Large-Scale Hydrological Models and Transboundary River Basins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study Basins
2.2. Large-Scale Hydrological Models and Data Sources
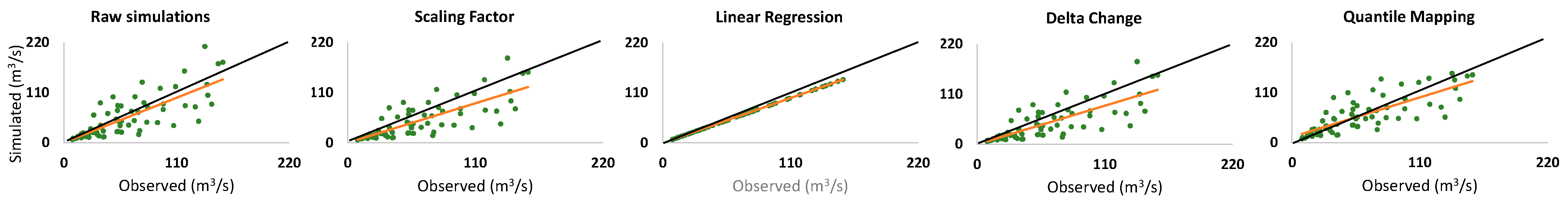
2.3. Bias Correction and Output Validation
3. Results
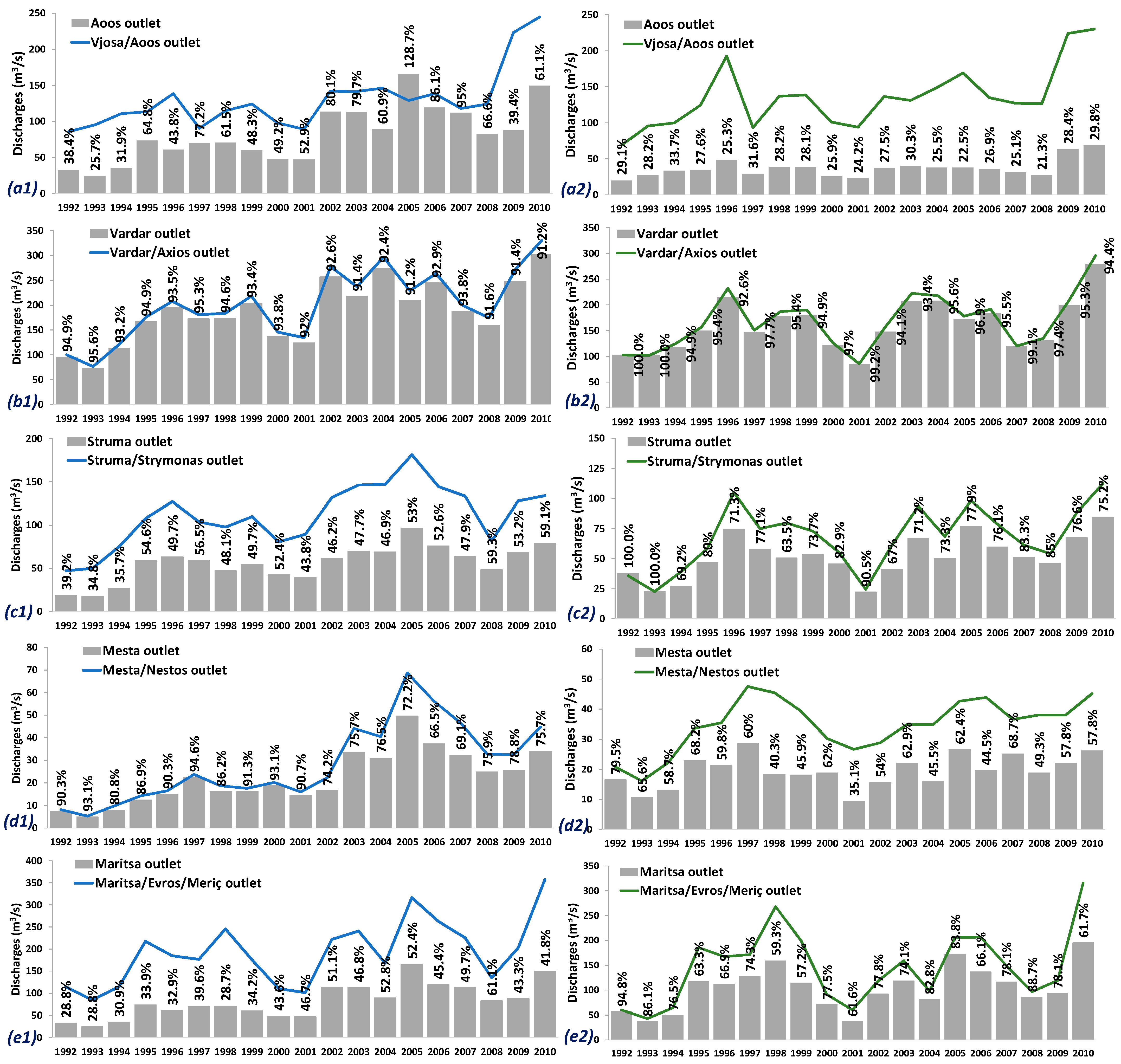
3.1. Upstream Waters’ Contribution to Total Discharges
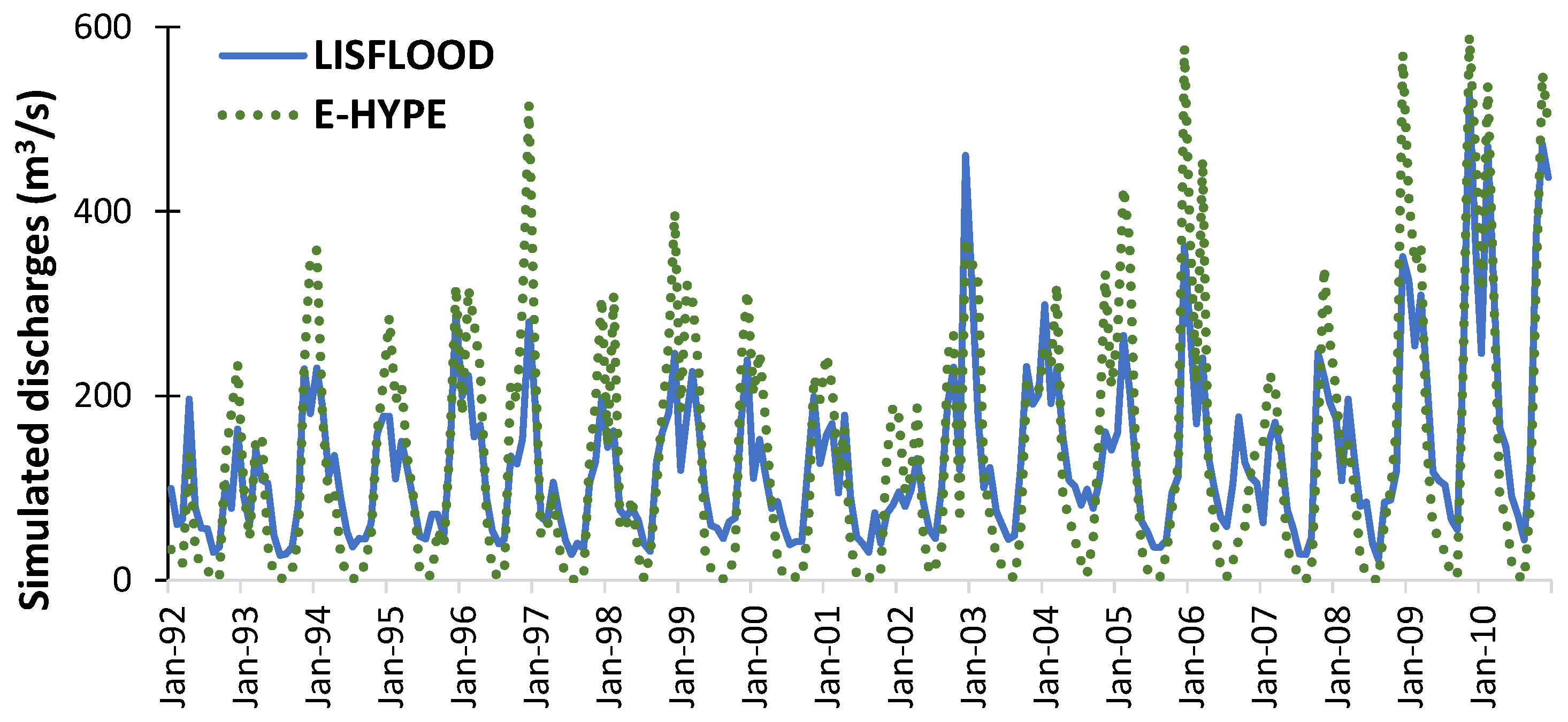
3.2. Basins’ Climatology and Transboundary Rivers Discharges per LSM
3.3. Bias-Corrected LSM Outflows and Comparison to Measurements
3.3.1. Vardar/Axios Basin
3.3.2. Mesta/Nestos Basin
3.3.3. Struma/Strymonas Basin
3.3.4. Maritsa/Evros/Meriç Basin
3.3.5. Vjosa/Aoos Basin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giordano, M.; Drieschova, A.; Duncan, J.A.; Sayama, Y.; De Stefano, L.; Wolf, A.T. A review of the evolution and state of transboundary freshwater treaties. Int. Environ. Agreem. Politics Law Econ. 2014, 14, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, Y. The hydro-political dilemma in Africa water geopolitics: The case of the Nile river basin. Afr. Secur. Rev. 2020, 30, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, T.; Böhmelt, T. International conflict and cooperation over freshwater resources. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, S.P.; Schmeier, S.; van Beek, R.; Gulpen, M. Projecting conflict risk in transboundary river basins by 2050 following different ambition scenarios. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2024, 40, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikaris, C.; Zafirakou, A. River Basin Management Plans as a tool for sustainable transboundary river basins’ management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14835–14848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe). United Nation Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes. 1992. Available online: https://unece.org/DAM/env/water/publications/WAT_Text/ECE_MP.WAT_41.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- UNEP-DHI; UNE. Transboundary River Basins: Status and Trends; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Skoulikaris, C.; Krestenitis, Y. Cloud Data Scraping for the Assessment of Outflows from Dammed Rivers in the EU. A Case Study in South Eastern Europe. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikaris, C.; Piliouras, M. Hydrological simulation of ungauged basins via forcing by large-scale hydrology models. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, A.M.; Mao, F.; Mendes, T.S.G.; Simões, S.J.C.; Balestieri, J.A.P.; Hannah, D.M. Estimation of River Flow Using CubeSats Remote Sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salat, J.; Pascual, J.; Flexas, M.; Chin, T.M.; Vazquez-Cuervo, J. Forty-five years of oceanographic and meteorological observations at a coastal station in the NW Mediterranean: A ground truth for satellite observations. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Wagener, T.; Tallaksen, L.; Engeland, K. Evaluation of nine large-scale hydrological models with respect to the seasonal runoff climatology in Europe. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archfield, S.A.; Clark, M.; Arheimer, B.; Hay, L.E.; McMillan, H.; Kiang, J.E.; Seibert, J.; Hakala, K.; Bock, A.; Wagener, T.; et al. Accelerating advances in continental domain hydrologic modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 10078–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffeldt, A.; Wetterhall, F.; Pappenberger, F.; Salamon, P.; Thielen, J. Technical review of large-scale hydrological models for implementation in operational flood forecasting schemes on continental level. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 75, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.C.M.; Pechlivanidis, I.G.; Gustafsson, D.; Donnelly, C.; Arheimer, B. Key factors for improving large-scale hydrological model performance. Eur. Water. 2015, 49, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Avesani, D.; Galletti, A.; Piccolroaz, S.; Bellin, A.; Majone, B. A dual-layer MPI continuous large-scale hydrological model including Human Systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 139, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivoni, E.R.; Mascaro, G.; Mniszewski, S.; Fasel, P.; Springer, E.P.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Bras, R.L. Real-world hydrologic assessment of a fully-distributed hydrological model in a parallel computing environment. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jia, Y.; Niu, C.; Su, H.; Wang, J.; Du, J.; Khaki, M.; Hu, P.; Liu, J. Development and validation of a physically-based, national-scale hydrological model in China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, H.K. A Review of Hydrologic Signatures and Their Applications. Wires Water 2021, 8, e1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, J.; Langaas, S. Water information: What is it good for? The use of information in transboundary water management. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2005, 5, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.B.; Kwon, H.H.; Han, D. Intercomparison of joint bias correction methods for precipitation and flow from a hydrological perspective. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Torre, D.; Di Marco, N.; Menapace, A.; Avesani, D.; Righetti, M.; Majone, B. Suitability of ERA5-Land reanalysis dataset for hydrological modelling in the Alpine region. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, M.T.; Shrestha, S.; Weesakul, S.; Shrestha, P.K. Multi-model climate change projections for Belu River Basin, Myanmar under representative concentration pathways. J. Earth Sci. Clim. Change 2016, 7, L323. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, D.W.; Cayan, D.R.; Maurer, E.P.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Hegewisch, K.C. Improved bias correction techniques for hydrological simulations of climate change. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 2421–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, U.; Srinivasan, G.; Agarwal, A. Assessment of rainfall bias correction techniques for improved hydrological simulation. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2386–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; Acharya, S.C.; Shrestha, P.K. Bias Correction of Climate Models for Hydrological Modelling—Are Simple Methods Still Useful? Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, T.; Dadson, S.; Buys, G.; Prudhomme, C. Bias correction of daily precipitation simulated by a regional climate model: A comparison of methods. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikaris, C.; Ganoulis, J.; Aureli, A. A critical review of the transboundary aquifers in South-Eastern Europe and new insights from the EU’s water framework directive implementation process. Water Int. 2021, 46, 1060–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe). Second Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters; United Nations Publications: Geneva, Switzerland; New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 428. ISBN 9789210549950. [Google Scholar]
- Skoulikaris, C. Transboundary Cooperation through Water Related EU Directives’ Implementation Process. The Case of Shared Waters between Bulgaria and Greece. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4977–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.; Andersson, J.C.; Arheimer, B. Using flow signatures and catchment similarities to evaluate the E-HYPE multi-basin model across Europe. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, G.; Pers, C.; Rosberg, J.; Strömqvist, J.; Arheimer, B. Development and testing of the HYPE (Hydrological Predictions for the Environment) water quality model for different spatial scales. Hydrol. Res. 2010, 41, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundecha, Y.; Arheimer, B.; Donnelly, C.; Pechlivanidis, I. A regional parameter estimation scheme for a pan-European multi-basin model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 6, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedon, G.P.; Balsamo, G.; Bellouin, N.; Gomes, S.; Best, M.J.; Viterbo, P. The WFDEI meteorological forcing data set: WATCH Forcing Data methodology applied to ERA-Interim reanalysis data. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7505–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Donnelly, C.; Gustafsson, D. Near-Real-Time Adjusted Reanalysis Forcing Data for Hydrology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikaris, C. Run-Of-River Small Hydropower Plants as Hydro-Resilience Assets against Climate Change. Sustainability 2021, 13, 14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, J.; Bartholmes, J.; Ramos, M.-H.; De Roo, A. The European flood alert system–part 1: Concept and development. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roo, A.P.J.; Wesseling, C.G.; van Deursen, W.P.A. Physically based river basin modelling within a GIS: The LISFLOOD model. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Knijff, J.M.; Younis, J.; De Roo, A.P.J. LISFLOOD: A GIS-based distributed model for river basin scale water balance and flood simulation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntegeka, V.; Salamon, P.; Gomes, G.; Sint, H.; Lorini, V.; Thielen, J. EFAS-Meteo: A European Daily High-Resolution Gridded Meteorological Data Set for 1990–2011; JRC Technical Reports; EUR 26408; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cantoni, E.; Tramblay, Y.; Grimaldi, S.; Salamon, P.; Dakhlaoui, H.; Dezetter, A.; Thiemig, V. Hydrological performance of the ERA5 reanalysis for flood modeling in Tunisia with the LISFLOOD and GR4J models. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, S.J.; van Lanen, H.A.J. Catchment memory explains hydrological drought forecast performance. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dottori, F.; Mentaschi, L.; Bianchi, A.; Alfieri, L.; Feyen, L. Cost-effective adaptation strategies to rising river flood risk in Europe. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 13, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigiak, O.; Lutz, S.; Mentzafou, A.; Chiogna, G.; Tuo, Y.; Majone, B.; Beck, H.; de Roo, A.; Malagó, A.; Bouraoui, F.; et al. Uncertainty of modelled flow regime for flow-ecological assessment in Southern Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1028–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Azariadi, T. Overview of the River Basin Management Plans Developed in Greece Under the Context of the Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC Focusing on the Economic Analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 3149–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Special Secretariat for Water (SSW). The River Basin Management Plan of Thrace Water District (GR11); Ministry of Environment and Energy: Athens, Greece, 2013; (In Greek with Extended English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Fekete, B.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Lammers, R.B. Scaling gridded river networks for macroscale hydrology: Development, analysis, and control of error. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Xu, Z.; Lv, M.; Huang, X. Assessment of Runoff Components Simulated by GLDAS against UNH–GRDC Dataset at Global and Hemispheric Scales. Water 2018, 10, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali Shahrood, A.; Ahrari, A.; Rossi, P.M.; Klöve, B.; Torabi Haghighi, A. RiTiCE: River Flow Timing Characteristics and Extremes in the Arctic Region. Water 2023, 15, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.; Maathuis, B.; Hein-Griggs, D.; Alvarado-Gamboa, L.-F. Performance Evaluation of Bias Correction Methods for Climate Change Monthly Precipitation Projections over Costa Rica. Water 2020, 12, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.; Park, C.; Yoon, J.; Kim, J. Interpretation of mean-field bias correction of radar rain rate using the concept of linear regression. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5081–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, R.; Krapp, M.; Manica, A. An empirical evaluation of bias correction methods for palaeoclimate simulations. Clim. Past 2020, 16, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Zhang, C.; Wen, Z.; Park, E.; Jakada, H. Climate variability impacts on runoff projection under quantile mapping bias correction in the support CMIP6: An investigation in Lushi basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikaris, C.; Venetsanou, P.; Lazoglou, G.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Voudouris, K. Spatio-Temporal Interpolation and Bias Correction Ordering Analysis for Hydrological Simulations: An Assessment on a Mountainous River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, D.; Rodrigues, L.N. Goodness-of-Fit Criteria for Hydrological Models: Model Calibration and Performance Assessment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.P.; Fase, F. Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Sabater, J. ERA5-Land Monthly Averaged Data from 1950 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/10.24381/cds.68d2bb30?tab=overview (accessed on 21 January 2024).
- Ganoulis, J.; Skoulikaris, C. Impact of Climate Change on Hydropower Generation and Irrigation: A Case Study from Greece. In NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Knapp, H.V.; Arnold, J.G.; Demissie, M. Hydrological modeling of the Iroquois river watershed using HSPF and SWAT 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzafou, A.; Dimitriou, E.; Papadopoulos, A. Long-Term Hydrologic Trends in the Main Greek Rivers: A Statistical Approach. In Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 59, pp. 129–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zajac, Z.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Salamon, P.; Burek, P.; Gentile, A.; Bianchi, A. Calibration of the LISFLOOD Hydrological Model for Europe; JRC Technical Report JRC87717; Joint Research Centre: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, A.T.; Yoffe, S.B.; Giordano, M. International waters: Identifying basins at risk. Water Policy 2003, 5, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munia, H.A.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; Mirumachi, N.; Wada, Y.; Kummu, M. How downstream sub-basins depend on upstream inflows to avoid scarcity: Typology and global analysis of transboundary rivers. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2795–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, L.; Petersen-Perlman, J.D.; Sproles, E.A.; Eynard, J.; Wolf, A.T. Assessment of transboundary river basins for potential hydro-political tensions. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 45, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, L.; Duncan, J.; Dinar, S.; Stahl, K.; Strzepek, K.M.; Wolf, A.T. Climate change and the institutional resilience of international river basins. Peace Res. 2012, 49, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffrey, S. The International Law Commission’s flawed Draft Articles on the Law of Transboundary Aquifers: The way forward. Water Int. 2011, 36, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikaris, C. Toponyms: A neglected asset within the water framework and flood directives implementation process; the case study of Greece. Acta Geophys. 2023, 71, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| River Basin | Countries in Basin | Population 4 | Area (km2) | Area (%) per Country | Mean Elevation (m) | River Length (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maritsa/Evros/Meriç | Bulgaria | 2,037,865 | 35,230 | 65.9 | 579 | 310 |
| Greece | 144,285 | 3685 | 6.9 | 175 | 208 | |
| Turkey | N/A | 14,560 | 27.2 | 600 | 283 1 | |
| Basin’s total | 2,182,150 | 53,475 | 100% | 471 | 801 | |
| Mesta/Nestos | Bulgaria | 130,583 | 2785 | 49.6 | 1225 | 125 |
| Greece | 45,082 | 2834 | 50.4 | 606 | 130 | |
| Basin’s total | 175,665 | 5619 | 100% | 916 | 255 | |
| Struma/Strymonas 2 | Bulgaria | 416,133 | 8545 | 48.9 | 900 | 290 |
| Greece | 384,151 | 7282 | 41.7 | 863 | 110 | |
| North Macedonia | 124,079 | 1648 | 9.4 | 863 | 81 | |
| Basin’s total | 924,363 | 17,475 | 100% | 875 | 481 | |
| Vardar/Axios 3 | North Macedonia | 1,462,366 | 19,737 | 88.7 | 1124 | 302 |
| Greece | 210,138 | 2513 | 11.3 | 180 | 87 | |
| Basin’s total | 1,772,504 | 22,250 | 100% | 652 | 389 | |
| Vjosa/Aoos | Greece | 20,127 | 2154 | 33.0 | 885 | 70 |
| Albania | 239,349 | 4365 | 67.0 | 800 | 190 | |
| Basin’s total | 259,473 | 6519 | 100% | 843 | 260 | |
| LISFLOOD Model | E-HYPE Model | RBMPs and Literature | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runoff (m3/s) | Percentage (%) | Runoff (m3/s) | Percentage (%) | Runoff (m3/s) | Percentage (%) | ||
| Vjosa/Aoos | bor 1 | 81.85 | 63.04 | 36.87 | 27.21 | 34.47 | 16.90 |
| out 2 | 129.85 | 135.48 | 204.10 | ||||
| Vardar/Axios | bor | 187.02 | 92.84 | 160.59 | 95.77 | 107.34 | 80.88 |
| out | 201.44 | 167.68 | 132.71 | ||||
| Struma/Strymonas | bor | 55.7 | 49.97 | 51.75 | 76.52 | 65.16 | 65.19 |
| out | 111.46 | 67.63 | 99.95 | ||||
| Mesta/Nestos | bor | 22.08 | 77.95 | 19.41 | 55.86 | 27.20 | 54.36 |
| out | 28.33 | 34.75 | 50.04 | ||||
| Maritsa/Evros/Meriç | bor | 81.85 | 42.53 | 103.72 | 70.92 | 224.60 | 84.12 |
| out | 192.45 | 146.24 | 267.00 | ||||
| Statistic Measures | LISFLOOD Raw Data | SF | LR | DC | QM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.349 | 0.349 | 1.000 | 0.349 | 0.342 |
| NSE | −0.657 | 0.111 | 0.423 | 0.274 | 0.183 |
| PBIAS | 54.678 | 20.068 | 54.678 | 3.295 | −0.355 |
| KGE | 0.259 | 0.544 | 0.403 | 0.566 | 0.584 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 118.176 | 86.537 | 69.707 | 78.202 | 82.992 |
| Statistic Measures | E-HYPE Raw Data | SF | LR | DC | QM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.595 | 0.595 | 1.000 | 0.595 | 0.594 |
| NSE | 0.268 | 0.497 | 0.797 | 0.548 | 0.551 |
| PBIAS | 33.028 | 16.409 | 33.028 | −16.068 | −0.503 |
| KGE | 0.574 | 0.719 | 0.649 | 0.605 | 0.769 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 78.532 | 65.139 | 41.412 | 61.717 | 61.496 |
| Statistic Measures | LISFLOOD Raw Data | SF | LR | DC | QM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.353 | 0.353 | 1.000 | 0.353 | 0.357 |
| NSE | 0.301 | 0.138 | 0.664 | 0.250 | 0.203 |
| PBIAS | −12.499 | 16.723 | −12.499 | −23.436 | −0.201 |
| KGE | 0.507 | 0.561 | 0.431 | 0.418 | 0.597 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 18.654 | 20.711 | 12.924 | 19.311 | 19.907 |
| Statistic Measures | E-HYPE Raw Data | SF | LR | DC | QM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.473 | 0.473 | 1.000 | 0.473 | 0.501 |
| NSE | 0.308 | 0.312 | 0.772 | −2.311 | 0.420 |
| PBIAS | −23.653 | −18.679 | −23.653 | 68.611 | −0.099 |
| KGE | 0.604 | 0.636 | 0.574 | −0.312 | 0.708 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 19.051 | 18.992 | 10.938 | 41.665 | 17.444 |
| Statistic Measures | E-HYPE Raw Data | SF | LR | DC | QM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.619 | 0.619 | 1.000 | 0.619 | 0.629 |
| NSE | 0.472 | 0.475 | 0.965 | 0.476 | 0.589 |
| PBIAS | −10.381 | −21.153 | −10.381 | −23.046 | −0.151 |
| KGE | 0.726 | 0.700 | 0.852 | 0.685 | 0.793 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 28.951 | 28.887 | 7.448 | 29.126 | 25.567 |
| Statistic Measures | E-HYPE Raw Data | SF | LR | DC | QM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.714 | 0.714 | 1.000 | 0.714 | 0.749 |
| NSE | 0.444 | 0.438 | 0.737 | −1.396 | 0.741 |
| PBIAS | −36.689 | −37.449 | −36.689 | 37.964 | 0.983 |
| KGE | 0.602 | 0.595 | 0.616 | −0.273 | 0.856 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 52.499 | 52.791 | 36.097 | 109.005 | 35.816 |
| Basin | Model | Min 1 | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max 2 | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vardar/Axios | Obs. | 51.72 | 92.39 | 117.64 | 147.26 | 165.63 | 121.01 | |
| LISFLOOD | Raw | 76.49 | 160.26 | 199.68 | 250.54 | 330.36 | 201.44 | |
| LR | 134.44 | 165.39 | 184.61 | 207.15 | 221.13 | 187.17 | ||
| QM | 45.06 | 90.09 | 116.04 | 151.52 | 215.61 | 120.58 | ||
| E-HYPE | Raw | 85.72 | 125.38 | 157.45 | 200.52 | 295.77 | 167.68 | |
| LR | 70.02 | 93.97 | 113.88 | 141.67 | 201.68 | 121.01 | ||
| QM | 59.07 | 86.75 | 110.18 | 148.75 | 239.10 | 122.73 | ||
| Mesta/Nestos | Obs. | 10.22 | 22.97 | 29.97 | 39.26 | 51.06 | 30.64 | |
| LISFLOOD | Raw | 5.26 | 16.25 | 22.32 | 42.31 | 68.71 | 28.33 | |
| LR | 17.39 | 23.07 | 26.18 | 30.32 | 35.58 | 26.48 | ||
| QM | 7.54 | 15.10 | 30.86 | 40.44 | 59.72 | 29.28 | ||
| E-HYPE | Raw | 16.07 | 29.52 | 35.44 | 41.00 | 47.55 | 34.75 | |
| LR | 10.25 | 18.48 | 23.01 | 29.01 | 36.63 | 23.44 | ||
| QM | 21.66 | 26.71 | 30.48 | 33.61 | 42.33 | 30.46 | ||
| Struma/Strymonas | Obs. | 53.23 | 54.90 | 60.22 | 66.73 | 78.27 | 59.10 | |
| E-HYPE | Raw | 22.66 | 54.67 | 68.53 | 84.00 | 112.46 | 67.63 | |
| LR | 47.71 | 49.21 | 53.97 | 59.78 | 70.11 | 52.97 | ||
| QM | 48.53 | 56.71 | 60.29 | 62.42 | 66.32 | 59.01 | ||
| Maritsa/Evros/ Meriç | Obs. | 141.62 | 90.33 | 80.69 | 121.22 | 65.70 | 66.72 | |
| E-HYPE | Raw | 42.93 | 93.85 | 148.95 | 192.51 | 315.88 | 146.24 | |
| LR | 100.15 | 56.29 | 48.05 | 82.71 | 35.22 | 36.10 | ||
| QM | 113.40 | 98.46 | 82.03 | 124.57 | 71.36 | 82.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skoulikaris, C. Large-Scale Hydrological Models and Transboundary River Basins. Water 2024, 16, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060878
Skoulikaris C. Large-Scale Hydrological Models and Transboundary River Basins. Water. 2024; 16(6):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060878
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkoulikaris, Charalampos. 2024. "Large-Scale Hydrological Models and Transboundary River Basins" Water 16, no. 6: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060878
APA StyleSkoulikaris, C. (2024). Large-Scale Hydrological Models and Transboundary River Basins. Water, 16(6), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060878








