Response of Soil Detachment Capacity to Hydrodynamic Characteristics Under Different Slope Gradients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Devices and Designs
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Hydrodynamic Characteristics Measurement
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
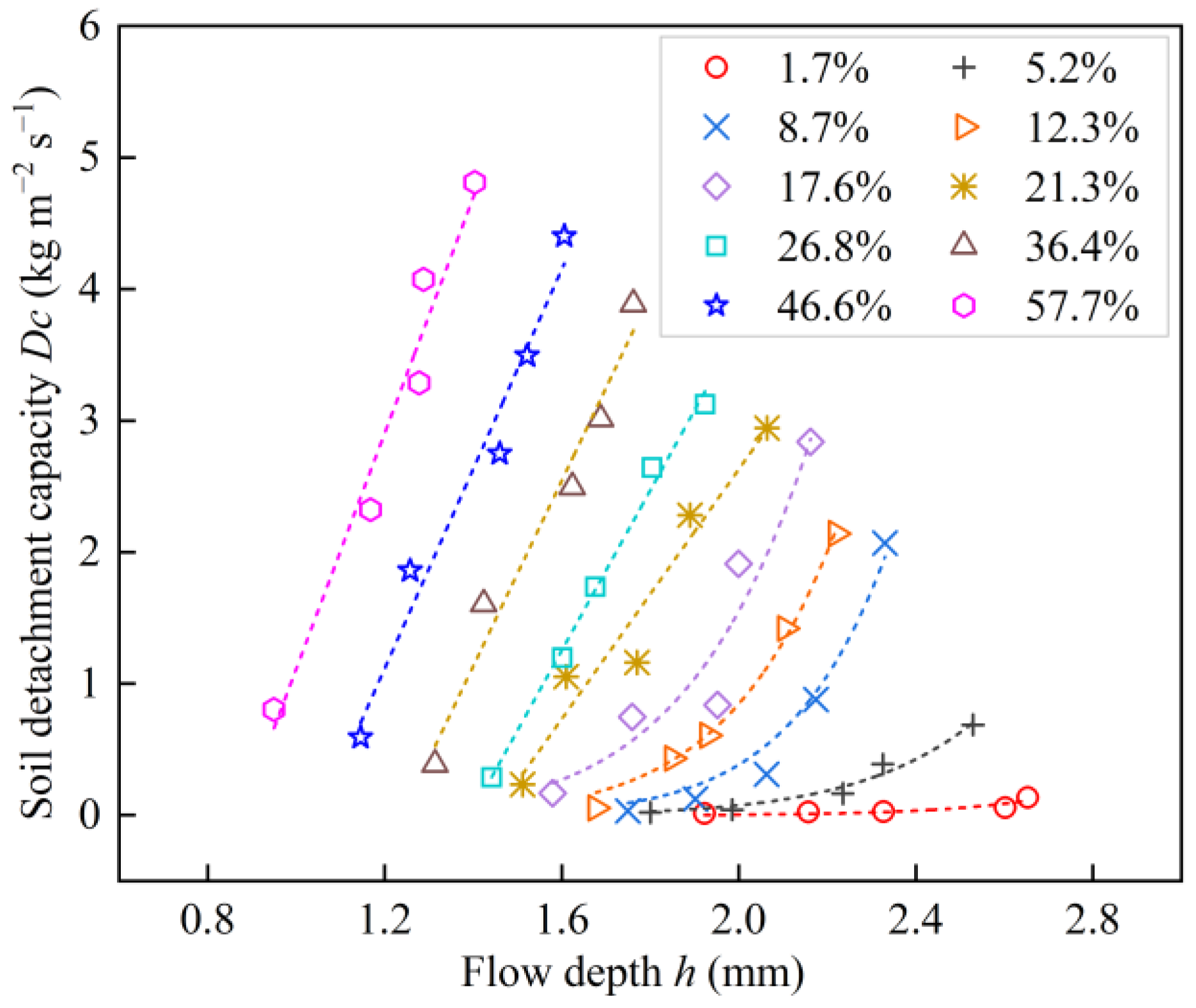
3.1. The Effect of Hydrodynamic Characteristics on the Soil Detachment Capacity
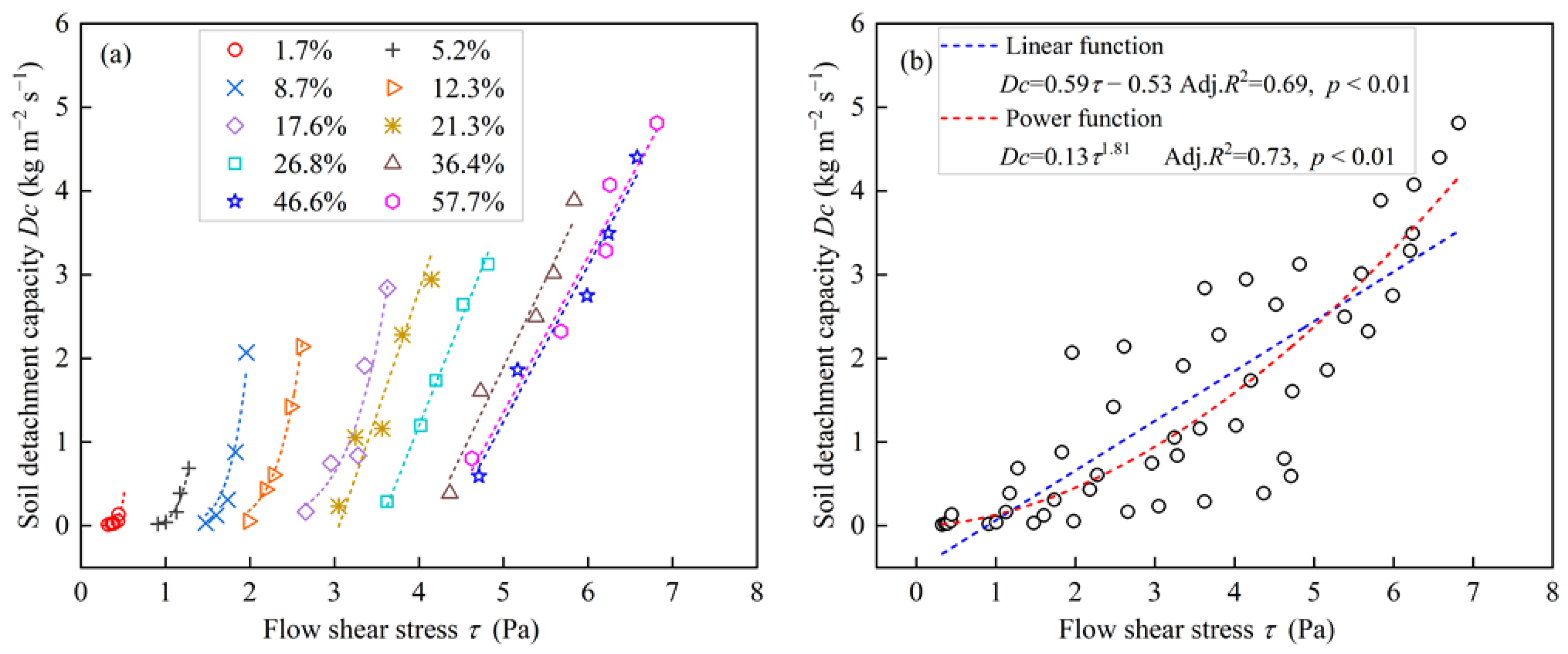
3.2. The Effect of Flow Shear Stress on the Soil Detachment Capacity
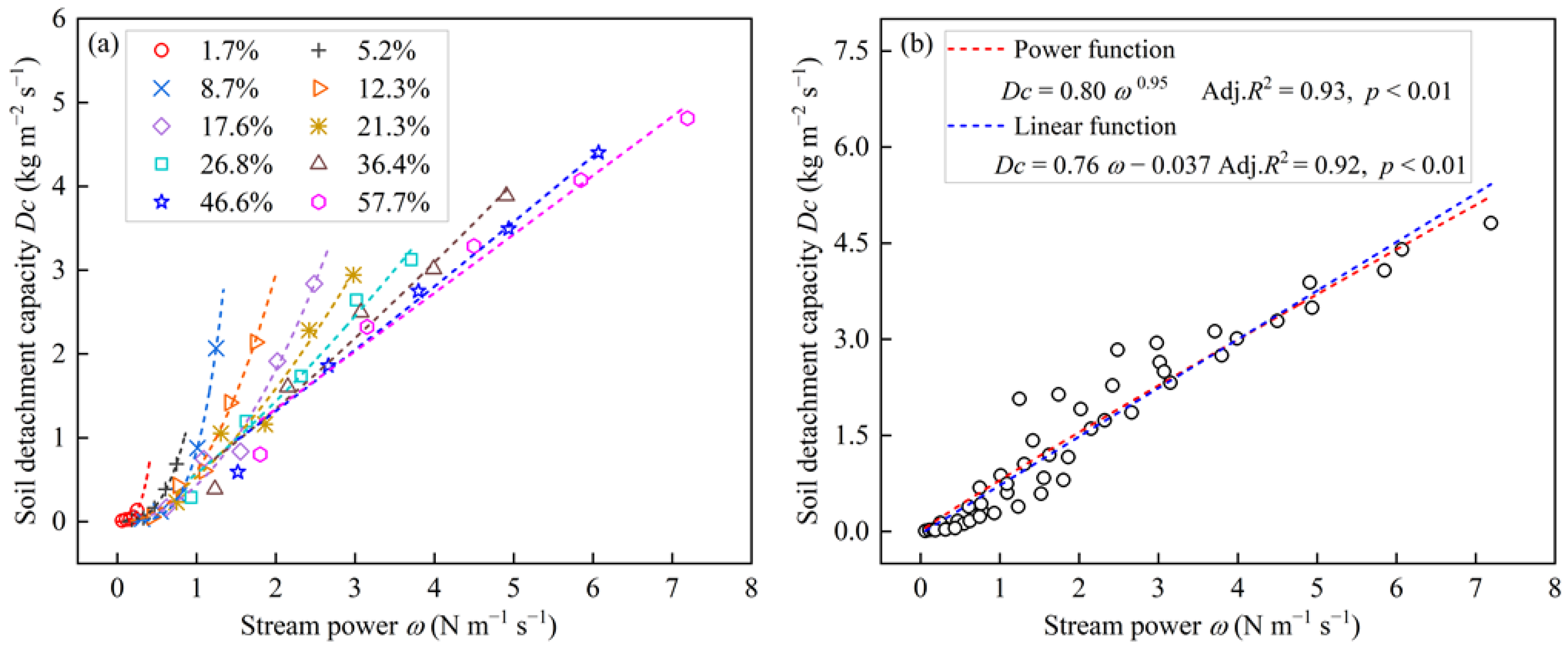
3.3. The Effect of Stream Power on Soil Detachment Capacity
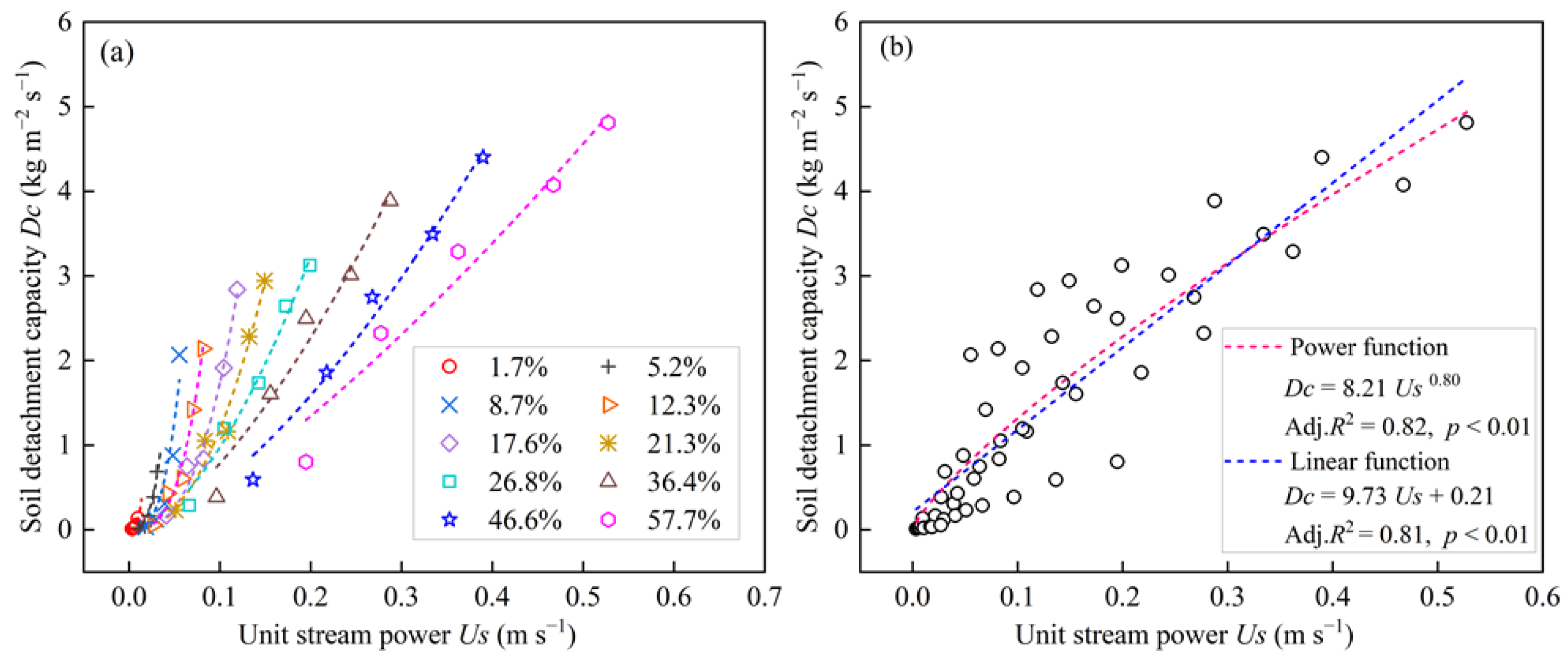
3.4. The Effect of Unit Stream Power on Soil Detachment Capacity
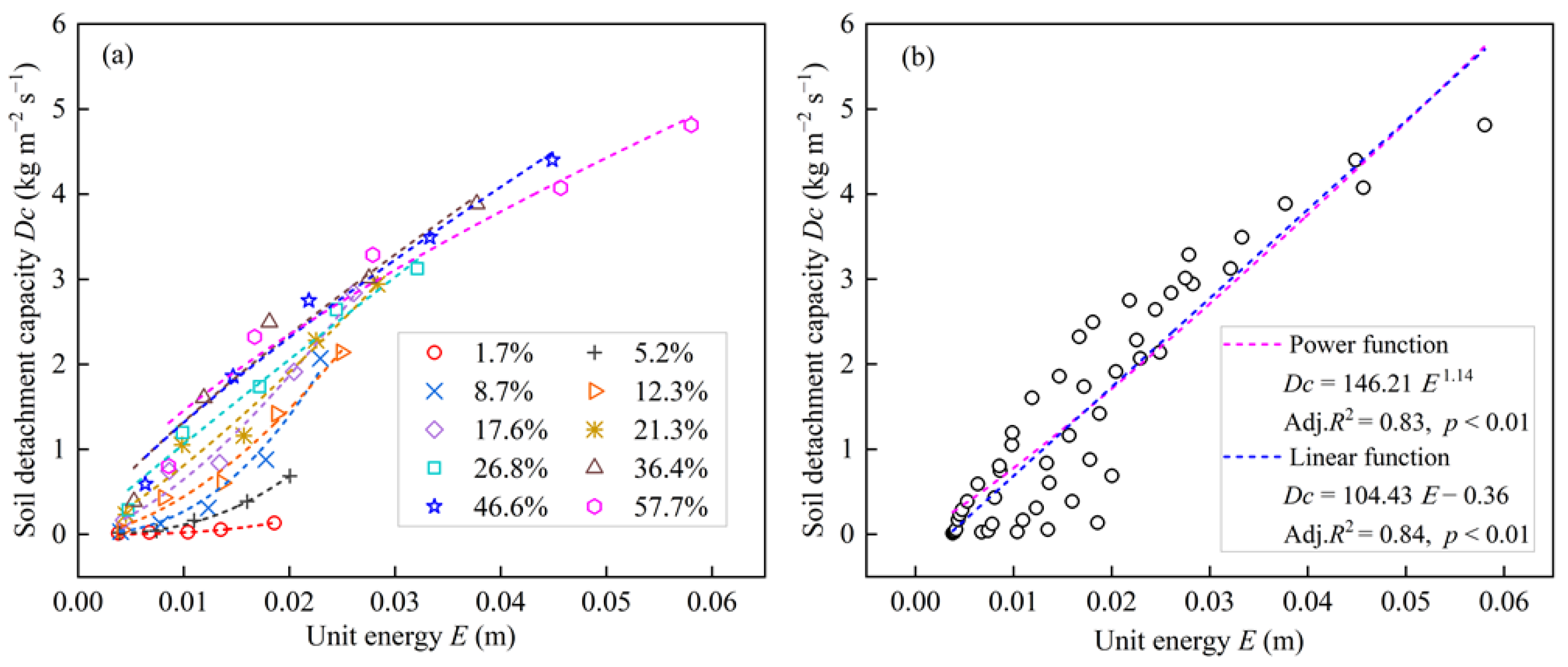
3.5. The Effect of Unit Energy on Soil Detachment Capacity
4. Discussion
4.1. Modeling the Soil Detachment Capacity Using Different Hydrodynamic Parameters
4.2. Slope Effect of the Relationship Between Soil Detachment Capacity and Hydrodynamic Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, D.W.; Yu, B.F.; Fu, X.D.; Li, T.J. Improved hillslope erosion module for the Digital Yellow-River Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, C4014011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Fu, X.D.; Wang, B.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.P. Modeling feedback processes between soil detachment and sediment transport along hillslopes on the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.R.; Meyer, L.D. A closed-form soil erosion equation for upland areas. In Sedimentation Symposium; Einstein, H.A., Shen, H.W., Eds.; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1972; pp. 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nearing, M.A.; Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J.; Finkner, S.C. A process-based soil erosion model for USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project technology. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Fu, X.D.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, G.; Gong, Z. Modeling soil erosion dynamic processes along hillslopes with vegetation impact across different land uses on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2024, 243, 108202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.K.; Rose, C.W. Application and sensitivity analysis of process-based erosion model GUEST. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; An, C.G.; Wang, C.F.; Wang, B.J.; Yu, B.F.; Fu, X.D. Numerical modeling of effects of vegetation restoration on runoff and sediment yield on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2024, 247, 108501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Simanton, J.R.; Norton, L.D.; Bulygin, S.J.; Stone, J. Soil erosion by surface water flow on a stony, semiarid hillslope. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 1999, 24, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Liu, Y.M.; Han, Y.F.; Zhang, X.C. Sediment transport and soil detachment on steep slopes: I. Transport capacity estimation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, Z.L.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Q.W.; Wu, B.; Liu, J.E.; Ma, C.Y.; Delang, C.O.; Zhang, F.B. Soil detachment capacity by rill flow for five typical loess soils on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, Q.W.; Wang, C.F.; Ren, J.; Li, H.K.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.Q. Response of sediment transport capacity to soil properties and hydraulic parameters in the typical agricultural regions of the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nearing, M.A.; Bradford, J.M.; Parker, S.C. Soil detachment by shallow flow at low slopes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Tao, T.T.; Han, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, F.L.; Tan, W.T.; Kong, L.Y.; Feng, T.; Zhu, P.Z. Field simulation experiment on the relationships between hydrodynamics and soil detachment rate in formed rills. Catena 2023, 233, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.X.; Zhang, K.L.; Dai, H.L.; Guo, Z.L. Modeling soil detachment on unpaved road surfaces on the Loess Plateau. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, M.; Shabanpour, M.; Khaledian, M.; Asadi, H. The evaluation of soil detachment capacity induced by vegetal species based on the comparison between natural and planted forests. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, S.; Ghorbani-Dashtaki, S. Deriving and evaluating hydraulics and detachment models of rill erosion for some calcareous soils. Catena 2018, 164, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Study on hydraulic properties of shallow flow. Adv. Water Sci. 2002, 13, 159–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez, R.; Govers, G. Flow detachment by concentrated flow on smooth and irregular beds. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Wang, Z.L.; Shen, N.; Chen, H. Modeling soil detachment capacity by rill flow using hydraulic parameters. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, M.; Shabanpour, M.; Miralles, I.; Cerdà, A.; Tanaka, N.; Asadi, H.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Zema, D.A. Evaluating the effects of forest tree species on rill detachment capacity in a semi-arid environment. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 161, 106158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.W.; Williams, J.R.; Sander, G.C.; Barry, D.A. A Mathematical Model of Soil Erosion and Deposition Processes: I. Theory for a Plane Land Element. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, R.; Torri, D. Detachment of soil particles by shallow flow: Sampling methodology and observations. Catena 1998, 32, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.; Shi, P.J.; Jia, Z.W. Slope length effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Yue, X.L.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.M.; Xu, W.L.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Sun, W.Y. Comparison of the suspended sediment dynamics in two Loess Plateau catchments, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1398–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Liu, Q.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, L.; Xuan, H.; Fang, N.F.; Yue, Z.J. Study on soil erosion and conservation in the past 10 Years: Progress and prospects. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 1117–1127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Parhizkar, M.; Shabanpour, M.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Zema, D.A. Variability of rill detachment capacity with sediment size, water depth and soil slope in forest soils: A flume experiment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. An Approach to the Sediment Transport Problem from General Physics. Geological Survey Professional Paper; 422–J; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.T. Unit stream power and sediment transport. J. Hydraul. Div. 1972, 98, 1805–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Huggins, L.F.; Meyer, L.D. A Laboratory Study of Rill Hydraulics: II. Shear Stress Relationships. Trans. ASAE 1984, 27, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.S.; Liu, G.; Dan, C.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Ye, S.M.; Li, R.Q.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z. Estimating Manning’s coefficient n for sheet flow during rainstorms. Catena 2023, 226, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.K.; Xie, J.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Yang, Y.S.; Wang, C.F.; Wang, J. Rigid Vegetation Affects Slope Flow Velocity. Water 2024, 16, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Liang, C.; He, B.H.; Bush, R.T. Erosion vulnerability of sandy clay loam soil in Southwest China: Modeling soil detachment capacity by flume simulation. Catena 2019, 178, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, G.; Liu, P.L.; Zheng, F.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Hu, F.N. Response of soil detachment rate to the hydraulic parameters of concentrated flow on steep loessial slopes on the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.L.; Fu, S.H.; Wu, Q.Y.; Wang, A.J. Soil detachment capacity of shallow overland flow in Earth-Rocky Mountain Area of Southwest China. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Huang, C.H.; Zhang, K.L. Soil detachment by shallow flow. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Laflen, J.M.; Elliot, W.J.; Simanton, J.R.; Holzhey, C.S.; Kohl, K.D. WEPP: Soil erodibility experiments for rangeland and cropland soils. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.L.; Zhang, G.H.; Yi, T.; Liu, F. Soil detachment capacity by overland flow for soils of the Beijing region. Soil Sci. 2014, 179, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, D.C.; Frankenberger, J.R.; Ascough, J.C., II. WEPP: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.P.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.T. Overland flow velocities measured using a high-resolution particle image velocimetry system. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.F.; Sun, S.X.; Gong, Z.W. Experimental analysis on characteristics of vertical velocity of overland flow on low sediment concentration. J. Lanzhou Jiaotong Univ. 2022, 41, 96–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Slope Gradient % | Power Function Dc = a1 h b1 | Linear Function Dc = k1 (h–hc) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | b1 | Adj. R2 | p | k1 | vc | Adj. R2 | p | |
| 1.7 | 0.0000010 | 11.91 | 0.80 | 0.025 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.53 | 0.10 |
| 5.2 | 0.00010 | 9.54 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 0.90 | 1.89 | 0.80 | 0.025 |
| 8.7 | 0.00023 | 10.69 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 3.33 | 1.84 | 0.74 | 0.039 |
| 12.3 | 0.0016 | 9.05 | 0.99 | <0.010 | 3.85 | 1.71 | 0.93 | <0.010 |
| 17.6 | 0.0068 | 7.84 | 0.89 | <0.010 | 4.33 | 1.59 | 0.79 | 0.029 |
| 21.3 | 0.07 | 5.30 | 0.89 | <0.010 | 4.75 | 1.45 | 0.93 | <0.010 |
| 26.8 | 0.09 | 5.49 | 0.92 | <0.010 | 6.09 | 1.39 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 36.4 | 0.18 | 5.43 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 7.05 | 1.24 | 0.96 | <0.010 |
| 46.6 | 0.52 | 4.53 | 0.95 | <0.010 | 7.59 | 1.05 | 0.96 | <0.010 |
| 57.7 | 1.27 | 4.05 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 8.96 | 0.88 | 0.95 | <0.010 |
| Slope Gradient % | Power Function Dc = a2 v b2 | Linear Function Dc = k2 (v–vc) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a2 | b2 | Adj. R2 | p | k1 | vc | Adj. R2 | p | |
| 1.7 | 5.59 | 4.26 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.67 | 0.057 |
| 5.2 | 7.16 | 4.39 | 0.99 | <0.010 | 1.70 | 0.26 | 0.80 | 0.027 |
| 8.7 | 7.42 | 3.32 | 0.88 | 0.011 | 3.96 | 0.26 | 0.83 | <0.010 |
| 12.3 | 8.11 | 3.20 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 4.50 | 0.25 | 0.86 | 0.014 |
| 17.6 | 6.97 | 2.52 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 5.66 | 0.24 | 0.88 | 0.011 |
| 21.3 | 6.13 | 2.24 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 5.52 | 0.23 | 0.91 | <0.010 |
| 26.8 | 5.04 | 1.73 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 5.67 | 0.22 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 36.4 | 5.17 | 1.53 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 6.12 | 0.20 | 0.98 | <0.010 |
| 46.6 | 5.07 | 1.55 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 5.99 | 0.20 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 57.7 | 4.56 | 1.34 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 5.59 | 0.20 | 0.96 | <0.010 |
| 1.7–57.7 | 5.08 | 2.08 | 0.85 | <0.010 | 6.08 | 0.27 | 0.84 | <0.010 |
| Slope Gradient % | Power Function Dc = a3 τ b3 | Linear Function Dc = k3 (τ–τc) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a3 | b3 | Adj. R2 | p | k3 | τc | Adj. R2 | p | |
| 1.7 | 210.44 | 9.40 | 0.72 | 0.028 | 0.80 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.099 |
| 5.2 | 0.066 | 9.68 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 1.81 | 0.96 | 0.80 | 0.026 |
| 8.7 | 0.0031 | 9.51 | 0.92 | <0.010 | 2.10 | 1.39 | 0.74 | 0.018 |
| 12.3 | 0.00032 | 9.17 | 0.99 | <0.010 | 2.40 | 1.91 | 0.94 | <0.010 |
| 17.6 | 0.00010 | 7.94 | 0.89 | <0.010 | 2.61 | 2.67 | 0.84 | 0.029 |
| 21.3 | 0.00039 | 6.36 | 0.86 | <0.010 | 2.97 | 3.05 | 0.96 | <0.010 |
| 26.8 | 0.00054 | 5.55 | 0.92 | <0.010 | 2.54 | 3.53 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 36.4 | 0.00057 | 4.99 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 2.10 | 4.10 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 46.6 | 0.00080 | 4.57 | 0.95 | <0.010 | 1.87 | 4.32 | 0.96 | <0.010 |
| 57.7 | 0.0020 | 4.08 | 0.95 | <0.010 | 1.86 | 4.26 | 0.95 | <0.010 |
| 1.7–57.7 | 0.13 | 1.81 | 0.73 | <0.010 | 0.59 | 0.90 | 0.69 | <0.010 |
| Slope Gradient % | Power Function Dc = a4 ω b4 | Linear Function Dc = k4 (ω–ωc) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a4 | b4 | Adj. R2 | p | k4 | ωc | Adj. R2 | p | |
| 1.7 | 15.82 | 3.44 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 0.60 | 0.072 | 0.71 | 0.047 |
| 5.2 | 1.66 | 3.01 | 0.99 | <0.010 | 1.20 | 0.25 | 0.87 | 0.014 |
| 8.7 | 0.85 | 4.05 | 0.99 | <0.010 | 2.07 | 0.45 | 0.76 | 0.033 |
| 12.3 | 0.60 | 2.29 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 1.58 | 0.50 | 0.92 | <0.010 |
| 17.6 | 0.43 | 2.06 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 1.40 | 0.62 | 0.91 | <0.010 |
| 21.3 | 0.53 | 1.57 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 1.19 | 0.58 | 0.95 | <0.010 |
| 26.8 | 0.57 | 1.32 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 1.03 | 0.57 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 36.4 | 0.59 | 1.20 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 0.91 | 0.58 | 0.97 | <0.010 |
| 46.6 | 0.62 | 1.09 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 0.81 | 0.58 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 57.7 | 0.66 | 1.02 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 0.73 | 0.28 | 0.97 | <0.010 |
| 1.7–57.7 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 0.93 | <0.010 | 0.76 | 0.049 | 0.92 | <0.010 |
| Slope Gradient % | Power Function Dc = a5 Us b5 | Linear Function Dc = k5 (Us–Usc) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a5 | b5 | Adj. R2 | p | k5 | Usc | Adj. R2 | p | |
| 1.7 | 238,466.60 | 3.13 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 17.53 | 0.0038 | 0.67 | 0.057 |
| 5.2 | 34,907.71 | 3.13 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 32.58 | 0.014 | 0.80 | 0.027 |
| 8.7 | 13,919.94 | 3.10 | 0.91 | <0.010 | 35.13 | 0.019 | 0.69 | 0.040 |
| 12.3 | 5126.22 | 3.10 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 36.94 | 0.031 | 0.86 | 0.014 |
| 17.6 | 946.12 | 2.74 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 39.58 | 0.049 | 0.88 | <0.010 |
| 21.3 | 207.81 | 2.24 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 29.98 | 0.055 | 0.91 | <0.010 |
| 26.8 | 52.18 | 1.73 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 24.27 | 0.063 | 0.97 | <0.010 |
| 36.4 | 26.83 | 1.53 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 18.89 | 0.075 | 0.98 | <0.010 |
| 46.6 | 19.34 | 1.55 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 14.86 | 0.093 | 0.99 | <0.010 |
| 57.7 | 11.51 | 1.34 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 11.38 | 0.097 | 0.96 | <0.010 |
| 1.7–57.7 | 8.21 | 0.80 | 0.82 | <0.010 | 9.73 | -0.022 | 0.81 | <0.010 |
| Slope Gradient % | Power Function Dc = a6 E b6 | Linear Function Dc = k6 (E–Ec) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a6 | b6 | Adj. R2 | p | k6 | Ec | Adj. R2 | p | |
| 1.7 | 19,708.05 | 2.98 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 8.00 | 0.0044 | 0.80 | 0.026 |
| 5.2 | 18,130.64 | 2.60 | 0.99 | <0.010 | 41.77 | 0.0055 | 0.91 | <0.010 |
| 8.7 | 14,855.03 | 2.37 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 91.20 | 0.0050 | 0.90 | < 0.010 |
| 12.3 | 1289.04 | 1.73 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 99.36 | 0.0045 | 0.94 | < 0.010 |
| 17.6 | 743.64 | 1.53 | 0.98 | <0.010 | 119.21 | 0.0037 | 0.95 | < 0.010 |
| 21.3 | 241.68 | 1.24 | 0.96 | <0.010 | 110.64 | 0.0023 | 0.95 | < 0.010 |
| 26.8 | 85.70 | 0.95 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 103.76 | 0.00046 | 0.99 | < 0.010 |
| 36.4 | 60.06 | 0.83 | 0.95 | <0.010 | 101.92 | -0.0023 | 0.93 | < 0.010 |
| 46.6 | 56.90 | 0.82 | 0.97 | <0.010 | 95.09 | -0.0034 | 0.96 | < 0.010 |
| 57.7 | 35.13 | 0.69 | 0.94 | <0.010 | 73.83 | -0.010 | 0.90 | < 0.010 |
| 1.7–57.7 | 146.21 | 1.14 | 0.83 | <0.010 | 104.43 | 0.0034 | 0.84 | < 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J. Response of Soil Detachment Capacity to Hydrodynamic Characteristics Under Different Slope Gradients. Water 2025, 17, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010028
Zhang K, Wang C, Wang J, Zhu S, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhu J. Response of Soil Detachment Capacity to Hydrodynamic Characteristics Under Different Slope Gradients. Water. 2025; 17(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kerui, Chenfeng Wang, Jian Wang, Shoujun Zhu, Xiaoping Wang, Yunqi Wang, Xiaoming Zhang, and Jinqi Zhu. 2025. "Response of Soil Detachment Capacity to Hydrodynamic Characteristics Under Different Slope Gradients" Water 17, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010028
APA StyleZhang, K., Wang, C., Wang, J., Zhu, S., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., & Zhu, J. (2025). Response of Soil Detachment Capacity to Hydrodynamic Characteristics Under Different Slope Gradients. Water, 17(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010028








