Electrodeionization for Wastewater Reuse in Petrochemical Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Wastewater under Study
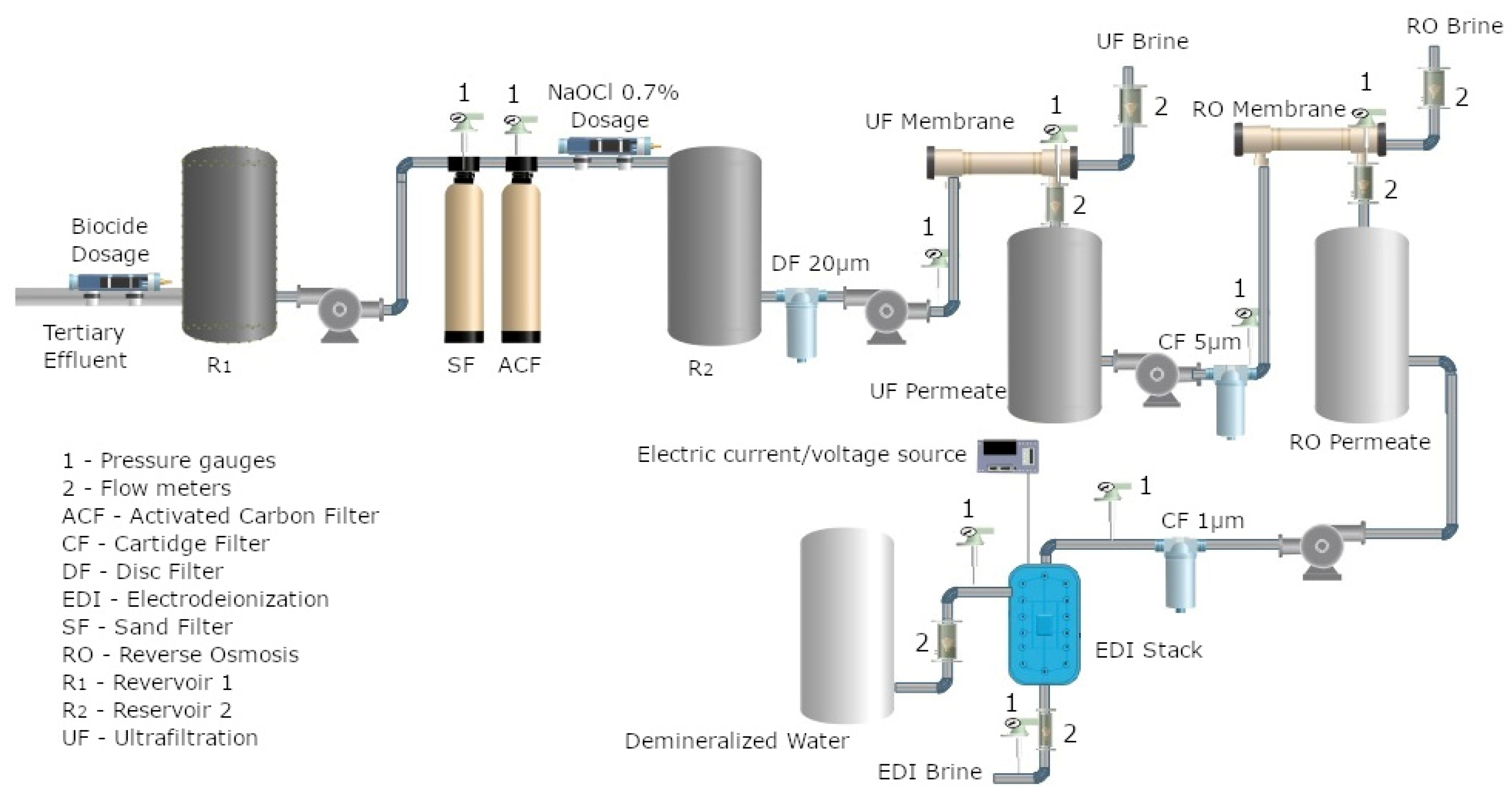
2.2. Hybrid UF/RO/EDI Treatment System
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Technical and Economic Feasibility Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Tertiary Petrochemical Effluent
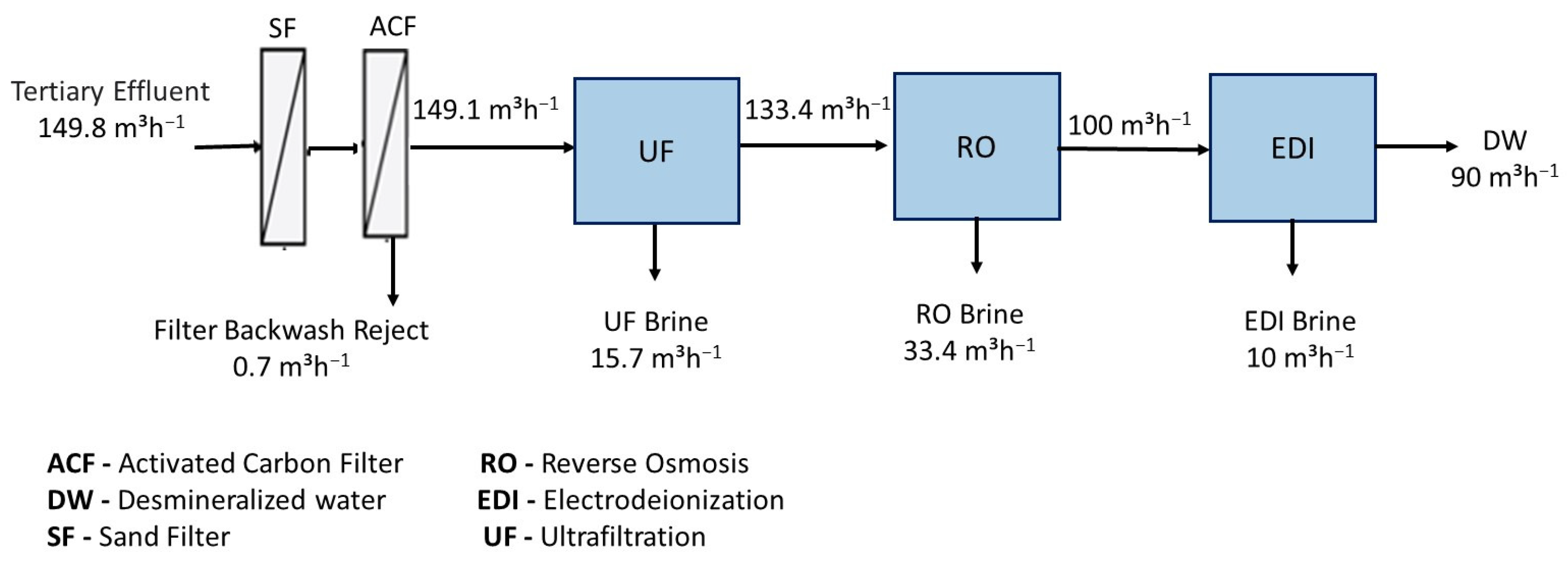
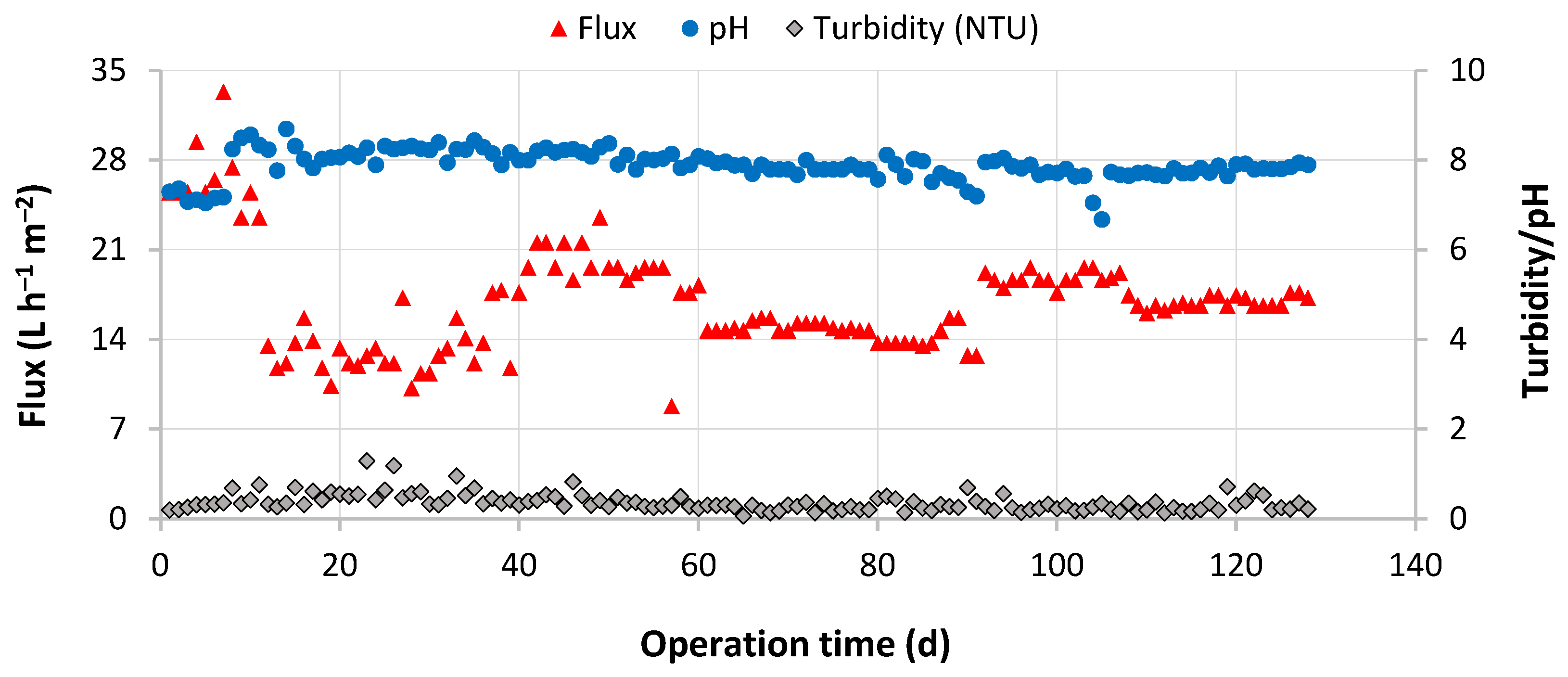
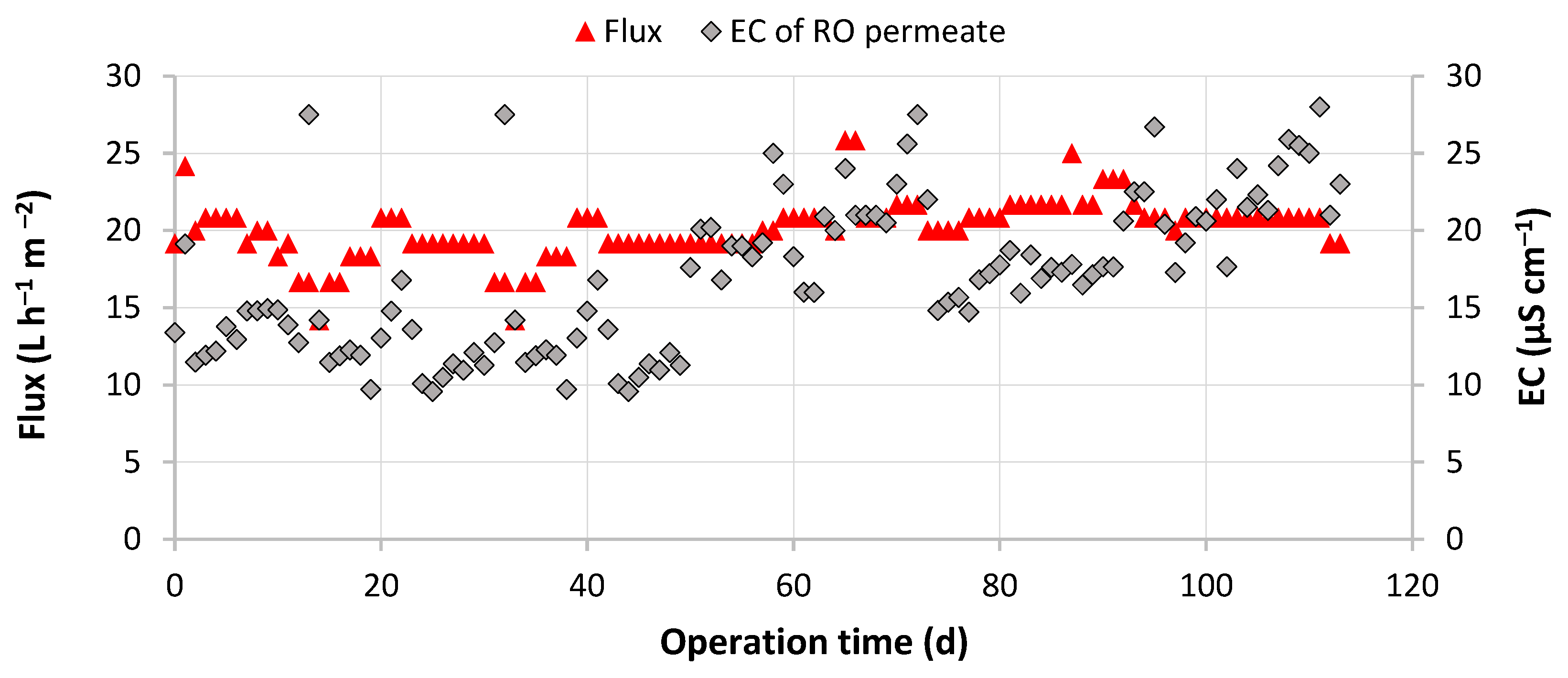
3.2. Performance of the UF/RO/EDI Hybrid Treatment System
3.3. Technical and Economic Feasibility Analysis of the UF/RO/EDI Hybrid Treatment System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashemi, F.; Hashemi, H.; Shahbazi, M.; Dehghani, M.; Hoseini, M.; Shafeie, A. Reclamation of Real Oil Refinery Effluent as Makeup Water in Cooling Towers Using Ultrafiltration, Ion Exchange and Multioxidant Disinfectant. Water Resour. Ind. 2020, 23, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, É.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; de Aquim, P.M. Characterization of Aqueous Streams in a Petrochemical Industry: A Study for the Reuse of Industrial Effluents. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 27, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, P.B.; Ricci, B.C.; Reis, B.G.; Neta, L.S.F.; Cerqueira, A.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Effect of MBR-H2O2/UV Hybrid Pre-Treatment on Nanofiltration Performance for the Treatment of Petroleum Refinery Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Al-Kaabi, M.A.; Ashfaq, M.Y.; Da’na, D.A. Produced Water Characteristics, Treatment and Reuse: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 28, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Suhas, D.P.; Costa, M.E.; Capela, I.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Sustainability Considerations in Membrane-Based Technologies for Industrial Effluents Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 474–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Varsha, M.; Senthil Rathi, B.; Rangasamy, G. Electrodeionization: Principle, Techniques and Factors Influencing Its Performance. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.N.; Khoiruddin, K.; Ariono, D.; Wenten, I.G. Ionic Separation in Electrodeionization System: Mass Transfer Mechanism and Factor Affecting Separation Performance. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2020, 49, 294–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadjafi, M.; Reyhani, A.; Al Arni, S. Feasibility of Treatment of Refinery Wastewater by a Pilot Scale MF/UF and UF/RO System for Reuse at Boilers and Cooling Towers. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2018, 40, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjeeth, R.; Aditya, D.; Gautam, A.; Singh, S.P.; Bhattacharya, S. Failure Investigation of a Water-Wall Tube of Fossil-Fuel Fired Boiler. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 155, 107727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Reverse Osmosis Pretreatment Technologies and Future Trends: A Comprehensive Review. Desalination 2019, 452, 159–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Gkotsis, P.; Castellana, M.; Cartechini, F.; Zouboulis, A.I. Production of Demineralized Water for Use in Thermal Power Stations by Advanced Treatment of Secondary Wastewater Effluent. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.; Moon, S.H. Investigation of the Performance Determinants in the Treatment of Arsenic-Contaminated Water by Continuous Electrodeionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Electrodeionization Theory, Mechanism and Environmental Applications. A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1209–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenten, I.G.; Khoiruddin; Arfianto, F. Zudiharto Bench Scale Electrodeionization for High Pressure Boiler Feed Water. Desalination 2013, 314, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.B.; Giacobbo, A.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M. Integrated Membrane Process (UF/RO/EDI) for Treating a Petrochemical Wastewater to Obtain Ultrapure Water for Industrial Reuse. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 177, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.B.; Barreto, A.S.; Gonçalves, L.R.; Pires, A.N.; Giacobbo, A.; Rodrigues, M.A.S. Industrial Reuse of Petrochemical Effluents: A Case Study of Ultrafiltration and Reverse Osmosis. Ciência Nat. 2022, 44, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Wang, R. The Coming of Age of Water Channels for Separation Membranes: From Biological to Biomimetic to Synthetic. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 4537–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritzmann, C.; Löwenberg, J.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. State-of-the-Art of Reverse Osmosis Desalination. Desalination 2007, 216, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Ma, Y.; Chew, J.W.; Wang, R. Assessing the Potential of Highly Permeable Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Desalination: Specific Energy and Footprint Analysis. Desalination 2022, 533, 115771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Englehardt, J.; Wu, T. Review of Cost versus Scale: Water and Wastewater Treatment and Reuse Processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valizadeh, B.; Zokaee Ashtiani, F.; Fouladitajar, A.; Dabir, B.; Seyed Mahmoud Baraghani, S.; Armand, S.B.; Salari, B.; Kouchakiniya, N. Scale-up Economic Assessment and Experimental Analysis of MF-RO Integrated Membrane Systems in Oily Wastewater Treatment Plants for Reuse Application. Desalination 2015, 374, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venzke, C.D.; Giacobbo, A.; Klauck, C.R.; Viegas, C.; Hansen, E.; Monteiro de Aquim, P.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M. Integrated Membrane Processes (EDR-RO) for Water Reuse in the Petrochemical Industry. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2018, 4, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venzke, C.D.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Giacobbo, A.; Bacher, L.E.; Lemmertz, I.S.; Viegas, C.; Striving, J.; Pozzebon, S. Application of Reverse Osmosis to Petrochemical Industry Wastewater Treatment Aimed at Water Reuse. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2017, 28, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DOW Water & Process Solutions Ultrafiltration Product Manual. Available online: https://www.lenntech.com/Data-sheets/Dow-Ultrafiltration-L.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2023).
- Dupont FilmTecTM FortilifeTM CR100i Element Data Sheet, Form No. 45-D01760-En, Rev. 3. Available online: https://www.dupont.com/content/dam/dupont/amer/us/en/water-solutions/public/documents/en/RO-FilmTec-Fortilife-CR100i-PDS-45-D01760-en.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2023).
- APHA. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; APHA, AWWA, WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, C.E.; Hipólito, M. Processos de Gerenciamento de Portfólio e Projetos Da Braskem, ABEAV. 7 October 2008. Available online: https://www.assender.com.br/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/palestra2.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2023).
- Zuo, W.; Zhang, G.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, H. Characteristics and Application of Multiple Membrane Process in Plating Wastewater Reutilization. Desalination 2008, 222, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Operating Energy Consumption Analysis of RO Desalting System: Effect of Membrane Process and Energy Recovery Device (ERD) Performance Variables. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 14135–14144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venzke, C.D.; Giacobbo, A.; Ferreira, J.Z.; Bernardes, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S. Increasing Water Recovery Rate of Membrane Hybrid Process on the Petrochemical Wastewater Treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarinejad, S. A Comprehensive Study on the Application of Reverse Osmosis (RO) Technology for the Petroleum Industry Wastewater Treatment. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernon, B.P.; Zanapalidou, R.H.; Zhang, L.; Sims, K.J.; Siwak, L.R. Electrodeionization in Power Plant Applications. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Ultrapure Water Expo’94, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 9–11 May 1994; GE Technical Paper 2010, TP1073EN. pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Dave, P.N. Removal of Iron for Safe Drinking Water. Desalination 2012, 303, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Wood, J. Design, Construction and Operation of a 6,730 Gpm RO/CEDI System for Con Edison’s East River Repowering Project. IWC 2006, 6, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, J. Continuous Electrodeionization for Water Treatment at Power Plants. Power Eng. 2008, 112, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Long, T. A Critical Review on Challenges and Trend of Ultrapure Water Production Process. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younos, T. The Economics of Desalination. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2005, 132, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.H.; Gifford, J.D. Continuous Electrodeionization. In Desalination: Water from Water; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 287–328. ISBN 9781119407874. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, G.; Gómez, P.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Techno-Economic Assessment of a Membrane-Based Wastewater Reclamation Process. Desalination 2022, 522, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, W.; Bradford-Hartke, Z.; Cran, M.J.; Duke, M.; Leslie, G.; Ladewig, B.P.; Le-Clech, P. Towards New Opportunities for Reuse, Recycling and Disposal of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Desalination 2012, 299, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abada, B.; Safarik, J.; Ishida, K.P.; Chellam, S. Surface Characterization of End-of-Life Reverse Osmosis Membranes from a Full-Scale Advanced Water Reuse Facility: Combined Role of Bioorganic Materials and Silicon on Chemically Irreversible Fouling. J. Memb. Sci. 2022, 653, 120511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Álvarez, G.; Garralón, G.; Plaza, F.; Garralón, A.; Pérez, J.; Gómez, M.A. Autopsy of SWRO Membranes from Desalination Plant in Ceuta after 8 Years in Operation. Desalination 2010, 263, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Melián-Martel, N.; Mena, V. Fouling Characterization of RO Membranes after 11 Years of Operation in a Brackish Water Desalination Plant. Desalination 2018, 430, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, K.P.; Mara, D.D.; Angelakis, A.N. Application of Cost Criteria for Selection of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 142, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittholz, M.K.; O’Neill, B.K.; Colby, C.B.; Lewis, D. Estimating the Cost of Desalination Plants Using a Cost Database. Desalination 2008, 229, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | UF Membrane a | RO Membrane b |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane Type | PVDF | Polyamide Thin-Film Composite |
| Product Type | Hollow fiber | Spiral-wound element |
| Active Area (m2) | 51 | 7.2 |
| pH Range Continuous Operation | 4–11 | 2–11 |
| Maximum Operating Temperature (°C) | 50 | 45 |
| Maximum Operating Pressure (bar) | 5–9.5 | 15.5 |
| Free Chlorine Tolerance (mg L−1) | 5 | <0.1 |
| Maximum Feed Silt Density Index (SDI) | 5 | |
| Minimum Salt Rejection (%) | 99.5 |
| Parameter | Method | Parameter | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | SM 3111D | pH | SM 4500H+ |
| Calcium | SM 3111D | Potassium | SM 3500KB |
| Chloride | SM 4110B | Silica | SM 4500-SiO2C |
| Color | SM 2120B | Sodium | SM 3500NaB |
| Electrical Conductivity | SM 2510B | Sulfate | SM 4110B |
| Iron | SM 3111B | Total Organic Carbon | SM 5310B |
| Magnesium | SM 3111B | Total Phosphorus | SM 4500PD |
| Nitrate | SM 4110B | Turbidity | SM 2130B |
| Parameter | Tertiary Effluent | Standard for DW a |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (mg L−1) | <2.50 | ns |
| Calcium (mg L−1) | 23.2 | 0.12 |
| Chloride (mg L−1) | 103 | ns |
| Color (mg Pt-Co L−1) | 31.6 | ns |
| Electrical Conductivity (µS cm−1) | 1222 | <0.30 |
| Iron (mg L−1) | 0.51 | <0.01 |
| Magnesium (mg L−1) | 5.27 | 0.25 |
| Nitrate | 2.12 | ns |
| pH | 7.77 | 6–7 |
| Potassium (mg L−1) | 64.0 | ns |
| Silica (mg L−1) | 25.0 | 0.02 |
| Sodium (mg L−1) | 170 | ns |
| Sulfate (mg L−1) | 272 | ns |
| Total Organic Carbon—TOC (mg L−1) | 10.0 | ns |
| Total Phosphorus (mg L−1) | 1.38 | ns |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 13.7 | ns |
| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| UF/RO/EDI (This Study) | RO/EDI (Wenten et al. [14]) | |
| CapEx in USD | ||
| Equipment and materials | ||
| Pre-treatment | 93,617.02 | |
| UF | 672,340.43 | |
| RO | 704,255.32 | |
| EDI | 308,510.64 | |
| Taxes and other fees (20% on equipment value) | 355,744.68 | |
| Construction | 115,114.21 | |
| Total CapEx | 2,249,582.30 | |
| OpEx in USD | ||
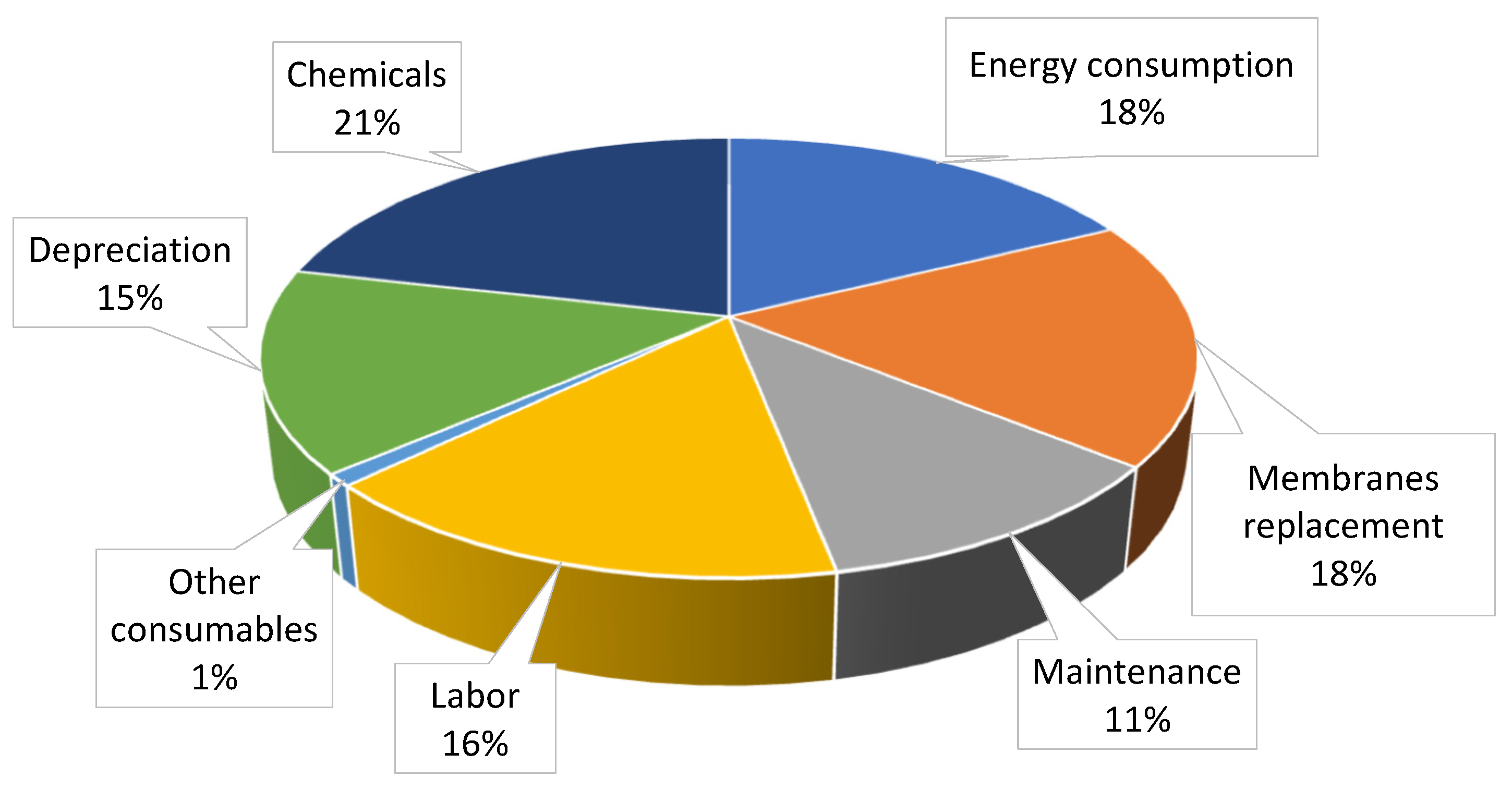
| Feed water cost | ----- | 106,275.84 |
| Energy consumption | 89,262.54 | 97,240.07 |
| Membranes’ replacement | 91,323.83 | 170,048.00 |
| Maintenance | 56,239.56 | 11,473.12 |
| Labor | ||
| Plant operation (3 technicians) | 80,074.47 | ----- |
| Chemicals | ||
| For Pre-treatment | 10,026.49 | |
| For UF | 32,122.20 | |
| For RO | 41,582.04 | 4724.00 |
| For EDI | 24,546.80 | ----- |
| Other consumables | 4427.23 | |
| Total OPEX | 429,605.16 | 389,761.03 |
| Production capacity (m3 year−1) | 788,400 | 950,000 |
| Specific water production cost (USD m−3) | 0.54 | 0.42 |
| Depreciation of DWPP (USD m−3) a | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| Total specific water production cost (USD m−3) | 0.64 | 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, A.B.d.; Giacobbo, A.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M. Electrodeionization for Wastewater Reuse in Petrochemical Plants. Water 2024, 16, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030401
Santos ABd, Giacobbo A, Rodrigues MAS, Bernardes AM. Electrodeionization for Wastewater Reuse in Petrochemical Plants. Water. 2024; 16(3):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030401
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Andréia Barros dos, Alexandre Giacobbo, Marco Antônio Siqueira Rodrigues, and Andréa Moura Bernardes. 2024. "Electrodeionization for Wastewater Reuse in Petrochemical Plants" Water 16, no. 3: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030401
APA StyleSantos, A. B. d., Giacobbo, A., Rodrigues, M. A. S., & Bernardes, A. M. (2024). Electrodeionization for Wastewater Reuse in Petrochemical Plants. Water, 16(3), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030401








