Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in an Urban River in Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of River Water Samples
2.2. Preparation of Antibiotics
2.3. Screening of Culturable Bacterial Strains
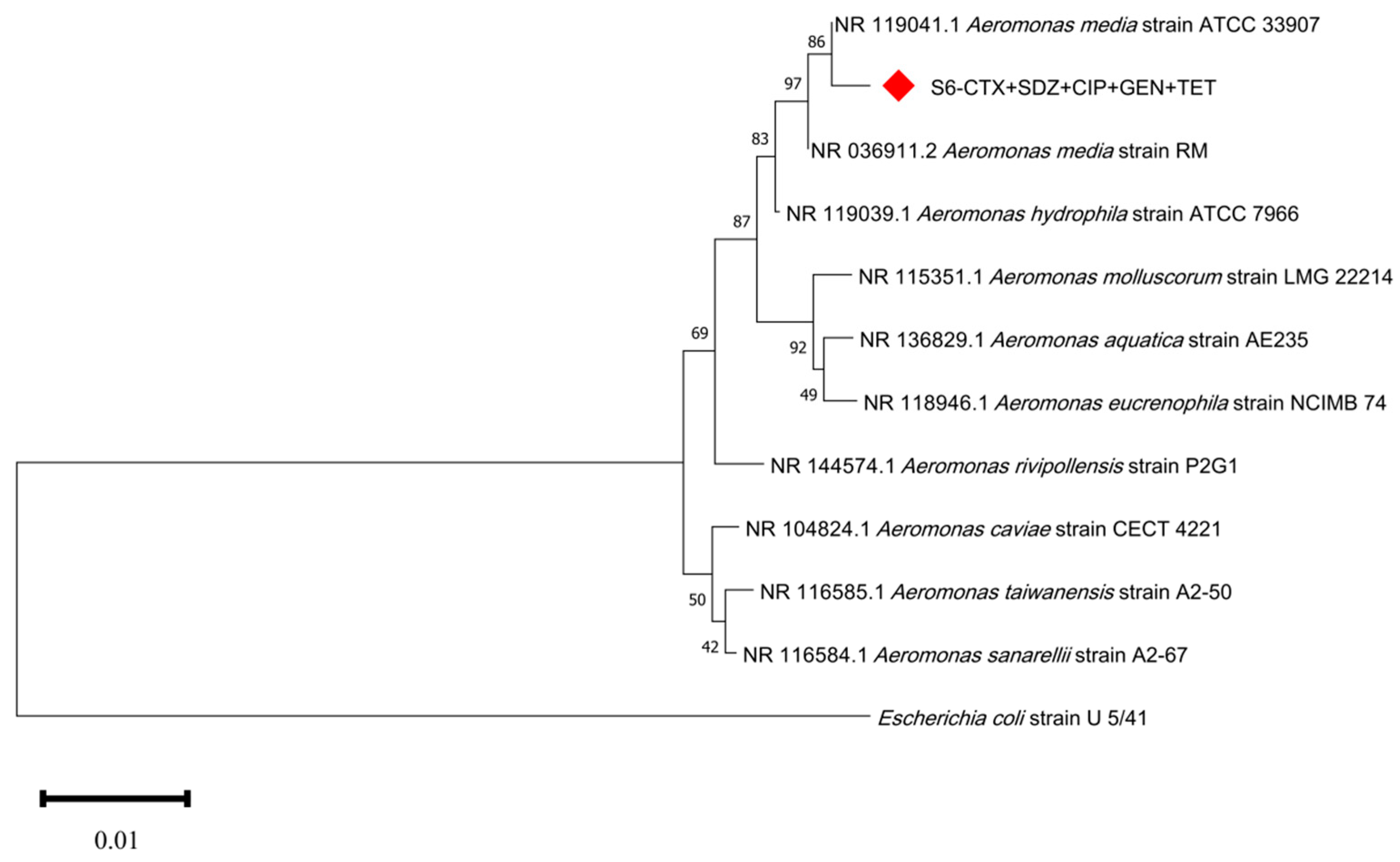
2.4. Identification of Culturable Antibiotic-Resistant Strains
2.5. Statistical Analysis
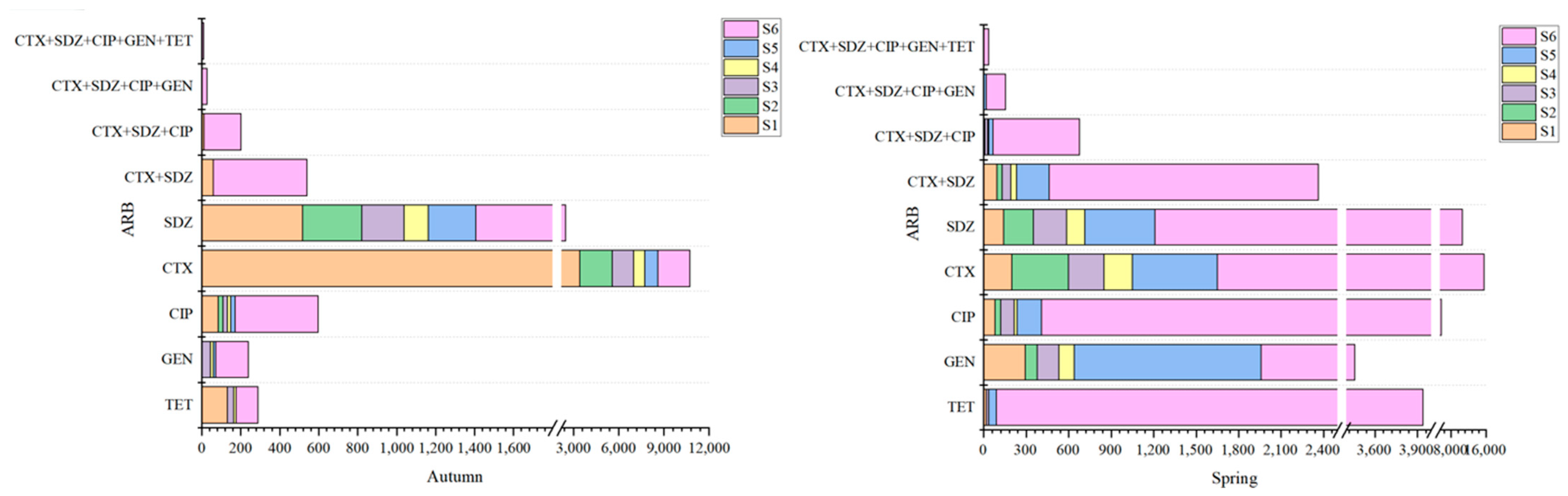
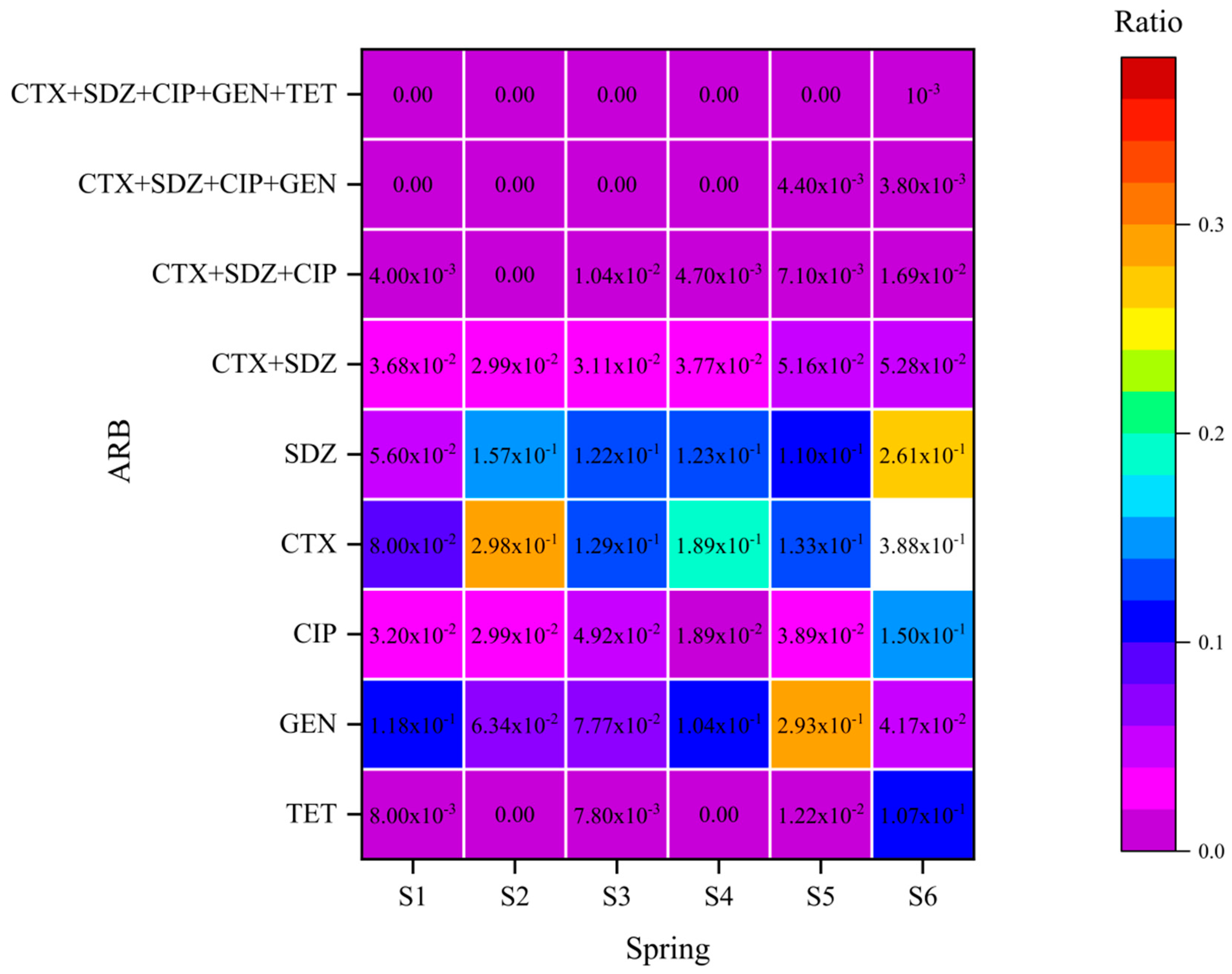
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Culturable Bacteria
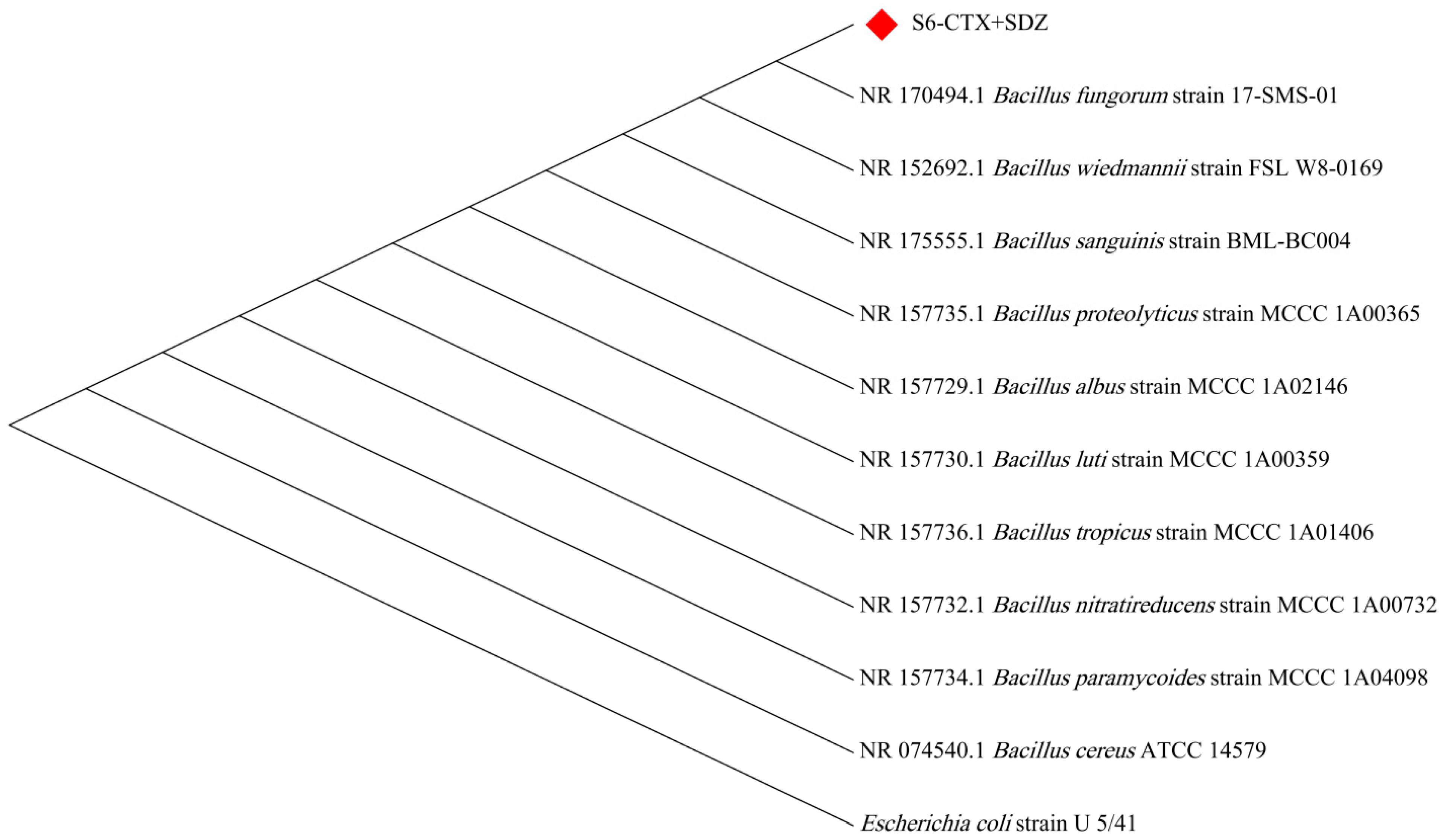
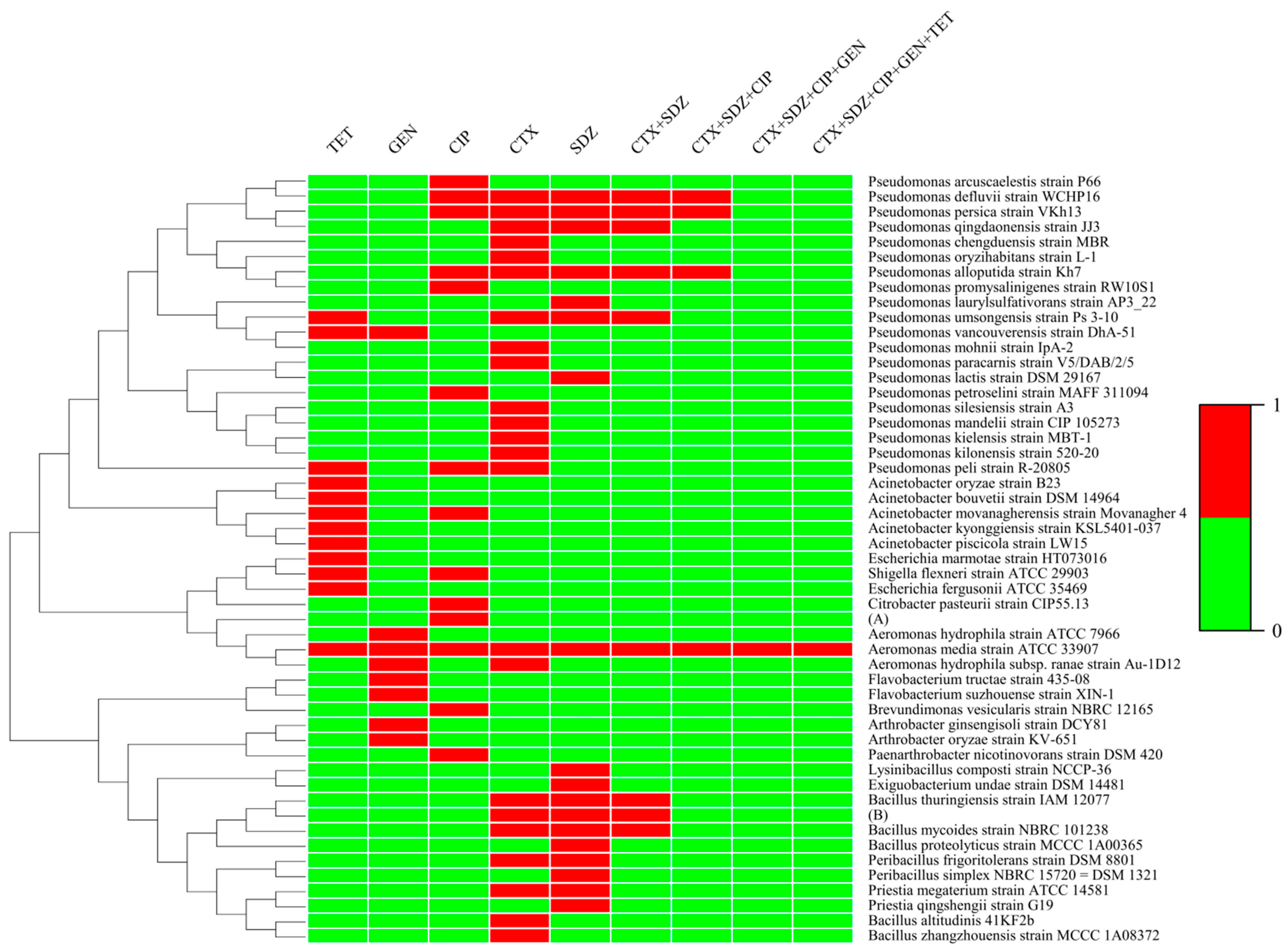
3.2. Identification Results of ARB
3.3. Distribution of Antibiotic-Resistant Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhao, K.; Song, G.; Zhao, S.; Liu, R. Risk control of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) during sewage sludge treatment and disposal: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, H.K.; Donato, J.; Wang, H.H.; Cloud-Hansen, K.A.; Davies, J.; Handelsman, J. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerminiaux, N.A.; Cameron, A.D.S. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 65, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ram, B.; Sewwandi, H.; Sulfikar; Honda, R.; Chaminda, T. Treatment enhances the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in the wastewater of Sri Lanka, and India. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruden, A.; Pei, R.; Storteboom, H.; Carlson, K.H. Antibiotic Resistance Genes as Emerging Contaminants: Studies in Northern Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7445–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, J.I.; Álvarez-Arroyo, R.; Arrieta, J.; Suescun, J.M.; Paunero, S.; Gómez, M.A. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) in the Nervión river. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.C.; Wilson, M.J.; Esser, S.M.; Lee, N.L.; Wheeler, M.E.; Aubee, A.; Aw, T.G. Assessing visitor use impact on antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in soil and water environments of Rocky Mountain National Park. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Ding, P.; Wang, Y.; Ding, C.; Wu, L.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z. Comparison of culturable antibiotic-resistant bacteria in polluted and non-polluted air in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, B.M.C.; Bennett, M.; Waller, K.; Dodd, C.; Murray, A.; Gomes, R.L.; Humphreys, B.; Hobman, J.L.; Jones, M.A.; Whitlock, S.E.; et al. Anthropogenic environmental drivers of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichamnong, W.; Kalambaheti, N.; Woskie, S.; Kongtip, P.; Sirivarasai, J.; Matthews, K.R. Occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria on hydroponically grown butterhead lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitata). Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ondon, B.S.; Ho, S.-H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, F. Drinking water sources as hotspots of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs): Occurrence, spread, and mitigation strategies. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, F.; Matamoros, V.; Bayona, J.; Piña, B. Antibiotic resistance genes distribution in microbiomes from the soil-plant-fruit continuum in commercial Lycopersicon esculentum fields under different agricultural practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.S.; Punia, A. Chapter 8—Antibiotic pollution and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in water bodies. In Degradation of Antibiotics and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria from Various Sources; Singh, P., Sillanpää, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 179–201. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, S. Understanding the contribution of environmental factors in the spread of antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2015, 20, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Guo, Y.; Isabwe, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, J. Urbanization drives riverine bacterial antibiotic resistome more than taxonomic community at watershed scale. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, D.; Du, L.; Song, B.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Huang, H.; Zeng, G. Antibiotic resistance in soil-plant systems: A review of the source, dissemination, influence factors, and potential exposure risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Hu, H.-W.; Chen, Q.-L.; Singh, B.K.; Yan, H.; Chen, D.; He, J.-Z. Transfer of antibiotic resistance from manure-amended soils to vegetable microbiomes. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nnadozie, C.F.; Odume, O.N. Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaccia, N.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Manaia, C.M. The risk of transmitting antibiotic resistance through endophytic bacteria. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, A.F.C.; Zhang, L.; Balfour, A.J.; Garside, R.; Gaze, W.H. Human recreational exposure to antibiotic resistant bacteria in coastal bathing waters. Environ. Int. 2015, 82, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotade, I.F.; Lasisi, K.H.; Ajibade, F.O.; Ajibade, T.F.; Adelodun, B.; Kumar, P.; Nwogwu, N.A.; Adeoye, I.A.; Olanrewaju, O.O.; Adewumi, J.R. Chapter 9—Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in natural water bodies: Causes, routes, and remedies. In Degradation of Antibiotics and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria from Various Sources; Singh, P., Sillanpää, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 203–229. [Google Scholar]
- Calero-Cáceres, W.; Méndez, J.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Muniesa, M. The occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes in a Mediterranean river and their persistence in the riverbed sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero-Cáceres, W.; Muniesa, M. Persistence of naturally occurring antibiotic resistance genes in the bacteria and bacteriophage fractions of wastewater. Water Res. 2016, 95, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czekalski, N.; Sigdel, R.; Birtel, J.; Matthews, B.; Bürgmann, H. Does human activity impact the natural antibiotic resistance background? Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in 21 Swiss lakes. Environ. Int. 2015, 81, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickler, K.M.; Fremier, A.K.; Goldberg, C.S. Quantifying effects of UV-B, temperature, and pH on eDNA degradation in aquatic microcosms. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyaduba, T. Fate and Transport of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Aquatic Ecosystem; Imperial College London: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Scoullos, I.M.; Lopez Vazquez, C.M.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Hammond, M.; Brdjanovic, D. Effect of Artificial Solar Radiation on the Die-Off of Pathogen Indicator Organisms in Urban Floods. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcclary, J.S.; Sassoubre, L.M.; Boeh, A.B. Staphylococcus aureus Strain Newman Photoinactivation and Cellular Response to Sunlight Exposure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01052-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L.; Olds, B.P.; Shogren, A.J.; Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Mahon, A.R.; Bolster, D.; Tank, J.L. Influence of Stream Bottom Substrate on Retention and Transport of Vertebrate Environmental DNA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8770–8779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaPara, T.M.; Madson, M.; Borchardt, S.; Lang, K.S.; Johnson, T.J. Multiple Discharges of Treated Municipal Wastewater Have a Small Effect on the Quantities of Numerous Antibiotic Resistance Determinants in the Upper Mississippi River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11509–11515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, N.; Laffite, A.; Mulaji, C.K.; Otamonga, J.-P.; Mpiana, P.T.; Mubedi, J.I.; Prabakar, K.; Ibelings, B.W.; Poté, J. Occurrence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Bacterial Markers in a Tropical River Receiving Hospital and Urban Wastewaters. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sta Ana, K.M.; Madriaga, J.; Espino, M.P. β-Lactam antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in Asian lakes and rivers: An overview of contamination, sources and detection methods. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Muzammil, S.; Aslam, B.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Hayat, S.; Bilal, M.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Nisar, M.A.; Khurshid, M. Chapter 2—Antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the environment: Sources and impacts. In Degradation of Antibiotics and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria from Various Sources; Singh, P., Sillanpää, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B.; Davies-Colley, R.J.; Dodd, M.C.; Kohn, T.; Linden, K.G.; Liu, Y.; Maraccini, P.A.; McNeill, K.; Mitch, W.A.; et al. Sunlight-mediated inactivation of health-relevant microorganisms in water: A review of mechanisms and modeling approaches. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 1089–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.-T.; Yuan, Q.-B.; Yang, J. Distinguishing Effects of Ultraviolet Exposure and Chlorination on the Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Municipal Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5771–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, L.; Nguyen, S.H.; Duarte, T.; Coin, L.; Bond, P.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J. Triclosan at environmentally relevant concentrations promotes horizontal transfer of multidrug resistance genes within and across bacterial genera. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Lu, H.; Yan, B.; Chen, S. Nutrients, heavy metals and microbial communities co-driven distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in adjacent environment of mariculture. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Feng, M.; Ye, C.; Yu, X. Effects and relevant mechanisms of non-antibiotic factors on the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in water environments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Z. Pseudomonas. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety, 2nd ed.; Smithers, G.W., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 236–251. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, M.E.P.; Gomes, M.A.d.S.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Lima, N.C.d.S.; Carvalho, A.G.; Taborda, R.L.M.; Matos, N.B. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter spp. from hospital intensive care units in Brazilian Amazon. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 27, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H. Bacteremia due to Brevundimonas vesicularis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Waśkiewicz, A.; Irzykowska, L. Flavobacterium spp.—Characteristics, Occurrence, and Toxicity. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 938–942. [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra, W.; Kusters, J.G.; van Duijkeren, E.; Lipman, L.J.A. Escherichia fergusonii. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Shen, X.; Chen, F.; Tao, S. Complete genome sequence data of multidrug-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila Ah27 isolated from intussusception channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Gene Rep. 2023, 33, 101807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegun, B.R.; Oluduro, A.O.; Aregbesola, O.A. Isolation and molecular characterization of citrobacter species in fruits and vegetables sold for consumption in ILE-IFE, Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2019, 6, e00173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumy, K.L. Shigella. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 4th ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 501–503. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhou, L. Is Shigella an under-recognized pathogen? A case of pyogenic cervical spondylitis caused by Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri infection. IDCases 2024, 35, e01930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Position Number | Positional Information | North Latitude | East Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Near Heilongjiang Shipyard Machinery Factory | 45°83′31.31″ | 126°72′33.72″ |
| S2 | Songpu Bridge | 45°80′44.89″ | 126°66′45.87″ |
| S3 | Songhua River Railway Bridge | 45°79′13.18″ | 126°63′45.78″ |
| S4 | Near People’s Square | 45°78′10.61″ | 126°60′71.49″ |
| S5 | Songhua River Highway Bridge | 45°76′94.94″ | 126°59′83.28″ |
| S6 | The intersection of Hejiagou River and Songhua River | 45°76′10.44″ | 126°58′22.34″ |
| Antibiotic | Reserve Solution Concentration | Final Concentration | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| TET | 50 mg/mL | 16 μg/mL | Tetracycline class |
| GEN | 16 mg/mL | 16 μg/mL | Aminoglycosides |
| CIP | 4 mg/mL | 4 μg/mL | Quinolones |
| CTX | 4 mg/mL | 4 μg/mL | β-Lactamides |
| SDZ | 512 mg/mL | 512 μg/mL | Sulfonamides |
| No. | Species | Length (bp) | Coverage | Identity | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acinetobacter bouvetii | 1530 | 100% | 98.34% | NR_117628.1 |
| 2 | Acinetobacter movanagherensis | 1331 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_145841.1 |
| 3 | Acinetobacter kyonggiensis | 1395 | 100% | 99.17% | NR_116714.1 |
| 4 | Acinetobacter piscicola | 1501 | 99% | 96.32% | NR_159919.1 |
| 5 | Acinetobacter oryzae | 1499 | 100% | 99.72% | NR_180005.1 |
| 6 | Pseudomonas vancouverensis | 1492 | 100% | 99.72% | NR_041953.1 |
| 7 | Pseudomonas silesiensis | 1539 | 100% | 100% | NR_156815.1 |
| 8 | Pseudomonas oryzihabitans | 1527 | 100% | 99.31% | NR_025881.1 |
| 9 | Pseudomonas mohnii | 1459 | 100% | 98.89% | NR_042543.1 |
| 10 | Pseudomonas paracarnis | 1431 | 100% | 99.31% | NR_178976.1 |
| 11 | Pseudomonas alloputida | 1464 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_179595.1 |
| 12 | Pseudomonas umsongensis | 1455 | 100% | 100% | NR_025227.1 |
| 13 | Pseudomonas qingdaonensis | 1525 | 100% | 100% | NR_169411.1 |
| 14 | Pseudomonas kielensis | 1537 | 100% | 100% | NR_181570.1 |
| 15 | Pseudomonas kilonensis | 1528 | 100% | 100% | NR_028929.1 |
| 16 | Pseudomonas peli | 1497 | 100% | 99.31% | NR_042451.1 |
| 17 | Pseudomonas promysalinigenes | 1331 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_178291.1 |
| 18 | Pseudomonas petroselini | 1494 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_179384.1 |
| 19 | Pseudomonas mandelii | 1518 | 100% | 100% | NR_024902.1 |
| 20 | Pseudomonas lactis | 1428 | 100% | 100% | NR_156986.1 |
| 21 | Pseudomonas chengduensis | 1529 | 99% | 97.49% | NR_125523.1 |
| 22 | Pseudomonas laurylsulfativorans | 1499 | 100% | 99.72% | NR_179728.1 |
| 23 | Pseudomonas arcuscaelestis | 1567 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_181857.1 |
| 24 | Pseudomonas defluvii | 1532 | 100% | 100% | NR_179168.1 |
| 25 | Pseudomonas persica | 1472 | 100% | 98.34% | NR_179596.1 |
| 26 | Priestia qingshengii | 1455 | 100% | 99.31% | NR_133978.1 |
| 27 | Priestia megaterium | 1495 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_117473.1 |
| 28 | Bacillus mycoides | 1477 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_113996.1 |
| 29 | Bacillus thuringiensis | 1544 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_121761.1 |
| 30 | Bacillus proteolyticus | 1509 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_157735.1 |
| 31 | Bacillus altitudinis | 1506 | 100% | 100% | NR_042337.1 |
| 32 | Bacillus zhangzhouensis | 1513 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_148786.1 |
| 33 | Bacillus fungorum | 1576 | 87% | 88.32% | NR_170494.1 |
| 34 | Arthrobacter oryzae | 1465 | 100% | 99.72% | NR_041545.1 |
| 35 | Arthrobacter ginsengisoli | 1454 | 100% | 99.31% | NR_178602.1 |
| 36 | Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans | 1468 | 100% | 99.58% | NR_026194.1 |
| 37 | Brevundimonas vesicularis | 1386 | 100% | 99.72% | NR_113586.1 |
| 38 | Flavobacterium tructae | 1458 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_133749.1 |
| 39 | Flavobacterium suzhouense | 1477 | 100% | 99.31% | NR_178734.1 |
| 40 | Peribacillus frigoritolerans | 1503 | 100% | 98.89% | NR_117474.1 |
| 41 | Peribacillus simplex | 1522 | 100% | 100% | NR_042136.1 |
| 42 | Exiguobacterium undae | 1550 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_043477.1 |
| 43 | Escherichia marmotae | 1504 | 100% | 99.17% | NR_136472.1 |
| 44 | Escherichia fergusonii | 1542 | 100% | 99.45% | NR_074902.1 |
| 45 | Shigella flexneri | 1488 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_026331.1 |
| 46 | Aeromonas media | 1460 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_119041.1 |
| 47 | Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. ranae | 1350 | 100% | 99.72% | NR_042518.1 |
| 48 | Aeromonas hydrophila | 1460 | 100% | 100% | NR_119039.1 |
| 49 | Aeromonas sanarellii | 1503 | 85% | 84.71% | NR_116584.1 |
| 50 | Citrobacter pasteurii | 1492 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_178769.1 |
| 51 | Lysinibacillus composti | 1475 | 100% | 99.86% | NR_126171.1 |
| ARBs | Antibiotics |
|---|---|
| Acinetobacter bouvetii strain DSM 14964 | S1-TET |
| Acinetobacter movanagherensis strain Movanagher 4 | S1-TET, CIP |
| Acinetobacter kyonggiensis strain KSL5401-037 | S1-TET |
| Acinetobacter piscicola strain LW15 | S1-TET |
| Acinetobacter oryzae strain B23 | S6-TET |
| Acinetobacter movanagherensis strain Movanagher 4 | S6-TET |
| Pseudomonas vancouverensis strain DhA-51 | S1-TET |
| Pseudomonas alloputida strain Kh7 | S1-CIP, SDZ, CTX |
| Pseudomonas umsongensis strain Ps 3-10 | S1-SDZ, CTX |
| Pseudomonas qingdaonensis strain JJ3 | S1-SDZ, CTX |
| Pseudomonas silesiensis strain A3 | S1-CTX |
| Pseudomonas oryzihabitans strain L-1 | S1-CTX |
| Pseudomonas mohnii strain IpA-2 | S1-CTX |
| Pseudomonas paracarnis strain V5/DAB/2/5 | S1-CTX |
| Pseudomonas alloputida strain Kh7 | S1-CTX + SDZ |
| Pseudomonas umsongensis strain Ps 3-10 | S1-CTX + SDZ |
| Pseudomonas qingdaonensis strain JJ3 | S1-CTX + SDZ |
| Pseudomonas alloputida strain Kh7 | S1-CTX + SDZ + CIP |
| Pseudomonas kielensis strain MBT-1 | S2-CTX |
| Pseudomonas kilonensis strain 520-20 | S2-CTX |
| Pseudomonas silesiensis strain A3 | S2-CTX |
| Pseudomonas peli strain R-20805 | S2-CTX, CIP |
| Pseudomonas promysalinigenes strain RW10S1 | S2-CIP |
| Pseudomonas petroselini strain MAFF 311094 | S2-CIP |
| Pseudomonas vancouverensis strain DhA-51 | S3-TET, GEN |
| Pseudomonas umsongensis strain Ps 3-10 | S3-TET |
| Pseudomonas silesiensis strain A3 | S3-CTX |
| Pseudomonas mandelii strain CIP 105273 | S3-CTX |
| Pseudomonas lactis strain DSM 29167 | S3-SDZ |
| Pseudomonas chengduensis strain MBR | S4-CTX |
| Pseudomonas silesiensis strain A3 | S4-CTX |
| Pseudomonas vancouverensis strain DhA-51 | S4-GEN |
| Pseudomonas peli strain R-20805 | S4-TET, CIP |
| Pseudomonas laurylsulfativorans strain AP3_22 | S5-SDZ |
| Pseudomonas silesiensis strain A3 | S5-CTX |
| Pseudomonas kielensis strain MBT-1 | S5-CTX |
| Pseudomonas umsongensis strain Ps 3-10 | S5-CTX |
| Pseudomonas peli strain R-20805 | S5-CIP |
| Pseudomonas arcuscaelestis strain P66 | S6-CIP |
| Pseudomonas defluvii strain WCHP16 | S6-CIP, CTX, SDZ |
| Pseudomonas persica strain VKh13 | S6-CIP, CTX, SDZ |
| Pseudomonas defluvii strain WCHP16 | S6-CTX + SDZ |
| Pseudomonas persica strain VKh13 | S6-CTX + SDZ |
| Pseudomonas persica strain VKh13 | S6-CTX + SDZ + CIP |
| Pseudomonas defluvii strain WCHP16 | S6-CTX + SDZ + CIP |
| Priestia qingshengii strain G19 | S1-SDZ |
| Priestia megaterium strain ATCC 14581 | S4-SDZ |
| Priestia megaterium strain ATCC 14581 | S6-CTX |
| Bacillus mycoides strain NBRC 101238 | S1-CTX, SDZ |
| Bacillus mycoides strain NBRC 101238 | S1-CTX + SDZ |
| Bacillus thuringiensis strain IAM 12077 | S2-CTX, SDZ |
| Bacillus proteolyticus strain MCCC 1A00365 | S3-SDZ |
| Bacillus altitudinis 41KF2b | S5-CTX |
| Bacillus zhangzhouensis strain MCCC 1A08372 | S5-CTX |
| Bacillus thuringiensis strain IAM 12077 | S6-CTX, SDZ |
| Bacillus fungorum strain 17-SMS-01 | S6-CTX, SDZ |
| Bacillus thuringiensis strain IAM 12077 | S6-CTX + SDZ |
| Bacillus fungorum strain 17-SMS-01 | S6-CTX + SDZ |
| Arthrobacter ginsengisoli strain DCY81 | S3-GEN |
| Arthrobacter oryzae strain KV-651 | S4-GEN |
| Arthrobacter oryzae strain KV-651 | S5-GEN |
| Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans strain DSM 420 | S3-CIP |
| Brevundimonas vesicularis strain NBRC 12165 | S3-CIP |
| Flavobacterium tructae strain 435-08 | S4-GEN |
| Flavobacterium suzhouense strain XIN-1 | S5-GEN |
| Peribacillus frigoritolerans strain DSM 8801 | S4-SDZ |
| Peribacillus simplex NBRC 15720 = DSM 1321 | S5-SDZ |
| Peribacillus frigoritolerans strain DSM 8801 | S6-CTX |
| Exiguobacterium undae strain DSM 14481 | S5-SDZ |
| Escherichia marmotae strain HT073016 | S6-TET |
| Escherichia fergusonii ATCC 35469 | S6-TET |
| Shigella flexneri strain ATCC 29903 | S6-TET, CIP |
| Aeromonas media strain ATCC 33907 | S6-TET, GEN, CTX, CIP, SDZ |
| Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. ranae strain Au-1D12 | S6-GEN, CTX |
| Aeromonas hydrophila strain ATCC 7966 | S6-GEN |
| Aeromonas sanarellii strain A2-67 | S6-CIP |
| Aeromonas media strain ATCC 33907 | S6-CTX + SDZ |
| Aeromonas media strain ATCC 33907 | S6-CTX + SDZ + CIP |
| Aeromonas media strain ATCC 33907 | S6-CTX + SDZ + CIP + GEN |
| Aeromonas media strain ATCC 33907 | S6-CTX + SDZ + CIP + GEN + TET |
| Citrobacter pasteurii strain CIP55.13 | S6-CIP |
| Lysinibacillus composti strain NCCP-36 | S6-SDZ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Q.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in an Urban River in Northeast China. Water 2024, 16, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091268
Xiao Q, Wang X, Xu C, Chen W, Huang Q, Wang X. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in an Urban River in Northeast China. Water. 2024; 16(9):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091268
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Qingshan, Xin Wang, Chongxin Xu, Wei Chen, Qianchi Huang, and Xin Wang. 2024. "Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in an Urban River in Northeast China" Water 16, no. 9: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091268
APA StyleXiao, Q., Wang, X., Xu, C., Chen, W., Huang, Q., & Wang, X. (2024). Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in an Urban River in Northeast China. Water, 16(9), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091268







