Abstract
The global scarcity of freshwater, particularly in arid regions, has intensified interest in sustainable desalination technologies. Among these, solar still (SS) systems stand out for their low operational costs and environmental compatibility. This review presents a comprehensive analysis of recent advancements in solar still technologies, with a particular emphasis on innovative materials, thermal management strategies, and hybrid systems aimed at improving water productivity and cost-efficiency. Key technologies such as phase change materials (PCMs) and thermoelectric modules (TEMs) are examined in detail, showing up to 140% and 6.7-fold improvements in productivity, respectively, in select configurations. The review also synthesizes results from various studies using a comparative lens, highlighting combinations such as double-glazed glass with fins and TEMs (5.7-fold increase) and CuO–water nanofluids coupled with TEMs and vibration (5.3-fold increase). Cost analyses reveal that some configurations achieve water production at as low as 0.011 USD/L under real-world conditions in Rajshahi, Bangladesh, using an integrated system with an external condenser and solar collector. Unlike general reviews, this work systematically compares performance metrics, cost-effectiveness, and design innovations across multiple studies to provide a clearer perspective on technology viability. Future directions suggest the integration of hybrid approaches using PCM, TEM, nanotechnology, and advanced geometries to overcome current limitations and further advance solar desalination efficiency.
1. Introduction
The increasing costs of fossil fuels, combined with the urgent challenges posed by global warming, have catalyzed a significant shift towards renewable energy sources in recent years. Among these, solar energy has emerged as a particularly effective and widely adopted alternative, especially in applications related to water production. The scarcity of accessible drinking water in arid and semi-arid regions presents profound challenges, leading to severe health risks and socio-economic difficulties for millions of people. As the global population continues to rise, the demand for freshwater resources has reached critical levels, making the development of innovative solutions for drinking water production more imperative than ever. Access to clean and safe drinking water remains a global challenge, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions where freshwater resources are limited. As global water demand increases due to population growth and climate variability, there is an urgent need for cost-effective, sustainable, and decentralized desalination technologies. Among the available solutions, solar still (SS) systems present a viable method for small-scale freshwater production by harnessing abundant solar energy. However, traditional solar stills suffer from low productivity, prompting the exploration of advanced materials and hybrid designs. This review aims to systematically evaluate recent innovations in solar still technologies, focusing on the integration of phase change materials (PCMs), thermoelectric modules (TEMs), and nanotechnology. By critically comparing these approaches across performance metrics, cost, and design strategies, the review seeks to identify viable pathways for scaling up SS systems and enhancing their real-world applicability. Solar stills, which utilize solar energy to desalinate water, represent a promising method to address this pressing issue. These devices harness sunlight to evaporate water, which then condenses on a transparent surface, allowing for the collection of distilled water. Despite their potential, solar stills face a significant limitation: their relatively low daily water production rates. Research has indicated that solar intensity (the amount of solar energy received) plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and productivity of these systems. This makes solar stills particularly advantageous in hot, arid climates, such as those found in South Africa and various regions of the Middle East, where both freshwater scarcity and high solar intensity are prevalent [1,2,3]. The solar still’s performance is primarily influenced by two key processes: evaporation of water and condensation on the glass. An increase in the difference in temperature between the surface of the glass and the water is essential for maximizing water productivity. Several studies have demonstrated that optimizing this temperature difference can lead to significant improvements in output [4,5,6,7]. Various factors, including alterations to the geometry of the still, the choice of absorption materials, the depth of the water, and the characteristics of insulation, have been shown to enhance the overall efficiency and the productivity of the solar still [8,9]. Recent research has explored a multitude of innovative approaches aimed at increasing the water produced by solar stills. These include the use of advanced materials, like nanofluids and phase change materials, as well as the combination of additional technologies like photovoltaic and thermal systems. By leveraging these advancements, researchers have reported considerable improvements in water output, showcasing the potential of solar stills as a sustainable resolution for water scarcity [10].
In recent decades, extensive research has been conducted to enhance the water productivity of solar stills through advanced thermal management technologies. Key advancements include the integration of thermoelectric modules (TEMs), phase change materials (PCMs), nanofluids, and innovative designs to optimize heat and mass transfer. TEMs have been widely applied for both heating and cooling purposes in solar stills. For instance, Shoeibi et al. [11] demonstrated the effectiveness of TEMs in thermoelectric cooling and heating, leading to a 218% improvement in productivity and 117% efficiency gains when combined with antibacterial-magnetic nanofluids. Similarly, Nasir et al. [12] achieved a remarkable 672% productivity increase by integrating TEMs with photovoltaic systems in hybrid solar distillers. Additionally, Farahmand Jam et al. [13] reported significant improvements in energy and exergy efficiencies by applying double-glazed glass with TEM cooling in solar stills.
PCMs have been pivotal in extending operational hours by storing solar heat for post-sunset productivity. For example, Kabeel et al. [14] demonstrated the role of PCMs in stabilizing basin temperatures and enhancing evaporation rates. In hybrid applications, combining PCMs with TEMs, as shown by Sadeghi and Nazari [15], yielded extended productivity with improved energy efficiency. Furthermore, Shanmugan et al. [16] highlighted that the addition of PCMs and cotton wick absorbers enhanced productivity by 56.7% to 79.3%, depending on the configuration.
Nanotechnology also plays a crucial role in solar still enhancements. Nanocoatings (Zanganeh et al.) [17] increased water productivity by up to 20.3% due to improved condensation and heat absorption properties, while nanofluids such as Al2O3–water and –water showed up to 32% improvement in productivity by enhancing thermal conductivity and heat absorption by Sahota et al. [18]. Combined methods, such as nanocoatings and nanofluids, further amplified these effects.
Advanced absorbed materials have also been investigated. For instance, Karthikeyan et al. [19] demonstrated that solar stills using Al2O3 nanoparticles improved water productivity by up to three times compared with conventional absorbers. In addition, Zeroual et al. [20] employed glass cooling and intermittent shading, achieving an 11.82% improvement over traditional designs. Glass cooling has proven effective in lowering condensation surface temperatures and improving freshwater yield, as demonstrated in studies by El-Samadony and Kabeel [21]. Hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) systems integrated with solar stills have shown promising results. Sahota et al. [22] reported that PV/T systems using CuO–water nanofluids increased water productivity by 31.49% in stills without heat exchangers. Similarly, Shoeibi et al. [23] optimized PV/T systems, achieving enhanced water and energy output through TEM integration.
Recent research has indeed highlighted the potential of tubular solar stills (TSS) operating under vacuum conditions to enhance desalination performance through improved heat and mass transfer dynamics. Numerical simulations conducted using COMSOL Multiphysics compared cylindrical and rectangular troughs inside tubular stills and found that positioning a cylindrical trough at the center of the shell yielded superior water production efficiency. In contrast, rectangular troughs demonstrated better performance when placed near the condensation surface, indicating that the position and shape of the trough play a critical role in system effectiveness [24]. In a related study, it was found that increasing the rib height of rectangular troughs led to a minimum improvement of 19.78% in distillation rate, while elevating the trough closer to the upper glass surface enhanced productivity by at least 12.88%, due to more efficient condensation at that location [25]. These insights underscore the importance of geometric and positional optimization in the design of TSS systems for maximizing freshwater output, particularly in high-solar-radiation regions.
In addition to solar-based desalination technologies, recent advances in bio-based and composite membrane materials have broadened the scope of sustainable water treatment solutions. For example, chitosan, a naturally derived polymer, has been enhanced through the incorporation of metal oxides to overcome its limited mechanical strength and chemical resistance. These modifications not only improve chitosan’s durability but also introduce photocatalytic and magnetic functionalities, enabling it to effectively remove organic pollutants with reported efficiencies approaching 100% [26]. Similarly, SiO2-embedded castor oil-based membranes have shown considerable potential for aqueous iron (Fe) removal, with improved swelling capacity, mechanical performance, and adsorption flux under optimal silica concentrations [27]. These findings suggest that integrating such green materials with solar still technologies could provide hybrid systems capable of both desalination and selective pollutant removal, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and applicability of decentralized water purification systems.
The amalgamation of these techniques—TEMs, PCMs, nanotechnology, and advanced absorbing designs—demonstrates the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and productivity of solar desalination systems. These innovations contribute to addressing global freshwater scarcity and energy sustainability challenges, offering scalable solutions for diverse environmental conditions.
This article aims to review and synthesize recent advancements in solar still technologies, highlighting the effectiveness of various modifications and methods employed to enhance water production rates. By providing a comprehensive overview of current research trends and innovations in this field, we hope to contribute to the ongoing discourse on sustainable water solutions and underscore the critical role that solar energy can play in addressing the global freshwater crisis. Figure 1 categorizes different evaporation and condensation methods in solar still technologies, highlighting their applications in water purification. This review focuses on research investigating the effect of several factors on solar slope and aims to enhance conventional solar distillation methods. Both numerical and empirical studies were conducted to explore different techniques that increase evaporation and condensation rates.
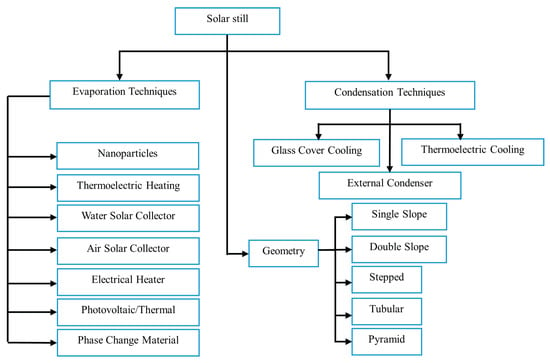
Figure 1.
Overview of condensation techniques and evaporation techniques used in solar still systems.
To optimize yield, researchers implemented several innovative approaches alongside solar stills. A comprehensive understanding of the scientific methods associated with single-slope basin systems and various still designs is essential. This chapter examines recent advancements made by investigators to improve the SS desalination performance, as well as the latest outgrowth in the literature concerning these systems. The chapter is organized into several sections: it begins with an introduction to conventional solar still (CSS) systems, followed by an overview of modifications made to these systems, including the following:
- Conventional solar still desalination (CSS).
- Modified solar still desalination systems (MSS):
- SS systems with external heat sources.
- SS systems with thermal energy storages.
- SS systems featuring reflective surfaces.
- SS systems equipped with external condensers.
- SS systems utilizing cover cooling.
- SS systems utilizing extended surface areas.
- Other improvements to the SS systems.
- Thermoelectric modules (TEC/TEH).
- SS systems productivity and cost.
- Future work.
- Conclusions drawn from the literature.
Additionally, the review emphasizes the importance of future research that involves the integration of different techniques within solar stills, providing a roadmap for ongoing advancements in the field. Classification of modification types to boost productivity in a solar still is depicted in Figure 2.
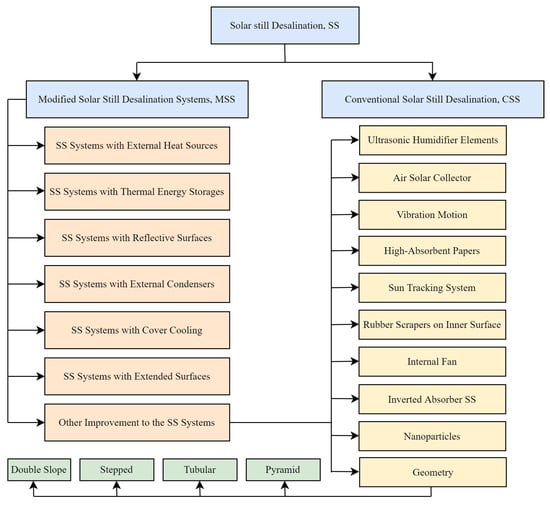
Figure 2.
Classification of modification types to boost productivity in a solar still.
2. Conventional Solar Still (CSS) Desalination
The conventional solar still (SS) system is recognized as a standard and widely employed method for solar desalination without any adjustments or modifications. Various researchers have investigated these conventional SS systems to gain insights into their operational principles and the influence of environmental conditions, design, and operational factors on their efficiency. The solar still desalination system is characterized by its simplicity, affordability, and minimal maintenance requirements. It primarily consists of a basin that is blackened and topped with sloping transparent covers. The operational mechanism of the SS system is straightforward, relying on the principles of evaporation, condensation, and gravity. Solar energy is absorbed by a blackened basin, which blackens the brackish (or saline) water within it, leading to a rise in the temperature of the water and the subsequent evaporation of water vapor. This vapor then condenses on the sloping cover, allowing fresh water to collect and drip into a drainage channel. An illustrative representation of a CSS system is provided in Figure 3 [28].
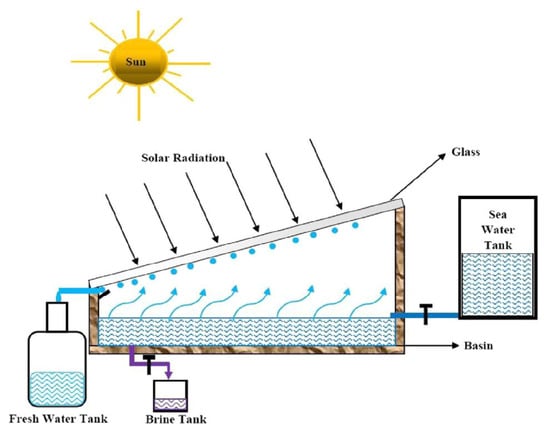
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of a CSS single-slope. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [28]. Copyright 2016, Elsevier.
Al-Hinai et al. [29] created a mathematical model to explore how different conditions of weather and factors of design affect the output of a dual-slope solar still (SS) system. By employing an ordinary energy balance method, they calculated the heat transfer coefficient of evaporation, enabling them to evaluate the system’s productivity. Their findings indicated that enhanced hourly productivity could be achieved under conditions of increased solar intensity, elevated ambient temperatures, higher wind speeds, larger cover slope angles in winter, steeper cover slope angles in summer, thicker blackened basin insulation, elevated feed water temperatures, and shallower water depths. The study reported a productivity per year of (4.15) kg/m²·day and a cost rate of 0.02 USD/L (equivalent to 19.5 USD/m³). In Figure 4, the illustrated diagram of the created SS system is shown.
Figure 4.
Conceptual representation of the SS with heat transfer and energy balance components. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [29]. Copyright 2002, Elsevier.
Jamil and Akhtar [30] conducted an experimental study to examine the impact of the distance between the blackened basin and the cover surface in a single-slope solar still (SS). The stationary designing parameters included basin dimensions of (0.7 × 1.4) m, a cover inclination angle of 28° (corresponding to the site’s latitude), and a water depth of 10 mm. They manipulated the gap height between the blackened basin and surface of the cover, which is achieved using sheets of polystyrene, achieving distances ranging from 0.266 m to 0.366 m. Their results indicated that a smaller void between the basin and the surface of the cover significantly enhances the productivity of the SS system. Specifically, the rate of daily productivity varied between known values from (1.341 to 4.186) L/m², while the rate of efficiency per day was regulated at 11.25 to 39.59%. Additionally, the produced water cost fluctuated between 0.074 USD/L and 0.024 USD/L. A graphic diagram of the experiential setup is presented in Figure 5.
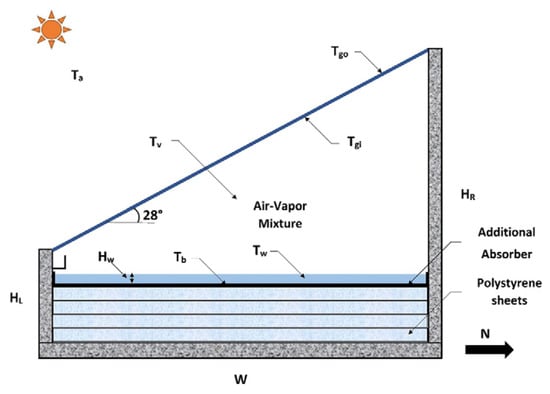
Figure 5.
Schematic of the experimental setup using polystyrene sheets to adjust basin-to-cover height. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [30]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier.
3. Modified Solar Still (MISS) Desalination Systems
A wide range of enhancements and modifications has been proposed by researchers to improve the performance of conventional solar still (SS) systems. The primary objective of these advancements is to enhance water production, also referred to as distillate yield. This section provides a comprehensive review of the relevant literature, systematically categorizing the studies based on the specific types of improvements implemented in SS systems:
3.1. SS Systems with Thermal Energy Storages
An important advancement in solar still (SS) systems involves the integration of an additional heat source with the traditional setup. Researchers have explored various methods to increase the water productivity of SS by increasing the evaporation rate. This is often achieved by incorporating a heat exchanger. The brackish (saline) water in the blackened basin was warmed by the heat exchanger, or the feed water, before it entered the SS system. Potential external heat sources include solar collectors, solar ponds, or waste heat from sources such as engine exhaust systems. In their 2023 study, Abdel-Aziz et al. [31] conducted experimental tests to enhance the single-sided solar still performance by integrating paraffin wax (PCM) with an electric heater powered by solar energy. Two identical single-sided solar stills were constructed and examined under similar climatic conditions in Al-Arish, Egypt, from the spring to the summer of 2021. One setup functioned as a CVSS, while the other incorporated both PCM and a heater that worked by electric ity (CVSSWPCM), as shown in Figure 6.
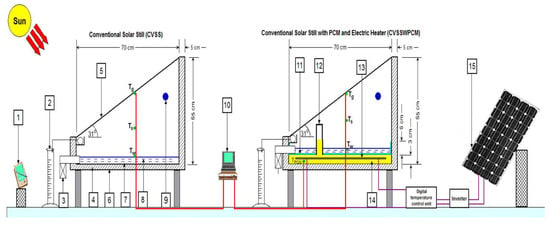
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the experimental setup incorporating paraffin wax and an electric heater in a single-sided solar still. Reprinted from Ref. [31]. Copyright 2023, Abdel-Aziz et al. Licensed under CC BY 4.0. 1-Solar wattmeter; 2-Measuring flask; 3-Water Drainage; 4-corkboard Insulation; 5-Glass cover; 6-Wooden frame; 7-Basin linear; 8-Water; 9-Water input; 10-Laptop and data logger; 11-Galvanized iron absorber plate; 12-PCM pouring tube; 13-Electric heater; 14-Paraffin wax; 15-PV solar modules.
The study investigated four scenarios: one without the heater (using only paraffin wax) and the other three with the heater set to operate at 58, 60, and 65 °C. Results demonstrated that activating the heater with paraffin wax significantly boosted production per day by factors of 2.38, 2.66, and 3.1 times in spring and by 2.2, 2.39, and 2.67 times in summer at the respective temperatures. The highest freshwater per day production rate was observed with paraffin wax at a temperature of 65 °C during both seasons. Additionally, the MSS with the heater set to 65 °C showed a higher exergoeconomic value compared with the conventional design. The max CO2 reduction achieved was approximately 28 tons in the first scenario and 160 tons in the fifth scenario. In a study conducted by Aqlan et al. [32], researchers developed a novel solar still that operates in direct connection with a solar parabolic trough, eliminating the need for a heat exchanger. This innovative system incorporated a specially designed feedwater tank integrated with the parabolic unit (see Figure 7). Field tests demonstrated a remarkable enhancement in water productivity; the modified solar still achieved a total increase of 177% compared with traditional stills. Specifically, the average hourly freshwater output from the modified solar still was recorded at 0.67 L/m2/h, while the unmodified model produced only 0.38 L/m2/h, as shown in Figure 8.
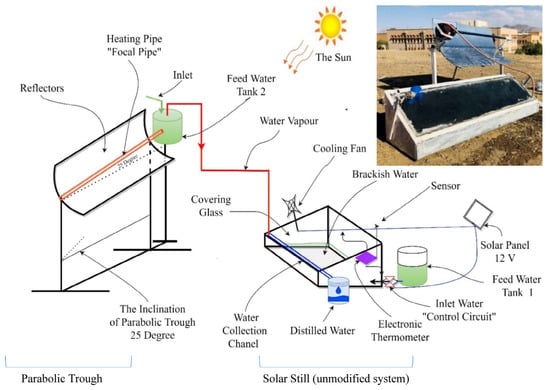
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of the modified solar still integrated with a parabolic trough and feedwater tank. Reprinted from Ref. [32]. Copyright 2021, Aqlan et al. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
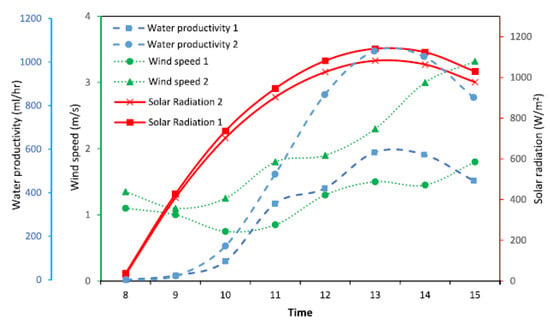
Figure 8.
Solar radiation per hour, wind speed, and productivity for CSS and MSS. Reprinted from Ref. [32]. Copyright 2021, Aqlan et al. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Kumar et al. [33] explored the integration of a single-sided SS system with a vacuum tube solar collector to preheat the brackish (saline) water before it enters the SS blackened basin (Figure 9).
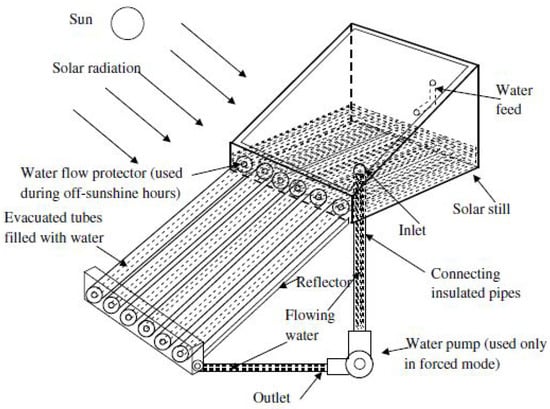
Figure 9.
Schematic Representation of a single-sided solar still integrated with a vacuum tube solar collector for preheating brackish water. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [33]. Copyright 2014, Elsevier.
Their research demonstrated that on an average summer day, the maximum daily product of this modified system was (3.47 kg/m²), which is approximately 20% higher than that of CSS. Furthermore, they reported a maximum efficiency of 33.8%, representing an increase of about 26% compared with solar stills without this modification. The study finished that the optimal depth of water in the blackened basin is (0.03 m). In a related study, Badran and Al-Tahaineh [34] examined the effects of combining the single slope SS system with a flat plate collector to heat brackish water in the SS basin. Their results of experiments indicated that this modification enhanced the productivity of the solar still system by 36%.
Abdel-Rehim and Lasheen [35] investigated a different approach by combining the solar still system integrated with A parabolic trough solar concentrator system, incorporating a burner tube and a heat exchanger utilizing oil as the working fluid to transfer heat to brackish (saline) water. Their findings revealed an average productivity increase of 18% with this configuration.
El-Sebaii et al. [36] further expanded on these concepts by coupling a solar still system integrated with a shallow solar pond using a tube-based heat exchanger, aimed at preheating the brackish (saline) water prior to its entry into the solar still pond. Their research found that the modified solar still system exhibited increases in productivity and efficiency of 52.36% and 43.8%. Productivity per day measurements varied from 1.904 kg/m² in winter to 6.570 kg/m² in summer (Figure 10).
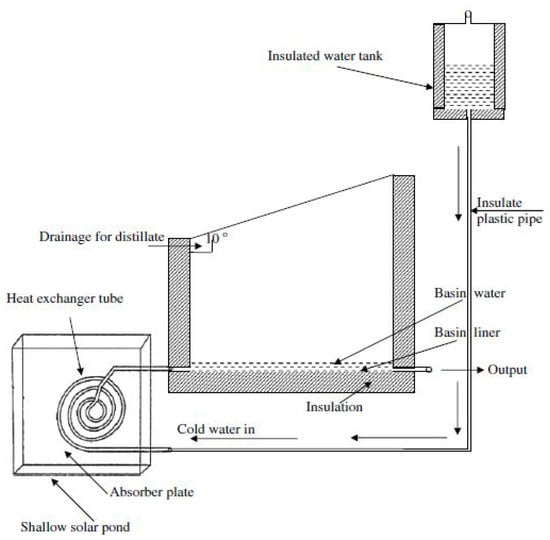
Figure 10.
Schematic Representation of a Solar Still System Integrated with a Shallow Solar Pond and Tube-Based Heat Exchanger for Preheating Brackish Water. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [36]. Copyright 2008, Elsevier.
3.2. SS Systems with Thermal Energy Storages
Further advancements in solar still (SS) systems have been achieved through the incorporation of thermal storage, enabling these systems to harness solar energy during sunny hours for increased freshwater production at night and during cloudy conditions. Various materials have been explored for this purpose, including sensible thermal storage options like rubber, stones, and marbles, along with phase change materials (PCMs), such as paraffin wax, for storing thermal energy in latent form. Several studies have investigated the integration of sensible heat storage materials and phase change materials (PCMs) in solar still (SS) systems to enhance productivity.
Shoeibi et al. [37] improved the performance of a solar desalination system by incorporating mirrors, repurposed materials for thermal energy storage, and thermoelectric generators (TEGs) to harness the waste heat from the absorber film.
The design utilized two mirrors to direct the radiation from the sun onto an absorber film, thereby raising the temperature of the water. Black-painted iron residues served as the heat storage medium, immersed in the SS blackened basin to raise the process of evaporation rates. In their experiments, they compared four configurations: CSS desalination, the SS with thermoelectric generators (SS-TEG), a solar still with TEG and iron residues (SS-TEG-WI), and a solar still with TEG, iron residues, and reflective sheets of mirrors (SS-TEG-WI-M) (Figure 11). The outcomes indicated that fresh and sweet water production was 0.64 L/m² for CSS, 0.63 L/m² for SS-TEG, 0.652 L/m² for SS-TEG-WI, and 0.796 L/m² for SS-TEG-WI-M, indicating a 24.4% increase in productivity for SS-TEG-WI-M, drawing an analogy to the conventional system (Figure 12).
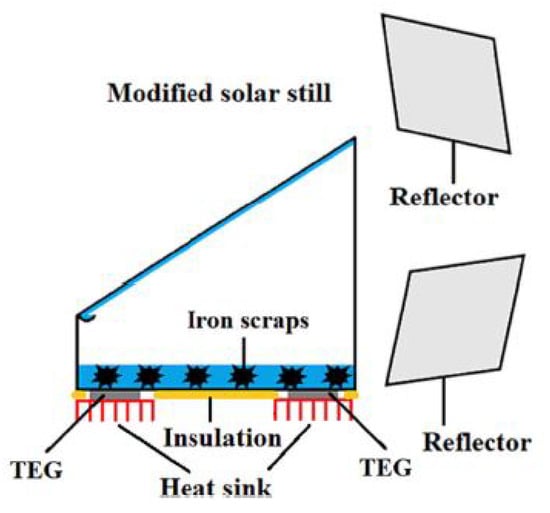
Figure 11.
Schematic representation of a solar still integrated with thermoelectric generators, iron-based thermal storage, and reflective mirrors for enhanced desalination efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [37]. Copyright 2023, Elsevier.
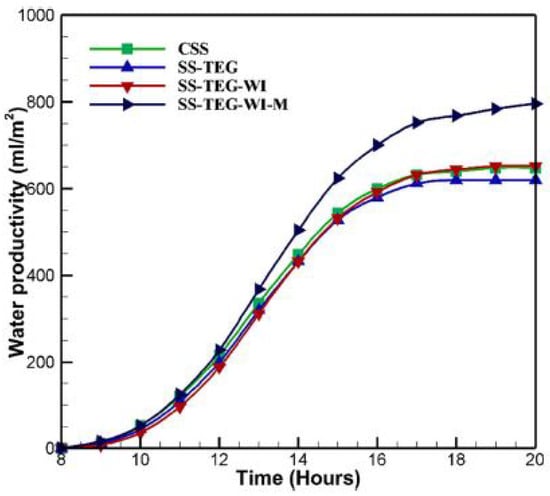
Figure 12.
Hourly power Production from thermoelectric generators in various solar stills. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [37]. Copyright 2023, Elsevier.
In a study conducted by Mohammed et al. [38], the performance of a single slope/single-tank solar still for saline water desalination was evaluated under the climatic conditions of Qena city in Upper Egypt. The study compared a CSS, a PCM-assisted solar still, and a local clay material-assisted solar still to enhance water yield during both day and night operations (Figure 13).
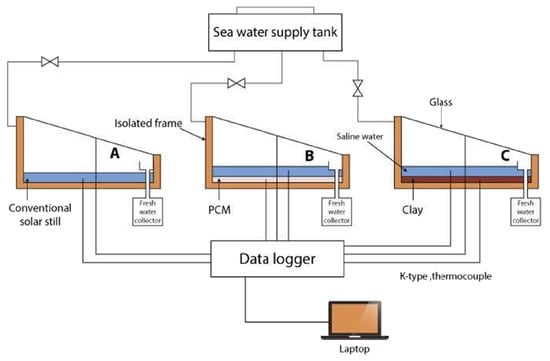
Figure 13.
Schematic representation of (A) a single-slope solar still enhanced (B) with phase change materials or (C) with local clay, for optimized daytime and nighttime desalination efficiency. Reprinted from Ref. [38]. Copyright 2022, Mohammed et al. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
The total desalinated water output from the conventional solar still, the solar still enhanced with phase change materials (PCMs), and the solar still utilizing local clay was approximately 3885 mL/m2, 4704 mL/m2, and 5388.6 mL/m2, respectively, with daytime yields of 3637.2 mL/m2 and nighttime yields of 247.8 mL/m2. The use of PCM resulted in a yield increase of about 21%, while the local clay material improved yields by approximately 38.7% (Figure 14).
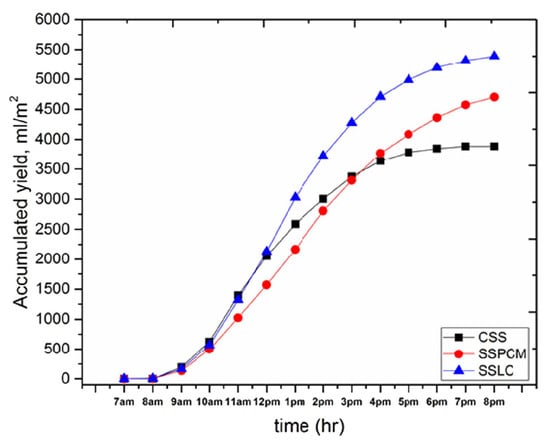
Figure 14.
Accumulated freshwater productivity over time for the CSS, SSPCM, and SSLC with time. Reprinted from Ref. [38]. Copyright 2022, Mohammed et al. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Notably, the local clay solar still outperformed the PCM-assisted system during the day, whereas the PCM system showed higher productivity at night. Daytime efficiencies were recorded at 34%, 41.2%, and 47% for the conventional, PCM-assisted, and local clay solar stills, respectively.
Parsa et al. [39] conducted a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of thermoelectric systems in two solar stills, both utilizing PCMs, nanopaint, and a turbulator for performance optimization. In their configurations, one system employed thermoelectric heating sides (TEH) in the blackened basin, while the other utilized thermoelectric cooling sides (TEC) on the glass surface (Figure 15). The findings revealed that the TEH system outperformed the TEC system in all measured aspects, exhibiting daily energy efficiency and exergy efficiency nearly 20% and 7% higher, respectively. Furthermore, the productivity of the TEH system improved by approximately 78.8% compared with the TEC system (Figure 16). Economically, the cost of productivity was about USD 0.0127 per liter for the TEH system and USD 0.023 per liter for the TEC system. Environmental assessments indicated that the TEH system achieved greater reductions in CO2, SO2, and NOx emissions compared with the TEC system.
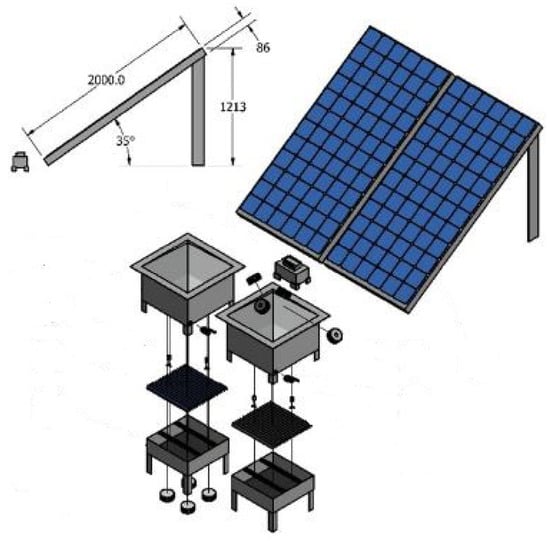
Figure 15.
Schematic representation of a solar still system incorporating thermoelectric heating and cooling configurations for enhanced performance optimization. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [39]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
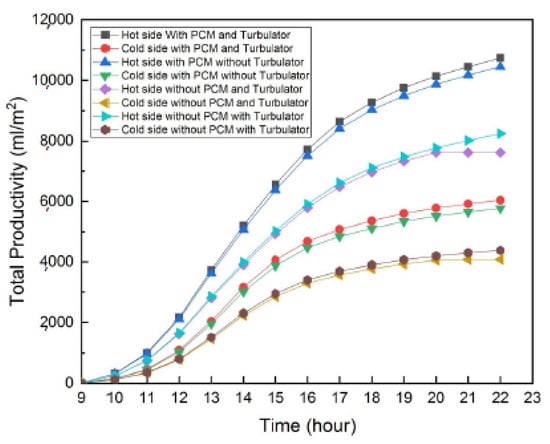
Figure 16.
Total accumulated yield across all scenarios for both systems. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [39]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
Kabeel and Abdelgaied [40] reported a significant improvement in the daily productivity of an SS system, which increased from 4.51 to 7.54 L/m2 through the use of a paraffin wax (PCM) layer placed under the absorber surface. This modification resulted in a productivity increase of 67.18% compared with systems without PCM. In a subsequent study, Kabeel and Abdelgaied [41] tested a modified SS system incorporating both a PCM as a heat energy storage in latent form device and a heat exchanger using oil for feedwater heating. Their experiments revealed maximum freshwater productivity of 4.48 L/m2/d for the conventional system and 10.77 L/m2/d for the modified system, with maximum daily efficiencies of 25.73% and 46%, respectively. These enhancements corresponded to productivity and efficiency improvements of approximately 140.4% and 44%, respectively. Figure 17 shows a graphic representation of the test setup.
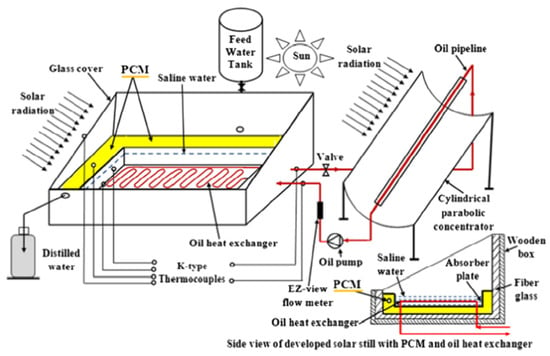
Figure 17.
Schematic representation of a solar still system incorporating paraffin wax for latent heat storage and an oil-based heat exchanger for enhanced feedwater heating. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [41]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier.
Dashtban and Tabrizi [42] demonstrated the potential of PCMs in a weir cascade SS system. Their experimental setup, illustrated in Figure 18, incorporated PCM, which was paraffin wax beneath an absorber of solar radiation. The results indicated a substantial 31% increase in daily productivity, reaching 6.7 kg/m2 compared with 5.1 kg/m2 for a system that did not utilize PCM. This improvement was attributed to PCM’s ability to store and release latent heat, enhancing the system’s overall thermal efficiency from 47% to 64%.
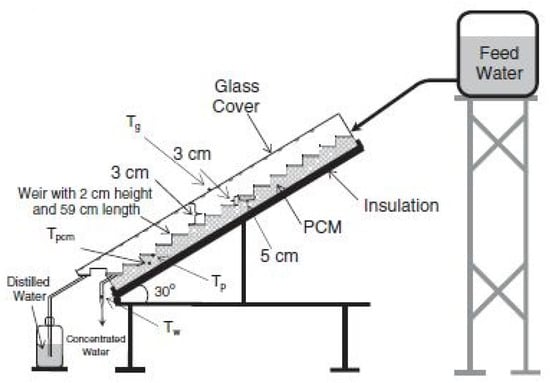
Figure 18.
Schematic representation of a weir cascade solar still integrated with paraffin wax-based phase change material for enhanced thermal efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [42]. Copyright 2011, Elsevier.
Shalaby et al. [43] focused on the performance of a V-corrugated single-sided SS integrated with paraffin wax PCM (Figure 19). Their findings revealed a contrasting effect of PCM on productivity during different periods. While daytime productivity decreased by 7.4%, nighttime productivity saw a significant boost of 72.7% due to the stored latent heat. Overall, PCM integration resulted in an 11.7% increase in total daily productivity.
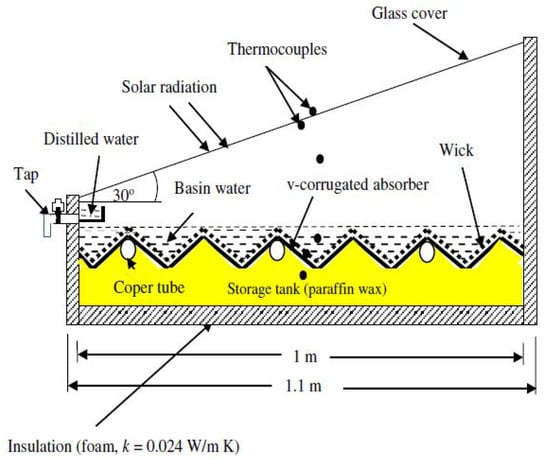
Figure 19.
Schematic representation of a V-corrugated single-sided solar still integrated with paraffin wax-based phase change material for optimized thermal performance. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [43]. Copyright 2016, Elsevier.
Murugavel et al. [44] explored the impact of various sensible heat storage materials on a double-slope SS system. They investigated materials like quartzite rock, washed stones, red bricks, cement concrete, and iron scrap placed in the system’s water basin (Figure 20). Their study revealed that utilizing 0.75-inch quartzite rock as the storage material yielded the highest productivity increase of 6.2%. Figure 21 illustrates the hourly productivity variations observed with different materials.

Figure 20.
Materials employed in the experiential study. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [44]. Copyright 2010, Elsevier.
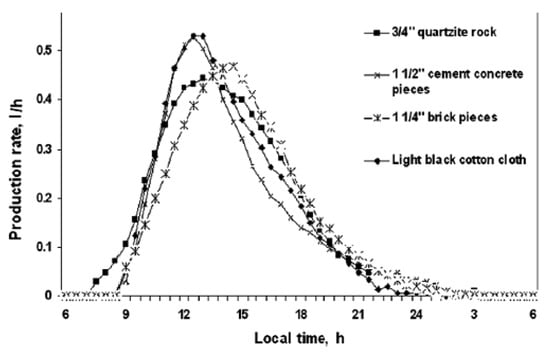
Figure 21.
Water productivity variation of the solar still utilizes various materials for sensible heat storage. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [44]. Copyright 2010, Elsevier.
El-Sebaii et al. [45] performed a theoretical study on a single-slope SS incorporating a 3.3 cm thick layer of stearic acid as a PCM placed beneath the absorber (Figure 22). Their simulations demonstrated a remarkable 80% enhancement in productivity per day, reaching 9.005 kg/m2 compared with 4.998 kg/m2 for the design without PCM. This highlighted the significant potential of PCMs for boosting SS system output. These studies collectively emphasize the potential of both PCMs and sensible heat storage materials for improving the efficiency and productivity of solar still systems.
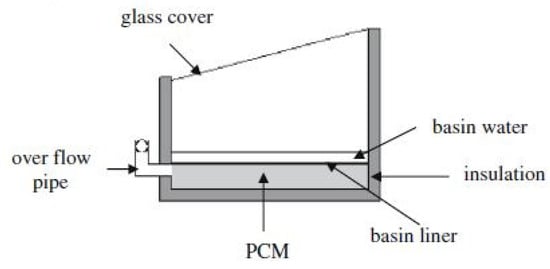
Figure 22.
Schematic representation of a single-slope solar still integrated with stearic acid-based phase change material for enhanced productivity and thermal efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [45]. Copyright 2009, Elsevier.
3.3. SS Systems Featuring Reflective Surfaces
Integrating reflectors into solar still (SS) systems presents another promising avenue for performance enhancement. By strategically positioning reflective surfaces within or around the still, incident solar irradiation can be amplified, leading to increased water temperatures and, consequently, higher evaporation rates. Soltanian et al. [46] proposed a mirror-enhanced SS design and compared its performance to conventional stills through mathematical modeling (Figure 23). Their study highlighted the advantages of the enhanced design, including reduced glass temperatures, elevated water temperatures, and significantly higher solar irradiance levels. Notably, the proposed system demonstrated a substantial increase in production of water, from 7.5 to 24 L/D.
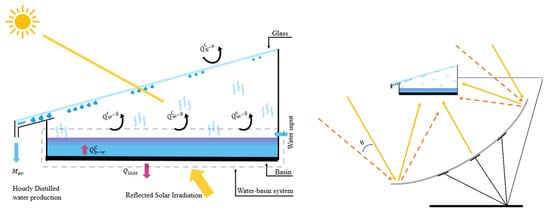
Figure 23.
Schematic illustrating the energy balance and structural design of a single slope SS. Reprinted from Ref. [46]. Copyright 2024, MDPI. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Estahbanati et al. [47] conducted both theoretical and experimental investigations to assess the impact of internal reflectors on SS system productivity. Their findings revealed that incorporating reflectors on all internal walls resulted in substantial productivity gains. Averaged annually, the increase was 34%, with more pronounced effects observed in winter (65%) compared with summer (22%). This suggests that internal reflectors are particularly beneficial during periods of lower solar insolation. Omara et al. [48] explored a stepped blackened basin SS system performance equipped with external and internal reflector surfaces. Compared to a classic conventional SS, the stepped basin design with both external and internal reflectors exhibited a remarkable 125% increase in productivity per day. The study also highlighted the individual contributions of the reflectors, with internal reflectors alone resulting in a 75% productivity enhancement. Figure 24 and Figure 25 illustrate the experimental setup and productivity comparisons, respectively. Additionally, the efficiency per day of the stepped blackened basin SS system with reflectors (56%) surpassed that of the conventional system (34%) and the stepped basin system without reflectors (53%).
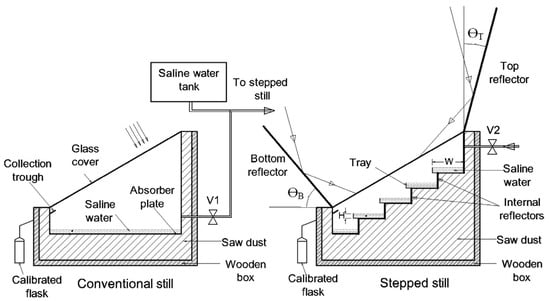
Figure 24.
Schematic representation of a stepped blackened basin solar still equipped with external and internal reflectors for enhanced productivity and efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [48]. Copyright 2014, Elsevier.
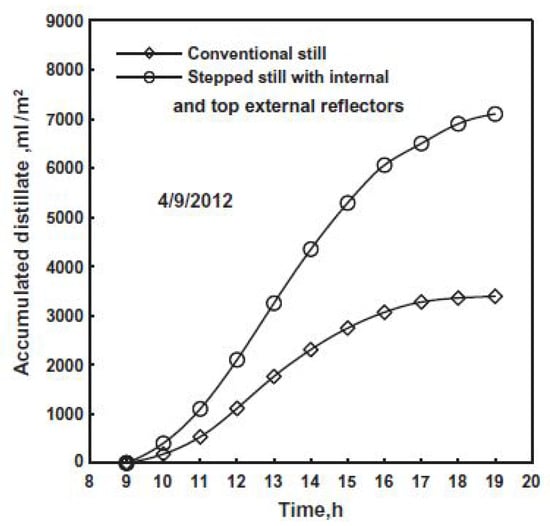
Figure 25.
Cumulative water productivity of CSS versus MSS [48]. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [48]. Copyright 2014, Elsevier.
Khalifa and Ibrahim [49] conducted experimental investigations focusing on the impact of internal reflectors, external reflectors, and varying external reflector tilt angles on SS system productivity across different seasons. Their results indicated that incorporating internal reflectors alone led to a 19.9% increase in annual productivity. Combining internal and external reflectors further enhanced productivity, with gains ranging from 24.7% to 34.8%, depending on the tilt angle of the external reflector. However, it is worth noting that the study observed a negative impact of reflectors during the summer months.
Tanaka and Nakatake [50] employed theoretical analysis to investigate the effects of external and internal reflector surfaces on the performance of SS. Their findings indicated a substantial average annual distillate productivity increase of 48% compared with a system without reflectors. In conclusion, incorporating reflectors, both internal and external, presents a viable strategy for significantly improving the productivity of solar still systems. However, the optimal configuration and the extent of the benefits may vary depending on factors such as geographic location, climate, and the specific design of the SS system.
3.4. SS Systems Equipped with External Condensers
Incorporating an external condenser represents another effective strategy for enhancing the productivity of solar still (SS) systems. The principle behind this modification lies in enhancing the condensation rate by rapidly cooling the vapor generated within the still. This, in turn, accelerates the evaporation process and leads to higher freshwater output. However, it is essential to acknowledge that integrating an external condenser increases the system’s complexity, footprint, and both capital and operational costs. Mandev et al. [51] investigated the integration of thermoelectric (TE) modules into SS systems to improve desalination performance (Figure 26). Their findings demonstrated that utilizing TE modules as efficient cooling elements significantly enhanced water production. Compared to conventional SS systems, the TE-integrated system exhibited an impressive 35% increase in productivity. The optimal volume of saltwater for their specific design ranged from 1.0 to 2.0 L, with 1.5 L yielding the best results.
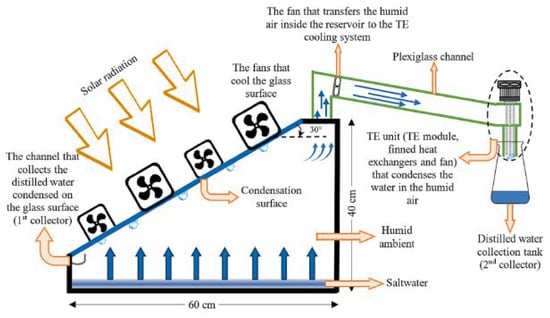
Figure 26.
Schematic representation of a solar still system integrated with thermoelectric modules for enhanced cooling efficiency and increased water productivity. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [51]. Copyright 2024, Elsevier.
Ibrahim et al. [52] explored the effects of attaching the condenser placed externally to the single-stage SS operating under vacuum conditions. Their study revealed a 16.2% enhancement in productivity compared with a conventional system. Moreover, the modified system exhibited higher daily efficiency (37.6%) compared with the conventional SS system (29%).
El-Samadony et al. [53] focused on modifying a graded/stepped SS by incorporating a condenser placed externally with external and internal surfaces working as reflectors. Their findings indicated a 66% increase in productivity when only the external condenser was employed. Remarkably, combining the external condenser with reflectors resulted in a substantial 165% productivity enhancement compared with a single-slope CSS.
Kabeel et al. [54] inspected the individual and combined effects of three modifications to a conventional single-tilt SS system: an external condenser, nanoparticle addition to water, and a vacuum fan. Their outcomes demonstrated that incorporating an external condenser alone led to a 53.2% increase in daily productivity. Combining the condenser with nanoparticles further enhanced productivity to 76%, while the inclusion of a vacuum fan, which facilitates the extraction of moist air, resulted in a remarkable 116% productivity increase. The empirical setup employed in their research is illustrated in Figure 27.
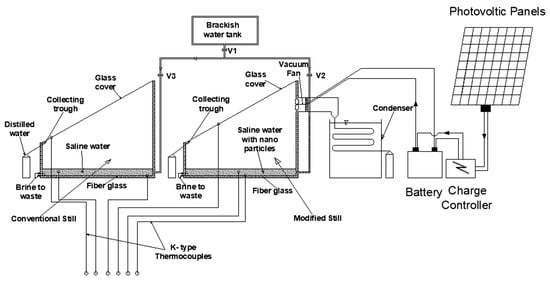
Figure 27.
Schematic representation of a single-tilt solar still system enhanced with an external condenser, nanoparticle-infused water, and a vacuum fan for optimized productivity. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [54]. Copyright 2014, Elsevier.
Monowe et al. [55] proposed a novel SS design for domestic applications, integrating a condenser placed externally and a reflector surface placed externalyl. Their system, designed to utilize the condensation latent heat for preheating the incoming brackish (saline) water, achieved an impressive efficiency of up to 77% and a daily productivity of the water above 8 L/m2. Figure 28 provides a graphical illustration of their experiential setup.
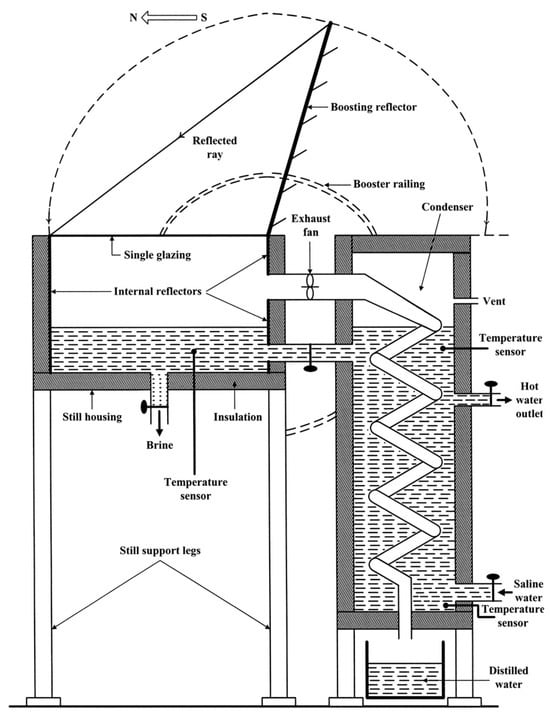
Figure 28.
Schematic representation of a solar still system integrated with an external condenser and reflector surface for enhanced efficiency and water productivity. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [55]. Copyright 2011, Elsevier.
El-Bahi and Inan [56] conducted experimental investigations on a single-sided SS system (4° tilt angle) fitted with a passive external condenser and an external reflector. Their modified system achieved a maximum productivity per day of approximately 7 L/m2, appearing to be a 70% advancement over conventional design. Furthermore, the system’s efficiency increased by about 75%.
Abu-Qudais and Othman [57] discussed two SS systems, especially the performance of this system, one with and one without an external separate condenser. Their study revealed a significant 47% increase in thermal efficiency for the system equipped with the external separate condenser. In summary, integrating an external separate condenser into SS systems is a highly effective method for enhancing productivity and efficiency. The studies discussed highlight the significant performance gains achievable through this modification, whether implemented independently or in conjunction with other enhancements such as reflectors, nanoparticle additions, or vacuum systems.
3.5. SS Systems Utilizing Cover Cooling
Another effective approach to enhancing the performance of solar still (SS) systems involve cooling the cover to accelerate the condensation process. By lowering the temperature of the condensing surface, vapor condenses more rapidly, leading to increased distillate yield. Various techniques have been explored to achieve this objective. Shatar et al. [58] developed an enhanced passive SS incorporating a partially coated condensing cover combined with thermoelectric cooling (TEC) technology. Their study investigated the impact of varying TECs powered by 12 and 36 W under tropical Malaysian weather conditions (Figure 29). The results demonstrated a noticeable 126% rise in production of freshwater with 36 W cooling power compared with the reference SS. While energy efficiency increased by 44%, exergy efficiency reduced by 25%. Their analysis revealed a minimum (Emin) energy payback period of 6.549 years, along with a max (Emax) energy output factor of 0.15 and a CO2 mitigation potential of 2.97 tons over the system’s lifetime. The estimated cost per liter of freshwater produced was lowest (USD 0.036) with the 36 W cooling capacity. The system achieved notable exergoeconomic and environmental economic values of 4.64 USD/kWh and USD 83.21, respectively.
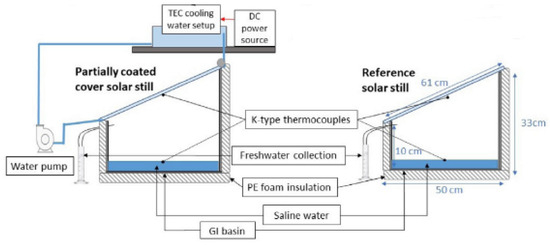
Figure 29.
Schematic representation of an enhanced passive solar still with a partially coated condensing cover and thermoelectric cooling technology for optimized freshwater production. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [58]. Copyright 2023, Elsevier.
Khanmohammadi et al. [59] explored the benefits of double-glazing cooling technology combined with a TEM in a solar desalination system. The system employed a thermoelectric module to generate cold air, which was then circulated between the two glass layers for cooling purposes. The experiment in Figure 30 has results indicating a 30% increase in the average productivity of freshwater compared with a conventional SS. Furthermore, they observed that increasing the linear airflow velocity enhanced productivity, with 14% and 25% increases achieved at air velocities of 2.5 and 4 m/s, respectively, compared with the baseline velocity of 1.5 m/s. Economic analysis estimated the distilled water cost for the modified system to be 0.1033 USD/L/m2.
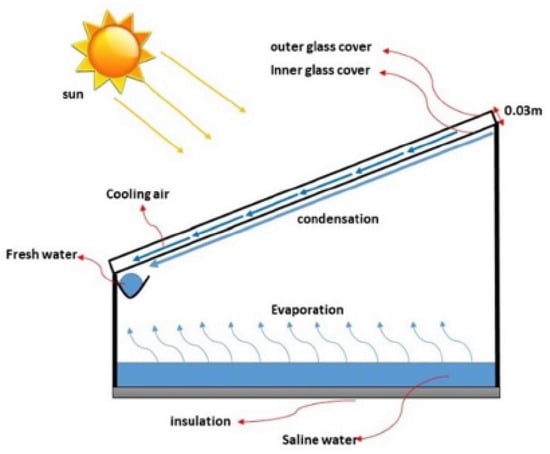
Figure 30.
Two-dimensional schematic illustrating the double-glazed cover and cool air flow in the solar still. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [59]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
Rahbar and Esfahani [60] proposed a novel approach utilizing a pipe to withstand heat as a heat exchanger for cooling the surface in an SS system. Their five-day experimental evaluation indicated a maximum daily efficiency of 70%, highlighting the potential of this cooling method. Figure 31 and Figure 32 depict the experiential setup and the performance characteristics of the modified system, respectively.
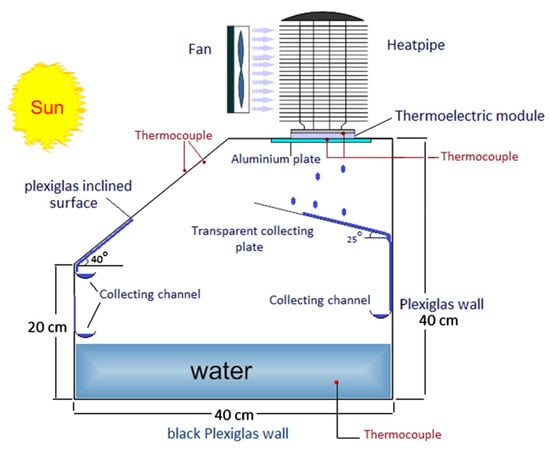
Figure 31.
Schematic representation of a solar still system incorporating a pipe-based heat exchanger for enhanced surface cooling efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [60]. Copyright 2012, Elsevier.
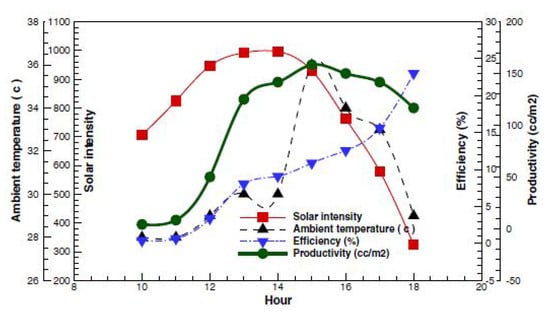
Figure 32.
Variations in climatic conditions, productivity, and instantaneous efficiency over the course of a typical day (8 February 2010). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [60]. Copyright 2012, Elsevier.
Sharshir et al. [61] performed a comparative analysis investigating effects and traces of the four different modifications on a single-slope SS. The modifications involved (A) Incorporating flake graphite nanoparticles into water, (B) combining nanoparticles with a phase change material (PCM), (C) incorporating nanoparticles and a cooled cover, and (D) implementing all three modifications (nanoparticles, PCM, and cover cooling). Their results demonstrated productivity enhancements of 50.28%, 65%, 56.15%, and 73.8% for models (A), (B), (C), and (D), respectively. Figure 33 illustrates the experimental setup employed in their study.
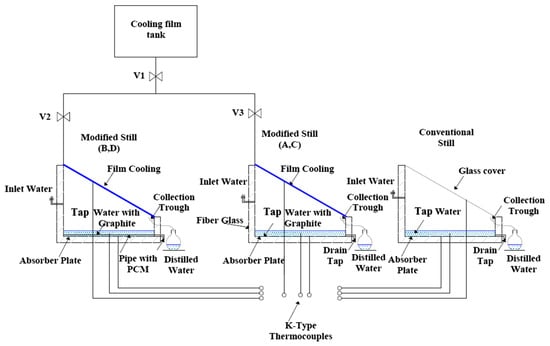
Figure 33.
Schematic representation of a single-slope solar still system with flake graphite nanoparticles, phase change material, and cooled cover for enhanced productivity. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [61]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier.
Somwanshi and Tiwari [62] explored a simple yet effective cooling method by flowing cold water from an air cooler tank over a single-slope SS system cover. Their findings indicated that this approach enhanced productivity and efficiency by 56.5% and 9.9%, respectively. The rate of an optimal cooling water flow of 0.075 kg/s was specified.
Gupta et al. [63] examined the effect of utilizing a water sprinkler to cool the cover of glass for a single-slope SS system. Their experimental setup, with a sprinkler discharge rate of 0.0001 kg/s, resulted in a 20% increase in productivity per day and a 21% advancement in efficiency. The productivity per day of the modified system (3.541 L/m2) surpassed that of the CSS system (2.940 L/m2). Zeroual et al. [20] demonstrated that employing a water film to cool the cover of glass enhanced MSS productivity by about 11.82% compared with a CSS design. Additionally, they implemented intermittent shading using a rectangular structure positioned 90 cm above the northern side of the still, resulting in a 2.94% improvement in water production.
Bhargva and Yadav [64] carried out an experiential investigation to evaluate the impact of glass cover shading on the efficiency of an SS integrated with a tube collector that is evacuated. The study involved shading the glass cover with different surface area ratios: 1/4, 1/2, 3/4, and the full surface area, to achieve glass cooling. The findings described that water productivity was highest when half of the glass surface area was shaded. The results further indicated that the productivity of water and the thermal efficiency increased by 16.4% and 3.8%, compared with a CSS without shading or cooling mechanisms. However, the authors concluded that shading more than half of the glass surface area led to a decline in the solar still’s overall performance, emphasizing the critical balance required in shading design to optimize productivity and efficiency.
3.6. SS Systems with Extended Surfaces
The efficiency of SS systems can be significantly improved by introducing additional surfaces into the water basin, thereby increasing the effective evaporation area. This approach aims to boost solar energy absorption and consequently improve the evaporation rate and productivity of the system. Various configurations and materials, such as fins, corrugated plates, perforated plates, wicks, and wire mesh, have been employed to achieve this objective. Çolak et al. [65] discussed the use of sponge pieces to boost the evaporation surface area and integrated the system with a novel condensation mechanism involving a water-spraying thermoelectric module (Figure 34). This arrangement notably increased the distillation rate by 100.5%. Additionally, incorporating an indoor fan to distribute water vapor improved distillation by 51.1%. Other factors, such as insulation to reduce thermal losses and the absorption effects of black coloration, further contributed to the system’s efficiency.
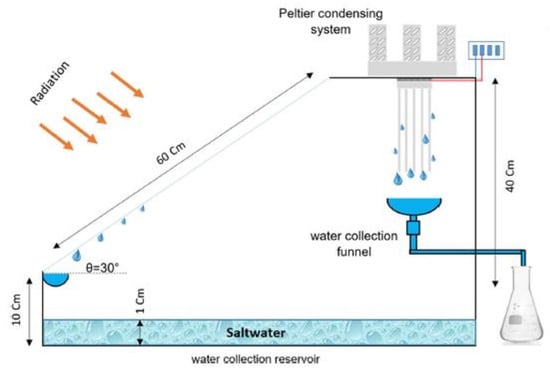
Figure 34.
Schematic representation of a solar still system enhanced with sponge-based evaporation surface expansion and a water-spraying thermoelectric condensation module for improved distillation efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [65]. Copyright 2023, Elsevier.
Omara et al. [66] performed an experimental analysis on the addition of ribs and plates in the form of a corrugated shape into the blackened basin of a single-slope SS. The system’s proportion was (0.5 × 2) m with a depth of water of (50 mm). Results demonstrated that ribs and corrugated plates improved freshwater productivity by 40% and 21%, respectively. This study highlighted the effectiveness of surface geometry in enhancing SS performance. Figure 35 shows the experiential setup schematic diagram, and Figure 36 displays the cumulative outputs for various configurations of the SS system.
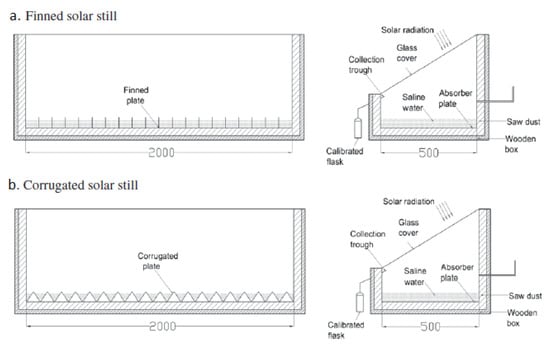
Figure 35.
Schematic representation of a single-slope solar still system with ribs and corrugated plates integrated into the blackened basin for enhanced freshwater productivity. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [66]. Copyright 2011, Elsevier.
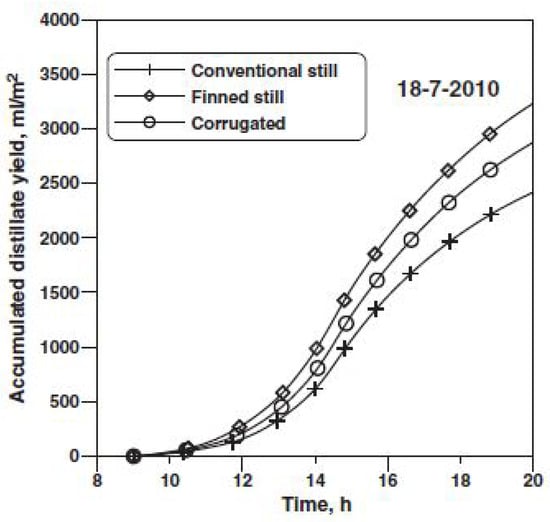
Figure 36.
Cumulative productivity of CSS versus MSS. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [66]. Copyright 2011, Elsevier.
Nafey et al. [67] investigated the impact of perforated black aluminum plates designed to float, placed in the water basin at various depths (3 to 6 cm). Their findings showed that the enhancement was most pronounced at greater water depths, with productivity increasing by 15% at 3 cm and 40% at 6 cm compared with a conventional SS system. Srivastava and Agrawal [68] utilized a floating water have the absorption property made of jute cloth that was black in color, achieving a productivity rise of 68% on clear days and 35% on cloudy days. When combined with external reflectors, the productivity further rose by up to 79%. Their research revealed that water depth had a minimal impact on productivity when using floating absorbers. In a follow-up study, Srivastava and Agrawal [69] examined the addition of porous slats or fins made from blackened cotton rags, which extended from the water tank’s base to above the surface. The modified system exhibited a 15% higher daily productivity in summer (May) and 48% in winter (February), with a maximum yield of 7.5 kg/m2 recorded in one of the months in the year, which was May. Figure 37 displays the diagrammatic representation of the experiential setup.
Figure 37.
Schematic representation of a solar still system incorporating floating perforated aluminum plates and blackened jute cloth absorbers for enhanced productivity. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [68]. Copyright 2013, Elsevier.
Abu-Hijleh and Rababa’h [70] evaluated the effects of inserting sponge cubes that had yellow color, blackened coal, blackened sponge cubes, and blackened cubes from steel into the SS and placed them in the water of the blackened basin. Among these, blackened sponge cubes were given most effectively, increasing productivity by 73%. Their experimental system had a basin dimension of 0.5 × 0.5 m, a cover inclination angle of 23°, and a water depth of 50 mm.
Sakthivel et al. [71] explored the use of expanded areas from jute fabric to increase the evaporation process by the new area of extended surface. Their findings indicated that the maximum productivity improvement per day was 20%, with an efficiency of 52% per day, which was 8% higher compared with a CSS.
The studies reviewed demonstrate that modifications to the evaporation surface area and basin configurations can substantially enhance the efficiency and productivity of SS systems. Approaches such as incorporating sponge materials, fins, corrugated plates, and floating absorbers, as well as using reflective surfaces and porous structures, have shown significant potential for improving performance. For instance, the integration of sponge materials [65] and floating absorbers [68] led to notable productivity gains. Furthermore, the effectiveness of these methods often depends on system parameters such as water depth and material properties. These findings provide valuable insights for designing advanced SS systems with improved sustainability and efficiency.
3.7. Other Improvements to the SS Systems
- Vibration motion: A recent study by Dawood et al. [72] explored enhancing freshwater production from solar stills through innovative modifications. The researchers combined an electric heater, vibratory motion, and thermoelectric cooling to improve evaporation and condensation rates. Using a 1 m2 footprint setup with a 450 W heater and vibration mechanism powered by solar panels, they tested various configurations (Figure 38). The most effective setup achieved a daily productivity of (12.82) kg/day at an evaluated cost of (0.01786) USD/L/m2. This modified system demonstrated higher exergo-economic efficiency and greater potential for CO2 reduction compared with conventional solar stills. The study highlights promising advancements in solar desalination technology for addressing water scarcity.
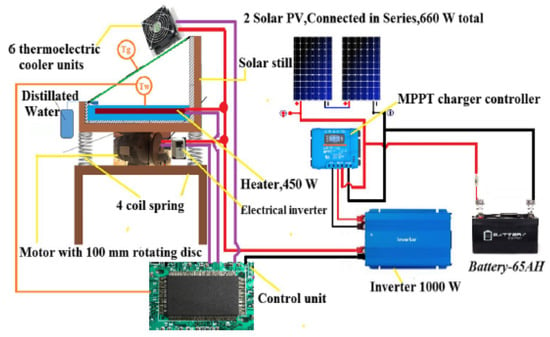 Figure 38. Schematic representation of an advanced solar still system incorporating an electric heater, vibratory motion, and thermoelectric cooling for optimized freshwater production. Reprinted from Ref. [72]. Copyright 2022, Dawood et al. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Figure 38. Schematic representation of an advanced solar still system incorporating an electric heater, vibratory motion, and thermoelectric cooling for optimized freshwater production. Reprinted from Ref. [72]. Copyright 2022, Dawood et al. Licensed under CC BY 4.0. - Sun tracking system: A study by Abdallah and Badran [73] examined the impact of a sun tracking system on solar still (SS) productivity. Using a simple single-slope, single-basin SS (1 m × 1.2 m, 32° cover tilt), they found that the tracking system increased daily water output by about 22% compared with a fixed SS. The researchers presented hourly productivity data comparing both systems, highlighting the tracking system’s enhanced performance. This research demonstrates the potential of sun-tracking mechanisms to significantly improve solar desalination efficiency. Figure 39 illustrates variation in productivity per hour for both SSs.
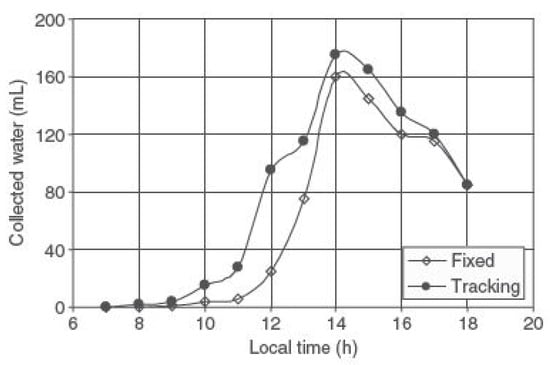 Figure 39. Productivity per hour variation between a fixed and the sun-tracking SSs. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [73]. Copyright 2008, Elsevier.
Figure 39. Productivity per hour variation between a fixed and the sun-tracking SSs. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [73]. Copyright 2008, Elsevier. - Internal fan: Kianifar et al. [74] examined the impact of integrating a fan into a pyramidal solar still (SS) system. Their investigation revealed that the addition of a fan significantly improved the system’s productivity during the summer, achieving an increase of 20%. This improvement was attributed to enhanced water vapor distribution and evaporation rates facilitated by the fan. However, during the winter season, the effect of the fan was negligible, likely due to lower ambient temperatures and reduced solar radiation. This finding highlights the seasonal dependency of fan-assisted modifications in solar still systems. Figure 40 illustrates the diagrammatic representation of the experiential setup.
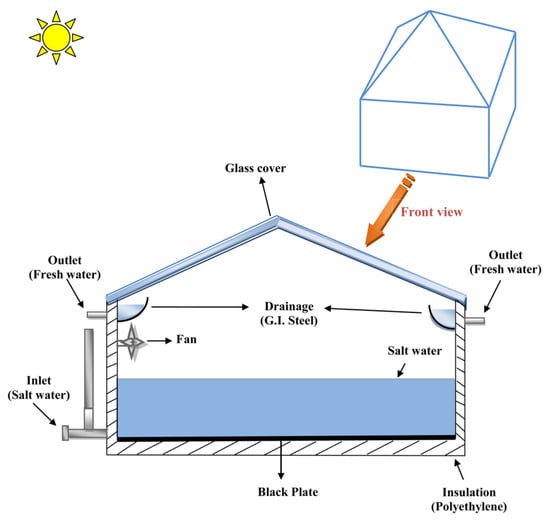 Figure 40. Schematic Representation of a Pyramidal Solar Still System Integrated with a Fan for Improved Water Vapor Distribution and Seasonal Productivity Enhancement. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [74]. Copyright 2012, Elsevier.
Figure 40. Schematic Representation of a Pyramidal Solar Still System Integrated with a Fan for Improved Water Vapor Distribution and Seasonal Productivity Enhancement. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [74]. Copyright 2012, Elsevier. - Inverted absorber SS system: Dev et al. [75] proposed an innovative inverted absorber solar still (SS) system and compared its performance with that of a conventional SS system. Their findings demonstrated that the inverted SS system achieved a maximum productivity per day of 6.3 kg/m2, significantly surpassing the 4.15 kg/m2 recorded for the conventional system. However, in terms of efficiency, the conventional SS system displayed a higher maximum efficiency per day of 48%, compared with 34.6% for the inverted system. Additionally, the study investigated the depth effect of water on system performance, identifying an optimum depth of 3 cm for maximizing productivity. This research highlights the potential trade-offs between productivity and efficiency in different SS configurations and emphasizes the role of water depth in optimizing system performance (Figure 41).
 Figure 41. Schematic representation of an inverted absorber solar still system for optimized productivity and water depth efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [75]. Copyright 2011, Elsevier.
Figure 41. Schematic representation of an inverted absorber solar still system for optimized productivity and water depth efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [75]. Copyright 2011, Elsevier. - Rubber scrapers on inner surface: Al-Sulttani et al. [76] inspected the performance of a double-tilt SS equipped with rubber scrapers on the inner surface of its cover. These scrapers, resembling windshield wiper blades, were designed to collect condensate from the inner cover surface (Figure 42). This mechanism prevents the re-evaporation of collected water droplets and allows more solar energy to penetrate the system by minimizing light obstruction caused by condensate accumulation. The study revealed that the modified SS system carried out an average productivity per day of 4.24 L/m2, representing a 63% improvement in productivity in comparison to the CSS. These findings underscore the effectiveness of rubber scrapers in enhancing light transmission and maintaining high productivity levels. Figure 43 displays the cumulative output of the modified and conventional SSs.
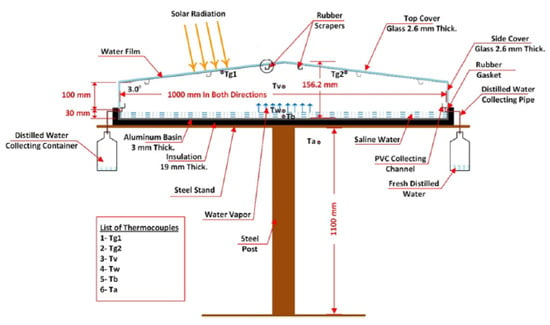 Figure 42. Schematic representation of a double-tilt solar still system integrated with rubber scrapers for enhanced condensate collection and solar energy penetration. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [76]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier.
Figure 42. Schematic representation of a double-tilt solar still system integrated with rubber scrapers for enhanced condensate collection and solar energy penetration. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [76]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier.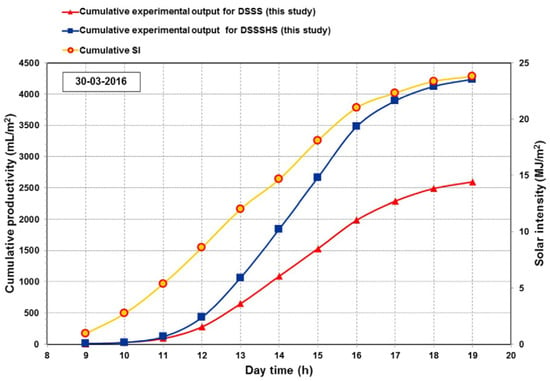 Figure 43. Cumulative output of CSS versus MSS. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [76]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier.
Figure 43. Cumulative output of CSS versus MSS. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [76]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier. - Ultrasonic humidifiers: Alwan et al. [77] carried out an empirical investigation to evaluate the impact of modifications aimed at improving condensation and evaporation processes in a solar still (SS) system. The modifications included the placement of ultrasonic humidifiers submerged in pool water within a cotton net tent and the integration of a cooling chamber equipped with TEM elements (Figure 44). The experimental findings demonstrated a remarkable increase in productivity of the modified MSS, achieving 124% improvement in comparison to the CSS. The highest efficiency of thermal was registered at 14:00, with the modified system achieving approximately 95.8%, significantly higher than the 35.6% observed for the conventional system. Additionally, the cost study revealed that the productivity cost of water produced by the distilled process was slightly lower for the adjusted system (0.040 USD/L) compared with the conventional system (0.042 USD/L).
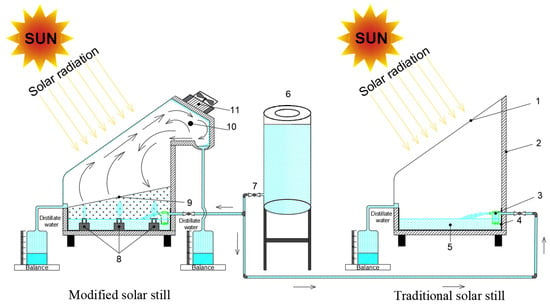 Figure 44. Schematic representation of modified and conventional solar stills: components include (1) transparent plexiglass cover; (2) MDF wooden board; (3) mechanical float; (4) water basin; (5) water reservoir; (6) storage tank; (7) globe control valve; (8) ultrasonic humidification device elements; (9) cotton tent; (10) cooling chamber; and (11) thermoelectric cooling elements. Reprinted from Ref. [77]. Copyright 2022, MDPI. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Figure 44. Schematic representation of modified and conventional solar stills: components include (1) transparent plexiglass cover; (2) MDF wooden board; (3) mechanical float; (4) water basin; (5) water reservoir; (6) storage tank; (7) globe control valve; (8) ultrasonic humidification device elements; (9) cotton tent; (10) cooling chamber; and (11) thermoelectric cooling elements. Reprinted from Ref. [77]. Copyright 2022, MDPI. Licensed under CC BY 4.0. - High-absorbent papers: Mandev et al. [78] investigated the impact of incorporating water-absorbing materials and a Peltier cooling module into a solar still (SS) system to enhance evaporation performance. To minimize heat loss and improve thermal efficiency, the SS housing was insulated with Styrofoam. The experimental setup included a metal housing that was painted black, with the cover of glass placed at an angle about 30° from horizontal. The study reported a recovery of 25 g of purified water under standard conditions. However, modifications using black superabsorbent paper on a frame made of metal in a triangular shape (Case 5) and superabsorbent paper in upright column arrangements (Case 6) resulted in significantly higher water recovery rates of approximately 34 g and 40 g, respectively. These configurations also demonstrated remarkable improvements in thermal efficiency, with increases of 29% for Case 5 and 45% for Case 6. Additionally, a cost analysis indicated that the use of in-house materials contributed to notable cost efficiency. Case 6 achieved a cost reduction of over 35% per liter of purified water compared with the conventional setup, demonstrating the economic viability of the proposed modifications (Figure 45).
 Figure 45. Main framework and materials of system. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [78]. Copyright 2024, Elsevier.
Figure 45. Main framework and materials of system. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [78]. Copyright 2024, Elsevier. - Nanoparticles: One effective approach to increasing water temperature and enhancing the efficiency of SSs was using nanofluids instead of pure water. Nanofluids, formed by mixing nanoparticles at various concentrations into a base liquid, have higher density, offer improved thermal conductivity, and have lower heat capacity compared to water, thereby enhancing heat transfer and water productivity. Nazari et al. [79] carried study on the efficiency of an SS utilizing Cu2O–water nanofluid at a concentration of 0.08% along with a glass cooling cover. The setup included a duct connected to four TEMs through which air temperature was reduced. A fan facilitated airflow through the glass cover, further cooling the system. Their results showed that using Cu2O–water nanofluid significantly improved the productivity of water, energy efficiency, and efficiency of exergy by 81%, 80.6%, and 112.5%, in comparison to a CSS. Although the cost of water production using nanofluids is higher than that of pure water due to the expense of nanoparticles, the study reported an optimal production cost of 0.0218 USD/L for the modified MSS. This demonstrates that while the use of nanofluids offers substantial performance enhancements, economic considerations remain critical in determining the feasibility of such modifications.
- Air solar collector: Solar collectors, functioning as solar air heaters, can enhance the temperature of water in an SS through convective heat transfer, utilizing a pool liner to facilitate this process. Abdullah [80] conducted an experimental investigation on the efficiency of a staged SS integrated with a heater using solar to heat the air and the cooled cover from a glass. The system included aluminum (Al) filling with a material that worked as a heat storage beneath the plate of absorption, which maintained a sufficiently high operating temperature to enable water distillation during nighttime. In this setup, hot air was directed beneath the staged solar still, raising the temperature of the saltwater, while cooling water flowed over the glass surface to improve condensation, as depicted in Figure 46. The study reported a 112% increase in the productivity of water for the staged SS compared with conventional designs. Furthermore, the addition of aluminum filling in the staged SS produced a 53% improvement in the productivity of water over the CSS.
 Figure 46. Schematic representation of a staged solar still system integrated with a solar-heated air mechanism and aluminum-based heat storage for improved water distillation efficiency SS. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [80]. Copyright 2013, Elsevier.
Figure 46. Schematic representation of a staged solar still system integrated with a solar-heated air mechanism and aluminum-based heat storage for improved water distillation efficiency SS. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [80]. Copyright 2013, Elsevier. - Geometry: Elashmawy [3] examined the influence of a cooling of the glass surface and solar collectors on the efficiency of a high-temperature tubular SS (HTS-SS). To enhance the evaporation rate, a concentrator with a parabolic shape and solar tracking was employed, optimizing the solar energy input. The study involved three configurations: a conventional high-temperature tubular SS, one using water cooling by spray, and another with film water cooling applied to the glass surface of the tubular still. In the cooling by spray configuration, water was sprayed and atomized upon the surface of the glass at a rate of 20 mL/h, while in the film cooling configuration, water was introduced into the space between the two glass tubes at a flow rate of 40 mL/min. Contrary to expectations, the results showed that the productivity of water decreased by approximately 10% with cooling through spray application and by 43.8% with film cooling compared with the conventional HTS-SS without glass cooling. The findings indicate that cooling of the glass cover is not an effective approach for stand-alone tubular SS, as illustrated in Figure 47.
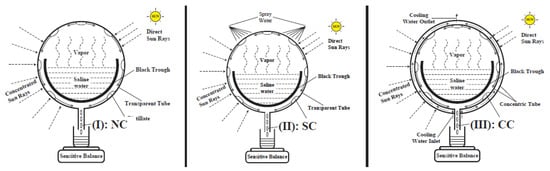 Figure 47. Schematic representation of HTC-SS: (I) without cooling of the glass surface; (II) with cooling through spray application; and (III) using water circulation between two cylindrical glass layers. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [3]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
Figure 47. Schematic representation of HTC-SS: (I) without cooling of the glass surface; (II) with cooling through spray application; and (III) using water circulation between two cylindrical glass layers. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [3]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
A comparative analysis of various modified solar still techniques, as summarized in Table A1 in Appendix A, highlighted significant differences in the productivity of water and the cost per liter (CPL). The highest increase in water productivity was achieved using a Hybrid Single Slope SS distiller equipped with PV-powered TEMs for dual heating and cooling functions (HSPT), which enhanced productivity by approximately 6.7 times under the climatic conditions of Amman, Jordan. In contrast, the lowest CPL was reported for a solar still incorporating an external separate condenser, a collector operated by solar, and a phase change material. This configuration achieved a cost of 0.011 USD/L, demonstrating exceptional cost efficiency in Bangladesh [81]. These findings underscore the importance of selecting appropriate modifications based on regional climatic conditions and economic feasibility to optimize the efficiency and affordability of SS.
4. Thermoelectric Modules (TEC/TEH)
The performance of SSs has been significantly enhanced through the integration of thermoelectric cooling (TEC), nanofluids of CuO–water, and vibratory agitation, as demonstrated by Khairat Dawood et al. [82]. Their study utilized CuO nanoparticles at concentrations of 0.5%, 1%, and 1.5%, with a setup that included four coil springs and a DC motor to induce vibration in a solar still. By connecting the cold side of TEMs to a glass cover, they effectively reduced the temperature of the glass. Notably, the yields per day of the solar stills with vibration and cooling of the glass surface increased by about 212.2% at 1.5% concentration, while those with vibration alone achieved a 47.9% increase compared with CSS.
Nazari et al. [79] further advanced the concept by combining thermoelectric cooling, an external separate condenser, and Cu2O–water nanofluid in a single-sided SS. Their findings indicated substantial improvements in productivity of water, energy, and exergy efficiency, with increases of approximately 38.5%, 38.9%, and 31.2%, respectively, compared with traditional systems. Additionally, incorporating a 0.08% fraction of the volume of Cu2O nanoparticles in saline (brackish) water resulted in even more impressive enhancements, with productivity, energy, and exergy efficiency improving by about 82.4%, 81.5%, and 92.6%. Parsa et al. [83] evaluated three different solar still configurations, including one with thermoelectric heating in the tank liner and another incorporating silver–water nanofluid. Their results revealed a remarkable 100.5% boost in productivity of water and a 26.7% boost in thermal efficiency for systems employing nanofluid and an external condenser compared with the conventional still. The combined effects of TEC and water film cooling contribute approximately 26.3% to the overall productivity, as presented in Figure 48.
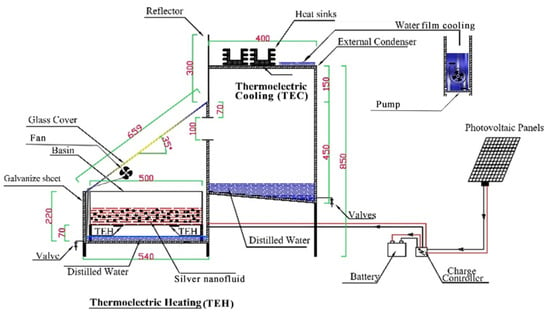
Figure 48.
Schematic representation of enhanced solar still configuration utilizing thermoelectric cooling and silver–water nanofluid for improved efficiency. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [83]. Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
Pounraj et al. [84] examined the effects of TEH and TEC of the cover of glass on the thermal efficiency and production of water rates of the system. By preheating the water inlet using a solar PV module and employing thermoelectric modules for heating and cooling (Figure 49), they reported a staggering 6.5-times boost in production of water in comparison to traditional systems.
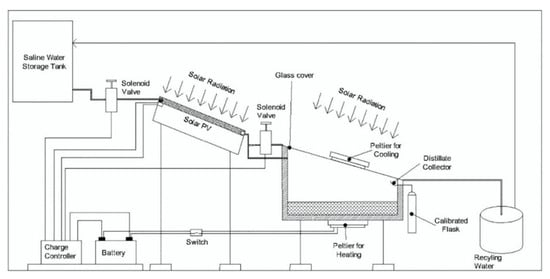
Figure 49.
Illustration of an SS integrated with a TEH and TEC. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [84]. Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
Manokar et al. [85] tested and proposed different solar still configurations, including those with TEH and TEC. Their research demonstrated that daily yields improved by approximately 50.13% and 58.55% for systems with thermoelectric heating and combined heating/cooling, respectively, compared with conventional setups. The energy and exergy efficiencies also saw remarkable increases of 248.4% and 269.2%, respectively. In a subsequent study, they found that annual freshwater yields could be enhanced by 50.92% and 59.21% in systems employing thermoelectric hot and cold sides, respectively. Further numerical studies by Esfe and Toghraie [86] explored the effects of TEC on solar still performance, revealing a direct correlation between solar radiation intensity and freshwater production rates. Their simulations indicated that applying thermoelectric cooling to a portion of the use of glass increased production of water by about 15% to 62%. In Figure 50, the distribution of various cooling techniques, including cooling of the glass, external condensers, and TEC, is illustrated to highlight their effectiveness in enhancing the rate of condensation for SS in conjunction with other evaporation processes. Moreover, Figure 51 presents a comparative analysis of different techniques, such as photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) systems, phase change materials (PCMs), water heaters using solar, nanofluids, solar air heaters, electric heaters, and TEH, which are employed to improve the rate of evaporation for solar stills alongside alternative condensation processes.
Figure 52 illustrates the contributions of various enhanced production methods based on different foundational techniques aimed at increasing the condensation rate of solar stills. Additionally, Figure 53 depicts the effectiveness of integrating multiple foundational techniques to optimize production methods, thereby enhancing both the condensation process and evaporation process rates of SS. Figure 54 shows the participation percentage of improved production methods by combining two or more types of techniques.
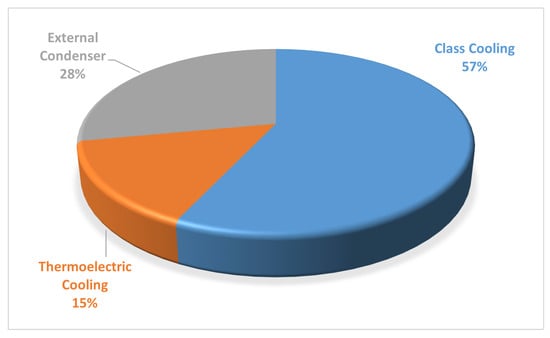
Figure 50.
Techniques for improving condensation efficiency in solar still systems. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [87]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier.
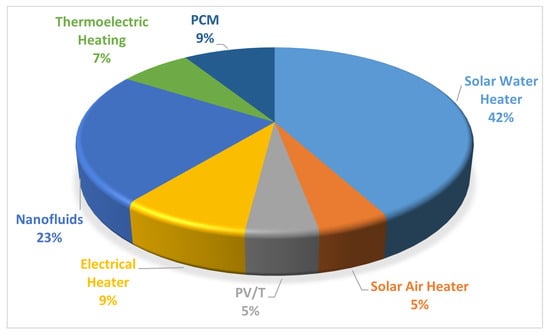
Figure 51.
Methods for enhancing evaporation efficiency in solar still systems. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [87]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier.
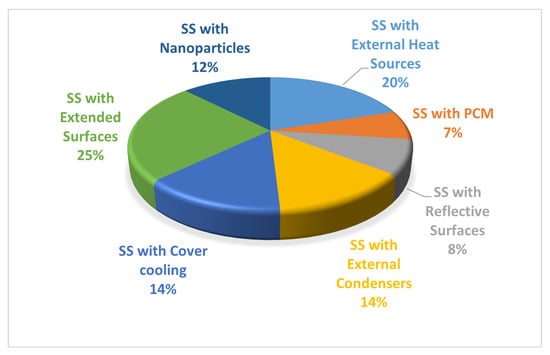
Figure 52.
The participation percentage of the improved production methods for base techniques in solar stills.
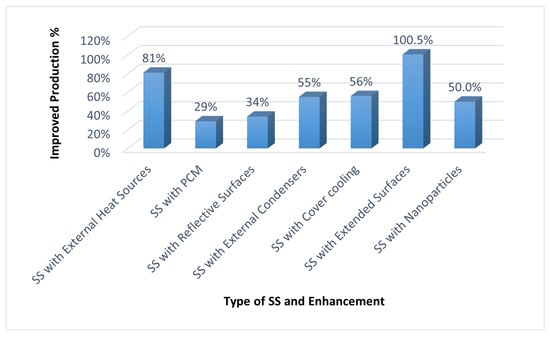
Figure 53.
The percentage of improved production for the main techniques in solar stills.
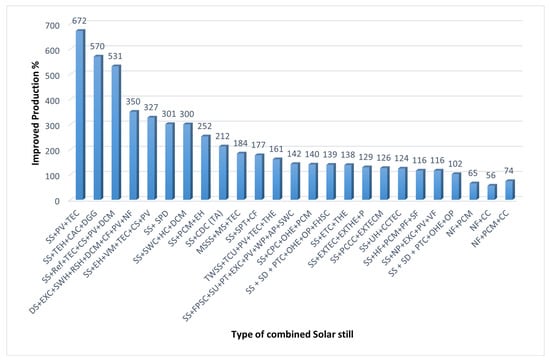
Figure 54.
The percentage of improved Production for the main techniques in solar stills (Meaning of the symbols see Table 1).

Table 1.
The meaning of the symbols in Figure 54.
5. SS Systems Productivity and Cost
One of the primary drawbacks of solar still (SS) systems is their low productivity per unit area. The cost of water produced by these systems often fails to compete with traditional desalination methods. However, SS systems can be particularly advantageous in specific contexts, such as remote locations, during travel, in small villages with sparse populations, and in less developed regions. Given their low productivity, the cost of distillate yield from SS systems is typically expressed in USD per liter. The cost of water generated through SS systems is influenced by several factors, including the initial capital investment, the average annual yield, and the system’s lifespan. These parameters are further affected by variables such as material costs, the quality and availability of feed water, manufacturing expenses, labor wages, and prevailing weather conditions in the operational area. As summarized in Table A2 in Appendix A, a comparison of the cost per liter for various types of SS systems reveals that the lowest cost was associated with solar stills equipped with external condensers, solar collectors, and phase change materials, at approximately USD 0.011 per liter [81]. Another competitive cost of USD 0.0117 per liter was noted for SS systems utilizing phase change materials [38]. Conversely, the highest cost per liter was reported for a reference solar still setup without modifications, which yielded about USD 0.452 per liter, while a system utilizing black hemp pieces covering triangular metal frames achieved a cost of approximately USD 0.427 per liter [78]. The findings indicate that the most significant increase in water productivity, quantified as 6.5 times that of conventional solar stills, was observed in systems employing external thermoelectric cooling and heating. It should be noted that the reported costs can vary based on the researchers’ assumptions, the timeframe of the study, and the geographical context, which may not accurately reflect actual expenses. Therefore, a comprehensive literature review suggests that precise estimations of water production and pricing from SS systems necessitate experimental investigations for validation. To move beyond a narrative aggregation of findings, Table 2 presents a critical comparison of solar still technologies based on key metrics, including annual productivity, cost per liter, and relative performance gains. This facilitates a more structured assessment of the practical implications of each method.

Table 2.
Comparison of solar still (SS) configurations with key enhancements, cost, and productivity.
Assumptions Behind Cost Calculations in the Articles
- Geographic location: The lowest reported cost of 0.011 USD/L was achieved under real-world conditions in Rajshahi, Bangladesh, a region with high solar irradiance that supports consistent freshwater production with low operating costs. For comparative context, other regions referenced include Erzurum, Turkey (up to 0.452 USD/L), and Al-Arish, Egypt.
- Scale of deployment: The cost analysis is based on small-to-medium-scale systems, typically involving single-slope basin designs with surface areas of approximately 1–2 m2. These setups are intended for domestic or community-level applications. While precise commercial scalability is not always stated in the source studies, these sizes represent realistic pilot or field-tested implementations.
- System configuration: The 0.011 USD/L cost is associated with a hybrid solar still incorporating a phase change material (PCM), external condenser, and solar collector. This configuration improves energy retention, prolongs operation hours, and enhances condensation efficiency—key factors in lowering the cost per liter.
- Operating time and productivity assumptions: Water production is typically measured on a daily basis and then annualized to estimate long-term yield. Productivity gains in the referenced systems range from 2 times to 6.7 times over conventional solar stills.
- Material and component costs: Cost efficiency is enhanced by the use of affordable and locally available materials, such as paraffin wax for PCM and passive solar components. Most systems avoid complex automation or high-energy devices, further minimizing capital and operating expenses.
- Maintenance and lifespan: While detailed maintenance schedules are not always provided, the reliance on passive technologies suggests low maintenance requirements. Assumed operational lifespans range between 5 and 10 years, consistent with other solar desalination systems. Some cost estimates are supported by exergoeconomic analysis, though detailed amortization models are not uniformly applied.
- Environmental and economic context: The cost estimates reflect conditions typical of developing regions, such as low labor costs, abundant solar availability, and minimal reliance on high-cost infrastructure. R&D and prototype fabrication costs are generally excluded from these calculations.
6. Future Work
Future research in the field of solar still (SS) systems should address several key areas to enhance performance and efficiency:
- Currently, glass and plexiglass are the predominant materials used as covers, yet these materials exhibit low thermal conductivity, which limits their effectiveness in glass cooling applications. Investigating alternative materials with superior thermal conductivity could significantly improve the condensation rate.
- Another avenue for optimization involves the thermoelectric modules utilized for both heating and cooling processes. Future studies should focus on refining the configuration of these systems, including the number of thermoelectric heating and cooling elements, as well as their power consumption, to maximize efficiency.
- Additionally, employing nanocoatings may enhance the absorption of solar intensity within the basin, thereby increasing the condensation rate, particularly when coupled with hydrophobic glass covers. This approach warrants further exploration to assess its potential benefits.
- To comprehensively understand the impacts of thermoelectric cooling and heating on the water productivity of various SS designs, computational fluid dynamics (CFDs) simulations or MATLAB modeling could be utilized. These tools would provide valuable insights into the operational dynamics of different configurations.
- Exploring the integration of solar refrigerators to lower the temperature of external condensers, along with the substitution of nanofluids for traditional liquid glass cooling, presents another promising area for research. This approach could further enhance the condensation rate.
- Finally, the utilization of low-cost materials, such as plastic in place of glass, could improve the economic viability of water production from solar still systems. This shift in materials could lead to more sustainable and accessible desalination solutions.
7. Future Outlook: Pathways for Integrating Hybrid Solar Still Technologies
The integration of phase change materials (PCMs), thermoelectric modules (TEMs), and nanotechnology into solar still (SS) systems offers unprecedented potential for boosting water productivity and sustainability. These hybrid solutions have demonstrated improvements ranging from 56% to over 670% in laboratory conditions, depending on the configuration. However, widespread adoption requires more than performance metrics; it demands scalable, durable, and economically feasible deployment models. This section explores the anticipated development trajectory, key integration challenges, and projected timelines for realizing hybrid SS technologies in real-world contexts.
7.1. Near-Term (1–3 Years): Experimental Optimization and Modeling
In the short term, efforts should focus on refining system configurations and evaluating component interactions. For instance, more studies are needed on the following:
- Optimizing the number and arrangement of TEM heating/cooling elements for varying climates,
- Developing CFD and MATLAB models that simulate hybrid systems under diverse environmental conditions,
- Testing novel nanomaterials, including hydrophobic nanocoatings, for improving condensation efficiency.
Pilot projects, particularly in sun-rich regions such as South Asia and the Middle East, can provide critical validation for modular, small-scale units.
7.2. Mid-Term (3–7 Years): Standardization and Field Deployment
By the mid-decade mark, efforts should shift toward standardizing components and maintenance protocols to ensure operational stability and scalability. This includes the following:
- Establishing guidelines for maintenance intervals, especially for cleaning and replacing nanofluids and TEM components,
- Evaluating material degradation over time under outdoor exposure,
- Creating field-deployable kits for schools, villages, or disaster-prone areas using low-cost materials like plastic in place of glass.
Integration with solar-powered refrigerators or waste heat recovery systems could also be explored to boost nighttime productivity or reduce condenser temperatures.
7.3. Long-Term (7–10+ Years): Commercialization and Policy Integration
To achieve widespread adoption, the next decade should see efforts focused on the following:
- Life-cycle assessments (LCA) and exergo-economic studies to benchmark environmental impact and return on investment,
- Collaborations with policymakers to embed SS systems in national water strategies, particularly in off-grid or post-disaster recovery programs,
- Encouraging open-source designs and localized manufacturing to reduce costs and increase access.
Furthermore, hybrid designs involving PV/T + TEM + PCM + nanofluids could mature into commercially available plug-and-play water production units, suitable for deployment in rural and urban areas alike.
8. Conclusions Drawn from the Literature
Solar stills are widely recognized as effective tools in desalination systems due to their low operational costs, adaptability to various climates, and environmentally friendly nature. The performance and water production of solar stills are significantly influenced by the temperature differential between the water and the glass cover; higher water temperatures enhance evaporation, while lower glass temperatures improve overall productivity. Extensive research has been conducted to optimize the productivity of solar stills, examining the impacts of various foundational techniques as well as combinations of these techniques to elevate water temperatures. Techniques such as nanoparticles, phase change materials (PCMs), thermoelectric heating, photovoltaic/thermal systems, solar collectors, air heaters, and electric heating have been explored to enhance condensation rates through methods like water and air glass cooling, external condensers, and thermoelectric cooling. From a comprehensive review of existing literature on solar still desalination systems, several conclusions have emerged:
- The highest cost per liter of water produced was recorded in a reference solar still setup with thermoelectric cooling and surface fans, which amounted to approximately USD 0.452 per liter in Erzurum, Turkey.
- Conversely, the lowest cost per liter was found in a solar still incorporating an external condenser, PCM, and wick material, at around USD 0.011 per liter in Rajshahi, Bangladesh.
- The reported cost of 0.011 USD/L was based on a prototype hybrid system operated under high solar radiation conditions in Rajshahi, Bangladesh, integrating an external condenser, PCM, and solar collector. The cost estimation assumes small-scale deployment, minimal maintenance, low material costs, and sustained productivity over typical solar daylight hours.
- Due to the intricate nature of evaporation and condensation processes in solar still systems, the majority of prior research has focused on experimental investigations, with relatively few studies utilizing theoretical or mathematical modeling and even fewer employing numerical methods.
- Given the inherently low productivity of solar stills, most research efforts have concentrated on enhancing the distillate yield, which can be achieved through several strategies:
- Increasing the evaporation rate: this can be accomplished by elevating brackish water temperatures via heaters, solar collectors, and heat exchangers; expanding the evaporation surface area using fins and wicks; enhancing solar gain with reflective surfaces; or storing solar heat with thermal storage materials.
- Increasing the condensation rate: this is typically achieved by lowering the cover temperature through film cooling or utilizing external condensers.
- Improving the thermo-optical properties of brackish water: this can be done by adding dyes and/or nanoparticles to enhance thermal conductivity and solar radiation absorption.
- Integrating multiple enhancements: some researchers have successfully combined various improvements to the solar still system or introduced innovative designs, such as multi-stage solar stills.
- Expanding the evaporation surface area is a promising approach to enhance productivity, as evaporation occurs at the water’s surface; thus, a larger surface area correlates with increased output.
- The use of nanoparticles, including nano-enhanced PCM, nanocoatings, and nano-fluids, has a direct and positive impact on the water production rate of solar stills.
- Accurately estimating water production rates or costs associated with solar still systems is challenging without experimental validation.
- The optimal tilt angle for the cover is generally recommended to match the geographical location’s latitude.
- A shallower water depth tends to enhance daytime productivity, while greater depth can improve nighttime yields.
- A double-slope cover configuration is preferred over a single-slope design for better performance.
- Utilizing low-cost materials and manufacturing techniques can significantly reduce the cost of producing one liter of water from solar stills.
- The integration of glass cover cooling with various evaporation methods has generally resulted in increased water production rates, with exceptions noted for tubular solar stills and shaded glass cooling.
- Employing an external heating source and effective water-cooling methods in solar stills has been shown to substantially increase thermal efficiency.
- The most significant productivity enhancements were observed in single-slope systems utilizing solar parabolic dishes. For example, the application of separate thermoelectric cooling and heating modules resulted in a 6.7-times increase in water productivity compared with conventional solar stills. Other configurations, such as those using double-glazed glass and fins along with thermoelectric cooling, achieved productivity increases of 5.7 times, while combinations of thermoelectric cooling, CuO–water nanofluid, and vibration motion led to a 5.3-times increase. Additionally, a drum distiller equipped with an external condenser and solar water heater, along with nanofluids, resulted in a 3.5-fold increase over traditional solar stills (see Table 3).
 Table 3. The combined methods of improved production for different techniques in SS.
Table 3. The combined methods of improved production for different techniques in SS. - The performance of solar stills is influenced by various factors, including solar radiation, water depth, thermal insulation, and the temperature difference between glass and water. To optimize this temperature differential, two main approaches can be employed: increasing the water temperature or decreasing the glass temperature.
9. Practical Challenges and Sustainability Considerations
While the reviewed innovations in solar still (SS) systems showcase significant advancements in productivity and cost-effectiveness, several practical and environmental challenges remain insufficiently addressed in the current body of literature. These limitations are critical to understanding the true sustainability and long-term viability of such systems, especially for deployment in real-world, resource-constrained environments.
9.1. Material Degradation and Durability
Advanced materials such as phase change materials (PCMs), thermoelectric modules (TEMs), and nanocoatings are central to performance enhancement, yet their long-term durability under harsh environmental conditions is seldom examined. PCMs may undergo leakage, thermal cycling fatigue, or chemical degradation after prolonged use, especially when not encapsulated properly [40]. Likewise, TEMs and nanostructured surfaces can degrade due to repeated thermal stress or ultraviolet (UV) exposure, which compromises efficiency and structural integrity over time.
9.2. System Maintenance and Operational Demands
Many studies highlight the low operating costs of SS systems, but routine maintenance such as descaling, cleaning of glass covers, restoring degraded nanofluids, or replacing oxidized metal components is rarely quantified. In high-salinity regions, salt scaling and biofouling may reduce evaporation rates and require regular cleaning cycles, increasing labor and material costs. The lack of standardized guidelines for cleaning intervals, maintenance frequency, or component replacement limits the reliability of these systems in field applications.
9.3. Environmental and Life-Cycle Impact
The term “environmental sustainability” is often used to describe solar still systems due to their passive operation and renewable energy source. However, few studies conduct a Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA) to account for the environmental impacts of material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, usage, and disposal. For instance, while paraffin wax used in PCMs is relatively inexpensive and effective, its petroleum origin and non-biodegradable nature raise concerns about long-term ecological effects. Similarly, the production of nanoparticles and thermoelectric elements can involve energy-intensive processes and generate hazardous byproducts if not properly managed [79].
9.4. Research Gaps and Future Work
Future studies should incorporate degradation modeling, maintenance scheduling, and comprehensive LCAs to evaluate the real-world feasibility of solar still technologies. Research should also address supply chain sustainability, availability of local materials, and waste management strategies, particularly in off-grid rural areas where replacement parts may be scarce. Incorporating these dimensions will provide a more holistic assessment of system sustainability, beyond laboratory-scale efficiency gains.
10. Barriers to Widespread Adoption of Solar Still Technologies
While solar stills (SSs) represent a promising solution for decentralized freshwater production, especially in regions with abundant solar resources, several practical barriers limit their widespread adoption and commercialization. Despite impressive performance improvements in experimental studies, such as 6.7-fold increases in water productivity using thermoelectric modules (TEMs) and nanofluids, these systems often remain confined to lab-scale prototypes or small-scale field trials. Broader implementation across communities, municipalities, or industries faces several real-world constraints.
10.1. Economic and Market Limitations
Although some configurations demonstrate extremely low costs (e.g., 0.011 USD/L in Bangladesh using PCM and external condensers), many hybrid designs involve high initial capital investment. For instance, systems incorporating TEMs, fans, photovoltaic panels, or advanced nanomaterials may have prohibitively high upfront costs, especially in low-income regions. Additionally, the lack of standardized economic modeling across studies makes it difficult to generalize cost performance across geographies and scales. These concerns are consistent with broader findings in decentralized desalination research, which emphasize the need for techno-economic optimization at scale [97].
10.2. Technological Complexity and Maintenance Needs
Widespread deployment requires systems that are robust, user-friendly, and maintainable without technical expertise. However, many advanced systems reviewed, particularly those integrating TEM cooling, nanofluids, or ultrasonic humidifiers, involve electrical, mechanical, or thermal components that require regular maintenance, calibration, and skilled labor for repair. The article reports on performance gains with these techniques but lacks discussion on technical training, part availability, and maintenance infrastructure. This aligns with concerns raised by Al-Karaghouli and Kazmerski [98], who highlight maintenance as a limiting factor for renewable-powered water technologies in remote areas.
10.3. Geographic and Climatic Constraints
Solar stills rely on direct solar radiation and ambient conditions for optimal performance. As such, their productivity is highly sensitive to seasonal variations, cloud cover, and geographic latitude. While many case studies are conducted in regions like India, Bangladesh, Egypt, and Turkey, the variability of solar availability in other parts of the world limits their feasibility as a universal solution. Furthermore, water source salinity and quality (e.g., presence of oil residues, turbidity, or biofilms) can affect both evaporation and long-term operation. These dependencies underscore the importance of site-specific design customization [99].
10.4. Policy, Awareness, and Regulatory Gaps
The absence of institutional support, subsidies, or policy frameworks for decentralized water desalination technologies further restricts their reach. Unlike large-scale reverse osmosis plants that benefit from government investment, solar still technologies lack commercial incentives and standardized certification, making it difficult for developers and entrepreneurs to secure funding or market adoption. Additionally, limited awareness among rural or periurban communities about SS benefits and operation procedures continues to hinder the bottom-up diffusion of these systems. As noted by Ghaffour et al. [100], the success of renewable desalination systems depends as much on policy and education as on technological readiness.
The following are recommendations to overcome these barriers through future efforts:
- Focus on cost-effective modular designs that balance simplicity and performance.
- Develop maintenance protocols and user training manuals for local deployment.
- Integrate climate-responsive models to customize designs by geography.
- Encourage policy initiatives and subsidy programs to support uptake at the grassroots level.
Author Contributions
All authors provided significant feedback and contributed to structuring the study. M.O.K. was made responsible for conceptualization, methodology, original draft writing, and substantial contributions to the conceptual development of the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RSS | Reference Solar Still | LC | Local Clay Material |
| WI | Wast Iron Residues | WCA | Wick Corrugated Absorber |
| M | Mirrors | MWCNT | Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes |
| SS-WT | Solar Still by Water Cooling and TEG | FA | Forced Air Cooling |
| PMMA | Acrylic | FW | Forced Water Cooling |
| PC | Polycarbonate | HE | Heat Exchanger |
| PMMSSS | Portable Modified Multi-Slope SS | EXSC | External Solar Collector |
| CDSSS | Conventional Double Slope SS | CPC | Compound Parabolic Concentrator |
| CGTCC | Cotton Gauze Top Cover Cooling | PTSS | Portable Thermoelectric Solar Still |
Appendix A

Table A1.
The comparative analysis of condensation and evaporation techniques across various types of solar stills.
Table A1.
The comparative analysis of condensation and evaporation techniques across various types of solar stills.
| SS Type | Condensation Techniques | Evaporation Techniques | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Solar Still (CSS) Desalination | ||||
| Double slope | Air | Conventional | Productivity = 4.15 kg/m2·day. Cost = 0.02 USD/L. | [29] |
| Single slope | Air | Conventional | Productivity = 1.341 L/m2 to 4.186 L/m2. Efficiency = 11.25 to 39.59%. Cost = 0.074 USD/L to 0.024 USD/L. | [30] |
| SS Systems with External Heat Sources (MSS) | ||||
| Single slope | Air | PCM and electric heater | Max freshwater production was at paraffin wax temperature of 65 °C. | [31] |
| Single slope | Air | Solar parabolic trough | Productivity increased by 177%. Hourly freshwater = 0.38 to 0.67 L/m2/h. | [32] |
| Double slope | TEC | TEH | Productivity (water-cooled) = 81.1%. Productivity MSS = 98.9%. | [101] |
| Single slope | Air | Evacuated tube solar collector | Daily yield higher by 20%. Efficiency higher by 26%. Optimum water depth = 0.03 m. | [33] |
| Single slope | Air | Solar parabolic trough | Productivity increased by 18%. | [35] |
| Single slope | Air | Solar pond | Productivity higher by 52.36%. Efficiency higher by 43.8%. | [36] |
| single slope | Air | Solar collector | Productivity increased by 36%. | [34] |
| SS systems with thermal energy storages (PCM) | ||||
| Single slope | Air | Mirrors reflector and PCM | Freshwater by CSS = 0.64, by SS-TEG = 0.63, by SS-TEG-WI = 0.652, and by SS-TEG-WI-M = 0.796 L/m2. | [37] |
| Single slope | Air | PCM and local clay | Using PCM, yield increased by 21%; with local clay, it increased by 38.7%. Daily efficiency of CSS = 34%, with PCM = 41.2%, with LC = 47%. | [38] |
| Single slope | TEC | PCM and nano-paint, TEH | TEH-S had 20% and 7% higher daily energy and exergy efficiency than TEC-S. Productivity of TEH- S to TEC-S improved by 78.8%. cost with TEH = 0.0127 USD/L, with TEC = 0.023 USD/L. | [39] |
| Double slope | External condenser | Solar collector and PCM | Productivity of finned solar still increased by 9.7%, and P of modified solar still increased by 24.7%. | [81] |
| Single slope | Air | PCM and oil heat exchanger | Productivity of CSS = 4.48 L/m2 day, MSS = 10.77 L/m2 day. Daily efficiency of CSS = 25.73%, enhanced daily efficiency = 46%. Productivity enhanced by 140.4%. Efficiency enhanced by 44%. | [40] |
| Single slope | Air | PCM | Productivity, P = from 4.51 to 7.54 L/m2/day. P higher by 67.18%. | [41] |
| Single slope | Air | PCM and V-corrugated absorber | Daily productivity higher by 11.7%. | [43] |
| Single slope | Air | Weir-type cascade with PCM | Daily productivity increased by 31%. Efficiency with PCM = 64%, without PCM = 47%. Daily yield with PCM = 6.7 kg/m2, without PCM = 5.1 kg/m2. | [42] |
| Double slope | Air | Quartzite rock as heat storage | Daily productivity enhancement = 6.2%. | [44] |
| Single slope | Air | Stearic acid PCM | Daily productivity with PCM = 9.005 kg/m2, without PCM = 4.998 kg/m2. Productivity improvement = 80%. | [45] |
| SS Systems with Reflective Surfaces | ||||
| Single slope | Air | Solar parabolic dish SPD and mirror | Productivity increased from 7.5 to 24 L/day. | [46] |
| Single slope | Air | Internal reflectors | Productivity (annual, winter, and summer) = (34%, 65%, and 22%). | [47] |
| Single slope Stepped | Air | Stepped SS and internal and external reflectors | Productivity higher by 57% with internal reflectors only 75% with internal and external reflectors up to 125%. Efficiency = 34%; efficiency of stepped without reflectors = 53%. Efficiency of stepped with reflectors = 56%. | [48] |
| Single slope | Air | Internal and external reflectors | Annual productivity with internal reflectors only = 19.9%; for combined internal and external reflectors at (0°, 10°, 20°, and 30°) slope angle of the external reflector = (34.4%, 34.5%, 34.8%, and 24.7%). | [49] |
| Single slope | Air | Internal and external reflectors | Productivity increased by 48%. | [50] |
| SS Systems with External Condensers | ||||
| Single slope | TEC and fans | CSS | Productivity increased by 35%; optimal amount of salt water = 1.5 L. | [51] |
| Single slope | TEC, THE, and tank | CSS | Productivity increased by 672%. | [12] |
| Double slope | EXTEC | TEH | Productivities = 3.07, 2.70, and 2.46 L/m2 for modified, finned, and CSS. MSS efficiency with and without EXC = 39.74% and 30%. Productivity by 10%. MSS daily efficiency = 14.23% and 22.33% higher than the finned and CSS. CPL for CSS, finned, MSS = 0.0135, 0.0133, and 0.0117 USD/L/m2. | [81] |
| Single slope | Ex. condenser and vacuum pump | CSS | Productivity higher by 16.2%. Daily efficiency of CSS = 29%, of MSS = 37.6%. | [52] |
| Single-slope stepped | Ex. condenser | internal and external reflector | Productivity higher by 66% with external condenser and by 165% with external condenser and internal–external reflectors. | [53] |
| Single slope | Ex. condenser and vacuum fan | Nanoparticles | Daily productivity with external condensers by 53.2%, and by 76% with external condenser and nanoparticles, and up to 116% with external condenser, nanoparticles, and vacuum fan. | [54] |
| Single slope | Ex. condenser | External reflector | Efficiency MSS up to 77%. Daily productivity up to 8 L/m2. | [55] |
| Single slope | Outside passive condenser | External reflector | Daily productivity of MSS improved by 70%, efficiency improved by 75%. | [56] |
| Single slope | External condenser | CSS | Efficiency with external condenser higher by 47%. | [57] |
| SS Systems with Cover Cooling | ||||
| Single slope | Partially coated cover, TEC (12 W and 36 W) | CSS | Productivity with 36 W increased by 126%, efficiency improved by 44%, exergy efficiency decreased by 25%. Lowest cost with TEC (36 W) = USD 0.036, exergo-economic = 4.64 USD/kWh/. | [58] |
| Single slope | Double-glazing and TEC | CSS | Hourly productivity increased by 30%. Production increased by 14% and 25%. Cost = 0.1033 USD/L/m2. | [59] |
| Single slope | Film cooling | Nanoparticles NP, PCM: A. NP into water, B. NP plus PCM, C. NP with cover, D. NP plus PCM with cover | Productivity improvement by (50.28% for A), (65% for B), (56.15% for C), and by (73.8% for D). | [61] |
| Single slope | Water sprinkled over glass | CSS | Daily productivity increased by 20%, efficiency by 21%. | [63] |
| Single slope | Cool water to flow over cover | CSS | Productivity improved by 56.5%, efficiency by 9.9%, optimum flow rate of cooling water = 0.075 kg/s. | [62] |
| Single slope | Heat exchanger as cooler and TEC | CSS | Daily efficiency = 70%. | [60] |
| SS Systems with Extended Surfaces | ||||
| Single slope | TEC and indoor fan | Sponge pieces | Water distillation without fan increased by 100.5%; with fan by 151.1%. | [65] |
| Single slope | Air | Blackened jute cloth | Distillate yield increased by 68% and productivity increased by 79%. | [68] |
| Single slope | Air | Blackened cotton rag | Daily productivity in summer is higher by 15% and in winter by 48%, max productivity = 7.5 kg/m2. | [69] |
| Single slope | Air | Fins and corrugated plates | Productivity with fins improved by 40%, with corrugated plate improved by 21%. | [66] |
| Single slope | Air | Jute cloth | Daily productivity improvement = 20%, daily efficiency of MSS = 52%, Daily efficiency of CSS = 44%. | [71] |
| Single slope | Air | Black coal, sponge cubes, and black steel cubes | Productivity increased about 18%–73%. The black sponge cubes were the most effective. | [70] |
| Single slope | Air | Floating black aluminum plate | Yield increased by 15% at a water depth of 3 cm and up to 40% at 6 cm. | [67] |
| Other Improvements to the SS Systems | ||||
| Single slope | TEC | Water-absorbing materials, Case 5 (triangular metal frame), Case 6 (form of upright columns) | Purified water recovered of Case 5 = 34 g and Case 6 = 40 g. Efficiency of Case 5 increased by 29% and Case 6 by 45%. Cost Case 6 reduction per liter by 35%. | [78] |
| Single slope | TEC | Electric heater and vibratory motion | Productivity in summer = 12.82 kg/day. Max cost = 0.01786 USD/L/m2. | [72] |
| Single slope | TEC | Ultrasonic humidifiers and cotton net tent | Productivity increased by 124%. Efficiency of MSS = 95.8% of CSS = 35.6%. Cost of MSS about 0.04 USD/L for CSS about 0.042 USD/L. | [77] |
| Double slope | TEC | Al2O3–water, TiO2–water, MWCNT–water, and CuO–water nanofluids | Productivity with MWCNT–water (0.9% volume fraction for all) increased by 11.57%, with Al2O3–water by 6.32%, with CuO–water by 7.16%, with TiO2–water by 4.66%. | [11] |
| Tubular | Water cooling | Compound parabolic concentrator | Productivity with spray cooling decreased by 10%, with film cooling decreased by 43.8%. | [3] |
| Single slope | Air | Cu2O–water nanofluid | Productivity improved by 81%. Efficiency by 80.6% and exergy efficiency by 112.5%. Optimal cost of MSS about 0.0218 USD/L. | [6] |
| Double-tilt SS | Rubber scrapers | CSS | Daily productivity = 4.24 L/m2. Productivity increased by 63%. | [76] |
| Staged solar still | Water cooling | Solar air heater and heat storage material | Water productivity of MSS increased by 112%; productivity with AL filling increased by 53%. | [80] |
| Pyramidal SS | Internal fan | CSS | Productivity increased by 20%. | [74] |
| Single slope | Air | Inverted absorber SS | Daily productivity of MSS = 6.3 kg/m2, for CSS = 4.15 kg/m2. Efficiency of MSS = 34.6%, for CSS = 48%. Optimum water depth = 3 cm. | [75] |
| Single slope | Air | Sun-tracking system | Daily productivity increased by 22%. | [73] |

Table A2.
Average annual water productivity and associated cost of various solar still (SS) systems reported in the literature. NA = Not Available (data could not be obtained).
Table A2.
Average annual water productivity and associated cost of various solar still (SS) systems reported in the literature. NA = Not Available (data could not be obtained).
| References | Type of SS and Enhancement | Study Location | Annual Productivity (L/m2) | Cost of Productivity (USD/L) | Improved Production % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 [46] | SS with SPD, mirror reflector | Iran | 8760 | NA | 301 |
| 2024 [46] | CSS | Iran | 2737 | NA | |
| 2024 [51] | SS with surface fans/RSS | Turkey | 186.95 | 0.197 | |
| 2024 [51] | SS with TEC, transfer fan | Turkey | 250.75 | 0.187 | 35 |
| 2024 [78] | RSS/SS with TEC, surface fans/Case 1 | Turkey | 97.19 | 0.452 | |
| 2024 [78] | RSS with hemp (greyish beige)/Case 2 | Turkey | 113.03 | 0.388 | 16 |
| 2024 [78] | RSS with black hemp in basin/Case 3 | Turkey | 122.32 | 0.359 | 25 |
| 2024 [78] | RSS with black hemp in triangle/Case 4 | Turkey | 102.79 | 0.427 | 5 |
| 2024 [78] | With black papers on triangle/Case 5 | Turkey | 130.58 | 0.336 | 34 |
| 2024 [78] | With papers in upright columns/Case 6 | Turkey | 150.53 | 0.292 | 54 |
| 2024 [12] | SS with PV powered TEM | Jordan | 281 | NA | 672 |
| 2024 [13] | CSS/single-glazed glass | Iran | 141.13 | 0.0739 | |
| 2024 [13] | MSS/DGG and fins, TEC | Iran | 586.26 | 0.0326 | 570 |
| 2023 [37] | CSS | Iran | 234 | 0.062 | |
| 2023 [37] | SS-TEG | Iran | 230 | 0.075 | |
| 2023 [37] | SS-TEG-WI | Iran | 238 | 0.074 | |
| 2023 [37] | SS-TEG-WI-M | Iran | 291 | 0.071 | 24 |
| 2023 [23] | CSS | Iran | 273 | 0.042 | |
| 2023 [23] | SS-WT | Iran | 303 | 0.098 | 16 |
| 2023 [23] | SS-HP | Iran | 386 | 0.077 | |
| 2023 [23] | SS-HP-WT | Iran | 424 | 0.084 | 55 |
| 2023 [58] | Partially coated, external TEC/12W | Malaysia | 292 | 0.047 | 49 |
| 2023 [58] | Partially coated, external TEC/36W | Malaysia | 383.98 | 0.036 | 126 |
| 2023 [102] | CSS | Malaysia | 381.06 | 0.0473 | |
| 2023 [102] | Glass cover, external TEC | Malaysia | 671.81 | 0.042 | 76 |
| 2023 [102] | PC cover, external TEC | Malaysia | 69.84 | 0.376 | |
| 2023 [102] | PMMA cover, external TEC | Malaysia | 177.05 | 0.1469 | |
| 2023 [31] | SS with PCM and electric heater | Egypt | 2884 | 0.0176 | 252 |
| 2023 [90] | PMMSSS | Iran | 565.75 | 0.081 | 184 |
| 2023 [90] | CDSSS | Iran | 282.875 | 0.072 | |
| 2022 [39] | Pyramid solar stills, TEH | Iran | 3240 | 0.0127 | 78 |
| 2022 [39] | Pyramid solar stills, TEC | Iran | 1812 | 0.023 | |
| 2022 [38] | CSS | Egypt | 1320.9 | 0.00254 | |
| 2022 [38] | SS with PCM/SSPCM | Egypt | 1599 | 0.0117 | 21 |
| 2022 [38] | SS with LC/SSCL | Egypt | 1832 | 0.00241 | 38 |
| 2022 [59] | Double-glazing cooling, TEG | Iran | 288.9 | 0.1033 | 30 |
| 2022 [59] | CSS, single glass | Iran | 201.3 | 0.0972 | |
| 2022 [95] | CSS | India | 790 | 0.022 | |
| 2022 [95] | With hollow fins, PCM, and sisal fibre. | India | 1710 | 0.036 | 116 |
| 2022 [72] | CSS | Egypt | 748 | 0.0192 | |
| 2022 [72] | EH, VM, TEC/MSS | Egypt | 3193 | 0.01786 | 327 |
| 2022 [77] | With UH cotton mesh, TEC | Russia | 846 | 0.04 | 124 |
| 2022 [77] | CSS | Russia | 377.1 | 0.042 | |
| 2022 [91] | TWSS | India | 503 | 0.25 | |
| 2022 [91] | TWSS+TCU+PV+TEC+THE | India | 1317 | 0.25 | 161 |
| 2022 [103] | WCA, nano-PCM, and PV-heaters | Saudi A. | 2108 | 0.025 | |
| 2021 [32] | SS with SPT | Yemen | 1925 | 0.0135 | 177 |
| 2021 [32] | CSS | Yemen | 1080 | 0.0145 | |
| 2021 [89] | With HC, external solar water heater | Russia | 2250 | 0.0268 | 296–300 |
| 2021 [89] | CSS | Russia | 558 | 0.0282 | |
| 2021 [104] | SS with ultrasonic humidifiers | Russia | 756 | 0.0259 | 68 |
| 2021 [104] | CSS | Russia | 450 | 0.0349 | |
| 2021 [11] | Al2O3–water nanofluid, TEC | Iran | 853.78 | 0.12 | 18 |
| 2021 [11] | MWCNT–water nanofluid, TEC | Iran | 895.9 | 0.1502 | 23 |
| 2021 [11] | TiO2–water nanofluid, TEC | Iran | 840.39 | 0.1431 | 16 |
| 2021 [11] | CuO–water nanofluid, TEC | Iran | 860.47 | 0.1652 | 19 |
| 2021 [101] | TEH, water-cooled | Iran | 385.5 | 0.243 | 81 |
| 2021 [101] | TEH, air-cooled | Iran | 212.8 | 0.277 | |
| 2021 [101] | Modified water-cooled | Iran | 468.4 | 0.201 | 21 |
| 2021 [15] | Ag/Fe3O4 hybrid nanofluid, TEC | Iran | 3160 | 0.019 | |
| 2021 [81] | ExC, Solar collector, PCM | Bangladesh | 1250 | 0.011 | |
| 2021 [82] | TEC, CuO–water nanofluid and VM | Egypt | 2500 | 0.027 | 531 |
| 2021 [82] | CSS | Egypt | 396 | 0.06 | |
| 2021 [93] | CSS | Egypt | 1140 | 0.02423 | |
| 2021 [93] | MSS | Egypt | 1263.5 | 0.023186 | |
| 2021 [95] | MSS + SD | Egypt | 1462.3 | 0.020288 | |
| 2021 [93] | MSS + PTC | Egypt | 2419.4 | 0.020308 | |
| 2021 [93] | MSS + SD + PTC | Egypt | 2725.4 | 0.018164 | 139 |
| 2020 [105] | SS with external solar collector | Russia | 2007 | 0.047 | |
| 2020 [106] | SS at different water depths at 1 cm | Russia | 584 | 0.033 | |
| 2020 [107] | SS with UH, SWH | Egypt | 2701 | 0.037 | |
| 2020 [94] | Double SS with TEH and TEC | Iran | 1032.5 | 0.1055 | 129 |
| 2020 [94] | CSS | Iran | 449 | 0.176 | |
| 2020 [108] | CSS + PTC | Egypt | 2182 | 0.0217 | |
| 2020 [108] | MSS + PTC | Egypt | 2419 | 0.0203 | |
| 2020 [108] | MSS + PTC + U | Egypt | 2236 | 0.0223 | |
| 2020 [108] | MSS + PTC + FA | Egypt | 2522 | 0.0211 | |
| 2020 [108] | MSS + PTC + FW | Egypt | 2618 | 0.0209 | 22 |
| 2020 [96] | CSS | Egypt | 1140 | 0.02422 | |
| 2020 [96] | CSS + PTC | Egypt | 2182 | 0.021754 | |
| 2020 [96] | CSS + SD + PTC | Egypt | 2469.7 | 0.01937 | 102 |
| 2020 [96] | CSS + WM | Egypt | 1230 | 0.02472 | |
| 2020 [96] | CSS + WM + PTC | Egypt | 2289 | 0.02195 | |
| 2020 [109] | EXC, Al2O3 nanoparticles into PCM | Egypt | 2263 | 0.014 | 55 |
| 2020 [109] | CSS | Egypt | 1460 | 0.015 | |
| 2020 [85] | TEC, TEH | India | 1664 | 0.32 | |
| 2020 [110] | Single slope using PV/T-Black steel | Egypt | 1085 | 0.0315 | |
| 2020 [2] | Tubular using Parabolic concentrator | Saudi A. | 92 | 0.29 | |
| 2020 [111] | Conventional single slope/CSS | India | 495.04 | 0.0268 | |
| 2020 [111] | SS with Ultrasonic fogger/MSS | India | 596.775 | 0.0268 | 20 |
| 2020 [83] | TEH-Reflectors | Iran | 2971.1 | 0.0261 | |
| 2020 [112] | Passive SS | Iran | 916.15 | 0.015 | |
| 2020 [64] | With ETC, HE, SGC (½ shading) | India | 771 | NA | 16.4 |
| 2020 [64] | EXSC, ETC, THE, SGC | India | 2250.9 | 0.0136 | 138 |
| 2020 [64] | CSS | India | 946.11 | 0.0084 | |
| 2019 [113] | SS with PCM | Iraq | 857 | 0.035 | |
| 2019 [6] | With Cu2O nanofluid at 0.04% volume | Iran | 1557 | 0.0235 | |
| 2019 [6] | External TEC, Cu2O–water nanofluid | Iran | 1860 | 0.023 | 81 |
| 2019 [88] | CSS | Saudi A. | 816 | 0.05 | |
| 2019 [88] | Drum distiller DDs with heater only | Saudi A. | 3638 | 0.034 | |
| 2019 [88] | DDs with EXC, SWH, nanofluid | Saudi A. | 3740 | 0.039 | 350 |
| 2019 [114] | SS With PCM (Paraffin wax) | India | 905 | NA | 29 |
| 2019 [114] | SS With PCM (stearic acid) | India | 837 | NA | |
| 2019 [114] | SS With PCM (lauric acid) | India | 806 | NA | |
| 2019 [3] | Compound Parabolic Concentrator | Saudi A. | 1558.5 | 0.015 | |
| 2019 [3] | Spray cooling, CPC | Saudi A. | 1402.6 | 0.02 | 10 |
| 2019 [3] | Water cooling, CPC | Saudi A. | 876 | 0.035 | 43 |
| 2018 [115] | Water cooling, Electrical heater-PV/T | India | 2628 | NA | |
| 2017 [30] | Changed average gap (basin-glass) | India | 1525 | 0.024 | 212 |
| 2017 [30] | CSS | India | 489 | 0.074 | |
| 2017 [76] | Double-tilt SS with rubber scrapers | Malaysia | 1420.4 | 0.034 | 63 |
| 2017 [41] | CPC with PCM, oil heat exchanger | Egypt | 3931 | 0.0174 | 140 |
| 2017 [41] | CSS | Egypt | 1635 | 0.0177 | |
| 2017 [116] | Double slope with TEH/night | Iran | 547 | 0.237 | |
| 2017 [116] | Double slope with TEH/day | Iran | 912 | 0.1422 | |
| 2017 [117] | Condenser type solar still | Egypt | 1511 | 0.0147 | 35 |
| 2016 [63] | MSS/spray cooling | India | 1292 | NA | 20 |
| 2016 [40] | MSS With PCM | Egypt | 2752 | 0.03 | 67 |
| 2016 [118] | CSS | India | 1153 | 0.057 | |
| 2016 [118] | Square fins with wick in basin | India | 1660 | 0.049 | 45 |
| 2015 [119] | Double SS, Flat plate solar collector | Egypt | 3671 | NA | 33 |
| 2014 [62] | Water cooling (for Jodhpur climate) | India | 900 | 0.012 | 56 |
| 2014 [120] | V-type with CGTCC and air over glass | India | 1679 | 0.028 | 39 |
| 2014 [120] | V-type with CGTCC | India | 1569 | 0.012 | 30 |
| 2014 [120] | V-type and water over glass | India | 1204 | 0.014 | |
| 2014 [54] | External condenser, nanofluid | Egypt | 2040 | 0.05 | 116 |
| 2014 [54] | Vacuum fan only | Egypt | 1360 | 0.041 | 53 |
| 2014 [92] | CSS/Conventional solar still | Egypt | 850 | 0.049 | |
| 2014 [92] | DSS/Developed solar still | Egypt | 1360 | 0.056 | 56 |
| 2014 [92] | ECSS/Equivalent CSS | Egypt | 1122 | 0.0485 | 142 |
| 2014 [92] | DSS/with WSC (forced mode) | Egypt | 2040 | 0.066 | 82 |
| 2012 [60] | TEM SS (PTSS), heat-pipe cooling | Iran | 180 | 0.18 | |
| 2012 [60] | Pyramid shape | Iran | 1533 | 0.031 | |
| 2012 [60] | Sun tracking | Iran | 250 | 0.23 | |
| 2012 [60] | Single slope | Iran | 1511 | 0.035 | |
| 2012 [60] | Transportable hemispherical | Iran | 1026 | 0.18 | |
| 2012 [60] | A weir type | Iran | 1001 | 0.054 | |
| 2011 [121] | SC, sprinkling system, TEC | Iran | 438 | 0.13 | |
| 2011 [121] | Thermoelectric solar still | Iran | 730 | 0.13 | 66 |
| 2011 [42] | Weir-type cascade with PCM | Iran | 2445 | NA | 31 |
| 2011 [55] | External reflector, external condenser | Botswana | 2920 | NA | |
| 2011 [75] | Inverted absorber SS (IASS) at 0.01 m | Oman | 2300 | 0.0148 | |
| 2011 [75] | Inverted absorber (IASS) at 0.02 m | Oman | 2035 | 0.0132 | |
| 2011 [75] | Inverted absorber (IASS) at 0.03 m | Oman | 1569 | 0.0124 | |
| 2009 [45] | SS with stearic acid PCM | Saudi A. | 3286 | NA | 27 |
| 2009 [122] | SS with hybrid (PV/T) active solar still | India | 1203 | 0.0321 | |
| 2007 [123] | Single-slope solar distiller | Pakistan | 1149 | 0.062 | |
| 2005 [34] | SS with solar collector | Jordan | 1281 | 0.115 | |
| 2002 [29] | Double slope | Oman | 1514 | 0.02 | |
| 1999 [56] | External reflector | Turkey | 2555 | NA |
References
- Madiouli, J.; Lashin, A.; Shigidi, I.; Badruddin, I.A.; Kessentini, A. Experimental study and evaluation of single slope solar still combined with flat plate collector, parabolic trough and packed bed. Sol. Energy 2020, 196, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashmawy, M.; Alshammari, F. Atmospheric water harvesting from low humid regions using tubular solar still powered by a parabolic concentrator system. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashmawy, M. Effect of surface cooling and tube thickness on the performance of a high temperature standalone tubular solar still. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 156, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, H.; Yang, Y.; Hou, L.A.; Chen, G. Analysis of the characteristics of heat and mass transfer of a three-effect tubular solar still and experimental research. Desalination 2013, 330, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargva, M.; Yadav, A. Experimental comparative study on a solar still combined with evacuated tubes and a heat exchanger at different water depths. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2020, 13, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Safarzadeh, H.; Bahiraei, M. Experimental and analytical investigations of productivity, energy and exergy efficiency of a single slope solar still enhanced with thermoelectric channel and nanofluid. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, S. Numerical analysis of optimizing a heat sink and nanofluid concentration used in a thermoelectric solar still: An economic and environmental study. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2021, 77, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadatare, M.; Verma, S.K. Influence of water depth on internal heat and mass transfer in a plastic solar still. Desalination 2007, 217, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, N.; Asadi, A.; Fotouhi-Bafghi, E. Performance evaluation of two solar stills of different geometries: Tubular versus triangular: Experimental study, numerical simulation, and second law analysis. Desalination 2018, 443, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.J.N.; Hamood, A.M. Effect of insulation thickness on the productivity of basin type solar stills: An experimental verification under local climate. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 2457–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, S.; Rahbar, N.; Esfahlani, A.A.; Kargarsharifabad, H. Improving the thermoelectric solar still performance by using nanofluids—Experimental study, thermodynamic modeling and energy matrices analysis. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Afaneh, D.; Abdallah, S.; Saleet, H. Novel Design of Hybrid Single Slope Solar Distiller with Photovoltaic Powered Thermoelectric System. J. Sustain. Dev. Energy Water Environ. Syst. 2024, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jam, R.F.; Gholizadeh, M.; Deymi-Dashtebayaz, M.; Khanjani, S.; Dartoomi, N. Experimental investigation of the thermoelectric and double-glazed glass effects on the performance of a solar still. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 246, 122898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Abdelgaied, M.; Harby, K.; Eisa, A. Augmentation of diurnal and nocturnal distillate of modified tubular solar still having copper tubes filled with PCM in the basin. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, G.; Nazari, S. Retrofitting a thermoelectric-based solar still integrated with an evacuated tube collector utilizing an antibacterial-magnetic hybrid nanofluid. Desalination 2021, 500, 114871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugan, S.; Palani, S.; Janarthanan, B. Productivity enhancement of solar still by PCM and Nanoparticles miscellaneous basin absorbing materials. Desalination 2018, 433, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, P.; Goharrizi, A.S.; Ayatollahi, S.; Feilizadeh, M. Nano-coated condensation surfaces enhanced the productivity of the single-slope solar still by changing the condensation mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahota, L.; Arora, S.; Singh, H.P.; Sahoo, G. Thermo-physical characteristics of passive double slope solar still loaded with MWCNTs and Al2O3-water based nanofluid. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 32, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, J.; Selvaraj, P.; Nagaraj, G. Day and night yield performance analysis of solar still for saline water using energetic materials with thermocol insulation. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 4848–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeroual, M.; Bouguettaia, H.; Bechki, D.; Boughali, S.; Bouchekima, B.; Mahcene, H.J.E.P. Experimental investigation on a double-slope solar still with partially cooled condenser in the region of Ouargla (Algeria). Energy Procedia 2011, 6, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samadony, Y.; Kabeel, A. Theoretical estimation of the optimum glass cover water film cooling parameters combinations of a stepped solar still. Energy 2014, 68, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahota, L.; Tiwari, G. Analytical characteristic equation of nanofluid loaded active double slope solar still coupled with helically coiled heat exchanger. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 135, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, S.; Saemian, M.; Khiadani, M.; Kargarsharifabad, H.; Mirjalily, S.A.A. Influence of PV/T waste heat on water productivity and electricity generation of solar stills using heat pipes and thermoelectric generator: An experimental study and environmental analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 276, 116504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, B.; Bechir, M. Numerical analysis of tubular solar still with rectangular and cylindrical troughs for water production under vacuum. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2023, 17, 2159172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, H.M.B.; Alshammari, F.; Alatawi, I.; Alhadri, M.; Almeshaal, M.A.; Hajlaoui, K. Potential of tubular solar still with rectangular trough for water production under vacuum condition. Therm. Sci. 2022, 26, 4271–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairunnas, A.; Chiari, W. Metal oxide/chitosan composite for organic pollutants removal: A comprehensive review with bibliometric analysis. Narra X 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisah, K.; Khairi, M.; Sukandar, R.; Nuzlia, C.; Nasution, R.S.; Ilhami, S.; Chiari, W. Fabrication and characterization of SiO2-embedded castor oil-based membrane (Ricinus communis L.) for aqueous Fe adsorption. Narra X 2024, 2, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshir, S.W.; Yang, N.; Peng, G.; Kabeel, A.E. Factors affecting solar stills productivity and improvement techniques: A detailed review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 100, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hinai, H.; Al-Nassri, M.; Jubran, B. Effect of climatic, design and operational parameters on the yield of a simple solar still. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, B.; Akhtar, N. Effect of specific height on the performance of a single slope solar still: An experimental study. Desalination 2017, 414, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, E.A.; Mansour, T.M.; Dawood, M.M.K.; Ismail, T.M.; Ramzy, K. Exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic evaluations of conventional solar still using PCM and electric heater powered by solar energy: An experimental study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 66135–66156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqlan, A.M.; Aklan, M.; Momin, A.E. Solar-powered desalination, a novel solar still directly connected to solar parabolic trough. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dubey, A.; Tiwari, G. A solar still augmented with an evacuated tube collector in forced mode. Desalination 2014, 347, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, O.; Al-Tahaineh, H. The effect of coupling a flat-plate collector on the solar still productivity. Desalination 2005, 183, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rehim, Z.S.; Lasheen, A. Experimental and theoretical study of a solar desalination system located in Cairo, Egypt. Desalination 2007, 217, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sebaii, A.A.; Ramadan, M.R.I.; Aboul-Enein, S.; Salem, N. Thermal performance of a single-basin solar still integrated with a shallow solar pond. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, S.; Saemian, M.; Parsa, S.M.; Khiadani, M.; Mirjalily, S.A.A.; Kargarsharifabad, H. A novel solar desalination system equipped with thermoelectric generator, reflectors and low-cost sensible energy-storage for co-production of power and drinking water. Desalination 2023, 567, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.H.; Attalla, M.; Shmroukh, A.N. Comparative study on the performance of solar still equipped with local clay as an energy storage material. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 74998–75012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Yazdani, A.; Javadi, D.; Afrand, M.; Karimi, N.; Ali, H.M. Selecting efficient side of thermoelectric in pyramid-shape solar desalination units incorporated phase change material (PCM), nanoparticle, turbulator with battery storage powered by photovoltaic. J. Energy Storage 2022, 51, 104448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.; Abdelgaied, M. Improving the performance of solar still by using PCM as a thermal storage medium under Egyptian conditions. Desalination 2016, 383, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.; Abdelgaied, M. Observational study of modified solar still coupled with oil serpentine loop from cylindrical parabolic concentrator and phase changing material under basin. Sol. Energy 2017, 144, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtban, M.; Tabrizi, F.F. Thermal analysis of a weir-type cascade solar still integrated with PCM storage. Desalination 2011, 279, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, S.; El-Bialy, E.; El-Sebaii, A. An experimental investigation of a v-corrugated absorber single-basin solar still using PCM. Desalination 2016, 398, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugavel, K.K.; Sivakumar, S.; Ahamed, J.R.; Chockalingam, K.K.; Srithar, K. Single basin double slope solar still with minimum basin depth and energy storing materials. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sebaii, A.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Al-Hazmi, F.S.; Faidah, A.S. Thermal performance of a single basin solar still with PCM as a storage medium. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanian, M.; Hoseinzadeh, S.; Astiaso Garcia, D. Proposal of a Reflector-Enhanced Solar Still Concept and Its Comparison with Conventional Solar Stills. Water 2024, 16, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estahbanati, M.K.; Ahsan, A.; Feilizadeh, M.; Jafarpur, K.; Ashrafmansouri, S.S.; Feilizadeh, M. Theoretical and experimental investigation on internal reflectors in a single-slope solar still. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, Z.; Kabeel, A.; Younes, M. Enhancing the stepped solar still performance using internal and external reflectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.J.N.; Ibrahim, H.A. Effect of inclination of the external reflector on the performance of a basin type solar still at various seasons. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2009, 13, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Nakatake, Y. Theoretical analysis of a basin type solar still with internal and external reflectors. Desalination 2006, 197, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandev, E.; Muratçobanoğlu, B.; Manay, E.; Şahin, B. Desalination performance evaluation of a solar still enhanced by thermoelectric modules. Sol. Energy 2024, 268, 112325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Allam, E.E.; Elshamarka, S.E. A modified basin type solar still: Experimental performance and economic study. Energy 2015, 93, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samadony, Y.; Abdullah, A.; Omara, Z. Experimental study of stepped solar still integrated with reflectors and external condenser. Exp. Heat Transf. 2015, 28, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.; Omara, Z.; Essa, F. Enhancement of modified solar still integrated with external condenser using nanofluids: An experimental approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monowe, P.; Masale, M.; Nijegorodov, N.; Vasilenko, V. A portable single-basin solar still with an external reflecting booster and an outside condenser. Desalination 2011, 280, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bahi, A.; Inan, D. A solar still with minimum inclination, coupled to an outside condenser. Desalination 1999, 123, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Qudais, M.; Othman, O.N. Experimental study and numerical simulation of a solar still using an external condenser. Energy 1996, 21, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatar, N.M.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Salleh, M.F.M.; Ani, M.H. Energy, exergy, economic, environmental analysis for solar still using partially coated condensing cover with thermoelectric cover cooling. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, S.; Khanjani, S.; Musharavati, F. Experimental study and economic examination of double-glazed solar still desalination with a thermoelectric cooling system. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 54, 102854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, N.; Esfahani, J. Experimental study of a novel portable solar still by utilizing the heatpipe and thermoelectric module. Desalination 2012, 284, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshir, S.W.; Peng, G.; Wu, L.; Essa, F.A.; Kabeel, A.E.; Yang, N. The effects of flake graphite nanoparticles, phase change material, and film cooling on the solar still performance. Appl. Energy 2017, 191, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somwanshi, A.; Tiwari, A.K. Performance enhancement of a single basin solar still with flow of water from an air cooler on the cover. Desalination 2014, 352, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Sharma, R.; Shankar, P.; Baredar, P. Performance enhancement of modified solar still using water sprinkler: An experimental approach. Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargva, M.; Yadav, A. Effect of shading and evaporative cooling of glass cover on the performance of evacuated tube-augmented solar still. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 4125–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, A.; Çelik, A.; Mandev, E.; Muratçobanoğlu, B.; Gülmüş, B.; Afshari, F.; Ceviz, M.A. Study on a novel inclined solar water distillation system using thermoelectric module for condensation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 177, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, Z.; Hamed, M.H.; Kabeel, A. Performance of finned and corrugated absorbers solar stills under Egyptian conditions. Desalination 2011, 277, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafey, A.S.; Abdelkader, M.; Abdelmotalip, A.; Mabrouk, A.A. Enhancement of solar still productivity using floating perforated black plate. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Agrawal, S. Experimental and theoretical analysis of single sloped basin type solar still consisting of multiple low thermal inertia floating porous absorbers. Desalination 2013, 311, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Agrawal, S. Winter and summer performance of single sloped basin type solar still integrated with extended porous fins. Desalination 2013, 319, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rababa’h, H.M. Experimental study of a solar still with sponge cubes in basin. Energy Convers. Manag. 2003, 44, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Sakthivel, M.; Shanmugasundaram, S.; Alwarsamy, T. An experimental study on a regenerative solar still with energy storage medium—Jute cloth. Desalination 2010, 264, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.M.K.; Omar, A.H.; Shehata, A.I.; Samir Shehata, A.; Taha, A.A.E.; El-Shaib, M.N.; Mohamed, M.K. 3E enhancement of freshwater productivity of solar still with heater, vibration, and cover cooling. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65787–65805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, S.; Badran, O. Sun tracking system for productivity enhancement of solar still. Desalination 2008, 220, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianifar, A.; Heris, S.Z.; Mahian, O. Exergy and economic analysis of a pyramid-shaped solar water purification system: Active and passive cases. Energy 2012, 38, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, R.; Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Tiwari, G. Performance study of the inverted absorber solar still with water depth and total dissolved solid. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sulttani, A.O.; Ahsan, A.; Rahman, A.; Daud, N.N.; Idrus, S. Heat transfer coefficients and yield analysis of a double-slope solar still hybrid with rubber scrapers: An experimental and theoretical study. Desalination 2017, 407, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.T.; Ahmed, A.S.; Majeed, M.H.; Shcheklein, S.E.; Yaqoob, S.J.; Nayyar, A.; Nam, Y.; Abouhawwash, M. Enhancement of the evaporation and condensation processes of a solar still with an ultrasound cotton tent and a thermoelectric cooling chamber. Electronics 2022, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandev, E.; Muratçobanoğlu, B.; Çelik, A.; Ceviz, M.A.; Di Nicola, G.; Afshari, F. Improving solar still efficiency through integration of cellulose-based water absorbers and Peltier condensation unit. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 49, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Safarzadeh, H.; Bahiraei, M. Performance improvement of a single slope solar still by employing thermoelectric cooling channel and copper oxide nanofluid: An experimental study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A. Improving the performance of stepped solar still. Desalination 2013, 319, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, S.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Sarker, M.R.I.; Beg, R.A. Combined influence of fin, phase change material, wick, and external condenser on the thermal performance of a double slope solar still. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairat Dawood, M.M.; Shehata, A.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Elharidi, A.M.; Abdelsalam Taha, A.; Bayoumi, S.; Abdalla, A.M. Increasing the freshwater productivity of a solar still loaded with CuO nanofluids using vibration motion and cover cooling techniques. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 9099–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Koleini, M.H.; Aberoumand, S.; Afrand, M.; Amidpour, M. A renewable energy-driven thermoelectric-utilized solar still with external condenser loaded by silver/nanofluid for simultaneously water disinfection and desalination. Desalination 2020, 480, 114354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pounraj, P.; Winston, D.P.; Kabeel, A.E.; Kumar, B.P.; Manokar, A.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Christabel, S.C. Experimental investigation on Peltier based hybrid PV/T active solar still for enhancing the overall performance. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 168, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu Manokar, A.; Vimala, M.; Prince Winston, D.; Rajendran, D.R.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kabeel, A.E. Year around distilled water production, energy, and economic analysis of solar stills—A comparative study. Heat Transf. 2020, 49, 3651–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfe, M.H.; Ardeshiri, E.M.; Toghraie, D. Experimental study and sensitivity analysis of a new generation of special ternary hybrid nanofluids (THNFs) and investigation of factors affecting its thermal conductivity. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 34, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, S.; Rahbar, N.; Esfahlani, A.A.; Kargarsharifabad, H. A review of techniques for simultaneous enhancement of evaporation and condensation rates in solar stills. Sol. Energy 2021, 225, 666–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Essa, F.A.; Omara, Z.M.; Rashid, Y.; Hadj-Taieb, L.; Abdelaziz, G.B.; Kabeel, A.E. Rotating-drum solar still with enhanced evaporation and condensation techniques: Comprehensive study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 112024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.T.; Shcheklein, S.; Ali, O.M. Evaluation of distilled water quality and production costs from a modified solar still integrated with an outdoor solar water heater. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabishokr, K.; Daghigh, R. A portable solar still’s productivity boost combining a magnetic stirrer and thermoelectric. Desalination 2023, 549, 116340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevadason, A.W.; Padmini, S.; Bharatiraja, C. Enhancing freshwater productivity of twin wedge solar still by temperature control through thermoelectric sensors and modules. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 9095–9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltawil, M.A.; Omara, Z. Enhancing the solar still performance using solar photovoltaic, flat plate collector and hot air. Desalination 2014, 349, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Yousef, M.S. An assessment of energy, exergy and CO2 emissions of a solar desalination system under hot climate conditions. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 145, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, S.; Rahbar, N.; Esfahlani, A.A.; Kargarsharifabad, H. Application of simultaneous thermoelectric cooling and heating to improve the performance of a solar still: An experimental study and exergy analysis. Appl. Energy 2020, 263, 114581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraparaju, S.K.; Natarajan, S.K. Combined enhancement of evaporation and condensation rates in the solar still for augmenting the freshwater productivity using energy storage and natural fibres. AQUA Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2022, 71, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Yousef, M.S.; Fathy, M.; Ahmed, M.S. Assessment of parabolic trough solar collector assisted solar still at various saline water mediums via energy, exergy, exergoeconomic, and enviroeconomic approaches. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karaghouli, A.; Kazmerski, L.L. Energy consumption and water production cost of conventional and renewable-energy-powered desalination processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Seawater desalination using renewable energy sources. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2005, 31, 242–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffour, N.; Missimer, T.M.; Amy, G.L. Technical review and evaluation of the economics of water desalination: Current and future challenges for better water supply sustainability. Desalination 2013, 309, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, S.; Rahbar, N.; Esfahlani, A.A.; Kargarsharifabad, H. Energy matrices, exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic analysis of air-cooled and water-cooled solar still: Experimental investigation and numerical simulation. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatar, N.M.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Salleh, M.F.M.; Ani, M.H. Investigation on the performance of solar still with thermoelectric cooling system for various cover material. Renew. Energy 2023, 202, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A.; Alqsair, U.F.; Aljaghtham, M.; Mansir, I.B.; Shanmugan, S.; Alawee, W.H. Enhancing trays solar still performance using wick finned absorber, nano-enhanced PCM. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 12417–12430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.T.; Shcheklein, S.; Ali, O.M. Experimental study and economic cost analysis about enhancement productivity for a conventional solar still combined with humidifiers ultrasonic. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 47, 7802–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.T.; Shcheklein, S.; Ali, O.M. Experimental investigation of modified solar still integrated with solar collector. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 19, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.T.; Shcheklein, S.; Ali, O.M. Evaluation of the productivity for new design single slope solar still at different saltwater depth. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1706, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Dawood, M.M.K.; Elharidi, A.M.; Abd_Elsalam, A.; Ramzy, K.; Mehanna, A. Enhancement of the productivity for single solar still with ultrasonic humidifier combined with evacuated solar collector: An experimental study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 208, 112592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Yousef, M.S.; Fathy, M.; Ahmed, M.S. Impact of condenser heat transfer on energy and exergy performance of active single slope solar still under hot climate conditions. Sol. Energy 2020, 204, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.A.; Omara, Z.M.; Abdullah, A.S.; Shanmugan, S.; Panchal, H.; Kabeel, A.E.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Alawee, W.H.; Manokar, A.M.; Elsheikh, A.H. Wall-suspended trays inside stepped distiller with Al2O3/paraffin wax mixture and vapor suction: Experimental implementation. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elbar, A.R.; Hassan, H. Energy, exergy and environmental assessment of solar still with solar panel enhanced by porous material and saline water preheating. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, P.; Mishra, D.R. Performance evaluation of single slope solar still augmented with the ultrasonic fogger. Energy 2020, 190, 116398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Javadi, D.; Koleini, M.H.; Afrand, M.; Amidpour, M. Energy-matrices, exergy, economic, environmental, exergoeconomic, enviroeconomic, and heat transfer (6E/HT) analysis of two passive/active solar still water desalination nearly 4000 m: Altitude concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.T.; Shcheklein, S.; Ali, O. A practical study of a rectangular basin solar distillation with single slope using paraffin wax (PCM) cells. Int. J. Energy Convers. 2019, 7, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonker, V.K.; Chakraborty, J.P.; Sarkar, A.; Singh, R.K. Solar distillation using three different phase change materials stored in a copper cylinder. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, D.P.; Pounraj, P.; Manokar, A.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kabeel, A.E. Experimental investigation on hybrid PV/T active solar still with effective heating and cover cooling method. Desalination 2018, 435, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Rahbar, N.; Gharaiian, A.; Rashidi, S. Exergy and economic analysis for a double slope solar still equipped by thermoelectric heating modules—An experimental investigation. Desalination 2017, 420, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Abo-Elfadl, S. Effect of the condenser type and the medium of the saline water on the performance of the solar still in hot climate conditions. Desalination 2017, 417, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaseenivasan, T.; Srithar, K. Performance investigation on solar still with circular and square fins in basin with CO2 mitigation and economic analysis. Desalination 2016, 380, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, M.; El-Maghawry, H.A.; Wasfy, K.I. Improving the double slope solar still performance by using flat-plate solar collector and cooling glass cover. Desalination 2015, 373, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneesh, P.U.; Jayaprakash, R.; Arunkumar, T.; Denkenberger, D. Effect of air flow on “V” type solar still with cotton gauze cooling. Desalination 2014, 337, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, J.A.; Rahbar, N.; Lavvaf, M. Utilization of thermoelectric cooling in a portable active solar still—An experimental study on winter days. Desalination 2011, 269, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tiwari, G. Life cycle cost analysis of single slope hybrid (PV/T) active solar still. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samee, M.A.; Mirza, U.K.; Majeed, T.; Ahmad, N. Design and performance of a simple single basin solar still. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).