Abstract
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of WWTP effluents on the sediment microbial communities throughout the Mureș River. This study shows the existence of an ecological equilibrium between the WWTP effluent disruptors and the resilience of the Mureș River sediment microbiomes, a fact that suggests the river’s stable/balanced ecological status in this regard, partly due to the microbial communities’ resilience to the local impact of WWTP effluents. High-throughput 16S bacterial metabarcoding was used to evaluate the bacterial communities in the sediment. Due to the lotic system’s sediment microbial communities’ sensitivity to environmental changes, we assumed the dependency of these community structures and functions on environmental abiotic and abiotic parameters. The study results show that, although bacterial communities are equally diverse in the three locations (upstream WWTP, WWTP effluents, and downstream WWTP), there is a difference in community structure between the upstream samples and the WWTP samples, while the downstream samples contain a mixture of the upstream and WWTP effluent communities. Just downstream of the WWTP sediment, microbial communities are influenced by the specific input from the WWTP effluents; nevertheless, the river sediment microbiome is resilient and able to further recover its natural microbial composition, as evidenced by the similarity in bacterial community structures at all upstream river locations. This study demonstrates the ecological equilibrium between the WWTP effluent disruptors and the resilience capacity of the Mureș River sediment microbiomes, a fact that indicates the river’s stable/balanced ecological status, in part due to the microbial communities’ resilience to the local impact of WWTP effluents. Based on these findings, a monitoring system should be implemented here in the future.
1. Introduction
Most ecosystems are highly dynamic in terms of both their species composition and abundances and their functioning [1]. At the top, lotic systems are excellent, diverse, dynamic, nonlinear, and natural systems created by the long-term interactions between natural abiotic and biotic elements and forces [2,3,4].
Since the Anthropocene began, a wide variety of human-induced stressors have significantly impacted these ecosystems [5]. In systems impacted by humans, elements of environmental flows are a key tool for the sustainable management of water [6,7]. As such, there is a need for in-depth knowledge of the compartments of the entire lotic ecosystem.
The abiotic and biotic elements of rivers and stream watersheds are described as having pronounced ecological unpredictability, particularly since the Industrial Age began [8,9,10,11]. Problems related to human impact can be found all over the earth, and the Danube Basin is no exception [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28], experiencing problems in terms of complexity, resilience, homeostasis, autopoiesis, etc.
The studied Mureș River is, regrettably, not excluded from this context; from this perspective, it is considered a European hotspot [29,30,31,32,33,34], having been impacted by humans from the Stone Age onwards [35,36,37,38,39]. It is the major tributary of the Tisza, situated between a longitude of 20°11′ E and 25°44′ E and a latitude of 45°14′ and 47°08′, with a length of 761 km and a basin surface area of 28,319 km2. It passes through 25% mountainous relief, 55% lower highlands, 15% valleys and meadows, and 5% plains [40,41].
The Mureș Basin was selected for this study for several reasons, including its large surface and rank within the Danube Basin [42], its large human population [40,43], and the related human activities and impact [29,33,34,37,38,39,44] that disturb the river basin’s ecological state.
The effects of some pollutants have rarely been evaluated in relation to the Mureş River’s taxonomical categories, including bacteria [45,46,47,48], which have been studied only with a focus on particular groups, such as fecal streptococci and coliforms [49,50,51,52], despite the fact that bacterial microbiomes are important both for the environment’s ecological status and for human health [53,54].
Alongside human evolution, various environmental interactions have exerted a profound influence on shaping symbiotic relationships with a multitude of species. Far from being a solitary entity, the human body hosts about 3.8 × 1013 bacterial cells—more than the latest human cell count, estimated at 3.0 × 1013 [55]. Weighing only 0.2 kg, the human microbiome has at least 100-fold more unique genes than the human host genome, with many of them directly influencing human health and inducing many illnesses [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71].
The diversity and structure of microbial communities are inevitably impacted by environmental stress; however, our knowledge of its effects is relatively limited [72]. Generally, insufficient research has been undertaken on the bacterial communities in Romania’s rivers and streams, with only one large-scale study focused on the Danube [73]. Research that focuses on the Mureș River basin has ordinarily had constricted aims, for instance, accounting for few pathogenic bacteria, coliforms, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and bacteria and sediment relations [74,75,76]. This research reveals some of the pollution-associated risks to the health of the studied lotic ecosystem and the dynamics of the bacterial microbiota community, as well as its capacity for resilience under the impact of stress from wastewater plant effluent.
Aquatic ecosystems are built and function in a complex and multi-dimensional spatiotemporal manner [77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. Such self-adaptive ecological systems demonstrate variability, with a high number of co-dependent self-governing elements organized into complex systems that have the ability to self-adjust and learn from the past [84].
The trend of ecological decline observed in lotic systems around the world, comprising those that are large in size [45,85,86,87] and are anticipated to have good levels of resilience, is a cause of significant concern regarding the challenges to their sustainable management [88]. Bacteria are the most primitive and adaptive cellular life forms on Earth and constitute its primary biomass, having made complex evolutionary achievements [89]. Historically, the field of bacterial microbiome research emerged from environmental microbiome research (microbial ecology), providing an interdisciplinary platform and a useful approach for many fields of interest [90].
Regarding microbial ecology, if significant advancements were made in finding answers to the question of “Who is on this long list?”, then researchers would face more complex challenges in terms of addressing questions such as “What and how are they doing” [91].
Although, in general, we can identify highly rich phylogenetic types of microbial associations, less is known about their communities’ structures and integrated means of their complex functioning. The main factors affecting river ecosystems include rainwater, drainage from the land along the riverbed, sediments and substances that are carried downstream, and, last but not least, sewage and polluted water that are released into the lotic systems.
Microbial communities in the sediment of lotic systems are among the most diverse communities described to date [92,93,94]; they constitute an essential component of the ecosystem, being implicated in all steps of the carbon cycle, for example, from primary producers all the way to decomposers [95,96,97]. Due to their plastic metabolism, microorganisms are involved in water decontamination processes and are able to metabolize a wide range of substances [98,99,100,101]. Rivers are under constant pressure from anthropogenic sources that also put pressure on the microbial communities in this type of ecosystem [102]. Due to their diversity and plasticity, microorganisms should be able to adapt to and counter most anthropogenic stressors but not all of them and not in all circumstances. This raises the question of what will happen to sediment microbial communities that are under pressure from wastewater treatment plants: will they be resilient and able to overcome the stressors, or will they change their structure to better survive in changing conditions?
In this context, sediments fulfil a vital role in the ecology of streams and rivers [103,104,105]. Some of the most essential ecological processes in rivers and streams, such as biogeochemical and nutrient cycling, are primarily undertaken by microbial communities that live in sediments [95,97,106] and that are responsible for over 90% of respiration [96,107,108,109,110,111]. The relatively good general ability of rivers and streams to sustain natural biodegradation and bioremediation processes is connected to the microbial communities’ diversity, flexibility, and health in the lowest levels of sediments [112]. Even though the microbiomes of sediments in lotic systems are much more varied than the microbiomes of water [92,93,94], they have been less thoroughly researched [113,114]. Microbial communities are sensitive to fluctuations and alterations in the environment’s physicochemical parameters [115,116,117,118] and can be used as reliable indicators of an environment’s ecological status [119]. Rather than focusing on the indication value of microbial biomes, we intend to identify their potential resilience to stress factors related to effluents from wastewater treatment plants (WWTP); this is an important quality that supports the resilience of ecosystems because this characteristic has positive significance for biogeochemical and nutrient cycling processes, which support other taxonomic groups/communities with lower levels of resilience [30].
WWTPs are major stressors on river ecosystems. Water released from wastewater treatment plants affects the microbial communities in the natural downstream waters in three ways: by changing the nutrient content of the water [120]; by introducing different chemical substances [121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128]; and by introducing new microbial strains [129]. The role of the WWTP is to clean the wastewater and make it safe to return to the natural environment. Conventional wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are designed to remove pathogens and coliforms and to reduce the amount of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in the wastewater [60,128,130,131]. However, the treatments and processes in the wastewater treatment plant are not usually able to remove all of the chemicals present in wastewater; for this reason, some are released into natural waters [128,131]. Although WWTPs focus on removing pathogenic bacteria such as coliforms, microorganisms in wastewater are very abundant, to the order of 109, and some of them persist and are released into natural waters [125,132,133]. Among the microorganisms that have been found to be released from WWTPs are signature human fecal bacteria belonging to orders including Bacteroidales, Clostridiales, and Bifidobacteriales [134]. Another major concern is the release and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes and other genetic elements [124,125,126].
Previous scientific studies have considered the impact of WWTP effluent on the diversity of the downstream microbial community; in some cases, they have found an increase in diversity [135,136], in other cases, a decrease in diversity [137], and in some instances, no change in levels of diversity [138]. Many factors have been assessed to determine their impact on the microbial communities’ structure. For planktonic bacteria, it has been shown that the bacterial community profiles downstream of WWTPs are a mixture of those found upstream of the WWTP and those found in the WWTP effluent due to the mixing of the two water flows [139,140]. Even though intensive studies have been conducted on the microbial community’s composition and function in hyporheic zones, far less attention has been paid to the impact of WWTP effluent on the microbial ecology of riverbed sediments [136,137,141]. To date, there is no consensus on how WWTP effluents impact microbial communities in the receiving river, and many factors have been shown to influence how the microbes are affected. The impact of a WWTP on the downstream sediment microbiota depends on different factors, such as the type of WWTP and hence the composition of the effluent, the population size of the riverine area, the climate and geography of the region, the size and flow rate of the river, and the buffering and self-purification capacity of the stream sediments under the impact of stresses [141].
Many studies have focused mainly on the immediate effect downstream of the WWTP; however, this research took a comparatively holistic approach to test how the input from a WWTP affects a river in its entirety. The main objective was to assess the impact of WWTP effluents on the microbial communities in sediments throughout the Mureș River.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
This river was chosen as it is the second longest river in Romania, after the Danube, and it traverses a significant portion of the country from east to west, passing some major cities including Târgu Mureș, Alba Iulia, Deva, Arad, etc. [33]. The samples were collected from 10 locations/cities with 3 sampling sites per location (on the river 200 m upstream of the WWTP effluent, on the river downstream of the WWTP effluent, and the WWTP effluent) and 3 extractions per sampling site, resulting in a total of 90 samples.
High-throughput 16S bacterial metabarcoding was used to evaluate the bacterial communities in the sediment samples. The bacterial communities upstream, downstream, and in the WWTP effluent from 10 different sites along the river were evaluated. River sediment was collected from 10 WWTP sites along the Mureș River watershed in the fall and winter of 2018–2019. At each WWTP site, three different samples were collected: sediment from the river upstream of the WWTP, sediment from the river downstream of the WWTP, and sediment from the WWTP effluent. A map of the sampling sites is shown in Figure 1. The samples were transported in a portable refrigerator at 4 °C and then kept in a freezer at −50 °C until they were analyzed.
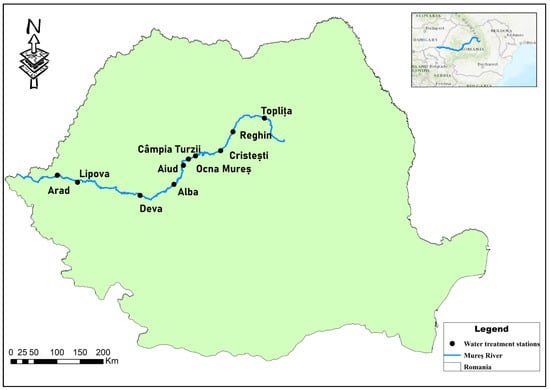
Figure 1.
Map depicting the 10 wastewater treatment stations along the Mureș River where the samples were collected.
2.2. DNA Extraction and Quantification
DNA was extracted from each sediment sample in triplicate. It was extracted from 500 milligrams of the sampled sediment using the Quick-DNA Fecal/Soil Microbe Miniprep kit from Zymo Research (Irvine, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the sampled sediment was weighted and added to a tube containing bashing beads and 750 μL bashing bead buffer. These tubes were vortexed at a maximum speed for 20 min and then centrifuged for 1 min at 10,000× g. The supernatant was filtered and then lysed using a genomic lysis buffer. The lysate was loaded onto a spin column that retained the genomic DNA. Once the DNA was bound to the column, it was washed once with pre-wash buffer and once with g-DNA wash buffer. After the washes, DNA was eluted from the column using a DNA elution buffer. As a last step, the DNA was cleared of humic acid by being filtered through another column. After the last cleaning step, the DNA’s quality and quantity were checked in preparation for the PCR and sequencing. The amount of DNA was quantified using a Specord 210 plus spectrophotometer (AnalyticJena, Jena, Germany), and the DNA quality was assessed via electrophoresis on 0.8% agarose gel. The DNA was then packed and sent to the LGC Group (Berlin, Germany) for next-generation sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform (San Diego, CA, USA).
2.3. 16S Metabarcoding Analysis
In this research, the gene for 16S ribosomal RNA was amplified using primers targeting the V3–V4 region [142]. Adapters were added to the PCR products, and a library was then created. The adapters also contained a barcode for multiplexing during sequencing. The 16S libraries were sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq platform at the LGC Group. The libraries were demutiplexed using Illumina bcl2fastq 2.17.1.14 conversion software [143]. When the barcode distances between all libraries on the lane permitted, one or two mismatches or Ns were allowed in the barcode read. Reads with missing barcodes, one-sided barcodes, or conflicting barcode pairs were discarded. Additionally, reads shorter than 100 nucleotides were discarded. After sorting, the barcode and adapter sequences were clipped. The next steps were performed using the QIIME 2 workflow [144,145]. First, sequence quality control and feature table construction were undertaken using the DADA2 plugin, which corrects amplicon sequence data and filters phiX reads and chimeric sequences [146]. During this step, nucleotides corresponding to the primer sequences were deleted, forward sequences were trimmed to a maximum length of 280 nucleotides, and reverse sequences were trimmed to 240 nucleotides based on the quality of the reads. This analysis generated two curated files, one containing the frequency and the other the sequence, of all the amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) obtained from the sequencing analysis. The sequences were aligned with MAFFT [147]; then, a phylogenetic tree was created using FastTree 2 [140]. Replicate sequences at each sampling site were grouped using the mean ceiling, and this was followed by rarefaction [148] to a maximum depth of 16,294. We trained a classifier using a naïve Bayes method [149] with the used primer pair [142] and the Greengenes 13.8 database [150] at 99% identity. The generated classifier was then used to reference our sequences with the sklearn plugin [149]. The sequence data generated in this study were deposited in the GenBank/NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRI)/ under the following accession number: PRJNA1015452 [151].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Most of the statistical analysis was conducted using the QIIME2 workflow. Several alpha diversity indices were obtained by computing a user-specified alpha diversity metric for all samples in a feature table: ACE [152], Chao1 [153], observed OTUs [150], Pielou Evenness [154], Shannon [155], and Simpson [156]. The command core–metrics–phylogenetics was used in this study to compute the alpha diversity index, Faith’s Phylogenetic Diversity, and beta unweighted UniFrac [157], generalized UniFrac [158], weighted normalized UniFrac, weighted unnormalized UniFrac [157], and the Bray–Curtis [159], Euclidean [160], and Jaccard [161] diversity metrics.
Within-group differences were assessed using group significance based on the Faith PD and evenness alpha diversity metrics, while between-group differences were assessed using PERMANOVA (permutational multivariate ANOVA) to test the pairwise unweighted UniFrac-type significance using QIIME 2 commands.
Data were graphed in QIIME 2 using the EMPeror tool software [162], which generated principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plots for each of the beta diversity metrics. Graphs depicting the bacterial community structures were generated in excel. The constrained RDA analysis of the data was realized in Canoco 5 [163]. The map depicting the sample location was generated using QGIS version 3.22.7.
3. Results and Discussions
Ten wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) serving the main cities along the Mureș River were selected for analysis (Figure 1). At each WWTP, sediment samples were collected from the portions of the river upstream and downstream of the WWTP and from the WWTP effluent. DNA was extracted in triplicate from each sediment sample and subjected to 16S rRNA sequencing. The primary reads obtained after sequencing were analyzed using the QIIME 2 workflow. A total of 2,352,102 high-quality reads were obtained after sequencing, with an average of 63,570 reads per sample replicate. The taxonomical classification of the sequences was performed against the GreenGenes database [150]. Sequences from other domains of life, except bacteria and archaea, were removed. Samples were rarefied to the lowest sample total of 16,294 reads.
The bacterial community structure in the sediment samples was analyzed at the phylum and class levels. At each of these two phylogenetic levels, the abundance of bacteria and archaea was calculated for each sample as the percentage relative to the total number of taxons/ASV (Figure 2). At the phylum level, we found Proteobacteria to be the best represented, with an average abundance of 41%. The highest abundance of Proteobacteria was in the WWTP effluent in the Arad locality (71%), while the lowest was in the WWTP effluent of the Cristești locality (23%). This result is in accordance with the literature, where Proteobacteria was also found to be the most abundant phylum in the river sediment as well as in WWTP microbial communities [137,138,141,164]. The second-best-represented phylum in our study was Firmicutes (19.9%), followed by Actinobacteria (14%) (Figure 2A). Here, we do not see the same predominance as with Proteobacteria, and there are instances where Actinobacteria is more abundant than Firmicutes. In the literature, however, Bacteroidetes seems to be more frequently in second place, before Firmicutes or Actinobacteria [137,138,164,165]. In our study, Bacteroidetes was the fourth most abundant phylum. At the class level, the best-represented class was Gammaproteobacteria (21%), followed by Bacilli (13%), Alphaproteobacteria (10%), and Actinobacteria (7%) (Figure 2B). In other studies, Alphaproteobacteria was found to be the most abundant class, followed by Gamaproteobacteria [165]. Huo et al. [138] also found Alphaproteobacteria to be the most abundant when they undertook sampling in the spring; however, when they did so in the fall, they saw a shift towards more Gamaproteobacteria [138]. Since we sampled in the fall, this could explain why we also found a higher abundance of Gamaproteobacteria in comparison to other studies.
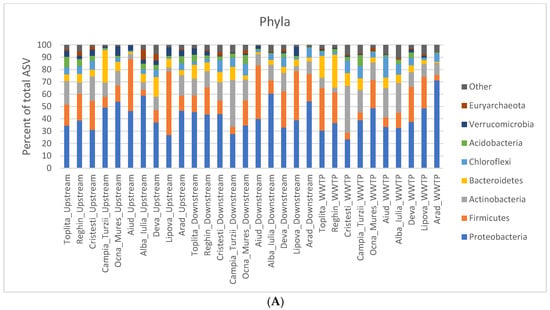
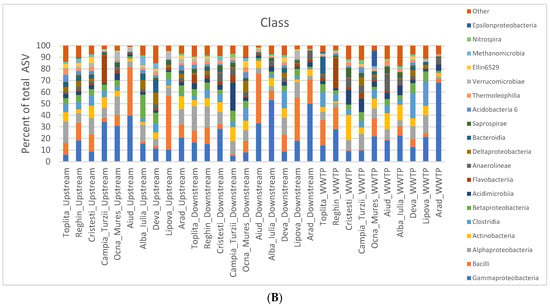
Figure 2.
Bar plots representing the relative abundance of bacteria at the (A) phyla and (B) class levels at each sampling site.
Phyla and class are not uniformly distributed among the samples, and there are instances where a phylum or class is more abundant in one sample compared to other samples. This difference in the bacterial distribution is probably due to sample properties; therefore, we considered whether it was possible to identify a distinct preference for a certain phylum or class in the samples taken upstream, downstream, or from the WWTP effluent. Therefore, we averaged the results based on these three sampling sites. When we averaged the results of the samples taken upstream, downstream, and from the WWTP effluent at the 10 sampling sites, we found no obvious difference between the three in the relative abundance at the phylum or class levels (Figure 3A,B). Although we did not detect a difference in the abundance of bacteria at the phylum and class levels between the upstream, downstream, and WWTP sampling sites, this does not mean there are no differences between their bacterial communities. However, these differences most likely manifest at the family and genus levels, as Chu et al. show [164].
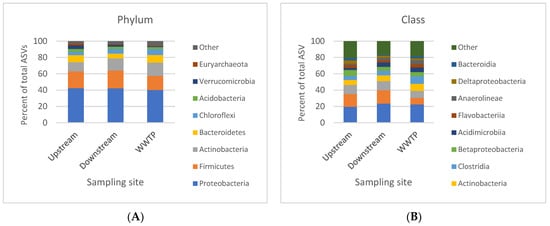
Figure 3.
Bar plots showing the average ASV for each (A) phyla and (B) class at the three different sampling sites: upstream, downstream, and WWTP.
We next assessed the alpha diversity found in the sediment samples by measuring the following indices for each sampling site: ACE, Chao1, observed OTUs, Pielou evenness, Shannon, and Simpson (Table 1). Kruskal–Wallis pairwise analysis showed that there was no significant difference in alpha diversity, based on Faith’s phylogenetic diversity or evenness, between the groups composed of samples taken upstream, downstream, or from the WWTP effluent (Table 2). As effluents from wastewater treatment plants bring nutrients, pollutants, and a mixture of microorganisms into the receiving river, they are expected to have an impact on the river’s microbial communities. Several studies have shown that this impact results in a reduction in the alpha diversity in sites immediately downstream of WWTPs [129,137], while others have shown a change in the balance between autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria [166]. Other studies detect no change in alpha diversity before and after the WWTP [167,168,169]. The apparent lack of impact on alpha diversity might be explained by the fact that, while micropollutants can negatively affect the abundance of certain taxa, nutrients can favor the growth of others [166]. The result would be microbial communities that are distinct, as far as beta-diversity is concerned, but which have similar alpha diversity indices [170].

Table 1.
Alpha diversity indices.

Table 2.
Group significance based on faith pd and evenness alpha diversity metrics.
Therefore, to determine whether the microbial communities upstream, downstream, and in the WWTP effluent were similar or not, we needed to measure the beta-diversity. To make comparisons between the samples, we assessed the beta diversity by measuring the Bray–Curtis, Jaccard, and unweighted UniFrac distances. To visualize the results, principal coordinate analysis was applied to the beta-diversity results for the three types of distance. The three emperor plots obtained using the program QIIME 2 and the Bray–Curtis, Jaccard, and unweighted UniFrac distances show the samples taken upstream of the WWTP separately from those taken from the WWTP effluent (Figure 4A–C); meanwhile, the samples taken downstream of the WWTP overlap with both the upstream and WWTP samples (Figure 4A–C). Moreover, when we measured the dissimilarity between the samples from the three different groups (upstream, downstream, and WWTP) according to the unweighted UniFrac beta-diversity, we found a significant difference between samples taken upstream of the WWTP and samples taken from the WWTP effluent (Permanova p < 0.002). Samples taken downstream of the WWTP were not significantly different from either the upstream or WWTP samples, suggesting that these samples are influenced by both microbial sources. In conclusion, the microbial communities from samples taken upstream of the WWTP are distinct from those taken from the WWTP effluent, while the communities in the studied river downstream of the WWTP are a mixture of the upstream and WWTP communities.
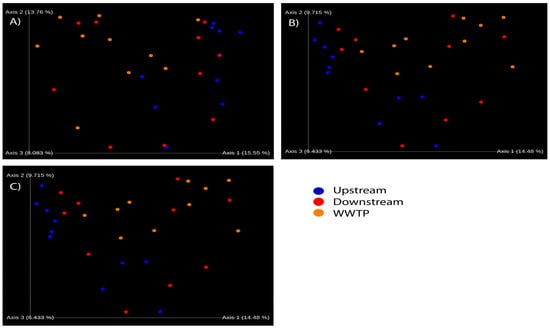
Figure 4.
Principal coordinate analyses based on (A) Bray–Curtis, (B) Jaccard, and (C) unweighted UniFrac distances. Each dot represents a sample. Based on the sampling site, the samples are color coded as blue—upstream; red—downstream; and orange—WWTP.
To further confirm this finding, we performed multivariate analysis (RDA) using Canoco 5 on the bacterial community composition at the species level and the sampling sites. The results clearly show specific bacterial species in the upstream and WWTP sites, with the downstream standing in the middle (Figure 5A). The results also show the upstream sites being grouped among themselves, with WWTP on the opposite end of the line, while the downstream samples lay in the middle between the two (Figure 5B). These results further confirm the presence of distinct microbial communities in the river sediment and WWTP effluent. Moreover, they show the impact of WWTP effluent on downstream microbial communities, which have shifted from the microbial structure found in the upstream sites to the microbial structure of the WWTP effluent. This result was expected, as other studies have also found WWTP effluent to have an impact on downstream microbial communities [93,136,139,169,171]. However, unlike our study, these studies only looked immediately downstream of the WWTP and not at the whole river. In this study, we sampled the length of the whole river; as such, we achieved findings that went unnoticed in previous studies. In the first instance, the river microbial community downstream of the WWTP only partially shifted towards WWTP bacteria and remained similar to the upstream microbial community. The results showed no significant difference between downstream and either WWTP or upstream. Moreover, because we looked at multiple sites along the same river, we were able to determine that the river’s microbial community structure recovers from the impact of the WWTP, as all the upstream sites have similar microbial communities. The resilience of the microbial community’s structure has been shown before, and our study confirms it [172,173].
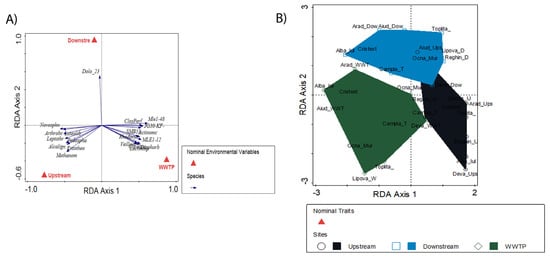
Figure 5.
Constrained RDA analysis depicting the distribution of (A) species and (B) sampling stations.
To answer our question regarding what happens when sediment microbial communities come under pressure from wastewater treatment plants, we can certainly say that the communities exhibit the plastic resistance needed to change, as well as the capacity to withstand the pollution induced by the WWTPs, at least in certain circumstances and up to a specific level of human impact.
Microbial communities in sediments play a key role in aquatic ecosystems. Identifying the structure and functional dynamics of these ecosystems’ sediment microbial communities will help us to assess the impact of humans on the environment and, moreover, to predict whether and how these ecosystems will transform and change [174,175,176,177,178].
4. Conclusions
Although the bacterial communities were found to be equally diverse in the three locations (upstream of the WWTP, WWTP effluents, and downstream of the WWTP), there is a difference in community structure between the upstream samples and the WWTP samples; meanwhile, the downstream samples contain a mixture of the upstream and WWTP effluent communities, even though, downstream of the WWTP, the sediment microbial communities are influenced by the WWTP effluents. The main finding of this study is that despite this type of impact, the river sediment microbiome is resilient and able to recover its natural microbial composition, at least to a certain level of impact; furthermore, this is evidenced by the similarity in the bacterial community structures at all upstream river locations. The overall results indicate the ongoing existence of an ecological equilibrium between the WWTP effluent disruptors and the resilience of the Mureș River sediment microbiomes. From this perspective, the Mureș River has a stable/balanced ecological status, partly due to the microbial communities’ resilience to the local impact of WWTP effluents. This study is significant because it presents the first dataset referring to microbial communities’ ecological status; it can be used as a reference in necessary monitoring activities in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.B. and A.C.-B.; data curation, I.B. and A.C.-B.; formal analysis, I.B. and A.C.-B.; funding acquisition, I.B. and A.C.-B.; methodology, I.B., A.B. and A.C.-B.; project administration A.C.-B. and I.B.; resources, A.C.-B. and I.B.; software, I.B. and A.B.; supervision, I.B. and A.C.-B.; validation, A.C.-B. and D.B.; visualization, I.B., D.B. and A.C.-B.; writing—original draft I.B., A.B., D.B., D.-I.F. and A.C.-B. writing—review and editing, I.B. and D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the RO04 Programme—Reduction of Hazardous Substances, through the EEA Grants 2009–2014 financial mechanism (“SIDPOP-Support instrument for decision making in POPS management. Case study: Mureş Catchment Area”). Supplementarily, this research project was financed by Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu through the research grant LBUS-IRG-2022-08, awarded to Ioana Boeraș.
Data Availability Statement
Supplementary data related to the ones presented in this study are not published and are not part of repositories, but can be available on request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the funding entities which supported this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Fukami, T.; Wardle, D.A. Long-term ecological dynamics: Reciprocal insights from natural and anthropogenic gradients. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiklomanov, I.A. Forthcoming World Water Resources at the Beginning of the 21th Century; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, N. Rivers: A Very Short Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, L. Rhoads, River Dynamics; Chapter 1; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bănăduc, D.; Simić, V.; Cianfaglione, K.; Barinova, S.; Afanasyev, S.; Öktener, A.; McCall, G.; Simić, S.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Freshwater as a sustainable resource and generator of secondary resources in the 21st century: Stressors, threats, risks, management and protection strategies, and conservation approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Garrote, L. Water-energy-ecosystem nexus: Balancing competing interests at a run-of-river hydropower plant coupling a hydrologic-ecohydraulic approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 223, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN Environmental Flows, Managing Water Allocation and Trade-Offs. Available online: https://www.iucn.org/downlowds/water_briefing_eflows.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Dudgeon, D. Anthropocene Extinctions: Global Threats to Riverine Biodiversity and the Tragedy of the Freshwater Commons. In River Conservation: Challenges and Opportunities; Sabater, S., Elosegi, A., Eds.; Fundación BBVA: Bilbao, Spain, 2013; pp. 129–167. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Sabater, S. Understanting global change in river ecosystems: Science to support policy in a changing world. Hydrobiologia 2010, 657, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Crutzen, P.J.; McNeill, J.R. The Anthropocene: Are Humans Noe Overwhelming the Great Forces of Nature? University of California Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2007; Volume 36, pp. 614–621. [Google Scholar]
- Meybeck, M. Global analysis of river systems: From Earth system controls to Anthropocene syndromes. Philos. Trans. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 358, 1935–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Binder, E. The Habitats Along the Upper Danube in Germany and Changes to Them Induced by Human Impacts. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar]
- Burga, C.A.; Landolt, E. The Upper Engandine: Headwater Region of the River Inn. A Swiss Hot Spot of Plant Diversity and Premium Tourism Region. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hübl, E. Vegetation and Flora Near the Danube in Austria. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 65–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cianfaglione, K.; Pedrotti, F. Italy in the Danube Geography: Territory, Landscape, Environment, Vegetation, Fauna, Culture, Human Management and Outlooks for the Future. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 87–118. [Google Scholar]
- Čarni, A.; Mastnak, N.J. Forest Vegetation Along the Mura River in Slovenia. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Adámek, Z.; Jurajdová, Z.; Janáč, M.; Zahrádková, S.; Němejcová, D.; Jurajda, P. The Response of Fish Assemblages to Human Impacts Along the Lower Stretch of the Rivers Morava and Dyje (Danube River Basin, Czech Republic). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 135–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ćaleta, M.; Mustafić, P.; Zanella, D.; Buj, I.; Marčić, Z.; Mrakovčić, M. Human Impact on the Dobra River (Croatia). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Dekić, R.; Ivanc, A.; Ćetković, D.; Lolić, A. Anthropogenic Impact and Environmental Quality of Different Tributaries of the River Vrbas (Bosnia and Hertzegovina). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 169–214. [Google Scholar]
- Gutti, G. Assessment of Long-Term Changes in the Szigetköz Floodplain of the Danube River. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 215–240. [Google Scholar]
- Đikanović, V.; Nikčević, M.; Mićković, B.; Hegediš, A.; Mrdak, D.; Pešić, V. Anthropogenic Pressures on Watercourses of the Danube River Basin in Montenegr. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 241–256. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhardt, M.; Smederevac-Lalić, M.; Hegediš, A.; Skorić, S.; Cvijanović, G.; Višnjić-Jeftić, Ž.; Djikanović, V.; Jovičić, K.; Jaćimović, M.; Jarić, I. Human Impacts of Fish Fauna in the Danube River in Serbia: Current Status and Ecological Implicatins. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 257–280. [Google Scholar]
- Mišiková Elexová, E.; Makovinská, J. Assessment of the Aquatic Ecosystem in the Slovak Stretch of the Danube River. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- Maślanko, W.; Ferencz, B.; Dawidek, J. State and Changes of Natural Environment in Polish Part of the Danube River Basin Poland. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 301–326. [Google Scholar]
- Afanasyev, S.; Lyashenko, A.; Iarochevitch, A.; Lietytska, O.; Zorina-Sakharova, K.; Marushevska, O. Pressures and Impacts on Ecological Status of Surface Water Bodies in Ukrainian part of the Danube River Basin. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 327–359. [Google Scholar]
- Bakiu, R. Drina River (Sava’s Tributary of Danube River) and Human Impact in Albania. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 359–380. [Google Scholar]
- Kostov, V.; Slavevska-Stamenkovic, V.; Ristovska, M.; Stojov, V.; Marić, S. Characteristics of the Danube Drainage Area in the Republic of Macedonia. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Kenderov, L.; Trichkova, T. Long-Term Changes in the Ecological Conditions of the Iskar River (Danube River Basin, Bulgaria). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 393–424. [Google Scholar]
- Burcea, A.; Boeraş, I.; Mihuţ, C.-M.; Bănăduc, D.; Matei, C.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Adding the Mureş River Basin (Transylvania, Romania) to the list of hotspots with high contamination with pharmaceuticals. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Mihuţ, C.; Burcea, A.; McCall, G.S.; Matei, C.; Bănăduc, D. Screening for Microplastic Uptake in an Urbanized Freshwater Ecosystem: Chondrostoma nasus (Linnaeus, 1758) Case Study. Water 2023, 15, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Burcea, A.; Mihuţ, C.-M.; Bănăduc, D. The benthic trophic corner stone compartment in POPs transfer from abiotic environment to higher trophic levels—Trichoptera and Ephemeroptera pre-alert indicator role. Water 2021, 13, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Burcea, A.; Mihuţ, C.-M.; Berg, V.; Lyche, J.L.; Bănăduc, D. Bioaccumulation of persistent organic pollutants in the gonads of Barbus barbus (Linnaeus, 1758). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D.; Burcea, A.; Berg, V.; Lyche, J.L.; Gheorghe, L.M. Persistent organic pollutants in Mureş watershed. In The Impact of Persistent Organic Pollutants on Freshwater Ecosystems and Human Health; Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Ed.; Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu: Sibiu, Romania, 2016; pp. 117–152. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D. The Transylvanian Water Tower through history, and an invitation to a much-needed conference. Danub. News 2015, 32, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Bănăduc, D.; Bakhshalizadeh, S.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Natura 2000 a Panacea? Natura 2000 Site Oltul Mijlociu-Cibin-Hârtibaciu (ROSCI132)—A local extinction of a native fish species and a new alien fish arrival case study. In Transylvanian Review of Systematical and Ecological Research; The Wetlands Diversity: Sibiu, Romania, 2023; Volume 25, pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Boeraş, I.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D.; Cioca, G. Anthropogenic sewage water circuit as vector for SARS-CoV-2 viral ARN transport and public health assessment, monitoring and forecasting—Sibiu metropolitan area (Transylvania/Romania) study case. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănăduc, D.; Sas, A.; Cianfaglione, K.; Barinova, S.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. The role of aquatic refuge habitats for fish, and threats in the context of climate change and human impact, during seasonal hydrological drought in the Saxon Villages area (Transylvania, Romania). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănăduc, D.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Cianfaglione, K.; Akeroyd, J.R.; Cioca, L.-I. Proposed environmental risk management elements in a Carpathian valley basin, within the Roşia Montană European historical mining area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D.; Bucşa, C. Watersheds Management (Transylvania/Romania): Implications, risks, solutions, Strategies to enhance environmental Security in transition countries. In NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C-Environmental Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 225–238. ISSN 1971-4668. ISBN 978-1-4020-5994-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutihac, V. Structura Geologică a Teritoriului României; Editura Tehnică: Bucharest, Romania, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Posea, G. Enciclopedia Geografică a României; Editura Științifică și Enciclopedică: București, Romania, 1982; p. 262. [Google Scholar]
- Diaconu, C.; Stănculescu, S. Rîurile României, Monografie Hidrologică; Institutul de Meteorologie și Hidrologie: București, Romania, 1971; pp. 1–750. [Google Scholar]
- Badea, L.; Bugă, D.; Cioflica, G.; Cucu, V.; Doniță, I.; Gâștescu, P.; Iordan, I.; Morariu, T.; Niculescu, G.; Oancea, D.; et al. Geografia României, I; Geografia Umană și Economică, Editura Academiei Republicii Socialiste România: Bucharest, Romania, 1984; pp. 1–543. [Google Scholar]
- Triebskorn, R.; Telcean, I.; Casper, H.; Farkas, A.; Sandu, C.; Stan, G.; Colărescu, O.; Dori, T.; Köhler, H.-R. Monitoring pollution in River Mureş, Romania, part II: Metal accumulation and histopathology in fish. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 141, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bănăduc, D.; Rey, S.; Trichkova, T.; Lenhardt, M.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. The Lower Danube River—Danube Delta—North West Black Sea: A pivotal area of major interest for the past, present and future of its fish fauna—A short review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănăduc, D.; Oprean, L.; Bogdan, A. Fish species of community interest management issues in Natura 2000 site Sighişoara-Târnava Mare (Transylvania, Romania). Rev. Econ. 2011, 3, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D. Benthic macro-invertebrate and fish communities of some southern Tarnava Mare River tributaries (Transylvania, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2007, 4, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Bănăduc, D. Fish associations—Habitats quality relation in the Târnave rivers ecological assessment. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, H.-R.; Sandu, C.; Scheil, V.; Nagy-Petrică, E.M.; Segner, H.; Telcean, I.; Stan, G.; Triebskorn, R. Monitoring Pollution in River Mureș, Romania, Part III: Biochemical effect markers in fish and integrative reflection. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 127, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, H.-R.; Triebskorn, R.; Sandu, C. Monitoring pollution in the river Mureş. Bull. Int. Assoc. Danub. Res. Danub. News 2005, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sandu, C.; Farkas, A.; Musa-Iacob, R.; Ionică, D.; Parpală, L.; Zinevici, V.; Dobre, D.; Radu, M.; Presing, M.; Casper, H.; et al. Monitoring Pollution in River Mureş, Romania, Part I: How Aquatic Communities are Affected. In Environmental Monitoring and Assessment; Springer: Bucureşti, Romania, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mureş Water Directorate (MWD): Report for 2004—Annual Synthesis Concerning the Water Quality Protection in Mureş Hydrographic Basin, Vol. I and II. (1) (PDF) The Mureş River Ecosystem—Scientific Background Information as the Basis for a Catchment Approach in the Framework of IAD. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242267567_The_Mures_River_ecosystem_-_scientific_background_information_as_the_basis_for_a_catchment_approach_in_the_framework_of_IAD (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Mohajeri, M.H.; Brummer, R.J.M.; Rastall, R.A.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faas, M.; Eggersdorfer, M. The role of the microbiome for human health: From basic science to clinical applications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57 (Suppl. S1), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, M.; Munawar, I.F.; Weisse, T.; Leppard, G.G.; Legner, M. The significance and future potential of using microbes for assessing ecosystem health: The Great Lakes example. J. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health 1994, 3, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzutsev, A.; Badger, J.H.; Perez-Chanona, E.; Roy, S.; Salcedo, R.; Smith, C.K.; Trinchieri, G. Microbes and cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, E.; Marín, M.L.; Martín, R.; Odriozola, J.M.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M. Is meconium from healthy newborns actually sterile? Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirota, I.; Zarek, S.; Segars, J. Potential Influence of the Microbiome on Infertility and Assisted Reproductive Technology. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2014, 32, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, L.; Ge, W.; Yu, S.; Hao, Y.; Shen, W.; Han, X.; Ma, D.; Yin, S.; et al. Improvement in sperm quality and spermatogenesis following faecal microbiota transplantation from alginate oligosaccharide dosed mice. Gut 2021, 70, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Cao, X.; Qin, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hua, J.; Peng, S. Gut microbiota supports male reproduction via nutrition, immunity, and signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 977574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.M.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Kober, O.I.; Juge, N.; Avershina, E.; Rudi, K.; Narbad, A.; Jenmalm, M.C.; et al. The composition of the gut microbiota throughout life, with an emphasis on early life. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.K.; Al-Beltagi, M.; Bediwy, A.S.; El-Sawaf, Y.; Toema, O. Gut microbiota in various childhood disorders: Implication and indications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1875–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, R. Role of different neurotransmitters in anxiety: A systemic review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 411. [Google Scholar]
- Sampson, T.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Thron, T.; Janssen, S.; Shastri, G.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Challis, C.; Schretter, C.E.; Rocha, S.; Gradinaru, V.; et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 2016, 167, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E. Microbiota-brain-gut axis and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, J.M.; Scarmeas, N.; Celenti, R.S.; Elkind, M.S.; Wright, C.B.; Schupf, N.; Papapanou, P.N. Serum IgG antibody levels to periodontal microbiota are associated with incident Alzheimer disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Labrada, A.G.; Isla, D.; Artal, A.; Arias, M.; Rezusta, A.; Pardo, J.; Galvez, E.M. The influence of lung microbiota on lung carcinogenesis, immunity, and immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejman, D.; Livyatan, I.; Fuks, G.; Gavert, N.; Zwang, Y.; Geller, L.T.; Rotter-Maskowitz, A.; Weiser, R.; Mallel, G.; Gigi, E.; et al. The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science 2020, 368, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, L.V. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea: Epidemiology, trends and treatment. Future Microbiol. 2008, 3, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johanesen, P.A.; Mackin, K.E.; Hutton, M.L.; Awad, M.M.; Larcombe, S.; Amy, J.M.; Lyras, D. Disruption of the Gut Microbiome: Clostridium difficile Infection and the Threat of Antibiotic Resistance. Genes 2015, 6, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, T. Pollutant effects on the microbial ecosystem. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savio, D.; Sinclair, L.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Parajka, J.; Reischer, G.; Stadler, P.; Blaschke, A.P.; Blöschl, G.; Mach, R.; Kirschner, A.; et al. Bacterial diversity along a 2600 km river continuum. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4994–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, I.; Carpa, R.; Oltean, A.; Kelemen, B.; Popescu, O. Release of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria by a Waste Treatment Plant from Romania. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florea, A.B. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolated from Arieş river (Romania). An. Univ. Din Oradea Fasc. Biol. 2011, 18, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Boeraş, I.; Burcea, A.; Coman, C.; Bănăduc, D.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Bacterial microbiomes in the sediments of lotic systems ecologic drivers and role: A case study from the Mureş River, Transylvania, Romania. Water 2021, 13, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V. The four-dimensional nature of lotic ecosystems. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1989, 8, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte-Luna, P.; Brook, B.W.; Zetina-Rejón, M.J.; Cruz-Escalona, V.H. The carrying capacity of ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2004, 13, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.A. Ecology of wetland ecosystems: Water, substrate, and life. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2011, 3, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Afanasyev, S.A. Forming of Hydrobiota of the River Systems in the Territory of Ukraine in View of History of Hydrographic Net. Hydrobiol. J. 2015, 51, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, M.J.; Gamble, R.; Perretti, C.T. Dynamic Complexity in Exploited Marine Ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S. Empirical Model of the Functioning of Aquatic Ecosystems. Int. J. Oceanogr. Aquac. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfaglione, K. Plant Landscape and Models of French Atlantic Estuarine Systems. Extended Summary of the Doctoral Thesis. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2021, 23, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.; Lindberg, C.; Plsek, P. A Complexity Science Primer. In Edgeware: Insights from Complexity Science for Health Care Leaders, 2nd ed.; Zimmerman, B., Lindberg, C., Plsek, P., Eds.; VHA Inc.: Irving, TX, USA, 2001; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, P.E.; Hamblin, W.K. Big Rivers Worldwide; Brigham Young University Geology Studies: Provo, UT, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J. Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, K.; Zarfl, C.; Robinson, C. Rivers of Europe, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Bayern, Germany, 2021; p. 800. [Google Scholar]
- Dahm, C.; Bulton, A.; Correa, L.; Kingsford, R.; Jenkins, K.; Sheldon, F. The role of science in planning, policy and conservation of river ecosystems. In Rivers Conservation: Challenges and Opportunities; Sabater, S., Elosegi, A., Eds.; Fundación BBVA: Bilbao, Spain, 2013; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Amyes, S. What’s the Secret of Bacteria’s Success? Bacteria: A Very Short Introduction; Oxford University Press’s Academic Insights for the Thinking World: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Champomier Vergès, M.-C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Herrero Corral, G.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Konopka, A. What is microbial community ecology? ISME J. 2009, 3, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, S.M.; Jones, E.; Bearquiver, A.; Blackwolf, F.; Roundstone, W.; Scott, N.; Hooker, J.; Madsen, R.; Coleman, M.; Gilbert, J.A. Human and Environmental Impacts on River Sediment Microbial Communities. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, H.-F.; He, Y.; Wu, J.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Zhou, H.-W. Comparison of the Levels of Bacterial Diversity in Freshwater, Intertidal Wetland, and Marine Sediments by Using Millions of Illumina Tags. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G.; et al. A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, E.L. Microorganisms and their roles in fundamental biogeochemical cycles. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusch, M.; Fiebig, D.; Brettar, I.; Eisenmann, H.; Ellis, B.K.; Kaplan, L.A.; Lock, M.A.; Naegeli, M.W.; Traunspurger, W. The role of micro-organisms in the ecological connectivity of running waters. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 40, 453–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, M.E.; Boyer, E.W.; Dent, C.L.; Gergel, S.E.; Grimm, N.B.; Groffman, P.M.; Hart, S.C.; Harvey, J.W.; Johnston, C.A.; Mayorga, E.; et al. Biogeochemical hot spots and hot moments at the interface of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniran, A.O.; Igbinosa, E.O. Chlorophenols and other related derivatives of environmental concern: Properties, distribution and microbial degradation processes. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufarté, L.; Laville, É.; Duquesne, S.; Potocki-Veronese, G. Metagenomics for the discovery of pollutant degrading enzymes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.L.; Marques, S.; van Dillewijn, P.; Espinosa-Urgel, M.; Segura, A.; Duque, E.; Krell, T.; Ramos-González, M.I.; Bursakov, S.; Roca, A.; et al. Laboratory research aimed at closing the gaps in microbial bioremediation. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.J.; Kjellerup, B.V. Applications of biofilms in bioremediation and biotransformation of persistent organic pollutants, pharmaceuticals/personal care products, and heavy metals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9909–9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köchling, T.; Sanz, J.L.; Galdino, L.; Florencio, L.; Kato, M.T. Impact of pollution on the microbial diversity of a tropical river in an urbanized region of northeastern Brazil. Int. Microbiol. 2017, 20, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Maddock, I. The importance of physical habitat assessment for evaluating river health. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, H.; Patrik, L.; Günther, U.; Ulrich, P.; Habersack, H. The Role of Sediment and Sediment Dynamics in the Aquatic Environment. In Riverine Ecosystems Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 151–169. [Google Scholar]
- Bănăduc, D.; Voicu, R.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Sediments as factor in the fate of the threatened endemic fish species Romanichthys valsanicola Dumitrescu, Bănărescu and Stoica, 1957 (Vâlsan River basin, Danube Basin). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2020, 22, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Luyssaert, S.; Kaplan, L.A.; Aufdenkampe, A.K.; Richter, A.; Tranvik, L.J. The boundless carbon cycle. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaqué, D.; Pace, M.L.; Findlay, S.; Lints, D. Fate of bacterial production in a heterotrophic ecosystem: Grazing by protists and metazoans in the Hudson Estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 89, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naegeli, M.W.; Uehlinger, U. Contribution of the hyporheic zone to ecosystem metabolism in a prealpine gravel-bed-river. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1997, 16, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, C.S.; Valett, H.M.; Dahm, C.N. Whole-stream metabolism in two montane streams: Contribution of the hyporheic zone. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, J.; Mathieu, J.; Fournier, F. Groundwater/Surface Water Ecotones: Biological and Hydrological Interactions and Management Options, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Craft, J.A.; Stanford, J.A.; Pusch, M. Microbial respiration within a floodplain aquifer of a large gravel-bed river. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.H.; Ugwuanyi, I.R.; Malkaram, S.A.; Montenegro-Garcia, N.A.; Noundou, V.L.; Chavarria-Palma, J.E. Metagenome Sequences of Sediment from a Recovering Industrialized Appalachian River in West Virginia. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00350-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, A.S.; Meisinger, D.B.; Porter, M.L.; Payn, R.A.; Schmid, M.; Stern, L.A.; Schleifer, K.H.; Lee, N.M. Linking phylogenetic and functional diversity to nutrient spiraling in microbial mats from Lower Kane Cave (USA). ISME J. 2010, 4, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansson, E.; Fick, J.; Janzon, A.; Grabic, R.; Rutgersson, C.; Weijdegård, B.; Söderström, H.; Larsson, D.J. Pyrosequencing of antibiotic-contaminated river sediments reveals high levels of resistance and gene transfer elements. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeglin, L.H.; Dahm, C.N.; Barrett, J.E.; Gooseff, M.; Fitpatrick, S.K.; Takacs-Vesbach, C.D. Bacterial Community Structure Along Moisture Gradients in the Parafluvial Sediments of Two Ephemeral Desert Streams. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 61, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, P.W.; Rillig, M.C.; Feris, K.P.; Gordon, N.S.; Moore, J.N.; Holben, W.E.; Gannon, J.E. Relationship between communities and processes; new insights from a field study of a contaminated ecosystem. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feris, K.P.; Ramsey, P.W.; Frazar, C.; Rillig, M.C.; Gannon, J.E.; Holben, W.E. Structure and seasonal dynamics of hyporheic zone microbial communities in free-stone rivers of the estern United States. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 46, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feris, K.P.; Ramsey, P.W.; Frazar, C.; Rillig, M.; Moore, J.N.; Gannon, J.E.; Holben, W.E. Seasonal dynamics of shallow-hyporheic-zone microbial community structure along a heavy-metal contamination gradient. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2323–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feris, K.P.; Ramsey, P.W.; Gibbons, S.M.; Frazar, C.; Rillig, M.C.; Moore, J.N.; Gannon, J.E.; Holben, W.E. Hyporheic microbial community development is a sensitive indicator of metal contamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6158–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.O.; Migliaccio, K.W. Contribution of wastewater treatment plant effluents to nutrient dynamics in aquatic systems: A review. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Zoh, K.D. Occurrence and removals of micropollutants in water environment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 21, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aukidy, M.; Verlicchi, P.; Jelic, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelò, D. Monitoring release of pharmaceutical compounds: Occurrence and environmental risk assessment of two WWTP effluents and their receiving bodies in the Po Valley, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, N.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Gros, M.; Rubirola, A.; Barceló, D.; Comas, J.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Buttiglieri, G. Pharmaceuticals occurrence in a WWTP with significant industrial contribution and its input into the river system. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Jofre, J.; Balcazar, J.L. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in a river influenced by a wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, M.; Wong, K.; Xagoraraki, I. Release of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes in the effluent and biosolids of five wastewater utilities in Michigan. Water Res. 2011, 45, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Li, P.; He, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J. Unveiling dynamics of size-dependent antibiotic resistome associated with microbial communities in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carles, L.; Wullschleger, S.; Joss, A.; Eggen, R.I.; Schirmer, K.; Schuwirth, N.; Stamm, C.; Tlili, A. Wastewater microorganisms impact microbial diversity and important ecological functions of stream periphyton. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Yoo, K.; Kim, M.S.; Han, I.; Lee, M.; Kang, B.R.; Lee, T.K.; Park, J. The capacity of wastewater treatment plants drives bacterial community structure and its assembly. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanseverino, I.; Gómez, L.; Navarro, A.; Cappelli, F.; Niegowska, M.; Lahm, A.; Barbiere, M.; Porcel-Rodríguez, E.; Valsecchi, S.; Pedraccini, R.; et al. Holistic approach to chemical and microbiological quality of aquatic ecosystems impacted by wastewater effluent discharges. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Yu, S.; Rysz, M.; Luo, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, F.; Hou, J.; Mu, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Prevalence and proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes in two municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2015, 85, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.J.; McClary, J.S. The flux and impact of wastewater infrastructure microorganisms on human and ecosystem health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, S.L.; Huse, S.M.; Mueller-Spitz, S.R.; Andreishcheva, E.N.; Sogin, M. Diversity and population structure of sewage-derived microorganisms in wastewater treatment plant influent. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goñi-Urriza, M.; Capdepuy, M.; Raymond, N.; Quentin, C.; Caumette, P. Impact of an urban effluent on the bacterial community structure in the Arga River (Spain), with special reference to culturable Gram-negative rods. Can. J. Microbiol. 1999, 45, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelin, S.A.; Colloff, M.J.; Kookana, R.S. Effect of wastewater treatment plant effluent on microbial function and community structure in the sediment of a freshwater stream with variable seasonal flow. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, B.; Rosi-Marshall, E.; Kelly, J.J. Wastewater treatment effluent reduces the abundance and diversity of benthic bacterial communities in urban and suburban rivers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Bai, Y.; Qu, J. Unravelling riverine microbial communities under wastewater treatment plant effluent discharge in large urban areas. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6755–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeldt, C.; Deiner, K.; Mächler, E.; Fenner, K.; Eggen, R.I.; Stamm, C.; Schönenberger, U.; Walser, J.C.; Altermatt, F. Microbial community shifts in streams receiving treated wastewater effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 135727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashgahi, S.; Aydin, R.; Dimitrov, M.R.; Sipkema, D.; Hamonts, K.; Lahti, L.; Maphosa, F.; Kruse, T.; Saccenti, E.; Springael, D.; et al. Impact of a wastewater treatment plant on microbial community composition and function in a hyporheic zone of a eutrophic river. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundberg, C.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Larsson, M.; Alm, E.; Yekta, S.S.; Svensson, B.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Karlsson, A. 454 pyrosequencing analyses of bacterial and archaeal richness in 21 full-scale biogas digesters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina. bcl2fastq2 Conversion Software. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/downloads/bcl2fastqconversion-software-v2-19.html (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Clemente, J.C.; Kuczynski, J.; Rideout, J.R.; Stombaugh, J.; Wendel, D.; Wilke, A.; Huse, S.; Hufnagle, J.; Meyer, F.; et al. The Biological Observation Matrix (BIOM) format or: How I learned to stop worrying and love the ome-ome. GigaScience 2012, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Peddada, S.; Amir, A.; Bittinger, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Lozupone, C.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Birmingham, A.; et al. Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 2017, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Keller, K.; Karaoz, U.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Singh, N.N.; Brodie, E.L.; Pei, Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Larsen, N. Rapid and sensitive general-purpose k-mer search tool. BMC Ecol. 2011, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioProject Accession Number PRJNA1015452. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/PRJNA1015452 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Chao, A.; Lee, S.M. Estimating the number of classes via sample coverage. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1992, 87, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illonois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bittinger, K.; Charlson, E.S.; Hoffmann, C.; Lewis, J.; Wu, G.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Associating microbiome composition with environmental covariates using generalized UniFrac distances. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, T.A. A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species content and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Biol. Skar. 1948, 5, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; De Cáceres, M. Beta diversity as the variance of community data: Dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1908, 44, 223–270. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Šmilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, B.T.T.; Petrovich, M.L.; Chaudhary, A.; Wright, D.; Murphy, B.; Wells, G.; Poretsky, R. Metagenomics reveals the impact of wastewater treatment plants on the dispersal of microorganisms and genes in aquatic sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02168-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, E.; McLellan, S.L.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Sogin, M.L.; Gast, R.J. Comparison of Bacterial Communities in Sands and Water at Beaches with Bacterial Water Quality Violations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristi, I.; von Schiller, D.; Arroita, M.; Barceló, D.; Ponsatí, L.; García-Galán, M.J.; Sabater, S.; Elosegi, A.; Acuña, V. Mixed effects of effluents from a wastewater treatment plant on river ecosystem metabolism: Subsidy or stress? Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, L.; Wullschleger, S.; Joss, A.; Eggen, R.I.; Schirmer, K.; Schuwirth, N.; Stamm, C.; Tlili, A. Impact of wastewater on the microbial diversity of periphyton and its tolerance to micropollutants in an engineered flow-through channel system. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebkuecher, J.G.; Bojic, S.; Breeden, C.A.; Childs, S.L.; Evans, M.C.; Hauskins, B.S.; Irick, Z.A.; Kraft, J.C.; Krausfeldt, J.M.; Santoyo, N.I. Photoautotrophic-Periphyton Composition in Reaches with Differing Nutrient Concentrations in the Harpeth River of Middle Tennessee. Castanea 2018, 83, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwole, P.; Guta, A.; Draper, M.; Atkinson, S. Spatio-temporal variations in the physiological profiles of streambed bacterial communities: Implication of wastewater treatment plant effluents. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugerth, L.W.; Andersson, A.F. Analysing Microbial Community Composition through Amplicon Sequencing: From Sampling to Hypothesis Testing. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merbt, S.N.; Auguet, J.C.; Blesa, A.; Martí, E.; Casamayor, E.O. Wastewater treatment plant effluents change ab undance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in mediterranean urban stream biofilms. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, J.R.; Ledford, S.H.; Ryan, M.O.; Toran, L.; Sales, C.M. Wastewater treatment plant effluent introduces recoverable shifts in microbial community composition in receiving streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenelt, S.; Wang, G.; Kasmanas, J.C.; Musat, F.; Richnow, H.H.; da Rocha, U.N.; Müller, J.A.; Musat, N. The fate of sulfonamide resistance genes and anthropogenic pollution marker intI1 after discharge of wastewater into a pristine river stream. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1058350. [Google Scholar]
- Banchi, E.; Del Negro, P.; Celussi, M.; Malfatti, F. Sediment features and human activities structure the surface microbial communities of the Venice Lagoon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 762292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lennon, J.T.; Ruan, A. Anthropogenic activities mediate stratification and stability of microbial communities in freshwater sediments. Microbiome 2023, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehuan, L.; Yen, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Ke, D.; Liu, C. Differential responses of stream water and bed sediment microbial communities to watershed degradation. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105198. [Google Scholar]
- Beattie, R.E.; Bandla, A.; Swarup, S.; Hristova, K.R. Freshwater sediment microbial communities are not resilient to disturbance from agricultural land runoff. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 539921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, T. Temporal and spetial patterns of sediment communities and driving environment variables in a shallow temperate mountain river. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).