Impacts on Soil and Cowpea Plants Fertigated with Sanitary Sewage through Subsurface Drip Irrigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
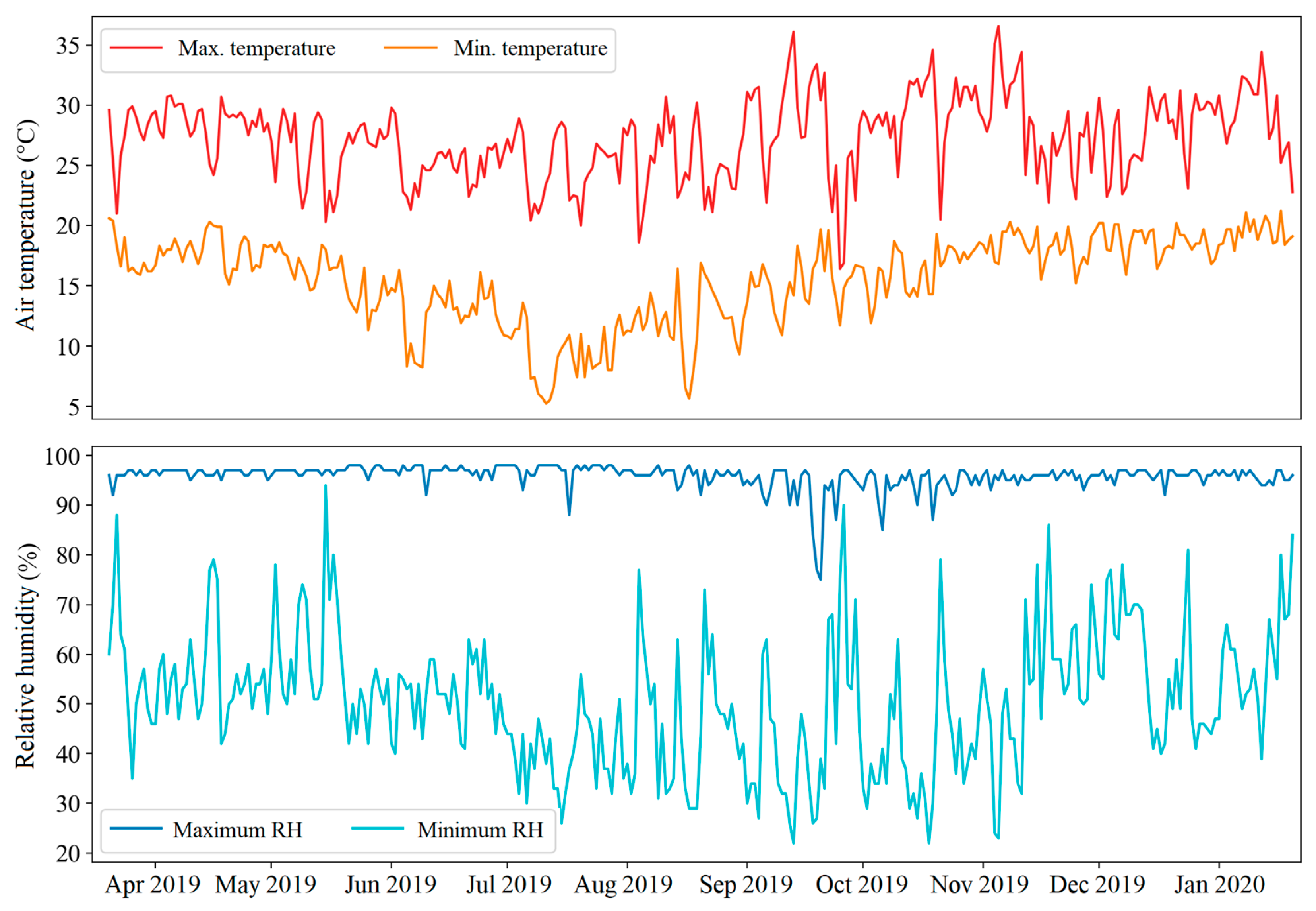
2.1. Local Experiment Conditions
2.2. Treatments and Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Experimental Evaluations
2.4.1. Productive Components and CO2 and Water Emissions
2.4.2. Soil Chemical Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
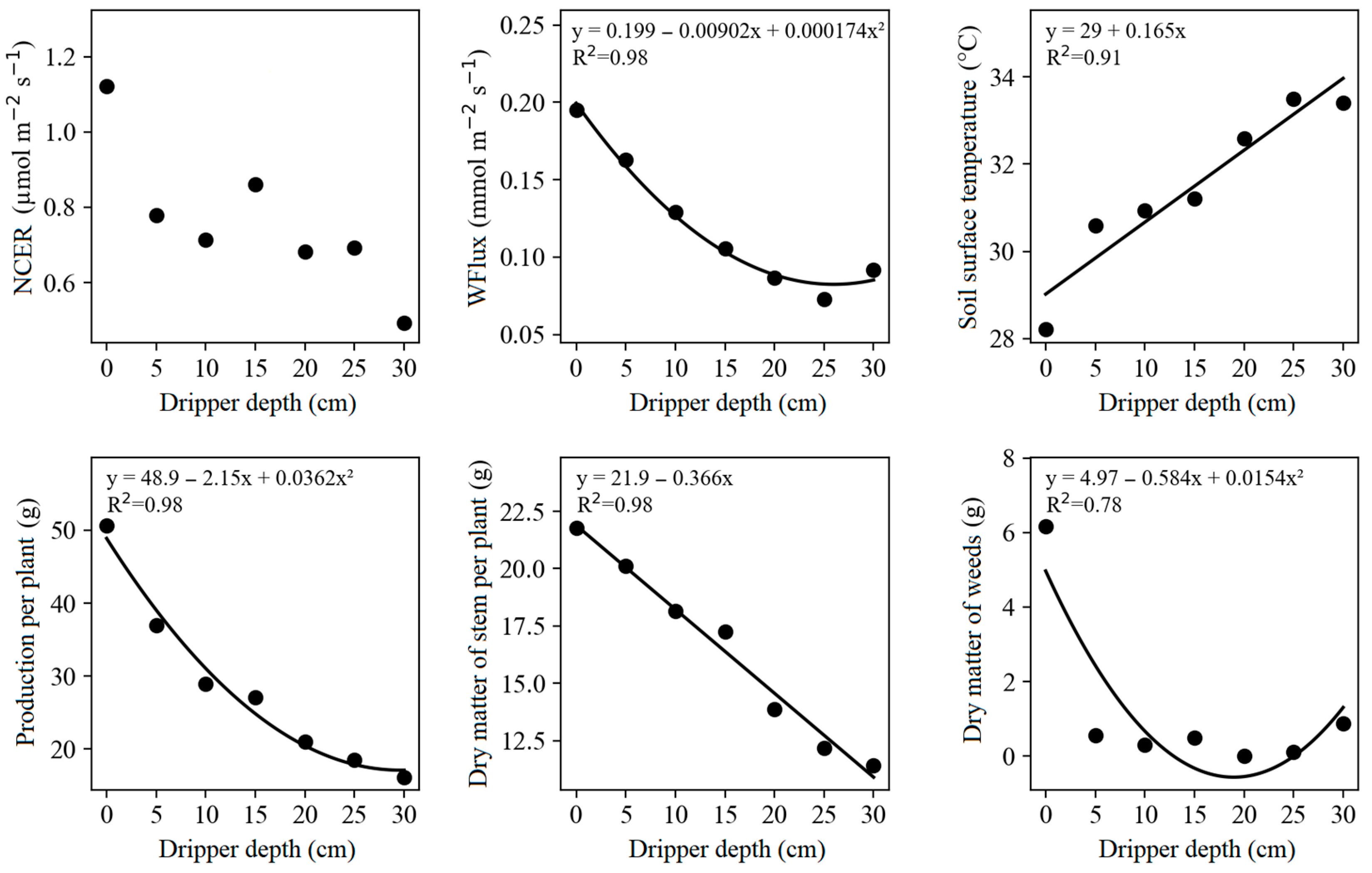
3.1. Productive Components and CO2 and Water Emissions
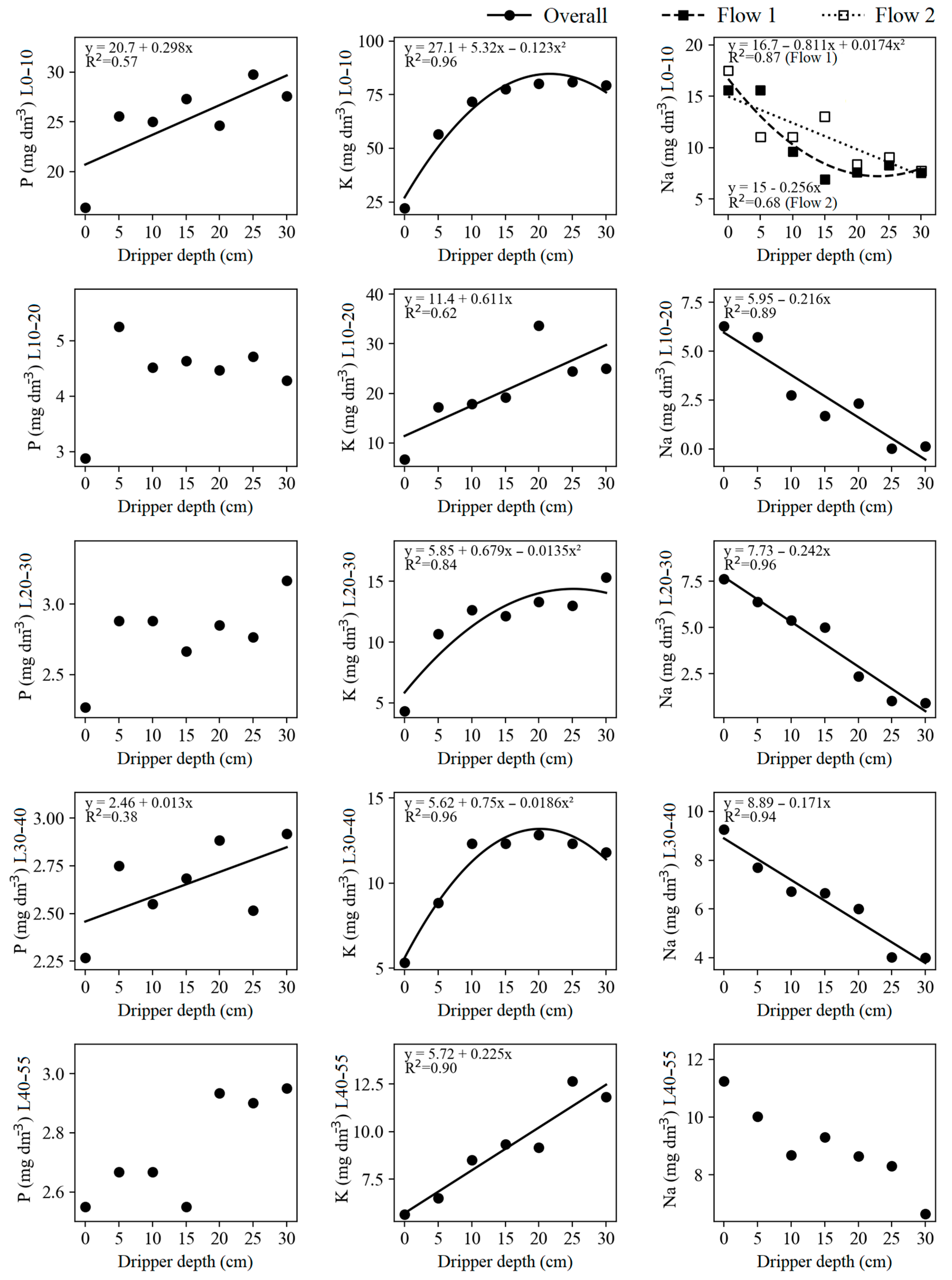
3.2. Phosphorus, Potassium, and Sodium
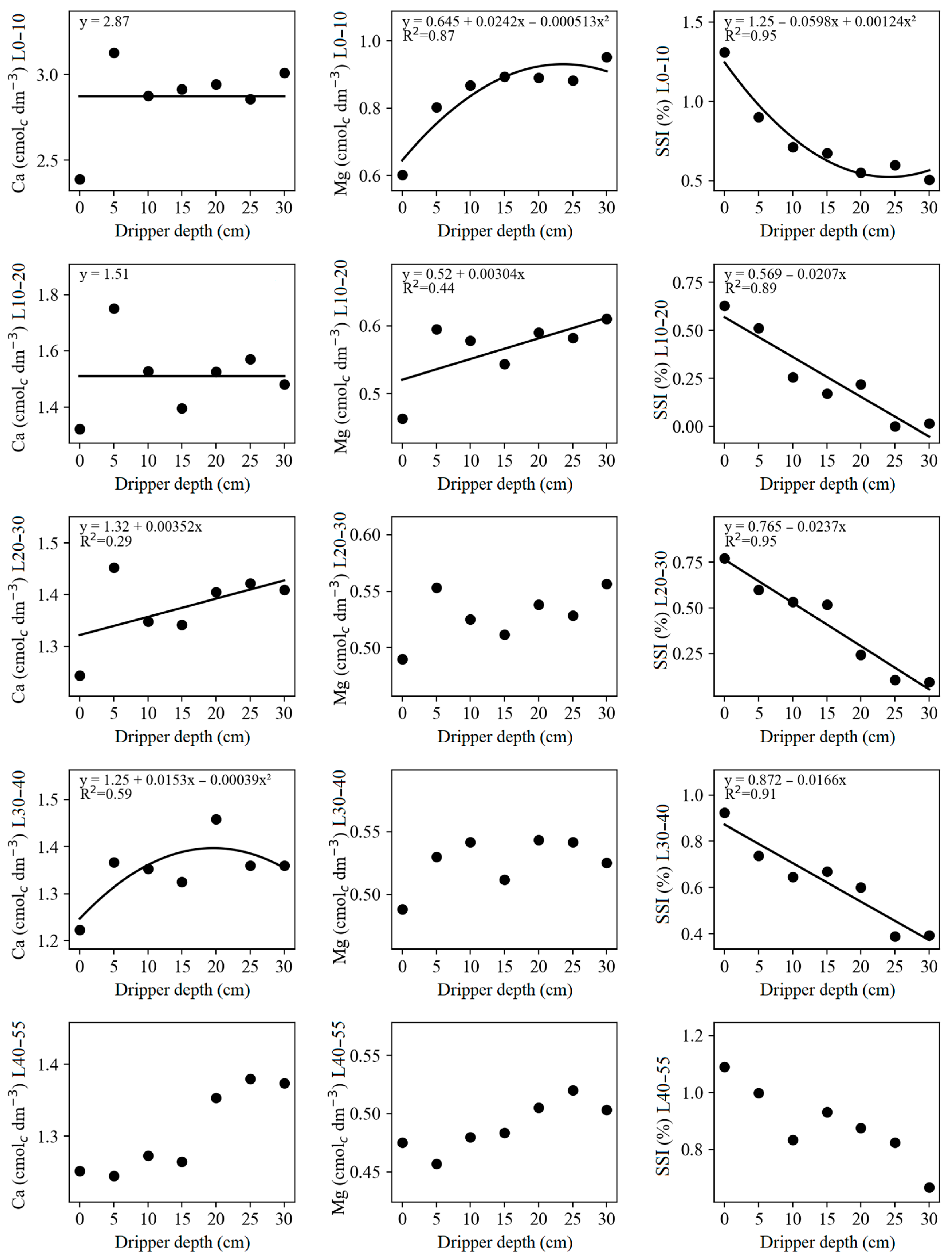
3.3. Calcium, Magnesium, and Sodium Saturation Index
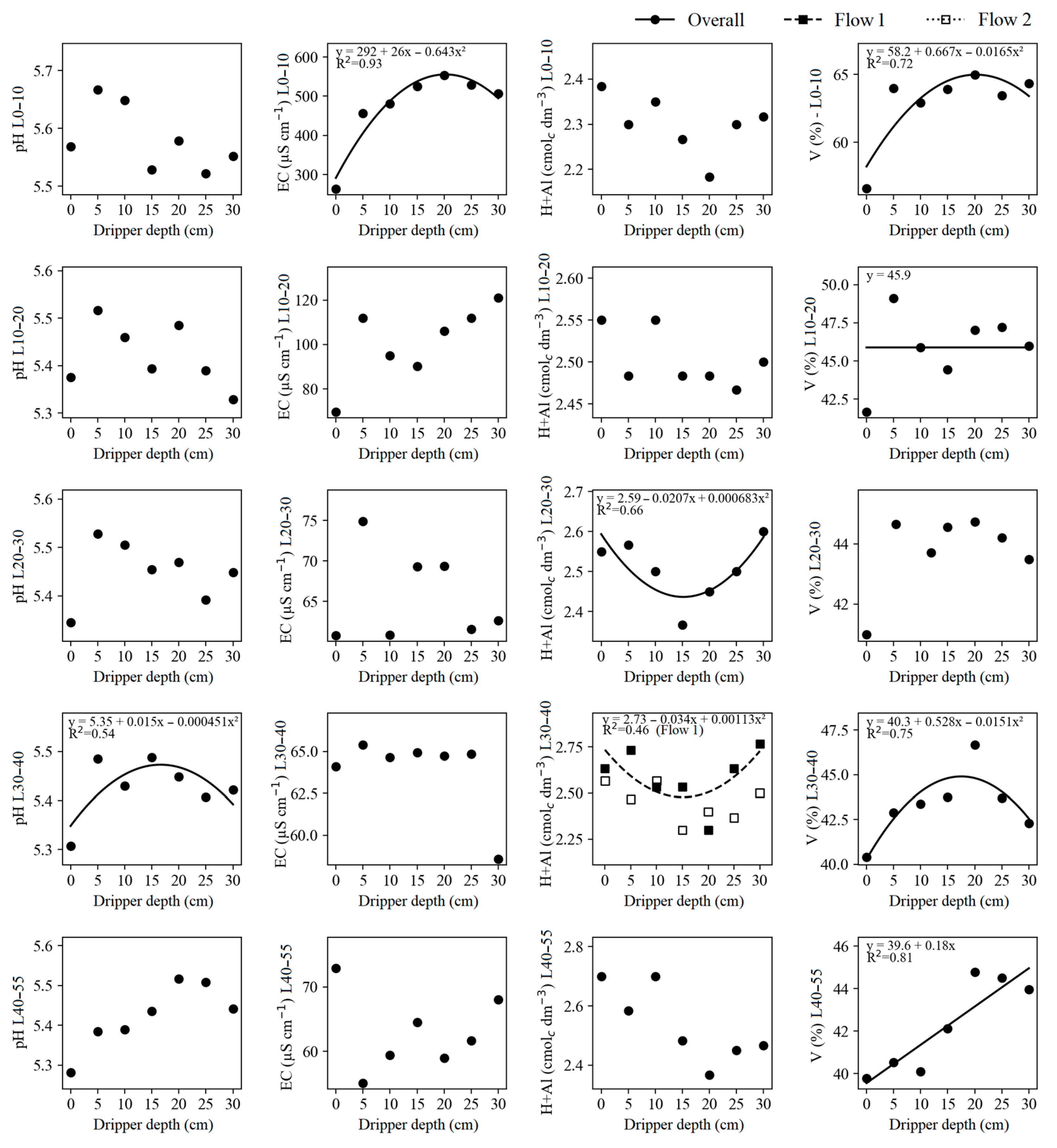
3.4. Hydrogenionic Potential, Electrical Conductivity, Potential Acidity, and Base Saturation
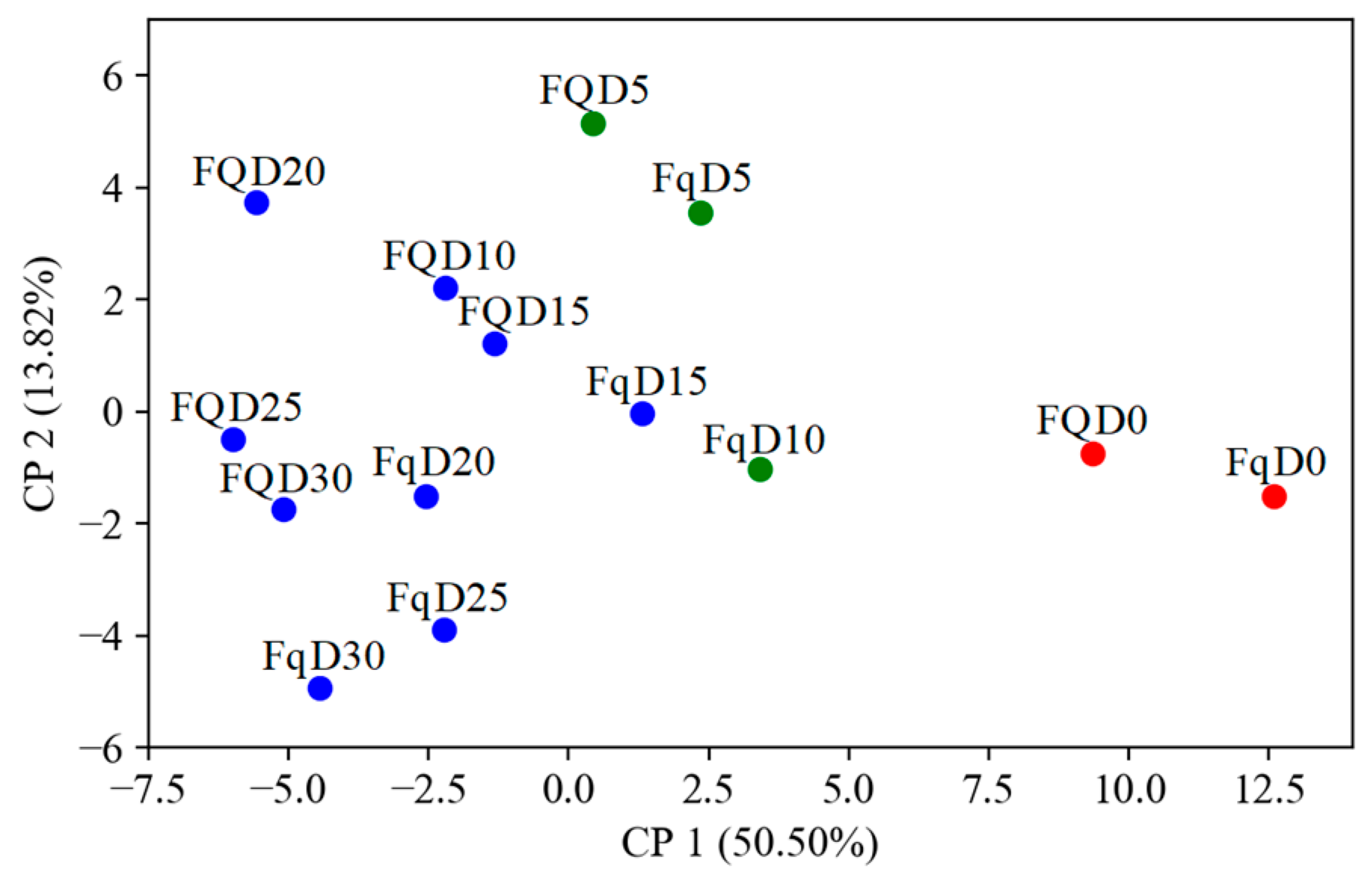
3.5. Principal Component Analysis and Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khondoker, M.; Mandal, S.; Gurav, R.; Hwang, S. Freshwater shortage, salinity increase, and global food production: A need for sustainable irrigation water desalination—A scoping review. Earth 2023, 4, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Engel, B.A.; Qian, H.; Hua, E.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y. Will reaching the maximum achievable yield potential meet future global food demand? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, E.D.; Santos, S.R.; Alves, P.F.S.; Kondo, M.K.; Carvalho, A.J.; Feitosa, F.M. Agronomic performance of common bean crops fertigated with treated sewage and mineral fertilizer. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2020, 24, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.F.S.; Santos, S.R.; Kondo, M.K.; Pegoraro, R.F.; Portugal, A.F. Soil chemical properties in banana crops fertigated with treated wastewater. Caatinga 2019, 32, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuki, K.; Zohan, M.H.S.; Shahidi, A.; Etminan, S. Effect of application of wastewater treatment on soil chemical and physical properties under millet cultivation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 11851–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.W.; Zou, T.; Liu, X.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Liu, Z. The collaborative operation and application influence of sprinkler drip irrigation: A systematic progress review. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wu, L.; Cheng, M.; Fan, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Qian, L. Review on drip irrigation: Impact on crop yield, quality, and water productivity in China. Water 2023, 15, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.I.E.; Morad, M.M.; Wasfy, K.I.; Moursy, M.A.M. Utilization of aquaculture drainage for enhancing onion crop yield under surface and subsurface drip irrigation systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, Y.B.; Yazar, A.; Sesveren, S.; Çolak, İ. Evaluation of yield and leaf water potential (LWP) for eggplant under varying irrigation regimes using surface and subsurface drip systems. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 219, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.H.; Cunha, F.F.; Brito, L.F.A. Advance time to determine injection and flushing times in drip fertigation. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Mouheb, N.; Mange, A.; Froment, G.; Lequette, K.; Bru-Adan, V.; Maihol, J.C.; Molle, B.; Wéry, N. Effect of untreated or reclaimed wastewater drip-irrigation for lettuces and leeks on yield, soil and fecal indicators. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 8, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Patel, N.; Tossou, A.G.; Patra, S.; Singh, N.; Singh, P.K. Incidence of Escherichia coli in vegetable crops and soil profile drip irrigated with primarily treated municipal wastewater in a semi-arid peri urban area. Agriculture 2020, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, F.; Li, Y. Effects of Phosphorus Fertigation and Lateral Depths on Distribution of Olsen-P in Soil and Yield of Maize under Subsurface Drip Irrigation; ASABE Paper, No. 1701105; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J.; Pendergast, L. Yield, water-use efficiencies and root distribution of soybean, chickpea and pumpkin under different subsurface drip irrigation depths and oxygation treatments in vertisols. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.O.; Miranda, A.G.S.; Silva, P.A.; Teixeira, A.S.; Cunha, F.F. Predicting the spatial distribution of water applied by subsurface drip in clay soil. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2024, 28, e277102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, F.R. Irrigation and Nitrogen Management for Subsurface Drip Irrigated Corn—25 Years of K-State’s Efforts; ASABE Paper, No. 141914980; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Shao, H.; Sokolowski, E.; Mi, G. Effect of different drip fertigation methods on maize yield, nutrient and water productivity in two-soils in Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Niu, W.; Li, Y.; Lv, W. Subsurface drip irrigation enhances soil nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism in tomato root zones and promotes tomato growth. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.H.G.; Silva, E.M.; Oliveira, A.M.; Jesus, J.S.; Barbosa, E.A.; Neves, J.M.G.; Oliveira, J.A.A.; Camelo, G.N. Rendimento econômico de consórcio irrigado de quiabo e feijão–caupi. Rev. Educ. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2023, 5, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Rehman, A.; Al-Alawi, A.K.M.; Al-Busaidi, W.M.; Lee, D.J. Integrated use of seed priming and biochar improves salt tolerance in cowpea. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, S.; Mantovani, E.C.; Silva, D.D.; Soares, A.A. Manual de Irrigação, 9th ed.; Editora UFV: Viçosa, Brazil, 2019; 545p. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, H.G.; Jacomine, P.K.T.; Anjos, L.H.C.; Oliveira, V.A.; Lumbreras, J.F.; Coelho, M.R.; Almeida, J.A.; Araújo Filho, J.C.; Oliveira, J.B.; Cunha, T.J.F. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 5th ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; 356p. [Google Scholar]
- Nopens, I.; Capalozza, C.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Stability Analysis of a Synthetic Municipal Wastewater, 1st ed.; University of Gent: Gent, Belgium, 2001; 22p. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, A.C.; Guimarães, P.T.G.; Alvarez, V.H. Recomendações Para o Uso de Corretivos e Fertilizantes em Minas Gerais, 5th ed.; Editora SBCS: Viçosa, Brazil, 1999; 359p. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, F.B.; Cardoso, M.J.; Salviano, A.A.C. Fertilidade do Solo e Adubação. In Feijão Caupi: Avanços Tecnológicos, 1st ed.; Freire Filho, F.R., Lima, J.A.A., Ribeiro, V.Q., Eds.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2005; pp. 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, A.T.; Matos, M.P. Disposição de Águas Residuárias no solo e Em Sistemas Alagados Construídos, 1st ed.; Editora UFV: Viçosa, Brazil, 2017; 71p. [Google Scholar]
- Kodinariya, T.; Makwana, P.R. Review on determining number of Cluster in K-Means Clustering. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Manag. Stud. 2013, 1, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Li, B.; Ding, D.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, T.; Li, Z. Subsurface drip irrigation reduces cadmium accumulation of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants in upland soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, E.D.; Assis, M.O.; Guimarães, C.M.; Araújo, E.F.; Borges, A.C.; Cunha, F.F. Superabsorbent polymers and sanitary sewage change water availability during the cowpea emergence phase. Nativa 2024, 12, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.R.L.; Pinheiro, P.R.; Pinheiro, C.L.; Lima, K.A.P.; Dutra, A.S. Germination and vigour in seeds of the cowpea in response to salt and heat stress. Caatinga 2019, 32, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, V.H.B.; Diotto, A.V.; Thebaldi, M.S.; Colombo, A.; Silva, Y.F.; Lima, E.M.C.; Resende, G.F.L. Variation in the flow rate of drip emitters in a subsurface irrigation system for different soil types. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, S.S.; Ramachandrappa, B.K.; Nanjappa, H.V.; Prabhakar, M. Studies on NPK drip fertigation in field grown tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 21, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, B.; Xue, B.; Gao, R.; Ndzana, G.M.; Liu, R.; Huang, J.; An, H.; Du, L.; Kamran, M. Changes in soil organic carbon and nutrient pools in aggregate-sized fractions along a chronosequence of wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.) plantations in arid areas of Northwest China. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 39, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.C.; Corrêa, G.R.; Gradella, F.S.; Campos, P.V.; Koch, V.A.; Vasconcelos, B.N.F. Solos de ambientes lacustres do Pantanal Sul-Mato-Grossense. Soc. Nat. 2023, 35, e67560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primavesi, A.C.; Primavesi, O.; Corrêa, L.A.; Cantarella, H.; Silva, A.G. Cations and anions uptake by coastcross grass fertilized with urea and ammonium nitrate. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2005, 40, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| pH | 1 OM | 2 Ca | 2 Mg | 3 SB | 4 eCEC | 5 CEC | 6 H + Al | |
| H2O | g kg−1 | cmolc L−1 | ||||||
| 5.8 | 18.82 | 1.01 | 0.50 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 4.20 | 2.64 | |
| 7 P | 7 K | 8 S | 7 Cu | 7 Fe | 7 Mn | 7 Zn | 9 Pres | 10 V |
| mg L−1 | % | |||||||
| 4.6 | 20.0 | 25.3 | 3.0 | 68.2 | 33.1 | 4.7 | 21.6 | 37.1 |
| 11 FC | 12 PWP | 13 Sd | Sand | Silt | Clay | Textural Classification | ||
| m³ m−³ | g cm−3 | g kg−1 | ||||||
| 0.376 | 0.254 | 1.17 | 517 | 122 | 361 | Sand clay soil | ||
| Salts | 1 Quantity | 2 COD | N | P | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg L−1 | |||||
| Urea | 92 | 23 | 43 | 0 | 0 |
| MAP | 13 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Sodium acetate * | 132 | 79 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Peptone | 17 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MgSO4 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| KH2PO4 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 |
| KCl | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| FeSO4·7H2O | 5.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ingredients | |||||
| Starch | 122 | 122 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Powdered milk | 116 | 116 | 7 | 1 | 0 |
| Yeast | 52 | 52 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Soybean oil | 29 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 438 | 58 | 9 | 20 | |
| ¹ Vol. of SSS (L) | N (kg ha−1) | P2O5 (kg ha−1) | K2O (kg ha−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSS | Sowing | Total | SSS | Sowing | Total | SSS | Sowing | Total | |
| 8.26 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 13.56 | 46.44 | 60 | 15.85 | 24.15 | 40 |
| Variable Analyzed | Method |
|---|---|
| Phosphorus (P) | Extractant Mehlich-1 |
| Potassium (K) | Extractant Mehlich-1 |
| Sodium (Na) | Extractant Mehlich-1 |
| Calcium (Ca) | Extractant: KCl—1 mol L−1 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Extractant: KCl—1 mol L−1 |
| Sodium saturation index (SSI) | SSI = Na/CEC × 100 |
| pH | In water, KCl, and CaCl—Ratio 1:2.5 |
| Potential acidity (H + Al) | Extractant: 0.5 mol L−1 calcium acetate—pH 7.0 |
| Base saturation index (V) | V = (K + Na + Ca + Mg)/CEC × 100 |
| Variables | Source of Variation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow | Depth | Flow × Depth | CV (%) | |
| NCER | 3.30 × 10−1 ns | 2.25 × 10−1 ns | 1.06 × 10−1 ns | 42.33 |
| WFlux | 2.58 × 10−3 ns | 1.19 × 10−2 *** | 5.55 × 10−4 ns | 29.05 |
| Ts | 2.54 × 10−1 ns | 2.09 × 101 *** | 2.59 × 100 ns | 5.25 |
| Prod. | 1.53 × 101 ns | 8.73 × 102 *** | 2.31 × 101 ns | 15.37 |
| DM-stem | 8.70 × 10−2 ns | 9.56 × 101 *** | 3.30 × 100 ns | 17.87 |
| DM-weed | 1.06 × 101 ns | 2.92 × 101 * | 9.76 × 100 ns | 251.51 |
| Variables | Source of Variation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow | Depth | Flow × Depth | CV (%) | |||||
| P L0−10 | 7.28 × 102 ns | 1.09 × 102 * | 3.32 × 102 ns | 26.06 | ||||
| P L10−20 | 9.45 × 10−1 ns | 3.21 × 100 ns | 2.73 × 100 ns | 27.15 | ||||
| P L20−30 | 8.60 × 10−2 ns | 4.52 × 10−1 ns | 1.43 × 10−1 ns | 15.59 | ||||
| P L30−40 | 4.61 × 10−1 ns | 3.11 × 10−1 ** | 7.60 × 10−2 ns | 9.70 | ||||
| P L40−55 | 5.71 × 10−1 ns | 1.90 × 10−1 ns | 2.89 × 10−2 ns | 12.60 | ||||
| K L0−10 | 7.46 × 102 ns | 2.77 × 103 *** | 1.01 × 102 ns | 18.78 | ||||
| K L10−20 | 1.84 × 102 ns | 4.21 × 102 * | 1.36 × 102 ns | 52.85 | ||||
| K L20−30 | 8.86 × 101 * | 7.40 × 101 *** | 1.63 × 101 ns | 31.19 | ||||
| K L30−40 | 1.34 × 102 * | 4.60 × 101 ** | 9.21 × 100 ns | 31.10 | ||||
| K L40−55 | 9.15 × 101 ** | 3.92 × 101 ** | 4.97 × 100 ns | 34.38 | ||||
| Na L0−10 | 9.47 × 100 ns | 6.22 × 101 *** | 1.47 × 101 * | 21.33 | ||||
| Na L10−20 | 8.98 × 10−1 ns | 3.69 × 101 *** | 4.82 × 100 ns | 81.92 | ||||
| Na L20−30 | 1.79 × 100 ns | 4.27 × 101 *** | 1.67 × 100 ns | 35.54 | ||||
| Na L30−40 | 8.95 × 10−1 ns | 2.16 × 101 *** | 1.68 × 100 ns | 28.73 | ||||
| Na L40−55 | 1.10 × 10−1 ns | 1.23 × 101 ns | 6.53 × 10−1 ns | 28.26 | ||||
| Variables | Flow (L h−1) | Drip emitter installation depth (cm) | ||||||
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| Na L0−10 | 1.6 | 15.58 a | 15.58 a | 9.64 a | 6.91 b | 7.58 a | 8.31 a | 7.57 a |
| 3.8 | 17.50 a | 11.04 b | 11.04 a | 13.03 a | 8.41 a | 9.07 a | 7.73 a | |
| Flow (L h−1) | Variables | |||||||
| K L20−30 | K L30–40 | K L40–55 | ||||||
| 1.6 | 10.19 b | 9.05 b | 7.62 b | |||||
| 3.8 | 13.09 a | 12.61 a | 10.57 a | |||||
| Variables | Source of Variation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow | Depth | Flow × Depth | CV (%) | |
| Ca L0–10 | 1.20 × 104 ns | 3.25 × 10−1 * | 1.85 × 10−1 ns | 11.12 |
| Ca L10–20 | 8.60 × 10−4 ns | 1.12 × 10−1 ** | 3.02 × 10−2 ns | 10.90 |
| Ca L20–30 | 6.44 × 10−3 ns | 2.96 × 10−2 * | 6.49 × 10−3 ns | 6.66 |
| Ca L30–40 | 7.47 × 10−3 ns | 2.89 × 10−2 * | 7.23 × 10−3 ns | 7.65 |
| Ca L40–55 | 1.72 × 10−2 ns | 2.17 × 10−2 ns | 1.22 × 10−2 ns | 9.25 |
| Mg L0–10 | 1.04 × 10−2 ns | 7.85 × 10−2 *** | 5.16 × 10−3 ns | 11.72 |
| Mg L10–20 | 2.88 × 10−4 ns | 1.48 × 10−2 * | 5.70 × 10−3 ns | 11.58 |
| Mg L20–30 | 2.75 × 10−3 ns | 3.28 × 10−3 ns | 1.85 × 10−3 ns | 7.59 |
| Mg L30–40 | 1.27 × 10−2 ns | 2.43 × 10−3 ns | 3.21 × 10−4 ns | 8.33 |
| Mg L40–55 | 1.61 × 10−3 ns | 2.78 × 10−3 ns | 2.30 × 10−3 ns | 8.47 |
| SSI L0–10 | 5.94 × 10−2 ns | 4.65 × 10−1 *** | 4.06 × 10−2 ns | 19.07 |
| SSI L10–20 | 4.00 × 10−3 ns | 3.37 × 10−1 *** | 4.38 × 10−2 ns | 81.24 |
| SSI L20–30 | 2.83 × 10−2 ns | 4.14 × 10−1 *** | 1.69 × 10−2 ns | 35.17 |
| SSI L30–40 | 9.75 × 10−3 ns | 2.13 × 10−1 *** | 1.59 × 10−2 ns | 27.59 |
| SSI L40–55 | 5.72 × 10−3 ns | 1.11 × 10−1 ns | 8.74 × 10−3 ns | 25.74 |
| Variables | Source of Variation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow | Depth | Flow × Depth | CV (%) | |||||
| pH L0–10 | 9.52 × 10−4 ns | 1.92 × 10−2 ns | 3.80 × 10−2 ns | 2.78 | ||||
| pH L10–20 | 3.15 × 10−2 ns | 2.72 × 10−2 ns | 1.35 × 10−2 ns | 2.03 | ||||
| pH L20–30 | 1.30 × 10−1 ns | 2.40 × 10−2 ns | 1.62 × 10−2 ns | 2.03 | ||||
| pH L30–40 | 1.97 × 10−1 ns | 2.25 × 10−2 ** | 4.81 × 10−3 ns | 1.43 | ||||
| pH L40–55 | 1.72 × 10−1 ns | 3.90 × 10−2 ns | 8.98 × 10−3 ns | 2.48 | ||||
| EC L0–10 | 3.28 × 104 ns | 5.76 × 104 *** | 7.98 × 103 ns | 17.72 | ||||
| EC L10–20 | 1.78 × 101 ns | 1.79 × 103 ns | 6.48 × 101 ns | 29.82 | ||||
| EC L20–30 | 1.23 × 101 ns | 1.85 × 102 ns | 1.12 × 102 ns | 18.17 | ||||
| EC L30–40 | 7.90 × 10−1 ns | 3.36 × 101 ns | 4.83 × 101 ns | 12.21 | ||||
| EC L40–55 | 8.65 × 101 ns | 2.18 × 102 ns | 4.22 × 102 ns | 29.05 | ||||
| H + Al L0–10 | 2.14 × 10−1 ns | 2.44 × 10−2 ns | 1.65 × 10−2 ns | 6.76 | ||||
| H + Al L10–20 | 1.48 × 10−1 * | 6.91 × 10−3 ns | 1.33 × 10−2 ns | 5.42 | ||||
| H + Al L20–30 | 2.38 × 10−2 ns | 3.71 × 10−2 * | 2.10 × 10−2 ns | 4.77 | ||||
| H + Al L30–40 | 2.00 × 10−1 ns | 6.65 × 10−2 ** | 3.75 × 10−2 * | 4.61 | ||||
| H + Al L40–55 | 2.01 × 10−1 ns | 9.97 × 10−2 ns | 1.30 × 10−2 ns | 8.36 | ||||
| V L0–10 | 4.08 × 101 ns | 4.85 × 101 *** | 9.91 × 100 ns | 4.54 | ||||
| V L10–20 | 2.36 × 101 ns | 3.34 × 101 ** | 5.71 × 100 ns | 5.81 | ||||
| V L20–30 | 2.88 × 100 ns | 1.02 × 101 ns | 1.27 × 100 ns | 4.62 | ||||
| V L30–40 | 5.13 × 101 ns | 2.14 × 101 *** | 2.76 × 100 ns | 3.71 | ||||
| V L40–55 | 1.36 × 101 ns | 2.82 × 101 ** | 3.46 × 100 ns | 5.86 | ||||
| Variables | Flow (L h−1) | Drip emitter installation depth (cm) | ||||||
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| H + Al L30–40 | 1.6 | 2.63 a | 2.73 a | 2.53 a | 2.53 a | 2.30 a | 2.63 a | 2.77 a |
| 3.8 | 2.57 a | 2.47 b | 2.57 a | 2.30 b | 2.40 a | 2.37 b | 2.50 b | |
| Flow (L h−1) | Variables | |||||||
| H + Al L10–20 | ||||||||
| 1.6 | 2.56 a | |||||||
| 3.8 | 2.44 b | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araújo, E.D.; Ferreira, L.B.; Oliveira, J.T.d.; Borges, A.C.; Cunha, F.F.d. Impacts on Soil and Cowpea Plants Fertigated with Sanitary Sewage through Subsurface Drip Irrigation. Water 2024, 16, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091194
Araújo ED, Ferreira LB, Oliveira JTd, Borges AC, Cunha FFd. Impacts on Soil and Cowpea Plants Fertigated with Sanitary Sewage through Subsurface Drip Irrigation. Water. 2024; 16(9):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091194
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraújo, Edcássio Dias, Lucas Borges Ferreira, Job Teixeira de Oliveira, Alisson Carraro Borges, and Fernando França da Cunha. 2024. "Impacts on Soil and Cowpea Plants Fertigated with Sanitary Sewage through Subsurface Drip Irrigation" Water 16, no. 9: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091194
APA StyleAraújo, E. D., Ferreira, L. B., Oliveira, J. T. d., Borges, A. C., & Cunha, F. F. d. (2024). Impacts on Soil and Cowpea Plants Fertigated with Sanitary Sewage through Subsurface Drip Irrigation. Water, 16(9), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091194








