Assessing the Impact of Weirs on Water Quality and Phytoplankton Dynamics in the South Han River: A Two-Year Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Period
2.2. Water Analysis
2.3. Phytoplankton Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
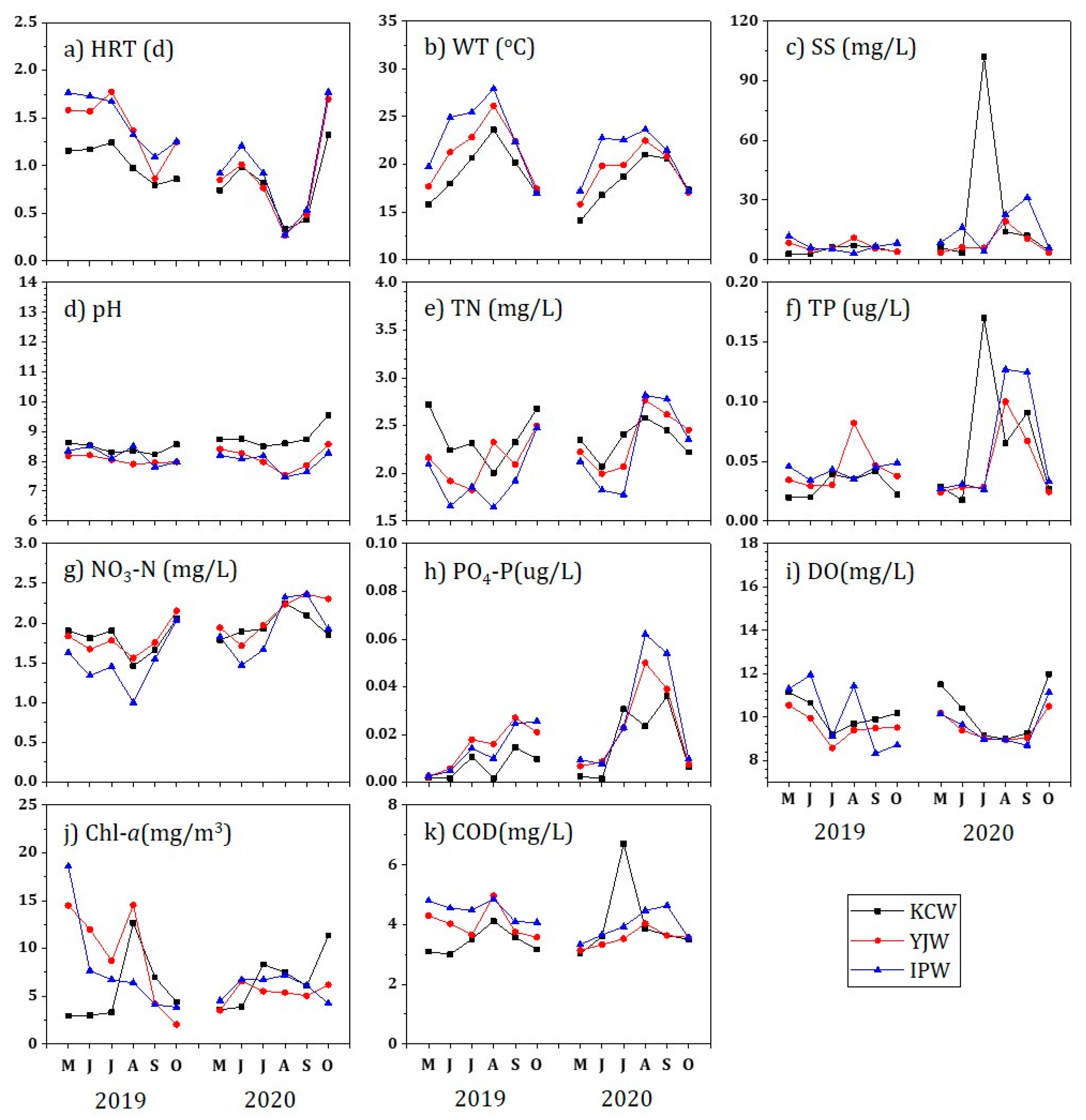
3.1. Water Environment at Three Weirs
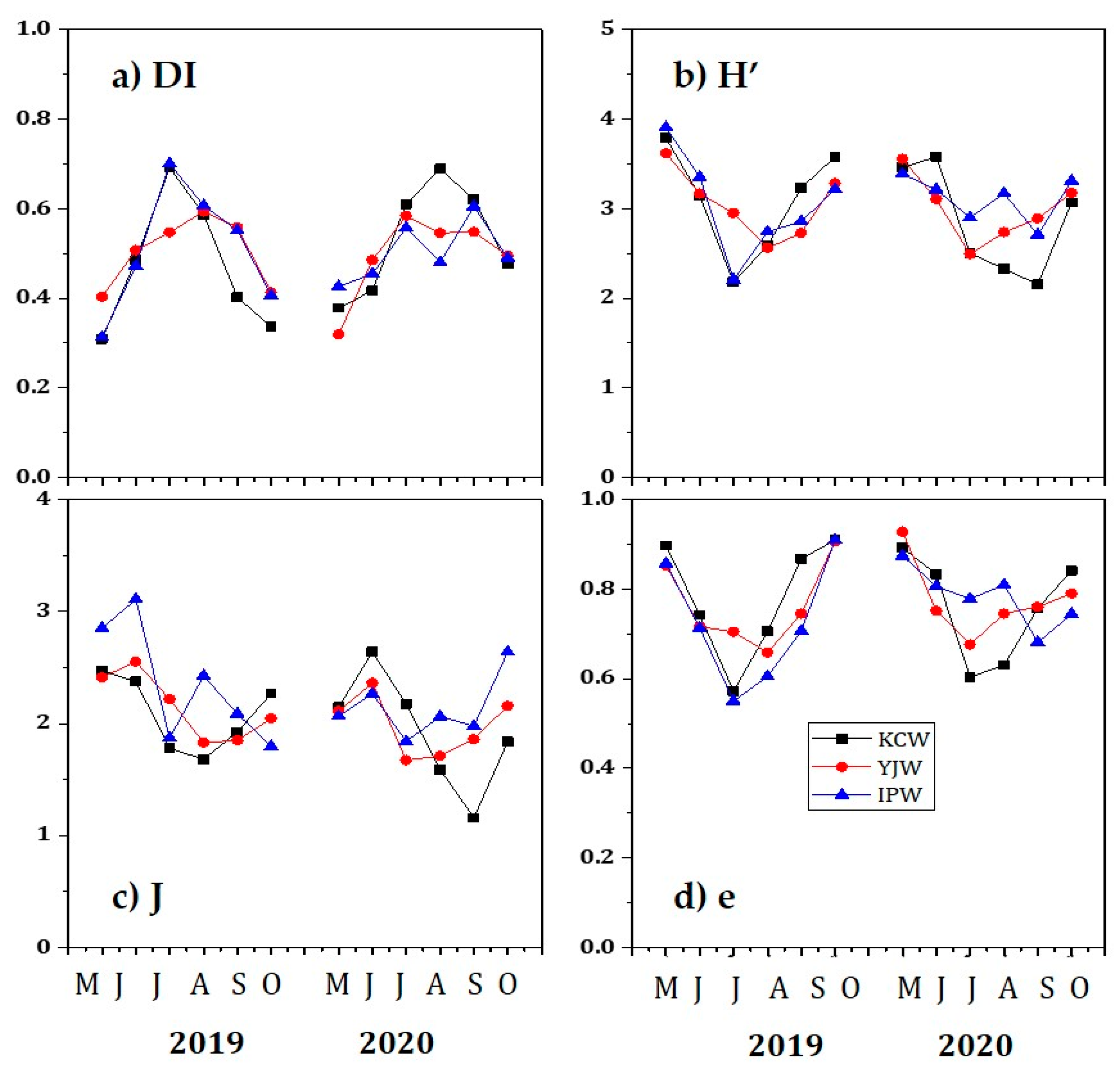
3.2. Phytoplankton Abundance and Community Dynamics
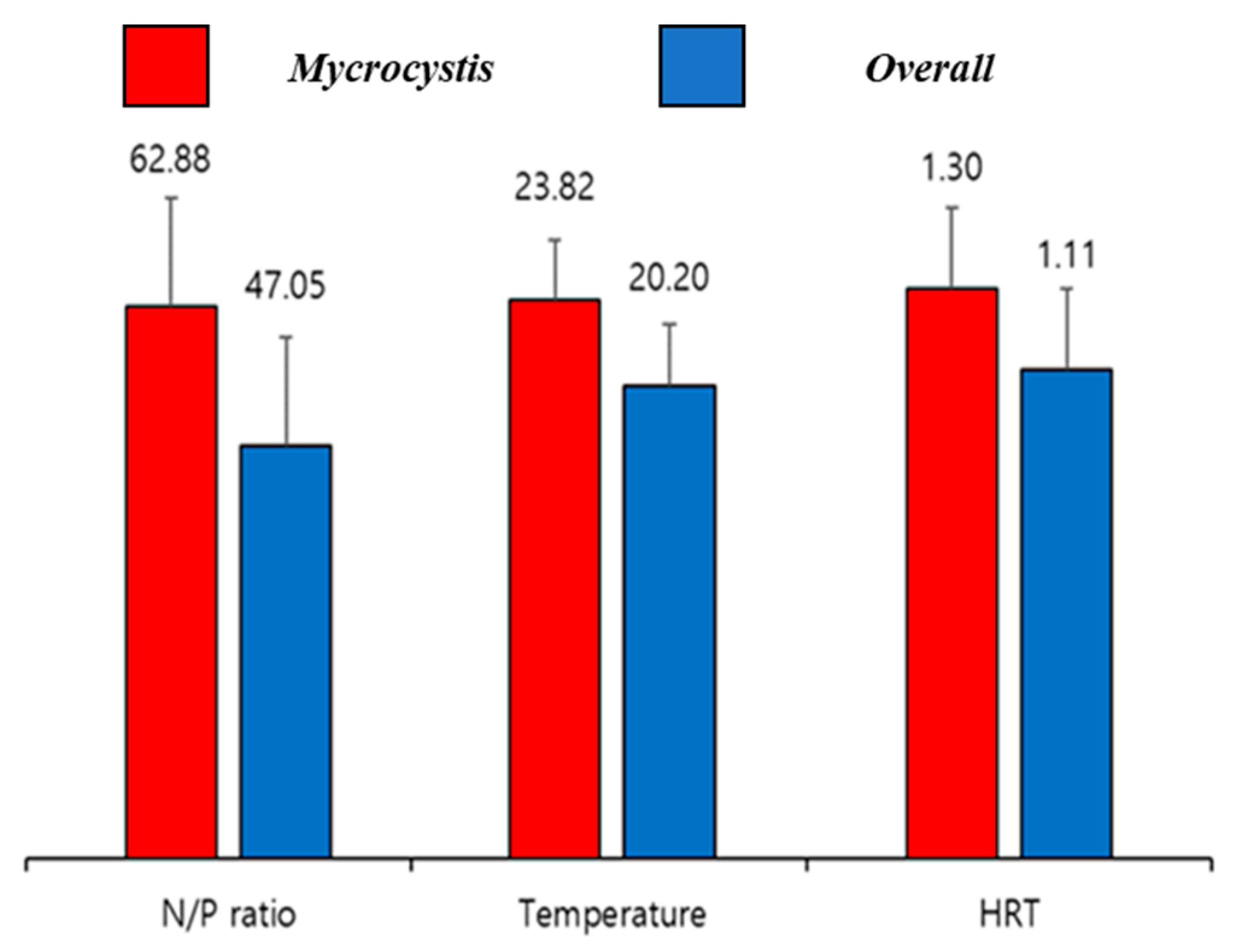
3.3. Environmental Influences on Phytoplankton Dynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baxter, R.M. Environmental effects of dams and impoundments. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1977, 8, 255–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhar, S.; Sendzimir, J.; Jungwirth, M.; Hohensinner, S. Restoration in integrated river basin management. In Riverine Ecosystem Management: Science for Governing towards a Sustainable Future; Schmutz, S., Sendzimir, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 273–299. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Yuan, S.; Cao, H. Theory and practice of hydrodynamic reconstruction in plain river networks. Engineering 2023, 24, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.S. Water quality modeling of the eutrophic transition zone in a river-type reservoir Paldang. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2014, 30, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, H.K.; Byeon, M.S.; Choi, M.J.; Kim, Y.J. The effect factors on the growth of phytoplankton and the sources of organic matters in downstream of Namhan-River. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2008, 24, 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, M.W.; Stanley, E.H.; Orr, C.H.; Selle, A.R.; Sethi, S.A.; Harbor, J.M. Stream ecosystem response to small dam removal: Lessons from the Heartland. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E.; Gurnell, A.M. Dams and geomorphology: Research progress and future directions. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V.; Stanford, J.A. The serial discontinuity concept: Extending the model to floodplain rivers. Regul. Rivers Res. MGMT 1995, 10, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Jacobson, R.B.; Poff, N.L.; Rathburn, S.L.; Walters, D.M.; Wilcox, A.C. The natural sediment regime in rivers: Broadening the foundation for ecosystem management. BioScience 2015, 65, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, B.D.; Braun, D.P.; Mendelson, M.A.; Master, L.L. Threats to imperiled freshwater fauna. Conserv. Biol. 1997, 11, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, C.M.; Naiman, R.J.; Bretschko, G.; Karr, J.R.; Oswood, M.W.; Webster, J.R.; Welcomme, R.L.; Winterbourn, M.J. Patch dynamics in lotic systems: The stream as a mosaic. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1988, 7, 503–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.R.; Infante, D.M.; Wehrly, K.E.; Wang, L.; Brenden, T.O. Identifying indicators and quantifying large-scale effects of dams on fishes. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humborg, C.; Ittekkot, V.; Cociasu, A.; Bodungen, B. Effect of Danube River dam on Black Sea biogeochemistry and ecosystem structure. Nature 1997, 386, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, M.B.; Finn, J.T.; Booke, H.E. Stream flow regulation and fish community structure. Ecology 1998, 69, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Ward, J.V. Implications of streamflow variability and predictability for lotic community structure: A regional analysis of streamflow patterns. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, V.J. Influence of reservoirs on solute transport: A regional-scale approach. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Fang, F.; Gao, X.; Long, M. Responses of phytoplankton diversity to physical disturbance under manual operation in a large reservoir, China. Hydrobiologia 2012, 684, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouterfas, R.; Belkoura, M.; Dauta, A. Light and temperature effects on the growth rate of three freshwater algae isolated from a eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 2002, 489, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Webster, I.T.; Revill, A.T.; Kenyon, R.A.; Whittle, M.; Curwen, G. Controls on phytoplankton productivity in a wet–dry tropical estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chu, Z.; Du, Y.; Hou, Z.; Wang, S. Phytoplankton dynamics and their relationship with environmental variables of Lake Poyang. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázár, A.N.; Wade, A.J.; Whitehead, P.G.; Neal, C.; Loewenthal, M. Reconciling observed and modelled phytoplankton dynamics in a major lowland UK river, the Thames. Hydrol. Res. 2012, 43, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lai, S.; Gao, X.; Xu, L. Potential impacts of climate change on water quality in a shallow reservoir in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 14971–14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Seo, D.; Jones, J.R. Harmful algal bloom dynamics in a tidal river influenced by hydraulic control structures. Ecol. Modell. 2022, 467, 109931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Jun, K.S. Flood Level Mitigation Effect of River Dredging. Korean Soc. Civ. Eng. 2010, 2, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Pringle, C. What is hydrologic connectivity and why is it ecologically important? Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, W.-Y.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.-W.; Cheng, B.-X.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wu, Z.-H.; Qing, J.; Sun, G.; et al. Impact of low-head dam removal on river morphology and habitat suitability in mountainous rivers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymore, A.S.; Ward, A.S.; Wohl, E.; Harvey, J.W. Viewing river corridors through the lens of critical zone science. Front. Water. 2023, 5, 1147561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.H.; Jung, I.I.; Han, H.J. Climate Change Impact Assessment and Adaptation Strategy on Water Resources in the Han River Basin. Gyunggi Nondan 2007, 9, 95–115. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D. Four Major South Korea’s Rivers Using Deep Learning Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Chung, Y.R.; Suh, E.H.; Song, W.W. Eutrophication of Nakdong River and statistical analysis of environmental factors. Algae 2002, 17, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.S. Evaluation of Chungju Lake Water Quality Using SWAT and CE-QUAL-W2 Model. Master’s Thesis, Konkuk University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S., III; Moisander, P.H.; Dyble, J. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 76–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, A.; Kaplan, A. Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems: A comprehensive outlook on current and emerging mitigation and control approaches. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Whalen, J.K.; Cai, C.; Shan, K.; Zhou, H. Harmful cyanobacteria-diatom/dinoflagellate blooms and their cyanotoxins in freshwaters: A nonnegligible chronic health and ecological hazard. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.M.; Oliver, R.L.; Rees, C.; Bowling, L.C.; Buckney, R.T. Critical flow velocities for the growth and dominance of Anabaena circinalis in some turbid freshwater rivers. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.K.; Oh, S.E.; Chun, S.H.; Ahn, H.K. Study on change of algae occurrence before & after Gangcheon and Ipoh weir construction at Namhan River. J. Wetl. Res. 2016, 18, 394–400. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Feng, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Daily samples revealing shift in phytoplankton community and its environmental drivers during summer in Qinhuangdao coastal area, China. Water 2022, 14, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Torres, O.; de Anda, J.; Lugo-Melchor, O.Y.; Pacheco, A.; Orozco-Nunnelly, D.A.; Shear, H.; Senés-Guerrero, C.; Gradilla-Hernández, M.S. Rapid changes in the phytoplankton community of a subtropical, shallow, hypereutrophic lake during the rainy season. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 617151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangolte, I.; Lévy, M.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Clayton, S.; Jahn, O. Plankton community response to fronts: Winners and losers. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; p. 1220. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. In Siij3wasserfiora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1986; Volume 2/1, p. 876. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. In Siij3wasserfiora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1988; Volume 2/2, p. 596. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. In Siij3wasserfiora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1991; Volume 2/3, p. 576. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. Teil: Achnanthaceae. Kritische Erganzungen zu Navicula (Lineolatae) und Gomphonema. In Susswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gartner, G., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1988; Volume 2/4, p. 437. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, H.; Akiyama, M.; Ioriya, T.; Imahori, K.; Kasaki, H.; Kumano, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Takahashi, E.; Tsumura, K.; Hirano, M.; et al. Illustration of the Japanese Freshwater Algae; Uchida Rokakuho Publishing Co.: Tokyo, Japan, 1977; p. 932. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi, T.; Akiyama, M. Photomicrographs of the Freshwater Algae; Uchida Rokakuho Publishing Co.: Tokyo, Japan, 1984; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J. Illustration of the Korea Freshwater Algae; Academic Publishing Co., Ltd.: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1993; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, G.W. How to Know the Freshwater Algae; W.M.C. Company Publishers: Dubuque, IA, USA, 1964; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton, S.J. Relationship among functional properties of California grassland. Nature 1967, 216, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weiner, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Margalef, R. Information theory in biology. Gen. Syst. Yearb. 1958, 3, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, B.; Mefford, M.J. PC-ORD Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data, Version 4; MjM Software Design: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Vodopianova, V.V.; Bulavina, A.S. Effects of climate change on chlorophyll a in the Barents Sea: A long-term assessment. Biology 2023, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaliar, A.; Pandya, U. Assessment of cyanobacterial chlorophyll a as an indicator of water quality in two wetlands using multi-temporal Sentinel-2 images. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, D. Both dissolved oxygen and chlorophyll explain the large-scale longitudinal variation of deep scattering layers in the tropical Pacific Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 782032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Z.; Wang, T.; Huang, R.; Yi, X.; Zhang, D.; Beardall, J.; Hutchins, D.A.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z.; et al. Enhancement of diatom growth and phytoplankton productivity with reduced O2 availability is moderated by rising CO2. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zennaro, F.; Furlan, E.; Canu, D.; Alcazar, L.A.; Rosati, G.; Solidoro, C.; Aslan, S.; Critto, A. Venice lagoon chlorophyll-a evaluation under climate change conditions: A hybrid water quality machine learning and biogeochemical-based framework. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Alcazar, L.A.; Rosati, G.; Solidoro, C.; Aslan, S.; Critto, A. Impacts of environmental variables on a phytoplankton community: A case study of the tributaries of a subtropical river, Southern China. Water 2018, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, T.; Ma, W.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H. Effects of rainfall patterns on water quality in a stratified reservoir subject to eutrophication: Implications for management. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Mishra, R.K.; Sahu, K.C.; Lotliker, A.A.; Panda, U.S.; Mishra, P. Monsoonal influence and variability of water quality, phytoplankton abundance in the tropical coastal waters–A multivariate statistical approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Campbell, L.; Yin, K.; McDonald, K.S. Tropical cyclones: What are their impacts on phytoplankton ecology? J. Plankton Res. 2023, 45, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, M.M.; Somlyai, I.; Berta, C.; Bácsi, I.; Al-Tayawi, A.N.; Al-Ahmady, K.K.; Mohammed, R.H.; Alalami, O.; Grigorszky, I. The impacts of land use and seasonal effects on phytoplankton taxa and physical-chemical variables in the Tigris River within the City of Mosul. Water 2023, 15, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.; Eum, J.; Jung, S.; Choi, Y.; Owen, J.S.; Kim, B. Export of non-point source suspended sediment, nitrogen, and phosphorus from sloping highland agricultural fields in the East Asian monsoon region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-C.; Im, J.-K.; Han, J.; Kim, S.-H.; Kang, T.; Lee, S. Comprehensive water quality assessment using Korean water quality indices and multivariate statistical techniques for sustainable water management of the Paldang reservoir, South Korea. Water 2023, 15, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Sung, J.W.; Kim, T.-H.; Cho, H.-M.; Kim, J.; Park, H.J. Comparative seasonality of phytoplankton community in two contrasting temperate estuaries on the western coast of Korea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1257904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Youn, S.-H.; Oh, H.J.; Joo, H.-T.; Kim, Y.; Kang, J.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.; Jang, H.K.; Jo, N.; et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of phytoplankton community in relation to environmental factors in the southern coastal waters of Korea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 950234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boss, E.S.; Halsey, K.H. Phytoplankton community structuring and succession in a competition-neutral resource landscape. ISME Commun. 2021, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Miki, T.; Ye, H.; Souissi, S.; Adrian, R.; Anneville, O.; Agasild, H.; Ban, S.; Beeri-Shlevin, Y.; Chiang, Y.R.; et al. Causal networks of phytoplankton diversity and abundance are modulated by environmental context. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs, M.E.; Mori, C.; Dlugosch, L. Complex interactions between aquatic organisms and their chemical environment elucidated from different perspectives. In YOUMARES 9–The Oceans: Our Research, Our Future; Jungblut, S., Liebich, V., Bode-Dalby, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loerracher, A.K.; Schmidt, J.; Ebke, P.; Schmolke, A.; Abi-Akar, F.; Galic, N.; Ashauer, R. Characterization of patterns and variability in the dynamics of outdoor aquatic mesocosms: Exploring the capabilities and challenges in data supporting aquatic system models. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 782–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Lara-Gutiérrez, J.; Stocker, R. Environmental fluctuations and their effects on microbial communities, populations and individuals. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuaa068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lim, J.H.; Chun, Y.; Nayna, O.K.; Begum, M.S.; Park, J.H. Phytoplankton nutrient use and CO2 dynamics responding to long-term changes in riverine N and P availability. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, M.; Li, N.; Zhao, H.; Yang Pu, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, S.; Qin, X.; Dong, K.; Li, M.; et al. Effects of environmental factors on mycoplankton diversity and trophic modes in coastal surface water. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, W.; Núria, B.; Brown Lee, E.; Death, R.G.; Durance, I.; Gray, C.; Hladyz, S.; Ledger, M.E.; Milner, A.M.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. The effects of climatic fluctuations and extreme events on running water ecosystems. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2016, 371, 20150274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, H.; Kim, B.-H. The effect of monsoon rainfall patterns on epilithic diatom communities in the Hantangang River, Korea. Water 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Pinheiro, M.M.; Temponi Santos, B.L.; Vieira Dantas Filho, J.; Perez Pedroti, V.; Cavali, J.; Brito Dos Santos, R.; Oliveira Carreira Nishiyama, A.C.; Guedes, E.A.C.; de Vargas Schons, S. First monitoring of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in freshwater from fish farms in Rondônia state, Brazil. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Tian, Y.; Xue, J. Effect of land use and environmental variables on phytoplankton community structure in high-elevation river, upper Yangtze River, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1084461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.L.; Cunha, C.J.; Lima, M.O.; Sousa, E.B.; Costa-Tavares, V.B.; Martinelli-Lemos, J.M. Biodiversity and interannual variation of cyanobacteria density in an estuary of the Brazilian Amazon. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2021, 93, e20191452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Xiao, R.; Gao, G.; Yin, B.; Liang, S.; Lv, X. Influence of a heavy rainfall event on nutrients and phytoplankton dynamics in a well-mixed semi-enclosed bay. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jargal, N.; An, K.-G. Seasonal and interannual responses of blue-green algal taxa and chlorophyll to a monsoon climate, flow regimes, and N:P ratios in a temperate drinking-water reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y. The effects of temperature and nutrient ratios on Microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China: An 11-year investigation. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, T.; Vidussi, F.; Mas, S.; Parin, D.; Simier, M.; Mostajir, B. Water temperature drives phytoplankton blooms in coastal waters. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Zhu, Y.; Andersen, T.; Andersen, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Lu, J.; Song, Y.; Cao, T.; Yu, J.; et al. Light-dominated selection shaping filamentous cyanobacterial assemblages drives odor problem in a drinking water reservoir. NPJ Clean Water 2022, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Aguilera, A.; Aubriot, L.; Huszar, V.; Almanza, V.; Haakonsson, S.; Izaguirre, I.; O’Farrell, I.; Salazar, A.; Becker, V.; et al. Nutrients and not temperature are the key drivers for cyanobacterial abundance in the Americas. Harmful Algae 2023, 21, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.D.; Quach, E.; Buscho, S.; Ricciardelli, A.; Kannan, A.; Naung, S.W.; Phillip, G.; Sheppard, B.; Ferguson, L.; Allen, A.; et al. Nitrogen form, concentration, and micronutrient availability affect microcystin production in cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Xue, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, L. Spatiotemporal dynamics of microcystin variants and relationships with environmental parameters in Lake Taihu, China. Toxins 2015, 7, 3224–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Fastner, J.; Welker, M. Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in a Changing Environment: Concepts, Controversies, Challenges. Water 2021, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausfeldt, L.E.; Farmer, A.T.; Castro, H.F.; Krausfeldt, L.E.; Farmer, A.T.; Castro, H.F.; Boyer, G.L.; Campagna, S.R.; Wilhelm, S.W. Nitrogen flux into metabolites and microcystins changes in response to different nitrogen sources in Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Mynett, A.E.; Yan, H.; Hu, L. Physiological effects of nitrate, ammonium, and urea on the growth and microcystins contamination of Microcystis aeruginosa: Implication for nitrogen mitigation. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Martin, R.M.; Dearth, S.P.; Sun, X.; Boyer, G.L.; Campagna, S.R.; Lin, S.; Wilhelm, S.W. Seasonally relevant cool temperatures interact with N chemistry to increase microcystins produced in lab cultures of Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4127–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tong, Y. Differential effects of nitrate and ammonium on the growth of algae and microcystin production by nitrogen-fixing Nostoc sp. and non-nitrogen-fixing Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwata, A.; Miyazaki, T. Effects of ammonium supply rates on competition between Microcystis novacekii (Cyanobacteria) and Scenedesmus quadricauda (Chlorophyta): Simulation study. Ecol. Modell. 2000, 135, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashkova, V.; Malashenkov, D.V.; Baishulakova, A.; Davidson, T.A.; Vorobjev, I.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Barteneva, N.S. Changes in phytoplankton community composition and phytoplankton cell size in response to nitrogen availability depend on temperature. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarafdar, L.; Mohapatra, M.; Muduli, P.R.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, D.R.; Rastogi, G. Co-occurrence patterns and environmental factors associated with rapid onset of Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a tropical coastal lagoon. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Shang, M.; Song, L.; Shan, K. Revealing physiochemical factors and zooplankton influencing Microcystis Bloom toxicity in a large-shallow lake using bayesian machine learning. Toxins 2022, 14, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Johnson, F.; Tamburic, B.; Crosbie, N.D.; Glamore, W. The effectiveness of global constructed shallow waterbody design guidelines to limit harmful algal blooms. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S. Microcystis rising: Why phosphorus reduction isn’t enough to stop CyanoHABs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, A34–A39, Erratum in Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, A62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Straškraba, M.; Tundisi, J.G.; Duncan, A. State-of-the-art of reservoir limnology and water quality management. Comp. Reserv. Limnol. Water Qual. Manag. Kluwer Dev. Hydrobiol. 1993, 77, 213–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.H. Considerations for Establishing Nutrient Criteria for Reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2001, 17, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items | KCW | YJW | IPW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude N | 37°16′37.6″ | 37°19′37.12″ | 37°24′17.68″ |
| Longitude E | 127°40′54.87″ | 127°36′22.14″ | 127°32′1.68″ |
| Catchment (km2) | 10,972 | 11,115 | 11,803 |
| Type | Concrete Gravity | Concrete Gravity | Concrete Gravity |
| Height (m) | 8 | 8 | 6 |
| Length (m) | 440 | 513 | 521 |
| Volume (106 m3) | 8.7 | 11.3 | 14.3 |
| Real time water quality site | Wonju | Yeoju1 | Yeoju2 |
| HRT (h) * | 17.5 | 18.0 | 23.0 |
| Distance (km) ** | 11.2 1 | 10.0 2 | 11.8 3 |
| Yr | Month | KCW | YJW | IPW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | May | Nitzschia acicularis (13) | Stephanodiscus hantzschii (20) | Stephanodiscus hantzschii (20) |
| June | Merismopedia glauca (52) | Pandorina morum (52) | Pandorina morum (31) | |
| July | Aphanocapsa sp. (56) | Aphanocapsa sp. (33) | Aphanocapsa sp. (51) | |
| August | Microcystis aeruginosa (31) | Pseudanabaena limnetica (45) | Microcystis aeruginosa (38) | |
| September | Oscillatoria sp. (13) | Merismopedia glauca (44) | Aulacoseira granulata (14) | |
| October | Melosira varians (10) | Nitzschia palea (11) | Navicula viridula var. rostellata (12) | |
| 2020 | May | Rhodomonas lacustris (17) | Stephanodiscus hantzschii (9) | Navicula cryptocephala (11) |
| June | Aulacoseira granulata (13) | Aphanocapsa sp. (25) | Pandorina morum (37) | |
| July | Aphanocapsa muscicola (61) | Aphanocapsa sp. (64) | Merismopedia glauca (27) | |
| August | Micractinium pusillum (22) | Pseudanabaena limnetica (20) | Pandorina morum (20) | |
| September | Volvox sp. (45) | Skeletonema potamos (17) | Merismopedia glauca (33) | |
| October | Westella botryoides (19) | Actinastrum hantzschii (18) | Skeletonema potamos (25) |
| Parameters * | KCW | YJW | IPW | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRT | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.530 | 0.232 |
| WT | 18.6 ± 0.8 | 20.3 ± 0.9 | 21.8 ± 1.0 | 3.252 | 0.051 |
| SS | 14.2 ± 8.0 | 7.4 ± 1.3 | 10.8 ± 2.5 | 0.484 | 0.620 |
| pH | 8.6 ± 0.1 b | 8.1 ± 0.1 a | 8.1 ± 0.1 a | 11.964 | 0.000 |
| TN | 2.36 ± 0.06 | 2.25 ± 0.08 | 2.11 ± 0.12 | 1.935 | 0.160 |
| TP | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.127 | 0.881 |
| N/P ratio | 47.2 ± 6.0 ab | 56.3 ± 8.0 a | 42.2 ± 12.0 b | 4.112 | 0.033 |
| DO | 10.2 ± 0.3 | 9.6 ± 0.2 | 9.9 ± 0.4 | 1.159 | 0.326 |
| BOD | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.540 | 0.229 |
| COD | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 1.571 | 0.223 |
| Chl-a | 6.2 ± 1 | 7.4 ± 1.2 | 6.9 ± 1.1 | 0.297 | 0.745 |
| CYANO | 688.9 ± 262.4 | 871.8 ± 429.3 | 1689.6 ± 1011.4 | 0.668 | 0.520 |
| BACILL | 713.2 ± 103.8 | 773.3 ± 108.2 | 1085.1 ± 158.5 | 2.512 | 0.097 |
| CHLORO | 541.4 ± 172.9 | 714.4 ± 284.9 | 881.1 ± 291.5 | 0.441 | 0.647 |
| Other | 88.2 ± 17.9 b | 121.8 ± 31.3 a | 207.4 ± 50.4 a | 2.950 | 0.066 |
| Microcystis | 143.4 ± 120.3 | 24.1 ± 16.5 | 494.9 ± 444.0 | 0.848 | 0.437 |
| Anabaena | 12.5 ± 12.5 | 3.3 ± 3.3 | - | 0.751 | 0.480 |
| Oscillatoria | 4.4 ± 4.4 | - | 12.5 ± 12.5 | 0.684 | 0.511 |
| Aphanizomenon | - | 11.7 ± 11.7 | - | 1.000 | 0.379 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-H.; Cho, I.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Hwang, E.-A.; Han, B.-H.; Kim, B.-H. Assessing the Impact of Weirs on Water Quality and Phytoplankton Dynamics in the South Han River: A Two-Year Study. Water 2024, 16, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060833
Kim Y-H, Cho I-H, Kim H-K, Hwang E-A, Han B-H, Kim B-H. Assessing the Impact of Weirs on Water Quality and Phytoplankton Dynamics in the South Han River: A Two-Year Study. Water. 2024; 16(6):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060833
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-Hyo, In-Hwan Cho, Ha-Kyung Kim, Eun-A Hwang, Byung-Hun Han, and Baik-Ho Kim. 2024. "Assessing the Impact of Weirs on Water Quality and Phytoplankton Dynamics in the South Han River: A Two-Year Study" Water 16, no. 6: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060833
APA StyleKim, Y.-H., Cho, I.-H., Kim, H.-K., Hwang, E.-A., Han, B.-H., & Kim, B.-H. (2024). Assessing the Impact of Weirs on Water Quality and Phytoplankton Dynamics in the South Han River: A Two-Year Study. Water, 16(6), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060833







