; Ribeiro, I.C.A.; Fia, R.; Matos, A.T. Sewage phosphorus removal using hen eggshells through different contact systems. Eng. Na Agric. 2020, 28, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeem, A.; Mizi, F.; Ali, M.F.; Shariffuddin, J.H. Utilization of cockle shell powder as an adsorbent to remove phosphorus-containing wastewater. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Li, Y.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, H. Effective adsorption and removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions and eutrophic water by Fe-based MOFs of MIL-101. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, M. Effective removal of phosphorus from high phosphorus steel slag using carbonized rice husk. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, M.T.; Nguyen, L.N.; Johir, M.A.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Skidmore, C.; Fontana, A.; Galway, B.; Bustamante, H.; Nghiem, L.D. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solution by steel making slag—Mechanisms and performance optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.G.; Franco, D.M.; Siqueira, J.C.; Ribeiro, I.C.A.; Crippa, R.A.; Fia, R.; Matos, M.P. Sewage phosphorus recovery through sachets loaded with water treatment plant sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradelo, R.; Conde-Cid, M.; Cutillas-Barreiro, L.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Phosphorus removal from wastewater using mussel shell: Investigation on retention mechanisms. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, S.; Gaffney, P.P.J.; Bremner, B.; Sekulic, M.T.; Maletic, S.; Gibb, S.W.; Taggart, M.A. Enhanced phosphate removal and potential recovery from wastewater by thermo-chemically calcinated shell adsorbents. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.A.A.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Fulazzaky, M.A.; Puteh, M.H.; Abdullah, N.H.; Nuid, M.; Lazim, Z.M.; Ahmad, N. A two-stage batch system for phosphate removal from wastewater by iron-coated waste mussel shell to assess the optimum adsorbent dosage. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2022, 44, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.A.A.; Fulazzaky, M.A.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Puteh, M.H.; Khamidun, M.H.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Abdullah, N.H.; Ahmad, N.; Lazim, Z.M.; Nuid, M. Phosphate removal from wastewater in batch system using waste mussel shell. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 11473–11486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, S. A golden menace. Science 2021, 374, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welz, B.; Sperling, M. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; 965p. [Google Scholar]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA/AWWA/WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; 1496p. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, A.T.; Costa Neto, A.M.; Martins, M.A.; Matos, M.P. Isoterma de adsorção de fósforo em pó coletado no sistema de tratamento de efluentes atmosféricos gerados em indústria siderúrgica (Sorption isotherm of phosphorus powder collected in exhaust treatmentsystem of steel industry). Eng. Na Agric. 2012, 20, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.T. Manual de Análise de Resíduos Sólidos e Águas Residuárias, 1st ed.; UFV: Viçosa, Brazil, 2015; 23p. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, A.T. Qualidade do Meio Físico Ambiental: Práticas de Laboratório, 1st ed.; UFV: Viçosa, Brazil, 2012; 21p. [Google Scholar]
- Monaco, P.A.V.; Matos, A.T.; Eustáquio Júnior, V.; Ribeiro, I.C.A.; Teixeira, D.L. Utilização do farelo de conchas de vôngole na adsorção de fósforo e como corretivo da acidez do solo (Utilization of ground clam shells in the adsorption of phosphorus and for correction of soil acidity). Eng. Agrícola 2012, 32, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baty, F.; Ritz, C.; Charles, S.; Brutsche, M.; Flandrois, J.-P.; Delignette-Muller, M.-L. A toolbox for nonlinear regression in R: The package nlstools. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 66, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, C.V.; von Sperling, M.; Fernandes, F. Sludge Treatment and Disposal, 1st ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007; Available online: http://iwaponline.com/ebooks/book-pdf/1984/wio9781780402130.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2024).
- Monicelli, F.; Cunha, K.P.V.; Araújo, F.; Becker, V. Phosphorus sorption potential of natural adsorbent materials from a Brazil semiarid region to control eutrophication. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2021, 33, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, D.B.P. The Use of Golden Mussel (Limnoperna Fortunei Dunker, 1857) Ground Residue as a Soil Acidity Neutralizing Material and Plant Nutrient Source. Master’s Dissertation, Soil Science, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2009; 145p. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/handle/10183/17698 (accessed on 18 February 2024). (In Portuguese).
- Matos, M.P.; von Sperling, M.; Matos, A.T.; Miranda, S.T.; Souza, T.D.; Costa, L.M. Key factors in the clogging process of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands receiving anaerobically treated sewage. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besen, M.A.; Marengoni, N.G. Bioaccumulation of metals and evaluation of golden mussels encrusted on different screens of net cages. Bol. Do Inst. Pesca 2021, 47, e624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazulha, V.; Mansur, M.C.D.; Cybis, L.F.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Feeding behavior of the invasive bivalve Limnoperna fortunei (Dunker, 1857) under exposure to toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa. Braz. J. Biol. 2012, 72, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Babatunde, A.O.; Wang, L.; Ren, Y.X.; Han, Y. Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption on dewatered alum sludge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C. Phosphate removal from wastewaters by a naturally occurring, calcium-rich sepiolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 198, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Qin, Y.; Islam, E.; Yue, M.; Wang, W. Phosphate removal from solution using powdered freshwater mussel shells. Desalination 2011, 276, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Rahman, T.; Sakhakarmy, M.; Jahromi, H.; Eisa, M.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Lamba, J.; Torbet, A.; Adhikari, S. Phosphorus adsorption using chemical and metal chloride activated biochars: Isotherms, kinetics and mechanism study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Singh, R.P. Enhanced phosphorus removal from wastewater using RSPRC and a novel reactor. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meina, L.; Qiao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, D. Sudy on the dynamic adsorption and recycling of phosphorus by Fe–Mn oxide/mulberry branch biochar composite adsorbent. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yu, Q.; Gauvin, F.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Liu, C. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solutions by adsorptive concrete aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Liang, S.; Qin, Y.; Chen, W.; Xue, B.; Zhang, B.; Xu, G. Significant improvement of adsorption for phosphate removal by lanthanum-loaded biochar. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 24853–24864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.L.; Cvitanich, C.; Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Thau, M.; Malmgren-Hansen, B. Precipitation and recovery of phosphorus from the wastewater hydrolysis tank. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Remmers, J.C.; Saakes, M.; van der Weijden, R.; Buisman, C.J.N. Is there a precipitation sequence in municipal wastewater induced by electrolysis? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8399–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kausor, M.; Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Chakrabortty, D. Montmorillonite and modified montmorillonite as adsorbents for removal of water soluble organic dyes: A review on current status of the art. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ρ | NP | pHH2O | pHKCl | ∆pH | K | Ca | Fe | P | N | Mg | Cu | Zn | S | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g cm−3 | % | – | – | – | ------------------------------ g kg−1 ---------------------------------- | |||||||||
| 1.35 | 85.65 | 8.35 | 8.30 | −0.05 | 0.1 | 379.3 | 3.06 | 0.6 | 9.7 | 0.2 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.1 | 0.053 |
| Fitting Model | Equation Coefficients | Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) | Coefficient of Dettermination (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | 31.38 | 0.92 | |
| Langmuir | 31.43 | 0.90 | |
| Temkin | 51.51 | 0.85 |
| Mussel Species | Pretreatment of the Shells | Aqueous Medium | Contact Time | Adsorbent Concentration in the Liquid Medium (g L−1) | Maximum Adsorption Capacity * (mgP g−1) | Maximum P Recovery Efficiency (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) | Grinding to <2 mm | Synthetic solution (46.5 mmolP L−1, pH 8.5, and 20 °C) | 24 h | 13.3 | 18.23 | 60 | [26] |
| Calcination | 38.75 | 78 | |||||
| Not specified | Synthesis of nano-calcium hydroxide | Synthetic solution (20 mgP L−1, pH 7.5, and 21 °C) | 10 min | 0.08 | – | 99.3 | [11] |
| Not specified | Grinding to 0.60–1.18 mm | Treated sewage (7 mgP L−1 and pH 7.66) | 5 d | 100 | 0.248 | 66.2 | [29] |
| Not specified | Incorporation of Fe | Treated sewage (7 mgP L−1 and pH 7.1) | 120 h | 100 | 3.14 | 95.7 | [28] |
| Not specified | Grinding to 1.18 mm | Synthetic solution | 1.000 min | 20 | 0.04 | 15 | [9] |
| Calcination | 10 min | 1.32 | 97 | ||||
| Blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) | Thermochemical calcination with KOH | Treated sewage (20 mgP L−1, pH 7.32, and 22 °C) | 2 h | 4 | 12.44 | 99 | [27] |
| Golden mussel (Golden mussel) | Grinding to <0.425 mm | Treated university sewage (10 mgP L−1, pH 3.0, and 23 °C) | 3 h | 40–50 | 59.9 | 60 | Present study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Souza, D.A.; de Siqueira, J.C.; Crippa, R.A.; Watanabe, A.L.; Pompeu, P.d.S.; Teodoro, J.C.; Ribeiro, I.C.A.; de Matos, M.P. Valorization of Golden Mussel Shells for Sustainable Phosphorus Recovery in Wastewater Treatment. Water 2025, 17, 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101528
de Souza DA, de Siqueira JC, Crippa RA, Watanabe AL, Pompeu PdS, Teodoro JC, Ribeiro ICA, de Matos MP. Valorization of Golden Mussel Shells for Sustainable Phosphorus Recovery in Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2025; 17(10):1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101528
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Souza, Danielle Andrade, Juliano Curi de Siqueira, Rodolfo Appoloni Crippa, Andre Luiz Watanabe, Paulo dos Santos Pompeu, Jéssica Cristina Teodoro, Ivan Célio Andrade Ribeiro, and Mateus Pimentel de Matos. 2025. "Valorization of Golden Mussel Shells for Sustainable Phosphorus Recovery in Wastewater Treatment" Water 17, no. 10: 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101528
APA Stylede Souza, D. A., de Siqueira, J. C., Crippa, R. A., Watanabe, A. L., Pompeu, P. d. S., Teodoro, J. C., Ribeiro, I. C. A., & de Matos, M. P. (2025). Valorization of Golden Mussel Shells for Sustainable Phosphorus Recovery in Wastewater Treatment. Water, 17(10), 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101528






