Grey Situation Decision Method Based on Improved Whitening Function to Identify Water Inrush Sources in the Whole Cycle of Coal Mining
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
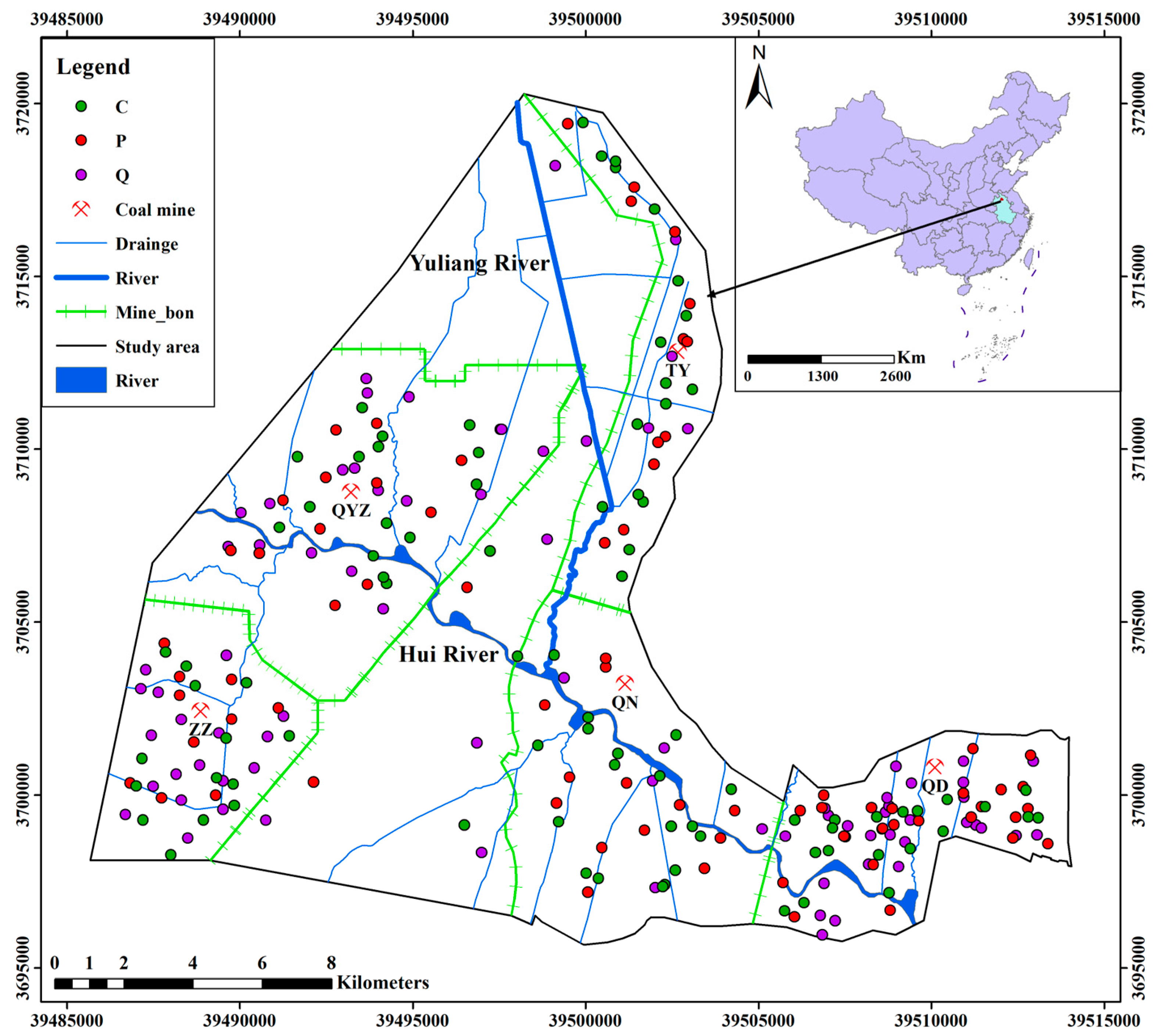
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sampling and Testing
2.2.2. A Water Source Discrimination Model Integrating Exponential Whitening Function and Weighted Grey Situational Decision Method
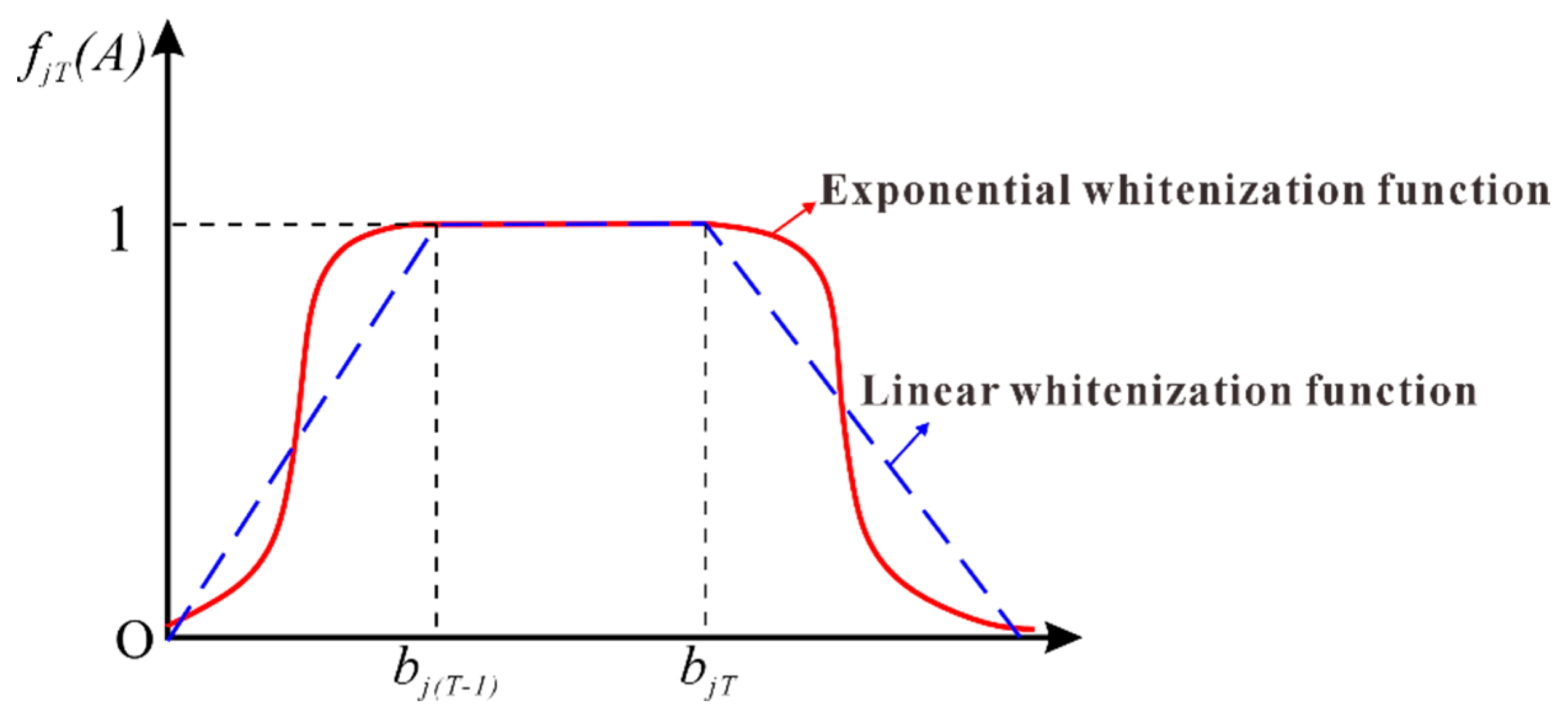
2.2.3. Establishing the Exponential Whitening Function
2.2.4. Calculation of CRITIC Weights
2.3. Establishment of Comprehensive Discrimination Model
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Z. Characteristics of Water Hazards in China’s Coal Mines: A Review. Mine Water Environ. 2021, 40, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Kim, S.-M.; Yi, H.; Choi, Y. An Overview of GIS-Based Modeling and Assessment of Mining-Induced Hazards: Soil, Water, and Forest. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sui, W.; Ranville, J.F. Hazard identification and risk assessment of groundwater inrush from a coal mine: A review. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Brill, E.D.; Mahinthakumar, G.; Ranjithan, S.R. Contaminant source characterization in water distribution systems using binary signals. J. Hydroinform. 2012, 14, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Auckenthaler, P. Optimal sensor placement for event detection and source identification in water distribution networks. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2014, 63, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Mei, A.; Wu, Q.; Meng, S.; Zhao, D.; Hua, Z. Double verification and quantitative traceability: A solution for mixed mine water sources. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. Identification of groundwater hydrogeochemistry and the hydraulic connections of aquifers in a complex coal mine. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Huang, P.; Hu, Y.; Chai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Application of dynamic weight in coal mine water inrush source identification. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Chai, N.; Liu, T.; Jin, Z.; Rinklebe, J. Groundwater hydrochemistry, source identification and pollution assessment in intensive industrial areas, eastern Chinese loess plateau. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyka, J.; Cien, D.; d’Obyrn, K. The Use of Hydrochemical Zoning to Predict Water Hazards: The Example of the Olkusz-Pomorzany Zn-Pb Mine. Mine Water Environ. 2024, 43, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Suh, J.; Oh, S.; Son, J.; Hyun, C.-U.; Park, H.-D.; Shin, S.-H.; Choi, Y. Assessing and prioritizing environmental hazards associated with abandoned mines in Gangwon-do, South Korea: The Total Mine Hazards Index. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowska, M.; Bukowski, P. Changes of Properties of Carboniferous Rock Mass and the Occurrence of Some Natural Hazards in the Conditions of Flooding of Roadways within Abandoned Coal Mines. J. Min. Sci. 2021, 57, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Heib, M.; Varouchakis, E.A.; Galetakis, M.; Renaud, V.; Burda, J. A framework for assessing hazards related to pit lakes: Application on European case studies. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.K.; Samadder, S.R.; Singh, V. Groundwater vulnerability assessment in degraded coal mining areas using the AHP-Modified DRASTIC model. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2351–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Niu, Y. Effects of coal mining on the evolution of groundwater hydrogeochemistry. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2245–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Qi, K.; Zhang, X. Quantitative prediction of the impact of deep extremely thick coal seam mining on groundwater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 178, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, H.; Hino, M.; Shinohara, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Muraoka, H. Simplified Neural Network Equalizer With Noise Whitening Function for GPRML System. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 3777–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, Y. A Grey Evaluation Method Based on the Center-point Double S-shaped Whitening Weight Function. J. Grey Syst. 2013, 25, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Ju, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chai, H.; Liu, Y. Source identification of mine water inrush based on the exponential whitenization function and the grey situation decision model. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2022, 40, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzanegan, B.; Moghadam, R.; Jagannathan, S.; Natarajan, P. Optimal Adaptive Tracking Control of Partially Uncertain Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems Using Lifelong Hybrid Learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 17254–17265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haktanir, E.; Kahraman, C. A Novel CRITIC Based Weighted FMEA Method: Application to COVID-19 Blood Testing Process. J. Mult. Valued Log. Soft Comput. 2021, 37, 247–275. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, A.R.; Kasim, M.M.; Hamid, R.; Ghazali, M.F. A Modified CRITIC Method to Estimate the Objective Weights of Decision Criteria. Symmetry 2021, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkasi, N.; Rezakhah, S. A modified CRITIC with a reference point based on fuzzy logic and hamming distance. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 255, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Hu, B.; Chang, G.; Li, A. Robust derivative-free Kalman filter based on Huber’s M-estimation methodology. J. Process Control 2013, 23, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyazi Cankaya, M.; Arslan, O. M-Estimation Method Based Asymmetric Objective Function. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.00378. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, K. Spatial and Temporal Evolutions of Shallow Groundwater with Anthropogenic Activities: A Case Study of Sunan Mine Region, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

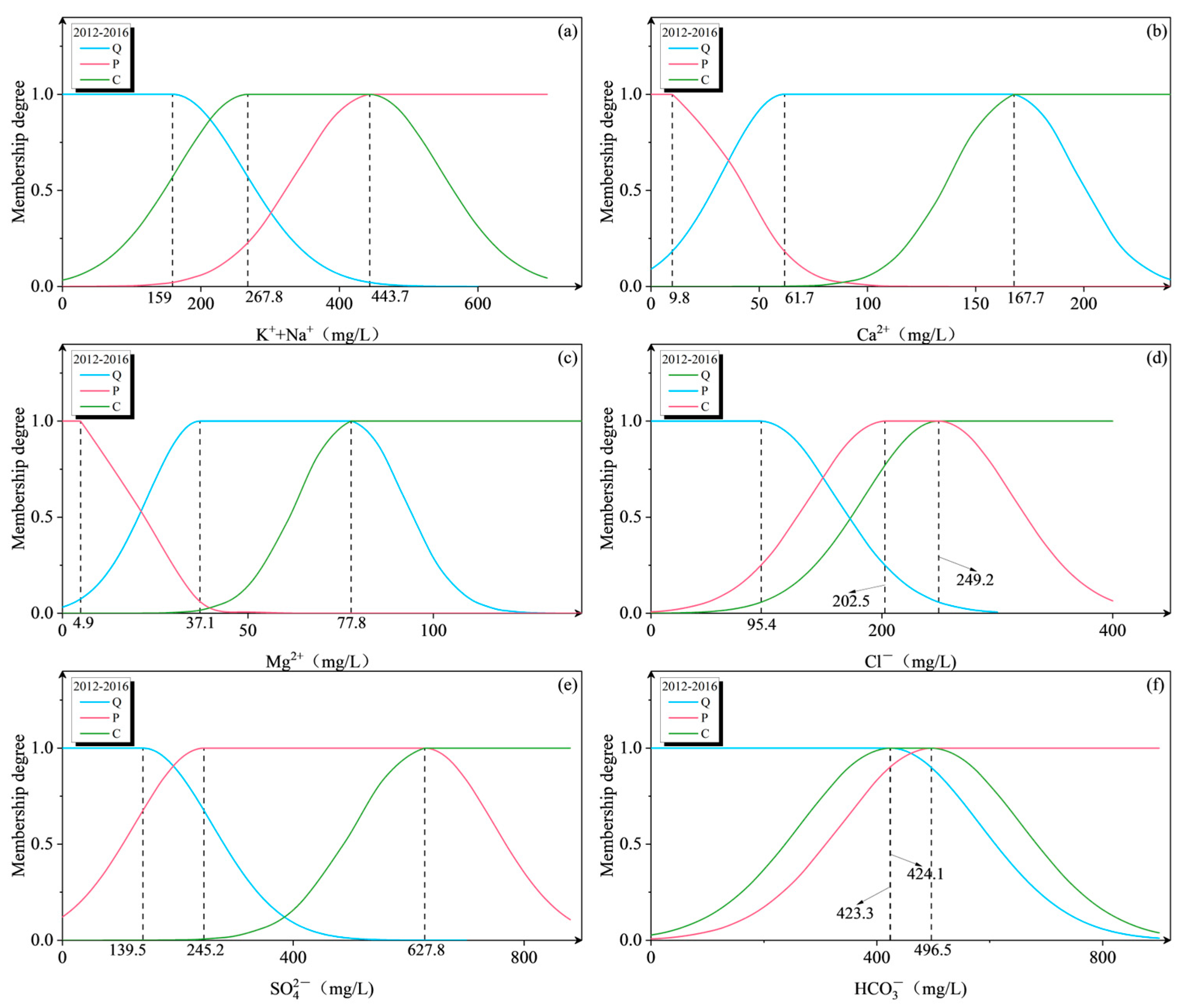
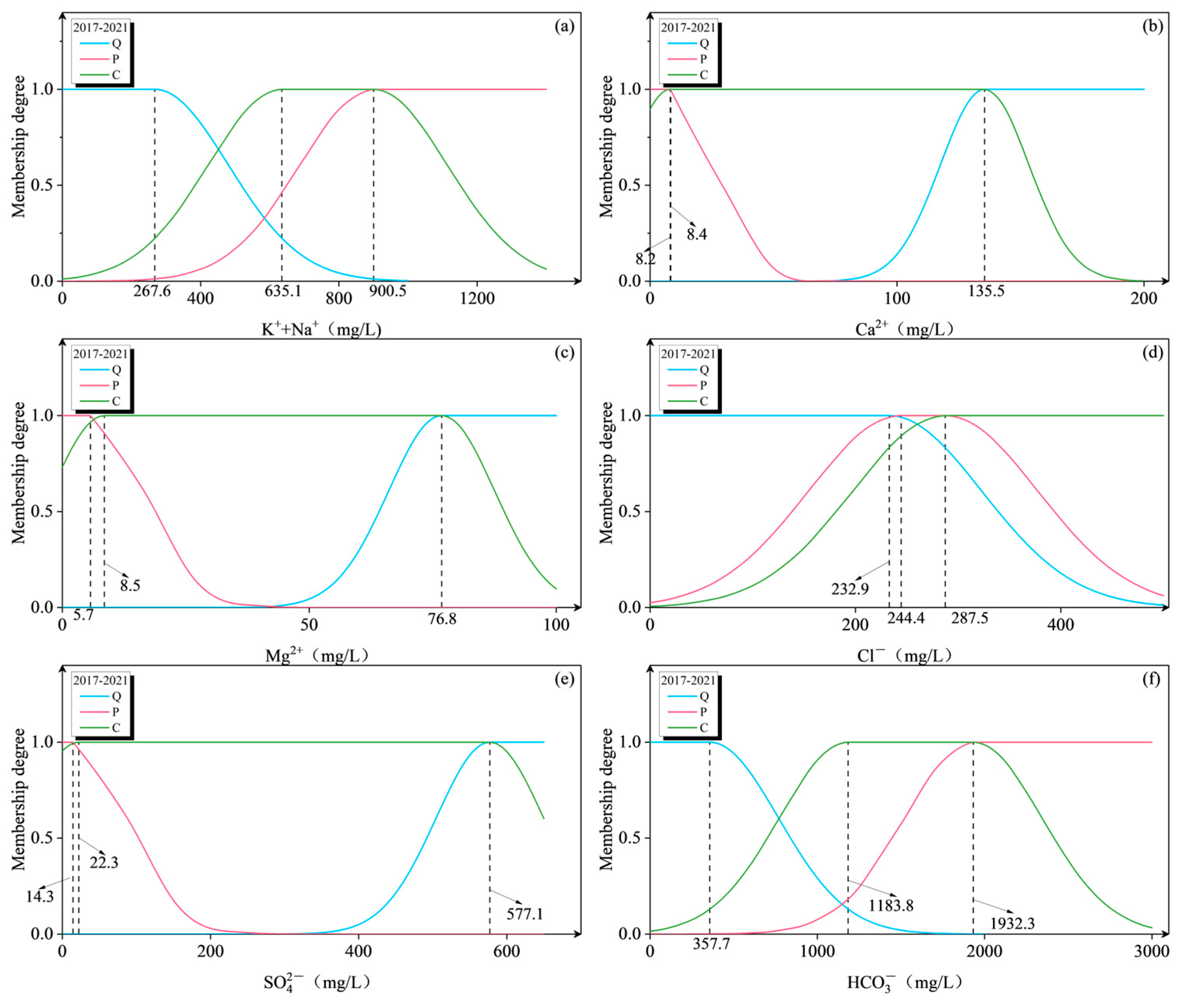
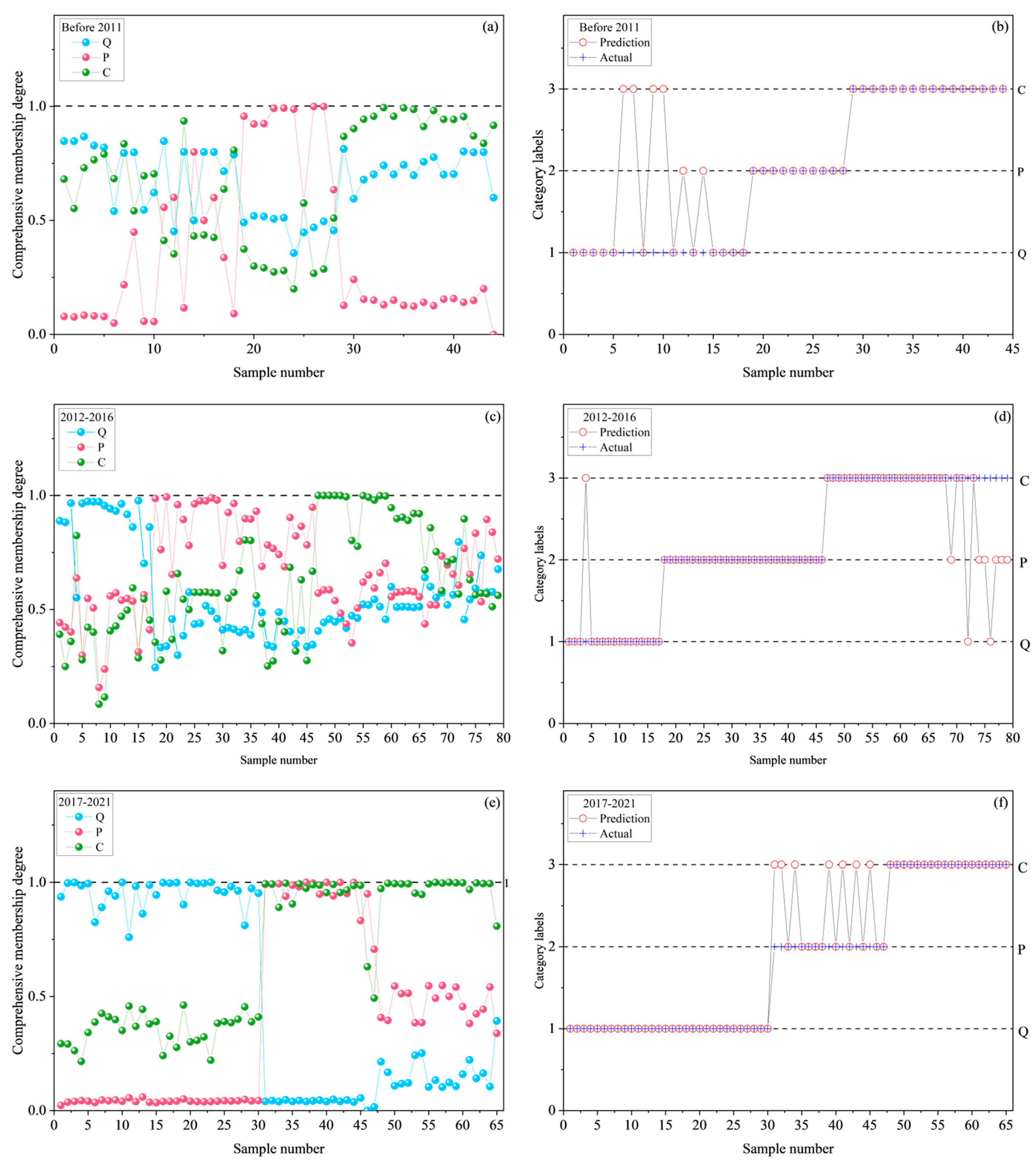
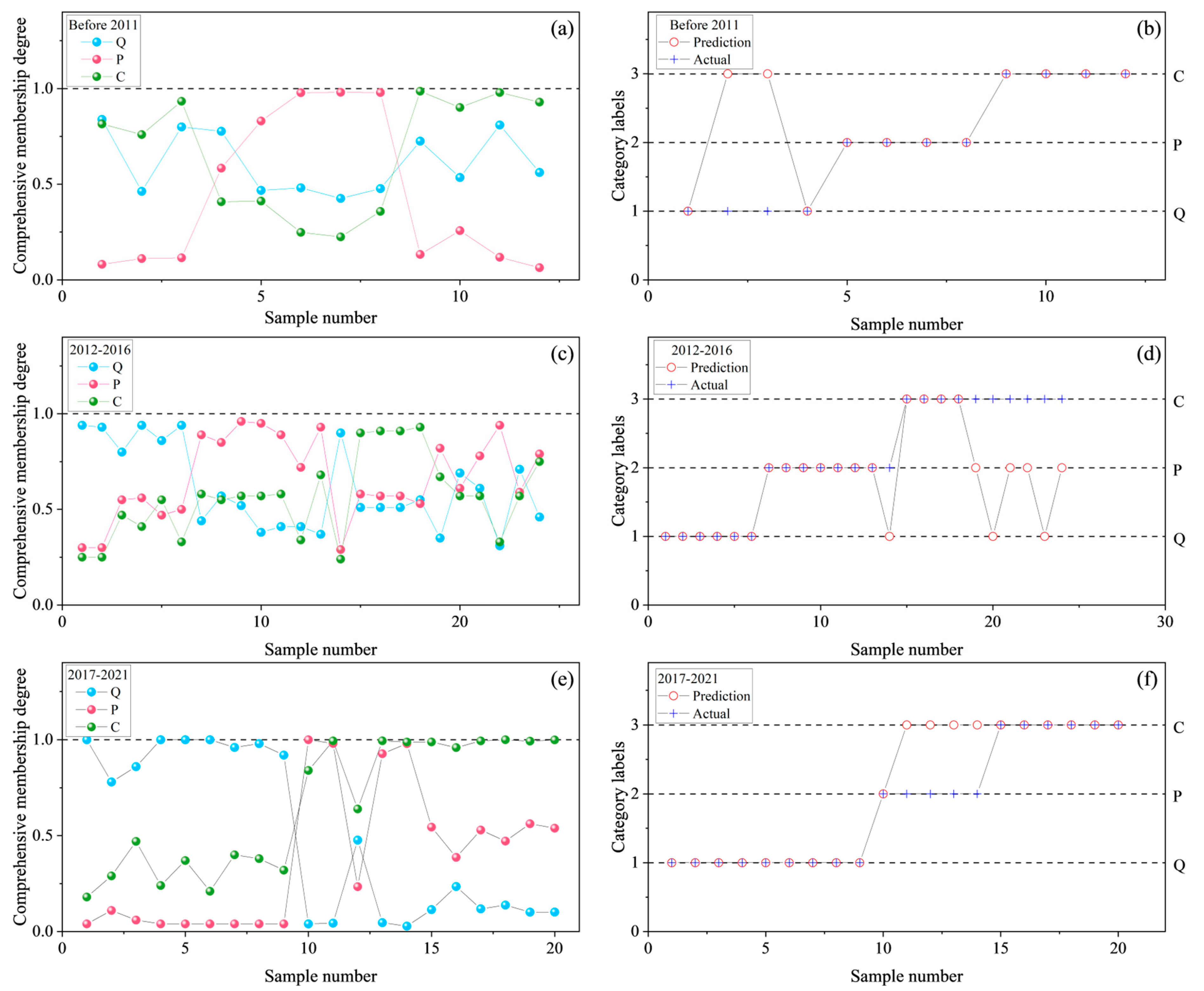
| Stage (Year) | Category | K+ + Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | ||
| Before 2011 | Quaternary | 476.5 | 225.7 | 121.1 | 551.6 | 1007.9 | 298.4 |
| Permian | 1262.2 | 23.9 | 5.5 | 117.8 | 2369.7 | 324.1 | |
| Carboniferous | 503.5 | 177.2 | 76.6 | 325.2 | 921.2 | 476.5 | |
| Mean | 747.40 | 142.26 | 67.74 | 331.51 | 1432.93 | 366.36 | |
| Weight | 0.22 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.43 | 0.08 | |
| 2012–2016 | Quaternary | 159.0 | 61.7 | 37.1 | 95.4 | 139.5 | 423.3 |
| Permian | 443.7 | 9.8 | 4.9 | 202.5 | 245.2 | 496.5 | |
| Carboniferous | 267.8 | 167.7 | 77.8 | 249.2 | 627.8 | 424.1 | |
| Mean | 290.2 | 79.7 | 40.0 | 182.3 | 337.5 | 448.0 | |
| Weight | 0.23 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 0.27 | |
| 2017–2021 | Quaternary | 267.6 | 135.5 | 76.8 | 232.9 | 577.1 | 357.7 |
| Permian | 900.5 | 8.2 | 5.7 | 244.4 | 14.3 | 1932.3 | |
| Carboniferous | 635.1 | 8.4 | 8.5 | 287.5 | 22.3 | 1183.8 | |
| Mean | 601.1 | 50.7 | 30.4 | 254.9 | 204.6 | 1157.9 | |
| Weight | 0.2140 | 0.0418 | 0.0239 | 0.0390 | 0.1804 | 0.5009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ju, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Q. Grey Situation Decision Method Based on Improved Whitening Function to Identify Water Inrush Sources in the Whole Cycle of Coal Mining. Water 2025, 17, 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101479
Ju Q, Hu Y, Liu Q. Grey Situation Decision Method Based on Improved Whitening Function to Identify Water Inrush Sources in the Whole Cycle of Coal Mining. Water. 2025; 17(10):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101479
Chicago/Turabian StyleJu, Qiding, Youbiao Hu, and Qimeng Liu. 2025. "Grey Situation Decision Method Based on Improved Whitening Function to Identify Water Inrush Sources in the Whole Cycle of Coal Mining" Water 17, no. 10: 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101479
APA StyleJu, Q., Hu, Y., & Liu, Q. (2025). Grey Situation Decision Method Based on Improved Whitening Function to Identify Water Inrush Sources in the Whole Cycle of Coal Mining. Water, 17(10), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101479






