Monthly Streamflow Prediction of the Source Region of the Yellow River Based on Long Short-Term Memory Considering Different Lagged Months
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
2.2. Feature Selection
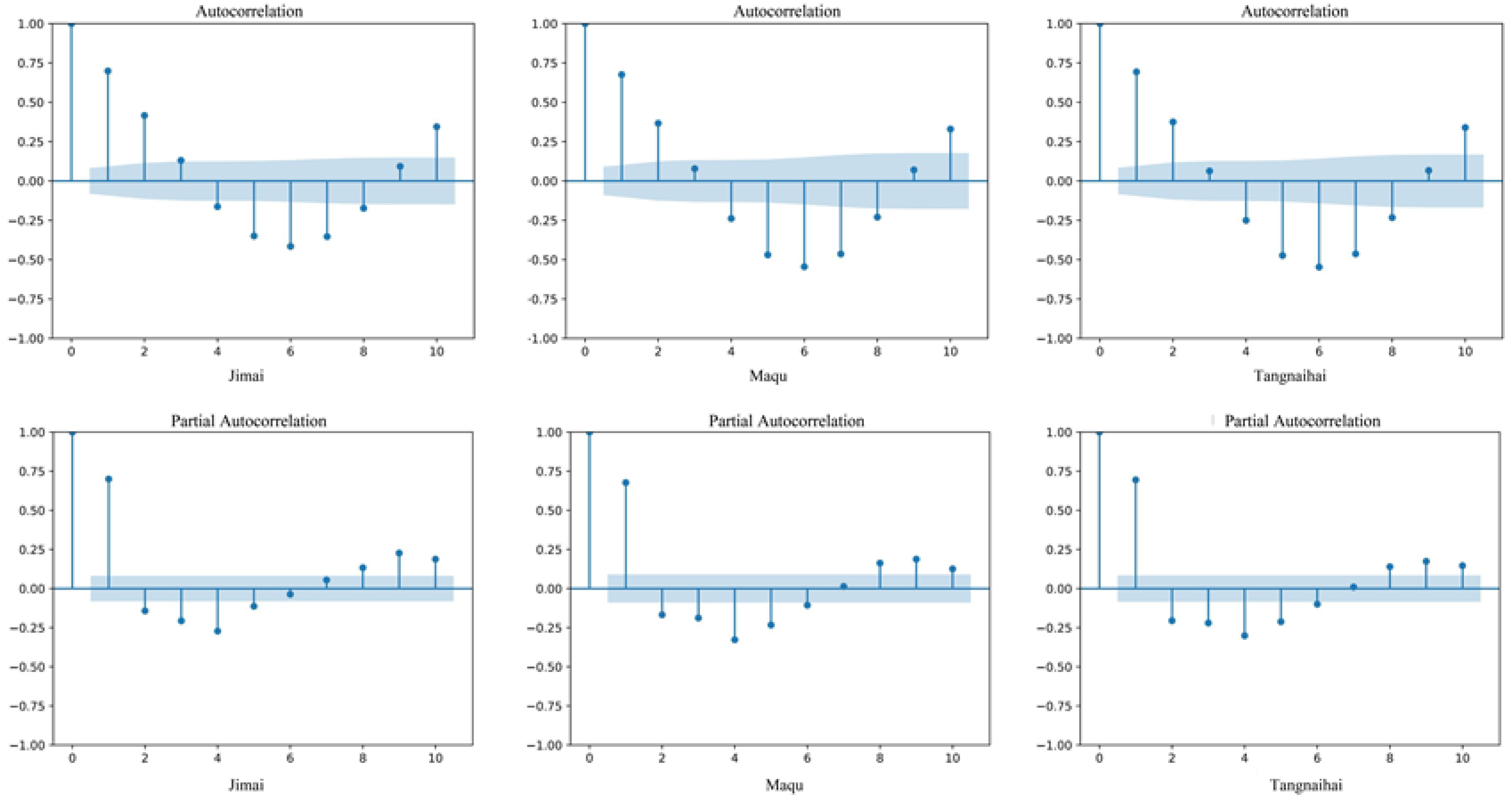
2.2.1. Autocorrelation Function and Partial Autocorrelation Function
2.2.2. Time-Lag Cross-Correlation
2.3. Performance Measures
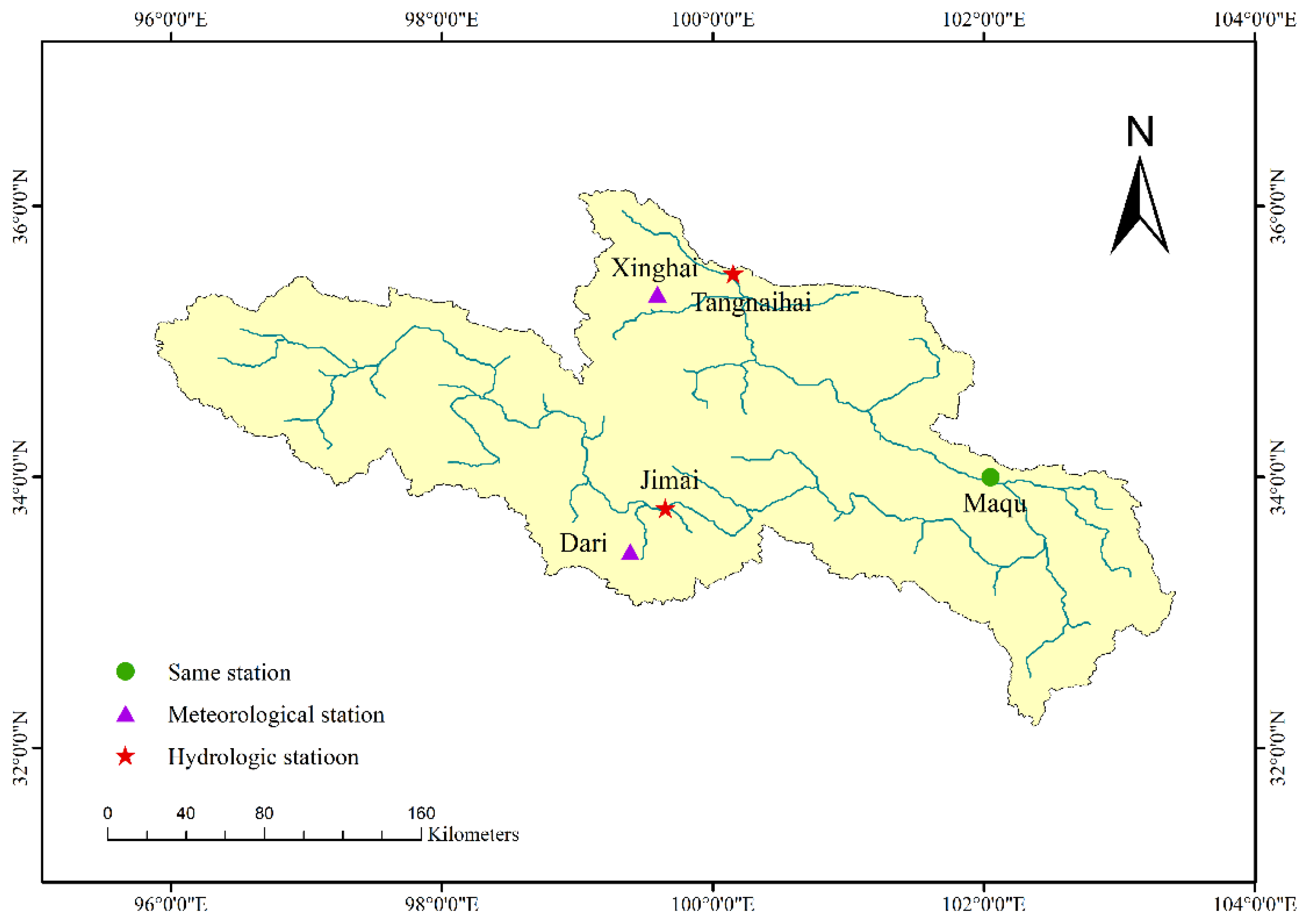
3. Study Area and Data
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Model Input Variables Selection
4.2. Model Structure Optimization
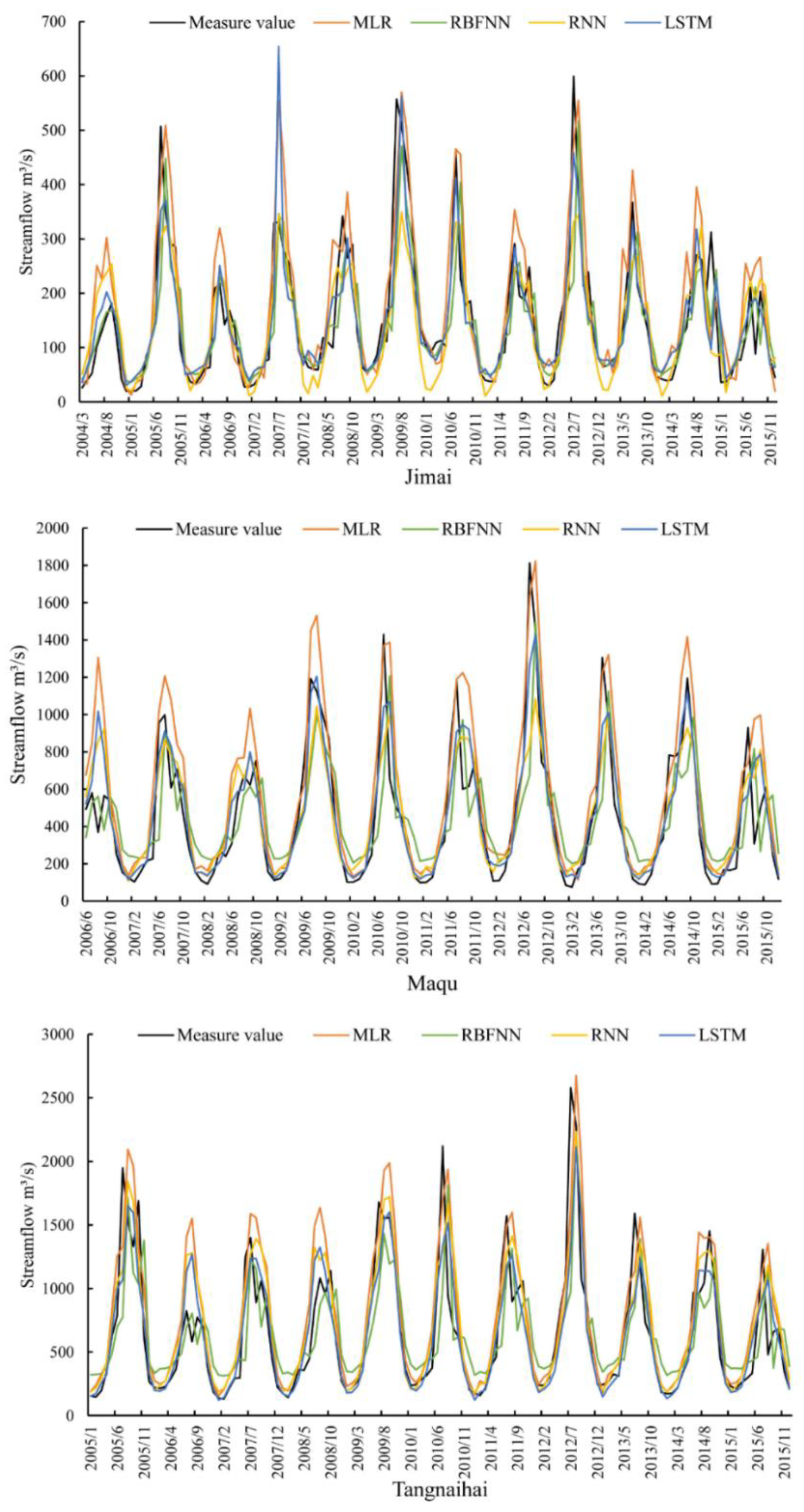
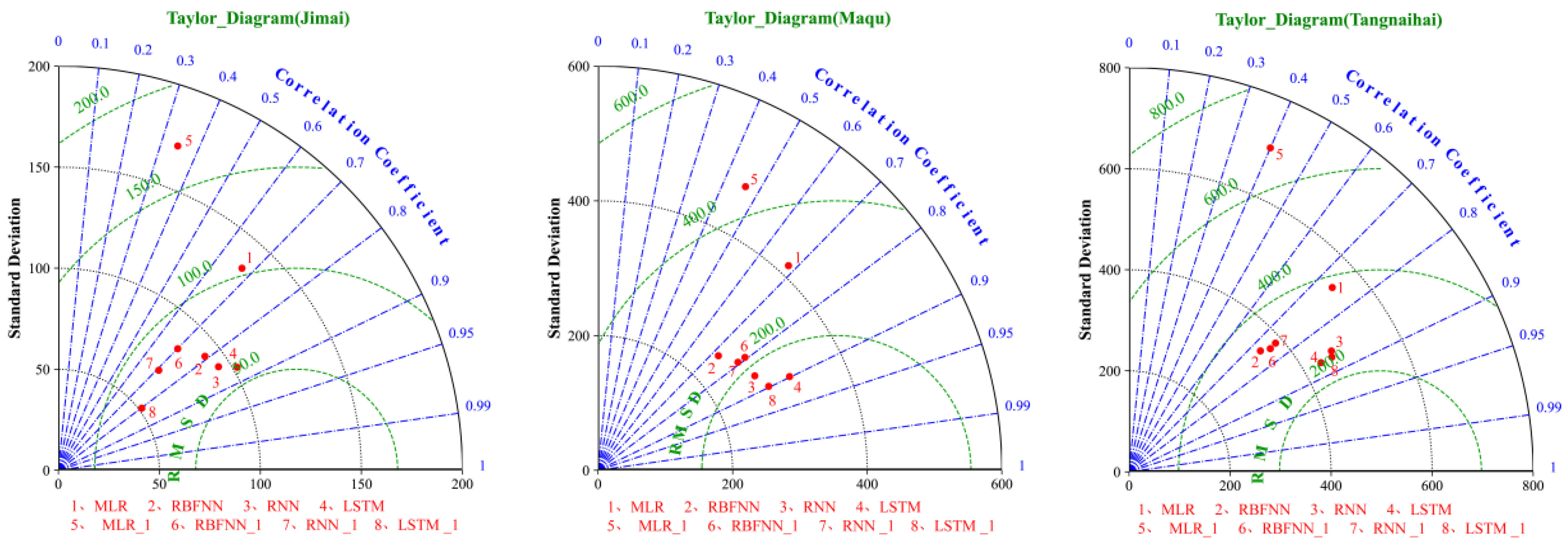
4.3. Models Performance Comparison
4.4. Comprehensive Comparison of Different Models with or without Lagged Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Q.H.; Ke, L.H.; Wang, J.D.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Allen, G.H.; Sheng, Y.W.; Duan, X.J.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Satellites reveal hotspots of global river extent change. Nat Commun. 2023, 14, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, J.; Chang, F.; Yue, Y.; Frolova, N.; Magritsky, D.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Ciais Philippe Wang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Walling, D.E. Global trends in water and sediment fluxes of the world’s large rivers. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhao, F.; Sun, K.; Li, T.; Sivakumar, B.; Qiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Jin, Z. Predicting long-term hydrological change caused by climate shifting in the 21st century in the headwater area of the Yellow River Basin. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 36, 1651–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkilic, H.Y.; Hashimi, S.A. Prediction of daily streamflow using artificial neural networks (ANNs), wavelet neural networks (WNNs), and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) models. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.B.; Wei, J.H.; Li, J.Y.; Qiao, Z.; Cao, J.W. Improved Medium- and Long-Term Runoff Forecasting Using a Multimodel Approach in the Yellow River Headwaters Region Based on Large-Scale and Local-Scale Climate Information. Water 2017, 9, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Wang, T.H.; Yang, D.W.; Yang, Y.T. Insights into runoff changes in the source region of Yellow River under frozen ground degradation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.B.; Wen, X.H.; Liu, H.; Du, J. A comparative study of artificial neural network, adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and support vector machine for forecasting river flow in the semiarid mountain region. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, F.F. Hybrid Models Combining EMD/EEMD and ARIMA for Long-Term Streamflow Forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, F.D.; Zhang, Y.N.; Xia, R.L.; Jin, J. Rainfall-runoff modeling using LSTM-based multi-state-vector sequence-to-sequence model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Komasi, M. A geomorphology-based ANFIS model for multi-station modeling of rainfall-runoff process. J. Hydrol. 2013, 490, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.B.; Wei, J.H.; Qiu, J. Monthly Streamflow Forecasting Using EEMD-Lasso-DBN Method Based on Multi-Scale Predictors Selection. Water 2018, 10, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.N.; Luo, J.G.; Xue, W.; Zuo, G.G.; Zhang, S.Y. Cause-driven Streamflow Forecasting Framework Based on Linear Correlation Reconstruction and Long Short-term Memory. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 1661–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londhe, S.; Charhate, S. Comparison of data-driven modelling techniques for river flow forecasting. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, X.Q.; Qin, H. A data-driven model based on Fourier transform and support vector regression for monthly reservoir inflow forecasting. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2018, 18, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.H.; Li, G.; Li, J.D. Data-driven runoff forecasting for Minjiang River: A case study. Water Supply 2020, 20, 2284–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sang, Y.F.; Li, X.X.; Hu, J.; Liang, K. Long-Term Streamflow Forecasting Based on Relevance Vector Machine Model. Water 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L. Runoff forecasting model based on CEEMD and combination model: A case study in the Manasi River, China. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3921–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modaresi, F.; Araghinejad, S.; Ebrahimi, K. A Comparative Assessment of Artificial Neural Network, Generalized Regression Neural Network, Least-Square Support Vector Regression, and K-Nearest Neighbor Regression for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting in Linear and Nonlinear Conditions. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Singh, M.P.; Kaloop, M.R.; Kumar, D.; Hu, J.W.; Kumar, R.; Hwang, W.S. Data-Driven Approach for Rainfall-Runoff Modelling Using Equilibrium Optimizer Coupled Extreme Learning Machine and Deep Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Yang, D.W.; Chen, J.S.; Zhao, B.X. Real-time reservoir operation using recurrent neural networks and inflow forecast from a distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin, H.; Feizi, H.; Sattari, M.T.; Colak, M.S.; Shamshirband, S.; Chau, K.W. Comparative Analysis of Recurrent Neural Network Architectures for Reservoir Inflow Forecasting. Water 2020, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Luo, X.G.; Yuan, X.H.; Xu, Z.Y. An improved long short-term memory network for streamflow forecasting in the upper Yangtze River. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk. A. 2020, 34, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzad, M.; Nia, A.M.; Zolfonoon, H.; Soltani, J.; Mehr, A.D.; Kwon, H.H. Performance Comparison of an LSTM-based Deep Learning Model versus Conventional Machine Learning Algorithms for Streamflow Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4167–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Jian, S.Q.; Li, N.; Lou, Z.Z. Deep Learning with a Long Short-Term Memory Networks Approach for Rainfall-Runoff Simulation. Water 2018, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Brenner, C.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. Rainfall-runoff modelling using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6005–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.K.; Zhu, Y.L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, P.C.; Cheng, Z.R. Interpretable spatio-temporal attention LSTM model for flood forecasting. Neurocomputing 2020, 403, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.Y.; Ding, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, H.X.; Zhou, H.C.; Chu, J.G. Flash Flood Forecasting Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks. Water 2020, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi Ostadkalayeh, F.; Moradi, S.; Asadi, A.; Moghaddam Nia, A.; Taheri, S. Performance improvement of LSTM-based deep learning model for streamflow forecasting using Kalman filtering. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 3111–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.; Matthews, G.R.; Pappenberger, F.; Prudhomme, C. Using a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network to boost river streamflow forecasts over the western United States. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 5449–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Partoviyan, A. Hybrid denoising-jittering data pre-processing approach to enhance multi-step-ahead rainfall-runoff modeling. Stochastic Stoch. Env. Res. Risk. A. 2018, 32, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, M.M.; Alomar, M.K.; Al-Saadi, A.A.A.; Alsaadi, M.A. Inflow forecasting using regularized extreme learning machine: Haditha reservoir chosen as case study. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk. A. 2022, 36, 4201–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Kim, J. Machine learning modeling structures and framework for short-term forecasting and long-term projection of Streamflow. Stoch Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Li, Z.J.; Tong, B.X.; Liu, Z.T.; Sun, M.K.; Jiang, F.Q.; Zhang, H.C. The Applicability of LSTM-KNN Model for Real-Time Flood Forecasting in Different Climate Zones in China. Water 2020, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.T.; Jardani, A.; Massei, N.; Fournier, M. Reconstruction of missing groundwater level data by using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) deep neural network. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 125776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhang, S.; Han, J.C.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, M.X.; Lin, Q.S. Short-term runoff prediction with GRU and LSTM networks without requiring time step optimization during sample generation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, B.; Bafti, A.G.; Kamangir, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wright, D.B.; Franz, K.J. A novel attention-based LSTM cell post-processor coupled with Bayesian optimization for streamflow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Liu, X.M.; Xie, J.X. Simulating runoff under changing climatic conditions: A comparison of the long short-term memory network with two conceptual hydrologic models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Si, Y.; Chu, H.B. Daily streamflow prediction and uncertainty using a long short-term memory (LSTM) network coupled with bootstrap. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 4575–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.B.; Wu, J.; Wu, W.Y.; Wei, J.H. A dynamic classification-based long short-term memory network model for daily streamflow forecasting in different climate regions. Ecol Indic. 2023, 148, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Shalev, G.; Klambauer, G.; Hochreiter, S.; Nearing, G. Towards learning universal, regional, and local hydrological behaviors via machine learning applied to large-sample datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 5089–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Fu, G.T.; Chen, X.X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.J. Surface water temperature prediction in large-deep reservoirs using a long short-term memory model Surface water temperature prediction in large-deep reservoirs using a long short-term memory model. Ecol Indic. 2022, 134, 108491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, K.S.; Bhardwaj, R. Statistical, time series, and fractal analysis of full stretch of river Yamuna (India) for water quality management. Environ. Sci. And Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, B.B.; Gong, H.L.; Lei, K.C.; Zhou, C.F.; Lu, Z.Z.; Zhao, D.N. Inversion of Groundwater Storage Variations Considering Lag Effect in Beijing Plain, from RadarSat-2 with SBAS-InSAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Li, Z.X.; Qi, F.; LiU, X.Y.; Gui, J.; Xue, J. Quantitative analysis of recharge sources of different runoff types in the source region of Three River. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Station | Longitude | Latitude | Time Span | Average Annual Temperature | Average Annual Precipitation | Average Annual Streamflow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dari | 33.45 | 99.39 | 1956–2015 | −0.785 | 153.986 | |
| Xinghai | 35.35 | 99.56 | 1960–2015 | 1.438 | 102.495 | |
| Maqu | 34.00 | 102.05 | 1967–2015 | 1.718 | 168.923 | 452.087 |
| Jimai | 33.76 | 99.65 | 1956–2015 | 127.698 | ||
| Tangnaihai | 35.5 | 100.15 | 1960–2015 | 648.235 |
| Station | Dropout | Dense | Neuron | Epoch | Batch Size | Optimizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jimai | 0.1 | 1 | 311 | 301 | 101 | Adam |
| Maqu | 0.1 | 1 | 91 | 101 | 101 | Adam |
| Tangnaihai | 0.1 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 11 | Adam |
| Model | Calibration | Validation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | RBFNN | RNN | LSTM | MLR | RBFNN | RNN | LSTM | ||
| Jimai | R2 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.77 |
| RMSE | 57.12 | 73.10 | 67.18 | 60.14 | 60.39 | 72.92 | 65.22 | 56.53 | |
| MAE | 37.02 | 44.97 | 46.06 | 42.94 | 41.80 | 45.33 | 43.60 | 40.54 | |
| NSE | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.69 | 0.75 | |
| KGE | 0.57 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.82 | |
| Maqu | R2 | 0.53 | 0.49 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.73 | 0.81 |
| RMSE | 196.58 | 270.50 | 217.58 | 196.06 | 154.74 | 244.20 | 185.54 | 155.93 | |
| MAE | 116.97 | 184.99 | 132.31 | 118.40 | 98.86 | 176.85 | 118.41 | 100.23 | |
| NSE | 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.89 | |
| KGE | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.83 | |
| Tangnaihai | R2 | 0.47 | 0.51 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| RMSE | 287.87 | 363.60 | 283.60 | 285.87 | 249.77 | 337.39 | 266.36 | 247.20 | |
| MAE | 171.77 | 249.59 | 179.44 | 164.60 | 149.91 | 238.95 | 174.47 | 146.43 | |
| NSE | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.68 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.88 | |
| KGE | 0.54 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.77 | 0.83 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, H.; Wang, Z.; Nie, C. Monthly Streamflow Prediction of the Source Region of the Yellow River Based on Long Short-Term Memory Considering Different Lagged Months. Water 2024, 16, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040593
Chu H, Wang Z, Nie C. Monthly Streamflow Prediction of the Source Region of the Yellow River Based on Long Short-Term Memory Considering Different Lagged Months. Water. 2024; 16(4):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040593
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Haibo, Zhuoqi Wang, and Chong Nie. 2024. "Monthly Streamflow Prediction of the Source Region of the Yellow River Based on Long Short-Term Memory Considering Different Lagged Months" Water 16, no. 4: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040593
APA StyleChu, H., Wang, Z., & Nie, C. (2024). Monthly Streamflow Prediction of the Source Region of the Yellow River Based on Long Short-Term Memory Considering Different Lagged Months. Water, 16(4), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040593






