Abstract
The tannery wastewater from the tanning stage (TWT) comprises organic and Cr pollutants, which can adversely affect aquatic life and have carcinogenic effects. In this study, we investigated the performance of a Fenton-like process using commercial Nano-scale zero-valent iron (nZVI) for the simultaneous removal of Cr and organic matter from real TWT. We used an experimental design to select the principal operating parameters. A Plackett–Burman design identified variables for Cr-total and COD removal, followed by a central composite design (CC-D) to determine optimal variable levels. Finally, the response surface methodology (RSM) was used to find the optimum concentration of individual variables influencing Cr-total removal. Additionally, the effect of the leather-related, co-existing substances that influenced the efficiency of the process and the possibility of recycling nZVI were explored. The inclusion of nZVI was significantly more effective at removing both Cr-total and COD (97.3% ± 5.7% and 73.9% ± 9.1%, respectively), whereas the traditional Fenton process achieved lower removal rates (55.6% ± 10.0% for Cr-total and 34.8% ± 10.9% for COD). The optimal conditions for the Fenton-like process were nZVI/H2O2 = 1.05 w/w, and pH = 2.93. We obtained the best results during the first 5 min of the reaction, which increased after 48 h of agitation and subsequent neutralization. According to the results of four consecutive cycles, nZVI exhibited high reusability (97%) without compromising its adsorption potency. XPS analysis confirmed Cr removal through the adsorption mechanism on the nZVI surface. Hence, a Fenton-like process based on nZVI can be used as a promising alternative for treating organic and Cr wastewater.
1. Introduction
The tanning industry generates a significant volume of wastewater, approximately 1 × 105 m3 annually on a global scale, leading to severe environmental challenges [1]. This wastewater originates from three distinct processing phases (beamhouse, tanning, and finishing) that convert animal skin into leather. During the tanning stages, various chemicals induce crosslinking among collagen fibers, rendering the hide resistant to decay while ensuring durability and flexibility [2]. Consequently, tannery wastewater from the tanning stage (TWT) comprises elements such as organic substances, which are quantified by the chemical oxygen demand (COD), as well as chromium (III and VI), sulfates (SO42−), chlorides (Cl−), ammoniacal nitrogen (NH4–N), and other compounds that present challenges during their biological breakdown, which occurs over multi-stage processes [1].
The total chromium (Cr-total) (encompassing both Cr (III) and Cr (VI)) in TWT exhibits concentrations spanning from 1000 to 5000 mg L−1 [3]. Cr (III) salts are commonly used during tanning because they are inexpensive and produce better quality leather (wet blue) [4]. Cr (III) can be converted to Cr (VI) under environmental conditions, such as natural oxidation, when there are high levels of manganese, or when the medium is highly alkaline (pH > 9.0) [5]. Cr (III) is relatively less harmful to organisms than Cr (VI), which is more toxic and carcinogenic. Releasing TWT into the environment without proper treatment, in order to mitigate the Cr-total content, is environmentally hazardous and it adversely affects human health [6].
Additionally, TWT contains a high level of leather-related, co-existing substances, such as animal fat, keratin, and collagen. This organic matter often coexists with Cr-total contamination and Cl−, which complicates and increases the cost of treating wastewater [7]. Several treatment methods have been developed to remove Cr-total and organic matter from TWT. Conventional treatment processes include chemical coagulation and flocculation [8], membrane filtration [9], adsorption [10], chemical precipitation [3], and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) [11].
Among AOPs, Fenton processes have become one of the most extensively employed technologies for removing pollutants [12] because they can oxidize recalcitrant contaminants through radical oxidation mechanisms [13]. The conventional Fenton process typically introduces a ferrous iron salt (FeSO4•7H2O), along with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), under specific acidic pH conditions. However, this treatment method comes with challenges, such as accumulating substantial amounts of ferrous ions (Fe2+) and H2O2, high operating costs, limited optimum pH ranges (always at around PH 3), difficulties in recycling the catalyst (Fe2+), as well as creating a build-up of iron sludge [14,15]. To address these limitations, different catalysts have been proposed to replace Fe2+ (Fenton-like processes) including Fe3+ [16], iron oxides, hydroxides, clay minerals [17], bimetallic Fe/Cu Nanoparticles [18], Nano-scale zero-valent iron (nZVI) [19,20,21,22,23], and ZVI-based materials [24].
nZVI is considered to be a suitable option for treating wastewater due to its high surface area, chemical reactivity, and strong ability to reduce both organic and inorganic contaminants [25]. In recent years, nZVI has emerged as a successful agent for remediating diverse contaminants present in soil and water systems. The efficacy of nZVI has been explored in a Fenton-like process for treating synthetic TWT, both in batch tests [26] and laboratory-plant applications [22]. Nevertheless, nZVI presents several drawbacks, including susceptibility to aggregation, oxidation, and passivation in aerobic environments, which limits its ability to interact with contaminants and it reduces its reactivity and effectiveness in various applications, such as environmental remediation [27].
To overcome these disadvantages, the use of a commercial nZVI (Nanofer STAR, Židlochovice, Czech Republic) should be considered. This type of nZVI has an inorganic surface layer that protects the iron core against rapid oxidation when in contact with air or water [28]. This layer allows for easy storage, transportation, handling, and deployment in routine applications, and it facilitates the upscaling of the procedure to an industrial scale [29]. To date, Nanofer STAR has been evaluated during groundwater remediation [30,31]. Nevertheless, using Nanofer STAR to treat real TWT, which is characterized by high levels of Cr-total (>3000 mg L−1) and organic matter (COD > 12,000 mg L−1), has not been investigated.
The use of nZVI as a catalyst can enhance the efficiency of the Fenton-like process [32]. This enhancement is attributed to its reaction with hydronium ions (H+) and dissolved oxygen, resulting in the generation of an additional quantity of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which can subsequently improve the production of hydroxyl radicals (OH•) [33]. Additionally, the nZVI can be effectively recovered post-treatment using magnetic methods while maintaining its activity for subsequent operations [27]. In this study, we evaluated whether commercial nZVI nanoparticles could improve the efficiency of the Fenton-like process for the simultaneous removal of Cr-total and organic matter from the real TWT, in comparison with the efficiency of the conventional Fenton process used by tanners in the upper Bogota River basin, where FeSO4 is employed as a catalyst. To facilitate this comparison, it is crucial to comprehend the influences and optimize the operating conditions that lead to a desirable performance in this technological approach to environmental remediation [34]. However, determining independent variables, designing experiments, conducting data statistics, and validating models requires numerous experiments, making the process expensive and time-consuming [35].
As an alternative to determining the optimum operating conditions, we propose applying design of experiments (DOE) tools that could effectively model the Fenton-like process, adjusting the combined effects of different variables, determining the optimal operating condition, and predicting the performance of the catalysts [36]. A Plackett–Burman design (PB-D) experiment was implemented to identify variables favoring the Fenton-like process. Subsequently, a central composite design (CC-D) was used to determine the optimal levels of the independent variables selected in the PB-D experiment. The CC-D model offers useful data on direct, pairwise interactions and curvilinear variable effects [37]. Finally, a response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to obtain the optimum concentration of individual variables that may potentially influence the impact of removing Cr-total and COD from real TWT.
In this context, the main purposes of this work were to (1) evaluate the performance of a Fenton-like process using commercial nZVI as a catalyst for the simultaneous removal of Cr-total and organic matter from real TWT using DOE tools; (2) identify the effect of leather-related, co-existing substances that influence the efficiency of the Fenton-like process; and (3), assess whether commercial nZVI can be recycled during the Fenton-like process. This work offers a promising method for TWT treatment and a future field test for environmental remediation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and TWT Characterization
In Colombia, approximately 700 tanneries are in operation, and 30% of them are causing severe environmental problems in the Bogota River basin [38]. Tanners have implemented conventional water treatment processes to reduce detrimental impacts. However, these are insufficient, and more efficient technologies and drastic approaches need to be employed. Consequently, they discharge TWT into the river without complying with the parameters established by Colombian legislation [39]. The Bogota River basin is north of Cundinamarca (5°11′46.86″ N 73°36′26.824″ W; Colombia), and is located at 2738 m above sea level (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Location of tanneries within the upper basin of the Bogota River (Colombia).
A total of 120 TWT samples were collected from 10 tanneries over the course of 1 year. On average, TWT had the following composition: COD 12,300 ± 127 mg L−1, Cl− 7731 ± 842 mg L−1, Cr (III) 3600.4 ± 74.2 mg L−1, and Cr (VI) 49.6 ± 12.8 mg L−1 at pH 3.3 ± 0.9. pH and temperature (T°) were measured with a portable multi-parameter probe (HI 9828, Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, USA). Cr (VI) was determined with dyphenylcarbazide, using method 7196A [40]. Cr-total was quantified with atomic absorption, using method 7000B [41]. Cr (III) was determined by calculating the difference between Cr-total and Cr (VI). COD was calculated using the closed reflux colorimetric method that was corrected for Cl− [40]. Cl− determination was performed using a titrimetric method involving silver nitrate, thus, method 9253 was employed [40].
2.2. Design of Experiments and Relevant Statistical Analysis
We developed an experimental design (DOE) to evaluate the Fenton-like process performance for the simultaneous removal of Cr-total and organic matter from real TWT. The PB-D experiment included seven factors at two levels (Table 1). Parameter ranges were chosen via preliminary experiments based on the literature. We aimed to assess the impact of pH and nZVI/H2O2 because these parameters directly contributed to the generation of Fe2+ and OH• radicals during the Fenton-like process. The values of nZVI/H2O2 and pH were determined using the results reported by Vilardi et al. [22,26], which were based on experiments conducted with synthetic water and nZVI, and synthesized by the research group. Additionally, the ratio of H2O2/COD was adapted from the findings of Hodaifa et al. [42], who applied a Fenton-like process to treat wastewater with a high concentration of organic matter. Furthermore, we considered the influence of the flow regime on mixing and removal efficiency, paying attention to the impact of agitation speed and sedimentation time on removal efficiency, given the potential precipitation abilities of certain components, which become apparent towards the conclusion of the process.

Table 1.
Factors and levels selected for PB-design.
During PB-D, 8 experiments (Table 2) were performed in duplicate using commercial nZVI or FeSO4•7H2O as catalysts. Minitab 0.2.1v software (Minitab, State College, PA, USA) was used to determine the level of experimental error, corroborate the fit of the first-order model, and perform regression analysis on the experimental results that were obtained. Cr-total and COD removal efficiency (% R) were calculated in the supernatant using the following equation:

Table 2.
Matrix of the results of the PB-D-based experiment that was used to evaluate factors which favored higher levels of Cr-total and COD removal from TWT.
Based on the CC-D principle, the design consisted of ‘2k’ fractional factorial points, plus ‘2k’ axial points, and ‘1’ center point, where ‘k’ is the number of variables [36]. The experimental region of the CC-D consisted of five levels (−1.68, −1, 0, 1, and 1.68), with K = 3, and variables selected from the PB-D. The experiment was conducted with 20 modifications (Table 3), in duplicate, and it used FeSO4•7H2O as a control. Minitab 0.2.1v software was used to assess the level of experimental error, verify first and second order model adequacy, develop the response of the surface methodology (RSM), and conduct a regression analysis on the experimental data. Subsequently, analyses of variance (ANOVAs, α < 0.05) were performed in order to assess the results obtained from the PB-D and CC-D experiments, as well as to determine the fitting degree between the values obtained from the experiment and the predicted response calculated by the regression model. The statistical significance was evaluated by the coefficient of determination, R2.

Table 3.
Matrix of results of the CC-D-based experiment used to evaluate treatment factors that favored higher levels of Cr-total removal from TWT.
2.3. Experimentation
The sets of PB-D and CC-D experiments were conducted in triplicate using commercial nZVI as the treatment and FeSO4•7H2O as the control. Samples of real TWT (100 mL) were set in glass flasks, and the pH was adjusted using HNO3 and NaOH solutions (1N). The samples were then shaken in an orbital shaker, and the temperature was controlled using a thermostatic bath set. Selected amounts of H2O2 (30% w/w) and nZVI or FeSO4•7H2O were added simultaneously. After the contact time had elapsed, the mixture was neutralized to pH 7.0. It was then decanted for 8 h, and the supernatant was collected for Cr-total analysis. Manganese oxide was subsequently introduced to eliminate the residual unreacted hydrogen peroxide present in the samples. Afterwards, COD analyses were conducted. All experiments were conducted in dark conditions to avoid interference from UV light which may impact the results. Commercial nZVI (Nanofer STAR) was purchased from NANOIRON s.r.o. (Židlochovice, Czech Republic) and prepared in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. It was activated in a blender and left for 36 h in the dark, at a regular refrigeration temperature. All experiments were conducted using commercial nZVI, the morphological characterization of which has been previously reported in earlier studies, with an average size, specific surface area (SSA) and pore surface area of approximately 70 nm, 18.5, and 13.6 m2/g, respectively [29].
2.4. Validation the DOE Results
Two duplicate experiments were conducted using a 2 L jar test assembly with real TWT. In each experiment, two trials incorporated the use of nZVI, whereas the other two trials utilized FeSO4•7H2O as controls. Supernatant samples (50 mL) were collected at a contact time of 5 min, 30 min, 90 min, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. Subsequently, they were neutralized and left to decant for 8 h. Duplicate analyses were performed to determine Cr (III), Cr (VI), and COD, whereas sludge production was quantified by measuring the total suspended solids (TSS), using method 2540B [40]. Statistical analyses were conducted using one-way ANOVA to determine differences between treatments (α < 0.05), and Tukey’s multiple comparison test was employed to contrast the means of all possible pairs for experimental factors.
2.5. Identifying the Effect of the Leather-Related Co-Existing Substances
To assess the potential impact of individual coexisting substances on the Fenton-like process performance during Cr-total and COD removal, we selected factors with concentrations resembling those found in real TWT, such as Cl− (7000 mg L−1) and organic matter (COD 12,000 L−1). Cl− was used, and its concentration in tannery effluents was simulated, as it is commonly used as a salt in preservation and pickling. Additionally, BSA was added to simulate the presence of organic matter. We conducted the experiments in conical flasks containing 50 mL of a 3200 mg L−1 solution of CrOHSO4 (25% w/w), which corresponds with the salt that is commonly used to tan leather. Salt (NaCl), BSA, or a combination of both, was introduced into the Cr solution, and the mixture was sonicated to achieve a uniform dispersion. Subsequently, nZVI was added to the mixture, and the reaction was initiated using H2O2, in accordance with a Fenton-like process. Then, supernatant samples, with and without neutralization, were collected for analysis.
To assess the chromium removal mechanism in the system using nZVI, three samples of the solid present in the system were collected and evaluated via X-ray photo-electron spectroscope analysis (XPS), as follows: one sample of the solid derived from the post-activation of nZVI; another sample was collected after the Fenton-like process; and a final sample was collected after neutralization. The sample was freeze-dried for XPS and was used to reveal the elemental compositions and oxidation state on the surface of nZVI. The sludge produced after neutralization underwent three washes with deionized water. The resulting sample was then dried at room temperature. Subsequently, it underwent analysis through scanning electron spectroscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping for composite analysis.
2.6. Recycled of Comercial nZVI
For recycling experiments, nZVI was reclaimed through magnetic separation, followed by centrifugation. Subsequently, nZVI was washed three times with deionized water and once with ethanol. Then, it was vacuum-dried in preparation for the next experiment. The tests were conducted using a Cr solution (3200 mg L−1 CrOHSO4; 25% w/w) and TWT, with the addition of nZVI and H2O2, in accordance with the DOE results of the Fenton-like process.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Plackett–Burman Results to Identify Factors
To identify factors that significantly affect Cr-total and COD removal from TWT, a PB-D was developed in duplicate. Table 3 shows that the second treatment exhibited the highest Cr-total removal, at a rate of 97.3% ± 5.7%. By contrast, the control with FeSO4•7H2O only achieved a removal rate of 55.6% ± 10.0%. This treatment consisted of lower levels (−) of H2O2/COD (0.5 w/w), pH (3.0), a sedimentation time of 2 h, an agitation rate of 100 rpm, the highest levels (+) of nZVI/H2O2 (1.0 w/w), a temperature of 30 °C, and a reaction time of 1 h. The Cr-total removal efficiency in treatment two may have been due to the combined effect of several parameters, as follows: a lower pH (3.0) can lead to the increased generation of hydroxyl radicals from H2O2, enhancing their reactivity to pollutants [43]; and a higher reaction time (1 h) allows for a greater number of generated hydroxyl radicals, leading to increased interaction with chromium species and their removal [44].
The PB-D were further analyzed using Pareto charts (Supplementary Materials, Figure S1), which illustrate the influence of the analyzed variables on Cr-total removal. The data reveal that the nZVI/H2O2, pH, and reaction time were the most influential variables, whereas H2O2/COD, temperature, and agitation rate showed a negative correlation. The analysis of variance (ANOVA; α < 0.05; Supplementary Materials, Table S1) of the PB-D revealed significant differences in pH, nZVI/H2O2, and reaction time for Cr-total removal. The first-order model generated through data analysis (Supplementary Materials, Equation (S1)) indicated a sample variation of 76.5%. As a result, identifying a relationship between treatment factors and Cr-total removal was possible. The linear dependence between predicted and experimental data with R2 = 79.6% (Supplementary Materials, Figure S2) demonstrated the high accuracy of the model generated in PB-D. The positive regression coefficients of Equation (S1) for nZVI/H2O2, the reaction time (1.474 and 0.935), as well as the negative result for the pH (−1.054), confirmed that these factors had a significant effect on Cr-total removal during the Fenton-like process. Therefore, we used these factors in the CC-D experiment.
On the other hand, although no significant differences (ANOVA; α < 0.05; Supplementary Materials, Table S2) were observed in nZVI treatments for COD removal efficiency, their values ranged from 63.8 ± 8.2% to 73.9 ± 9.1%. Furthermore, treatments with FeSO4•7H2O had a lower COD removal efficiency between 22.9 ± 4.7% and 40.0 ± 19.1% in the PB-D (Table 2). Similar results were obtained by Vilardi et al. who calculated a COD removal efficiency of >70% for synthetic TWT [26]. This result indicated that organic matter removal increased as the initial pH value decreased, which can be attributed to the generation of more hydroxyl radicals via nZVI/H2O2 under acidic conditions. The reduction in COD concentration indicates floc disruption, protein lysis, and the release of organic materials into the liquid phase [7]. Similar outcomes were reported by Hodaifa et al. in their study of Fenton-like processes for olive oil mill wastewater treatment, which revealed that operating conditions determine high rates of COD conversion [42].
3.2. Optimization of the Process to Maximize Cr-Total Removal
The combined results obtained from PB-D and the subsequent CC-D emphasized the significant factors affecting the complete Cr-total removal using commercial nZVI as a catalyst during the Fenton-like process, and it offered insights into their optimal settings. Treatment 10 in CC-D (Table 3) demonstrated that the most efficient method yielded the greatest Cr-total removal. This consisted of a pH of 3.0, a nZVI/H2O2 of 1.25, and a reaction time of 3.0 h, the chromium removal efficiencies in the experimental results ranged from 86.85% ± 1.50% to 97.74% ± 1.38%.
The Pareto chart provides a visual depiction of the magnitude of effects, to aid in the prioritization of the most influential factors that optimize the process. In this study, the standardized effects of the Pareto chart provided a clear representation of the relative importance of the variables, highlighting nZVI/H2O2 and pH (Supplementary Materials, Figure S3) in particular. These variables exhibited effects on Cr-total removal, indicating that higher levels of nZVI/H2O2 and low pH values were associated with increased Cr-total removal. These variables were significantly influential, both in linear and quadratic forms. The experimental data obtained in CC-D were analyzed using the surface response methodology. The fit of the second-order model was evaluated using the generation coefficients of the second-order polynomial through multiple regressions (Supplementary Materials, Equation (S2)). ANOVA results for the CC-D-based experiment (Supplementary Materials, Table S3) showed that the model was statistically significant to nZVI*nZVI (0.044, p < 0.05). Moreover, the result showed a strong correlation between the predicted values of the model and the corresponding experimental values. The data points are closely distributed and exhibit linear behavior, indicating a high level of agreement between the real and predicted data (R2 = 95.82%; Supplementary Materials, Figure S4).
Response surface curves (Figure 2) for the interaction between pH and nZVI/H2O2 show that the influence of those variables affected Cr-total removal differently. Numerical optimization, using RSM/Minitab software, was used to determine the optimum process parameters for maximizing the results. We found that the best optimization treatment occurred at pH 2.93 and 1.05 w/w of nZVI/H2O2 for 97.5% Cr-total removal. These results are comparable with the findings of Vilardi et al. [26], who used nZVI in synthetic TWT, and obtained optimal conditions at H2O2/COD (w/w) = 0.5, nZVI/H2O2 (w/w) = 0.75, and pH = 3, achieving a total Cr (VI) and COD removal of 73% and 88%, respectively. In addition, it is noteworthy that the optimal pH was predicted at a value favoring catalytic activity in the Fe2+/Fe3+/H2O2 system [45].
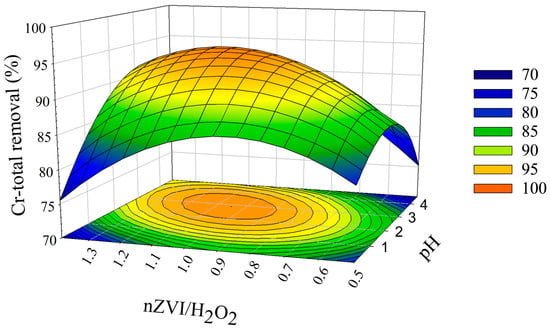
Figure 2.
Response surface methodology (RSM) showing the interaction between pH and nZVI/H2O2 and its effects on Cr-total removal.
3.3. Validation of the DOE Results
To confirm the model’s reliability, an additional laboratory experiment was conducted using optimum conditions found by the DOE results at reaction times of 5 min, 30 min, 90 min, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. After the process was scaled up to 2 L, the efficiency of Cr (III), Cr (VI), and COD removal was 20% lower than the data determined in the model (Figure 2). This limitation was due to the mass transfer of substances required in the Fenton reaction (nZVI and H2O2), making it difficult to maintain adequate agitation [46]. In a previous work, Vilardi et al. [22] achieved a COD removal efficiency of 75.5%. However, it is important to note that this study was performed using synthetic TWT, with lower concentrations of Cr-total, COD, and Cl− (61.61 ± 8.4 mg L−1, 1454.0 ± 35.0 mg L−1, and 792.0 ± 9.4, respectively).
Furthermore, there were significant differences (ANOVA; α < 0.05) between the nZVI treatment and the control with FeSO4•7H2O (Figure 3). These differences occurred because, during the first 5 min of the reaction, the pH of the control (2.7 ± 0.8) was more acidic than that of nZVI (3.7 ± 1.1). This pH value can be attributed to the rapid corrosion of nZVI in water, which produces hydroxyl ions and increases pH [32]. pH directly affects the generation and performance of hydroxyl radicals (OH•), which are the main oxidants responsible for degrading organic contaminants in water [47]. The reported optimum pH for Fenton-like processes, using nZVI in synthetic tanning wastewater, is 3.0 [4]; this is consistent with the optimum value determined by the RSM model.
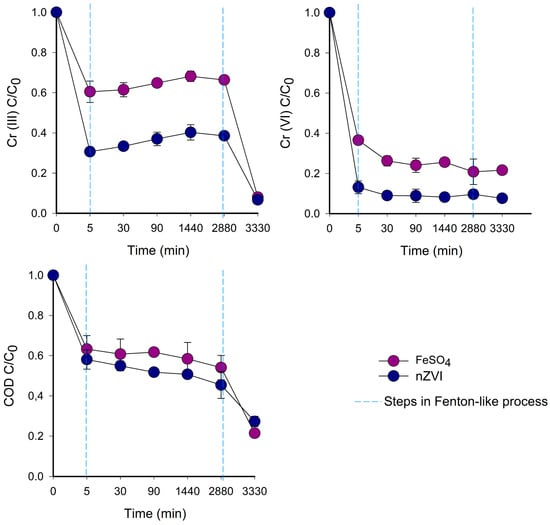
Figure 3.
Changes in Cr (III), Cr (VI), and COD removal during Fenton-like processes for TWT using nZVI as the treatment and FeSO4•7H2O as the control.
The reaction time also significantly influenced the Fenton-like processes (Figure 3). The removal of Cr (III), Cr (VI), and COD involved three distinct steps; during the initial step, which occurred within the first 5 min, the values rapidly decreased, which was more pronounced for nZVI than for the control, whereas in the second step, the values decreased gradually until they reached equilibrium, and the third step occurred after neutralization. During the first 5 min, hydroxyl radicals were produced, which then attacked the nZVI surface and mineralized the organic matter present in TWT [48]. This process aligns with the high removal efficiency of nZVI, with respect to the control. After 30 min, the reaction slowly ceased. This reduction can be attributed to the production of other types of radicals, such as hydroperoxyl radicals (HOO•), which might hinder the reaction [49]. Similar results were also obtained by Ling et al. [48], where Fenton-like processes for the simultaneous removal of Cr (VI) and bisphenol-A demonstrated remarkable efficiency (complete removal within 20 min) at pH 5. Additionally, Vilardi et al. [26] reported that combining a Fenton process with FeSO4•7H2O and nZVI at pH 2.5 exhibited COD removal efficiencies exceeding 94% during the first 5 min of the reaction.
There was also a temperature difference, which was higher for nZVI (22.7 ± 2.5 °C) than the control (19.5 ± 4.8 °C), during the first five minutes of the reaction. The Fenton process is an exothermic reaction, mainly due to the interaction between hydroxyl radicals (OH•) and organic matter [50]. When the temperature increases, the number of radicals increases, which increases the level of kinetic energy in the reaction. An optimum temperature of 30 °C was reported for the Fenton process [22].
The highest removal of Cr (III) and COD was observed after neutralization (the third step) at 3360 min (56 h). Then, Cr (III) removal increased from 65 to 95%, and COD removal increased from 46 to 57% (Figure 3). Cr-total removal that was mediated by nZVI comprised a combination of sorption, reduction, and co-precipitation phenomena [20,51]. Cr-total was adsorbed onto the surface of nZVI, which is where electron transfer occurs, allowing the precipitation of the Cr-total into chromium hydroxides. Additionally, the oxidation of Fe0 to Fe3+ promotes the precipitation of mixed Fe3+/Cr (III)(Oxy) hydroxides [52]. In the presence of nZVI, COD removal occurs initially through oxidation processes. Subsequently, the increased rate of removal occurs through coagulation and flocculation processes [7]. In this sense, neutralization is a critical aspect in the process of scaling to promote coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation.
The production of sludge (TSS) was significantly lower (ANOVA; α < 0.05) for nZVI (162.8 ± 31.1 mL L−1) than for the control (576.3 ± 261.6 mL L−1). Similar results were obtained in previous studies. For instance, Vilardi et al. [22] reported a 17.5% sludge production for nZVI compared with the 21.6% observed in synthetic waters in the control group (FeSO4•7H2O). The low production of dissolved iron is attributed to the higher surface area of the nZVI-to-volume ratio. This characteristic facilitates a more comprehensive degradation of contaminants and it reduces the formation of intermediate products that may result in the massive formation of sludge [53].
In summary, the Fenton-like process with nZVI as a catalyst was more efficient at removing Cr-total and COD compared with FeSO4•7H2O, which was used as a control (Supplementary Materials, Figure S5). The optimal operating parameters determined from the response surface curves comprised a pH of 2.93 and an nZVI/H2O2 ratio of 1.05 w/w. Furthermore, the results showed that during the first 5 min of the reaction, the Fenton-like process exhibited the highest percentage of Cr-total and COD removal, which increased with the supernatant’s neutralization.
3.4. Identifying the Effect of the Leather-Related Co-Existing Substances
TWT can contain high concentrations of complex components (COD > 12,000 mg L−1; Cr-total > 3000 mg L−1) that depend on the nature of the animal hides and chemicals used in the tanning process. Therefore, Cl−, BSA, and Cr (III) were isolated in a solution and treated as controls, as were mixtures of two of them, and a mixture of all three. This strategy was used to evaluate the influence of each co-existing substance on the performance of the Fenton-like process for Cr-total and COD removal. For Cr-total removal, statistical analysis (ANOVA, Tukey’s test: α < 0.05) revealed that three different groups could produce an unnaturalized Fenton-like process (Figure 4). The first group, comprising Cr + Cl, had a removal rate of 27%. The second group, consisting of TTW and BSA + Cr + Cl, had a removal rate of around 70%. The final group, which included BSA + Cr and only Cr, had a removal rate of around 50%. nZVI can reportedly remove Cr (III) through adsorption depending on the pH conditions of the medium [12]. This process has been attributed to the interaction between Cr (III) and Fe3+ on the surface of nZVI, which forms Cr–Fe hydroxides and oxyhydroxides [54]. At the end of the experiment, the pH of both the TWT and control samples rose to a range between 5 and 6.5. It is widely recognized that nZVI can raise pH by reacting with water, producing H2 and OH− ions [54]. At a pH exceeding 5, Cr (III) tends to precipitate in the form of hydroxides [55]. Following neutralization, it is plausible that Cr can be predominantly removed (with nearly 100% efficiency) in the form of Cr (OH)3. This finding has been attributed to the dominance of Cr in the system, in the form of Cr (III), which tends to precipitate into hydroxides in neutral pH conditions [54].
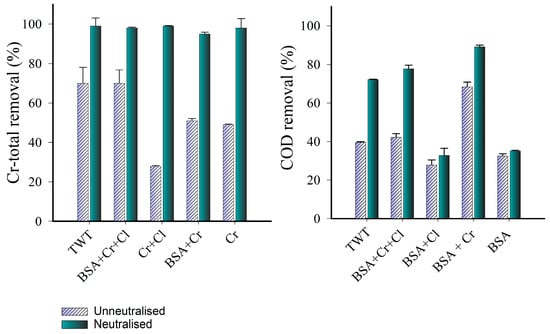
Figure 4.
Leather-related, coexisting substances during Cr-total and COD removal in a Fenton-like process.
Regarding COD removal, our results suggest that the presence of Cr in the system enhanced COD removal that is associated with organic matter. This phenomenon was clear in treatments with BSA, which exhibited the lowest removal efficiency (37 ± 6.5%). However, when Cr was added (BSA + Cr), its efficiency increased up to 77 ± 8.3%. Increased COD removal can be attributed to Cr’s capacity to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the presence of H2O2, thereby contributing to the degradation of organic compounds. Cr can produce free radicals through Cr (III) to Cr (VI) oxidation with H2O2 via the Haber–Weiss-type reaction, leading to a Cr Fenton-like reaction [7,20]. Although Cr (III) typically flocculates in solutions with a pH > 8, it can also occur when the pH < 5. This phenomenon occurs when the Fenton reaction generates hydroxyl ions in situ, leading to flocs formation. These flocs become a heterogeneous catalyst due to their negative zeta potential and Cr (III) ion adsorption capabilities. Additionally, these ions react with peroxide to form OH• and OH−, generating regions around the flocs where the pH is more alkaline than that in the rest of the medium, facilitating Cr flocculation. Inevitably, Cr (VI) is formed via the oxidation of Cr (III) in the flocs; however, due to the acidic conditions of the external medium, it can be reduced again [7]. Figure 4b shows that the COD removal efficiency was lower when chloride ions were present in the medium. This may be because the chloride ion can lead to the formation of inactive iron (III)-chlorocomplexes and Cl2•−, which are much less reactive than OH• [48].
Furthermore, research has demonstrated nZVI ‘s intrinsic ability to produce H2O2 when exposed to aqueous environments, particularly under acidic conditions, owing to its high reducing potential. This phenomenon may elucidate the enhanced removal effect observed in treatments involving chromium. As an additional point of interest, the presence of transition metals can reportedly trigger an Fe3+ to Fe2+ reduction via the catalytic decomposition of H2O2, potentially amplifying the generation of OH• radicals [56]
To assess the chromium removal mechanism in the system using nZVI, three samples were evaluated via XPS, as follows (Figure 5a): nZVI activated before the Fenton-like process (Figure 5b); nZVI after the Fenton-like process (Figure 5c); and nZVI after neutralization (Figure 5d). The Fe 2p spectrum for nZVI activated before the reaction was deconvoluted into five sub-peaks corresponding with Fe0 (705.1 eV), Fe2+ (709.1 and 722.5 eV) and Fe3+ (711.4 and 724.7 eV), with a concentration ratio of Fe0:Fe2+:Fe3+ = 0.05:3:1 [57]. Similarly, the Fe 2p spectrum for nZVI after the Fenton-like process was deconvoluted into four sub-peaks corresponding with Fe2+ (708.5 and 722.5 eV) and Fe3+ (710.9 and 724.7), with a concentration ratio of Fe2+:Fe3+ = 2:1. These results indicate a slight increase in the surface concentration of Fe3+ post-reaction. Additionally, zero-valent iron vanished from the nanoparticle surface in the aftermath of the process. This phenomenon can be attributed to the gradual deterioration of the iron oxide layer after activation, facilitating contact between zero-valent iron inside the nanoparticle and water, leading to Fe2+ and OH− formation, which could potentially explain the observed increase in pH during the reaction [48]. Fe3+ was also produced during hydroxyl radical formation due to the reaction between Fe2+ and H2O2, the scavenging of radicals, reduced Cr (VI) on the surface, and the reaction between Fe2+ and Cl−. Furthermore, under acidic conditions, exposed nZVI may undergo a reaction with H+, resulting in the formation of Fe2+ and H2O2. According to Babuponnusami and Muthukumar, this mechanism may increase efficiency compared with iron salts [33].
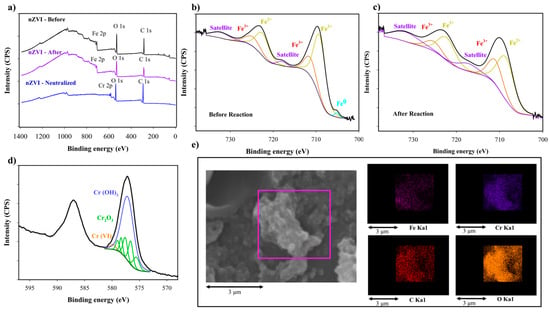
Figure 5.
XPS spectra of nZVI (a); wide-scan and narrow-scan spectra of Fe 2p (b,c); Cr2p (d); and X-ray (EDX) mapping for composite analysis of the sludge produced after neutralization (e).
Cr 2p spectrum is shown after neutralization (Figure 5d). Speciation was characterized using XPS, based on values summarized in Biesinger et al. [58]. The narrow Cr 2p spectra revealed that 97.33% of chromium was present in the reduced state Cr (III), primarily in the form of hydroxide (66.45%), and to a lesser extent, as an oxide (30.88%), with a small proportion of Cr (VI) (2.67%). These findings suggest that the primary mechanism for chromium removal is Cr(OH)3 formation and its fixation on the surface of the nanoparticles, which occur under neutral pH conditions after neutralization [54] This finding is supported by the nearly absent iron signal in nZVI after the neutralization process, indicating that the removed Cr coated the nanoparticles. Additionally, these observations confirmed that Cr (III) can flocculate at pH values < 8, and the presence of Cr (VI) may be caused by the hydroxyl radicals which form during the reaction between Cr (III) and H2O2 on the surface [7]. After treatment, the Eh values of the treated water ranged between 325.9 and 493.4 mV. In the Pourbaix diagram for Chromium, all data points fall within the field of Cr(OH)3, suggesting the stability of this amorphous chemical species, and it verifies the ability of Cr(III) to precipitate [51]. In addition to mapping the sludge using the EDX technique in SEM (Figure 5e), a distinct pattern emerged upon comparing the positions of Cr, O, and Fe. Notably, the quantities of Cr and O were quite similar, whereas the amount of Fe was slightly lower. This observation further supports the hypothesis that Cr removal may occur through Cr (OH)3 formation, which subsequently adsorbs onto the nanoparticle’s surface.
3.5. Recycled nZVI for Cr-Total and COD Removal
The stability and recyclability of nZVIs are crucial to practical applications. After each Fenton-like process, the nZVI was magnetically separated, washed with water and ethanol, vacuum-dried, and subsequently used for the next run after H2O2 was added. After four cycles of experiments, the Fenton-like process for Cr-total was >60% unneutralized and >96% neutralized. Our results indicate that nZVI remained effective at removing chromium from the system even after four usage cycles (Figure 6a). Furthermore, chromium removal remained relatively constant from 5 min up to 90 min, indicating that the majority of chromium was removed within the first few minutes. The removal mechanism under acidic conditions implies the formation of Cr–Fe complexes on the surface. Nevertheless, even after multiple cycles, the creation of such compounds does not saturate the material’s surface [54].
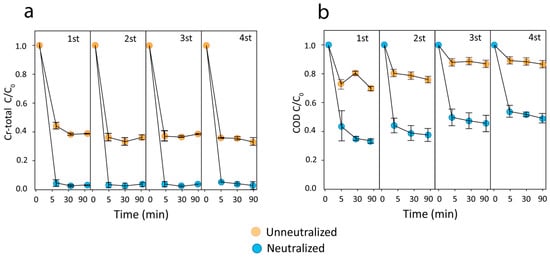
Figure 6.
The recyclability of nZVI (H2O2 added each cycle) for: (a) Cr-total and (b) COD removal.
Cr removal after neutralization exhibited no significant differences during the four cycles (ANOVA: Tukey, α < 0.05), reaching 97% removal at 5 min. These results suggest, as observed in XPS analyses and Lu et al.’s findings, that although Cr almost entirely covers the nanoparticle surface, chromium can be removed through an adsorption mechanism, which enables the self-promoting removal from the aqueous medium due to particle’s Z potential [7].
After four cycles of experiments, the Fenton-like process successfully removed >20% of unnaturalized organic matter and >60% neutralized organic matter (Figure 6b), with the greatest removal rate occurring during the first 5 min. Despite a chromium coating on the nanoparticle, as it developed radicals over the cycles, it can generate free radicals. Although the kinetics inherently depend on the system, our results suggest that the formation rate of OH• due to Cr (III) are lower than the rate exhibited by Fe (II) reaction. This finding is evident in the reduction in COD removal efficiency after four cycles, despite the constant removal of chromium [59].
4. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the performance of Fenton-like processes using commercial nZVI for the simultaneous removal of Cr-total and organic matter from real TWT. The DOE results highlighted the effects that pH and nZVI/H2O2 have on Cr-total removal. The most appropriate fitting model was determined to be the quadratic model from the CC-D/RSM analysis. The optimal parameters comprised a pH of 2.93 and a nZVI/H2O2 ratio of 1.05 w/w. The Fenton-like process using an nZVI catalyst demonstrated a superior efficiency (97.3% ± 5.7% for Cr-total, 73.9% ± 9.1% for COD) compared with the FeSO4•7H2O control (55.6% ± 10.0% for Cr-total, 34.8% ± 10.9% for COD). Recycling experiments demonstrated consistent Cr-total removal after four cycles of experiments, thus affirming the stability of commercial nZVI. XPS analysis confirmed Cr removal through an adsorption mechanism over the nZVI surface. Finally, the Fenton-like process using commercial nZVI worked efficiently in the presence of high concentrations of Cr-total and COD, demonstrating a good performance in the presence of realTWT contaminants. Overall, a Fenton-like process using commercial nZVI is a promising approach for the rapid and efficient treatment of organic wastewater.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16050754/s1, Figure S1: Pareto charts for PB-D, depicting the frequency distribution of the data presented for Cr-total removal. Red line indicates the significant variables at a 0.05; Table S1: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the Plackett-Burman experimental design (PB-D) used to identify the variables that favored higher levels of Cr-total removal during Fenton-like process with commercial nZVI as catalyst; Equation (S1): Linear model the PB-D; Figure S2: Validation graphs showing predicted vs Observed values for PB-D; Table S2: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the Plackett-Burman experimental design (PB-D) used to identify the variables that favored COD removal during Fenton-like process with commercial nZVI as catalyst; Figure S3: Pareto charts for CC-D, depicting the frequency distribution of the data presented for Cr-total removal. Red line indicates the significant variables at a 0.05; Equation (S2): The quadratic model of the response surface; Table S3: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the central composite design (CC-D) used to identify the variables that favored Cr-total removal during Fenton-like process with commercial nZVI as catalyst; Figure S4: Validation graphs showing predicted vs Observed values for CC-D; Figure S5: (a) TWTs before Fenton-like process and (b) TWTs after Fenton-like process.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to collecting and reviewing papers for this editorial. Y.V. primarily led and coordinated this effort. J.F. (Jair Franco), M.V. and F.A. wrote the first draft of this document, and all authors contributed to reviewing and editing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation (MINCIENCIAS) and Sistema General de Regalias (SGR), Colombia [grant number: 2020000100441].
Data Availability Statement
The data used in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Colombiana de curtido and Colombo Italiana industries for allowing us to take samples and work in their facilities. We also thank the Gobernación de Cundinamarca for their support during the execution of this project. We acknowledge the Research Infrastructure NanoEnviCz, supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under Project No. LM2023066.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhao, J.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Guo, H. Tannery Wastewater Treatment: Conventional and Promising Processes, an Updated 20-Year Review. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2022, 4, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina-suarez, N.A.; Machuca-martínez, F.; Barajas-solano, A.F. Advanced Oxidation Processes and Biotechnological Alternatives for the Treatment of Tannery Wastewater. Molecules 2021, 26, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Serrano, A.; López-Alejo, J.E.; Hernández-Cortázar, M.A.; Elizalde, I. Removing Contaminants from Tannery Wastewater by Chemical Precipitation Using CaO and Ca(OH)2. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Stoller, M.; Verdone, N.; Di Palma, L. Fenton Oxidation and Chromium Recovery from Tannery Wastewater by Means of Iron-Based Coated Biomass as Heterogeneous Catalyst in Fixed-Bed Columns. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesMarias, T.L.; Costa, M. Mechanisms of Chromium-Induced Toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalvão, M.F.; de Souza, J.M.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; de Menezes, I.P.P.; da Silva Castro, A.L.; de Lima Rodrigues, A.S.; Malafaia, G. The Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Tannery Effluent in Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus). Chemosphere 2017, 183, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Gao, M.; Sun, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Simultaneous Removal of Cr and Organic Matters via Coupling Cr-Fenton-like Reaction with Cr Flocculation: The Key Role of Cr Flocs on Coupling Effect. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, A.; Fersi, C.; Djebali, K.; Salah, I.B.; Touati, F. Modeling and Optimizing of Coagulation–Flocculation Process by Response Surface Methodology for Rehabilitation of Tannery Wastewater Treatment Plant. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 225, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Peleka, E.N.; Ntolia, A. Treatment of Tannery Wastewater with Vibratory Shear-Enhanced Processing Membrane Filtration. Separations 2019, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.D.; Obayomi, K.S.; Abdulkadir, M.B.; Iyaka, Y.A.; Olugbenga, A.G. Characterization of Cobalt Ferrite-Supported Activated Carbon for Removal of Chromium and Lead Ions from Tannery Wastewater via Adsorption Equilibrium. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpe, S.; Rao, P.V. Application of Advanced Oxidation Processes and Cavitation Techniques for Treatment of Tannery Wastewater—A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A Review on Fenton-like Processes for Organic Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagami, K.; Sakthivel, K.P.; Nambi, I.M. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Tannery Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3656–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, S.; Shan, C.; Ye, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B. Chromium Speciation in Tannery Effluent after Alkaline Precipitation: Isolation and Characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.Q.; Wang, L.F.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.Q. A Fenton-like Process for the Enhanced Activated Sludge Dewatering. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 272, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Ramírez, E.G.; Theng, B.K.G.; Mora, M.L. Clays and Oxide Minerals as Catalysts and Nanocatalysts in Fenton-like Reactions—A Review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.S.; Mohamed, N.Y.; Mostafa, M.K.; Mahmoud, M.S. Effective Chromium Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions and Tannery Wastewater Using Bimetallic Fe/Cu Nanoparticles: Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Network. Air Soil Water Res. 2021, 14, 11786221211028162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; Sebastiani, D.; Miliziano, S.; Verdone, N.; Di Palma, L. Heterogeneous NZVI-Induced Fenton Oxidation Process to Enhance Biodegradability of Excavation by-Products. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Du, Q. Effect of Spatial Distribution of NZVI on the Corrosion of NZVI Composites and Its Subsequent Cr(VI) Removal FromWater. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, J.; Arencibia, A.; López-Muñoz, M.J. Evaluation of NZVI for the Degradation of Atrazine in Heterogeneous Fenton-like Systems at Circumneutral PH. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Verdone, N.; Martinez-Ferez, A.; Di Palma, L. Large Laboratory-Plant Application for the Treatment of a Tannery Wastewater by Fenton Oxidation: Fe(II) and NZVI Catalysts Comparison and Kinetic Modelling. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.F.; Chen, H.W.; Cheng, W.P.; Lin, Y.J.; Huang, C.L. Monitoring of ORP, PH and DO in Heterogeneous Fenton Oxidation Using NZVI as a Catalyst for the Treatment of Azo-Dye Textile Wastewater. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wu, X.; Dai, M.; Lopez-Valdivieso, A.; Raza, S.; Ali, I.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Naz, I. The Sequestration of Aqueous Cr(VI) by Zero Valent Iron-Based Materials: From Synthesis to Practical Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, H. The Use of Zero-Valent Iron for Groundwater Remediation and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilardi, G.; Di Palma, L.; Verdone, N. On the Critical Use of Zero Valent Iron Nanoparticles and Fenton Processes for the Treatment of Tannery Wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 22, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ken, D.S.; Sinha, A. Recent Developments in Surface Modification of Nano Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): Remediation, Toxicity and Environmental Impacts. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprčkal, P.; Mladenovič, A.; Vidmar, J.; Mauko Pranjić, A.; Milačič, R.; Ščančar, J. Critical Evaluation of the Use of Different Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Particles for the Treatment of Effluent Water from a Small Biological Wastewater Treatment Plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 321, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kašlík, J.; Kolařík, J.; Filip, J.; Medřík, I.; Tomanec, O.; Petr, M.; Malina, O.; Zbořil, R.; Tratnyek, P.G. Nanoarchitecture of Advanced Core-Shell Zero-Valent Iron Particles with Controlled Reactivity for Contaminant Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelková, A.; Stejskal, V.; Pluhař, T.; Nosek, J. Advanced Remediation Using Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron and Electrical Current in Situ—A Comparison with Conventional Remediation Using Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron Alone. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.M.; Javed, M.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Mohamed, M.M. Groundwater Remediation Using Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles (NZVI). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 15, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Fenton/Fenton-like Processes with in-Situ Production of Hydrogen Peroxide/Hydroxyl Radical for Degradation of Emerging Contaminants: Advances and Prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. A Review on Fenton and Improvements to the Fenton Process for Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Aslam, Z.; Asghar, A.; Bello, M.M.; Raman, A.A.A. Electrocoagulation of Congo Red Dye-Containing Wastewater: Optimization of Operational Parameters and Process Mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, R.; Aslam, Z.; Abbas, A.; Ahmad, W.; Ramzan, N.; Shawabkeh, R. Adsorptive Potential of Acacia Nilotica Based Adsorbent for Chromium(VI) from an Aqueous Phase. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djimtoingar, S.S.; Derkyi, N.S.A.; Kuranchie, F.A.; Yankyera, J.K. A Review of Response Surface Methodology for Biogas Process Optimization. Cogent. Eng. 2022, 9, 2115283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.O.; Azizli, K.; Isa, M.H.; Bashir, M.J.K. Application of CCD in RSM to Obtain Optimize Treatment of POME Using Fenton Oxidation Process. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 8, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Buitrago, S.Y.; Romero Coca, J.A. Current State Review of the Industry of Tanneries in Its Processes and Products: A Competitiveness Analysis. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Económ. 2017, 26, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible “Resolución 0631 de 2015”. 2015, 73. Available online: https://www.minambiente.gov.co/documento-normativa/resolucion-631-de-2015/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater 22nd Ed; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 5, ISBN 978-087553-013-0. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. In Method 7000B; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; Volume 30, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hodaifa, G.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Rodriguez-Vives, S.; Martinez-Ferez, A. Optimization of Continuous Reactor at Pilot Scale for Olive-Oil Mill Wastewater Treatment by Fenton-like Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Aneggi, E.; Goi, D. Catalytic Activity of Metals in Heterogeneous Fenton-like Oxidation of Wastewater Contaminants: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2405–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Hidaka, T.; Nishimura, F. Linear Relationship between Temperature and the Apparent Reaction Rate Constant of Hydroxyl Radical with 4-Chlorobenzoic Acid. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofrano, G.; Meric, S.; Inglese, M.; Nikolau, A.; Belgiorno, V. Fenton Oxidation Treatment of Tannery Wastewater and Tanning Agents: Synthetic Tannin and Nonylphenol Ethoxylate Based Degreasing Agent. Desalination Water Treat. 2010, 23, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Mohapatra, T.; Ghosh, P. Hydrodynamics, Mass and Heat Transfer Study for Emerging Heterogeneous Fenton Process in Multiphase Fluidized-Bed Reactor System for Wastewater Treatment—A Review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 171, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtab, M.S.; Farooqi, I.H.; Khursheed, A. Sustainable Approaches to the Fenton Process for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Mater Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, T.; Su, F.; Du, J.; Bao, J. Hydrogen Peroxide Activation with Sulfidated Zero-Valent Iron for Synchronous Removal of Cr(VI) and BPA. Catalysts 2022, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusevova, K.; Kopinke, F.D.; Georgi, A. Nano-Sized Magnetic Iron Oxides as Catalysts for Heterogeneous Fenton-like Reactions-Influence of Fe(II)/Fe(III) Ratio on Catalytic Performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241–242, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Mao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Sun, X.; Ma, C. Exothermic Laws Applicable to the Degradation of: O-Phenylenediamine in Wastewater via a Fe3+/H2O2 Homogeneous Quasi-Fenton System. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26283–26290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumovský, M.; Oborná, J.; Lacina, P.; Hegedüs, M.; Sracek, O.; Kolařík, J.; Petr, M.; Kašlík, J.; Hofmann, T.; Filip, J. Sulfidated Nano-Scale Zerovalent Iron Is Able to Effectively Reduce in Situ Hexavalent Chromium in a Contaminated Aquifer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Misra, V.; Singh, R.P. Synthesis, Characterization and Role of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticle in Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Chromium-Spiked Soil. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 4063–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, X.-T.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Fujioka, T.; Varjani, S. (Eds.) Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-3259-3. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, M.; Fan, Z.; Sang, W.; Hao, H.; Wei, X. Removal Mechanisms of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by Biochar Supported Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron: Synergy of Adsorption, Reduction and Transformation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Ma, J.; Xie, L.; Tang, B.; Han, W.; Lin, S. Chromium Removal Using Resin Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Gao, X. Research on the Performance of Modified Blue Coke in Adsorbing Hexavalent Chromium. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Xia, P.; Duan, X.; He, Q.; Sirés, I.; Ye, Z. Accelerating Fe(III)/Fe(II) Redox Cycling in Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process via S/Cu-Mediated Electron Donor-Shuttle Regime. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 342, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Brown, C.; Mycroft, J.R.; Davidson, R.D.; McIntyre, N.S. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Studies of Chromium Compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 1550–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettine, M.; Gennari, F.; Campanella, L.; Millero, F.J. The Effect of Organic Compounds in the Oxidation Kinetics of Cr(III) by H2O2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5692–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).