The Fate and Clogging Mechanisms of Suspended Particles in Natural Biofilm-Coated Porous Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of Porous Medium and Suspended Particles
2.1.2. Microbial Cultivation
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Analysis Method
2.4.1. Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity
2.4.2. Zeta Potential and Contact Angle
2.4.3. Biomass and Suspended Particle Deposition in Each Layer of Sand Column
2.4.4. Extraction and Determination of EPSs
2.4.5. Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging
2.4.6. Microtopography of Sand Grain Surface
2.4.7. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4.8. XDLVO Theory
2.4.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
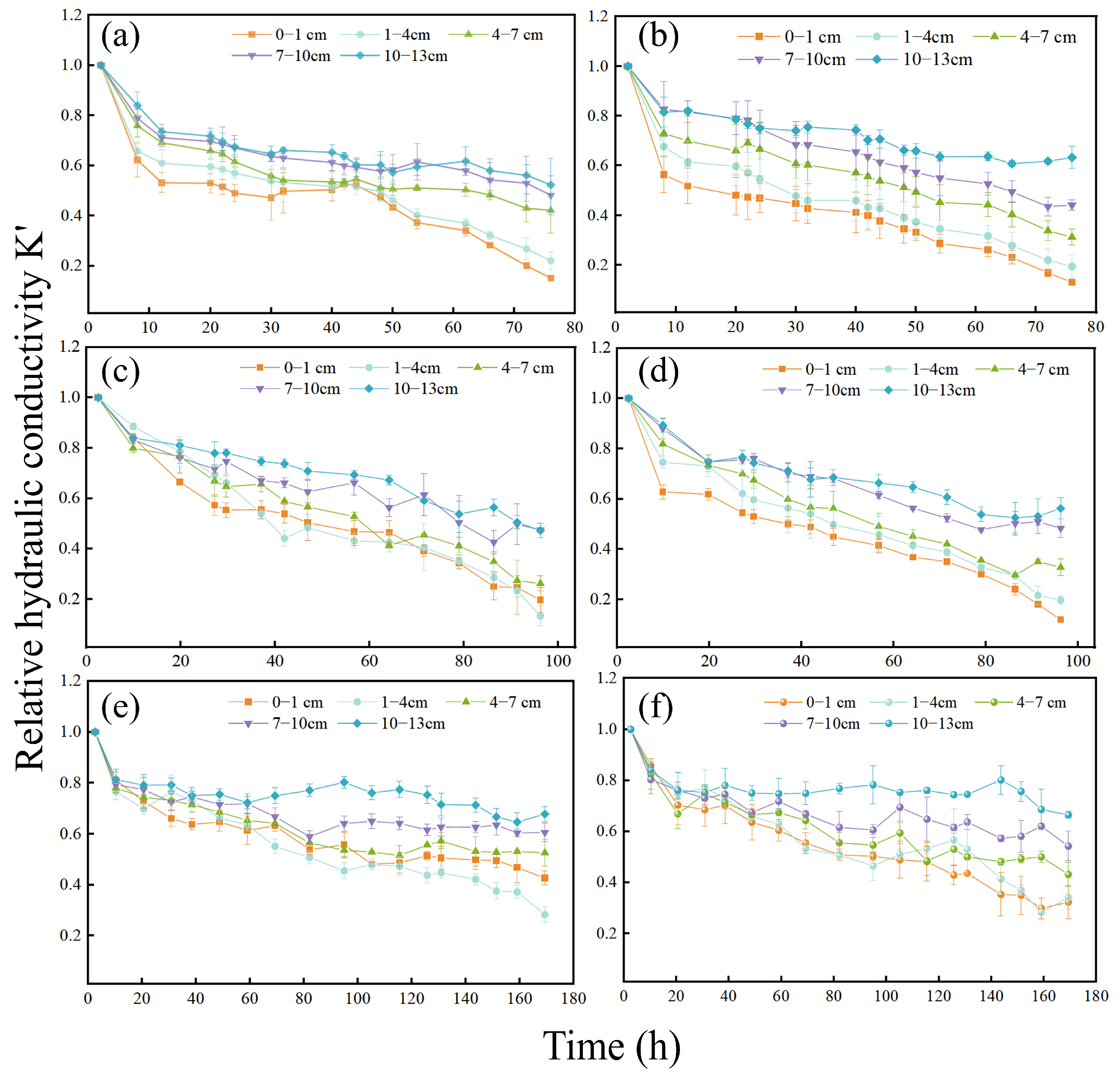
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation in the Relative Hydraulic Conductivity of Porous Media
3.1.1. Effect of Biofilm-Coated Porous Media on the Relative Hydraulic Conductivity
3.1.2. Effect of Suspended Particle Concentration in Recharge Water on Relative Hydraulic Conductivity
3.1.3. Relative Hydraulic Conductivity of Different Layers of the Sand Column
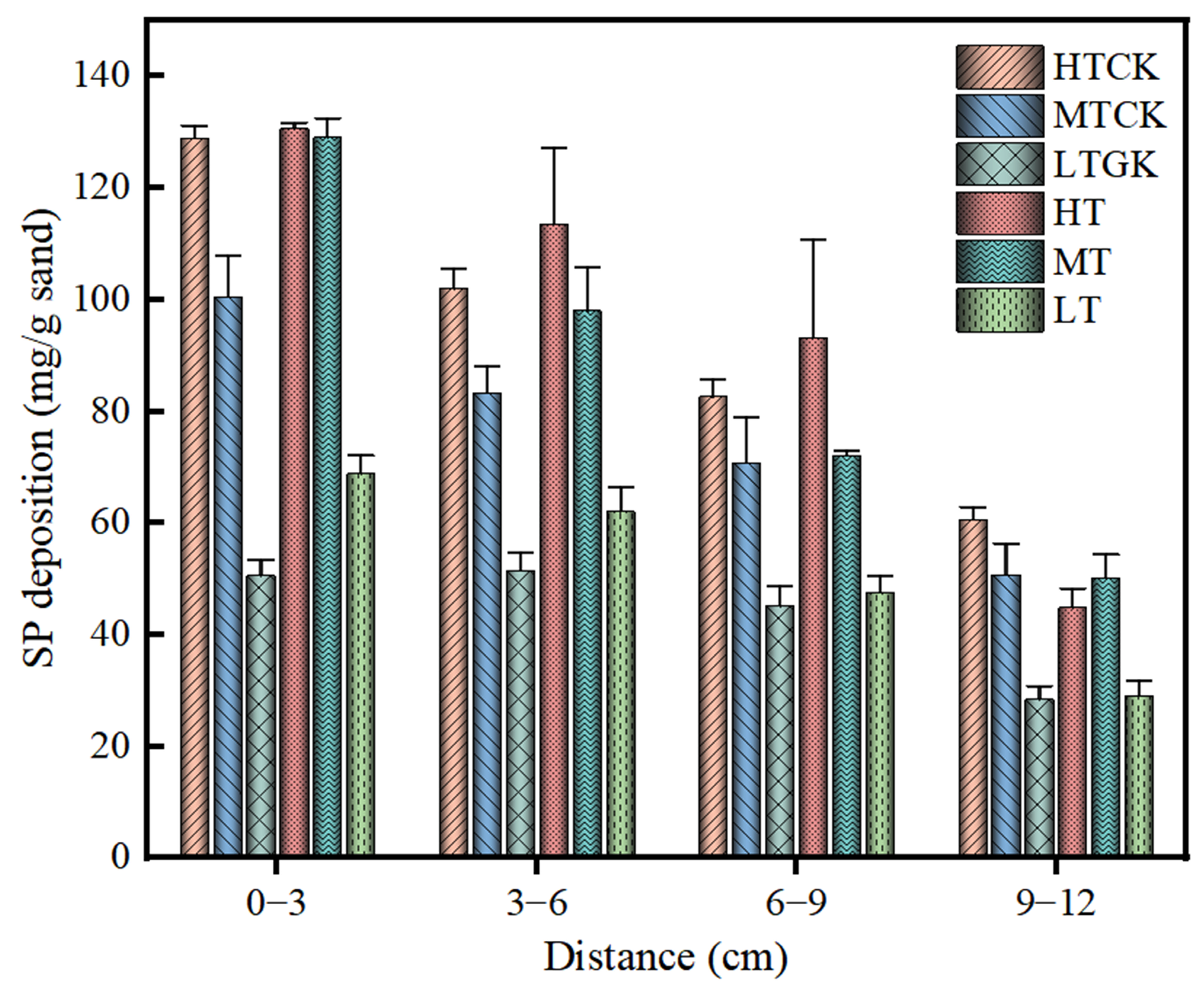
3.2. Analysis of Distribution Difference in Biomass and Suspended Particle Deposition in Porous Media
3.2.1. Distribution of Biomass in the Porous Media
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution of Suspended Particles in the Porous Media
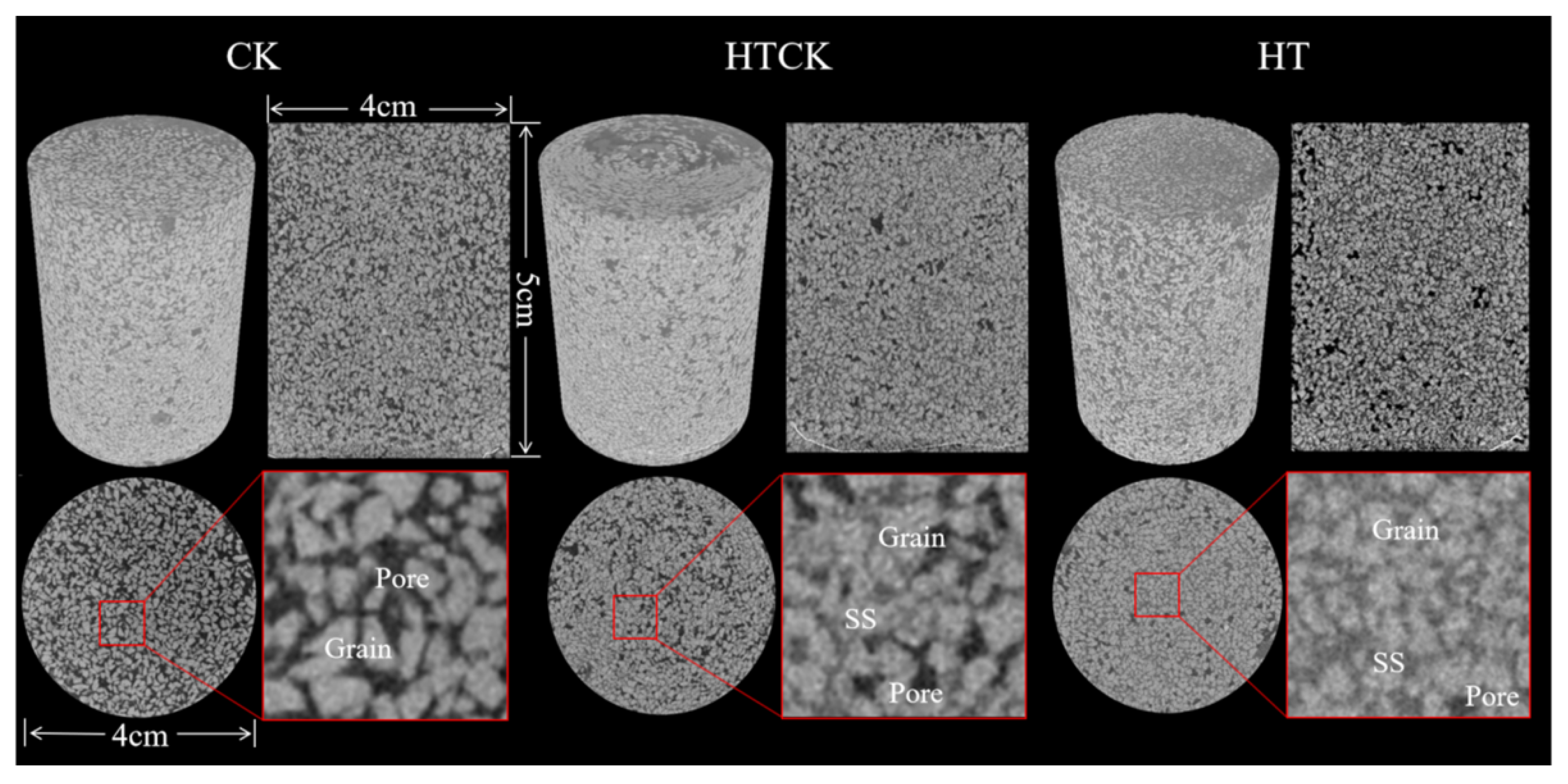
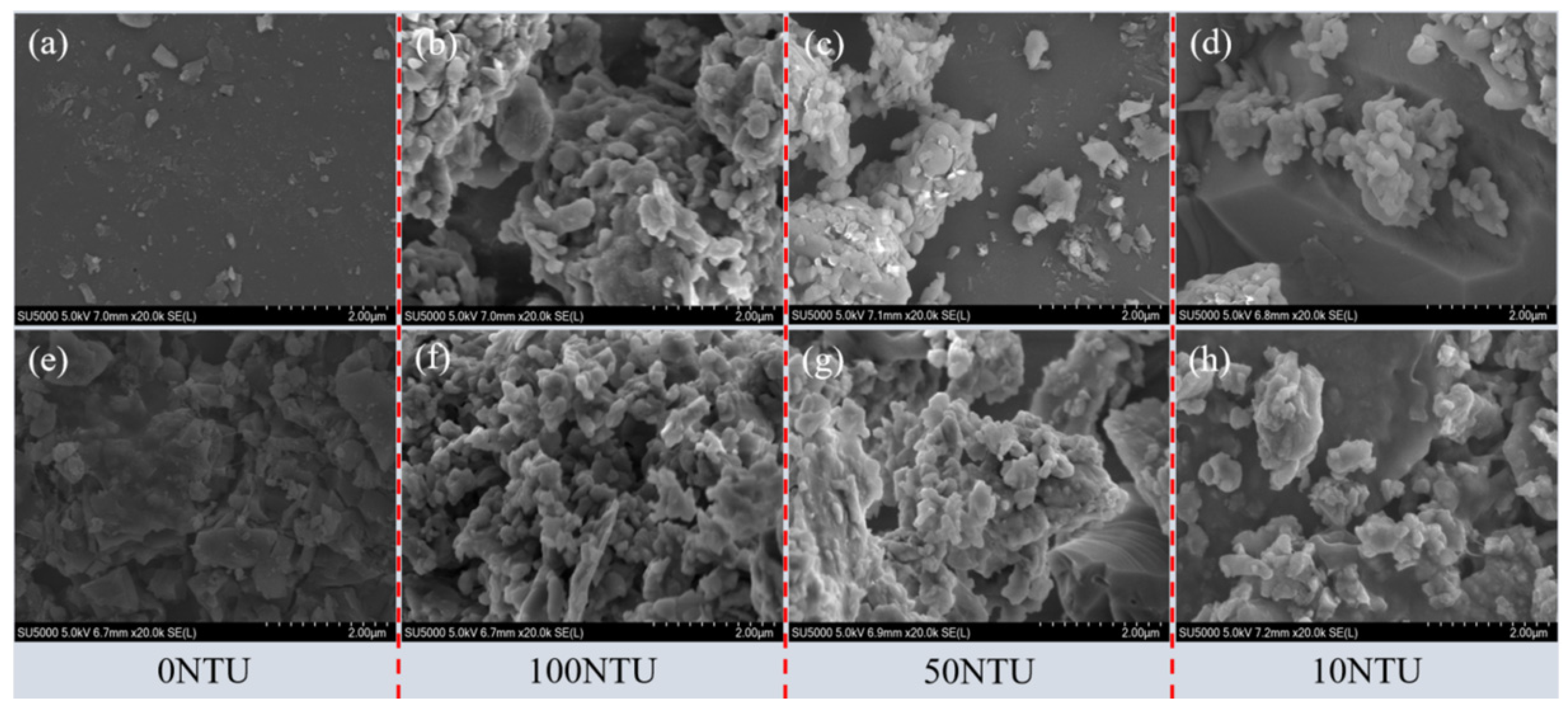
3.3. Surface Property Analysis of Porous Media
3.3.1. Surface Morphology of Porous Media
3.3.2. Effect of Biofilm Coating on Zeta and Contact Angle of Porous Medium Surface
3.3.3. EPS Component and Content
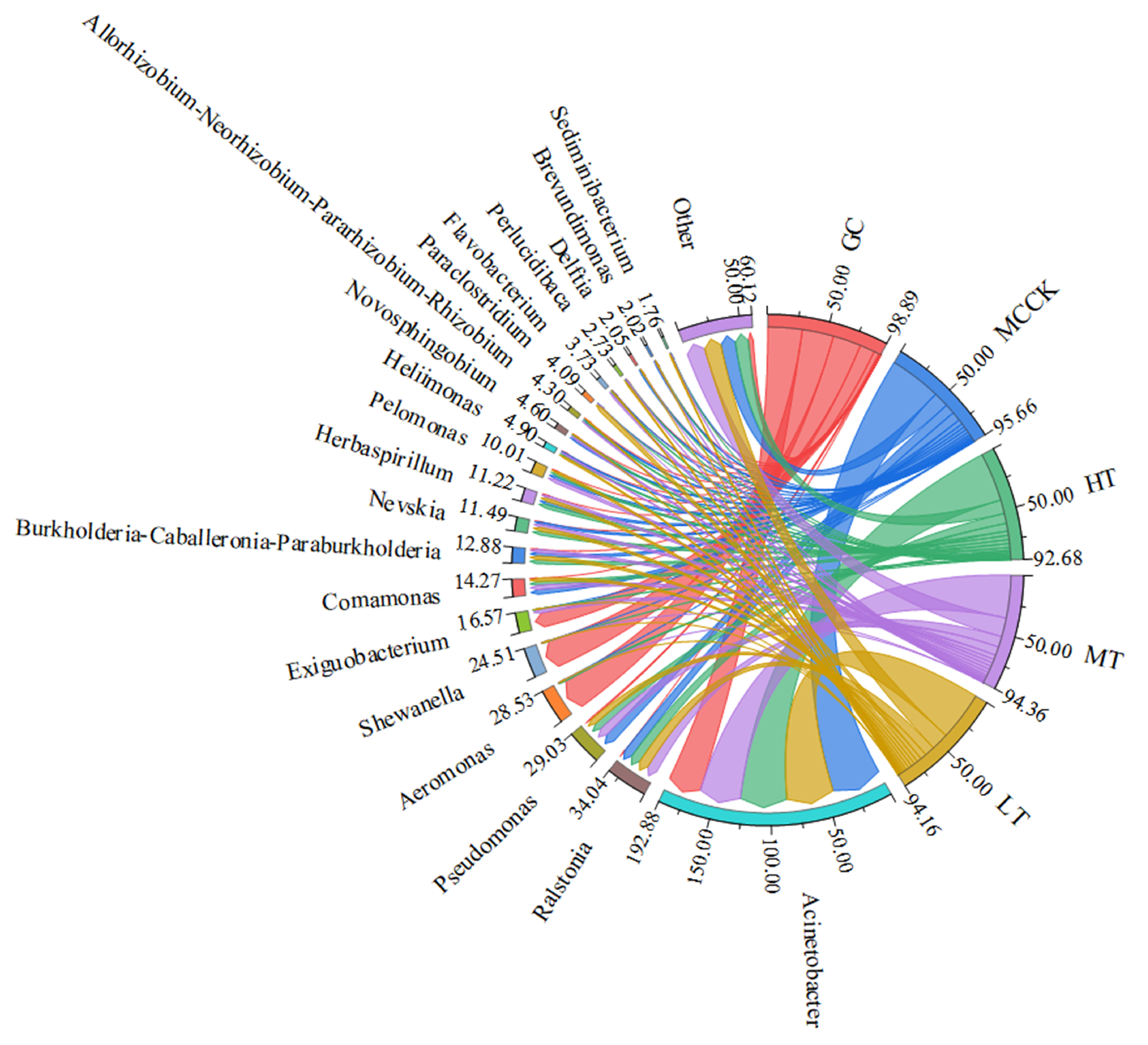
3.4. Microbial Community Analysis
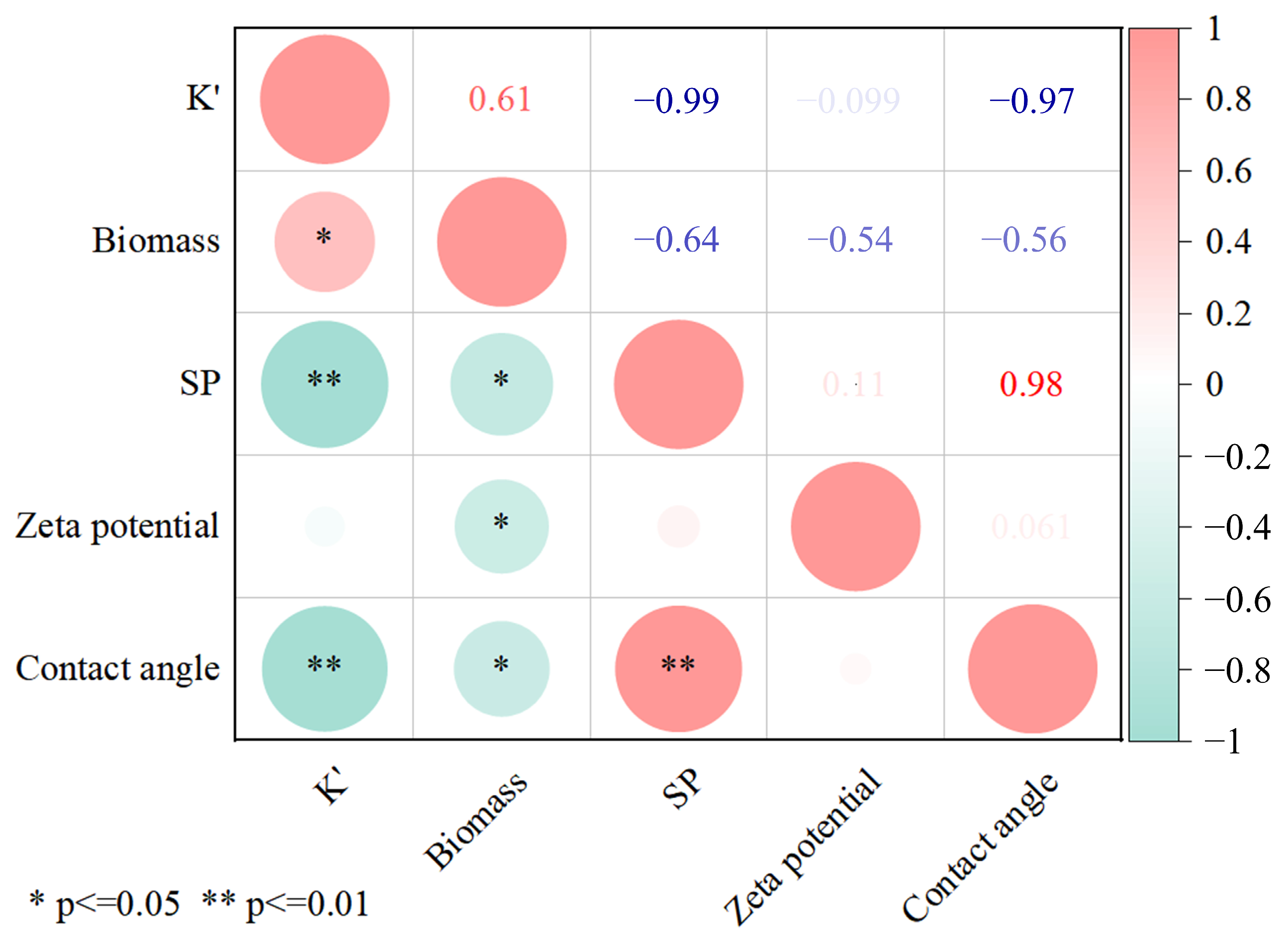
3.5. Analysis of the Clogging Mechanism of the Porous Medium
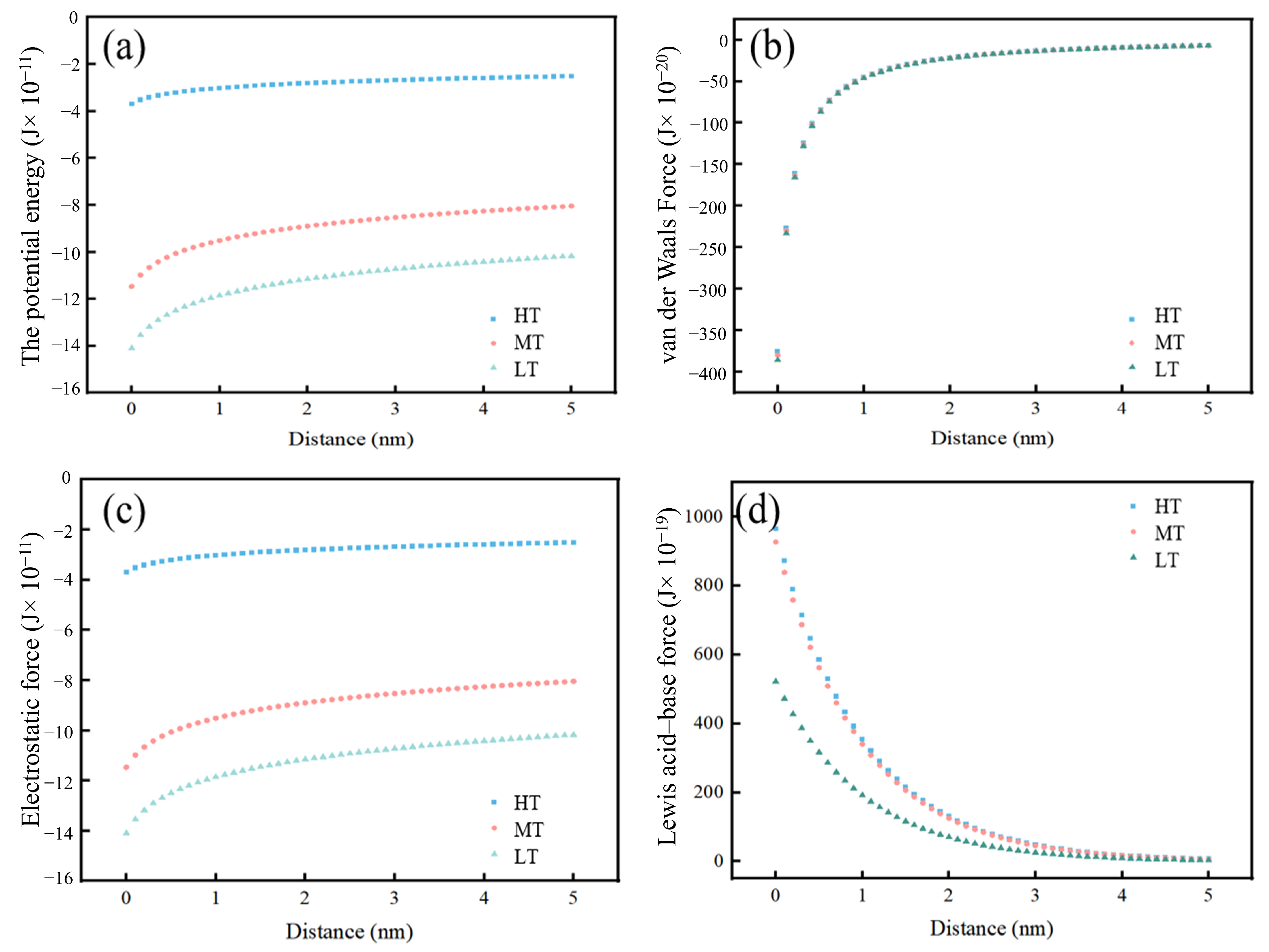
3.5.1. Interaction Between the Suspended Particulate and the Biofilm
3.5.2. Main Mechanism of Combined Clogging of Porous Media
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pyne, R.D.G. Groundwater Recharge and Wells: A Guide to Aquifer Storage Recovery; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rinck-Pfeiffer, S. Interrelationships between biological, chemical, and physical processes as an analog to clogging in aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) wells. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, C.; Hartog, N.; Hernández, M.; Vilanova, E.; Grützmacher, G.; Scheibler, F.; Hannappel, S. Inventory of managed aquifer recharge sites in Europe: Historical development, current situation and perspectives. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1909–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X. Development of managed aquifer recharge in China. Bol. Geol. Min. 2014, 125, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Betancourt, W.Q.; Kitajima, M.; Wing, A.D.; Regnery, J.; Drewes, J.E.; Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P. Assessment of virus removal by managed aquifer recharge at three full-scale operations. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2014, 49, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kennedy, M.D. Soil aquifer treatment for wastewater treatment and reuse. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, G.L.; Lee, L.P. High-Density Silver Nanoparticle Film with Temperature-Controllable Interparticle Spacing for a Tunable Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrate. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Research situation and prospect of artificial supplement to groundwater. Coal Geol. Explor. 2006, 34, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.; Dong, J.; Yao, Y.; Shen, C.; Qv, D.; Zhang, X. A review of heat pump systems for heating and cooling of buildings in China in the last decade. Renew. Energy 2015, 84, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.J.; Hickinbotham, M.R.; Pavelic, P. Review of International Experience in Injecting Water into Aquifers for Storage and Reuse. In Water Down Under 94: Groundwater Papers; Preprints of Papers; Institution of Engineers: Barton, Australia, 1994; pp. 13–14, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi, M.; Ahfir, N.-D.; Alem, A.; El Mansouri, B.; Wang, H.; Taibi, S.; Duchemin, B.; Merzouk, A. Assessment of clogging of managed aquifer recharge in a semi-arid region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Yang, Y.; Ye, X. Surface clogging process modeling of suspended solids during urban stormwater aquifer recharge. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedescoll, A.; Passos, F.; Alba, E.; García, J.; Puigagut, J. Mechanical resistance properties of gravel used in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Implications for clogging. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yong, C.F.; McCarthy, D.T.; Deletic, A. Predicting physical clogging of porous and permeable pavements. J. Hydrol. 2013, 481, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lu, M.; Bian, H.; Sheng, L.; He, C. Effects of physical clogging on the performance of a lab-scale vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland system and simulation research. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzer, J.; Holzner, M.; Plötze, M.; Furrer, G. Clogging of an Alpine streambed by silt-sized particles—Insights from laboratory and field experiments. Water Res. 2017, 126, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, J.P.; Leclerc, D.M.; Goff, P.L. Flow of Suspensions through Porous Media—Application to Deep Filtration. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1970, 62, 8–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baveye, P.; Vandevivere, P.; Hoyle, B.L.; DeLeo, P.C.; De Lozada, D.S. Environmental Impact and Mechanisms of the Biological Clogging of Saturated Soils and Aquifer Materials. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 28, 123–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Ye, X.; Zhang, X. Clogging of saturated porous media by silt-sized suspended solids under varying physical conditions during managed aquifer recharge. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2254–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardene, N.R.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D. Clogging of stormwater gravel infiltration systems and filters: Insights from a laboratory study. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Nakashima, Y.; Nishigaki, M. Clogging mechanisms and preventive measures in artificial recharge systems. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Kanyerere, T. A review of the managed aquifer recharge: Historical development, current situation and perspectives. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 118–119, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelic, P.; Dillon, P.J.; Barry, K.E.; Vanderzalm, J.L.; Correll, R.L.; Rinck-Pfeiffer, S.M. Water quality effects on clogging rates during reclaimed water ASR in a carbonate aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelic, P.; Dillon, P.J.; Mucha, M.; Nakai, T.; Barry, K.E.; Bestland, E. Laboratory assessment of factors affecting soil clogging of soil aquifer treatment systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, R.C. Soil Clogging during Infiltration of Secondary Effluent. J. (Water Pollut. Control Fed.) 1974, 46, 708–716. [Google Scholar]
- Ahfir, N.-D.; Hammadi, A.; Alem, A.; Wang, H.; Le Bras, G.; Ouahbi, T. Porous media grain size distribution and hydrodynamic forces effects on transport and deposition of suspended particles. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 53, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Chen, C.; Sun, S.; Zhou, D.; Ndayisenga, F.; Huo, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, L.; Crittenden, J.C. Acceleration of saturated porous media clogging and silicon dissolution due to low concentrations of Al(III) in the recharge of reclaimed water. Water Res. 2018, 143, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevivere, P.; Baveye, P. Effect of bacterial extracellular polymers on the saturated hydraulic conductivity of sand columns. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.W.; Jaffé, P.R. Biofilm growth and the related changes in the physical properties of a porous medium: 1. Experimental investigation. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomer, M.E.; Hubbard, S.S.; Fleckenstein, J.H.; Maier, U.; Schmidt, C.; Thullner, M.; Ulrich, C.; Flipo, N.; Rubin, Y. Simulating bioclogging effects on dynamic riverbed permeability and infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2883–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwager, A.; Boller, M. Transport phenomena in intermittent filters. Water Sci. Technol. Small Wastewater Treat. Plants III 1997, 35, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenu, C. Clay- or sand-polysaccharide associations as models for the interface between micro-organisms and soil: Water related properties and microstructure. Geoderma Int. Workshop Methods Res. Soil Struct./Soil Biota Interrelat. 1993, 56, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, K.R.; Drummond, J.D.; Boano, F.; Packman, A.I.; Battin, T.J.; Hunter, W.R. Benthic biofilm controls on fine particle dynamics in streams. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zheng, X.; Shao, H.; Xin, J.; Peng, T. Influences of environmental factors on bacterial extracellular polymeric substances production in porous media. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalla, T.M. Studies on the Effect of Microorganisms on Rate of Percolation of Water Through Soils. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1951, 15, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. Clogging Issues Associated with Managed Aquifer Recharge Methods; IAH Commission on Managing Aquifer Recharge: Perth, Australia, 2013; 213p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. A comparative analysis for the development and recovery processes of different types of clogging in lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24073–24083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Du, X.; Zhang, H.; Cui, R. Effects of solution ionic strength and flow velocity on colloid clogging in saturated porous media during artificial recharge. CIESC J. 2017, 68, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Escalante, E. Practical Management to Minimize the Effects of Clogging in Managed Aquifer Recharge Wells at Two Sites in the Guadiana Basin, Spain. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, B5014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; He, Q.; Ma, J.; Ma, C.; Huang, R. A review on the interactions between engineered nanoparticles with extracellular and intracellular polymeric substances from wastewater treatment aggregates. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 766–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Rong, H.; Wu, D.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Tong, M. Influence of biofilm on the transport and deposition behaviors of nano- and micro-plastic particles in quartz sand. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Ding, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, P. Influence of biofilm on the transport of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles in porous media. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wiesner, M.R. Transport and Retention of Selected Engineered Nanoparticles by Porous Media in the Presence of a Biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peulen, T.-O.; Wilkinson, K.J. Diffusion of Nanoparticles in a Biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitzel, M.R.; Tufenkji, N. Transport of Industrial PVP-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles in Saturated Quartz Sand Coated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Biofilm of Variable Age. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlanda-Witek, H.; Ngwenya, B.T.; Butler, I.B. The influence of biofilms on the mobility of bare and capped zinc oxide nanoparticles in saturated sand and glass beads. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 179, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-Zhou, H.; Cheng-Cheng, L.; Deng-Jun, W.; Zhou, D.-M. Biofilms and extracellular polymeric substances mediate the transport of graphene oxide nanoparticles in saturated porous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrega, J.; Renshaw, J.C.; Lead, J.R. Interactions of silver nanoparticles with Pseudomonas putida biofilms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9004–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, R.N.; Lu, Q.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y. The effects of biofilm on the transport of stabilized zerovalent iron nanoparticles in saturated porous media. Water Res. 2012, 46, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampon, M.; Hellal, J.; Mouvet, C.; Wille, G.; Michel, C.; Wiener, A.; Braun, J.; Ollivier, P. Do natural biofilm impact nZVI mobility and interactions with porous media? A column study. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernissee, J.; Abbott, W. Binding of mineral grains by a species of Thalassiosira. Nova Hedwig. Beih. 1975, 53, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, R.; Ye, X.; Du, X. Coupled effects of bacteria and suspended solids on clogging during managed aquifer recharge. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazanpour Esfahani, A.; Batelaan, O.; Hutson, J.L.; Fallowfield, H.J. Combined physical, chemical and biological clogging of managed aquifer recharge and the effect of biofilm on virus transport behavior: A column study. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xin, J.; Zheng, X.; Li, M.; Fang, Y.; Zheng, T. Clogging evolution in porous media under the coexistence of suspended particles and bacteria: Insights into the mechanisms and implications for groundwater recharge. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkhaus, E.; Meisen, S.; Telgheder, U.; Wingender, J. Chemical and physical methods for characterisation of biofilms. Microchim. Acta 2007, 158, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. Relevance of microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs)—Part I: Structural and ecological aspects. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xin, J.; Zheng, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, T. Effect of biofilms on the clogging mechanisms of suspended particles in porous media during artificial recharge. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Champagne, D.; Tufenkji, N. Transport behavior of selected nanoparticles with different surface coatings in granular porous media coated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6942–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Good, R.J. Interfacial Lifshitz-van der Waals and polar interactions in macroscopic systems. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, D.; Subramaniam, K.; Butkus, M.; Strevett, K.; Bergendahl, J. A review of non-DLVO interactions in environmental colloidal systems. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2002, 1, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; He, L.; Ge, Z.; Tong, M.; Kim, H. Different electrically charged proteins result in diverse bacterial transport behaviors in porous media. Water Res. 2018, 143, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Du, X.; Ye, X. Clogging process by suspended solids during groundwater artificial recharge: Evidence from lab simulations and numerical modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 3226–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorni, S.; Natarajan, K.A. Microbially induced selective flocculation of hematite from kaolinite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 125, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghashoghchi, R.A.; Hosseini, M.R.; Ahmadi, A. Effects of microbial cells and their associated extracellular polymeric substances on the bio-flocculation of kaolin and quartz. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 138, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezawada, J.; Hoang, N.V.; More, T.T.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, N.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by Serratia sp.1 using wastewater sludge as raw material and flocculation activity of the EPS produced. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, T.T.; Yadav, J.S.S.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances of bacteria and their potential environmental applications. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuboori, A.H.R.; Idris, A.; Al-joubory, H.H.R.; Uemura, Y.; Ibn Abubakar, B.S.U. Flocculation behavior and mechanism of bioflocculant produced by Aspergillus flavus. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 150, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; He, L.; Su, X.; Wang, S.; Tong, M. Starvation Process Would Induce Different Bacterial Mobilities and Attachment Performances in Porous Media without and with Nutrients on Surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 13879–13889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermak, D.L.; McCammon, J.A. Brownian dynamics with hydrodynamic interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 69, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.A.; Bettahar, M. Concentration dependent transport of colloids in saturated porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2006, 82, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Group | Porous Media with or Without Biofilm Coating | The Turbidity of Recharge Water |
|---|---|---|
| High-turbidity group (HT) | with biofilm coating | 100 NTU |
| High-turbidity control check group (HTCK) | without biofilm coating | 100 NTU |
| Medium-turbidity group (MT) | with biofilm coating | 50 NTU |
| Medium-turbidity control check group (MTCK) | without biofilm coating | 50 NTU |
| Low-turbidity group (LT) | with biofilm coating | 10 NTU |
| Low-turbidity control check group (LTCK) | without biofilm coating | 10 NTU |
| Microbial consortium control check group (MCCK) | with biofilm coating | 0 NTU |
| Control check group (CK) | without biofilm coating | 0 NTU |
| Parameters | Units | MC | SPs | MC + SPs (100 NTU) | MC + SPs (50 NTU) | MC + SPs (10 NTU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θDii | (°) | 23.65 | 30.17 | 35.15 | 32.86 | 30.43 |
| θG | (°) | 36.85 | 16.18 | 38.01 | 35.52 | 40.18 |
| θW | (°) | 18.31 | 9.60 | 23.70 | 23.08 | 18.15 |
| γLW | (mJ/m−2) | 46.82 | 43.94 | 42.07 | 43.00 | 43.94 |
| γ− | (mJ/m−2) | 53.31 | 46.53 | 50.98 | 49.15 | 28.41 |
| γ+ | (mJ/m−2) | 0.18 | 1.94 | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.88 |
| A132 | (J/m−2) | 7.78 | 7.48 | 7.27 | 7.37 | 7.48 |
| Group | Zeta Potential (mV) | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite | 29.03 ± 0.67 | 9.60 ± 2.55 |
| CK | −3.95 ± 0.75 | 8.55 ± 1.19 |
| MCCK | −22.87 ± 1.70 | 10.67 ± 1.98 |
| HTCK | −20.70 ± 1.00 | 22.90 ± 2.39 |
| HT | −21.50 ± 2.40 | 23.70 ± 1.56 |
| MT | −33.93 ± 0.47 | 23.08 ± 0.94 |
| LT | −36.07 ± 0.63 | 18.15 ± 0.86 |
| Groups | Richness Index | Diversity Index | Coverage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao | Ace | Shannon | Simpson | ||
| MCCK | 895.92 | 949.80 | 3.10 | 0.16 | 0.998 |
| HT | 913.48 | 960.09 | 3.22 | 0.12 | 0.998 |
| MT | 988.83 | 1038.15 | 3.25 | 0.14 | 0.998 |
| LT | 1018.05 | 1065.00 | 3.37 | 0.12 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y. The Fate and Clogging Mechanisms of Suspended Particles in Natural Biofilm-Coated Porous Media. Water 2025, 17, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101480
Wang H, Wu J, Yang D, Chen Y, Xia Y. The Fate and Clogging Mechanisms of Suspended Particles in Natural Biofilm-Coated Porous Media. Water. 2025; 17(10):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101480
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huan, Junjie Wu, Dengbo Yang, Yudao Chen, and Yuan Xia. 2025. "The Fate and Clogging Mechanisms of Suspended Particles in Natural Biofilm-Coated Porous Media" Water 17, no. 10: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101480
APA StyleWang, H., Wu, J., Yang, D., Chen, Y., & Xia, Y. (2025). The Fate and Clogging Mechanisms of Suspended Particles in Natural Biofilm-Coated Porous Media. Water, 17(10), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101480





