Abstract
The paper presents a wind–photovoltaic-thermal hybrid-driven two-stage humidification and dehumidification desalination system for remote island regions lacking access to electricity and freshwater resources. By conducting an analysis of the wind and solar energy resources at the experimental site, a suitable wind power station and photovoltaic power station are constructed. The performance of the wind–solar complementary power generation system is then evaluated based on factors such as output power, seawater desalination load power, battery compensation output, system energy consumption, and water production costs. A variable step gradient disturbance method based on the power–duty ratio is proposed for tracking the maximum power point (MPPT) of wind power generation. The output power of the photovoltaic power generation system is optimized, employing a fuzzy logic control (FLC) method to track the MPPT of photovoltaic power generation. This approach effectively addresses the issues of slow speed and low accuracy encountered by traditional MPPT algorithms in tracking the maximum power point (MPP) of both photovoltaic and wind power generations. In order to ensure that the desalination system can operate stably under different weather conditions, eight working modes are designed, and a programmable logic controller (PLC) is used to control the system, which provides a guarantee for stable water production. Experimental results demonstrate that the system exhibits stable performance, achieving a maximum water output of 80.63 Kg/h and daily water yield is 751.32 Kg, the cost of desalination equipment is 1.4892 USD/t.
1. Introduction
The development of the marine economy relies heavily on islands as strategic hubs; however, challenges in electricity and freshwater supply have emerged as significant obstacles to island development. Traditional methods of obtaining freshwater on water-scarce islands primarily involve costly and inefficient transportation and rainwater collection, which only partially fulfills drinking water demands [1]. The majority of islands possess abundant solar and wind energy resources, making the utilization of wind–solar complementary power generation both eco-friendly and capable of reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Consequently, employing renewable energy for seawater desalination holds promising prospects and feasibility [2].
In recent years, desalination technologies have improved in terms of environmental protection, efficiency, and large-scale implementation goals, including reverse osmosis (RO) [3,4,5,6], multistage flash (MSF) [7,8,9], multi-effect distillation (MED) [10,11,12] and humidification and dehumidification (HDH) [13,14,15,16,17]. The application of diverse desalination technologies varies according to different scenarios. RO method requires a high-pressure pump to create the necessary pressure difference across the membrane, leading to significant energy consumption and limited cost-effectiveness, especially in island regions [18]. The MSF evaporation method is well-suited for large-scale equipment and high seawater circulation volumes, but its applicability in remote island areas is limited [19,20,21]. Compared with traditional distillation technology, the advantage of MED [22,23] is that the water making process is simple, but both it and multi-stage flash evaporation are suitable for large-scale equipment, and it is difficult to construct small-scale use in remote island areas. HDH [24,25] desalination is frequently combined with solar energy, has equipment that is easily miniaturized, does not require high pressure, and consumes little energy, making it appropriate for small populations [16].
The process of HDH seawater desalination requires a significant amount of heat energy, which is utilized to warm the air and water. This energy is commonly sourced from geothermal energy, solar power, and factory waste gas. Considering the demand for water production and environmental conditions, the desalination method of HDH combined with wind and solar energy is suitable for island areas.
Wu [26] proposed a three-stage multi-effect isothermal heating method to supply energy to the system. The heat energy comes from the solar collector, the upper and middle stages are isothermal heating, and the lower-level recovers heat, which further improves the equipment performance and water production. The performance coefficient is up to 2.65, and the water production is 182.37 kg/h. Zhao et al. [27] proposed a renewable-driven standalone combined power and water supply system with cascade electricity and heat storage. The hybrid wind–solar power generation system is used as energy, the HDH desalination technology is used to produce freshwater, and the cascades of electricity and heat storage devices are used. The heat source is a heat storage system based on a carbon dioxide heat pump, and underwater compressed air energy storage (UW-CAES) is introduced to smooth the fluctuations of renewable energy and significantly improve energy efficiency. Elminshawy et al. [28] designed a geothermal energy and solar energy integrated humidification and dehumidification desalination system, where the geothermal energy heats the seawater in the humidification chamber, and it was tested that the geothermal energy heats the water at a temperature of more than 60 °C, with 0.15 Kg/s as the optimum working condition, with a GOR of 1.2–1.58, and a cost of freshwater of 0.003 USD/L. R. Santosh et al. [29] recovered waste heat from an air conditioning unit to be used for humidification and dehumidification desalination, where hot air is mixed with sprayed seawater to form high-temperature, high-humidity air, which enters a condenser to produce freshwater. The cost per kilogram of freshwater was verified by simulation and experiment to be USD 0.1658.
The present study introduces a two-stage HDH desalination system that utilizes wind–solar complementary power supply, along with the incorporation of solar thermal energy. The seawater desalination process begins at the top and works downward, spraying hot seawater for mass transfer and heat into high-temperature, high-humidity air that is sent to the dehumidification cavity, where cold freshwater is sprayed to allow the hot, humid air to condense and produce freshwater. The paper proposes a fuzzy logic control-based approach for optimizing photovoltaic MPPT, faster tracking and less fluctuation than perturbation observation and conductivity increment methods; the gradient perturbation method based on the power duty ratio is employed to optimize the MPPT of wind power generation, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the power supply system. Subsequently, a comprehensive investigation into multi-mode energy control and management is conducted. This work is innovative in that it designs a two-stage HDH desalination unit with reheat to minimize heat loss and increase water production efficiency, and utilizing green energy to power the seawater desalination system and adjusting the power supply mode based on environmental circumstances to ensure that it operates normally.
2. System Scheme and Design
The whole desalination system comprises wind–solar complementary power supply device and seawater desalination device. Power supply devices primarily consist of wind–solar complementary power stations and energy storage equipment. The desalination part mainly consists of solar collectors, HDH devices, freshwater collection tanks, and seawater supply devices. The experiment site is located on the coast of Maowei, Qinzhou, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, the coordinates are 21°53′10″ N, 108°37′22″ E, Qinzhou is located south of the Tropic of Cancer, within the monsoon zone of southeastern Asia, with strong solar radiation and pronounced monsoon circulation.
2.1. Design of a Two-Stage HDH Seawater Desalination System
HDH seawater desalination device technology is based on the theory of evaporation and condensation to carry out, with flowing air as the carrier of water vapor, the air in the humidification chamber is humidified by vaporized seawater and becomes high-temperature, high-humidity air, which then enters the dehumidification chamber and condenses to obtain freshwater. Between the air and water can be heat and mass transfers, so the thermal performance characteristics of HDH seawater desalination technology need to be guaranteed, and the use of solar energy for HDH seawater desalination systems to provide thermal energy, not only is the structure simple, but it also is able to reduce environmental pollution [30]. The two-stage HDH seawater desalination system includes solar collectors, humidifiers, dehumidifiers, fans, water pumps, coils, and heat storage tanks.
In this paper, the heating seawater type of HDH technology is selected, and hot seawater is sprayed in the humidification chamber for air humidification. The vacuum tube solar collector heating seawater, as shown in Figure 1, has a heating area of 120 square meters and an inclination angle of 22° faces due south. The heated seawater is stored in the hot water tank, which uses polyurethane material as the insulation layer and has a height of 1.8 m and a capacity of 2 tons.

Figure 1.
Solar heat collection device.
The principle of a two-stage HDH desalination system with reheat is shown in Figure 2. Each stage is a humidifier on the bottom and a dehumidifier on the top. The first HDH process on the top is high temperature, and the second HDH process on the bottom is low temperature. The air is flowed from the bottom to the top, which is in line with the law of air convection and reduces heat loss.
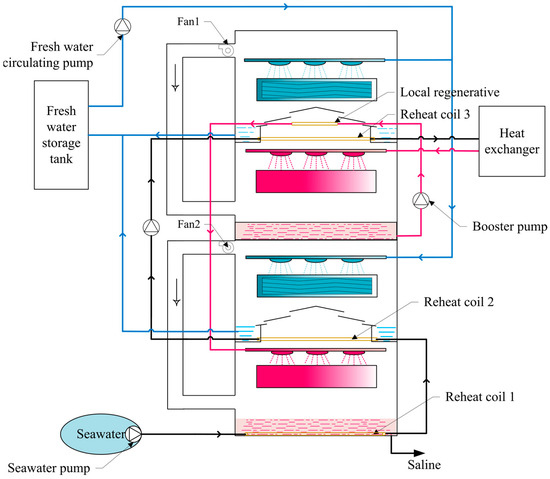
Figure 2.
Two-stage humidification and dehumidification desalination schematic diagram.
Seawater flows first into the low-temperature level humidification chamber reheat coil, after a return heat of seawater, and then into the low-temperature level dehumidification chamber of freshwater in the return coil, resulting in the formation of the second reheat. The second reheat of seawater will then be pumped into the high-temperature level humidification chamber back to the return coil, resulting in the formation of three times the heat. Following three rounds of heat recovery, it enters the heat exchanger, which is linked to the solar energy gathering system to raise the seawater temperature even further. It is then sprayed in the high-temperature humidification chamber. The air in the humidification chamber becomes high-temperature and high-humidity air after high-temperature spraying, which meets the cold water sprayed through the circulating air ducts inside the humidification chamber and dehumidification chamber for condensation. Seawater is fed into the low-temperature stage humidification chamber for secondary evaporation and condensation after initial evaporation in the high-temperature humidification chamber. This device improves condensation efficiency and heat usage when compared to single stage humidification and dehumidification.
The primary reheating coil is placed in the low-temperature level humidification chamber thick brine, thick brine to provide heat; secondary reheating coil is placed in the low-temperature level humidification chamber and dehumidification chamber in the middle of the ventilation sink, the flow of high-temperature high-moisture air to play a role in heat preservation; tertiary reheating coil at the bottom of the high-temperature level dehumidification chamber, high-temperature high-moisture air condensation to emit heat. Each time the seawater reheating process is in the low-temperature stage humidification chamber reheating coil, the low-temperature stage dehumidification chamber reheating coil, and the high-temperature stage dehumidification chamber reheating coil, respectively, after three times of reheating, seawater can increase the temperature of the seawater sprayed in the low-temperature stage humidification chamber to avoid the loss of heat by directly discharging the seawater after one time of evaporation. As shown in Table 1, this idea is verified by comparing the temperature increase at the reheat after spraying seawater at different temperatures.

Table 1.
Increases in reheat temperature for different spray temperatures.
From Table 1, it can be seen that after three cycles of reheating, the seawater temperature after reheating shows a warming phenomenon. As the temperature of the seawater sprayed for the first time in the high-temperature stage increases, the effect of reheating becomes more and more obvious. This indicates that the temperature of the primary evaporated seawater did not decrease when it passed through the reheat coil and then the secondary spray.
A water production test was carried out under the same environmental conditions in order to look into the differences between the water production performance with and without reheat coils. The experimental results are displayed in Figure 3.
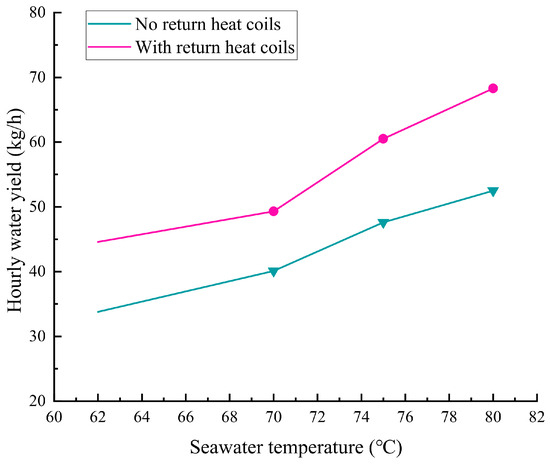
Figure 3.
Water yields with and without return coils at different seawater spray temperatures.
From the Figure 3, it is easy to see that the water production rate of the desalination device appears to increase rapidly with the increase in spraying temperature, especially when the temperature of the sprayed seawater is higher than 70 °C. For the condition of the reheated water, the water production rate is obviously increased when the temperature of the sprayed seawater is the same. This is due to the fact that the setting of the reheat coil strengthens the condensation effect of the dehumidification chamber of the high-temperature stage on the one hand and increases the temperature of the sprayed seawater in the humidification chamber of the low-temperature stage on the other hand, which strengthens the humidification effect. In addition, when the temperature of the sprayed seawater is low, the effect of the heat return device on improving the performance of the desalination unit is not obvious.
2.2. Energy Consumption Analysis of Seawater Desalination System
The use of solar collectors for saltwater heating efficiently reduces power consumption and relieves strain on power supply systems. The principal electrical components of the desalination plant are pumps and fans, with full power specifications supplied in Table 2.

Table 2.
Loads power of seawater desalination devices.
2.3. Wind Power Station Design
Wind power generation is primarily determined by wind turbine performance and wind speed dispersion. A wind turbine is chosen after an analysis of the wind energy resources in the Qinzhou. Using an environmental observing device to collect environmental data for the entire year of 2022, analysis reveals that the average annual wind speed at the experimental site is 3.61 m/s, as shown in Figure 4. The wind turbine model chosen is the NE-2000L1 (Jiangsu Naier Wind Power Company, Wuxi, China), with a rated power of 2 kW.
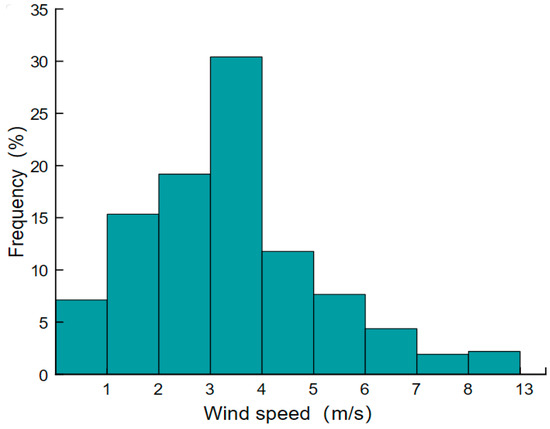
Figure 4.
Wind speed frequency distribution.
Combining the frequency of wind speed distribution throughout the year in Figure 4 and the power generated by the wind turbine at different wind speeds, the annual power generation of the wind turbine is estimated to determine the specifications of the wind turbine selection. The specific data are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Estimated power generated by wind turbine.
Combined with the data in Table 3, the calculation shows that the wind turbine generates an average of 3.1 kWh per day. The wind generator in this design is primarily complimentary to the solar power station, charging the battery during the night to satisfy the next day start-up conditions. The seawater extraction pump for the desalination system must operate for 0.5 h, using 0.25 kWh of electricity, before 8:00 a.m. every day. The wind generator in this design is primarily complimentary to the solar power station, charging the battery during the night to satisfy the next day start-up conditions. The seawater extraction pump for the desalination system must operate for 0.5 h, using 0.25 kWh of electricity, before 8:00 a.m. every day. During this time, the photovoltaic power generation device is ineffective due to low solar irradiance, and the wind power generation device and energy storage device are out of power. If only the next day’s start-up is considered, fitting a wind turbine model NE-2000L1 can meet the demand. Figure 5 depicts the wind turbine operation curve on the test day (2 July 2022).
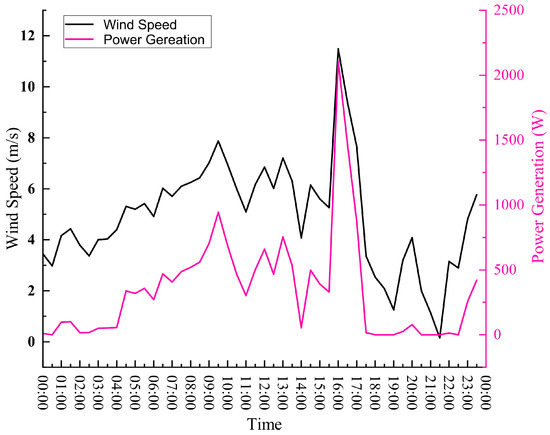
Figure 5.
Wind speed and wind turbine power generation changing curve over time.
2.4. Photovoltaic Power Station Design
Photovoltaic cells are subject to various factors during the generation process, including temperature, solar radiation intensity, load impedance, and shadow blockage. Therefore, it is imperative to accurately estimate electricity demand and photovoltaic power generation while controlling costs and avoiding resource waste.
Solar photovoltaic cell power generation is calculated by Equation (1).
where is the solar radiation in the horizontal plane (kWh/m2); is the nominal power of the photovoltaic cell module (kW); is the irradiance of the photovoltaic cell under standard conditions, 1 kWh/m2; and is the correction factor, taken as 75–85%, depending on the actual device.
The photovoltaic power station employs photovoltaic modules with a rated power of 275 W each, and the estimation of power generation is based on measured solar irradiance, thereby determining the quantity of photovoltaic panels. The monthly solar radiation of Qinzhou in 2022 is shown in Table 4. Combined with Equation (1) to estimate the monthly power generation of a single photovoltaic panel, and these specific values are illustrated in Table 5.

Table 4.
Solar radiation in different months at the experimental site in 2022.

Table 5.
Estimated power generation of a single photovoltaic panel.
According to the design scheme, the power supply of the independent solar cell needs to meet the normal operation of the desalination device for 6 h. The power consumption of seawater desalination equipment is calculated by Equation (2).
where is the load power (kW); is the system uptime (h); is the safety factor, generally taken as 1.1~1.2; and is the number of days the equipment is running.
From Table 2, it can be seen that the maximum power consumption of the seawater desalination system equipment is 2.75 kW, the stable operating power is 2 kW, and the daily working time is 6 h. According to Equation (2), the average monthly power consumption is 528 kWh. Considering wind power generation and energy storage equipment as complementary energy sources, selecting nine solar panels arranged in three parallel groups with each group consisting of three panels connected in series. The power output of each group is 1.08 kW, resulting in a total power capacity of 2.4 kW.
Solar irradiance not only affects photovoltaic power generation but also relates to the efficiency of solar collector systems in heating seawater. The variation curves of seawater temperature and power generation with irradiance are shown in Figure 6.
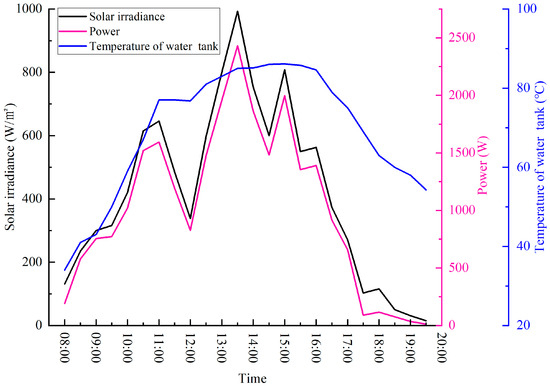
Figure 6.
Seawater temperature and power generation with irradiance curve.
2.5. Energy Storage System Design
When a wind turbine or solar power generation device fails to function, it must be equipped with energy storage equipment with adequate capacity as a backup power supply, and desalination equipment must be turned off at night. Wind turbine power generated at night is stored in a battery. Estimation of battery capacity using Equation (3).
where is the battery discharge, Ah; is the safety coefficient, generally 1.1–1.4; is the power of the equipment, W; is the working time, h; is the temperature coefficient, generally above 0 °C to take 1; is the battery discharge voltage, V; is the depth of discharge, typically 0.85 for lead batteries; and is the discharge efficiency.
The design goal of this desalination system is to ensure the daily water consumption of three to five persons, which requires approximately 400 kg of freshwater, thus the battery storage capacity is set to keep the device operational for roughly 5 h. After computation, the battery’s total capacity is 1135.19 Ah, and in this system, five lead-acid batteries with a capacity of 250 Ah and a voltage of 12 V are utilized in conjunction with a 5 kW inverter.
3. Power Generation Efficiency Optimization of Wind–Solar Energy Hybrid
3.1. Power Generation Efficiency Optimization of Wind Power Generation
In a wind power generation system, the random variability of wind speed affects the output power of the generator and reduces the quality of power generation. Reasonable use of MPPT methods can achieve maximum utilization of wind energy. The common MPPT methods in wind power generation devices include the following: optimal blade tip speed ratio method, mountain climbing search method, and power feedback method [31].
The climbing search method [32] is widely used in small wind turbines, as shown in Figure 7; the principle is to compare the output power of two consecutive control cycles Pn and Pn−1, if Pn > Pn−1 to maintain the original direction to continue to the speed of the perturbation; otherwise, to the opposite direction of the speed of the perturbation, until the perturbation of the search for the MPP (maximum power point).
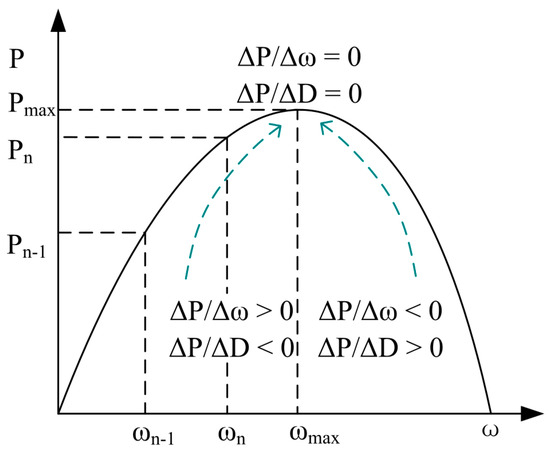
Figure 7.
Relationship between output power and rotating speed of a wind turbine generator.
The power duty cycle-based gradient perturbation method, like the hill-climbing search method, regulates the equivalent load of the wind turbine by varying the duty cycle of the switching devices in the boost circuit, so that the generator can output the maximum power when the generator’s output characteristic matches the load’s output characteristic.
Combining Figure 7 and Figure 8, the following can be seen: at the maximum power point, and in the boost circuit; according to the existence of the relationship between the angular velocity of the machinery and the generator’s angular velocity , it is introduced that ; the generator’s output phase voltage is directly proportional to the input voltage of the dc-regulator circuit, , and the phase voltage is also directly proportional to the , and so The synthesis leads to the following relationship:
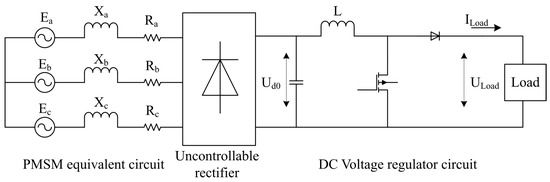
Figure 8.
Equivalent circuit diagram of wind power generation.
As a result, the condition for determining the MPP can be substituted with . This approach uses the duty cycle directly as a control parameter, adjusting the output power by increasing or reducing the duty cycle. On the other hand, perturbation with a fixed step size results in decreased accuracy and extended tracking time. This paper proposes a disturbance method with variable step size for power duty cycle, which first tracks with a high step size before switching to tracking with a small step size after quickly approaching the MPP.
It is worth noting that when the duty cycle approaches the MPP, the disturbance step size decreases, resulting in cyclic disturbances. Therefore, a scheme to automatically change the step size according to the power duty cycle slope is proposed. Set two thresholds, λ1 and λ2 (both are very small non-negative real values), and the gradient-based optimization search approach is utilized when . When , it is proved that the search area has reached the near the maximum power point, and the disturbance is stopped at this time; the mountain climbing search method is used when between λ1 and λ2. Its flow chart is shown in Figure 9.
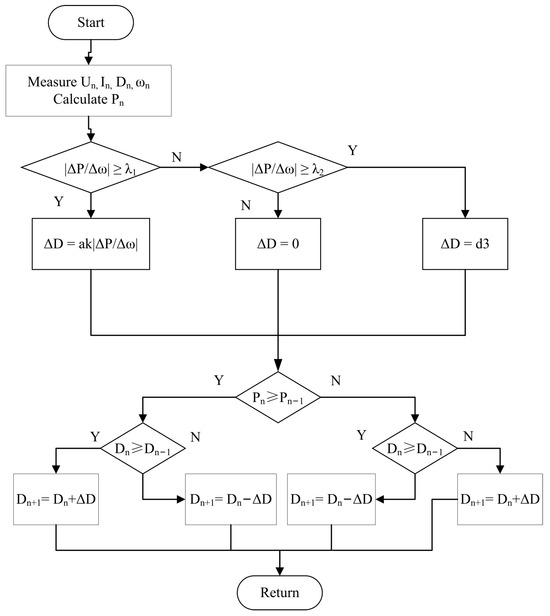
Figure 9.
The flowchart of the MPPT algorithm.
Build a wind power generation simulation model in MATLAB/Simulink, the air density is set to be 1.29 kg/m3, the radius of the wind turbine blade is 1.6 m, the simulation duration is 3 s, the initial value of the duty cycle is 0.3, and the perturbation value of the fixed step size . The experiment was carried out in 1 s, and 2 s; the wind speed was 7 m/s and 10 m/s. Simulation model is shown in Figure 10.
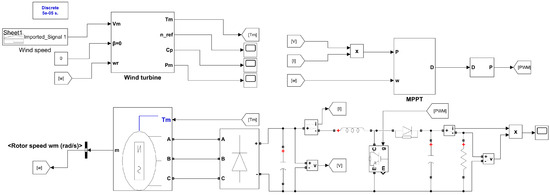
Figure 10.
MATLAB/Simulink model of the wind power generation module with MPPT.
The results of a simulation using the power duty cycle perturbation method with variable step sizes to track the MPP are shown in Figure 11. When the wind speed changes from 7 m/s to 10 m/s at 1 s, the maximum power at this wind speed is tracked at 1.06 s with a tracking time of 0.06 s. The wind speed drops from 10 m/s to 7 m/s in 2 s, and the power output is stabilized by a 0.05 s time delay. The power duty cycle perturbation approach with variable step size not only swiftly tracks the highest power point, but it also lowers variation.
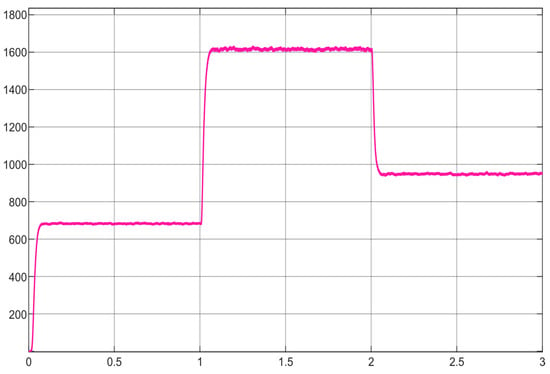
Figure 11.
Performance of a power duty cycle gradient perturbation MPPT.
3.2. Power Generation Efficiency Optimization of PV Power Generation
The PV panel exhibits a fixed maximum power point under specific temperature and solar irradiance conditions, which results in nonlinear fluctuations in the output rate when this point changes [33]. The power output characteristic curve (P-U) of the PV panel under different irradiance and temperature are shown in Figure 12.
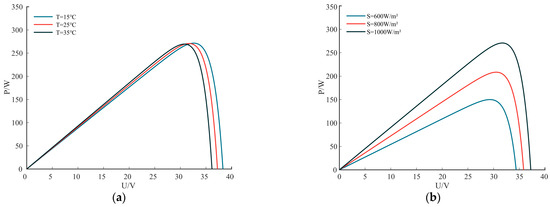
Figure 12.
(a) Characteristic curves at different temperatures; (b) Characteristic curves at different irradiances.
The fuzzy logic control (FLC) algorithm is employed for MPPT control of photovoltaic power generation in this design. The FLC [34] algorithm enables the realization of complex nonlinear mappings, exhibiting strong robustness and adaptability. Consequently, it finds extensive application in systems characterized by inaccuracies in modeling. Conventional control methods, such as the disturbance observation method and conductivity increment method [35], exhibit sluggish tracking speed and significant power fluctuations in response to changing external conditions. The designed fuzzy controller is a dual-input single-output with error and error variation as inputs, and the output is the variation of duty cycle D of the boost circuit. The input variables are shown in Equations (5) and (6), and and denote the current sampling data and the last sampling data.
From Figure 12, it can be seen that when , the PV cell works at the maximum power point in the current environment; when , it is on the left side of the maximum power point; and when , it is on the right side of the maximum power point. This leads to the following conclusions:
- (1)
- When and , the output power is to the left of the maximum power point and is moving away from it.
- (2)
- When and , the output power is to the left of the maximum power point and is approaching the maximum power point.
- (3)
- When and the output power is to the right of the maximum power point and is moving away from the maximum power point.
- (4)
- When and , the output power is to the right of the maximum power point and is approaching the maximum power point.
Based on the foregoing findings, fuzzy rules are created to make close to the direction equal to zero, and when is far from the maximum power point, the trapezoidal affiliation function [26] is used to regulate in small steps, while the triangular affiliation function is used to regulate in large steps. The structure of MPPT control is shown in Figure 13.
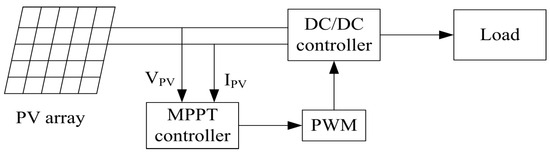
Figure 13.
MPPT control block diagram.
The MATLAB/Simulink model of a solar PV array with FLC control algorithm is shown in Figure 14. The simulation time was 1.5 s, and the test temperature was set at 25 °C. The irradiance abruptly increased from 800 W/m2 to 1000 W/m2 at 0.5 s. At 1 s, the irradiance decreases to 600 W/m2. Figure 15 compares the FLC method to the P&O and Inc methods. It can be seen that the tracking of the maximum power point using the FLC method is fast and accurate and can achieve optimization of the output power.
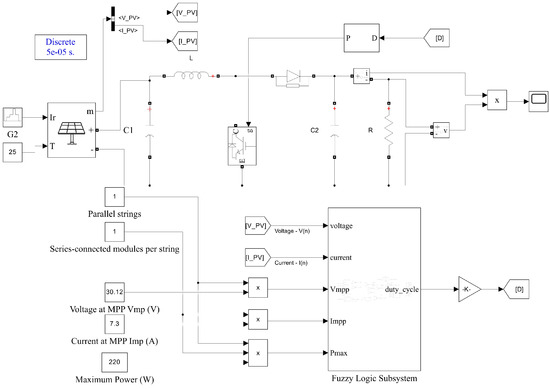
Figure 14.
MATLAB/Simulink model of the solar PV module with FLC MPPT method.
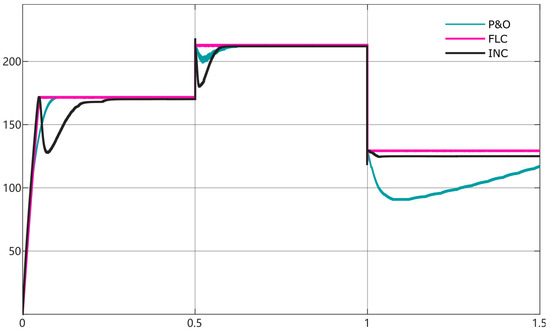
Figure 15.
Performance of FLC MPPT.
4. Energy Optimization Management Strategy
The energy management and coordination control approach are linked to the efficiency of wind–solar hybrid power generation and desalination system water output. The coordinated management is optimized in terms of the desalination system’s own characteristics, the stability of the power supply system, and the overall system coordination by taking the power generation efficiency and the charging and discharging rules of the storage battery and ensuring the stability of the load’s power consumption into account.
The control system adopts a Siemens S7-1200 series PLC, and the programming environment is SIMATC STEP 7 BASIC/PROFESSIONAL. The control system is divided into three sub-systems, which are the wind and solar complementary power generation systems, the collector cycle system, and the desalination system. The control system structure diagram is shown in Figure 16.
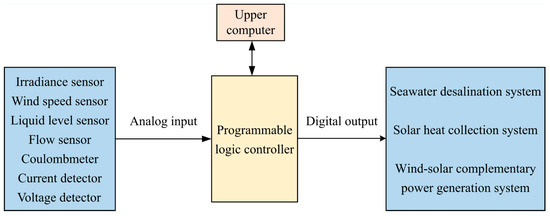
Figure 16.
Control system structure diagram.
4.1. Analysis of the Operation of Wind–Solar Hybrid Power System
According to changes in meteorological conditions, wind–solar complementary power generation systems exhibit wind–solar–battery complementary power supply, independent wind power supply, independent solar power supply, and energy storage battery power supply under wind and solar, wind no solar, no wind no solar, and no wind no light meteorological conditions. In these four operating states, changes in solar energy intensity, wind energy intensity, and load power consumption lead to changes in the power balance of the system, which manifests itself in different operating modes.
When the wind turbine and photovoltaic panels, as well as the energy storage battery, work together, the overall energy flow is shown in Figure 17. The power relationship is as shown in Equations (7)–(12) based on the wind turbine output power , photovoltaic battery output power , load power , and battery charging and discharging power to carry out the system power balance judgment and to determine the operate state of each supply electronic system.
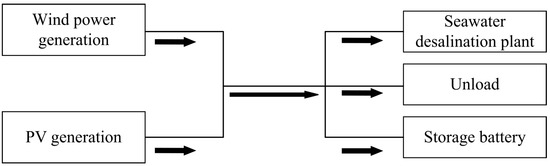
Figure 17.
Schematic diagram of energy distribution.
The desalination technique described in this research is a two-stage humidification and dehumidification method using solar-heated saltwater, and the system must consider energy processing methods throughout the day and night, thus the operating mode is designed based on power generation.
4.2. Desalination System Operation Mode Control
A desalination system’s energy supply from solar and wind power, changes in environment and load power both affect the energy utilization of the power supply system. How to use the limited energy generated by the wind–solar hybrid power supply system to ensure the continuous and stable water production of the seawater desalination system is a prerequisite for designing control strategies.
Through the use of sensors to collect solar irradiance, wind speed, seawater temperature, hot water tank temperature, current and voltage, and other data to the signal module, in the signal module to complete the A/D conversion, the current signal into a data volume signal, winding and sent to the CPU, the CPU through the logic of the control program to complete the processing of the data volume, converted to the actual value of the project to be stored in the registers, and the PLC through the cable to communicate with the upper computer to facilitate the control of managers.
According to the changes in the wind and solar environment, it can be divided into eight modes (considering the full power operation of the seawater desalination system), as shown in Figure 18.
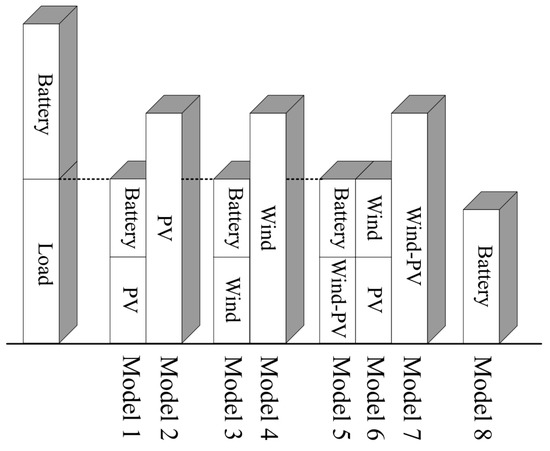
Figure 18.
Schematic diagram of the working mode of the power supply device.
Modes 1–4 separate the photovoltaic power supply or the wind power supply. If the photovoltaic power generation or wind power generation is unable to meet the load of electricity, the need for battery-assisted power supply, at this time the energy relationship as shown in Equations (7) and (8). To meet the desalination device under the premise of the demand for electricity excess power stored in the battery, the battery is fully charged to access the unloading device, the power generation device, and the load relationship to meet the Equations (9) and (10). Mode 4 also represents the state of the wind turbine at night. Considering that the desalination unit does not work at night, when there is no power demand for the desalination unit, the wind turbine power is input to the battery to prepare for the next day’s start-up.
Modes 5–7 refer to the wind and solar environment meeting the working conditions of the wind and the photovoltaic power generation device. When the power of wind and solar complementary power generation cannot meet the power of seawater desalination devices, energy storage devices need to intervene, and the energy relationship is shown in Equation (11). When meeting the electricity demand of the seawater desalination device, the power relationship conforms to Equation (12), and the excess electricity is stored in the battery.
Mode 8: The wind–solar hybrid power generation device has not reached its starting conditions; the battery alone supplies power to the load.
5. System Operation Experiment and Water Production Cost Analysis
After the trial setup was completed, the performance of the desalination system was evaluated by assessing the plant’s power generation, water production, and energy consumption. Figure 19 shows part of experimental devices and repeated water production tests were conducted in July 2022, with daily testing time from 08:00 to 20:00.

Figure 19.
(a) Solar collectors and desalination devices; (b) Two-stage humidification and dehumidification desalination device.
The wind speed and solar irradiance on the day of the test are displayed in Figure 20, and the weather was cloudy to sunny, with a southeasterly breeze of 4 and a temperature range of 25–33 °C, making for a pleasant picturesque scene.
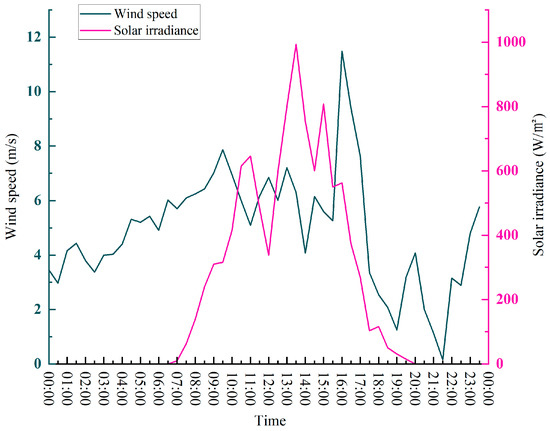
Figure 20.
Wind speed and solar irradiance curves on the test day.
Figure 21 shows the 24 h power generation of the power supply device and the SOC of the energy storage battery on that day. Before 08:00, the initial SOC of the battery is 26%, and the solar irradiance does not meet the conditions of photovoltaic power generation; at this time, the power supply mode is Mode 4. The wind generator outputs power to charge the battery, and by the time the seawater desalination system is switched on (08:00), the SOC of the battery is 40.71%, which is consistent with the system power-on operation conditions.
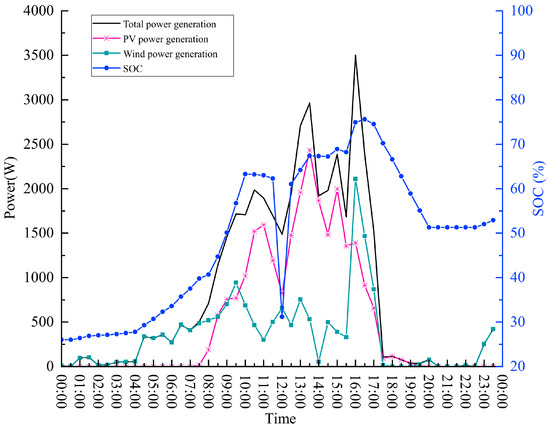
Figure 21.
Wind and solar hybrid supply system operation curves.
5.1. System Operation Experiment
The performance of the desalination system was evaluated by wind and solar power generation, load power, battery compensation power, and water production. The data were recorded every half hour during power-on operation, as shown in Figure 22. When the system is started, the set power supply shall be more than 500 W, and the battery capacity shall be more than 20%; the shutdown condition is when battery capacity is less than 10%.
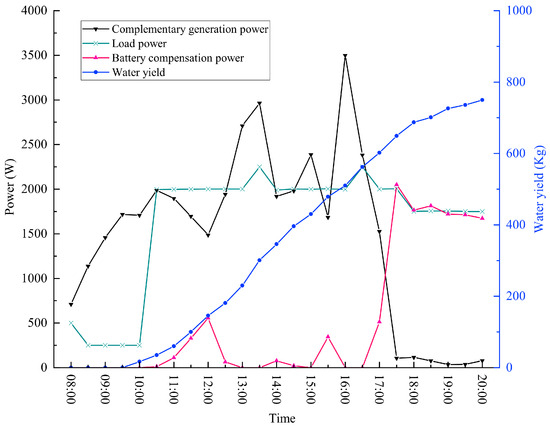
Figure 22.
Relationship between output power of power supply system and water yield on test day.
During 08:00–10:00, switch to Mode 6. Wind turbine and photovoltaic panels complement each other to generate electricity. When the temperature of the hot water storage tank does not reach 75 °C, the desalination device does not work, the submersible pump needs to pump seawater to the hot water storage tank, the desalination device, and the solar collector, and the collector circulating pump circulates the hot water to the solar collector and the hot water storage tank.
After 10:00, the temperature of the hot water storage tank reaches the system’s set temperature, the entire set of seawater desalination devices begins to work, the power generation power reaches 2000 W, and the complementary power generation power is greater than the seawater desalination device when the excess power for battery charging is insufficient.
During 11:00–12:30, 13:30–14:30, 15:00–16:00, and 16:00–20:00, the wind and solar hybrid power fail to reach the power demanded by the desalination unit, switching to Mode 5, with power compensation by the battery. The hot water storage tank and solar collector are thermally insulated, and their temperatures begin to fall between 17:00 and 20:00, when they drop to around 55 °C, which is insufficient to meet the desalination plant’s working parameters. The system has been turned off, and the battery’s SOC is 51.34%. In this test, the system operated stably for 10 h and produced water at a rate of 75.13 kg/h. The freshwater production reached 751.32 kg, which can meet the daily freshwater demand of 3 to 4 adults.
5.2. Water Production Cost Analysis
On the test day, it was noted that the solar panel produced 12.16 kWh of electricity while the wind turbine produced 8.33 kWh. Figure 22 illustrates how the wind–solar hybrid power generation device stores electricity in the storage battery once it satisfies the load demand of the seawater desalination equipment, where the equipment’s actual power consumption falls short of the total power generation. After the meter record, the system uses 12.99 kWh of electricity on the day of the test, and 1 kWh of electricity consumption can drive the desalination device to produce 57.81 kg of water, and it can be deduced that the production of 1t of freshwater consumes 17 kWh.
The construction investment cost mainly includes equipment costs, installation costs, and maintenance costs. The wind and solar complementary power generation system mainly includes solar battery packs, wind turbines, storage batteries, controllers, inverters, distribution cabinets, mounting brackets, etc., and the total investment cost (including installation costs) is about USD 6778.33.
The main equipment of the desalination system includes solar collectors, pumps, piping, hot water storage tanks, stainless steel, heat exchangers, insulation, and humidifying fill materials, and its total cost is about USD 7675.78.
Operation and maintenance costs mainly include overhauls, maintenance, and replacement of equipment components. The annual equipment overhaul and maintenance cost is 0.8% of the fixed asset value, which is USD 115.63 a year, the battery replacement cycle is 4 years, with an average annual replacement cost of USD 139.06, the hot water storage tank replacement cycle is 3 years, with a replacement cost of USD 27.81 a year, and the humidification and dehumidification chamber internal device and piping replacement cycle is 2 months, with a yearly replacement cost of USD 66.75.
Analyzed in Section 2.3 and Section 2.4, the theoretical maximum total annual power generation of the wind power plant can be calculated from Equation (13).
where is the theoretical maximum power generation of the wind turbine, kWh; is the rated power of the wind turbine, kW; and is the number of hours of rated power operation in a year, h.
The theoretical maximum power generation of wind turbine is = 2 × 3 × 365 = 2190 kWh.
Equation (13) shows the calculation of the theoretical maximum value of the total annual power generation of the photovoltaic power.
where is the theoretical maximum power generation of the PV panel, kWh; is the rated power of the PV panel, kW; and is the number of hours of rated power operation in a year, h.
The theoretical maximum power generation of photovoltaic power station is kWh.
The theoretical power generation capacity of a wind–solar complementary power generation device for one year is 6802.14 kWh, taking into account the decline in the performance of solar panels and wind turbines, the efficiency of the control system, and climate change, and taking the actual output power of the system to be 85% of the peak power, so the annual power generation capacity of the whole set of system is about 5782.04 kWh, and the maximum service life of the equipment is 20 years, which when combined with the above analysis of the cost of inputs, it is concluded that the electricity generated by the wind and solar complementary power generation device is 0.0876 USD/L. It can be seen that 1t of freshwater requires 17 kWh of electricity, and when the cost of electricity is 0.0876 USD/L, the cost of desalination equipment is 1.4892 USD/t.
The higher cost of water production is due to the use of solar collectors in the desalination system, which cannot be operated at night, resulting in the power stored in the batteries not being able to drive the desalination unit at night, so that seawater heating devices should be installed in the subsequent improvement process, and pipelines corroded by seawater should be replaced in a timely manner, and geothermal energy can be combined with geothermal energy to drive the desalination unit in areas with abundant geothermal energy.
6. Conclusions
The present study proposes a two-stage humidification and dehumidification desalination system with regenerative heat, and the temperature of seawater sprayed twice after the regenerative device is added and the water production rate is compared. Furthermore, a well-designed wind–solar complementary power generation scheme is developed through an analysis of the energy consumption of the experimental equipment, as well as the available wind and solar energy resources. A fuzzy logic control-based method is proposed for maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of photovoltaic power plants. The fuzzy logic algorithm demonstrates superior performance in terms of faster tracking speed and smaller amplitudes at the maximum power point compared to the conductivity incremental method and the perturbation observation method, thereby enhancing the efficiency of photovoltaic power generation. The proposed method for wind power MPPT is a power duty cycle-based gradient perturbation approach, which automatically adjusts the search step according to the slope of the P-ω curve. It also proposes eight kinds of wind–solar–battery complementary power supply modes that realize reasonable energy distributions and switch different power supply schemes when the wind environment changes. The experimental results demonstrated that, under typical weather conditions, the daily water production achieved a value of 751.32 kg, with an average hourly water production rate of 75.13 kg and a maximum water production rate reaching 80.63 kg/h, which aligned precisely with the anticipated standard.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Q. and W.X.; methodology, K.H. and J.Y.; software, K.H., J.Y. and G.H.; validation, W.X., J.H. and C.Z.; formal analysis, K.H., Y.Z. and K.C.; investigation, W.Q., G.H. and J.H.; resources, W.Q., K.C., Y.Z. and C.Z.; data curation, K.H., W.Q. and G.H.; writing—original draft preparation, K.H. and C.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.H., K.C. and Y.Z.; visualization, G.H.; supervision, C.Q. and W.X.; project administration, K.H. and J.Y.; funding acquisition, C.Q. and W.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the High-end Foreign Expert Introduction Plan: G2022033007L; Project of Qinzhou Science and Technology Source: 202116622; Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Guangxi Minzu Normal University: 2023SBNGCC011; CSSC Guangxi Shipbuilding and Offshore Engineering Technology Collaboration Project: ZCGXJSB20226300222-06.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be obtained by contacting the author, Kaijie Huang (hkjynlo@163.com).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Karnauskas, K.B.; Donnelly, J.P.; Anchukaitis, K.J. Future Freshwater Stress for Island Populations. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Sharizal Abdul Aziz, M.; Palaniandy, P.; Shaik, F. A Review on Application of Renewable Energy for Desalination Technologies with Emphasis on Concentrated Solar Power. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Tansel, B. Novel Technologies for Reverse Osmosis Concentrate Treatment: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 150, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, K.; Yang, D.R.; Hong, S. A Comprehensive Review of Energy Consumption of Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination Plants. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse Osmosis Desalination: Water Sources, Technology, and Today’s Challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabelas, A.J.; Mitrouli, S.T.; Kostoglou, M. Scaling in Reverse Osmosis Desalination Plants: A Perspective Focusing on Development of Comprehensive Simulation Tools. Desalination 2020, 474, 114193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Lababidi, H.M.S.; Al-Adwani, H.; Gleason, K.K. A Review of Heterogeneous Nucleation of Calcium Carbonate and Control Strategies for Scale Formation in Multi-Stage Flash (MSF) Desalination Plants. Desalination 2018, 442, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, R.S. An Assessment of Multiple Effect Boiling Distillation in Relation to Multi-Stage Flash Distillation. Desalination 1971, 9, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghonemy, A.M.K. Performance Test of a Sea Water Multi-Stage Flash Distillation Plant: Case Study. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2401–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, L.; He, T.; Chen, S.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L. Seawater Desalination Technology and Engineering in China: A Review. Desalination 2021, 498, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Burhan, M.; Shahzad, M.W.; Ybyraiymkul, D.; Akhtar, F.H.; Li, Y.; Ng, K.C. A Zero Liquid Discharge System Integrating Multi-Effect Distillation and Evaporative Crystallization for Desalination Brine Treatment. Desalination 2021, 502, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsgerdi, H.R.; Chua, H.T. Thermo-Economic Analysis of Low-Grade Heat Driven Multi-Effect Distillation Based Desalination Processes. Desalination 2018, 448, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, D.U.; Antar, M.A.; Khalifa, A.; Zubair, S.M.; Al-Sulaiman, F. Experımental Investigation of Heat Pump Driven Humidification-Dehumidification Desalination System for Water Desalination and Space Conditioning. Desalination 2020, 475, 114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.A.; Lienhard, V.J.H. Impact of Extraction on a Humidification–Dehumidification Desalination System. Desalination 2013, 313, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.H.; Kabeel, A.E.; Omara, Z.M.; Sharshir, S.W. Mathematical and Experimental Investigation of a Solar Humidification–Dehumidification Desalination Unit. Desalination 2015, 358, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharqawy, M.H.; Antar, M.A.; Zubair, S.M.; Elbashir, A.M. Optimum Thermal Design of Humidification Dehumidification Desalination Systems. Desalination 2014, 349, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, S.; Xie, M.X.; Jia, T.; Dai, Y.J. Technical Improvements and Perspectives on Humidification-Dehumidification Desalination—A Review. Desalination 2022, 541, 116029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, D.; Franzitta, V.; Guercio, A. A Review of the Water Desalination Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsani, R.; Rebagliati, S. Fundamentals and Costing of MSF Desalination Plants and Comparison with Other Technologies. Desalination 2005, 182, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, A.N.; Fath, H.E.S. Technoeconomic Study of a Novel Integrated Thermal MSF–MED Desalination Technology. Desalination 2015, 371, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, D.U.; Antar, M.A.; Khalifa, A.E. Integration of a MSF Desalination System with a HDH System for Brine Recovery. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Bao, M.; Gong, L.; Shen, S. Effects of Preheater Arrangement on Performance of MED Desalination System. Desalination 2020, 496, 114702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshgoftar Manesh, M.H.; Ghadikolaei, R.S.; Modabber, H.V.; Onishi, V.C. Integration of a Combined Cycle Power Plant with MED-RO Desalination Based on Conventional and Advanced Exergy, Exergoeconomic, and Exergoenvironmental Analyses. Processes 2021, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsehli, M. A New Approach to Solar Desalination Using a Humidification–Dehumidification Process for Remote Areas. Processes 2021, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Wang, X.; Kefayati, G.; Hu, E. Cooling and Water Production in a Hybrid Desiccant M-Cycle Evaporative Cooling System with HDH Desalination: A Comparison of Operational Modes. Processes 2023, 11, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, W.; Zheng, H.; Kang, H.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Chang, Z. Experimental Investigation of a Multi-Effect Isothermal Heat with Tandem Solar Desalination System Based on Humidification–Dehumidification Processes. Desalination 2016, 378, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, W.; Liu, A.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z. Performance Evaluation of a Renewable Driven Standalone Combined Power and Water Supply System with Cascade Electricity and Heat Storage. Renew. Energy 2022, 199, 1283–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elminshawy, N.A.; Siddiqui, F.R.; Addas, M.F. Development of an active solar humidification-dehumidification (HDH) desalination system integrated with geothermal energy. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 126, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, R.; Kumaresan, G.; Selvaraj, S.; Arunkumar, T.; Velraj, R. Investigation of Humidification-Dehumidification Desalination System through Waste Heat Recovery from Household Air Conditioning Unit. Desalination 2019, 467, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okampo, E.J.; Nwulu, N. Optimisation of Renewable Energy Powered Reverse Osmosis Desalination Systems: A State-of-the-Art Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 140, 110712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Chatterjee, K. A Review of Conventional and Advanced MPPT Algorithms for Wind Energy Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Li, T.; Li, J.H.; Yao, Z.Y. An Improved Variable Step Hill-Climbing Searching Algorithm for Tracking Maximum Power Point of Wind Power System. In Proceedings of the China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), Xi’an, China, 10–13 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, A.; Nayak, B.; Das, P.; Mohanty, K.B. A Review on MPPT Techniques of PV System under Partial Shading Condition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadegan, A.; Porobic, L.; Ghazinoory, S.; Samouei, P.; Saman Kheirkhah, A. Fuzzy Logic in Manufacturing: A Review of Literature and a Specialized Application. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 132, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, U.; Kircay, A.; Borekci, S. PV System Fuzzy Logic MPPT Method and PI Control as a Charge Controller. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).