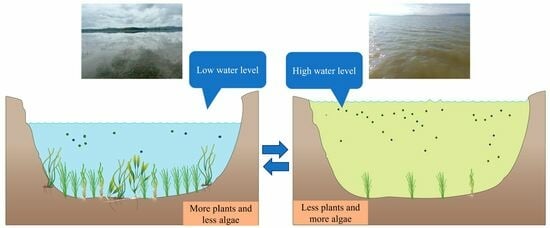
Water Level Fluctuation Rather than Eutrophication Induced the Extinction of Submerged Plants in Guizhou’s Caohai Lake: Implications for Lake Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
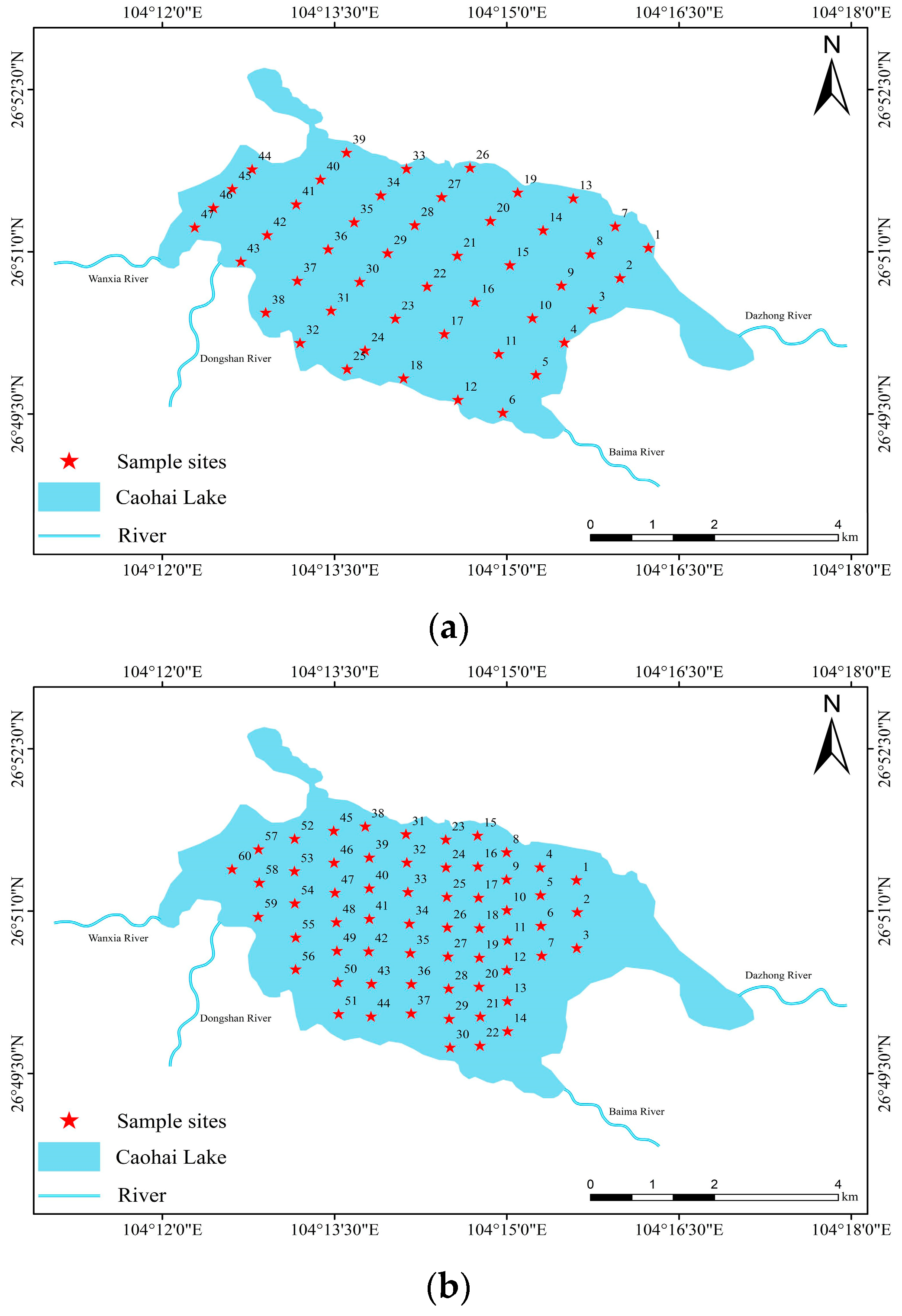
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
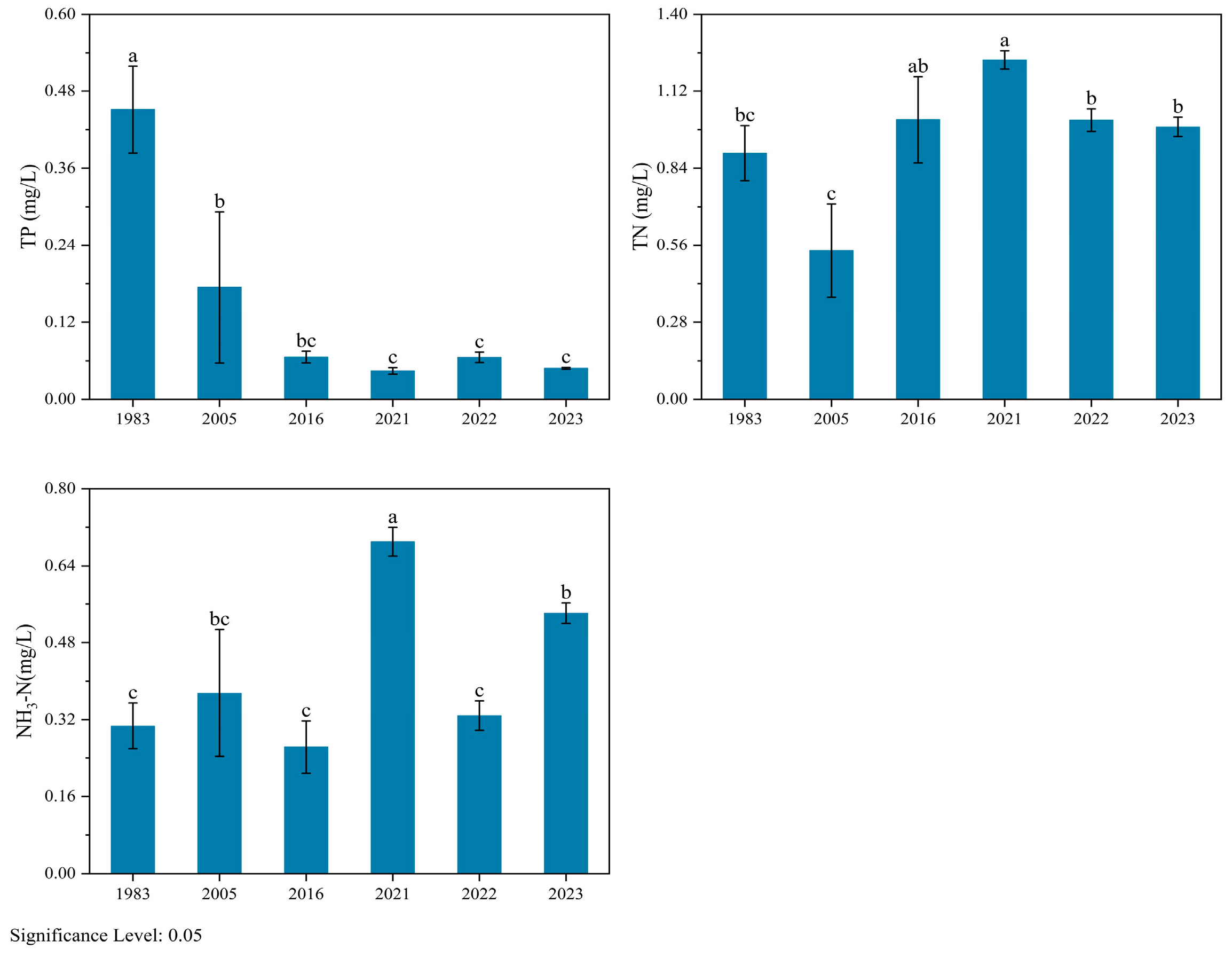
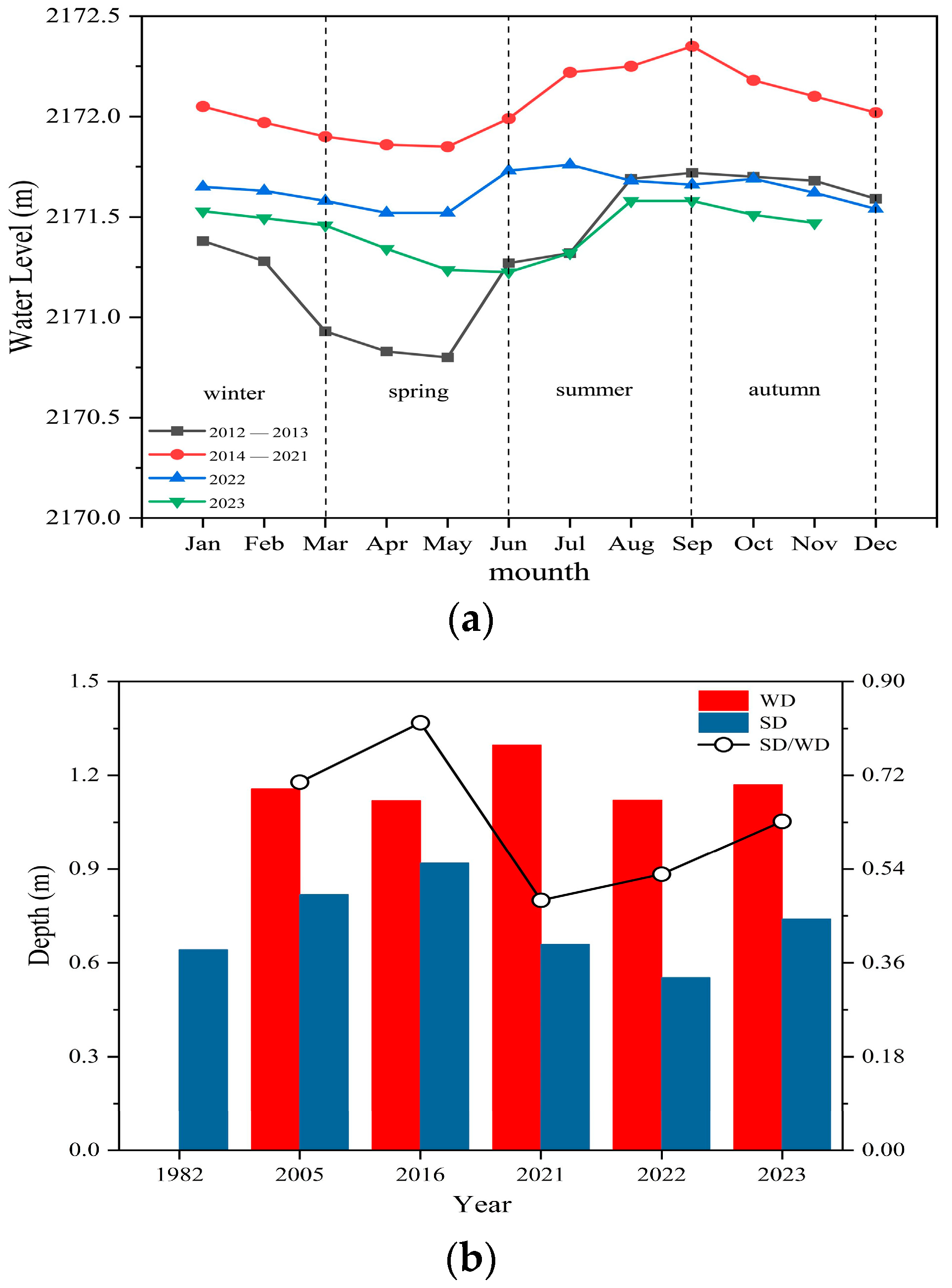
3.1. Changes in Nutrients and the Water Level
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations in the Submerged Plants
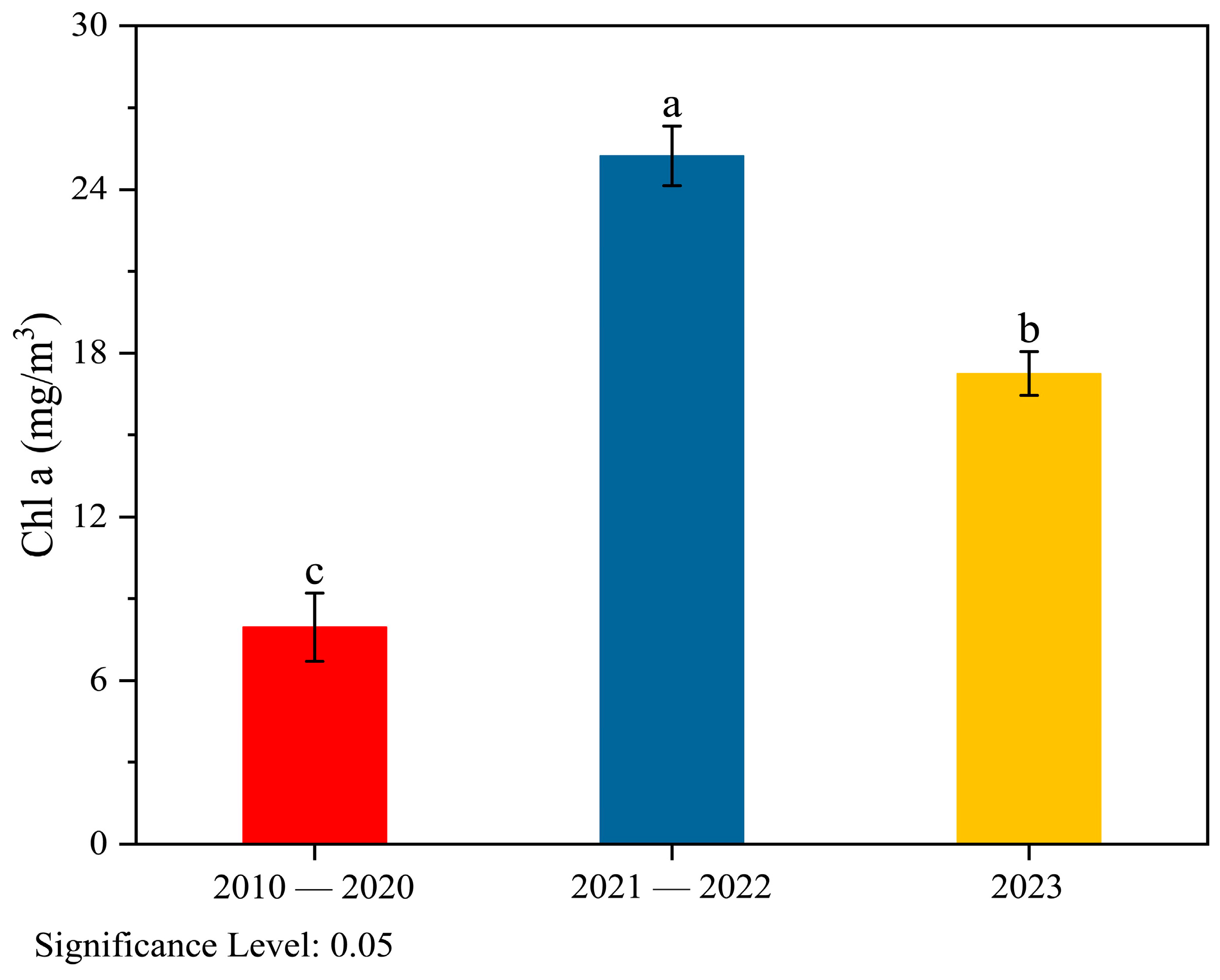
3.3. Characteristics of Chl a Variation
3.4. Relationship between Chl a, the Water Parameters, and the Submerged Plants
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship Between the Water Parameters and Submerged Plants
4.2. Importance of Water Level Manipulation to the Restoration of Submerged Plants in Lakes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, S.Q.; Ibrahim, M.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, S.; Li, G. Light intensity effects on the growth and biomass production of submerged macrophytes in different water strata. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.M.; Moussa, H.R.; Mahmoud, H.H.; El-Saied, F.A.; Dawoud, M.; Wahed, R.S.A. Potential of the submerged plant Myriophyllum spicatum for treatment of aquatic environments contaminated with stable or radioactive cobalt and cesium. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2020, 118, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.X.; Wang, L.G.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.W.; Liu, H.M.; Yu, D.; Liu, C.H. Response of sediment and water microbial communities to submerged vegetations restoration in a shallow eutrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Gan, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Jiang, S.F.; Zheng, X.Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Fan, C.Z.; Wu, S.Q.; Du, L.N. Research status on remediation of eutrophic water by submerged macrophytes: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2023, 169, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, X.H.; Qin, B.Q.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Thomaz, S.M.; Deng, J.M. Global loss of aquatic vegetation in lakes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, R.; Petzoldt, T.; Blumstock, M.; Moreira, S.; Paetzig, M.; Ruecker, J.; Janse, J.H.; Mooij, W.M.; Hilt, S. Extending one-dimensional models for deep lakes to simulate the impact of submerged macrophytes on water quality. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 61, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, J.L.; Beisner, B.E.; Giles, R.; Giani, A.; Domaizon, I.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Macrophytes moderate the taxonomic and functional composition of phytoplankton assemblages during a nutrient loading experiment. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botrel, M.; Maranger, R. Global historical trends and drivers of submerged aquatic vegetation quantities in lakes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 2493–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.Q. Shallow lake limnology and control of eutrophication in Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R. Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: Linking theory to observation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, M.; Montante, J.M.; Allenson, T.E.; Hough, R.A. Long-term responses of aquatic macrophyte diversity and community structure to variation in nitrogen loading. Aquat. Bot. 2003, 77, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.; Willby, N.; Moss, B. Submerged macrophyte decline in shallow lakes: What have we learnt in the last forty years? Aquat. Bot. 2016, 135, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.; Devey, M.; Leavitt, P.R.; Power, M.J.; Brothers, S.; Brahney, J. Anthropogenic forcing leads to an abrupt shift to phytoplankton dominance in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 69, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Rao, Q.; Luo, C.; Deng, X.; Shen, H.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y. Carp stocking and climate change are potentially more important factors than nutrient enrichment driving water quality deterioration in subtropical freshwater lakes in China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 68 (Supp. S1), S131–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Beck, M.W.; Cross, T.K.; Koch, J.D.; Bartodziej, W.M.; Sorensen, P.W. Biological invasion by a benthivorous fish reduced the cover and species richness of aquatic plants in most lakes of a large North American ecoregion. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.A.; Meeker, J.E.; Hudson, P.L.; Armitage, B.J.; Black, M.G.; Uzarski, D.G. Hydrologic variability and the application of Index of Biotic Integrity metrics to wetlands: A great lakes evaluation. Wetlands 2002, 22, 588–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Developing water level regulation strategies for macrophytes restoration of a large river-disconnected lake, China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 68, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wen, Z.H.; Ren, W.J.; Ni, L.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, K.Y.; Cao, T. What is the mechanism of submerged macrophyte biodiversity affecting biomass productivity along water depth: Niche complementarity or selection effect? Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.T.; Nan, J.; Li, J.H.; Lin, Y.; Yu, J.; Wu, J.B.; Shen, X.B. The role of mechanical harvesting on the recession of aquatic vegetation under an extreme water level increase in a eutrophic shallow lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 61682–61695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Shi, K.; Qin, B. Response of community composition and biomass of submerged macrophytes to variation in underwater light, wind and trophic status in a large eutrophic shallow lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.X.; Lv, T.; Wang, L.G.; Li, Y.; Han, C.; Yu, W.C.; Yan, Z.W.; Ma, X.W.; Zhao, H.C.; Zuo, Z.J.; et al. The spatiotemporal characteristics of water quality and phytoplankton community in a shallow eutrophic lake: Implications for submerged vegetation restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.X.; Yang, S.D.; Wu, P.; Liu, S.; Liao, J.H. Coupling stable isotopes to evaluate sources and transformations of nitrate in groundwater and inflowing rivers around the Caohai karst wetland, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 45826–45839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Xie, Y.W.; Song, C.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H.X. Ecogenomics of Zooplankton Community Reveals Ecological Threshold of Ammonia Nitrogen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.X.; Wu, P.; Han, Z.W.; Tu, H.; Zhang, S. Factors controlling the isotope composition of dissolved inorganic carbon in a karst-dominated wetland catchment, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.W.; Hu, C.S.; Zhang, M.M.; Li, Z.M.; Su, H.J. Foraging habitat selection of overwintering Black-necked Cranes in the farming area surrounding the Caohai Wetland, Guizhou Province, China. Avian Res. 2020, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Chen, L.Q.; Feng, T. Report on the Comprehensive Scientific Survey in the Caohai National Nature Reserve of Guizhou; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- SEPA. Water and Exhausted Water Monitoring Analysis Method; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Breslow; Norman, A generalized Kruskal-Wallis test for comparing K samples subject to unequal patterns of censorship. Biometrika 1970, 57, 579–594. [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Beets, J. Ecological models and the pitfalls of causality. Hydrobiologia 1994, 275, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Liang, X.M.; Wu, S.K. Total phosphorus thresholds for regime shifts are nearly equal in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes with moderate depths and areas. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, X.W.; Zheng, Y.; Yue, Z.Y. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration and Eutrophication Assessment (1987–2018) of Donghu Lake in Wuhan Using Landsat Images. Water 2020, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiao, R.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lv, X.; Shi, H. Three-dimensional spatial interpolation for chlorophyll-a and its application in the Bohai Sea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, C.; Ning, A.L.; Long, S.X. The Investigation of Phytoplankton and Eutrophication Level in Caohai Lake. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 7309–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.J.; Zhou, C.; Lin, Y.H.; Yu, L.F.; An, M. Zooplankton Community Structure and Water Quality Assessment of Caohai Plateau Wetland, Guizhou Province, China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, S.; Xia, P.; Song, S.; Wu, S.; Jie, Y. Correlation between chlorophyll a and environmental factors during wet season of Caohai Lake in Guizhou Province. Yangtze River 2018, 49, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.L.; Chen, X.; Li, L.J.; Li, C.H.; Yuan, G. Aquatic plant diversity and community succession in Caohai wetland, Guizhou Province. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2020, 44, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.L.; Li, L.J.; He, M.; Long, Y.C.; Lv, J.C.; Wan, H.F.; Yuan, G. Autumn phytoplankton community structure and its relationship with water quality parameters in Caohai wetland of Guizhou Province. J. Hydroecol. 2020, 41, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X. Algae Community Epiphyticed to Typical Submerged Plants Andtheir Phosphorus Stagnant Effect. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Y.; Huang, X.F.; Tian, Y.B.; Dong, J.X.; Zheng, F.F.; Xia, P.H. Chlorophyll a variation and its driving factors during phase shift from macrophyte- to phytoplankton-dominated states in Caohai Lake, Guizhou, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2023, 47, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voesenek, L.; Sasidharan, R.; Visser, E.J.W.; Bailey-Serres, J. Flooding stress signaling through perturbations in oxygen, ethylene, nitric oxide and light. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, R.; Hartman, S.; Liu, Z.G.; Martopawiro, S.; Sajeev, N.; van Veen, H.; Yeung, E.; Voeseneka, L. Signal Dynamics and Interactions during Flooding Stress. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Sharfstein, B.; Brady, M.A.; East, T.L.; Harwell, M.C.; Maki, R.P.; Rodusky, A.J. Recovery of submerged plants from high water stress in a large subtropical lake in Florida, USA. Aquat. Bot. 2004, 78, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coops, H.; Beklioglu, M.; Crisman, T.L. The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems—Workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindow, I.; Andersson, G.; Hargeby, A.; Johansson, S. Long-term pattern of alternative stable states in two shallow eutrophic lakes. Freshw. Biol. 1993, 30, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.Y. Growth of Potamogeton maackianus under Low-Light Stress in Eutrophic Water. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2001, 16, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wan, R.R.; Yang, G.S.; Wang, X.L.; Xu, L.G. Responses of wetland vegetation in Poyang Lake, China to water-level fluctuations. Hydrobiologia 2016, 773, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Brookes, J.D. Radiation dimming and decreasing water clarity fuel underwater darkening in lakes. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P. Reading About the Histories of Cyanobacteria, Eutrophication and Geological Evolution in Lake Chaohu; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Kristensen, P.; Søndergaard, M.; Olrik, K. Fish manipulation as a lake restoration tool in shallow, eutrophic, temperate lakes 2: Threshold levels, long-term stability and conclusions. Hydrobiologia 1990, 200–201, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucak, T.; Saraoğlu, E.; Levi, E.E.; Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N.; Çakiroğlu, A.İ.; Jeppesen, E.; Beklioğlu, M. The influence of water level on macrophyte growth and trophic interactions in eutrophic Mediterranean shallow lakes: A mesocosm experiment with and without fish. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.W.; Hu, W.P.; Deng, J.C.; Zhu, J.G.; Zhou, N.N.; Liu, X. Impacts of water depth and substrate type on Vallisneria natans at wave-exposed and sheltered sites in a eutrophic large lake. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Christofferson, K. The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Felpeto, A.B.; Roy, S.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Allelopathy prevents competitive exclusion and promotes phytoplankton biodiversity. Oikos 2018, 127, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozimek, T.; Gulati, R.D.; Donk, E.V. Can macrophytes be useful in biomanipulation of lakes? The Lake Zwemlust example. Hydrobiologia 1990, 200, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.L.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, P.; Yan, W.H.; Kong, L.W.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.S.; Liu, B.Y.; Ma, J.M.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variation of water parameters, sediment properties, and submerged macrophytes after ecological restoration in a long-term (6 year) study in Hangzhou west lake in China: Submerged macrophyte distribution influenced by environmental variables. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, X.F.; Chen, F.Z.; Du, Y.X.; Guan, B.H.; Yu, J.L.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yongdong, Z. The responses of the benthic-pelagic coupling to eutrophication and regime shifts in shallow lakes: Implication for lake restoration. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, D.H.; Jia, G.; Wu, H. Chlorophyll-a concentration variation characteristics of the algae-dominant and macro-phyte-dominant areas in Lake Taihu and its driving factors, 2007–2019. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jia, C.; Liang, W.; Hu, S.; Wu, Z. Effects of the submerged macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum L. on restoration of a eutrophic waterbody and its optimal coverage. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C. Construction and purification efficiency test of an ever-green aquatic vegetation in an eutrophic lake. China Environ. Sci. 1997, 1, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.; Yang, S.; Fang, T.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.D. Recovery of Aquatic Macrophytes by Use of Water Level Regulation Method in Eutrophicated Lakes-A Case Study of Wuli Lake, Wuxi City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Section | 1983 | 2005 | 2016 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East of Caohai | 1141.6 | 2980.6 | 5456 | 241.5 | 668.4 | 1475.7 |
| Middle of Caohai | 1195.0 | 826.8 | 2552.9 | 141.4 | 138.7 | 595.6 |
| West of Caohai | 1821.6 | 1012.1 | 4275.1 | 377.4 | 269.1 | 611.7 |
| Mean | 1386.07 | 1606.3 | 4094.7 | 255.1 | 383.2 | 922.6 |
| (a) | ||||||
| B | β | t | p | F | R2adj | |
| TN | 8.796 | 0.082 | 1.179 | 0.241 | 20.983 *** | 0.531 |
| TP | −496.817 | −0.184 | −2.432 | 0.017 | ||
| NH3-N | −11.719 | −0.068 | −0.965 | 0.337 | ||
| Chl a | −1.680 | −0.365 | −4.584 | <0.001 | ||
| WD | −31.552 | −0.455 | −4.821 | <0.001 | ||
| SD | 8.697 | 0.058 | 0.636 | 0.526 | ||
| (b) | ||||||
| b | B | β | t | p | F | R2adj |
| TN | 0.128 | 0.042 | 0.695 | 0.489 | 33.151 *** | 0.645 |
| TP | −21.280 | −0.278 | −4.219 | <0.001 | ||
| NH3-N | 0.018 | 0.004 | 0.059 | 0.953 | ||
| Chl a | −0.062 | −0.475 | −6.854 | <0.001 | ||
| WD | −0.628 | −0.319 | −3.855 | <0.001 | ||
| SD | 0.085 | 0.020 | 0.252 | 0.802 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, B.; Liu, J.; Xia, P. Water Level Fluctuation Rather than Eutrophication Induced the Extinction of Submerged Plants in Guizhou’s Caohai Lake: Implications for Lake Management. Water 2024, 16, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050772
Chao F, Jiang X, Wang X, Lu B, Liu J, Xia P. Water Level Fluctuation Rather than Eutrophication Induced the Extinction of Submerged Plants in Guizhou’s Caohai Lake: Implications for Lake Management. Water. 2024; 16(5):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050772
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Fusheng, Xin Jiang, Xin Wang, Bin Lu, Jiahui Liu, and Pinhua Xia. 2024. "Water Level Fluctuation Rather than Eutrophication Induced the Extinction of Submerged Plants in Guizhou’s Caohai Lake: Implications for Lake Management" Water 16, no. 5: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050772
APA StyleChao, F., Jiang, X., Wang, X., Lu, B., Liu, J., & Xia, P. (2024). Water Level Fluctuation Rather than Eutrophication Induced the Extinction of Submerged Plants in Guizhou’s Caohai Lake: Implications for Lake Management. Water, 16(5), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050772