A Framework for Assessing Food Baskets Based on Water and Carbon Footprints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
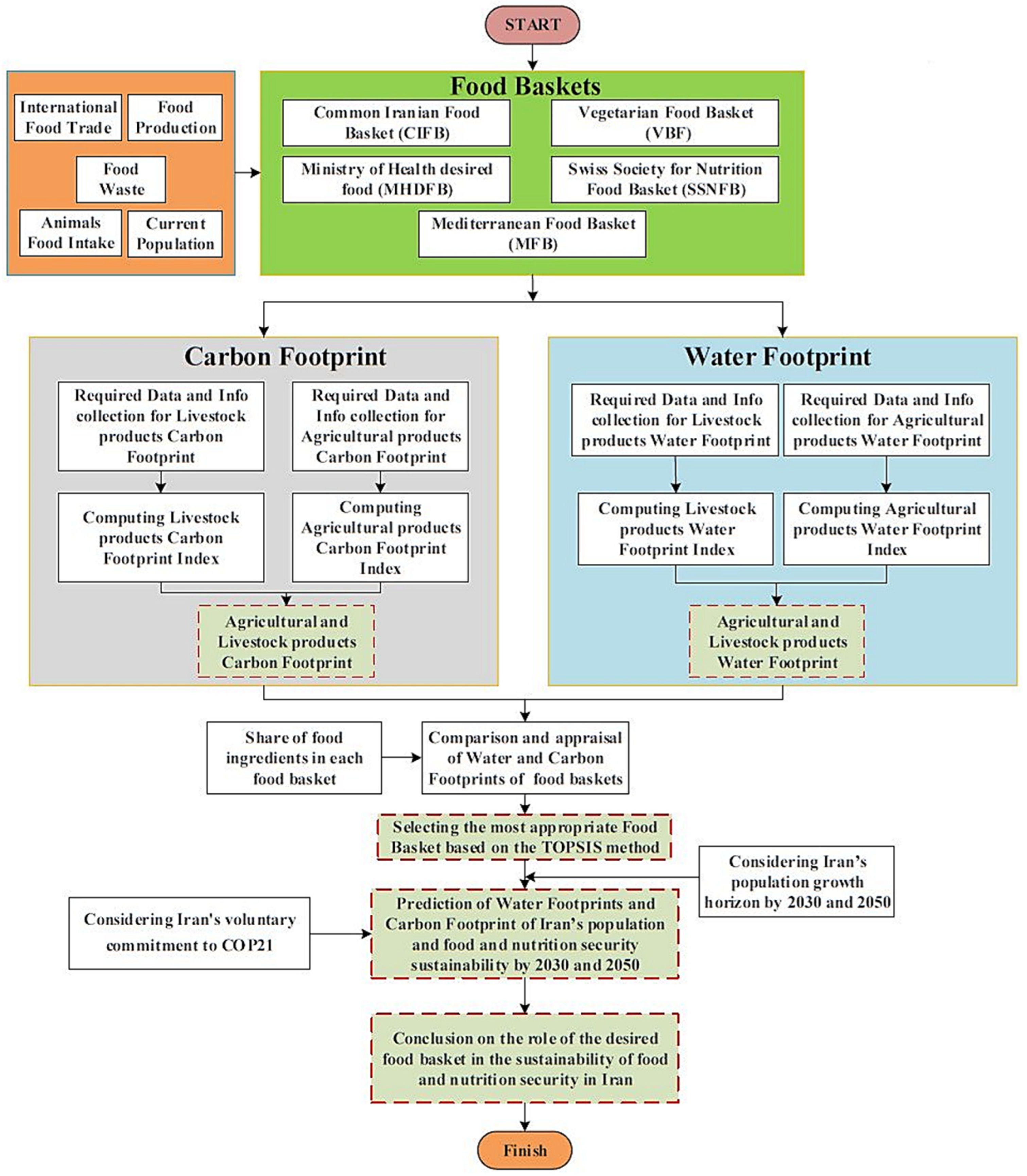
2.1. Data and Research Process
Food Baskets
2.2. Quantitative Impact Assessment of the Food Baskets on Water Resources and the Environment
2.2.1. Water Footprint
- Water Footprint of Agricultural Products
- Blue Water Footprint
- Gray Water Footprint
- 2.
- Water Footprint of Animal products
2.2.2. Carbon Footprint
- Agricultural Production Carbon Footprint
- 2.
- Animal production Carbon Footprint
2.3. TOPSIS Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Method
3. Results
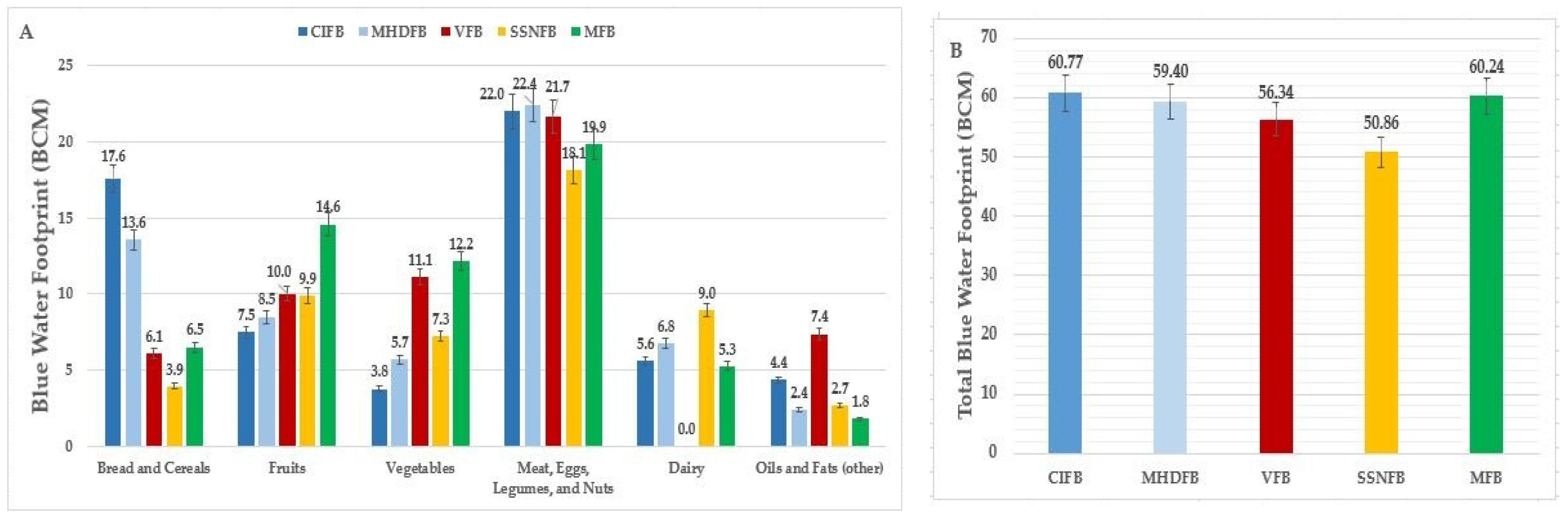
3.1. Evaluation of Studied Food Baskets from the Perspective of the Blue Water Footprint
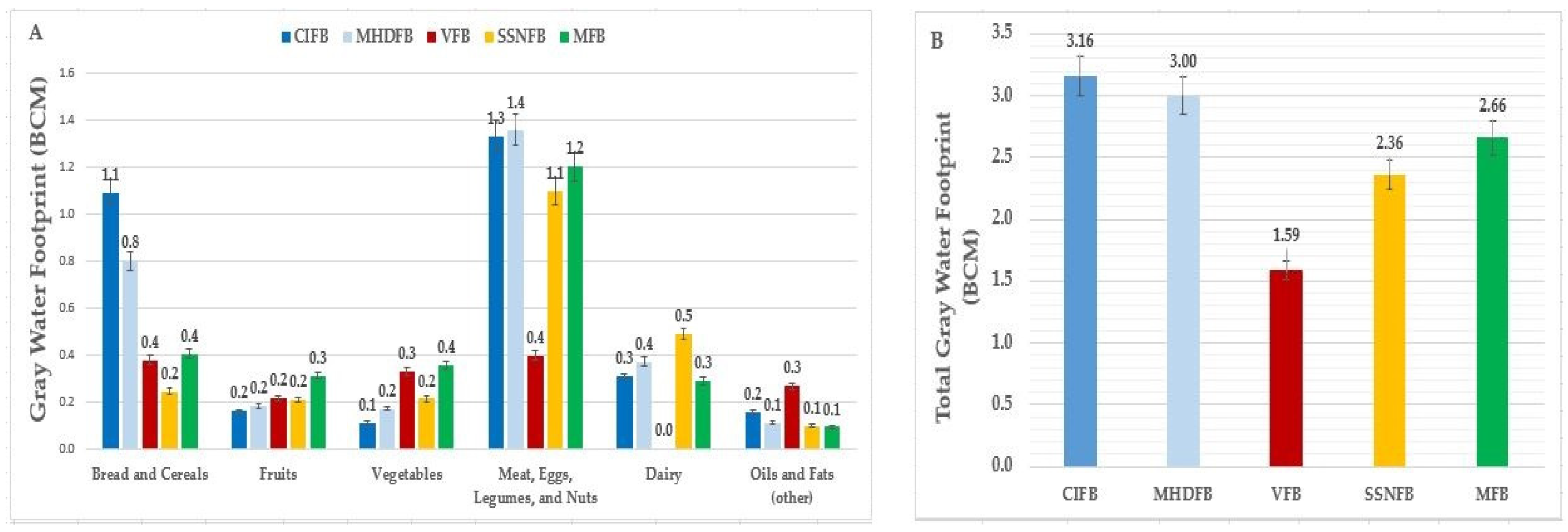
3.2. Evaluation of Studied Food Baskets from the Perspective of the Gray Water Footprint
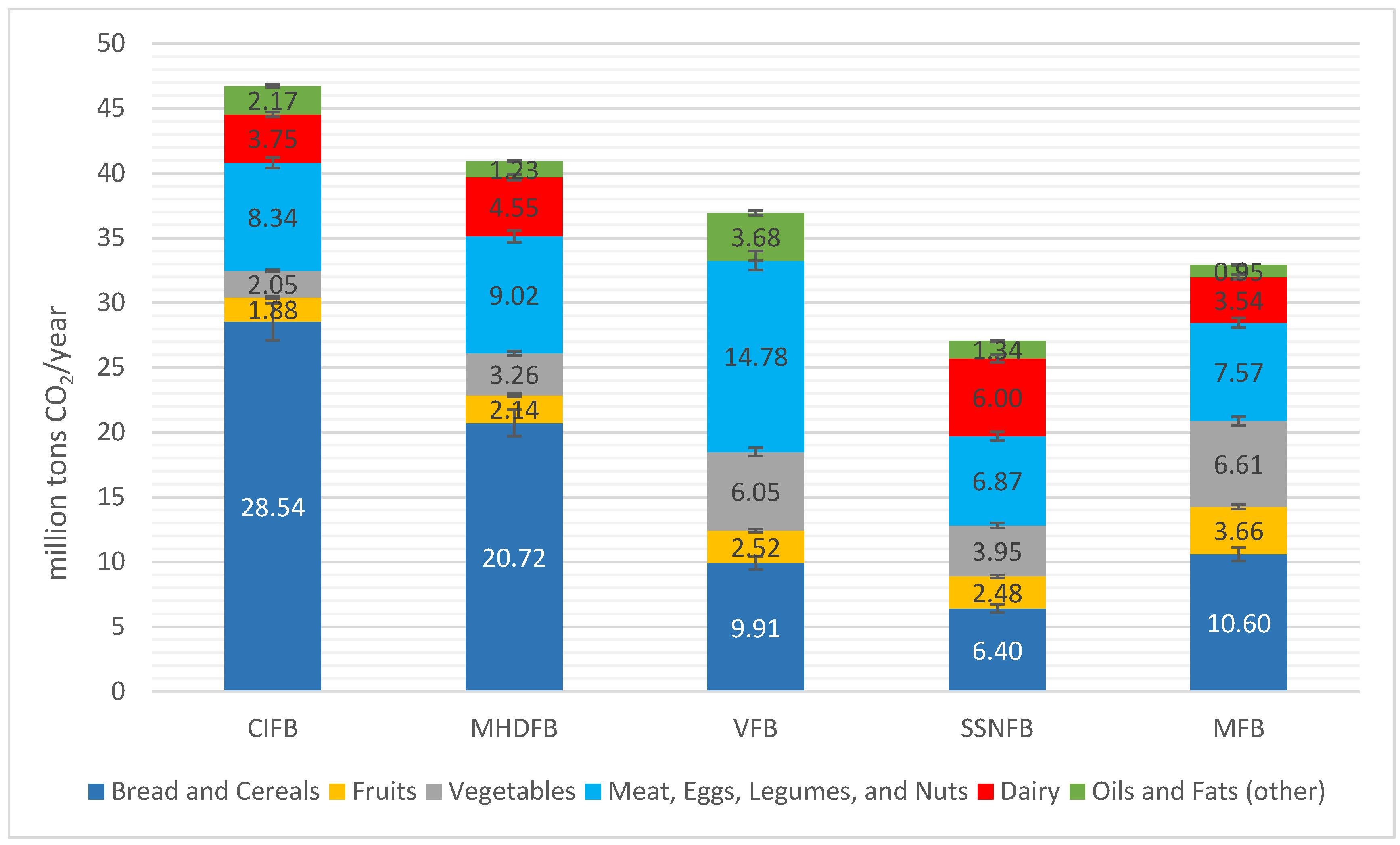
3.3. Evaluation of Studied Food Baskets from the Perspective of the Carbon Footprint
3.4. Selection of the Most Desirable Food Basket Using the TOPSIS Method
3.5. Predicting Water and Carbon Footprints of Food Baskets Based on Demographic Scenarios
3.5.1. Evaluating the Trend in, and Effects of, the Desired Food Basket (VFB) and CIFB on Water Resources from the Perspective of the Water Footprint in 2030 and 2050
3.5.2. Evaluating the Trend in, and Effects of, the Desired Food Basket (VFB) and CIFB on Water Resources from the Perspective of the Carbon Footprint in 2030 and 2050
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Campbell, B.M.; Ingram, J.S.I. Climate Change and Food Systems. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheewala, S.H.; Silalertruksa, T.; Nilsalab, P.; Mungkung, R.; Perret, S.R.; Chaiyawannakarn, N. Water Footprint and Impact of Water Consumption for Food, Feed, Fuel Crops Production in Thailand. Water 2014, 6, 1698–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a Cultivated Planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flachsbarth, I.; Willaarts, B.; Xie, H.; Pitois, G.; Mueller, N.D.; Ringler, C.; Garrido, A. The Role of Latin America’s Land and Water Resources for Global Food Security: Environmental Trade-Offs of Future Food Production Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElFetyany, M.; Farag, H.; Abd El Ghany, S.H. Assessment of National Water Footprint versus Water Availability—Case Study for Egypt. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 3577–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Wiedmann, T.; Ercin, E.; Knoblauch, D.; Ewing, B.; Giljum, S. Integrating Ecological, Carbon and Water Footprint into a “Footprint Family” of Indicators: Definition and Role in Tracking Human Pressure on the Planet. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 16, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Tan, X.; Ma, X.; An, M.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, X.; Hong, J. Water Footprint Analysis of Wheat Production. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y. A Critique on the Water-Scarcity Weighted Water Footprint in LCA. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, M.; Laiola, E.; Tricase, C.; Rana, R. Assessing the Urban Carbon Footprint: An Overview. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 66, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrowicz, L.; Green, R.; Joy, E.J.M.; Harris, F.; Hillier, J.; Vetter, S.H.; Smith, P.; Kulkarni, B.; Dangour, A.D.; Haines, A. Environmental Impacts of Dietary Shifts in India: A Modelling Study Using Nationally-Representative Data. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, R.; EL Labban, S.; Hwalla, N. Impacts of Shifting to Healthier Food Consumption Patterns on Environmental Sustainability in MENA Countries. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friel, S.; Barosh, L.J.; Lawrence, M. Towards Healthy and Sustainable Food Consumption: An Australian Case Study. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dooren, C.; Marinussen, M.; Blonk, H.; Aiking, H.; Vellinga, P. Exploring Dietary Guidelines Based on Ecological and Nutritional Values: A Comparison of Six Dietary Patterns. Food Policy 2014, 44, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, F.; Jomaa, L.; Itani, L.; Zidek, J.; El Labban, S.; Sibai, A.M.; Hwalla, N. Environmental Footprints of Food Consumption and Dietary Patterns among Lebanese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashiri, B.; Zehtabvar, M.; Gavrilova, O.; Vilu, R. Change in the Carbon Footprint of Iranians’ Food Consumption from 1961 to 2019: A Decomposition Analysis of Drivers. Agron. Res. 2023, 21, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, S.R.; Arzhang, P.; Soltani, E.; Soltani, A. Proposed Diets for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security in Iran. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 32, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eini-Zinab, H.; Sobhani, S.R.; Rezazadeh, A. Designing a Healthy, Low-Cost and Environmentally Sustainable Food Basket: An Optimisation Study. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, S.R.; Omidvar, N.; Abdollahi, Z.; Al Jawaldeh, A. Shifting to a Sustainable Dietary Pattern in Iranian Population: Current Evidence and Future Directions. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 789692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Pakravan Charvadeh, M.R.; Salami, H.; Flora, C. The Impact of the Targeted Subsidies Policy on Household Food Security in Urban Areas in Iran. Cities 2017, 63, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan-Charvadeh, M.R.; Khan, H.A.; Flora, C. Spatial Analysis of Food Security in Iran: Associated Factors and Governmental Support Policies. J. Public Health Policy 2020, 41, 351–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, M.; Almassi, M.; Bakhoda, H.; Kalantari, I. Agricultural Mechanization, a Key to Food Security in Developing Countries: Strategy Formulating for Iran. Agric. Food Secur. 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, F.; Amanollahi, J.; Poorhashemi, S.A.; Panahi, M. Paris Climate Changes Agreement 2015 Operational Requirements and Legal Restrictions of Joining Iran. Ekoloji 2019, 28, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Iran’s Ministry of Agriculture Jihad: Tehran, Iran. IMAJ. Available online: https://www.maj.ir (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Chen, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Mathys, A. Dietary Change Scenarios and Implications for Environmental, Nutrition, Human Health and Economic Dimensions of Food Sustainability. Nutrients 2019, 11, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, F.; Abdollahi, Z.; Abdollahi, M. Good Food Basket for the Iranian Community. Minist. Health Med. Educ. 2013, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez-Almendros, S.; Obrador, B.; Bach-Faig, A.; Serra-Majem, L. Environmental Footprints of Mediterranean versus Western Dietary Patterns: Beyond the Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2013, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamic Republic of Iran Customs Administration. IRICA. Available online: https://irica.ir/ (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Statistical Centre of Iran. AMAR. Available online: https://old.sci.org.ir/english (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- Komijani, M.; Shamabadi, N.S.; Shahin, K.; Eghbalpour, F.; Tahsili, M.R.; Bahram, M. Heavy Metal Pollution Promotes Antibiotic Resistance Potential in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. A Global Assessment of the Water Footprint of Farm Animal Products. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damkjaer, S.; Taylor, R. The Measurement of Water Scarcity: Defining a Meaningful Indicator. Ambio 2017, 46, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K.; Zhang, G. Water Footprints and Sustainable water Allocation. Sustainability 2016, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karandish, F.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Informing National Food and Water Security Policy through Water Footprint Assessment: The Case of Iran. Water 2017, 9, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Cui, S.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X. Assessment of Blue Water Migration and Efficiency in Water-Saving Irrigation Paddy Rice Fields Using the Water Flow Tracking Method. Agronomy 2024, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, O.; Vafaei, K.; Ramezani Etedali, H.; Zamani, H.; Hashemi, M. Economic Analysis of Water Footprint for Water Management of Rain-Fed and Irrigated Almonds in Iran. Irrig. Sci. 2024, 42, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, V.; Tuninetti, M.; Laio, F. Efficient Agricultural Practices in Africa Reduce Crop Water Footprint despite Climate Change, but Rely on Blue Water Resources. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karandish, F.; Šimůnek, J. A Comparison of the HYDRUS (2D/3D) and SALTMED Models to Investigate the Influence of Various Water-Saving Irrigation Strategies on the Maize Water Footprint. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Stroosnijder, L.; Girmay, G.; Keesstra, S.D. Crop Coefficient, Yield Response to Water Stress and Water Productivity of Teff (Eragrostis Tef (Zucc.). Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Sohrab, F.; Abbasi, N. Evaluation of Irrigation Efficiencies in Iran. Irrig. Drain. Struct. Eng. Res. 2017, 17, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Qiu, L.; Huang, X.; Wu, M.; Cao, X. Monitoring Grey Water Footprint and Associated Environmental Controls in Agricultural Watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 11334–11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, W.; Gao, R.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.; Wu, P.; Zhuo, L. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Crop Grey Water Footprint and Associated Water Pollution Levels in Arid Regions of Western China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, A.K.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Savenije, H.H.G. Water Saving through International Trade of Agricultural Products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaya, M.M.; Chapagain, A.K.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M. The Water Footprint Assessment Manual; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environment (DOE). Assortment of Laws and Regulations for Environmental Protection in Iran; Department of Environment (DOE): Tehran, Iran, 2000.
- Ababaei, B.; Ramezani Etedali, H. Water Footprint Assessment of Main Cereals in Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, N.A.; Boyacioglu, H.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Grey Water Footprint Accounting: Tier 1 Supporting Guidelines; UNESCO-IHE Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Song, G.; Fullana-i-Palmer, P.; Wang, Y.; Semakula, H.M.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Zhang, S. Water Footprint of Feed Required by Farmed Fish in China Based on a Monte Carlo-Supported von Bertalanffy Growth Model: A Policy Implication. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bertalanffy, L. A Quantitative Theory of Organic Growth (Inquiries on Growth Laws. II). Hum. Biol. 1938, 10, 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Carbon Footprint and Driving Forces of Saline Agriculture in Coastally Reclaimed Areas of Eastern China: A Survey of Four Staple Crops. Sustainability 2018, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.T.; Nonaka, R.; Win, A.T.; Sasada, Y.; Toyota, K.; Motobayashi, T. Effects of Water Saving Irrigation and Rice Variety on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Water Use Efficiency in a Paddy Field Fertilized with Anaerobically Digested Pig Slurry. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Yue, Q.; Yan, M.; Cheng, K.; Pan, G. Carbon Footprint of China’s Livestock System—A Case Study of Farm Survey in Sichuan Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 102, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, D.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Hospido, A.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Updating the Carbon Footprint of the Galician Fishing Activity (NW Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, G.; de Bruyn, C. Models and Methods in Multiple Objectives Decision Making. In Mathematical and Computer Modelling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 12, pp. 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Hwang, C.-L. Multiple Attribute Decision Making, 1st ed.; Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalakannan, R.; Ramesh, C.; Shunmugasundaram, M.; Sivakumar, P.; Mohamed, A. Evaluvation and Selection of Suppliers Using TOPSIS. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 2771–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmehr, A.; Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Loáiciga, H.A. Integrated Strategic Planning and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Framework with Its Application to Agricultural Water Management. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X. TOPSIS Model with Entropy Weight for Eco Geological Environmental Carrying Capacity Assessment. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 82, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Kim, K.B.; Hyung, J.S.; Kim, T.H.; Koo, J.Y. Decision-Making for the Hazard Ranking of Water Distribution Networks Using the TOPSIS Method. Water Supply 2023, 23, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan Rahimabadi, P.; Behnia, M.; Nasabpour Molaei, S.; Khosravi, H.; Azarnivand, H. Assessment of Groundwater Resources Potential Using Improved Water Quality Index (ImpWQI) and Entropy-Weighted TOPSIS Model. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałabun, W.; Wątróbski, J.; Shekhovtsov, A. Are MCDA Methods Benchmarkable? A Comparative Study of TOPSIS, VIKOR, COPRAS, and PROMETHEE II Methods. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, M.; Xiao, X. Improved TOPSIS Method for Power Distribution Network Investment Decision-Making Based on Benefit Evaluation Indicator System. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2017, 11, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, E.; Javid, N.; Mirzaie, S.; Nasiripour, M. Investigating the Trend of Changes in the Structure and Composition of the Country’s Population and Its Future up to the Horizon of 1430; Iran’s Statistics Research Institute: Tehran, Iran, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, A.; Zand, E.; Alimagham, S.; Nehbandani, A.; Barani, H.; Soltani, E.; Torabi, B.; Zeinali, E.; Mirkarimi, S.; Joulaie, R. Country Food Security Analysis Using Water, Land, Food and Environmental Nexus, Necessary Prospective and Policies; Iran’s Ministry of Agriculture Jihad, Organization of Research, Education and Promotion of Agriculture: Tehran, Iran, 2019.
- Gohari, A.; Mirchi, A.; Madani, K. Erratum to: System Dynamics Evaluation of Climate Change Adaptation Strategies for Water Resources Management in Central Iran. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4367–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saymohammadi, S.; Zarafshani, K.; Tavakoli, M.; Mahdizadeh, H.; Amiri, F. Prediction of Climate Change Induced Temperature & Precipitation: The Case of Iran. Sustainability 2017, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri Daneshvar, M.R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Nejadsoleymani, H. An Overview of Climate Change in Iran: Facts and Statistics. Environ. Syst. Res. 2019, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, G.R.; Oji, R.; Attia, S. Projecting the Impact of Climate Change on Design Recommendations for Residential Buildings in Iran. Build. Environ. 2019, 155, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbali, E.; Ziaee, S.; Najafabadi, M.M.; Zakerinia, M. Approaches to Adapting to Impacts of Climate Change in Northern Iran: The Application of a Hydrogy-Economics Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environment (DOE). Iran’s Third National Communication to UNFCCC; Department of Environment (DOE): Tehran, Iran, 2017.
- Liu, C.; Cutforth, H.; Chai, Q.; Gan, Y. Farming Tactics to Reduce the Carbon Footprint of Crop Cultivation in Semiarid Areas. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Liang, C.; Chai, Q.; Lemke, R.L.; Campbell, C.A.; Zentner, R.P. Improving Farming Practices Reduces the Carbon Footprint of Spring Wheat Production. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Yu, L.; Shu, Y.; Tan, F.; Gou, Y.; Luo, S.; Yang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Sugarcane/Soybean Intercropping with Reduced Nitrogen Input Improves Crop Productivity and Reduces Carbon Footprint in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, J.; Tian, C.; Hua, D.; Shi, C.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Xu, Y. Effects of Conservation Tillage on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Crop Yield in an Arid Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Mei, P.; Wang, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, M.; Ou, X.; Cui, Z. Effects of Super Absorbent Polymer on Crop Yield, Water Productivity and Soil Properties: A Global Meta-Analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 282, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phapumma, A.; Monkham, T.; Chankaew, S.; Kaewpradit, W.; Harakotr, P.; Sanitchon, J. Characterization of Indigenous Upland Rice Varieties for High Yield Potential and Grain Quality Characters under Rainfed Conditions in Thailand. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaie-Nodoushan, F.; Morid, S.; Dehghanisanij, H. Reducing Water Footprints through Healthy and Reasonable Changes in Diet and Imported Products. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2020, 23, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronts, S.; Gerbens-Leenes, P.W.; Guzmán-Luna, P. The Water, Land and Carbon Footprint of Conventional and Organic Dairy Systems in the Netherlands and Spain. A Case Study into the Consequences of Ecological Indicator Selection and Methodological Choices. Energy Nexus 2023, 11, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Noorollahi, Y. Prioritization in Exporting Agricultural Products Using Virtual Water Concept (Case Study: Melon and Watermelon). Ecopersia 2017, 5, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Mirzaaghabeik, M.; Noorollahi, Y. Virtual Water Evaluation for Grains Productsin Iran Case Study: Pea and Bean. J. Water Land Dev. 2017, 35, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.; Maruthi, V.; Pankaj, P.K.; Kumar, M.; Pushpanjali; Prabhakar, M.; Reddy, A.G.; Reddy, K.S.; Singh, V.K.; Koradia, A.K. Water Footprint Assessment of Rainfed Crops with Critical Irrigation under Different Climate Change Scenarios in SAT Regions. Water 2022, 14, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holka, M.; Kowalska, J.; Jakubowska, M. Reducing Carbon Footprint of Agriculture—Can Organic Farming Help to Mitigate Climate Change? Agriculture 2022, 12, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetoro, A.A.; Abraham, S.; Paraskevopoulos, A.L.; Owusu-Sekyere, E.; Jordaan, H.; Orimoloye, I.R. Alleviating Water Shortages by Decreasing Water Footprint in Sugarcane Production: The Impacts of Different Soil Mulching and Irrigation Systems in South Africa. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, B.; Agrawal, M. Carbon Footprints of Agriculture Sector. Environ. Footpr. Eco-Des. Prod. Process. 2020, 1, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchasara, H.; Samrat, N.H.; Islam, N. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Trends and Mitigation Measures in Australian Agriculture Sector—A Review. Agriculture 2021, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Zolghadr-Asli, B.; Sarzaeim, P.; Aboutalebi, M.; Chu, X.; Loáiciga, H.A. Evaluation of Water Shortage Crisis in the Middle East and Possible Remedies. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2020, 69, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evaporation–Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements–FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56. Food Agric. Organ. United Nations 1998, 300, 300. [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal, S.S.; Dhiman, S.D. Irrigation Water Requirements of Different Crops in Limbasi Branch Canal Command Area of Gujarat. J. Agrometeorol. 2015, 17, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Introduction BT—IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. IPCC Guidel. Natl. Greenh. Gas Invent. 2006, 1.1–1.21. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/meeting/pdfiles/Washington_Report.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- Yang, S.H. The Research of City Trees Effects of Carbon and Oxygen Balance. City Environ. Ecol. 1996, 9, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Weidema, B.P.; Bauer, C.; Hischier, R.; Mutel, C.L.; Nemecek, T.; Reinhard, J.; Vadenbo, C.; Wernet, G. Overview and Methodology: Data Quality Guideline for the Ecoinvent Database Version 3; Swiss Centre for Life Cycle Inventories: St. Gallen, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Pan, G.; Smith, P.; Luo, T.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Yan, M. Carbon Footprint of China’s Crop Production—An Estimation Using Agro-Statistics Data over 1993–2007. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Marland, G. A Synthesis of Carbon Sequestration, Carbon Emissions, and Net Carbon Flux in Agriculture: Comparing Tillage Practices in the United States. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Improvement and Application of Ecological Footprint Evaluation Model; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Di, X.; Nie, Z.; Yuan, B.; Zuo, T. Life Cycle Inventory for Electricity Generation in China. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2007, 12, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Alexander, L.V.; Allen, S.K.; Bindoff, N.L.; Bréon, F.-M.; Church, J.A.; Cubasch, U.; Emori, S. Technical Summary. In Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 33–115. [Google Scholar]
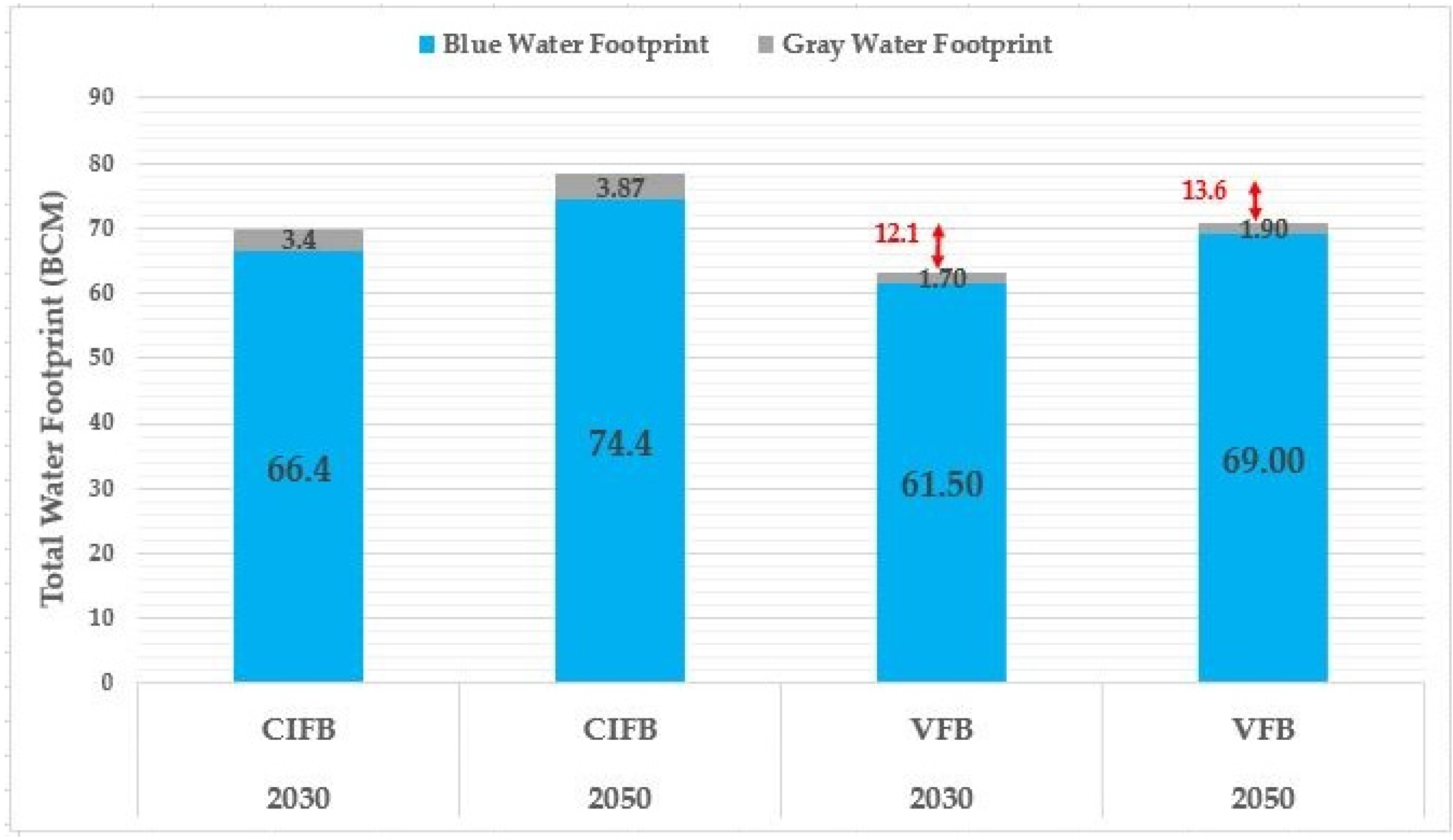
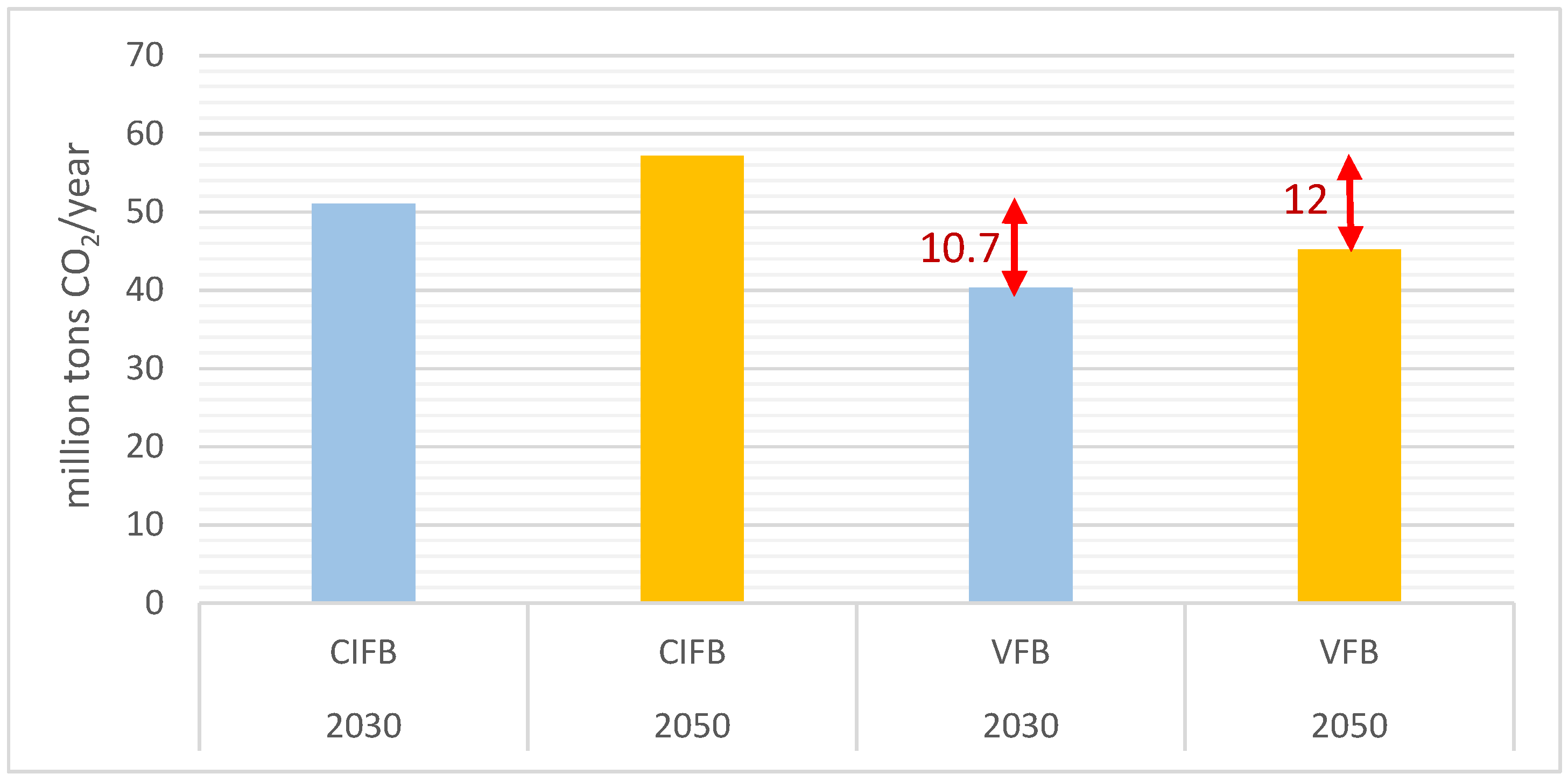
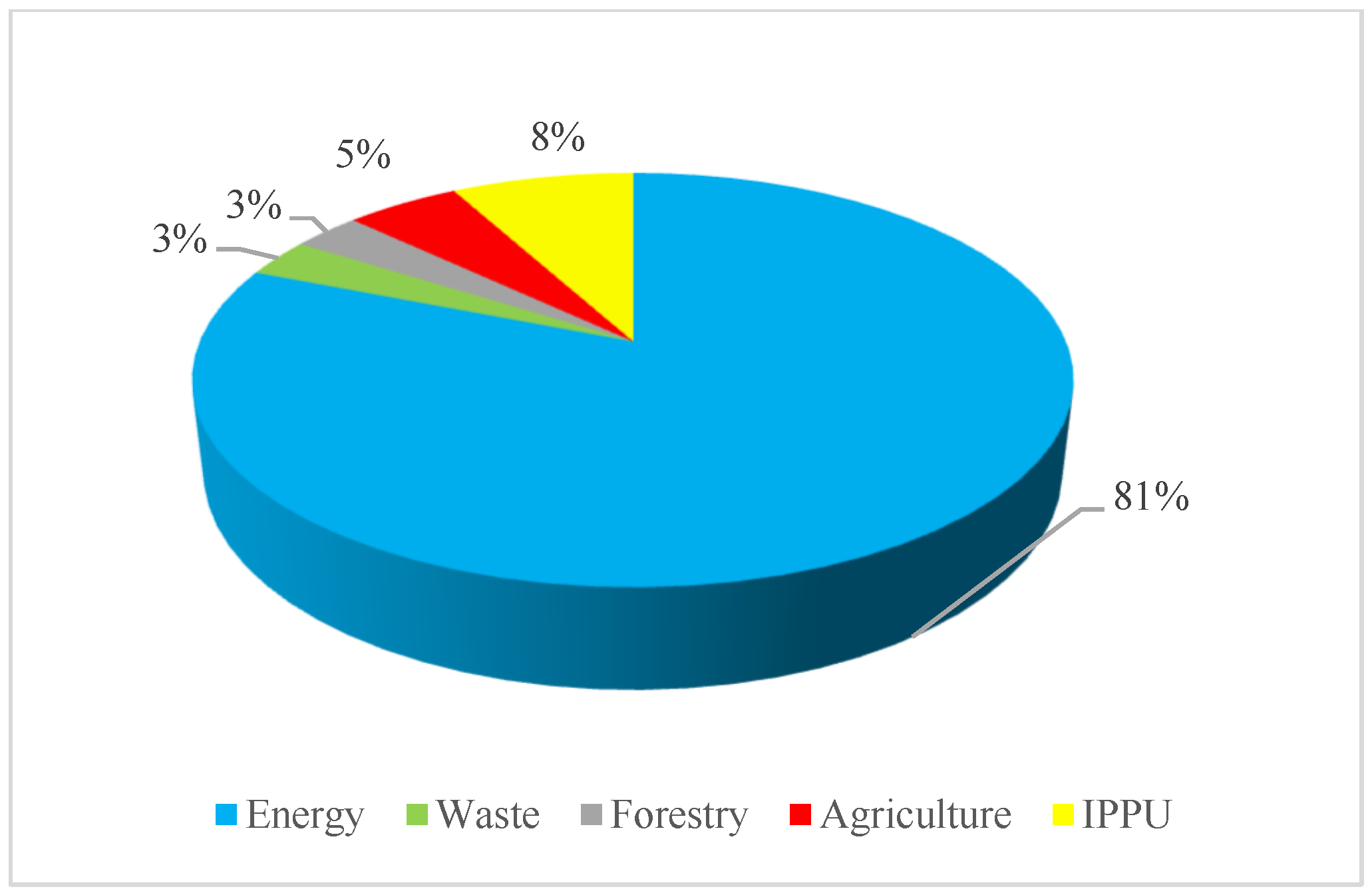
| Food Group | kg/capita/year | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIFB | MHDFB | VFB | SSNFB | MFB | |
| Bread and Cereals | 114 | 155.1 | 70 | 45.2 | 75 |
| Fruits | 100.5 | 102.2 | 120.4 | 118.6 | 175 |
| Vegetables | 103 | 135 | 246.3 | 160.6 | 269 |
| Meat, Eggs, Legumes, and Nuts | 61.4 | 59.4 | 57.3 | 48.5 | 55 |
| Dairy | 104.1 | 91.2 | 0 | 120.4 | 71 |
| Oils and Fats (other) | 36 | 27.3 | 133.5 | 94.1 | 16 |
| Food Baskets (Options) | Preference Coefficient (CL) | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| VFB | 0.701 | 1 |
| SSNFB | 0.681 | 2 |
| MFB | 0.469 | 3 |
| MHDFB | 0.200 | 4 |
| CIFB | 0.000 | 5 |
| Year | Allowable Water to Agricultural Sector (BCM) [63] | CIFB | VFB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Footprint (BCM) | Water Balance (BCM) | Water Footprint (BCM) | Water Balance (BCM) | ||
| 2021 | 62 | 63.9 | −1.9 | 57.9 | 4.1 |
| 2030 | 70 | 69.8 | −0.2 | 63.3 | 6.7 |
| 2050 | 66 | 78.2 | −12.2 | 70.9 | −4.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammadi, A.; Javadi, S.; Yousefi, H.; Pouraram, H.; Randhir, T.O. A Framework for Assessing Food Baskets Based on Water and Carbon Footprints. Water 2024, 16, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091196
Mohammadi A, Javadi S, Yousefi H, Pouraram H, Randhir TO. A Framework for Assessing Food Baskets Based on Water and Carbon Footprints. Water. 2024; 16(9):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091196
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammadi, Ali, Saman Javadi, Hossein Yousefi, Hamed Pouraram, and Timothy O. Randhir. 2024. "A Framework for Assessing Food Baskets Based on Water and Carbon Footprints" Water 16, no. 9: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091196
APA StyleMohammadi, A., Javadi, S., Yousefi, H., Pouraram, H., & Randhir, T. O. (2024). A Framework for Assessing Food Baskets Based on Water and Carbon Footprints. Water, 16(9), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091196








