Electrochemical Oxidation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrates from Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Ti4O7-Nanotube Reactive Electrochemical Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactant and Material
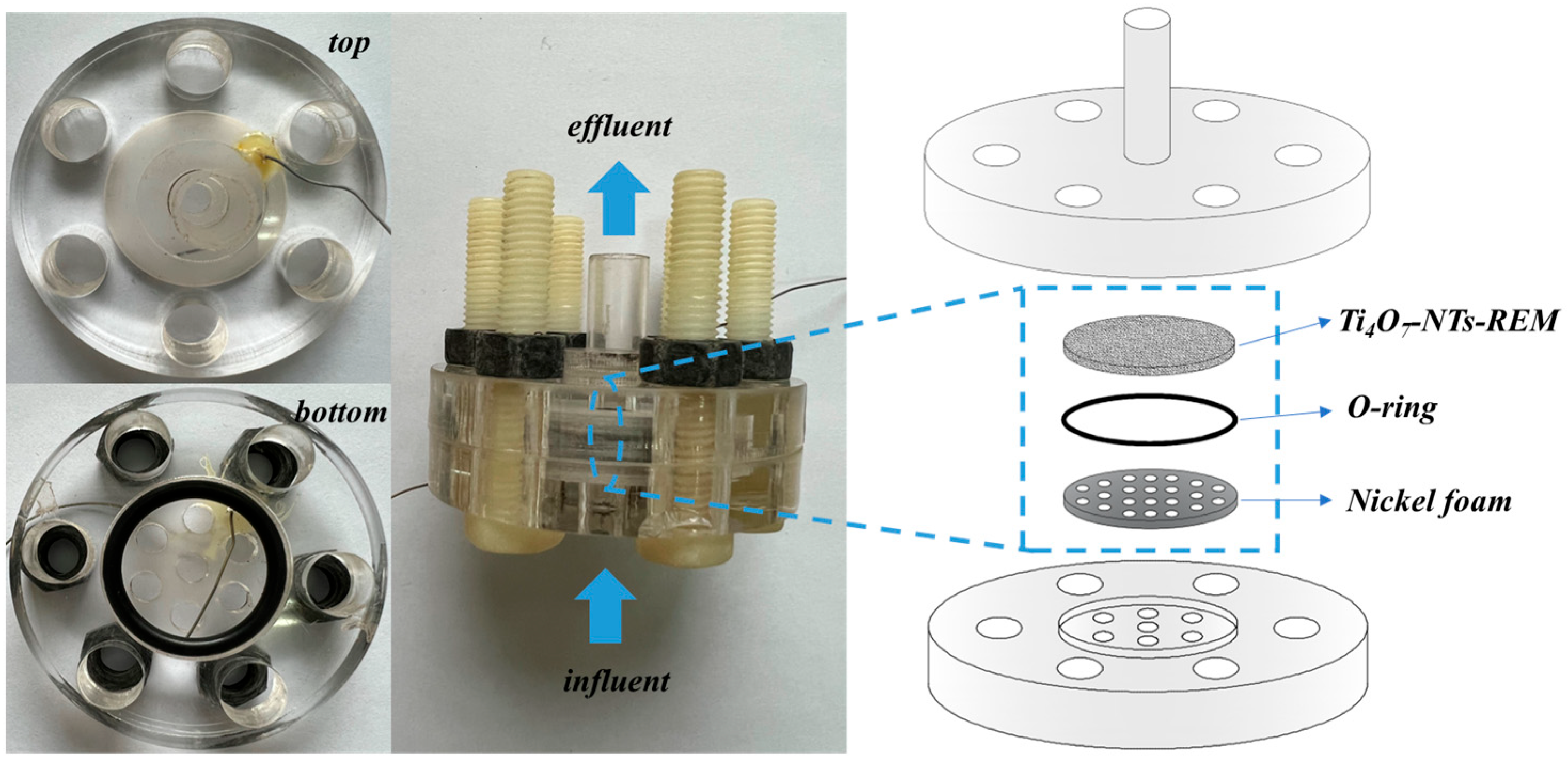
2.2. Fabrication of Ti4O7-NT-REM
2.3. Electrolysis Process
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. ROC Treatment by Ti4O7-NT-REM
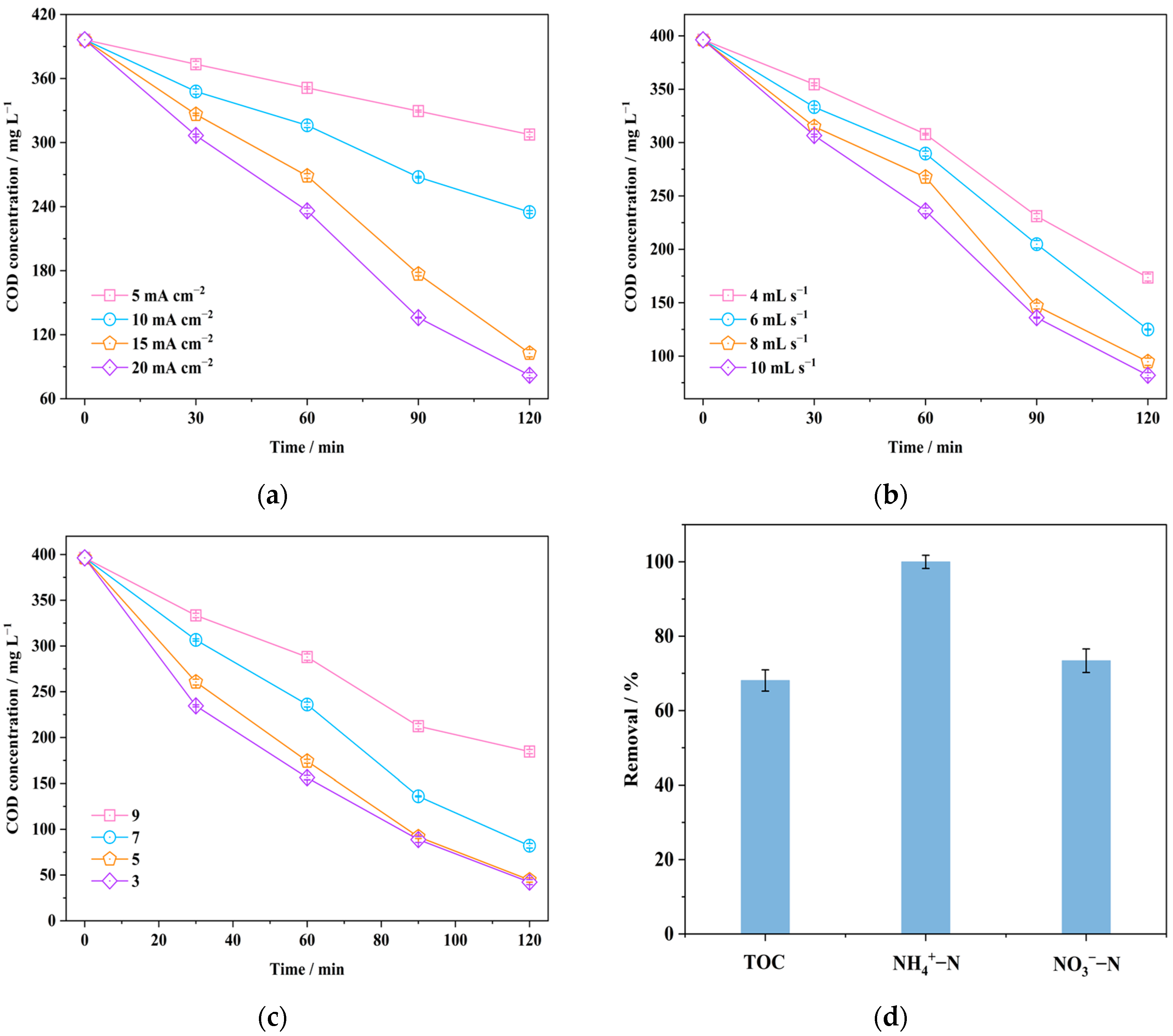
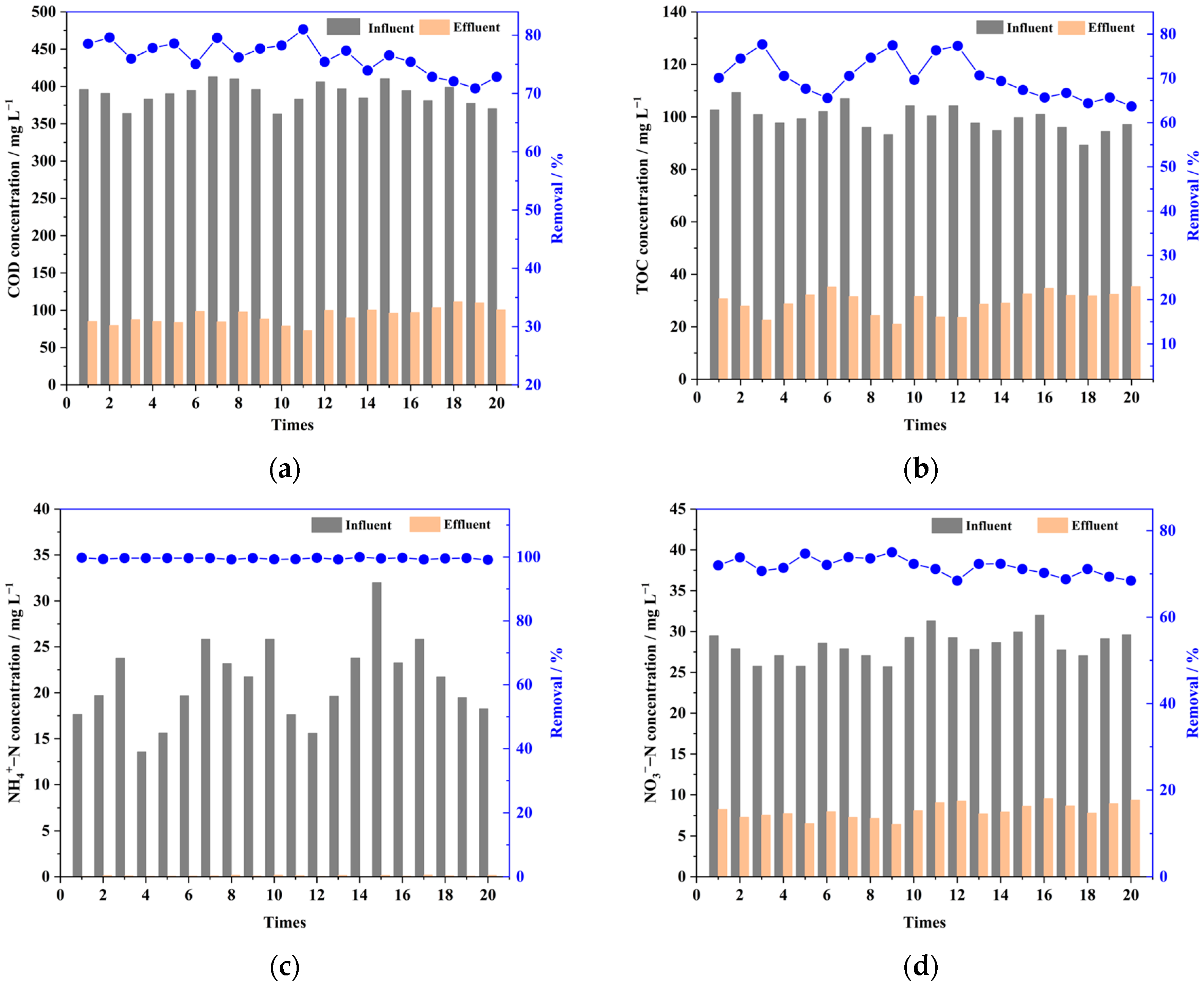
3.1.1. Contaminant Removal
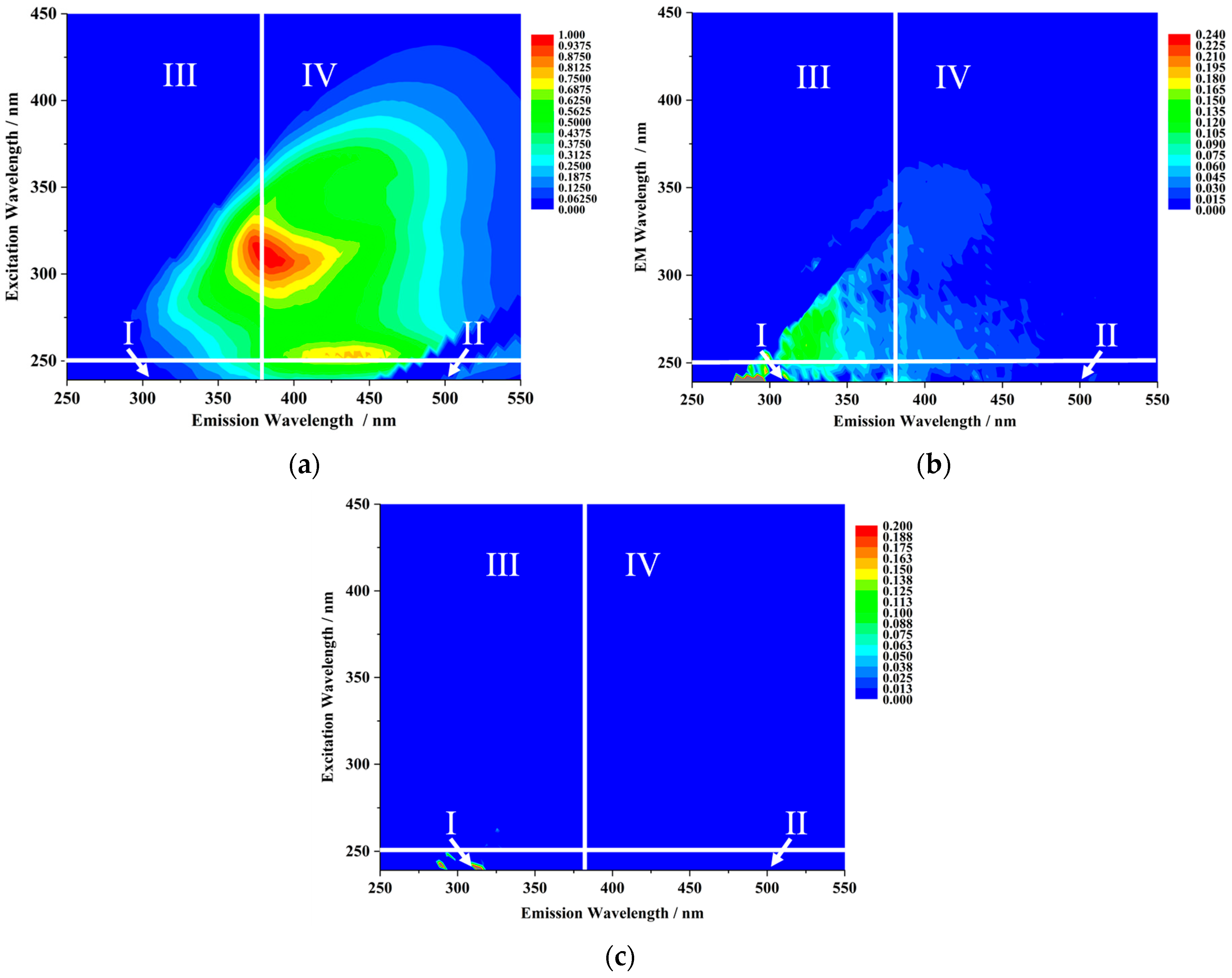
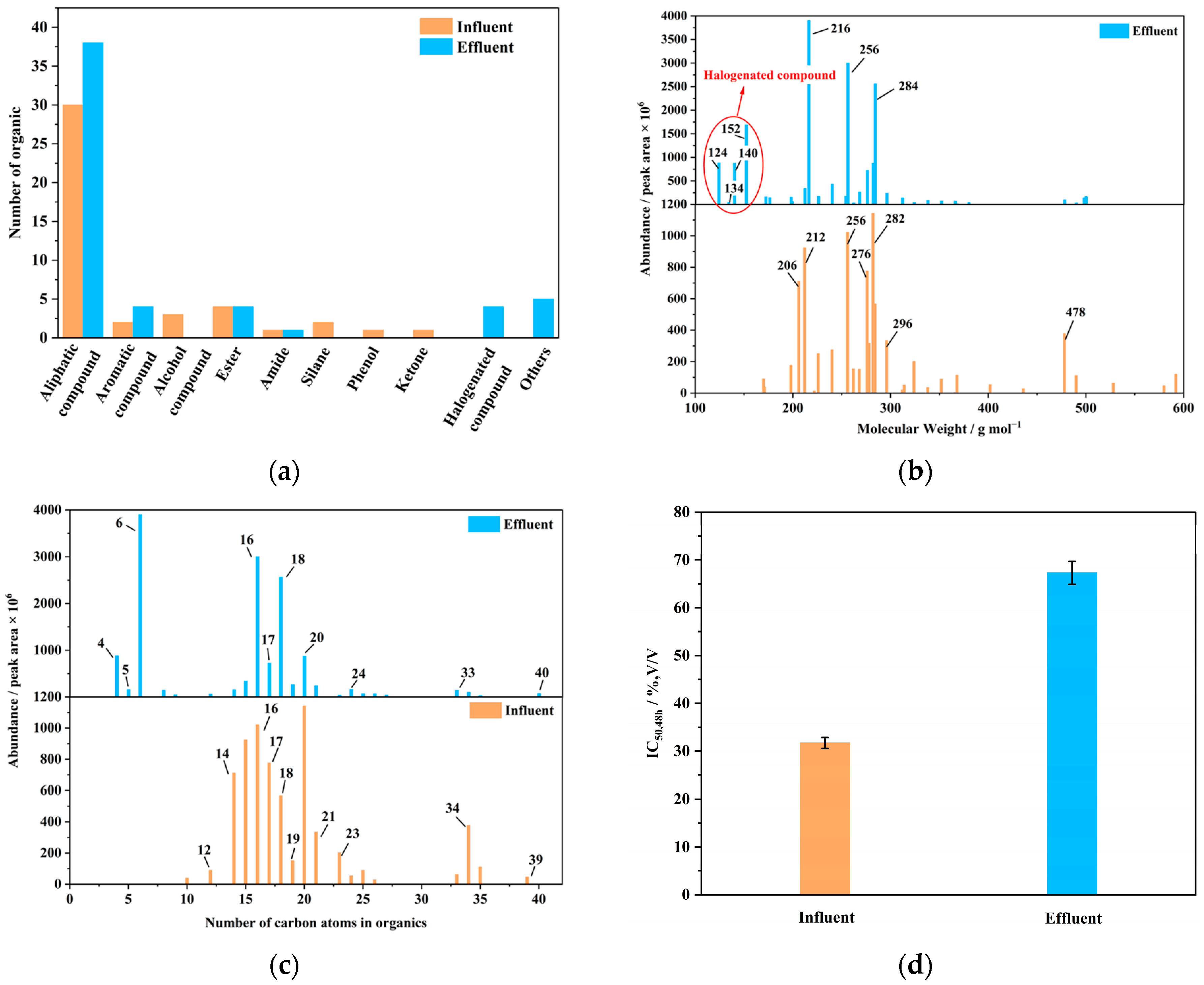
3.1.2. Variations in Dissolved Organic Matter
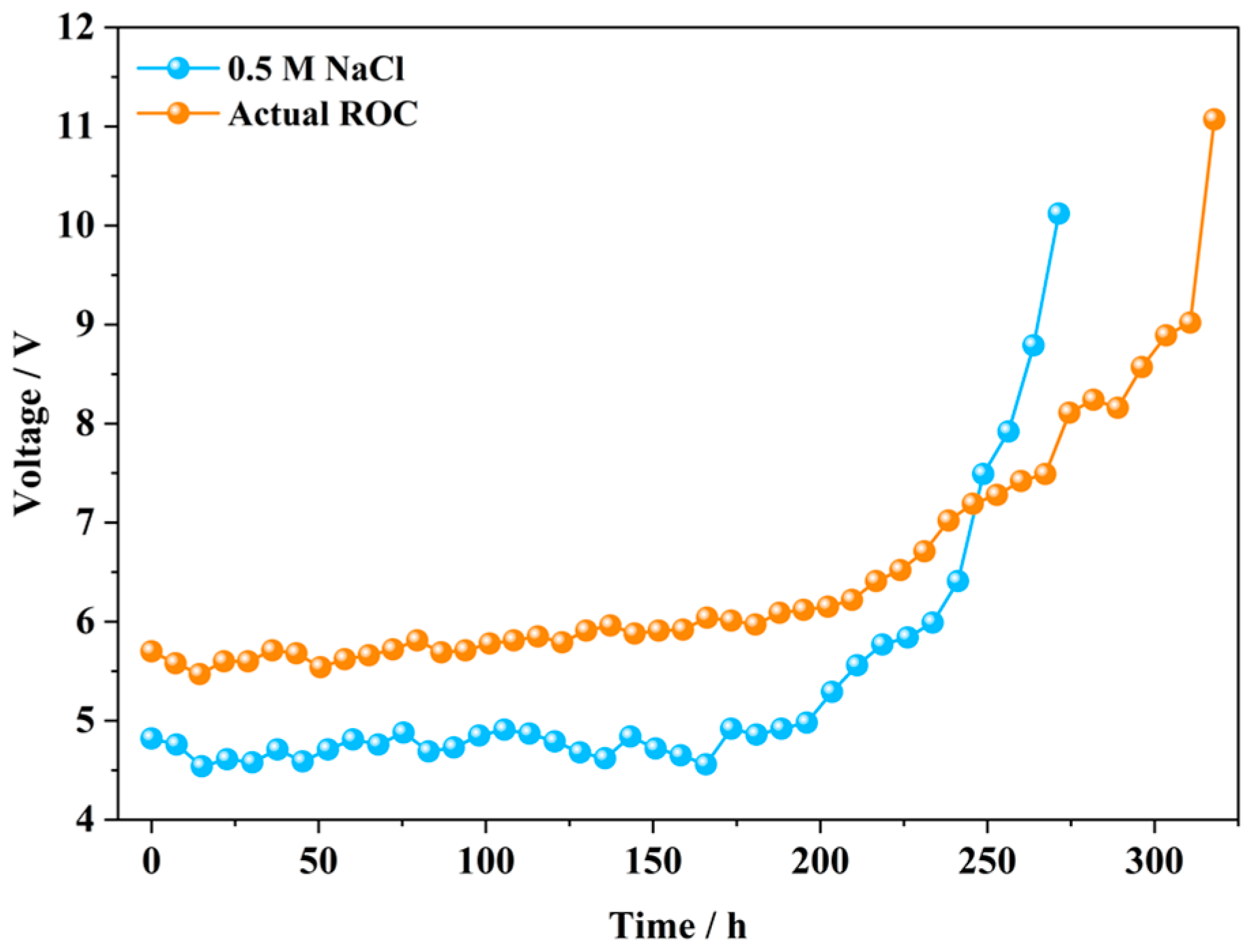
3.1.3. Long-Term Durability
3.1.4. Service Lifetime and Energy Consumption Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dos Santo, S.; Adams, E.A.; Neville, G.; Wada, Y.; Sherbinin, A.D.; Mullin Bernhardt, E.; Adamo, S.B. Urban growth and water access in sub-Saharan Africa: Progress, challenges, and emerging research directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, Z. Study of Comprehensive Utilization of Water Resources of Urban Water Distribution Network. Water 2021, 13, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.S.; Kargari, A. Water recovery from reverse osmosis concentrate by commercial nanofiltration membranes: A comparative study. Desalination 2022, 528, 115619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, A.; Urtiaga, A.M.; Ibáñez, R.; Ortiz, I. State of the art and review on the treatment technologies of water reverse osmosis concentrates. Water Res. 2012, 46, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J.; Wei, K.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Gu, L.; Han, W. Electrochemical treatment of municipal reverse osmosis concentrates by a TiO2-BNTs/SnO2-Sb reactive electrochemical membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, H. Treatment and recovery methods for leachate concentrate from landfill and incineration: A state-of-the-art review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.D.; Porto, R.F.; Quintaes, B.R.; Bila, D.M.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Campos, J.C. A review on membrane concentrate management from landfill leachate treatment plants: The relevance of resource recovery to close the leachate treatment loop. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 264–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Mansouri, J.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Huang, M.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, V. Omni phobic membrane via bioinspired silicification for the treatment of RO concentrate by membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 647, 120267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Koo, J.W.; Yuan, Z.; She, Q. Flow-through electrochemically assisted reverse-osmosis: A new process towards low-chemical desalination. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J. Effective and mechanistic insights into reverse osmosis concentrate of landfill leachate treatment using coagulation-catalytic ozonation-bioaugmentation-based AnMBR. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalgiri, K.; Cheng, Z.; Cervantes, S.; Spencer, S.; Liu, H. UV-based advanced oxidation of dissolved organic matter in reverse osmosis concentrate from a potable water reuse facility: A parallel-factor (PARAFAC) analysis approach. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, K.; Yi, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate using a pilot-scale reactive electrochemical membrane filtration system: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Ren, X.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, P. Toxicity reduction of reverse osmosis concentrates from petrochemical wastewater by electrocoagulation and fered-Fenton treatments. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, B.; Tu, Y. Reverse Osmosis Coupling Multi-Catalityc Ozonation (RO-MCO) in Treating Printing and Dyeing Wastewater and Membrane concentrate: Removal performance and Mechanism. Water Resour. Ind. 2023, 30, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagastyo, A.Y.; Radjenovic, J.; Mu, Y.; Rozendal, R.A.; Batstone, D.J.; Rabaey, K. Electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate on mixed metal oxide (MMO) titanium coated electrodes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.; Wang, H.; Mo, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, J. Optimal design and evaluation of electrocatalytic reactors with nano-MnOx/Ti membrane electrode for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.; Wang, H.; Mo, Y.; Li, L.; Yin, Z.; He, B.; Li, J.; Wang, T. A three-stage fixed-bed electrochemical reactor for biologically treated landfill leachate treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 121026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peng, H.X.; Feng Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, K.; Yang, K.; Liao, J.; Cheng, D.; Liu, X.; Lv, S.; et al. Energy-efficient for advanced oxidation of bio-treated landfill leachate effluent by reactive electrochemical membranes (REMs): Laboratory and pilot scale studies. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenc, S.; Bayat, M.; Can-Güven, E.; Varank, G. Hybrid and combined electro-oxidation and peroxi-coagulation processes in effective treatment of textile reverse osmosis concentrate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 298, 120365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ji, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Ke, S.; Wang, J. Effect of pH and Cl− concentration on the electrochemical oxidation of pyridine in low-salinity reverse osmosis concentrate: Kinetics, mechanism, and toxicity assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, Z.; Lai, J.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Efficient electrochemical oxidation of refractory organics in actual petrochemical reverse osmosis concentrates by Ti/SnO2-Sb mesh anode. Process Saf. Environ. 2024, 182, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Chen, Y.; Yin, F.; Lv, B.; Wu, F.; Xie, J.; Feng, D. Performance of electrochemical treatment of refractory organic matter in printing and dyeing reverse osmosis concentrate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.; Pei, J. Electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate using a novel electrode: Parameter optimization and kinetics study. Desalination 2016, 399, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Pan, S.; Huang, W.; Hakizimana, I.; Kong, W.; Wang, Y. Application of electrochemical flow-through oxidation technology in the treatment of concentrated water from nanofiltration and reverse osmosis in the coal chemical industry. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comninellis, C. Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste-water treatment. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P. Critical review of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for water treatment applications. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1182–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pletcher, D.; Walsh, F.C. Electrodeposited lead dioxide coatings. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3879–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P. The prospect of electrochemical technologies advancing worldwide water treatment. Accounts Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, D.; Malcolm, J.; Morrison, L.; Bunce, N. Mechanistic investigation of the conductive ceramic Ebonex® as an anode material. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 5548–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fan, W.; Chen, T.X.; Tang, J.Z.; Liu, Y.; Jia, H.Z.; Li, J.; Yao, J.L.; Liu, B.D. A novel synthetic strategy of mesoporous Ti4O7-coated electrode for highly efficient wastewater treatment. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 26503–26512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, W.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; et al. Electrochemical treatment of antibiotic wastewater containing ceftriaxone sodium by porous Ti/Magnéli Ti4O7 nanotube arrays. Water Resour. Ind. 2024, 31, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Su, J.Y.; Miles, C.; Comninellis, C.; Chen, G.H. Highly-ordered Magneli Ti4O7 nanotube arrays as effective anodic material for electro-oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 153, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Watanabe, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Tatarazako, N.; Masunaga, S.; Zhang, Y. Reduction in toxicity of coking wastewater to aquatic organisms by vertical tubular biological reactor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Yu, S.; Li, C.; Wei, K. Energy-efficient reuse of bio-treated textile wastewater by a porous-structure electrochemical PbO2 filter: Performance and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wei, K.J.; Xu, A.L.; Han, W.Q.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, J.S.; Shen, J.Y.; Wang, L.J. Pesticide tailwater deeply treated by tubular porous electrode reactor (TPER): Purpose for discharging and cost saving. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Liu, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Shen, C.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, P.; Liu, W. Silicate-enhanced heterogeneous flow-through electro-fenton system using iron oxides under nanoconfinement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4045–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, Y.; Elaoud, S.C.; Ammar, S.; Abdelhedi, R. Electrochemical degradation of 4-chloroguaiacol for wastewater treatment using PbO2 anodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhu, L.; Liang, S.; Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Lei, Z.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; Wei, C.; Feng, C. Discovering the Importance of ClO• in a coupled electrochemical system for the simultaneous removal of carbon and nitrogen from secondary coking wastewater effluent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9015–9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhu, L.; Yan, Z.; Lin, Z.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Dang, Z.; Wei, C.; Feng, C. Self-activated Ni cathode for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia: From fundamentals to scale-up for treatment of industrial wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13231–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Pan, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y. Electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrates using enhanced TiO2-NTA/SnO2-Sb anodes with/without PbO2 layer. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Hu, R.; Zou, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhong, N.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y. Highly efficient reverse osmosis concentrate remediation by microalgae for biolipid production assisted with electrooxidation. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Bai, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T.; Guan, X.; Zhou, B. Highly efficient removal of total nitrogen and dissolved organic compound in waste reverse osmosis concentrate mediated by chlorine radical on 3D Co3O4 nanowires anode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB16889-2008; Standard for Pollution Control on the Landfill Site of Municipal Solid Waste. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Ansari, A.; Nematollahi, D. Convergent paired electrocatalytic degradation of p-dinitrobenzene by Ti/SnO2-Sb/β-PbO2 anode. A new insight into the electrochemical degradation mechanism. Water. Res. 2018, 144, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Liao, D.; Lin, Y.; Hu, C.; Ju, J.; Chen, Y.; Feng, D. Electrochemical degradation of reverse osmosis concentrate (ROC) using the electrodeposited Ti/TiO2-NTs/PbO2 electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, L.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Q. Treatment of high-salinity reverse osmosis concentrate by electrochemical oxidation on BDD and DSA electrodes. Desalination 2011, 277, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P′erez, G.; Fern′andez-Alba, A.R.; Urtiaga, A.M.; Ortiz, I. Electro-oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrates generated in tertiary water treatment. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2763–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagastyo, A.Y.; Batstone, D.J.; Kristiana, I.; Escher, B.I.; Joll, C.; Radjenovic, J. Electrochemical treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate on boron-doped electrodes in undivided and divided cell configurations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Anode | Operating Mode | Current Density | COD Removal | TOC Removal | Energy Consumption | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDD | Flow-by | 40 mA cm−2 | 91.9% | 76.63% | 1500 kWh·kg COD−1 | [23] |
| Ti/TiO2-NTs/PbO2 | Flow-by | 40 mA cm−2 | 47.59% | / | 190 kWh·kg COD−1 | [45] |
| BDD | Batch | 25 mA/cm−2 | 100% | / | 158 kWh·kg COD−1 | [46] |
| BDD | Batch | 5 mA/cm−2 | 100% | / | 59 kWh·kg COD−1 | [47] |
| Ti/IrO2–Ta2O5 | Batch | 25 mA/cm−2 | <50% | / | 50 kWh·kg COD−1 | [46] |
| Si/BDD | Flow-by | 12.5 mA cm−2 | 100% | ~70% | 34 kWh·kg COD−1 | [48] |
| Ti4O7-NT-REM | Flow-through | 20 mA cm−2 | 74% | 68% | 7.6 kWh·kg COD−1 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Q.; Xiao, P.; Du, T.; Xu, D.; Guo, C.; Guan, Y.; Yan, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Electrochemical Oxidation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrates from Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Ti4O7-Nanotube Reactive Electrochemical Membrane. Water 2024, 16, 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243579
Qian Q, Xiao P, Du T, Xu D, Guo C, Guan Y, Yan M, Wang F, Zhang Y, Li Y. Electrochemical Oxidation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrates from Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Ti4O7-Nanotube Reactive Electrochemical Membrane. Water. 2024; 16(24):3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243579
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Qiujie, Pingzhong Xiao, Tinghui Du, Demin Xu, Chuanshuo Guo, Yue Guan, Minxuan Yan, Feihong Wang, Yonghao Zhang, and Yan Li. 2024. "Electrochemical Oxidation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrates from Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Ti4O7-Nanotube Reactive Electrochemical Membrane" Water 16, no. 24: 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243579
APA StyleQian, Q., Xiao, P., Du, T., Xu, D., Guo, C., Guan, Y., Yan, M., Wang, F., Zhang, Y., & Li, Y. (2024). Electrochemical Oxidation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrates from Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Ti4O7-Nanotube Reactive Electrochemical Membrane. Water, 16(24), 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243579





