Production, Toxicological Effects, and Control Technologies of Ochratoxin A Contamination: Addressing the Existing Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. OTA Production and Contamination Distribution
2.1. Chemical Structures and Properties of OTs
2.2. Unexpected but Existing OTA
2.3. Producers of OTA
2.3.1. Aspergillus spp.
2.3.2. Penicillium spp.
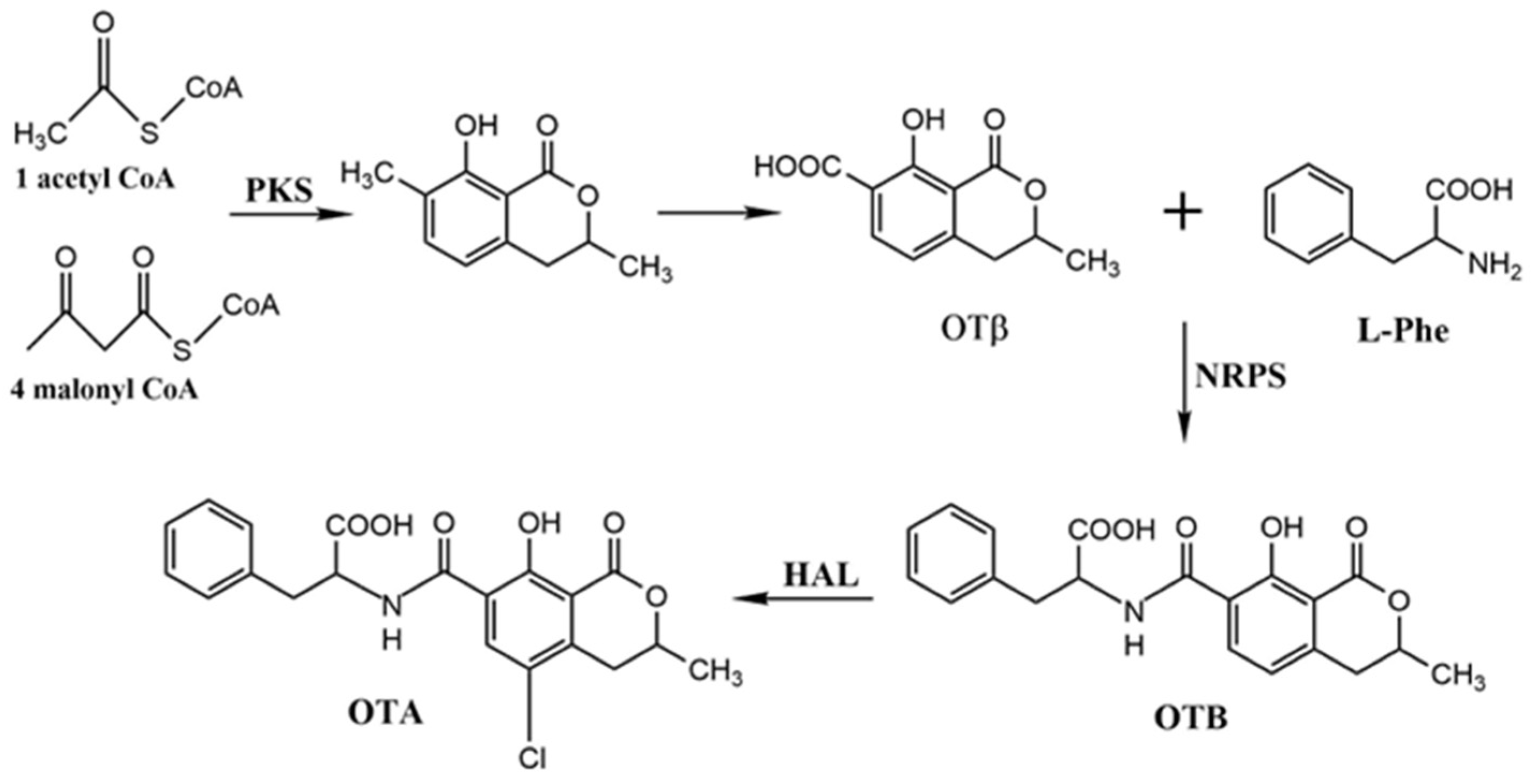
2.4. Precursors and Related Metabolites in OTA Biosynthesis
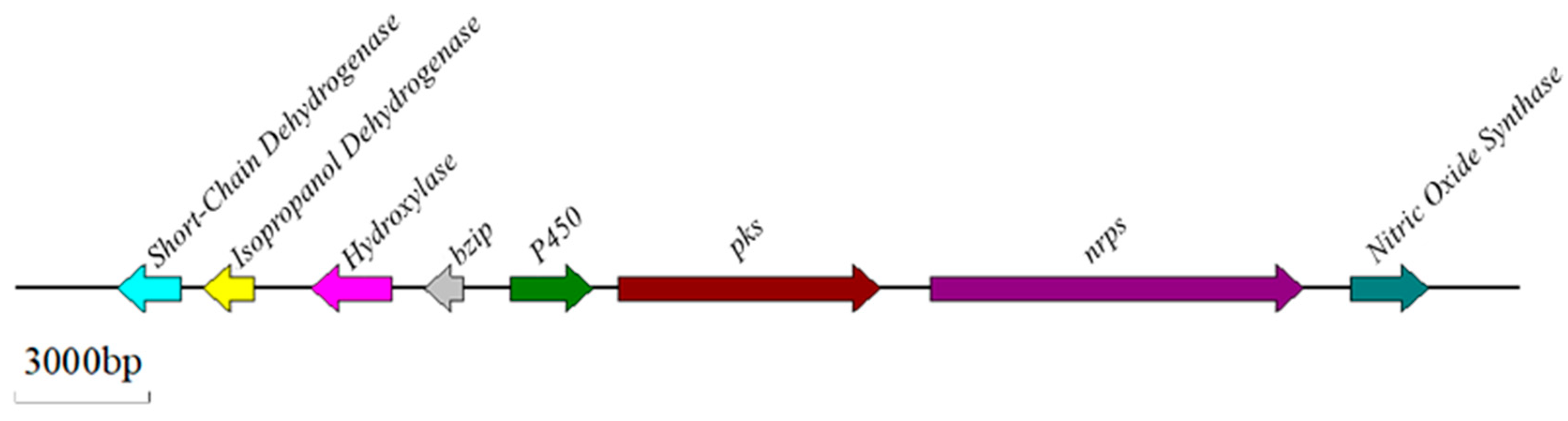
2.5. Biosynthetic Pathway and Genes Related to OTA
2.6. Regulatory Mechanisms of OT Biosynthesis
3. Toxicity of OTA
3.1. Renal Toxicity
3.2. Hepatotoxicity
3.3. Carcinogenic, Teratogenic, and Mutagenic Effects
3.4. Immunotoxicity
3.5. Gastrointestinal Toxicity
3.6. Neurotoxicity
4. Detoxification Technologies for OTA
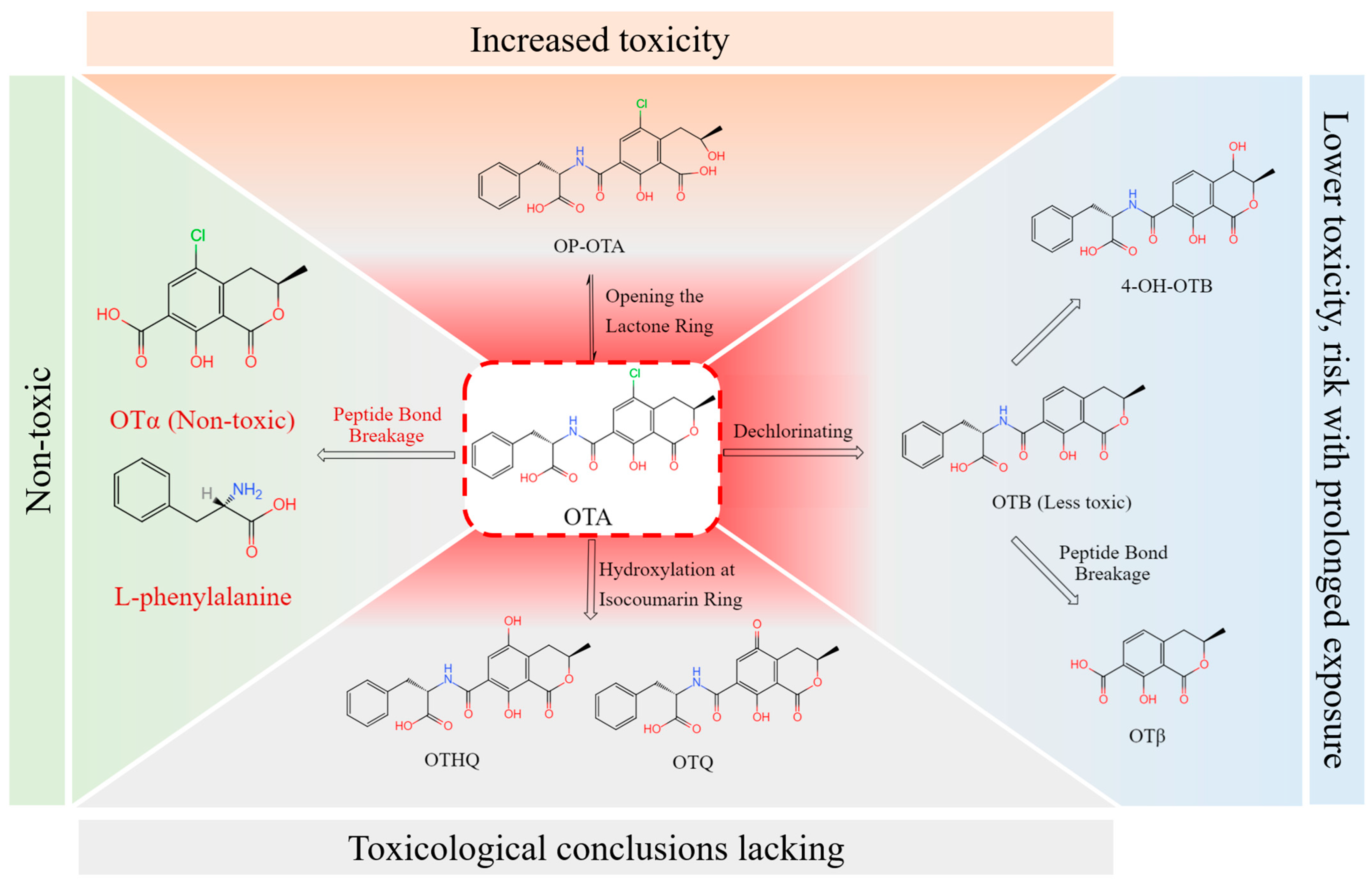
4.1. OTA Conversion Pathway
4.2. Physical Detoxification Technologies
4.3. Chemical Detoxification Technologies
4.4. Biological Detoxification Technologies
4.4.1. Microorganisms with Detoxification and/or Antagonistic Abilities
4.4.2. Enzymes for OTA Degradation
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pei, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Xiao, X.; Tang, S.; Li, D. Food-Origin Mycotoxin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Intend to Break the Rules of Neuroglia Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9967334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bellis, P.; Tristezza, M.; Haidukowski, M.; Fanelli, F.; Sisto, A.; Mule, G.; Grieco, F. Biodegradation of Ochratoxin A by Bacterial Strains Isolated from Vineyard Soils. Toxins 2015, 7, 5079–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Z. Biodegradation of ochratoxin A and ochratoxin B by Brevundimonas naejangsanensis isolated from soil. Food Control 2022, 133, 108611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Madhyastha, S.; Marquardt, R.R.; Li, S.; Vodela, J.K.; Frohlich, A.A.; Kemppainen, B.W. Toxicity of ochratoxin A, its opened lactone form and several of its analogs: Structure-activity relationships. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 137, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, G.; Burkert, B.; Möller, U.; Diller, R.; Rohrmann, B.; Rosner, H.; Köhler, H. Ochratoxin A and some of its derivatives modulate radical formation of porcine blood monocytes and granulocytes. Toxicology 2004, 199, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heussner, A.H.; Bingle, L.E.H. Comparative Ochratoxin Toxicity: A Review of the Available Data. Toxins 2015, 7, 4253–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Pedroso, I.R. Mycotoxins in Cereal-Based Products and Their Impacts on the Health of Humans, Livestock Animals and Pets. Toxins 2023, 15, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, S.; Yang, P.; Liu, Q.; Tang, S. Rapid detection and toxicity assessment of ochratoxin A by Photobacterium leiognathi in drinking water. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Herrera-Balandrano, D.D.; Shi, X.-C.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.-Q.; Laborda, P. Occurrence of aflatoxins in water and decontamination strategies: A review. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraschek, L.M.; Kappenberg, A.; Amelung, W. Mycotoxins in soil and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K.; Nowak, A.; Chlebicz, A.; Żbikowski, A.; Pawłowski, K.; Szeleszczuk, P. Probiotic microorganisms detoxify ochratoxin A in both a chicken liver cell line and chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4309–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Meng, S.; Liu, D.; You, T. Direct Z-scheme NiTiO3/polyaniline heterojunction based photoelectrochemical aptasensor for the efficient detection of ochratoxin A in corn and soil. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 401, 134976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odey, M.O.; Gulack, A.O.; Imojara, B.; Benjamin, I. Surface tailoring of Graphene via silicon co-doping with Group 15 Elements for the Detection of Ochratoxin (OTX): An Insilco Investigation. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.R.; Mata, A.T.; Ferreira, J.P.; Barreto Crespo, M.T.; Pereira, V.J.; Bronze, M.R. Production of mycotoxins by filamentous fungi in untreated surface water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17519–17528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.S.; Jeyaram, K.; Datta, S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Balaji, R.; Selvarajan, E. Detection, Contamination, Toxicity, and Prevention Methods of Ochratoxins: An Update Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 13974–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, E.; Gallo, A.; Perrone, G.; Varga, E.; Ma, J.; Yang, B.; Tai, B.; Xing, F. Impact of environmental factors on ochratoxin A: From natural occurrence to control strategy. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koko, D.T.; Alfred, M.O.; Bolujoko, N.B.; Olorunnisola, D.; Otitoju, O.B.; Alabi, P.; Ogunlaja, O.O.; Okonofua, F.; Omonkhua, A.A.; Msagati, T.A.M.; et al. Prevalence and health risk evaluations of mycotoxins in drinking water sources in Nigeria. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 34435–34447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonerba, E.; Manfredi, A.; Dimuccio, M.M.; Lorusso, P.; Pandiscia, A.; Terio, V.; Di Pinto, A.; Panseri, S.; Ceci, E.; Bozzo, G. Ochratoxin A in Poultry Supply Chain: Overview of Feed Occurrence, Carry-Over, and Pathognomonic Lesions in Target Organs to Promote Food Safety. Toxins 2024, 16, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Curbelo, M.Á.; Kabak, B. Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Dried Fruits Worldwide, with a Focus on Aflatoxins and Ochratoxin A: A Review. Toxins 2023, 15, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, J.; Kozakiewicz, Z. Ochratoxin A in grapes and grape-derived products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.R.; Mohan, K.; Karthick Rajan, D.; Pillay, A.A.; Palanisami, T.; Sathishkumar, P.; Conterno, L. Distribution, toxicity, interactive effects, and detection of ochratoxin and deoxynivalenol in food: A review. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 131978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, R.; Mishael, Y.G. Bifunctional clay based sorbent for ‘Ochratoxin A’ removal and wine fining. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahal, S.; Lee, H.J.; Gu, K.; Ryu, D. Heat Stability of Ochratoxin A in an Aqueous Buffered Model System. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazin, I.; Faucet-Marquis, V.; Monje, M.-C.; Khoury, M.; Marty, J.-L.; Leszkowicz, A. Impact of pH on the Stability and the Cross-Reactivity of Ochratoxin A and Citrinin. Toxins 2013, 5, 2324–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagkali, V.; Petrou, P.S.; Salapatas, A.; Makarona, E.; Peters, J.; Haasnoot, W.; Jobst, G.; Economou, A.; Misiakos, K.; Raptis, I.; et al. Detection of ochratoxin A in beer samples with a label-free monolithically integrated optoelectronic biosensor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Sun, Y.; Huo, B.; Yuan, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.; Yin, N.; Fan, L.; Yao, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Highly sensitive detection of ochratoxin A based on bio-barcode immunoassay and catalytic hairpin assembly signal amplification. Talanta 2020, 208, 120405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2761-2017; National Food Safety Standard: Maximum Levels of Mycotoxins in Food. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Chen, R.; de Sherbinin, A.; Ye, C.; Shi, G. China’s Soil Pollution: Farms on the Frontline. Science 2014, 344, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizel, T.; Jarvis, B.; Rolfe, E.J. A field survey of pistachio (Pistacia vera) nut production and storage in turkey with particular reference to aflatoxin contamination. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1976, 27, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalesi, M.; Khatib, N. The effects of different ecophysiological factors on ochratoxin A production. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 32, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézqueta, S.; Schorr-Galindo, S.; Murillo-Arbizu, M.; González-Peñas, E.; López de Cerain, A.; Guiraud, J.P. OTA-producing fungi in foodstuffs: A review. Food Control 2012, 26, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Malir, J.; Toman, J. Ochratoxin A: 50 Years of Research. Toxins 2016, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, S.C.; Pena, A.; Lino, C.M. A review on ochratoxin A occurrence and effects of processing of cereal and cereal derived food products. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, A.; Abarca, M.L.; Bragulat, M.R.; Cabañes, F.J. Effects of temperature and incubation time on production of ochratoxin A by black aspergilli. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, R.; Neri, L.; Costa, F.; Facini, O.; Rapparini, F. Ecophysiological and micromorphological characterization of green roof vegetation for urban mitigation. Urban Urban Green. 2018, 37, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; Mateo, R.; López-Ocaña, L.; Valle-Algarra, F.M.; Jiménez, M. Study of Spanish grape mycobiota and ochratoxin a production by isolates of Aspergillus tubingensis and other members of Aspergillus section Nigri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4696–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier Cabanes, F.; Rosa Bragulat, M.; Castella, G. Ochratoxin A Producing Species in the Genus Penicillium. Toxins 2010, 2, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limay-Rios, V.; Miller, J.D.; Schaafsma, A.W. Occurrence of Penicillium verrucosum, ochratoxin A, ochratoxin B and citrinin in on-farm stored winter wheat from the Canadian Great Lakes Region. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggblom, P. Production of Ochratoxin-A in barley by Aspergillus Ochraceus and Penicillium Viridicatum—Effect of fungal growth, time, temperature, and inoculum size. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1205–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; Rondan, J.J.; Nunez, F.; Rodriguez, A. Influence of an industrial dry-fermented sausage processing on ochratoxin A production by Penicillium nordicum. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 339, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Apaliya, M.T.; Mahunu, G.K.; Chen, L.; Li, W. Control of ochratoxin A-producing fungi in grape berry by microbial antagonists: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, C.W.; Ferreira, N.P. The biosynthesis of the ochratoxins, metabolites of Aspergillus ochraceus. Phytochemistry 1970, 9, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhland, M.; Engelhardt, G.; Wallnöter, P.R. Production of14C-ochratoxin A byPenicillium verrucosum sp. 1761 in liquid culture. Mycotoxin Res. 1996, 12, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Bruno, K.S.; Solfrizzo, M.; Perrone, G.; Mulè, G.; Visconti, A.; Baker, S.E. New insight into the ochratoxin A biosynthetic pathway through deletion of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene in Aspergillus carbonarius. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8208–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.P.; Mantle, P.G. Biosynthesis of ochratoxins by Aspergillus ochraceus. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Liu, L.; Xing, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y. Functional Characterization of New Polyketide Synthase Genes Involved in Ochratoxin A Biosynthesis in Aspergillus ochraceus fc-1. Toxins 2015, 7, 2723–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, J.; Stapleton, P.C.; Dobson, A.D.W. Ochratoxin A biosynthetic genes in Aspergillus ochraceus are differentially regulated by pH and nutritional stimuli. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2006, 43, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, J.; Gerber, R.; Du, L. Recent advancements in the biosynthetic mechanisms for polyketide-derived mycotoxins. Biopolymers 2010, 93, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, F.; Liu, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Zhao, Y.; Xing, F.; Yin, W.B.; et al. A Consensus Ochratoxin A Biosynthetic Pathway: Insights from the Genome Sequence of Aspergillus ochraceus and a Comparative Genomic Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, J.; Caddick, M.X.; Dobson, A.D.W. A polyketide synthase gene required for ochratoxin A biosynthesis in Aspergillus ochraceus. Microbiology 2003, 149, 3485–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.P.; Turner, G.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal secondary metabolism—From biochemistry to genomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karolewiez, A.; Geisen, R. Cloning a part of the ochratoxin A biosynthetic gene cluster of Penicillium nordicum and characterization of the ochratoxin polyketide synthase gene. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 28, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pel, H.J.; de Winde, J.H.; Archer, D.B.; Dyer, P.S.; Hofmann, G.; Schaap, P.J.; Turner, G.; de Vries, R.P.; Albang, R.; Albermann, K.; et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Serna, J.; Vázquez, C.; González-Jaén, M.T.; Patiño, B. Clustered array of ochratoxin A biosynthetic genes in Aspergillus steynii and their expression patterns in permissive conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 214, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.; Perrone, G.; Gambacorta, L.; Epifani, F.; Solfrizzo, M.; Gallo, A. Identification of a Halogenase Involved in the Biosynthesis of Ochratoxin A in Aspergillus carbonarius. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5631–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Hu, J.; Xue, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Deletion and Overexpression of the AnOTAbzip Gene, a Positive Regulator of Ochratoxin A Biosynthesis in Aspergillus niger. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, S.; Funk, A.N.; Scherlach, K.; Schroeckh, V.; Shelest, E.; Horn, U.; Hertweck, C.; Brakhage, A.A. Activation of a silent fungal polyketide biosynthesis pathway through regulatory cross talk with a cryptic nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 8143–8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woloshuk, C.P.; Foutz, K.R.; Brewer, J.F.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E.; Payne, G.A. Molecular characterization of aflR, a regulatory locus for aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Keller, N.P.; Adams, T.H. Sequence-specific binding by Aspergillus nidulans AflR, a C6 zinc cluster protein regulating mycotoxin biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, H.M. Cloning and bioinformatic analysis of lovastatin biosynthesis regulatory gene lovE. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zabala, A.O.; Xu, W.; Chooi, Y.H.; Tang, Y. Characterization of a silent azaphilone gene cluster from Aspergillus niger ATCC 1015 reveals a hydroxylation-mediated pyran-ring formation. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Yuan, G.-F.; Hsieh, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-S.; Wang, W.-Y.; Liaw, L.-L.; Tseng, C.-P. Identification of the mokH Gene Encoding Transcription Factor for the Upregulation of Monacolin K Biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhady, M.A.; Khalaf, A.A.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Hassanen, E.I.; Abdelrahman, R.E.; Noshy, P.A. Protective Effects of Bacillus subtilis Fermentation Extract Against Ochratoxin A-induced Nephrotoxicity and Immunotoxicity in Broiler Chickens. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 66, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kőszegi, T.; Poór, M. Ochratoxin A: Molecular Interactions, Mechanisms of Toxicity and Prevention at the Molecular Level. Toxins 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoi, C.S.; Chen, J.H.; Lin, T.Y.; Chiang, C.K.; Hung, K.Y. Ochratoxin A-Induced Nephrotoxicity: Up-to-Date Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denli, M.; Perez, J.F. Ochratoxins in feed, a risk for animal and human health: Control strategies. Toxins 2010, 2, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z. Production, toxicity and biosynthesis of ochratoxin A: A review. Microbiol. China 2023, 50, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadalupe, G.A.; Grandez-Yoplac, D.E.; Arellanos, E.; Doménech, E. Probabilistic Risk Assessment of Metals, Acrylamide and Ochratoxin A in Instant Coffee from Brazil, Colombia, Mexico and Peru. Foods 2024, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Qin, J. High-performance fabricated nano-adsorbents as emerging approach for removal of mycotoxins: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, Z.; Gül, G.; Yaman, I. Ochratoxin A activates opposing c-MET/PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK 1-2 pathways in human proximal tubule HK-2 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, T.; Ming, G.; Duan, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y. Molecular signatures of cytotoxic effects in human embryonic kidney 293 cells treated with single and mixture of ochratoxin A and citrinin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 123, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, G.S.; Caldwell, D.S.; Aziz, S.A.; Coady, L.C.; Armstrong, C.L.; Curran, I.H.; Koffman, R.L.; Kapal, K.; Lefebvre, D.E.; Mehta, R. Effects of Chronic Ochratoxin A Exposure on p53 Heterozygous and p53 Homozygous Mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, M.; Pexara, A.; Solomakos, N.; Govaris, A. Ochratoxin A in Slaughtered Pigs and Pork Products. Toxins 2022, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, S.; Navas, L.; Lombari, P.; Montagnaro, S.; Forte, I.M.; Giordano, A.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Effects of δ-tocotrienol on ochratoxin A-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 8731–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, S.; Iovane, V.; Squillacioti, C.; Mirabella, N.; Prisco, F.; Ariano, A.; Amenta, M.; Giordano, A.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Red orange and lemon extract prevents the renal toxicity induced by ochratoxin A in rats. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; He, X.; Dweep, H.; Guo, M.; Cheng, W.-H.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Gretz, N.; et al. Ochratoxin A induced early hepatotoxicity: New mechanistic insights from microRNA, mRNA and proteomic profiling studies. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, W.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H. Recent progress in determination of ochratoxin a in foods by chromatographic and mass spectrometry methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5444–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.W.; Ding, X.F.; Cao, H.J.; Ni, Q.Z.; Zhu, B.; Ma, N.; Zhang, F.K.; Wang, Y.K.; Xu, S.; Chen, T.W.; et al. Ochratoxin A Induces Steatosis via PPARγ-CD36 Axis. Toxins 2021, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. An update on direct genotoxicity as a molecular mechanism of ochratoxin a carcinogenicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limonciel, A.; Jennings, P. A review of the evidence that ochratoxin A is an Nrf2 inhibitor: Implications for nephrotoxicity and renal carcinogenicity. Toxins 2014, 6, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, G.S.; Curran, I.H.C.; Coady, L.C.; Armstrong, C.; Bourque, C.; Bugiel, S.; Caldwell, D.; Kwong, K.; Lefebvre, D.E.; Maurice, C.; et al. A one-generation reproductive toxicity study of the mycotoxin ochratoxin A in Fischer rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 153, 112247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Venancio, E.J.; Ono, M.A.; Fernandes, E.V.; Hirooka, E.Y.; Shimizu, C.F.; Oba, A.; Flaiban, K.; Itano, E.N. Effects of Subcutaneous Ochratoxin-A Exposure on Immune System of Broiler Chicks. Toxins 2019, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, R.E.; Khalaf, A.A.A.; Elhady, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Hassanen, E.I.; Noshy, P.A. Quercetin ameliorates ochratoxin A-Induced immunotoxicity in broiler chickens by modulation of PI3K/AKT pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 351, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, T.H.; Hong, M.-W.; Park, T.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.-J. Transcriptomic alterations induced by aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A in LMH cell line. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5265–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, P.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y. Ochratoxin A: Its impact on poultry gut health and microbiota, an overview. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção, R.; Martins, C.; Dupont, D.; Alvito, P. Patulin and ochratoxin A co-occurrence and their bioaccessibility in processed cereal-based foods: A contribution for Portuguese children risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Wang, W.C.; Lin, C.X.; Fouad, A.M.; Chen, W.; Xia, W.G.; Wang, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W.H.; Yan, S.J.; et al. Effects of curcumin on performance, antioxidation, intestinal barrier and mitochondrial function in ducks fed corn contaminated with ochratoxin A. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 13, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Wen, J.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Cao, W. Microstructures, Mechanical Properties, and Corrosion Behavior of As-Cast Mg−2.0Zn−0.5Zr⁻xGd (wt %) Biodegradable Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazhenov, V.E.; Li, A.V.; Komissarov, A.A.; Koltygin, A.V.; Tavolzhanskii, S.A.; Bautin, V.A.; Voropaeva, O.O.; Mukhametshina, A.M.; Tokar, A.A. Microstructure and mechanical and corrosion properties of hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Ca–(Mn) biodegradable alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleas, G.J.; Yan, J.; Goldberg, D.M. Assay of Ochratoxin A in Wine and Beer by High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Photodiode Array and Gas Chromatography Mass Selective Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Kocsubé, S.; Péteri, Z.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Tóth, B. Chemical, physical and biological approaches to prevent ochratoxin induced toxicoses in humans and animals. Toxins 2010, 2, 1718–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, N.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gerelt, K.; Qian, Y.; Lai, R.; Zhou, Y. A Superefficient Ochratoxin A Hydrolase with Promising Potential for Industrial Applications. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0196421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, A.; Cramer, B.; Harrer, H.; Humpf, H.U. Structure elucidation and in vitro cytotoxicity of ochratoxin α amide, a new degradation product of ochratoxin A. Mycotoxin Res. 2015, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Gonzalez, N.; Mintz, K.; Jaja-Chimedza, A.; De Jesus, C.L.; Lydon, C.; Welch, A.; Berry, J.P. Teratogenicity of Ochratoxin A and the Degradation Product, Ochratoxin α, in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryo Model of Vertebrate Development. Toxins 2016, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenczi, S.; Cserháti, M.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Kukolya, J.; Szőke, Z.; Kőszegi, B.; Albert, M.; Barna, T.; Mézes, M.; et al. A New Ochratoxin A Biodegradation Strategy Using Cupriavidus basilensis Őr16 Strain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitholtz Emanuelsson, A.; Fuchs, R.; Hult, K.; Appelgren, L.E. Distribution of 14C-ochratoxin A and 14C-ochratoxin B in rats: A comparison based on whole-body autoradiography. IARC Sci. Publ. 1991, 115, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Mally, A.; Keim-Heusler, H.; Amberg, A.; Kurz, M.; Zepnik, H.; Mantle, P.; Völkel, W.; Hard, G.C.; Dekant, W. Biotransformation and nephrotoxicity of ochratoxin B in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 206, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Dohnal, V.; Huang, L.; Kuča, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Z. Metabolic pathways of ochratoxin A. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Villeda, B.; Lobos, O.; Aguilar-Zuniga, K.; Carrasco-Sánchez, V. Ochratoxins in Wines: A Review of Their Occurrence in the Last Decade, Toxicity, and Exposure Risk in Humans. Toxins 2021, 13, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Marquardt, R.R.; Frohlich, A.A. Identification of ochratoxins and some of their metabolites in bile and urine of rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J.; Marín, S. Thermal stability and kinetics of degradation of deoxynivalenol, deoxynivalenol conjugates and ochratoxin A during baking of wheat bakery products. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, T.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Verde, S.C.; Venâncio, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Gamma irradiation effects on ochratoxin A: Degradation, cytotoxicity and application in food. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espejo, F.J.; Armada, S. Effect of activated carbon on ochratoxin A reduction in “Pedro Ximenez” sweet wine made from off-vine dried grapes. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Donat, P.; Marín, S.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J. New mycotoxin adsorbents based on tri-octahedral bentonites for animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 255, 114228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appell, M.; Jackson, M.A. Sorption of ochratoxin A from aqueous solutions using β-cyclodextrin-polyurethane polymer. Toxins 2012, 4, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi Pirouz, A.; Abedi Karjiban, R.; Abu Bakar, F.; Selamat, J. A Novel Adsorbent Magnetic Graphene Oxide Modified with Chitosan for the Simultaneous Reduction of Mycotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, R.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Assessment of traditional clarifiers on the adsorption of ochratoxin A in Cabernet sauvignon red wine and their kinetics. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Adsorption of aflatoxins and ochratoxins in edible vegetable oils with dopamine-coated magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appell, M.; Wegener, E.C.; Sharma, B.K.; Eller, F.J.; Evans, K.O.; Compton, D.L. In Vitro Evaluation of the Adsorption Efficacy of Biochar Materials on Aflatoxin B1, Ochratoxin A, and Zearalenone. Animals 2023, 13, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, S.A.; Khan, M.Z.; Saleemi, M.K.; Hassan, Z.U.; Khan, A. Ameliorative role of dietary activated carbon against ochratoxin-A induced oxidative damage, suppressed performance and toxicological effects. Toxin Rev. 2022, 41, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Advances in Biodetoxification of Ochratoxin A-A Review of the Past Five Decades. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheur, F.B.; Fedhila, K.; Chaieb, K.; Kouidhi, B.; Bakhrouf, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Adsorption of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone and ochratoxin A by microorganisms isolated from Kefir grains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 251, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridi, A.; Sidari, R.; Pulvirenti, A.; Meca, G.; Ritieni, A. Ochratoxin A adsorption phenotype: An inheritable yeast trait. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sheikh-Zeinoddin, M.; Khalesi, M. Biological detoxification of ochratoxin A in plants and plant products. Toxin Rev. 2019, 38, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xia, F.; Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Rao, S.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z. Reduction of ochratoxin A from contaminated food by Lactobacillus rhamnosus Bm01. Food Control 2023, 143, 109315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M. The Adsorption of Ochratoxin A by Lactobacillus Species. Toxins 2014, 6, 2826–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, S.; Gökmen, V. Alkali-based pre-treatment may prevent ochratoxin A in grapes. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Smith, I.N.; Mikiashvili, N. Reducing Ochratoxin A Content in Grape Pomace by Different Methods. Toxins 2020, 12, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogkaki, E.A.; Natskoulis, P.I.; Panagou, E.Z. Modeling the effect of natamycin, pine-resin and environmental factors on the growth and OTA production by Aspergillus carbonarius using response surface methodology. Food Res. Int. 2016, 79, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Ochratoxin A is degraded by Yarrowia lipolytica and generates non-toxic degradation products. World Mycotoxin J. 2015, 9, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Legrand Ngolong Ngea, G.; Abiso Godana, E.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, H. Cryptococcus podzolicus Y3 degrades ochratoxin A by intracellular enzymes and simultaneously eliminates citrinin. Biol. Control 2022, 168, 104857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yin, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, L.; Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, K.; Gan, F. Isolation, identification and safety evaluation of OTA-detoxification strain Pediococcus acidilactici NJB421 and its effects on OTA-induced toxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 172, 113604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Long, M. Complete Genome Sequence of Zearalenone Degrading Bacteria Bacillus velezensis A2. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Liu, Z.; Xue, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Isolation and identification of a Cytobacillus oceanisediminis strain with ochratoxin A detoxification ability. Food Control 2023, 151, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Nagarajan, K.; Loh, K.-C. Biodegradation of aromatic compounds: Current status and opportunities for biomolecular approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Zhou, T.; Christopher Young, J.; Goodwin, P.H.; Peter Pauls, K. Aerobic and anaerobic de-epoxydation of mycotoxin deoxynivalenol by bacteria originating from agricultural soil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tu, T.; Gong, W.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y. Characterization of Bacillus velezensis E2 with abilities to degrade ochratoxin A and biocontrol against Aspergillus westerdijkiae fc-1. Toxicon 2022, 216, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrunhosa, L.; Paterson, R.R.M.; Venâncio, A. Biodegradation of Ochratoxin A for Food and Feed Decontamination. Toxins 2010, 2, 1078–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Garcia, S.; Sibaja, K.V.M.; Nogueira, W.V.; Feltrin, A.C.P.; Pinheiro, D.F.A.; Cerqueira, M.B.R.; Badiale Furlong, E.; Garda-Buffon, J. Peroxidase as a simultaneous degradation agent of ochratoxin A and zearalenone applied to model solution and beer. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stander, M.A.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Henke, E.; Steyn, P.S. Screening of Commercial Hydrolases for the Degradation of Ochratoxin A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5736–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrunhosa, L.; Santos, L.; Venâncio, A. Degradation of Ochratoxin A by Proteases and by a Crude Enzyme of Aspergillus niger. Food Biotechnol. 2006, 20, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobritzsch, D.; Wang, H.; Schneider, G.; Yu, S. Structural and functional characterization of ochratoxinase, a novel mycotoxin-Degrading enzyme. Biochem. J. 2014, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Qian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, C.; Luo, M.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Y. Detoxification of ochratoxin A by Lysobacter sp. CW239 and characteristics of a novel degrading gene carboxypeptidase cp4. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liuzzi, V.C.; Fanelli, F.; Tristezza, M.; Haidukowski, M.; Picardi, E.; Manzari, C.; Lionetti, C.; Grieco, F.; Logrieco, A.F.; Thon, M.R.; et al. Transcriptional Analysis of Acinetobacter sp. neg1 Capable of Degrading Ochratoxin A. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Pei, P.; Li, X. Engineering a carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus niger M00988 by mutation to increase its ability in high Fischer ratio oligopeptide preparation. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 330, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Dai, Y.; Sun, C. Degradation of ochratoxin A by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ASAG1. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, H.; Huo, X.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q. Bacillus subtilis ANSB168 Producing d-alanyl-d-alanine Carboxypeptidase Could Alleviate the Immune Injury and Inflammation Induced by Ochratoxin A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.-N.; Jia, X.-k.; Wang, Y.P.; Liang, Z. Removal of ochratoxin A by a carboxypeptidase and peptides present in liquid cultures of Bacillus subtilis CW14. World Mycotoxin J. 2018, 11, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Biodegradation of ochratoxin A by Brevundimonas diminuta HAU429: Characterized performance, toxicity evaluation and functional enzymes. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Dai, L.; Xu, Y.; Niu, D.; Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Shen, P.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Functional characterization and structural basis of an efficient ochratoxin A-degrading amidohydrolase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, I.; Tai, B.; Ma, J.; Hussain, S.; Du, H.; Guo, L.; Wang, G.; Adegoke, T.V.; Ma, L.; Xing, F. Identification of a Novel Bacillus velezensis IS-6 Nudix Hydrolase Nh-9 Involved in Ochratoxin A Detoxification by Transcriptomic Profiling and Functional Verification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10155–10168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Y.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Xue, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, D.; et al. Isolation, identification, degradation mechanism and exploration of active enzymes in the ochratoxin A degrading strain Acinetobacter pittii AP19. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Z. Purification and characterization of the enzymes from Brevundimonas naejangsanensis that degrade ochratoxin A and B. Food Chem. 2023, 419, 135926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Heterologous expression and characterization of a novel ochratoxin a degrading enzyme, N-acyl-L-amino acid amidohydrolase, from Alcaligenes faecalis. Toxins 2019, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
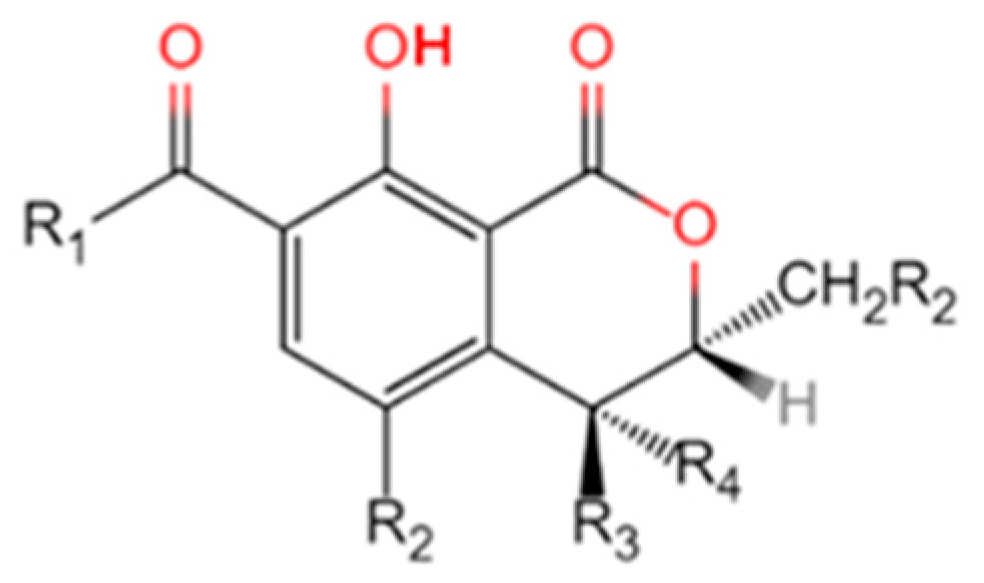

| Name | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTα | OH | Cl | H | H | H |
| OTβ | OH | H | H | H | H |
| OTA | Phenylalanyl group | Cl | H | H | H |
| OTB | Phenylalanyl group | H | H | H | H |
| OTC | Phenylalanyl ethyl ester | Cl | H | H | H |
| 4R-OH-OTA | Phenylalanyl group | Cl | H | OH | H |
| 4S-OH-OTA | Phenylalanyl group | Cl | OH | H | H |
| 4R-OH-OTB | Phenylalanyl group | H | H | OH | H |
| 4S-OH-OTB | Phenylalanyl group | H | OH | H | H |
| 10-OH-OTA | Phenylalanyl group | Cl | H | H | OH |
| Source | GenBank ID | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Expression Vector | Optimal pH | Optimal Temperature (°C) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus niger UVK143 | An14 g02080 | 47 | A. niger AP4 strain/pGAPT | 5.6–6.0 | 66 | [133] |
| Stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila CW117 | H7691_12935 | 45.6 | BL21/pGEX-4T-1 | 8.0 | 40–50 | [93] |
| Acinetobacter sp. neg1 | PJ15_1540 | 44.15 | BL21-CodonPlus(DE3)- RIL/pET-28a | NR | NR | [135] |
| Aspergillus niger M00988 | KJ854920 | 51.1 | BL21/pET-28a | NR | NR | [136] |
| Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ASAG1 | KP161493 | 48.6 | Rosetta/pEB | NR | NR | [137] |
| Bacillus subtilis ANSB168 | DacA (Gene name) | 46 | Rosseta/pET-31b | 7.0 | 37 | [138] |
| Bacillus subtilis ANSB168 | DacB (Gene name) | 41 | Rosseta/pET-31b | 7.5 | 37 | [138] |
| Lysobacter sp. CW239 | H2514_00995 | 43.32 | BL21/pET-32a | 7.0 | 37 | [134] |
| Bacillus subtilis CW14 | BCV50_12785 | 48.62 | BL21/pET-28a | NR | NR | [139] |
| Brevundimonas diminuta HAU429 | BT6 (Gene name) | NR | Rosseta/pET-31b | 8.0 | 47–52 | [140] |
| Brevundimonas diminuta HAU429 | BT7 (Gene name) | NR | Rosseta/pET-31b | 7.0 | 47 | [140] |
| Brevundimonas diminuta HAU429 | BT7 (Gene name) | NR | Rosseta/pET-31b | 7.0 | 37 | [140] |
| Pseudoxanthomonas wuyuanensis | WP_176520186 | 356.43 (octamer) | BL21/pET46 | 7.5–8.5 | 40–50 | [141] |
| Bacillus velezensis IS-6 | AAV34_RS17190 | 14 | BL21/pET-28a | 7.0 | NR | [142] |
| Acinetobacter pittii AP19 | BDGL_001905 | 41 | BL21/pET-28a | NR | NR | [143] |
| Brevundimonas naejangsanensis ML17 | gene009 (Gene name) | 79.7 | BL21/pET-28a | NR | NR | [144] |
| Brevundimonas naejangsanensis ML17 | gene1826 (Gene name) | 58.4 | BL21/pET-28a | NR | NR | [144] |
| Brevundimonas naejangsanensis ML17 | gene2253 (Gene name) | 67.7 | BL21/pET-28a | NR | NR | [144] |
| Brevundimonas naejangsanensis ML17 | gene0484 (Gene name) | 45.8 | BL21/pET-28a | NR | NR | [144] |
| Alcaligenes faecalis DSM 16305 | OSZ37025 | 47.0 | BL21/pET-28a | 6.5 | 50 | [145] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Lao, K.; Fan, F. Production, Toxicological Effects, and Control Technologies of Ochratoxin A Contamination: Addressing the Existing Challenges. Water 2024, 16, 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243620
Yang Y, Li M, Zhao J, Li J, Lao K, Fan F. Production, Toxicological Effects, and Control Technologies of Ochratoxin A Contamination: Addressing the Existing Challenges. Water. 2024; 16(24):3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243620
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yan, Mingtao Li, Junxiong Zhao, Jingxuan Li, Kangwen Lao, and Fuqiang Fan. 2024. "Production, Toxicological Effects, and Control Technologies of Ochratoxin A Contamination: Addressing the Existing Challenges" Water 16, no. 24: 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243620
APA StyleYang, Y., Li, M., Zhao, J., Li, J., Lao, K., & Fan, F. (2024). Production, Toxicological Effects, and Control Technologies of Ochratoxin A Contamination: Addressing the Existing Challenges. Water, 16(24), 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243620








