Geochemical Evolution in Historical Time of Thermal Mineral Springs at Campetti Southwest (Veii, Central Italy) through Geoarcheological Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Geological Settings
- “Pyroclastic fall deposits from Sacrofano” (PFS), which extensively outcrop over the SE sector of SVD;
- “Red tuff with black scoria” (RTBS) pyroclastic flow unit, interbedded in the PFS unit;
- “Sacrofano lower pyroclastic flow unit” (SLP), a tuff composed of centimetric pumices, sedimentary, and volcanic clasts, in a lithified ash matrix. SLP directly covers the sedimentary substratum.

2.2. Hydrogeological Settings
2.3. Veii and Campetti Southwest Archeological Site

3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Waters
3.1.1. Hydrogeological Survey
3.1.2. Water Sampling and Analysis
3.2. Rocks
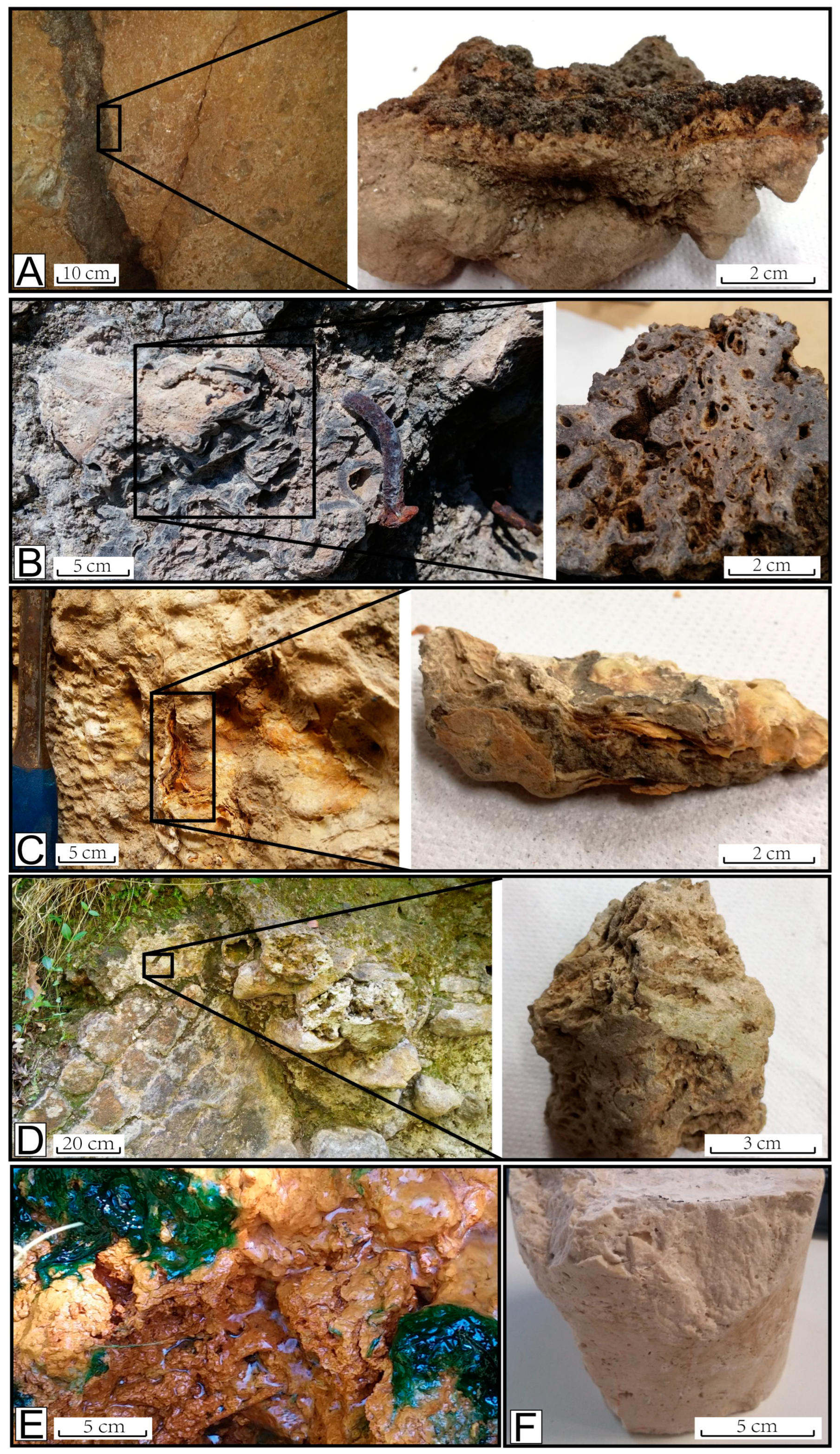
3.2.1. Rock Sampling and Description
3.2.2. Rock Geochemistry
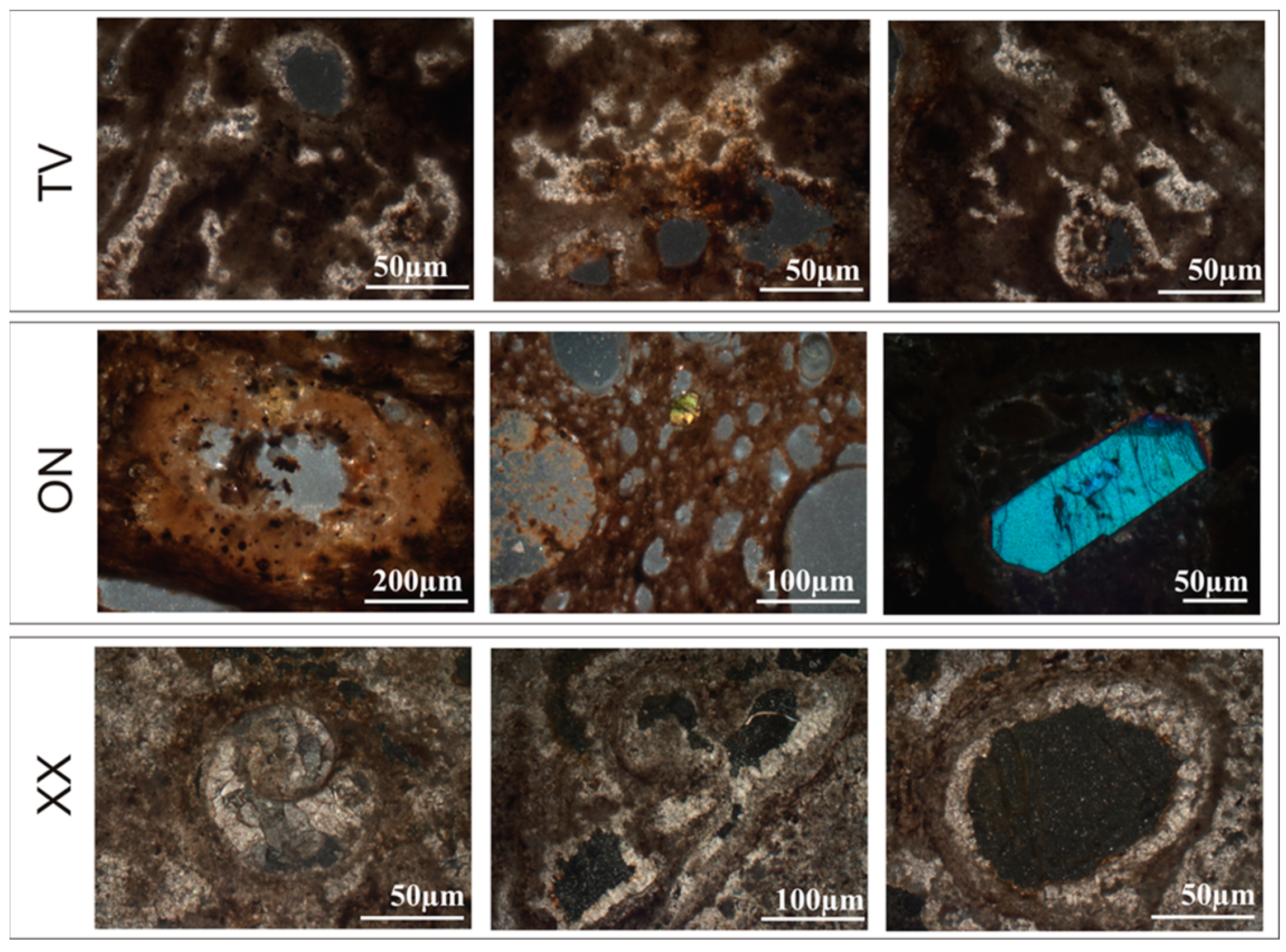
3.2.3. Mineralogical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Hydrogeological Results
4.2. Mineralogical Results
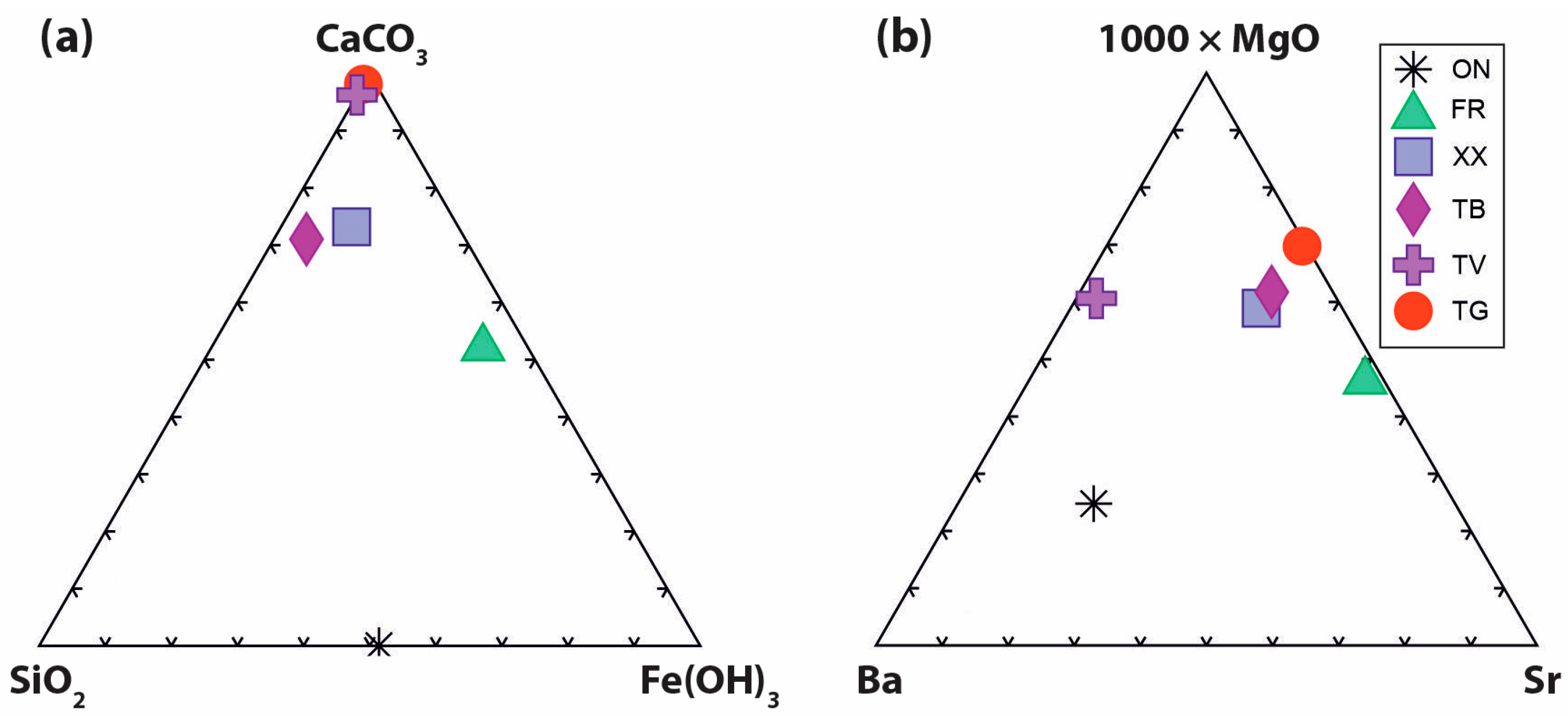
4.3. Chemical Results of Water and Rock Samples
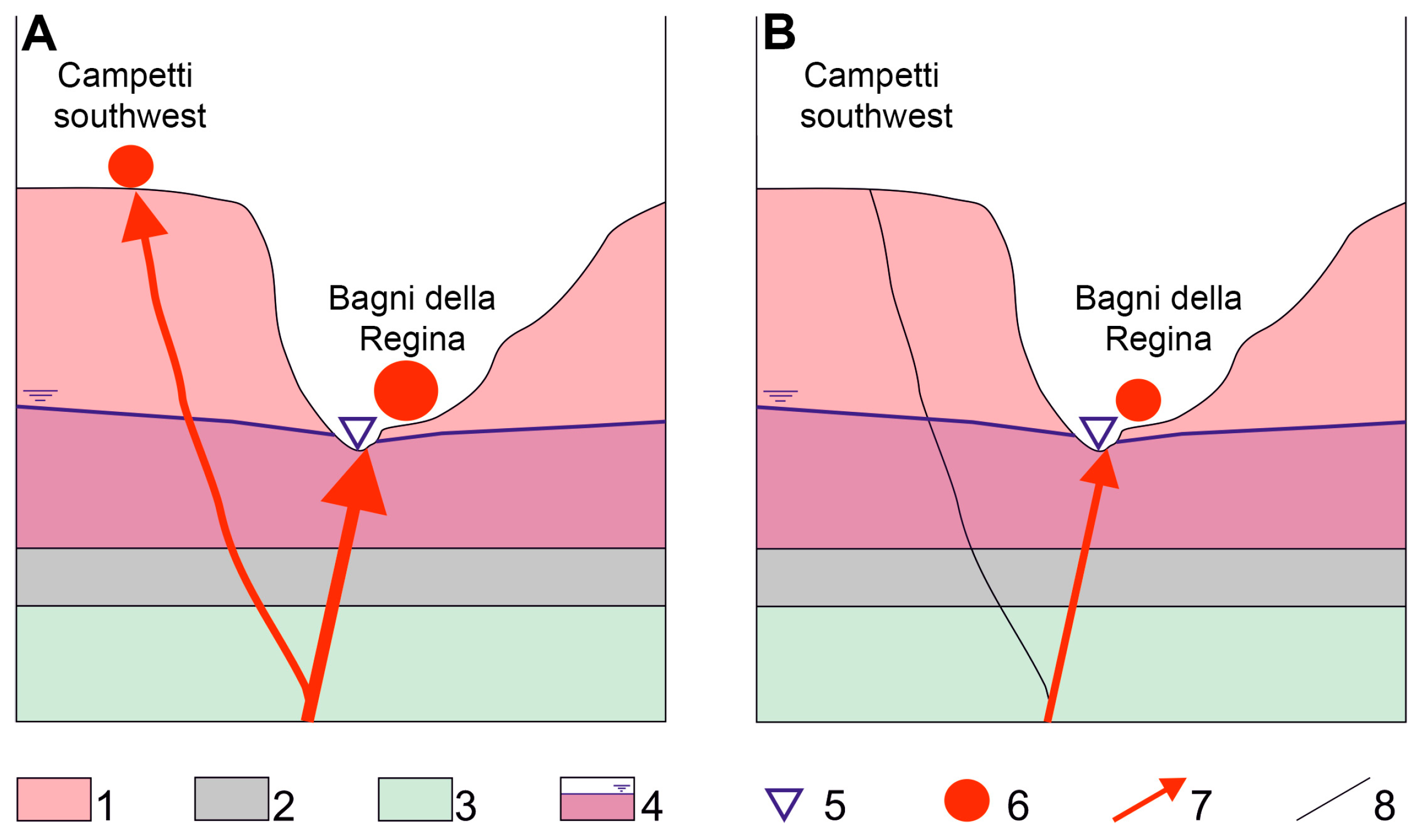
5. Discussion
- Before the Roman period (Figure 7A), an abundant and prevalent contribution of deep thermal and mineralized fluids from the carbonate aquifer occurred. They produced travertine deposits with a low concentration of volcanic-related elements. During Roman times, the discharge of Bagni della Regina springs was presumably higher than currently, since it was essential for feeding the spa. In this phase, at least one small, thermal mineralized spring was active at the Campetti Southwest site with a similar chemical composition.
- Later (Figure 7B), the progressive sealing of the fractures due to the calcite precipitation induced the reduction of spring flow at Bagni della Regina and the interruption in Campetti Southwest. The decreased contribution of the deep mineralized carbonate component reflects a shift toward a more volcanic-derived composition, as observed in the active springs and actual travertine deposits in the Valchetta Stream valley.
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lucero, L.J.; Fletcher, R.; Coningham, R. From ‘Collapse’ to Urban Diaspora: The Transformation of Low-Density, Dispersed Agrarian Urbanism. Antiquity 2015, 89, 1139–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, M.J. Water Histories and Spatial Archaeology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781316471142. [Google Scholar]
- Chiotis, E. Climate Changes in the Holocene; Chiotis, E., Ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, L. The Italian-Palestinian Expedition to Tell Es-Sultan, Ancient Jericho (1997–2015). In Digging Up Jericho; Archaeopress Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 175–214. [Google Scholar]
- Jazwa, C.S.; Duffy, C.J.; Leonard, L.; Kennett, D.J. Hydrological Modeling and Prehistoric Settlement on Santa Rosa Island, California, USA. Geoarchaeology 2016, 31, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensham, R.J.; Adinehvand, R.; Babidge, S.; Cantonati, M.; Currell, M.; Daniele, L.; Elci, A.; Galassi, D.M.P.; de la Hera Portillo, Á.; Hamad, S.; et al. Fellowship of the Spring: An Initiative to Document and Protect the World’s Oases. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 163936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, D.K. Water Culture in Roman Society. Brill Res. Perspect. Anc. Hist. 2018, 1, 1–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håland, E.J. Water Sources and the Sacred in Modern and Ancient Greece and Beyond. Water Hist. 2009, 1, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamini Simoni, M. Gli Etruschi Maestri Di Idraulica; Electa Editori Umbri: Perugia, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Raepsaet, G. The Nature and Function of Water, Bath, Bathing, and Hygiene from Antiquity through the Renaissance; Kosso, C., Scott, A., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Ward-Perkins, J.B. Indexes to Veii: The Historical Topography of the Ancient City. Pap. Br. Sch. Rome 1961, 29, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciano, R.; Fusco, U.; Smith, C. Novità Nella Ricerca Archeologica a Veio Dagli Studi Di John Ward-Perkins Alle Ultime Scoperte; Sapienza Università Editrice: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giuseppe, H. Lungo Il Tevere Scorreva Lento Il Tempo Dei Paesaggi Tra XV e I Secolo a.C.; British School at Rome; Scienze e Lettere: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, U. Aspetti Cultuali e Archeologici Del Sito Di Campetti, Area Sud-Ovest Dall’età Arcaica a Quella Imperiale. Atti Della Pontif. Accad. Romana Di Archeol. 2014, 86, 309–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sottili, G.; Palladino, D.M.; Zanon, V. Plinian Activity during the Early Eruptive History of the Sabatini Volcanic District, Central Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 135, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A. Plio-Quaternary Volcanism in Italy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; ISBN 3-540-25885-X. [Google Scholar]
- Mariotti, G. Basal Carbonate Succession. In Sabatini Volcanic Complex; Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche: Rome, Italy, 1993; Volume 114, pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Civitelli, G.; Corda, L.; Di Filippo, M. The Allochtonus Succession. In Sabatini Volcanic Complex; Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche: Rome, Italy, 1993; Volume 114, pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Barberi, F.; Buonasorte, G.; Cioni, R.; Fiordelisi, A.; Foresi, L.M.; Iaccarino, S.; Laurenzi, M.A.; Sbrana, A.; Vernia, L.; Villa, I.M. Lio-Pleistocene Geological Evolution of the Geothermal Area of Tuscany and Latium. Mem. Descr. Della Carta Geol. d’Italia 1994, 49, 77–134. [Google Scholar]
- Cinti, D.; Tassi, F.; Procesi, M.; Brusca, L.; Cabassi, J.; Capecchiacci, F.; Delgado Huertas, A.; Galli, G.; Grassa, F.; Vaselli, O.; et al. Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Fluids from the Eastern Sector of the Sabatini Volcanic District (Central Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2017, 84, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arragoni, S.; Maggi, M.; Cianfarra, P.; Salvini, F. The Cenozoic Fold-and-Thrust Belt of Eastern Sardinia: Evidences from the Integration of Field Data with Numerically Balanced Geological Cross Section. Tectonics 2016, 35, 1404–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioni, R.; Laurenzi, M.A.; Sbrana, A.; Villa, I.M. 40-Ar/39-Ar Chronostratigraphy of the Initial Activity in the Sabatini Volcanic Complex (Italy). Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1993, 112, 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- De Rita, D.; Di Filippo, M.; Rosa, C. Structural Evolution of the Bracciano Volcano-Tectonic Depression, Sabatini Volcanic District, Italy. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1996, 110, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karner, D.B.; Marra, F.; Renne, P.R. The History of the Monti Sabatini and Alban Hills Volcanoes: Groundwork for Assessing Volcanic-Tectonic Hazards for Rome. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2001, 107, 185–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottili, G.; Palladino, D.M.; Marra, F.; Jicha, B.; Karner, D.B.; Renne, P. Geochronology of the Most Recent Activity in the Sabatini Volcanic District, Roman Province, Central Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 196, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rita, D.; Funiciello, R.; Corda, L.; Sposato, A.; Rossi, U. Volcanic Units. In Sabatini Volcanic Complex; Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche: Rome, Italy, 1993; pp. 33–79. [Google Scholar]
- Biasini, A.; Buonasorte, G.; Cicacci, S.; Fredi, P.; Lupia Palmieri, E. Geomorphological Characteristics. In Sabatini Volcanic Complex; 1993; pp. 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Mattias, P.P.; Ventriglia, U. La Regione Vulcanica Dei Monti Sabatini e Cimini. Mem. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1970, 9, 331–384. [Google Scholar]
- Capelli, G.; Mazza, R.; Gazzetti, C. Strumenti e Strategie per La Tutela e l’uso Compatibile Della Risorsa Idrica Nel Lazio; Pitagora Editrice: Bologna, Italy, 2005; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, C.; Bono, P.; Capelli, G. Schema Idrogeologico Dell’Italia Centrale. Mem. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1986, 35, 991–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Manca, F.; Viaroli, S.; Mazza, R. Hydrogeology of the Sabatini Volcanic District (Central Italy). J. Maps 2017, 13, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippi, F.M.; Sappa, G. The Simulation of Bracciano Lake (Central Italy) Levels Based on Hydrogeological Water Budget: A Tool for Lake Water Management When Climate Change and Anthropogenic Impacts Occur. Environ. Process. 2024, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, R.; La Vigna, F.; Alimonti, C. Evaluating the Available Regional Groundwater Resources Using the Distributed Hydrogeological Budget. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funiciello, R.; Mariotti, G.; Parotto, M.; Preite-Martinez, M.; Tecce, F.; Toneatti, R.; Turi, B. Geology, Mineralogy and Stable Isotope Geochemistry of the Cesano Geothermal Field (Sabatini Mts. Volcanic System, Northern Latium, Italy). Geothermics 1979, 8, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, P.; Florio, G.; Gasparini, P. Structural Model of the Northern Latium Volcanic Area Constrained by MT, Gravity and Aeromagnetic Data. Ann. Geophys. 1997, 40, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, P.; Funiciello, R.; Locardi, E.; Parotto, M. Volcanologic and Structural Study of the Cesano Geothermal Area (Rome, Italy). In Proceedings of the International Congress on Thermal Waters, Geothermal Energy and Volcanism of the Mediterranean Area, Proc. Geoth. Energy, Athens, Greece, 5–7 October 1976; pp. 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Doveri, M.; Lelli, M.; Marini, L.; Raco, B. Revision, Calibration, and Application of the Volume Method to Evaluate the Geothermal Potential of Some Recent Volcanic Areas of Latium, Italy. Geothermics 2010, 39, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, G.; Corsi, R.; Culivicchi, G.; Di Falco, R.; Fiordelisi, A.; Grassi, A.; Nardini, G.; Nencetti, G.F.; Tomei, B. Fluid Management of the Cesano Reservoir: Experimental Activity. In Proceedings of the 1st Turkish-Italian seminar on geothermal energy, Ankara and Kizildere, Turkey, 6–28 September 1982; pp. 143–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bono, P. Valutazione Preliminare Del Potenziale Geotermico Della Regione Lazio. Geol. Romana 1981, 20, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini, G.; Frondini, F.; Kerrick, D.M.; Rogie, J.; Parello, F.; Peruzzi, L.; Zanzari, A.R. Quantification of Deep CO2 Fluxes from Central Italy. Examples of Carbon Balance for Regional Aquifers and of Soil Diffuse Degassing. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minissale, A. Origin, Transport and Discharge of CO2 in Central Italy. Earth Sci. Rev. 2004, 66, 89–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, P.; Ferrara, G.C.; Masselli, L.; Pieretti, G. Hydrogeochemistry of the Region between Monte Amiata and Rome. Geothermics 1973, 2, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Aglio, M.; Duchi, V.; Minissale, A.; Guerrini, A.; Tremori, M. Hydrogeochemistry of the Volcanic District in the Tolfa and Sabatini Mountains in Central Italy. J. Hydrol. 1994, 154, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minissale, A.; Evans, W.C.; Magro, G.; Vaselli, O. Multiple Source Components in Gas Manifestations from North-Central Italy. Chem. Geol. 1997, 142, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frondini, F.; Caliro, S.; Cardellini, C.; Chiodini, G.; Morgantini, N. Carbon Dioxide Degassing and Thermal Energy Release in the Monte Amiata Volcanic-Geothermal Area (Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, D.; Procesi, M.; Tassi, F.; Montegrossi, G.; Sciarra, A.; Vaselli, O.; Quattrocchi, F. Fluid Geochemistry and Geothermometry in the Western Sector of the Sabatini Volcanic District and the Tolfa Mountains (Central Italy). Chem. Geol. 2011, 284, 160–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, U.; Latini, T. Le Strutture in Materiale Deperibile Coperte Dell’abitato Di Veio (RM) Dalla Prima Età Del Ferro All’Orientalizzante Medio. In Terra, Legno e Materiali Deperibili Nell’architettura Antica 1. L’età Preromana, Atti del Convegno internazionale di Studi (Padova, 3-5 Giugno 2021), Costruire nel Mondo Antico; Previato, C., Bonetto, J., Eds.; Edizioni Quasar: Rome, Italy, 2023; Volume 6, pp. 459–477. [Google Scholar]
- Tabolli, J.; Cerasuolo, O. VEII (Cities and Communities of the Etruscans); University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.D.B. Veii: The Valghetta Baths (‘Bagni Della Regina’). Pap. Br. Sch. Rome 1960, 28, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, G. Il Santuario Di Portonaccio a Veio; Giorgio Bretschneider Editore: Rome, Italy, 2002; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Liverani, P. Municipium Augustum Veiens: Veio in Età Imperiale Attraverso Gli Scavi Giorgi (1811–13); “L’Erma” di Bretschneider: Rome, Italy, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, U.; Latini, T. Nuovi Aggiornamenti Dal Sito Archeologico Di Campetti Sud-Ovest, a Veio (RM): L’organizzazione Dell’abitato Della Prima Età Del Ferro. In Preistoria e Protostoria in Etruria. Ipogei. La Vita, la Morte, i Culti nei Mondi Sotterranei. Ricerche e Scavi, Atti del XV Incontro di Studi (Valentano, 11–13 Settembre 2020); Negroni Catacchio, N., Metta, C., Gallo, V., Aspesi, M., Eds.; Centro Studi di Preistoria e Archeologia: Milano, Italy, 2022; pp. 763–778. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, U. The Thermo-Mineral Springs at Veii (RM) and Its Territory: New Discoveries and Old Excavations. In Rethinking the Concept of ‘Healing Settlements’: Water, Cults, Constructions and Contexts in the Ancient World; Archaeopress Roman Archeology: Rome, Italy, 2019; Volume 52, pp. 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, U. I Sistemi Di Smaltimento Delle Acque Nel Sito Di Campetti, Area S-O, a Veio (RM): Testimonianze Dall’età Arcaica All’età Imperiale. In I sistemi di Smaltimento delle Acque Nel Mondo Antico; Brunora, M., Magnani, S., Eds.; Editreg: Trieste, Italy, 2018; pp. 503–523. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, U. Il Sito Di Veio (RM) Dall’età Arcaica (VI Secolo a.C.) a Quella Imperiale (I-III Secolo d.C.): Evidenze, Interpretazioni Ed Ipotesi Sui Sistemi Di Approvvigionamento Idrico. In Proceedings of the L’Acqua e la Città in età Romana—Water and the Roman Cities and Settlements, Belluno, Italy, 3–4 November 2017; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, U. Scrizioni Votive Ad Ercole, Alle Fonti e a Diana Dal Sito Di Campetti a Veio: Ulteriori Elementi per l’interpretazione Archeologica. Rend. Atti Della Pontif. Accad. Romana Di Archeol. (Ser. III) 2009, 81, 443–500. [Google Scholar]
- Maggi, M.; Latini, T. Prime Evidenze Di Paleo-Circolazione Di Acque Idrotermali. In Proceedings of the Novità nella ricerca archeologica a Veio. Dagli studi di John Ward-Perkins alle ultime scoperte; 2015; pp. 45–78. [Google Scholar]
- Canina, L. L’Antica Città Di Veii. 1847. Available online: http://arachne.uni-koeln.de/Tei-Viewer/cgi-bin/teiviewer.php?manifest=BOOK-ZID195320 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Del Bon, A.; Sbarbati, C.; Brunetti, E.; Carucci, V.; Lacchini, A.; Marinelli, V.; Petitta, M. Groundwater flow and geochemical modeling of the Acque Albule thermal basin (Central Italy): A conceptual model for evaluating influences of human exploitation on flowpath and thermal resource availability. Cent. Eur. Geol. 2015, 58, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- U.S. EPA. EPA Method 3015A: Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Aqueous Samples and Extracts; EPA: Washinghton, DC, USA, 2007.
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; Water Resources Investigations Report 99-4259; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Cuoco, E.; Viaroli, S.; Paolucci, V.; Mazza, R.; Tedesco, D. Fe and As Geochemical Self-Removal Dynamics in Mineral Waters: Evidence from the Ferrarelle Groundwater System (Riardo Plain, Southern Italy). Env. Geochem Health 2022, 44, 2065–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaselli, O.; Nisi, B.; Rappuoli, D.; Bianchi, F.; Cabassi, J.; Venturi, S.; Tassi, F.; Raco, B. Geochemical Characterization of the Ground Waters from the Former Hg-Mining Area of Abbadia San Salvatore (Mt. Amiata, Central Italy): Criticalities and Perspectives for the Reclamation Process. Ital. J. Geosci. 2015, 134, 304–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuoco, E.; Verrengia, G.; De Francesco, S.; Tedesco, D. Hydrogeochemistry of Roccamonfina Volcano (Southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, B.; Cardellini, C.; Chiodini, G.; Frondini, F.; Marini, L.; Ottonello, G.; Vetuschi Zuccolini, M. Fluxes of Deep CO2 in the Volcanic Areas of Central-Southern Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 136, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammanco, S.; Valenza, M.; Pignato, S.; Giammanco, G. Mg, Mn, Fe, and V Concentrations in the Ground Waters of Mount Etna (Sicily). Water Res. 1996, 30, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroli, M.; Lancia, M.; Albano, M.; Casale, A.; Giovinco, G.; Petitta, M.; Zarlenga, F.; dell’Isola, M. A Hydrogeological Conceptual Model of the Suio Hydrothermal Area (Central Italy). Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1811–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conticelli, S.; Francalanci, L.; Manetti, P.; Raffaello, C.; Sbrana, A. Petrology and Geochemistry of the Ultrapotassic Rocks from the Sabatini Volcanic District, Central Italy: The Role of Evolutionary Processes in the Genesis of Variably Enriched Alkaline Magmas. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1997, 75, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teboul, P.-A.; Durlet, C.; Gaucher, E.C.; Virgone, A.; Girard, J.-P.; Curie, J.; Lopez, B.; Camoin, G.F. Origins of Elements Building Travertine and Tufa: New Perspectives Provided by Isotopic and Geochemical Tracers. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 334, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Guadagno, F.M. Karst Spring Discharges Analysis in Relation to Drought Periods, Using the SPI. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambi, C.; Mirabella, F.; Petitta, M.; Banzato, F.; Beddini, G.; Cardellini, C.; Fronzi, D.; Mastrorillo, L.; Tazioli, A.; Valigi, D. Reaction of the Carbonate Sibillini Mountains Basal Aquifer (Central Italy) to the Extensional 2016–2017 Seismic Sequence. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrorillo, L.; Viaroli, S.; Petitta, M. Co-Occurrence of Earthquake and Climatic Events on Groundwater Budget Alteration in a Fractured Carbonate Aquifer (Sibillini Mts.—Central Italy). Water 2023, 15, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facca, G.; Tonani, F. The Self-Sealing Geothermal Field. Bull. Volcanol. 1967, 30, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal Solute Equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca Geoindicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, M.; Rossetti, F.; Ranalli, G.; Theye, T. Feedback between Fluid Infiltration and Rheology along a Regional Ductile-to-Brittle Shear Zone: The East Tenda Shear Zone (Alpine Corsica). Tectonics 2014, 33, 253–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Paton, D.A.; Knipe, R.J.; Wu, K. A Review of Fault Sealing Behaviour and Its Evaluation in Siliciclastic Rocks. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuoco, E.; Darrah, T.H.; Buono, G.; Eymold, W.K.; Tedesco, D. Differentiating Natural and Anthropogenic Impacts on Water Quality in a Hydrothermal Coastal Aquifer (Mondragone Plain, Southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7115–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuoco, E.; Minissale, A.; Di Leo, A.M.; Tamburrino, S.; Iorio, M.; Tedesco, D. Fluid Geochemistry of the Mondragone Hydrothermal Systems (Southern Italy): Water and Gas Compositions vs. Geostructural Setting. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 106, 2429–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | Discharge (L/s) | T (°C) | pH | EC (µS/cm) | O2 (%) | O2 (mg/L) | TDS (mg/L) | ORP (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | 186 | 17.8 | 7.92 | 599 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| V2 | 250 | 22.7 | 7.81 | 1426 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| P1 | 100 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| S1 | ~1 | 24.5 | 6.98 | 3245 | 48.8 | 4.1 | 2.08 | 56 |
| S2 | ~1 | 28.8 | 6.2 | 2906 | 8.4 | 0.6 | 1.86 | 77 |
| S3 | ~1 | 28.8 | 6.46 | 3097 | 14.4 | 1.1 | 1.98 | 51 |
| ID | Calcite | Amorphous | Fluoro-Apatite | Goethite | Hematite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ON | x | x | |||
| TV | x | ||||
| XX | x | x | |||
| FR | x | x |
| ID | HCO3− | F− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | SIcalcite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | ||
| S1 | 1242 | 1.9 | 184 | 3 | 751 | 195 | 299 | 69 | 346 | 0.82 |
| S2 | 1356 | 1.7 | 190 | 0 | 926 | 218 | 348 | 74 | 380 | 0.41 |
| S3 | 1347 | 1.7 | 189 | 0 | 896 | 226 | 348 | 77 | 383 | 0.14 |
| ID | Li | B | Ti | Mn | Fe | As | Rb | Sr | Zr | Ba | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | µg/L | |
| S1 | 442 | 3407 | 5 | 1053 | 3793 | 41 | 300 | 3753 | 4 | 13 | 5 |
| S2 | 517 | 3749 | 4 | 1146 | 4213 | 41 | 342 | 4185 | 3 | 17 | 4 |
| S3 | 544 | 3998 | 4 | 1145 | 4043 | 42 | 344 | 5124 | 3 | 19 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viaroli, S.; Latini, T.; Cuoco, E.; Mormone, A.; Piochi, M.; Maggi, M. Geochemical Evolution in Historical Time of Thermal Mineral Springs at Campetti Southwest (Veii, Central Italy) through Geoarcheological Investigation. Water 2024, 16, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081113
Viaroli S, Latini T, Cuoco E, Mormone A, Piochi M, Maggi M. Geochemical Evolution in Historical Time of Thermal Mineral Springs at Campetti Southwest (Veii, Central Italy) through Geoarcheological Investigation. Water. 2024; 16(8):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081113
Chicago/Turabian StyleViaroli, Stefano, Tiziano Latini, Emilio Cuoco, Angela Mormone, Monica Piochi, and Matteo Maggi. 2024. "Geochemical Evolution in Historical Time of Thermal Mineral Springs at Campetti Southwest (Veii, Central Italy) through Geoarcheological Investigation" Water 16, no. 8: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081113
APA StyleViaroli, S., Latini, T., Cuoco, E., Mormone, A., Piochi, M., & Maggi, M. (2024). Geochemical Evolution in Historical Time of Thermal Mineral Springs at Campetti Southwest (Veii, Central Italy) through Geoarcheological Investigation. Water, 16(8), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081113








