Analyzing the Effect of Sewer Network Size on Optimization Algorithms’ Performance in Sewer System Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sewer Network Hydraulic Optimization
2.2. Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm (GWO)
2.3. Cuckoo Search Algorithm (CS) via Lévy Flight
- Cuckoos produce one egg per egg laying and lay their eggs in a randomly selected nest;
- The characteristics of the best nests with high quality eggs are passed on to the next generation;
- The number of existing host nests where the egg is laid is fixed. The host bird of the nest may notice the egg laid by the cuckoo with probability p ∈ [0, 1]. In this case, the host bird can throw the egg out of the nest or can leave the nest and build a new one.
2.4. Application
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Euzébio, T.A.M.; Ramirez, M.A.P.; Reinecke, S.F.; Hampel, U. Energy Price as an Input to Fuzzy Wastewater Level Control in Pump Storage Operation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 93701–93712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchionni, V.; Lopes, N.; Mamouros, L.; Covas, D. Modelling Sewer Systems Costs with Multiple Linear Regression. Water Resour Manag. 2014, 28, 4415–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, D.; Marenjak, S.; Šperac, M. Estimating Maintenance Costs of Sewer System. Buildings 2023, 13, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Mehndiratta, S.L.; Khanna, P. Gravity Wastewater Collection Systems Optimization. J. Environ. Eng. 1983, 109, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A.; Bakhshipour, A.E. Optimization of Sewer Networks Using an Adaptive Genetic Algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3441–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-C.; Kao, J.-J. GA-QP Model to Optimize Sewer System Design. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navin, P.K.; Mathur, Y.P. Design Optimization of Sewer System Using Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of Fifth International Conference on Soft Computing for Problem Solving. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2016, 437, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R.; Afshar, M.H. Arc Based Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Optimal Design of Gravitational Sewer Networks. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, 8, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsie, M.; Wu, M.-Y.; Huang, C.Y. Optimal Urban Sewer Layout Design Using Steiner Tree Problems. Eng. Optim. 2019, 51, 1980–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, N.; Duque, D.; Aguilar, A.; Saldarriaga, J. Sewer Network Layout Selection and Hydraulic Design Using a Mathematical Optimization Framework. Water 2020, 12, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.W.; Yen, B.C. Optimal Cost Design of Branched Sewer Systems. Water Resour. Res. 1975, 12, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.Y.; Thompson, R.G.; Young, D.M. Optimising the Design of Sewer Networks Using Genetic Algorithms and Tabu Search. Engineering. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2004, 11, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.H. Application of a Genetic Algorithm to Storm Sewer Network Optimization. Sci. Iran. 2006, 13, 234–244. [Google Scholar]
- Afshar, M.H.; Afshar, A.; Mariño, M.A.; Darbandi, A.A.S. Hydrograph-based Storm Sewer Design Optimization by Genetic Algorithm. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 33, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.H. A Parameter Free Continuous Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for the Optimal Design of Storm Sewer Networks: Constrained and Unconstrained Approach. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2010, 41, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karovic, O.; Mays, L.W. Sewer System Design Using Simulated Annealing in Excel. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4551–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, N.; Duque, D.; Saldarriaga, J. A New Methodology for The Optimal Design of Series of Pipes in Sewer Systems. J. Hydroinformatics 2016, 18, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, T.; Yurdusev, M.A. Genetic Algorithm for Networks with Dynamic Mutation Rate. Gradevinar 2017, 69, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Villiers, N.; Van Rooyen, G.C.; Middendorf, M. Sewer Network Design: Heuristic Algorithm for Hydraulic Optimisation. J. S. Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2017, 59, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zaheri, M.M.; Ghanbari, R.; Afshar, M.H. A Two-Phase Simulation–Optimization Cellular Automata Method for Sewer Network Design Optimization. Eng. Optim. 2020, 52, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, A.F.; Graveto, V.M. Optimal Layout of Sewer Systems: A Deterministic Versus a Stochastic Model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A. Loop-by-Loop Cutting Algorithm to Generate Layouts for Urban Drainage Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.P.W.; Costa, L.H.M.; Farias, G.M.; Castro, M.A.H. A Depth-First Search Algorithm for Optimizing the Gravity Pipe Networks Layout. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4583–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.E.; Bacak-Turan, G.; Cetin, T.; Aslan, E. Feasible Sanitary Sewer Network Generation Using Graph Theory. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8527180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.H.; Attea, Z.H.; Mohammed, S.S. Optimum Layout Design of Sewer Networks by Hybrid Genetic Algorithm. J. Appl. Water Eng. Res. 2020, 8, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, I.; Snasel, V.; Abraham, A. Handbook of Optimization from Classical to Modern Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No Free Lunch Theorems for Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.H. Rebirthing Genetic Algorithm for Storm Sewer Network Design. Sci. Iran. A 2012, 19, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Walters, G.A.; Khu, S.T.; Keedwell, E. A Novel Cellular Automata Based Approach to Storm Sewer Design. Eng. Optim. 2007, 39, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.H.; Shahidi, M.; Rohania, M.; Sargolzaei, M. Application of Cellular Automata to Sewer Network Optimization Problems. Sci. Iran. A 2011, 18, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, M.; Afshar, M.H. Sewer Networks Optimization Using Cellular Automata. Stud. Eng. Technol. 2014, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moeini, R.; Afshar, M.H. Constrained Ant Colony Optimisation Algorithm for the Layout and Size Optimisation of Sanitary Sewer Networks. Urban Water J. 2013, 10, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R.; Afshar, M.H. Sewer Network Design Optimization Problem Using Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm and Tree Growing Algorithm. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2013, 227, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R. Ant Intelligent Applied to Sewer Network Design Optimization Problem: Using Four Different Algorithms. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.H. Rebirthing Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm: Application to Storm Water Network Design. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2008, 35, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Lu, H. An Integrated Model of Water Resources Optimization Allocation Based on Projection Pursuit Model–Grey Wolf Optimization Method in A Transboundary River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, M.; Ji, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, M.; Faiz, M.A.; Ali, S.; Li, T.; Cui, S.; Khan, M.I. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics Analysis of Water Resource System Resilience in Irrigation Areas Based on A Support Vector Machine Model Optimized by The Modified Gray Wolf Algorithm. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 125758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhamarine, Y.; Souag-Gamane, D.; Ahmed, A.N.; Kisi, O.; El-Shafie, A. Improving Artificial Intelligence Models Accuracy for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting Using Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO) Algorithm. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.-P.; Sun, M.; Xie, J. Multi-Step-Ahead Forecast of Reservoir Water Availability with Improved Quantum-Based GWO Coupled with the AI-Based LSSVM Model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 125769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushangar, K.; Nouri, A.; Shahnazi, S.; Md Azamathulla, H. Towards Design of Compound Channels with Minimum Overall Cost Through Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm. J. Hydroinformatics 2021, 23, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, F.; Masoumzadeh, S.; Zafari, N.; Skardi, M.J.E. Optimum Sanitary Sewer Network Design Using Shuffled Gray Wolf Optimizer. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2021, 12, 04021055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, B.; Chang, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S. Optimal Operation of Multi-Reservoir System Based-On Cuckoo Search Algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 5671–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangrang, A.; Pakoktom, W.; Nuannukul, W.; Chaleeraktrakoon, C. Adaptive Reservoir Rule Curves by Optimisation and Simulation. Water Manag. 2017, 170, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Leng, G.; Cheng, L.; Fang, W.; Li, P. A Nature-Based Reservoir Optimization Model for Resolving the Conflict in Human Water Demand and Riverine Ecosystem Protection. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donyaii, A.R. Evaluation of Climate Change Impacts on the Optimal Operation of Multipurpose Reservoir Systems Using Cuckoo Search Algorithm. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, R.; Zecchin, A.C.; Zheng, F.; Talatahari, S. A Hybrid Cuckoo–Harmony Search Algorithm for Optimal Design of Water Distribution Systems. J. Hydroinformatics 2016, 18, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankaj, B.S.; Naidu, M.N.; Vasan, A.; Varma, M.R.R. Self-Adaptive Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Optimal Design of Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3129–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, A.; Rajua, K.S.; Pankaj, B.S. Fuzzy Optimization-Based Water Distribution Network Design Using Self-Adaptive Cuckoo Search Algorithm. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Nong, X.; Tan, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, B.; Hu, N. Daily Water Quality Forecast of the South-To-North Water Diversion Project of China Based on the Cuckoo Search-Back Propagation Neural Network. Water 2018, 10, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komasi, M.; Sharghi, S.; Safavi, H.R. Wavelet and Cuckoo Search-Support Vector Machine Conjugation for Drought Forecasting Using Standardized Precipitation Index (Case Study: Urmia Lake, Iran). J. Hydroinformatics 2018, 20, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, T.; Turan, M.E. Kanalizasyon Şebekesi Optimizasyonunda Popülasyon Boyutunun Guguk Kuşu Arama Algoritmasi Üzerine Etkileri [Effects of Population Size on Cuckoo Search Algorithm in Sewer Network Optimization]. In Proceedings of the III International Congress of Applied Sciences, Karabagh, Azerbaijan, 7–10 June 2022; Volume I, pp. 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Melià, D.; Gutiérrez-Bahamondes, J.H.; Iglesias-Rey, P.L.; Martínez-Solano, F.J. Efficiency Criteria as a Solution to the Uncertainty in the Choice of Population Size in Population-Based Algorithms Applied to Water Network Optimization. Water 2016, 8, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chen, D. Prediction Model of Service Life for Tunnel Structures in Carbonation Environments by Genetic Programming. Geomech. Eng. 2019, 18, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuea, Y.; Liub, W.; Wang, Q.; Bu, F. Development of An Integrated Approach for The Inverse Design of Built Environment by A Fast Fluid Dynamics-based Generic Algorithm. Build. Environ. 2019, 160, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palod, N.; Prasad, V.; Khare, R. Non-Parametric Optimization Technique for Water Distribution in Pipe Networks. Water Supply 2020, 20, 3068–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, A.P.; Napiorkowski, J.J.; Piotrowska, A.E. Population Size in Particle Swarm Optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2020, 58, 100718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Grey Wolf Optimizer: A Review of Recent Variants and Applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, N.; Singh, U.; Sohi, B.S. Modified Grey Wolf Optimizer for Global Engineering Optimization. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2016, 2016, 7950348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.A.M.; Patri, S.R. An Enhanced Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm with Improved Exploration Ability for Analog Circuit Design Automation. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2018, 26, 2605–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Heidari, A.A.; Faris, H. Grey Wolf Optimizer: Theory, Literature Review, and Application in Computational Fluid Dynamics Problems. In Nature-Inspired Optimizers. Studies in Computational Intelligence; Mirjalili, S., Song Dong, J., Lewis, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Jiao, J.; Liang, X.; Cai, S.; Xu, M. A Random Opposition-Based Learning Grey Wolf Optimizer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 113810–113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, L.; Castillo, O.; Soria, J.; Melin, P.; Valdez, F.; Gonzalez, C.I.; Martinez, G.E.; Soto, J. A Fuzzy Hierarchical Operator in The Grey Wolf Optimizer Algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 57, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Mirjalili, S.M. Evolutionary Population Dynamics and Grey Wolf Optimizer. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 26, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ming, Z. An Optimized Grey Wolf Optimizer Based on A Mutation Operator and Eliminating-Reconstructing Mechanism and Its Application. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2017, 18, 1705–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.A.; Pahlavani, P. An Efficient Modified Grey Wolf Optimizer with Lévy Flight for Optimization Tasks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 60, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Wu, T.; Cai, S.; Liang, X.; Jiao, J.; Xu, M. A Novel Grey Wolf Optimizer Algorithm with Refraction Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 57805–57819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.-M.; Zhao, J. An Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm with Variable Weights. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 2981282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, W.; Cai, S.; Jiao, J.; Tang, M. An Efficient and Robust Grey Wolf Optimizer Algorithm for Large-Scale Numerical Optimization. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 997–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, K.; Masdari, M.; Gharehchopogh, F.S.; Saneifard, R. A Chaotic and Hybrid Gray Wolf-Whale Algorithm for Solving Continuous Optimization Problems. Prog. Artif. Intell. 2021, 10, 349–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Taghian, S.; Mirjalili, S. An Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer for Solving Engineering Problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, Z.; Du, C. Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm and Application. Sensors 2022, 22, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Bansal, J.C. Mutation-Driven Grey Wolf Optimizer with Modified Search Mechanism. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 194, 116450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, N.; Snasel, V.; Mirjalili, S. Dynamic Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm for Truss Optimization Under Natural Frequency Constraints. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 16188–16208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S.; Deb, S. Cuckoo Search via Lévy flights. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Nature & Biologically Inspired Computing (NaBIC), Coimbatore, India, 9–11 December 2009; pp. 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichelvam, M.K.; Prabaharan, T.; Yang, X.S. Improved Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Hybrid Flow Shop Scheduling Problems to Minimize Makespan. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 19, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R.; Afshar, M.H. Layout and Size Optimization of Sanitary Sewer Network Using Intelligent Ants. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 51, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
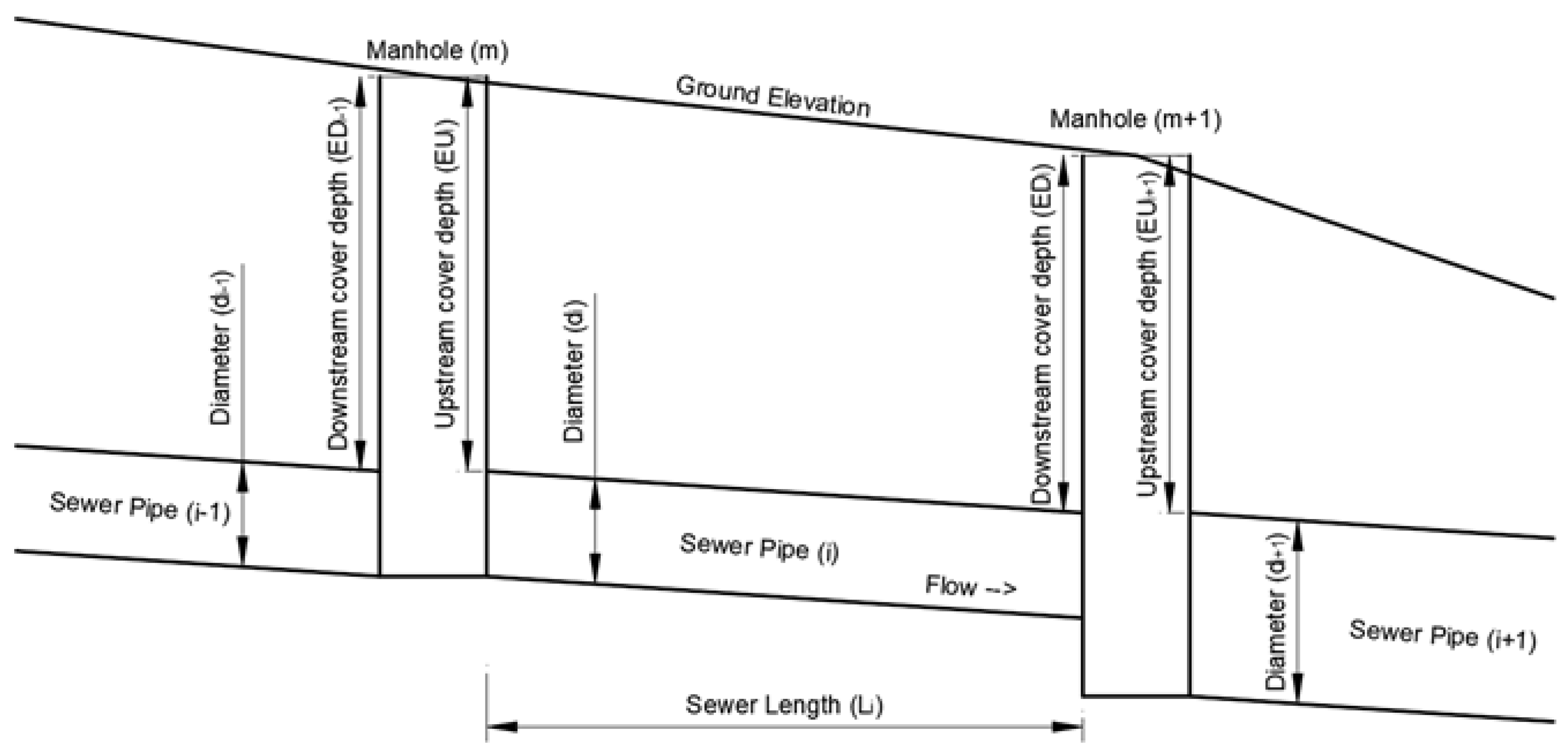


| Pipe lengths L (m) | 100 |
| Minimum velocity (m/s) | 0.75 |
| Maximum velocity (m/s) | 6 |
| Minimum allowable relative flow | 0.10 |
| Maximum allowable relative flow | 0.83 |
| Minimum slope | 0.0005 |
| Minimum cover depth (m) | 2.5 |
| Maximum cover depth (m) | 10 |
| Manning coefficient n | 0.013 |
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 550 | 600 | 650 |
| 700 | 750 | 800 | 850 | 900 | 950 | 1000 | 1100 | 1200 | 1300 | 1400 | 1500 |
| d1 | EU1 | ED1 | … | … | … | EUl | EDl |
| Average Rankings Achieved by Friedman Test | Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Sum of Ranks | CS-500 vs. | p-Value |
| GWO_V1-50 | 9.966667 (10) | GWO_V1-50 | 0.003609 |
| GWO_V1-100 | 9.600000 (8) | GWO_V1-100 | 0.008730 |
| GWO_V1-200 | 7.666667 (3) | GWO_V1-200 | 0.298944 |
| GWO_V1-500 | 8.466667 (6) | GWO_V1-500 | 0.245190 |
| GWO_V2-50 | 14.400000 (17) | GWO_V2-50 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V2-100 | 14.733333 (19) | GWO_V2-100 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V2-200 | 14.633333 (18) | GWO_V2-200 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V2-500 | 14.933333 (20) | GWO_V2-500 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V3-50 | 11.766667 (14) | GWO_V3-50 | 0.000014 |
| GWO_V3-100 | 10.333333 (11) | GWO_V3-100 | 0.000125 |
| GWO_V3-200 | 11.500000 (12) | GWO_V3-200 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V3-500 | 12.800000 (16) | GWO_V3-500 | 0.000031 |
| GWO_V4-50 | 8.366667 (5) | GWO_V4-50 | 0.110926 |
| GWO_V4-100 | 11.600000 (13) | GWO_V4-100 | 0.000241 |
| GWO_V4-200 | 9.666667 (9) | GWO_V4-200 | 0.000831 |
| GWO_V4-500 | 9.400000 (7) | GWO_V4-500 | 0.012453 |
| CS-50 | 11.933333 (15) | CS-50 | 0.000023 |
| CS-100 | 8.050000 (4) | CS-100 | 0.001953 |
| CS-200 | 5.850000 (2) | CS-200 | 0.125000 |
| CS-500 | 4.333333 (1) | ||
| Average Rankings Achieved by Friedman Test | Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Sum of Ranks | GWO_V2-50 vs. | p-Value |
| GWO_V1-50 | 8.933333 (11) | GWO_V1-50 | 0.071903 |
| GWO_V1-100 | 10.366667 (16) | GWO_V1-100 | 0.015658 |
| GWO_V1-200 | 9.466667 (14) | GWO_V1-200 | 0.013194 |
| GWO_V1-500 | 7.866667 (4) | GWO_V1-500 | 0.614315 |
| GWO_V2-50 | 6.300000 (1) | GWO_V2-100 | 0.360039 |
| GWO_V2-100 | 7.200000 (2) | GWO_V2-200 | 0.040702 |
| GWO_V2-200 | 8.900000 (10) | GWO_V2-500 | 0.328571 |
| GWO_V2-500 | 7.500000 (3) | GWO_V3-50 | 0.130592 |
| GWO_V3-50 | 8.633333 (9) | GWO_V3-100 | 0.097772 |
| GWO_V3-100 | 8.200000 (5) | GWO_V3-200 | 0.012453 |
| GWO_V3-200 | 9.600000 (15) | GWO_V3-500 | 0.152861 |
| GWO_V3-500 | 8.500000(8) | GWO_V4-50 | 0.082206 |
| GWO_V4-50 | 8.433333 (7) | GWO_V4-100 | 0.035009 |
| GWO_V4-100 | 9.033333 (12) | GWO_V4-200 | 0.047162 |
| GWO_V4-200 | 8.233333 (6) | GWO_V4-500 | 0.047162 |
| GWO_V4-500 | 9.033333 (13) | CS-50 | 0.000002 |
| CS-50 | 18.783333 (19) | CS-100 | 0.000002 |
| CS-100 | 19.300000 (20) | CS-200 | 0.000002 |
| CS-200 | 18.366667 (18) | CS-500 | 0.000002 |
| CS-500 | 17.350000 (17) | ||
| Average Rankings Achieved by Friedman Test | Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Sum of Ranks | CS-50 vs. | p-Value |
| GWO_V1-50 | 16.000000 (17) | GWO_V1-50 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V1-100 | 16.800000 (18) | GWO_V1-100 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V1-200 | 18.066667 (19) | GWO_V1-200 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V1-500 | 19.333333 (20) | GWO_V1-500 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V2-50 | 4.566667 (2) | GWO_V2-50 | 0.000332 |
| GWO_V2-100 | 5.633333 (3) | GWO_V2-100 | 0.000028 |
| GWO_V2-200 | 6.066667 (4) | GWO_V2-200 | 0.000016 |
| GWO_V2-500 | 8.266667 (9) | GWO_V2-500 | 0.000003 |
| GWO_V3-50 | 6.266667 (5) | GWO_V3-50 | 0.000005 |
| GWO_V3-100 | 7.533333 (7) | GWO_V3-100 | 0.000007 |
| GWO_V3-200 | 7.633333 (8) | GWO_V3-200 | 0.000006 |
| GWO_V3-500 | 11.566667 (13) | GWO_V3-500 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V4-50 | 10.233333 (10) | GWO_V4-50 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V4-100 | 11.166667 (11) | GWO_V4-100 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V4-200 | 11.800000 (14) | GWO_V4-200 | 0.000002 |
| GWO_V4-500 | 14.933333 (16) | GWO_V4-500 | 0.000002 |
| CS-50 | 1.900000 (1) | CS-100 | 0.000012 |
| CS-100 | 6.433333 (6) | CS-200 | 0.000003 |
| CS-200 | 11.166667 (12) | CS-500 | 0.000002 |
| CS-500 | 14.633333 (15) | ||
| Model | Cost | Optimality Gap (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
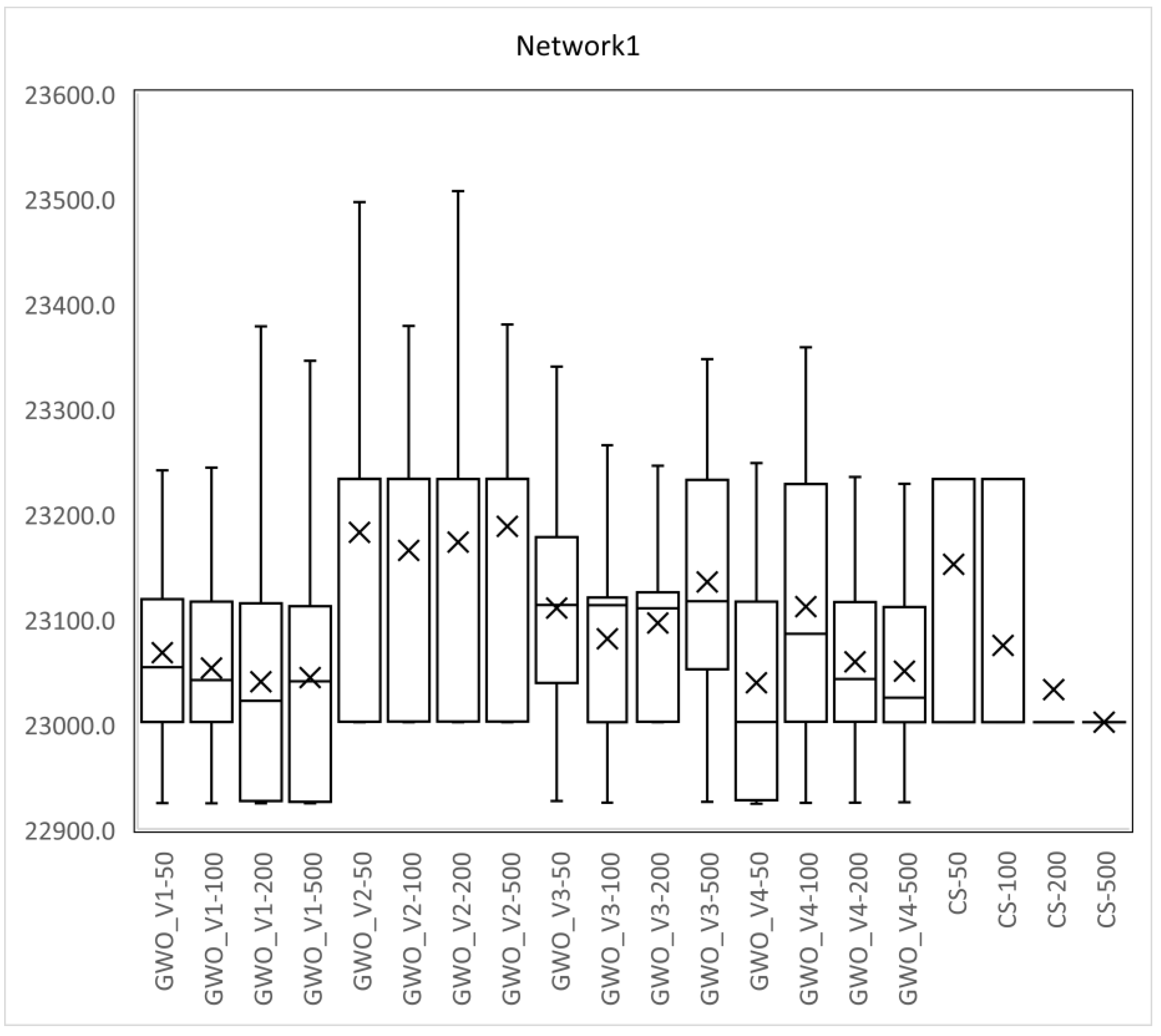
| Network1 Small-sized Network | CABACOATGA3 (Moeini and Afshar [8]) | 23,467.8 | |
| GWO_V1 | 22,924.4 | −2.32 | |
| GWO_V2 | 23,001.7 | −1.99 | |
| GWO_V3 | 22,925.0 | −2.31 | |
| GWO_V4 | 22,925.4 | −2.31 | |
| CS | 23,001.7 | −1.99 | |
| Network2 Medium-sized Network | CABACOATGA3 (Moeini and Afshar [8]) | 85,957.6 | |
| GWO_V1 | 85,033.4 | −1.08 | |
| GWO_V2 | 85,023.0 | −1.09 | |
| GWO_V3 | 84,730.3 | −1.43 | |
| GWO_V4 | 85,024.1 | −1.09 | |
| CS | 88,041.1 | 2.42 | |
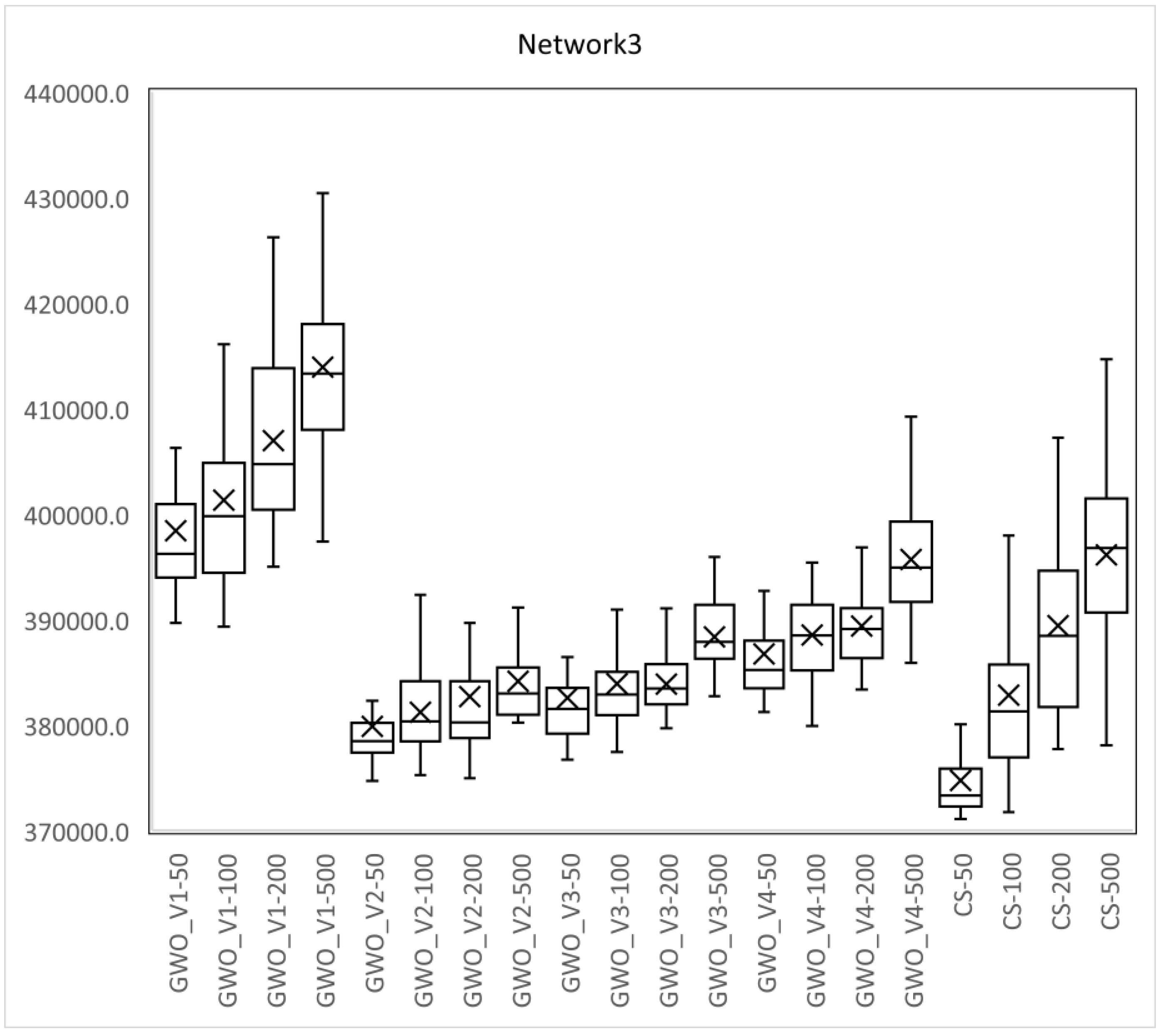
| Network3 Large-sized Network | CABACOATGA2 (Moeini and Afshar [8]) | 361,919.0 | |
| GWO_V1 | 389,667.5 | 7.67 | |
| GWO_V2 | 374,692.6 | 3.53 | |
| GWO_V3 | 379,684.0 | 4.91 | |
| GWO_V4 | 381,227.8 | 5.34 | |
| CS | 371,082.5 | 2.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turan, M.E.; Cetin, T. Analyzing the Effect of Sewer Network Size on Optimization Algorithms’ Performance in Sewer System Optimization. Water 2024, 16, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060859
Turan ME, Cetin T. Analyzing the Effect of Sewer Network Size on Optimization Algorithms’ Performance in Sewer System Optimization. Water. 2024; 16(6):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060859
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuran, Mustafa Erkan, and Tulin Cetin. 2024. "Analyzing the Effect of Sewer Network Size on Optimization Algorithms’ Performance in Sewer System Optimization" Water 16, no. 6: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060859
APA StyleTuran, M. E., & Cetin, T. (2024). Analyzing the Effect of Sewer Network Size on Optimization Algorithms’ Performance in Sewer System Optimization. Water, 16(6), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060859





